Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Sex Differences/Sexual Dimorphism/Gender Differences in Cancer
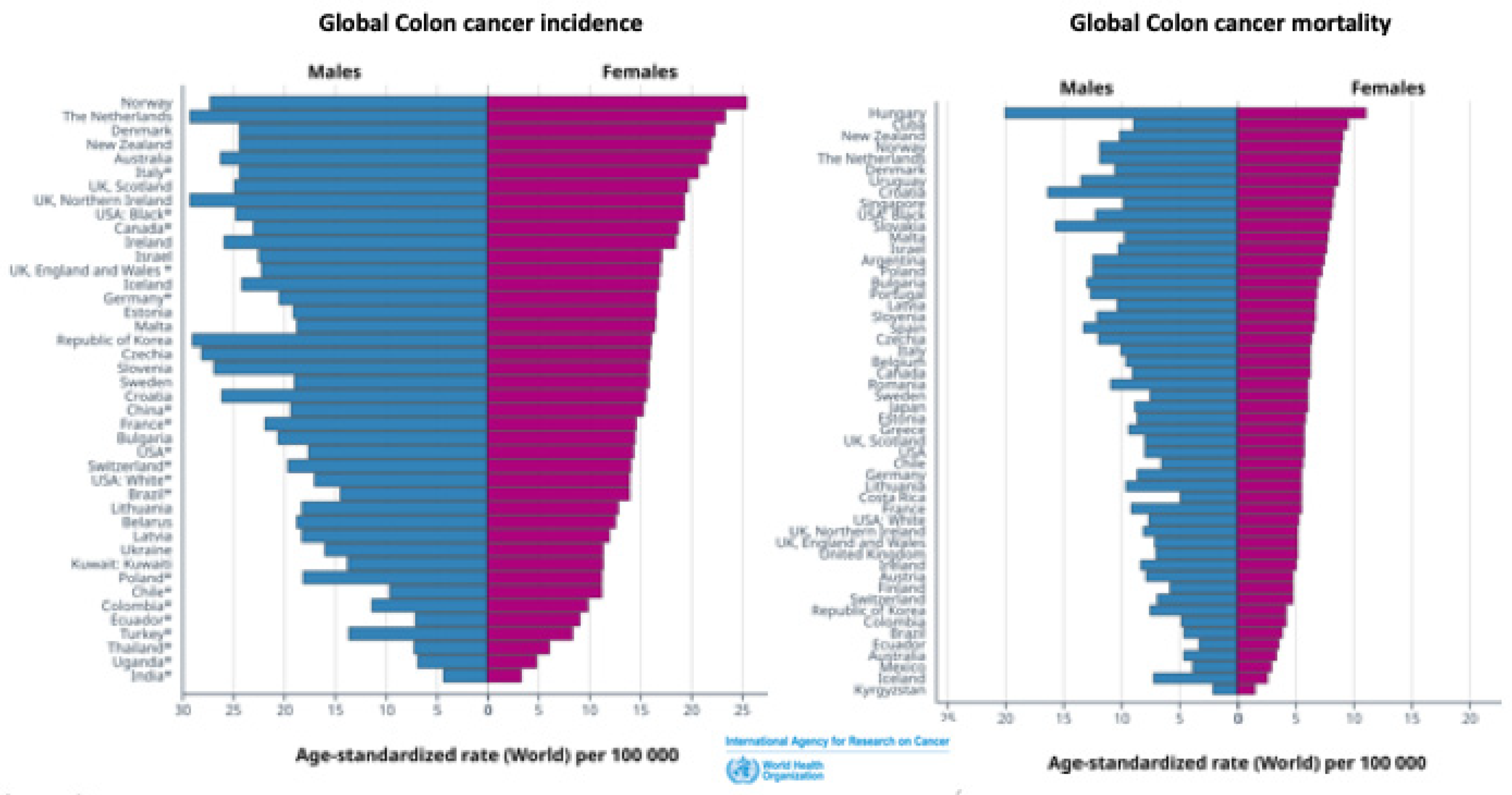
1.2. Sex Differences in Colon Cancer
1.3. Estrogen and Sex Differences in Colon Cancer
2. Estrogen Receptors in Colon Cancer
2.1. Nuclear Estrogen Receptors in Colon Cancer
2.2. Membrane Estrogen Receptors in in Colon Cancer
3. Genomic and non-Genomic Estrogen Signaling Pathways in Colon Cancer
3.1. Genomic Mechanisms of Estrogen Signaling in Colon Cancer
3.2. Non-Genomic Mechanisms of Estrogen Signaling in Colon Cancer
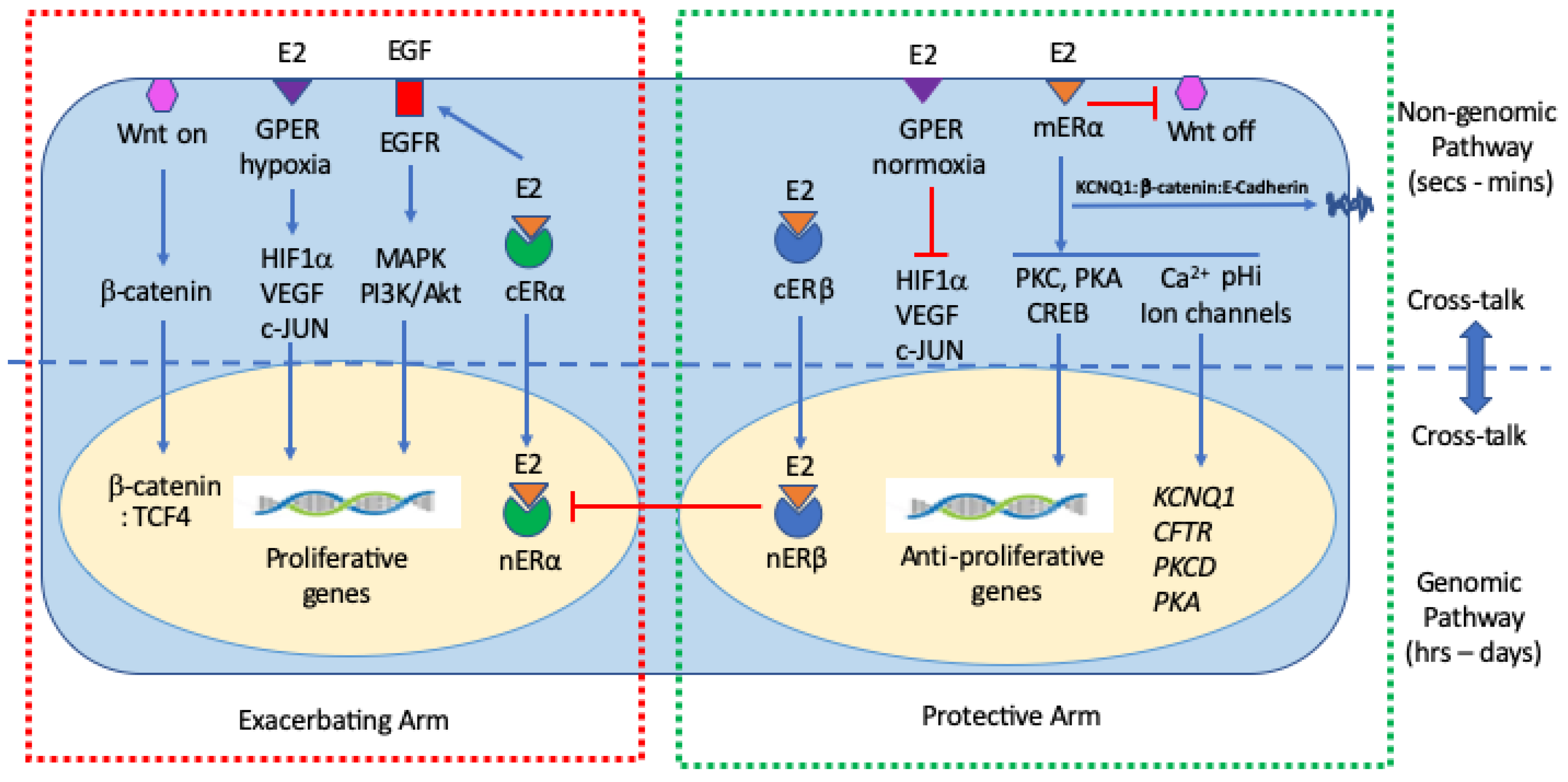
3.3. Cooperativity between Genomic and Non-Genomic Estrogen Signaling in Colon Cancer
4. Estrogen Signaling via ERα and ERβ in Colon Cancer
4.1. Non-Ligand Activation of Nuclear ERs in Colon Cancer
4.2. Membrane Estrogen Receptors mERα and mERβ in Colon Cancer
4.3. Estrogen Signaling via Truncated ERs in Colon Cancer
5. Estrogen Signaling via G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in Colon Cancer
5.1. Hypoxia and GPER Signaling in Colon Cancer
6. Estrogen Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Colon Cancer
6.1. Estrogen Regulation of Wnt-KCNQ1 Interactions in Colon Cancer
6.3. Estrogen Regulation of Wnt Receptor Oncogenic Signaling in Colon Cancer
7. Estrogen Regulation of Epigenetic, Microbiome and Metabolic Factors in Colon Cancer
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubin, J.B.; Lagas, J.S.; Broestl, L.; Sponagel, J.; Rockwell, N.; Rhee, G.; Rosen, S.F.; Chen, S.; Klein, R.S.; Imoukhuede, P.; Luo, J. Sex differences in cancer mechanisms. Biol. Sex. Differ. 2020, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clocchiatti, A.; Cora, E.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Sexual dimorphism in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorak, M.T. Sexual dimorphism in molecular biology of cancer, Principles of Gender-Specific Medicine [Fourth Edition], Editor[s]: Marianne J. Legato, Academic Press, 2023; Chapter 29, Pages 463-476. [CrossRef]
- Lassek, W.D.; Gaulin, S.J.C. Substantial but Misunderstood Human Sexual Dimorphism Results Mainly From Sexual Selection on Males and Natural Selection on Females. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 859931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regitz-Zagrosek, V. Sex and gender differences in health. Science & Society Series on Sex and Science. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maney, D.L. Perils and pitfalls of reporting sex differences. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2016; B3712015011920150119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Trynda, J.; Williams, C.; Vold, J.A.; Nguyen, J.H.; Harnois, D.M.; Bagaria, S.P.; McLaughlin, S.A.; Li, Z. Sexual dimorphism in the incidence of human cancers. BMC Cancer. 2019, 19, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Lim, H.; Moon, A. Sex Differences in Cancer: Epidemiology, Genetics and Therapy. Biomol Ther [Seoul]. 2018, 26, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, J.B. The spectrum of sex differences in cancer. Trends Cancer. 2022, 8, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, L.; Freyn, M.; Kalder, M.; Dinas, K.; Kostev, K. Impact of tobacco smoking on the risk of developing 25 different cancers in the UK: a retrospective study of 422,010 patients followed for up to 30 years. Oncotarget. 2018, 9, 17420–17429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumgay, H.; Shield, K.D.; Charvat, H.; Ferrari, P.; Sornpaisarn, B.; Obot, I. Global burden of cancer in 2020 attributable to alcohol consumption: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 2021. [CrossRef]
- Abancens, M.; Bustos, V.; Harvey, H.; McBryan, J.; Harvey, B.J. Sexual Dimorphism in Colon Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 607909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; He, J.; Ren, S.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F. Gender Differences in Colorectal Cancer Survival: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 14. Globocan. Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide 2018. Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/10_8_9-Colorectum-fact-sheet.pdf; at: https; Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/10_8_9-Colorectum-fact-sheet.pdf.
- Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/. (accessed on 14 July 2023).
- Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/trends?types=0_1&sexes=1_2&mode=population&group_populations=0&multiple_populations=1&multiple_cancers=1&cancers=8&populations=994&apc=cat_ca20v1.5_ca23v-1.
- Hogan, A.M.; Collins, D.; Baird, A.W.; Winter, D.C. Estrogen and gastrointestinal malignancy. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2009, 307, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.H.; Jalaludin, B.; Wong, S.K.; Kneebone, A.; Connor, S.J.; Leong, R.W. Improved survival in young women with colorectal cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennert, G.; Rennert, H.S.; Pinchev, M.; Lavie, O.; Gruber, S.B. Use of hormone replacement therapy and the risk of colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4542–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, H.D.; Humphrey, L.L.; Nygren, P.; Teutsch, S.M.; Allan, J.D. Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy: scientific review. JAMA. 2002, 288, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlebowski, R.T.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Ritenbaugh, C.; Hubbell, F.A.; Ascensao, J.; Rodabough, R.J.; Rosenberg, C.A.; Taylor, V.M.; Harris, R.; Chen, C.; Adams-Campbell, L.L.; White, E. Estrogen plus progestin and colorectal cancer in postmenopausal women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennelly, R.; Kavanagh, D.O.; Hogan, A.M.; Winter, D.C. Oestrogen and the colon: potential mechanisms for cancer prevention. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiazza, F.; Ryan, E.J.; Doherty, G.; Winter, D.C.; Sheahan, K. Estrogen receptors and their implications in colorectal carcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perotti, V.; Fabiano, S.; Contiero, P.; Michiara, M.; Musolino, A.; Boschetti, L.; Cascone, G.; Castelli, M.; Tagliabue, G.; Cancer Registries Working Group. Influence of Sex and Age on Site of Onset, Morphology, and Site of Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer: A Population-Based Study on Data from Four Italian Cancer Registries. Cancers 2023, 15, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Menter, D.G.; Kopetz, S. Right Versus Left Colon Cancer Biology: Integrating the Consensus Molecular Subtypes. J. Natl. Compr. Canc Netw. 2017, 15, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupon, C.; Hosseinian, A.; Kim, M.H. Simultaneous determination of plasma estrogens, androgens, and progesterone during the human menstrual cycle. Steroids. 1973, 22, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shutt, D.A.; Smith, I.D.; Shearman, R.P. Oestrone, oestradiol-17beta and oestriol levels in human foetal plasma during gestation and at term. J. Endocrinol. 1974, 60, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Banerjee, A.; Singh, D.; Thakur, G.; Kasarpalkar, N.; Gavali, S.; Gadkar, S.; Madan, T.; Mahale, S.D.; Balasinor, N.H.; Sachdeva, G. Estradiol: A Steroid with Multiple Facets. Horm. Metab. Res. 2018, 50, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, R.C.; Garratt, M.G. Life history evolution, reproduction, and the origins of sex-dependent aging and longevity. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2017, 1389, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, K.J.; Hewitt, S.C.; Arao, Y.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen Hormone Biology. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. [CrossRef]
- Barzi, A.; Lenz, A.M.; Labonte, M.J.; Lenz, H.J. Molecular pathways: Estrogen pathway in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5842–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemzadeh, M.; Haseefa, F.; Peyton, L.; Park, S.; Movahed, M.R. The effects of estrogen and hormone replacement therapy on platelet activity: a review. Am. J. Blood Res. 2022, 12, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henderson, B.E.; Feigelson, H.S. Hormonal carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.K.; Saha, J.; Pillai, S.; Lam, A.K.; Gopalan, V.; Islam, F. Implications of estrogen and its receptors in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 4367–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moggs, J.G.; Orphanides, G. Estrogen receptors: orchestrators of pleiotropic cellular responses. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topi, G.; Ghatak, S.; Satapathy, S.R.; Ehrnström, R.; Lydrup, M.L.; Sjölander, A. Combined Estrogen Alpha and Beta Receptor Expression Has a Prognostic Significance for Colorectal Cancer Patients. Front Med [Lausanne]. 2022, 9, 739620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.L.; Xu, X.; Norfleet, A.M.; Watson, C.S. The presence of functional estrogen receptors in intestinal epithelial cells. Endocrinology. 1993, 132, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.L.; Javid, S.H.; Carothers, A.M.; Redston, M.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Estrogen receptors α and β are inhibitory modifiers of Apc-dependent tumorigenesis in the proximal colon of Min/+ mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; DiLeo, A.; Niv, Y.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Estrogen receptor beta as target for colorectal cancer prevention. Cancer Lett. 2016, 372, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, E.F.; Jazaeri, A.A.; Shupnik, M.A.; Jazaeri, O.; Rice, L.W. Selective loss of estrogen receptor β in malignant human colon. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Baraibar, J. Ros, N. Saoudi, F. Salvà, A. García, M.R. Castells, J. Tabernero, E. Élez, Sex and gender perspectives in colorectal cancer, ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen signaling: a subtle balance between ER alpha and ER beta. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditonno, I.; Losurdo, G.; Rendina, M.; Pricci, M.; Girardi, B.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A. Estrogen Receptors in Colorectal Cancer: Facts, Novelties and Perspectives. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4256–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; DiLeo, A.; Niv, Y.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Estrogen receptor beta as target for colorectal cancer prevention. Cancer Lett. 2016, 372, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; et al. The prognostic and therapeutic role of hormones in colorectal cancer: a review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingi, J.W.; Tang, S.; Liu, S.; Ngenya, W.; Bao, E. Targeting estrogen receptors in colorectal cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4087–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Levin, E.R. Nature of functional estrogen receptors at the plasma membrane. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Mahony, F.; Thomas, W.; Harvey, B.J. Novel female sex-dependent actions of oestrogen in the intestine. J. Physiol. 2009, 587 Pt. 21, 5039–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquot, Y.; de Cremoux, P.; Harvey, B.J.; Wehling, M. The Rapid Responses to Steroid Hormones meetings: An important event for steroid science. Ann Endocrinol [Paris]. 2023, 84, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Frigo, D.E.; Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Prossnitz, E.R. Steroid Hormones and Receptors in Health and Disease: A Research Conference Co-Organized by FASEB and the International Committee on Rapid Responses to Steroid Hormones [RRSH], May 25-27, 2021. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, B.J. Guest editorial: 11th international meeting on rapid responses to steroid hormones RRSH2018. Steroids. 2020, 154, 108552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.R. Plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacenik, D.; Beswick, E.J.; Krajewska, W.M.; Prossnitz, E.R. G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in Colon Function, Immune Regulation and Carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4092–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkenfeld, S.R.; Lin, C.; Frigo, D.E. Communication between genomic and non-genomic signaling events coordinate steroid hormone actions. Steroids. 2018, 133, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R.; Hammes, S.R. Nuclear receptors outside the nucleus: extranuclear signalling by steroid receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Mahony, F.; Harvey, B.J. Sex and estrous cycle-dependent rapid protein kinase signaling actions of estrogen in distal colonic cells. Steroids. 2008, 73, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, N.; Silveyra, P. Estrogen receptor signaling mechanisms. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2019, 116, 135–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R. Extranuclear estrogen receptor's roles in physiology: lessons from mouse models. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 307, E133–E140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditonno, I.; Losurdo, G.; Rendina, M.; Pricci, M.; Girardi, B.; Ierardi, E.; Di Leo, A. Estrogen Receptors in Colorectal Cancer: Facts, Novelties and Perspectives. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4256–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koveitypour, Z.; Panahi, F.; Vakilian, M.; et al. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losordo, D.W.; Isner, J.M. Estrogen and angiogenesis: A review. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargett, C.E.; Zaitseva, M.; Bucak, K.; Chu, S.; Fuller, P.J.; Rogers, P.A. 17-Beta-estradiol up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression in human myometrial microvascular endothelial cells: role of estrogen receptor-alpha and -beta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 4341–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, W.M.; Yu, M.; Markowitz, S.D. Epigenetic Alterations in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Current and Emerging Use for Biomarkers of Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2021, 160, 690–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cignarella, A.; Boscaro, C.; Albiero, M.; Bolego, C.; Barton, M. Post-transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of estrogen signaling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoriki, K.; Mori, T.; Kokabu, T.; Matsushima, H.; Umemura, S.; Tarumi, Y.; Kitawaki, J. Estrogen-related receptor alpha induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition through cancer-stromal interactions in endometrial cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.; Datta, P.K. Regulation of EMT in Colorectal Cancer: A Culprit in Metastasis. Cancers 2017, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Zazzo, E.; Galasso, G.; Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Bilancio, A.; Perillo, B.; Sinisi, A.A.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Estrogen Receptors in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Prostate Cancer. Cancers [Basel]. 2019, 11, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouris, P.; Skandalis, S.S.; Piperigkou, Z.; Afratis, N.; Karamanou, K.; Aletras, A.J.; Moustakas, A.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Estrogen receptor alpha mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transition, expression of specific matrix effectors and functional properties of breast cancer cells. Matrix Biol. 2015, 43, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzołek, I.; Sobieraj, J.; Domagała-Kulawik, J. Estrogens, Cancer and Immunity. Cancers [Basel]. 2022, 14, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafari, N.; Khosravi, F.; Rezaee, Z.; Esfandyari, S.; Bahiraei, M.; Bahramy, A.; Ferns, G.A.; Avan, A. The role of the tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer and the potential therapeutic approaches. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hases, L.; Archer, A.; Williams, C. ERβ and Inflammation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1390, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolan, C.M.; Condliffe, S.B.; Harvey, B.J. Rapid non-genomic activation of cytosolic cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity and [Ca[2+]][i] by 17beta-oestradiol in female rat distal colon. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arterburn, J.B.; Prossnitz, E.R. G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor GPER: Molecular Pharmacology and Therapeutic Applications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoncini, T.; Genazzani, A.R. Non-genomic actions of sex steroid hormones. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 148, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slattery, M.L.; Lundgreen, A.; Wolff, R.K. MAP kinase genes and colon and rectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2012, 33, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irnaten, M.; Blanchard-Gutton, N.; Harvey, B.J. Rapid effects of 17beta-estradiol on epithelial TRPV6 Ca2+ channel in human T84 colonic cells. Cell Calcium. 2008, 44, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Mahony, F.; Alzamora, R.; Betts, V.; LaPaix, F.; Carter, D.; Irnaten, M.; Harvey, B.J. Female gender-specific inhibition of KCNQ1 channels and chloride secretion by 17beta-estradiol in rat distal colonic crypts. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24563–24573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R.; Shuba, Y. Ion Channels in Cancer: Are Cancer Hallmarks Oncochannelopathies? Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 559–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Pallottini, V.; Trentalance, A. Estrogens cause rapid activation of IP3-PKC-alpha signal transduction pathway in HEPG2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 245, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolan, C.M.; Harvey, B.J. Modulation of cytosolic protein kinase C and calcium ion activity by steroid hormones in rat distal colon. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8763–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Marino, M. Synergism between genomic and non genomic estrogen action mechanisms. IUBMB Life. 2003, 55, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Aitkenhead, M.; Hughes, C.C.; Levin, E.R. Integration of the non-genomic and genomic actions of estrogen. Membrane-initiated signaling by steroid to transcription and cell biology. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50768–50775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnström, L.; Sjöberg, M. Mechanisms of Estrogen Receptor Signaling: Convergence of Genomic and Nongenomic Actions on Target Genes. Mol. Endocrinol. Baltim. Md. 2005, 19, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.B.; Franke, T.F.; Stoica, G.E.; Chambon, P.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Stoica, B.A.; McLemore, M.S.; Olivo, S.E.; Stoica, A. A role for Akt in mediating the estrogenic functions of epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 2000, 141, 4503–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Endoh, H.; Masuhiro, Y.; Kitamoto, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Sasaki, H.; Masushige, S.; Gotoh, Y.; Nishida, E.; Kawashima, H.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P. Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science. 1995, 270, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R. Integration of the Extranuclear and Nuclear Actions of Estrogen. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Lupien, M.; Stossi, F.; Brown, M. Genomic Collaboration of Estrogen Receptor α and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 2 in Regulating Gene and Proliferation Programs. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2011, 31, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, B.A.; Harvey, B.J.; Healy, V. 17beta-Estradiol rapidly stimulates c-fos expression via the MAPK pathway in T84 cells. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2005, 229, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Mahony, F.; Alzamora, R.; Chung, H.L.; Thomas, W.; Harvey, B.J. Genomic priming of the antisecretory response to estrogen in rat distal colon throughout the estrous cycle. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, C.B.; Robinson, S.; Shapiro, R.A.; Dorsa, D.M. Estrogen receptor [ER]alpha and ERbeta exhibit unique pharmacologic properties when coupled to activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Endocrinology. 2001, 142, 2336–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R. Membrane estrogen receptors signal to determine transcription factor function. Steroids. 2018, 132, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Aitkenhead, M.; Hughes, C.C.; Levin, E.R. Integration of the non-genomic and genomic actions of estrogen. Membrane-initiated signaling by steroid to transcription and cell biology. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50768–50775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzi, A.; Lenz, A.M.; Labonte, M.J.; Lenz, H.J. Molecular pathways: Estrogen pathway in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5842–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Galluzzo, P.; Ascenzi, P. Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription. Curr. Genomics. 2006, 7, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, R.; Magner, A.; David, J.; Datta, J.; Vallabhaneni, M.; Kassem, M.; Manouchehri, J.; Willingham, N.; Stover, D.; Vandeusen, J.; Sardesai, S.; Williams, N.; Wesolowski, R.; Lustberg, M.; Ganju, R.K.; Ramaswamy, B.; Cherian, M.A. Estrogen Receptor Beta [ERβ]: A Ligand Activated Tumor Suppressor. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 587386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Hwang, P.M.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Cell. 2001, 7, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Barros, R.P.; Warner, M.; Ström, A.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Insight into the mechanisms of action of estrogen receptor β in the breast, prostate, colon, and CNS. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 51, T61–T74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topi, G.; Satapathy, S.R.; Dash, P.; Fred Mehrabi, S.; Ehrnström, R.; Olsson, R.; Lydrup, M.L.; Sjölander, A. Tumour-suppressive effect of oestrogen receptor β in colorectal cancer patients, colon cancer cells, and a zebrafish model. J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Waters, C.E.; Lewis, A.E.; Langman, M.J.; Eggo, M.C. Oestrogen-induced apoptosis in colonocytes expressing oestrogen receptor beta. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 174, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topi, G.; Satapathy, S.R.; Dash, P.; Fred Mehrabi, S.; Ehrnström, R.; Olsson, R.; Lydrup, M.L.; Sjölander, A. Tumour-suppressive effect of oestrogen receptor β in colorectal cancer patients, colon cancer cells, and a zebrafish model. J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineti, V.; Picariello, L.; Tognarini, I.; Carbonell Sala, S.; Gozzini, A.; Azzari, C.; et al. ERbeta is a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation in the HCT8 human colon cancer cell line through regulation of cell cycle components. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Huang, C.; Wu, H.; Huang, J. Estrogen Receptor Beta [ERβ] Mediated-CyclinD1 Degradation via Autophagy Plays an Anti-Proliferation Role in Colon Cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hases, L.; Indukuri, R.; Birgersson, M.; Nguyen-Vu, T.; Lozano, R.; Saxena, A.; et al. Intestinal estrogen receptor beta suppresses colon inflammation and tumorigenesis in both sexes. Cancer Lett. 2020, 492, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braniste, V.; Leveque, M.; Buisson-Brenac, C.; Bueno, L.; Fioramonti, J.; Houdeau, E. Oestradiol decreases colonic permeability through oestrogen receptor beta-mediated up-regulation of occludin and junctional adhesion molecule-A in epithelial cells. J. Physiol. 2009, 587 Pt. 13, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.S.; Lombardi, A.P.G.; de Souza, D.S.; Vicente, C.M.; Porto, C.S. Activation of estrogen receptor beta [ERβ] regulates the expression of N-cadherin, E-cadherin and β-catenin in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Vu, T.; Wang, J.; Mesmar, F.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Saxena, A.; McCollum, C.W.; Gustafsson, J.Å.; Bondesson, M.; Williams, C. Estrogen receptor beta reduces colon cancer metastasis through a novel miR-205 - PROX1 mechanism. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 42159–42171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hases, L.; Archer, A.; Indukuri, R.; Birgersson, M.; Savva, C.; Korach-André, M.; Williams, C. High-fat diet and estrogen impacts the colon and its transcriptome in a sex-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.; Wihlén, B.; Tujague, M.; Wan, J.; Ström, A.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptor [ER] beta modulates ERalpha-mediated transcriptional activation by altering the recruitment of c-Fos and c-Jun to estrogen-responsive promoters. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougelet, A.; Mueller, S.O.; Korach, K.S.; Renoir, J.M. Oestrogen receptors pathways to oestrogen responsive elements: the transactivation function-1 acts as the keystone of oestrogen receptor [ER]beta-mediated transcriptional repression of ERalpha. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 104, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paech, K.; Webb, P.; Kuiper, G.G.; et al. Differential ligand activation of estrogen receptors ERalpha and ERbeta at AP1 sites. Science. 1997, 277, 1508–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.L.; Javid, S.H.; Carothers, A.M.; Redston, M.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Estrogen receptors alpha and beta are inhibitory modifiers of Apc-dependent tumorigenesis in the proximal colon of min/+ mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland, A.G.; Oikarinen, S.I.; Bynoté, K.K.; Marttinen, M.; Rafter, J.J.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Roy, S.K.; Pitot, H.C.; Korach, K.S.; Lubahn, D.B.; Mutanen, M.; Gould, K.A. Disruption of estrogen receptor signaling enhances intestinal neoplasia in Apc[Min/+] mice. Carcinogenesis. 2009, 30, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topi, G.; Ghatak, S.; Satapathy, S.R.; Ehrnström, R.; Lydrup, M.L.; Sjölander, A. Combined Estrogen Alpha and Beta Receptor Expression Has a Prognostic Significance for Colorectal Cancer Patients. Front Med [Lausanne]. 2022, 9, 739620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.L.; Javid, S.H.; Carothers, A.M.; Redston, M.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Estrogen receptors alpha and beta are inhibitory modifiers of Apc-dependent tumorigenesis in the proximal colon of min/+ mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.Q.; Yu, J.P.; Luo, H.S. Expression of estrogen receptor beta in human colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.; DiLeo, A.; Niv, Y.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Estrogen receptor beta as target for colorectal cancer prevention. Cancer Lett. 2016, 372, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanato Filho, P.R.; Aguiar Júnior, S.; Begnami, M.D.; Ferreira, F.O.; Nakagawa, W.T.; Spencer, R.M.S.B.; et al. Estrogen receptor β as a prognostic marker of tumor progression in colorectal cancer with familial adenomatous polyposis and sporadic polyps. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2018, 24, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herichova, I.; Reis, R.; Hasakova, K.; Vician, M.; Zeman, M. Sex-dependent regulation of estrogen receptor beta in human colorectal cancer tissue and its relationship with clock genes and VEGF-A expression. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68 (Suppl. 3), :S297–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R. Levin, Bidirectional Signaling between the Estrogen Receptor and the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Molecular Endocrinology 2003, 17, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahcene Djaballah, S.; Daniel, F.; Milani, A.; Ricagno, G.; Lonardi, S. HER2 in Colorectal Cancer: The Long and Winding Road From Negative Predictive Factor to Positive Actionable Target. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2022, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, J.F.; Lenfant, F.; Metivier, R.; Flouriot, G.; Henrion, D.; Adlanmerini, M.; Fontaine, C.; Gourdy, P.; Chambon, P.; Katzenellenbogen, B.; Katzenellenbogen, J. Membrane and Nuclear Estrogen Receptor Alpha Actions: From Tissue Specificity to Medical Implications. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1045–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norfleet, A.M.; Thomas, M.L.; Gametchu, B.; Watson, C.S. Estrogen receptor-alpha detected on the plasma membrane of aldehyde-fixed GH3/B6/F10 rat pituitary tumor cells by enzyme-linked immunocytochemistry. Endocrinology. 1999, 140, 3805–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Levin, E.R. Nature of functional estrogen receptors at the plasma membrane. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.R. Plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acconcia, F.; Ascenzi, P.; Bocedi, A.; Spisni, E.; Tomasi, V.; Trentalance, A.; Visca, P.; Marino, M. Palmitoylation-dependent estrogen receptor alpha membrane localization: regulation by 17beta-estradiol. Mol Biol Cell. 2005, 16, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Ascenzi, P. Steroid hormone rapid signaling: the pivotal role of S-palmitoylation. IUBMB Life. 2006, 58, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evinger, A.J., 3rd; Levin, E.R. Requirements for estrogen receptor alpha membrane localization and function. Steroids. 2005, 70, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condliffe, S.B.; Doolan, C.M.; Harvey, B.J. 17beta-oestradiol acutely regulates Cl- secretion in rat distal colonic epithelium. J. Physiol. 2001, 530 Pt. 1, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, B.; Winter, D.C.; Cuffe, J.; Taylor, C.; O'Sullivan, G.C.; Harvey, B.J. Rapid activation of basolateral potassium transport in human colon by oestradiol. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 131, 1373–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolan, C.M.; Harvey, B.J. A Galphas protein-coupled membrane receptor, distinct from the classical oestrogen receptor, transduces rapid effects of oestradiol on [Ca2+]i in female rat distal colon. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2003, 199, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, J.F.; Lenfant, F.; Metivier, R.; Flouriot, G.; Henrion, D.; Adlanmerini, M.; Fontaine, C.; Gourdy, P.; Chambon, P.; Katzenellenbogen, B.; Katzenellenbogen, J. Membrane and Nuclear Estrogen Receptor Alpha Actions: From Tissue Specificity to Medical Implications. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1045–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Horkeby, K.; Henning, P.; Wu, J.; Lawenius, L.; Engdahl, C.; Gupta, P.; Movérare-Skrtic, S.; Nilsson, K.H.; Levin, E.; Ohlsson, C.; Lagerquist, M.K. Membrane estrogen receptor α signaling modulates the sensitivity to estradiol treatment in a dose- and tissue- dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefkovich, M.L.; Arao, Y.; Hamilton, K.J.; Korach, K.S. Experimental models for evaluating non-genomic estrogen signaling. Steroids. 2018, 133, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, T.C.; Gametchu, B.; Watson, C.S. Membrane estrogen receptors identified by multiple antibody labeling and impeded-ligand binding. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, W.R.; Kim, S.H.; Funk, C.C.; Madak-Erdogan, Z.; Schiff, R.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Estrogen dendrimer conjugates that preferentially activate extranuclear, nongenomic versus genomic pathways of estrogen action. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, A.; Razandi, M.; Kim, J.K.; O'Mahony, F.; Lee, E.Y.; Luderer, U.; Levin, E.R. Developmental phenotype of a membrane only estrogen receptor alpha [MOER] mouse. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3488–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlanmerini, M.; Solinhac, R.; Abot, A.; Fabre, A.; Raymond-Letron, I.; Guihot, A.L.; Boudou, F.; Sautier, L.; Vessières, E.; Kim, S.H.; Lière, P.; Fontaine, C.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Gourdy, P.; Shaul, P.W.; Henrion, D.; Arnal, J.F.; Lenfant, F. Mutation of the palmitoylation site of estrogen receptor α in vivo reveals tissue-specific roles for membrane versus nuclear actions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2014, 111, E283–E290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abot, A.; Fontaine, C.; Buscato, M.; Solinhac, R.; Flouriot, G.; Fabre, A.; Drougard, A.; Rajan, S.; Laine, M.; Milon, A.; Muller, I.; Henrion, D.; Adlanmerini, M.; Valéra, M.C.; Gompel, A.; Gerard, C.; Péqueux, C.; Mestdagt, M.; Raymond-Letron, I.; Knauf, C.; Ferriere, F.; Valet, P.; Gourdy, P.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Lenfant, F.; Greene, G.L.; Foidart, J.M.; Arnal, J.F. The uterine and vascular actions of estetrol delineate a distinctive profile of estrogen receptor α modulation, uncoupling nuclear and membrane activation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1328–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R. Rapid signaling by steroid receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1425–R1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Fiocchetti, M.; Busonero, C.; Fernandez, V.S.; Montalesi, E.; Cipolletti, M.; Pallottini, V.; Marino, M. The extra-nuclear interactome of the estrogen receptors: implications for physiological functions. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2021, 538, 111452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koveitypour, Z.; Panahi, F.; Vakilian, M.; et al. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolan, C.M.; Harvey, B.J. Modulation of cytosolic protein kinase C and calcium ion activity by steroid hormones in rat distal colon. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8763–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, D.C.; Taylor, C.; CO'Sullivan, G.; Harvey, B.J. Mitogenic effects of oestrogen mediated by a non-genomic receptor in human colon. Br. J. Surg. 2000, 87, 1684–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolan, C.M.; Condliffe, S.B.; Harvey, B.J. Rapid non-genomic activation of cytosolic cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity and [Ca[2+]][i] by 17beta-oestradiol in female rat distal colon. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Salazar, J.E.; Posadas-Rodríguez, P.; Lazzarini-Lechuga, R.C.; et al. Membrane-Initiated Estradiol Signaling of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Associated Mechanisms Through Regulation of Tight Junctions in Human Breast Cancer Cells. HORM CANC 2014, 5, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouni, E.; Nejad, M.M.; Mojtabavi, S.; Khoshduz, S.; Mojtabavi, M.; Nadafzadeh, N.; Nikpanjeh, N.; Mirzaei, S.; Hashemi, M.; Aref, A.R.; Khorrami, R.; Nabavi, N.; Ertas, Y.N.; Salimimoghadam, S.; Zandieh, M.A.; Rahmanian, P.; Taheriazam, A.; Hushmandi, K. Unraveling the function of epithelial-mesenchymal transition [EMT] in colorectal cancer: Metastasis, therapy response, and revisiting molecular pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouni, E.; Nejad, M.M.; Mojtabavi, S.; Khoshduz, S.; Mojtabavi, M.; Nadafzadeh, N.; Nikpanjeh, N.; Mirzaei, S.; Hashemi, M.; Aref, A.R.; Khorrami, R.; Nabavi, N.; Ertas, Y.N.; Salimimoghadam, S.; Zandieh, M.A.; Rahmanian, P.; Taheriazam, A.; Hushmandi, K. Unraveling the function of epithelial-mesenchymal transition [EMT] in colorectal cancer: Metastasis, therapy response, and revisiting molecular pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 160, 114395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.; Ascenzi, P. Membrane association of estrogen receptor alpha and beta influences 17beta-estradiol-mediated cancer cell proliferation. Steroids. 2008, 73, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, P.; Caiazza, F.; Moreno, S.; Marino, M. Role of ERbeta palmitoylation in the inhibition of human colon cancer cell proliferation. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2007, 14, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razandi, M.; Pedram, A.; Greene, G.L.; Levin, E.R. Cell membrane and nuclear estrogen receptors [ERs] originate from a single transcript: studies of ERα and ERβ expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Galluzzo, P.; Leone, S.; Acconcia, F.; Ascenzi, P. Nitric oxide impairs the 17β-estradiol-induced apoptosis in human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2006, 13, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Totta, P.; Ogawa, S.; Cardillo, I.; Inoue, S.; Leone, S.; Trentalance, A.; Muramatsu, M.; Marino, M. Survival versus apoptotic 17beta-estradiol effect: Role of ER alpha and ER beta activated non-genomic signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 203, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Cui, H. Estrogen Receptor Alpha Splice Variants, Post-Translational Modifications, and Their Physiological Functions. Cells. 2023, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon, S.P. Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Cancer. Cancers [Basel]. 2020, 12, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, E.M.; Schreihofer, D.A.; Periasamy, A.; Shupnik, M.A. Truncated estrogen receptor product-1 suppresses estrogen receptor transactivation by dimerization with estrogen receptors alpha and beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7158–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notas, G.; Panagiotopoulos, A.; Vamvoukaki, R.; Kalyvianaki, K.; Kiagiadaki, F.; Deli, A.; Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. ERα36-GPER1 Collaboration Inhibits TLR4/NFκB-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Activity in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.T.; Ortona, E.; Dupuis, M.L. A Role for Estrogen Receptor alpha36 in Cancer Progression. Front Endocrinol [Lausanne]. 2020, 11, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Huang, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. . A variant of estrogen receptor-alpha, ER-alpha36 is expressed in human gastric cancer and is highly correlated with lymph node metastasis. Oncol Rep. 24:171–6. 10. 3892. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Estrogen receptor mutations and functional consequences for breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Teng, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Cao, J.; Teng, L. Transcriptional analysis of estrogen receptor alpha variant mRNAs in colorectal cancers and their matched normal colorectal tissues. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 112, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revankar, C.M.; et al. A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science. 2005, 307, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edward, J. Filardo, Peter Thomas, Minireview: G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor-1, GPER-1: Its Mechanism of Action and Role in Female Reproductive Cancer, Renal and Vascular Physiology, Endocrinology 2012, 153, 2953–2962. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.; Pang, Y.; Filardo, E.J.; Dong, J. Identity of an estrogen membrane receptor coupled to a G protein in human breast cancer cells. Endocrinology.
- Qiu, Y.A.; Xiong, J.; Yu, T. Role of G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in Digestive System Carcinomas: A Minireview. Onco Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacenik, D.; Beswick, E.J.; Krajewska, W.M.; Prossnitz, E.R. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in colon function, immune regulation and carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4092–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, M.; Filardo, E.J.; Lolait, S.J.; Thomas, P.; Maggiolini, M.; Prossnitz, E.R. Twenty years of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor GPER: Historical and personal perspectives. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 176, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Barton, M. The G protein-coupled oestrogen receptor GPER in health and disease: an update. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R. G protein-coupled receptor 30: estrogen receptor or collaborator? Endocrinology. 2009, 150, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Liu, D. Does GPER Really Function as a G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in vivo? Front Endocrinol [Lausanne]. 2020, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacenik, D.; Krajewska, W.M. Significance of G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in the Pathophysiology of Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colorectal Cancer. Front Endocrinol [Lausanne] 2020, 11, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgert, R.; Emons, G.; Gründker, C. Estrogen Signaling in ERα-Negative Breast Cancer: ERβ and GPER. Front Endocrinol [Lausanne]. 2019, 9, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, V.; Nolan, Á.M.; Nijhuis, A.; Harvey, H.; Parker, A.; Poulsom, R.; et al. . GPER mediates differential effects of estrogen on colon cancer cell proliferation and migration under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 84258–84275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacenik, D.; Cygankiewicz, A.I.; Mokrowiecka, A.; Małecka-Panas, E.; Fichna, J.; Krajewska, W.M. Sex- and Age-Related Estrogen Signaling Alteration in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Modulatory Role of Estrogen Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Giessen, J.; van der Woude, C.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Fuhler, G.M. A Direct Effect of Sex Hormones on Epithelial Barrier Function in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models. Cells 2019, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhimoghadam, M.; Lu, A.S.; Salem, A.K.; Filardo, E.J. Therapeutic Perspectives on the Modulation of G-Protein Coupled Estrogen Receptor, GPER, Function. Front Endocrinol [Lausanne]. 2020, 11, 591217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypczak, M.; Goryca, K.; Rubel, T.; Paziewska, A.; Mikula, M.; Jarosz, D. Modeling oncogenic signaling in colon tumors by multidirectional analyses of microarray data directed for maximization of analytical reliability [published correction appears in PLoS One. 2010, 5. Ostrowsk, Jerzy [corrected to Ostrowski, Jerzy]]. PloS One Erratum: https://doi.org/10.1371/annotation/8c585739-a354-4fc9-a7d0-d5ae26fa06ca. 2010, 5, e13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J. Role of G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in Cancer Progression. Toxicological Res. 2019, 35, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepermans, R.A.; Sharma, G.; Prossnitz, E.R. G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in Cancer and Stromal Cells: Functions and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2021, 10, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, H.; et al. Epigenetic down regulation of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor [GPER] functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilligan, L.C.; Rahman, H.P.; Hewitt, A.M.; Sitch, A.J.; Gondal, A.; Arvaniti, A.; Taylor, A.E.; Read, M.L.; Morton, D.G.; Foster, P.A. Estrogen Activation by Steroid Sulfatase Increases Colorectal Cancer Proliferation via GPER. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 4435–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, E.K.K.; Lee, J.C.Y.; Turner, P.C.; et al. Low dose of zearalenone elevated colon cancer cell growth through G protein-coupled estrogenic receptor. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühler, M.; Fahrländer, J.; Sauter, A.; Becker, M.; Wistorf, E.; Steinfath, M.; Stolz, A. GPER1 links estrogens to centrosome amplification and chromosomal instability in human colon cells. Life Sci. Alliance. 2022, 6, e202201499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, E.M.; Sims, A.H.; Maggiolini, M.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P.; Clarke, R.B. GPER mediates the angiocrine actions induced by IGF1 through the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway in the breast tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepermans, R.A.; Sharma, G.; Prossnitz, E.R. G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in Cancer and Stromal Cells: Functions and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2021, 10, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia--a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Hou, M.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Y.; Gou, H. Expression of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in colorectal cancer: association with clinical outcomes and prognostic implications. BMC Cancer. 2009, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beggs, A.; Domingo, E.; McGregor, M.; Presz, M.; Johnstone, E.; Midgley, R.; Kerr, D.; Oukrif, D.; Novelli, M.; Abulafi, M.; Hodgson, S.V.; Fadhil, W.; Ilyas, M.; Tomlinson, I.P. Loss of expression of the double strand break repair protein ATM is associated with worse prognosis in colorectal cancer and loss of Ku70 expression is associated with CIN. Oncotarget. 2012, 3, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khatib, M.; Geara, F.; Haddadin, M.; Gali-Muhtasib, H. Cell death by the quinoxaline dioxide DCQ in human colon cancer cells is enhanced under hypoxia and is independent of p53 and p21. Radiat Oncol. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafari, N.; Khosravi, F.; Rezaee, Z.; Esfandyari, S.; Bahiraei, M.; Bahramy, A.; Ferns, G.A.; Avan, A. The role of the tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer and the potential therapeutic approaches. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatoff, E.M.; Leach, B.I.; Dow, L.E. Wnt Signaling and Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Colorectal. Cancer Rep. 2017, 13, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ming, T.; Tang, S.; Ren, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Tao, Q.; Xu, H. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: pathogenic role and therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer. 2022, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Sontz, R.A.; Vance, M.J.; Morris, J.M.; Sheriff, S.; Zhu, S.; Duan, S.; Zeng, J.; Koeppe, E.; Pandey, R.; Thorne, C.A.; Stoffel, E.M.; Merchant, J.L. High-fat diet plus HNF1A variant promotes polyps by activating β-catenin in early-onset colorectal cancer. JCI Insight. 2023, 8, e167163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzmenko, A.P.; Takeyama, K.; Ito, S.; Furutani, T.; Sawatsubashi, S.; Maki, A.; Suzuki, E.; Kawasaki, Y.; Akiyama, T.; Tabata, T.; Kato, S. Wnt/beta-catenin and estrogen signaling converge in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40255–40258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; Xie, W.; Man, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Estradiol promotes cells invasion by activating β-catenin signaling pathway in endometriosis. Reproduction. 2015, 150, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou X; et al. , Canonical Wnt Signaling Is Critical to Estrogen-Mediated Uterine Growth. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 3035–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, M.; Pasini, E.; Pastrello, C.; Angeli, M.; Baciu, C.; Abovsky, M.; Coffee, A.; Adeyi, O.; Kotlyar, M.; Jurisica, I. Estrogen Receptor 1 Inhibition of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Contributes to Sex Differences in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 777834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, G.W. Biology of the KCNQ1 Potassium Channel New. J. Sci. 2014, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, B.C.; Waldegger, S.; Fehr, S.; Bleich, M.; Warth, R.; Greger, R.; Jentsch, T.J. A constitutively open potassium channel formed by KCNQ1 and KCNE3. Nature 2000, 403, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than, B.L.; Goos, J.A.; Sarver, A.L.; O'Sullivan, M.G.; Rod, A.; Starr, T.K.; Fijneman, R.J.; Meijer, G.A.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Largaespada, D.A.; Scott, P.M.; Cormier, R.T. The role of KCNQ1 in mouse and human gastrointestinal cancers. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3861–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapetti-Mauss, R.; Bustos, V.; Thomas, W.; McBryan, J.; Harvey, H.; Lajczak, N.; Madden, S.F.; Pellissier, B.; Borgese, F.; Soriani, O.; Harvey, B.J. Bidirectional KCNQ1:β-catenin interaction drives colorectal cancer cell differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4159–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorthouse, D.; Zhuang, L.; Rahrmann, E.P.; Kosmidou, C.; Wickham Rahrmann, K.; Hall, M.; Greenwood, B.; Devonshire, G.; Gilbertson, R.J.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Hall, B.A. KCNQ potassium channels modulate Wnt activity in gastro-oesophageal adenocarcinomas. Life Sci. Alliance. 2023, 6, e202302124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzamora, R.; O'Mahony, F.; Bustos, V.; Rapetti-Mauss, R.; Urbach, V.; Cid, L.P.; Sepúlveda, F.V.; Harvey, B.J. Sexual dimorphism and oestrogen regulation of KCNE3 expression modulates the functional properties of KCNQ1 K⁺ channels. J. Physiol. 2011, 589 Pt. 21, 5091–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapetti-Mauss, R.; O'Mahony, F.; Sepulveda, F.V.; Urbach, V.; Harvey, B.J. Oestrogen promotes KCNQ1 potassium channel endocytosis and post-endocytic trafficking in colonic epithelium. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 2813–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapetti-Mauss, R.; Borgese, F.; Harvey, B.J.; Soriani, O. KCNQ1: a new regulator of the epithelio-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancers. Med Sci [Paris]. 2018, 34, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapetti-Mauss, R.; Berenguier, C.; Allegrini, B.; Soriani, O. Interplay Between Ion Channels and the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Cancers. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 525020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, C. Convergence between Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol. Cancer. 2010, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K. Signaling Cross Talk between TGF-β/Smad and Other Signaling Pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abancens, M.; Harvey, B.J.; McBryan, J. GPER Agonist G1 Prevents Wnt-Induced JUN Upregulation in HT29 Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasáková, K.; Bezakova, J.; Vician, M.; Reis, R.; Zeman, M.; Herichova, I. Gender-dependent expression of leading and passenger strand of miR-21 and miR-16 in human colorectal cancer and adjacent colonic tissues. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66 (Suppl. 4), S575–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamfjord, J.; Stangeland, A.M.; Hughes, T.; Skrede, M.L.; Tveit, K.M.; Ikdahl, T.; Kure, E.H. Differential expression of miRNAs in colorectal cancer: comparison of paired tumor tissue and adjacent normal mucosa using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e34150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, C.; Safadeh, E.; Sgueglia, G.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Altucci, L.; Dell'Aversana, C. MicroRNA-Assisted Hormone Cell Signaling in Colorectal Cancer Resistance. Cells. 2020, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herichova, I.; Reis, R.; Hasakova, K.; Vician, M. Downregulation of miR-30c-5p expression in colorectal cancer tissue is sex-dependent. Physiol Res. 2020, 69 (Suppl. 3), S479–S487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrgou, A.; Ebadollahi, S.; Seidi, K.; Ayoubi-Joshaghani, M.H.; Ahmadieh Yazdi, A.; Zare, P.; Jaymand, M.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R. Roles of miRNAs in Colorectal Cancer: Therapeutic Implications and Clinical Opportunities. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 11, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Unno, T.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, M.S. Sex Differences in Gut Microbiota. World J. Mens. Health. 2020, 38, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markle, J.G.; Frank, D.N.; Mortin-Toth, S.; Robertson, C.E.; Feazel, L.M.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; von Bergen, M.; McCoy, K.D.; Macpherson, A.J.; Danska, J.S. Sex differences in the gut microbiome drive hormone-dependent regulation of autoimmunity. Science. 2013, 339, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.M.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Estrogen-gut microbiome axis: Physiological and clinical implications. Maturitas 2017, 103, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.H.; Kim, N.; Nam, R.H.; Choi, S.I.; Lee, H.N.; Surh, Y.J. 17β-Estradiol supplementation changes gut microbiota diversity in intact and colorectal cancer-induced ICR male mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Yokoi, T. Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of estrogens and its regulation in human. Cancer Lett. 2005, 227, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 221. Reference 221.
- Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; Ramos-Molina, B.; Otero, A.; Laborda-Illanes, A.; Ordóñez, R.; Medina, J.A.; Gómez-Millán, J.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Colorectal Cancer Development and Therapy Response. Cancers 2020, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshan, M.H.; Tambo, A.; Pace, N.P. The role of testosterone in colorectal carcinoma: pathomechanisms and open questions. EPMA J. 2016, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lan, Z.; Liao, W.; et al. Histone demethylase KDM5D upregulation drives sex differences in colon cancer. Nature 2023, 619, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, H. How the Y chromosome makes some cancers more deadly for men. Nature. 2023, 618, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahbub, A.A. Therapeutic Strategies and Potential Actions of Female Sex Steroid Hormones and Their Receptors in Colon Cancer Based on Preclinical Studies. Life [Basel]. 2022, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrei, P.; Battuello, P.; Grasso, G.; Rovera, E.; Tesio, N.; Bardelli, A. Integrated approaches for precision oncology in colorectal cancer: The more you know, the better. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 84, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Lim, H.; Moon, A. Sex Differences in Cancer: Epidemiology, Genetics and Therapy. Biomol Ther [Seoul]. 2018, 26, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




