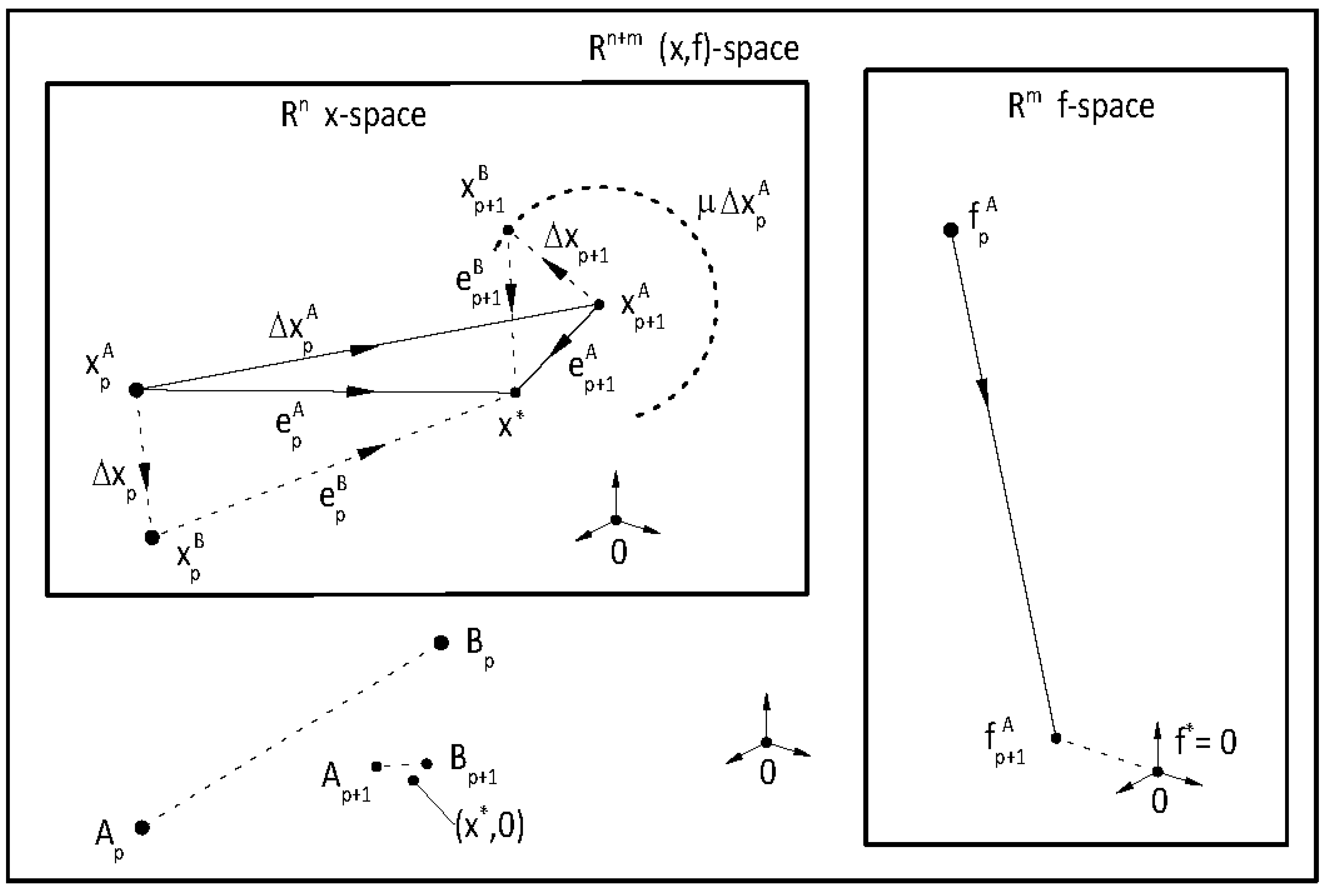
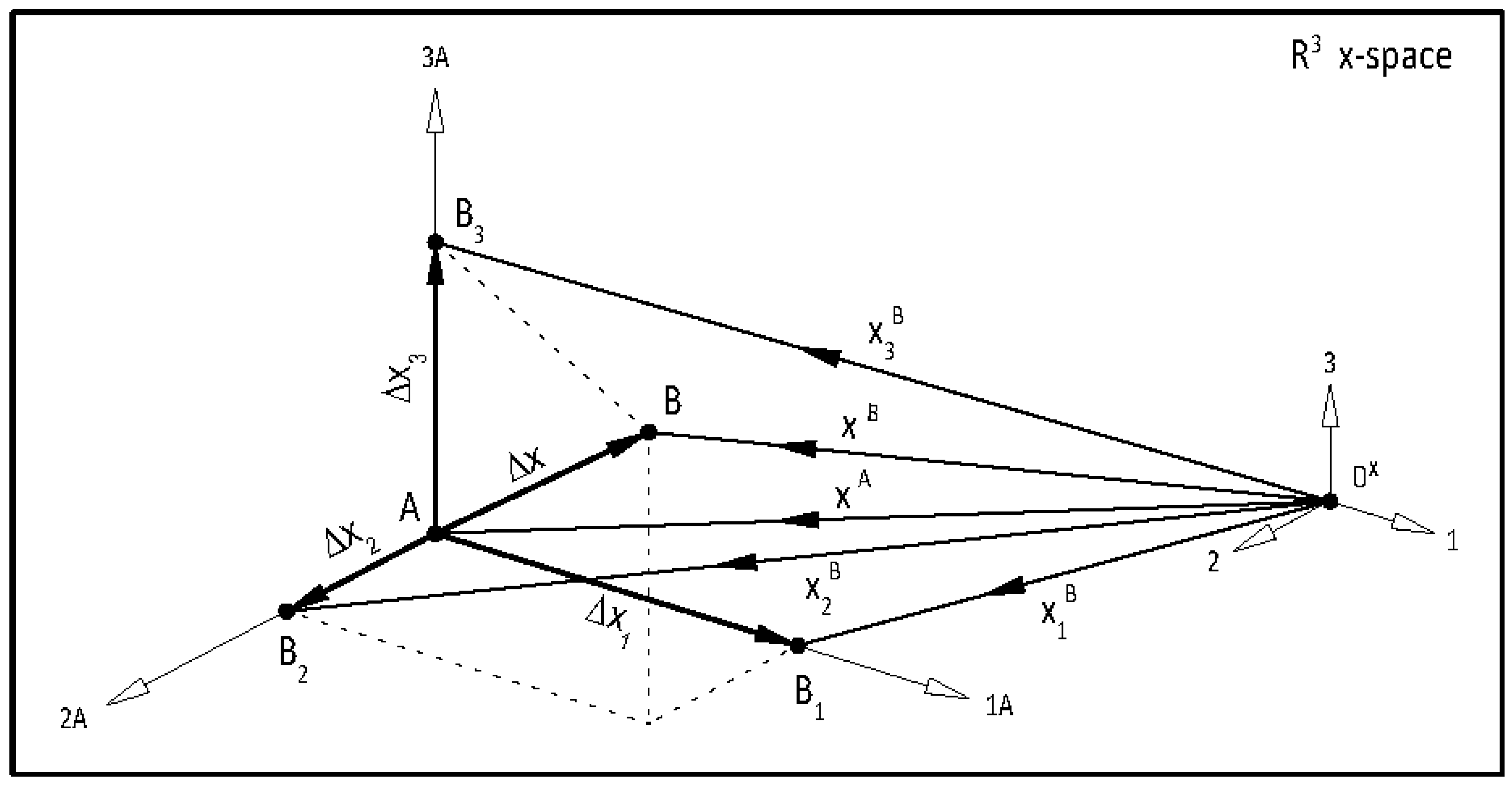
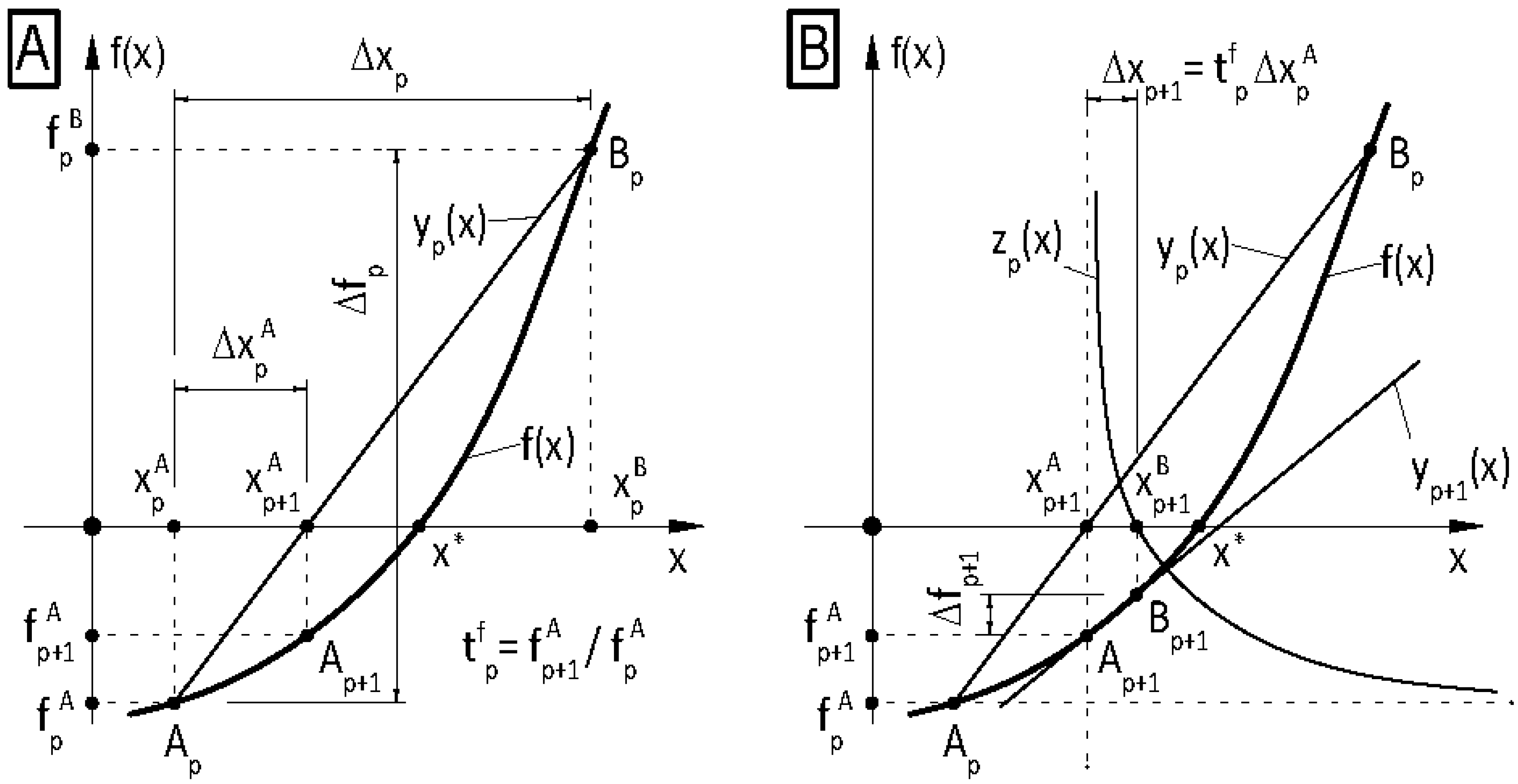
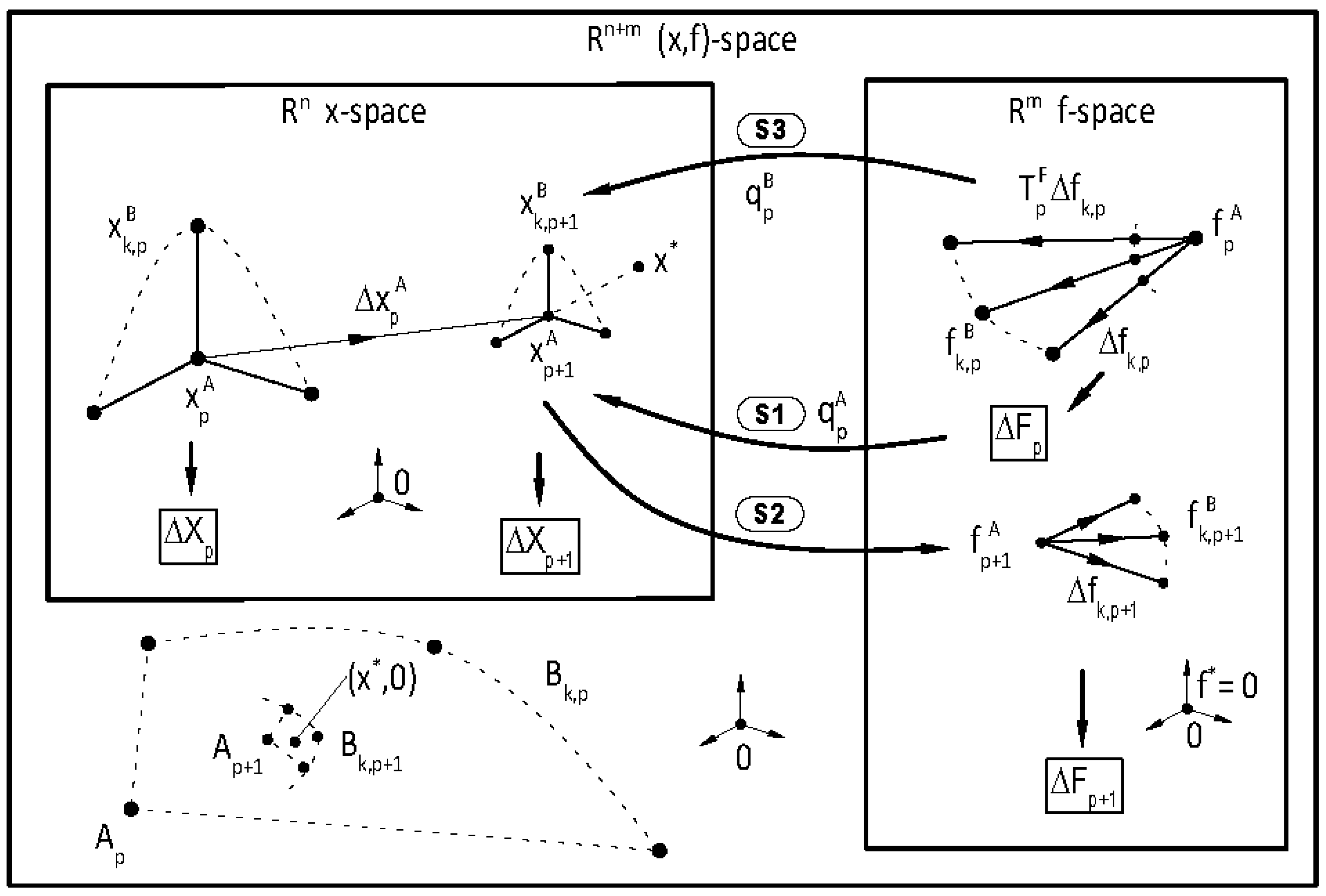
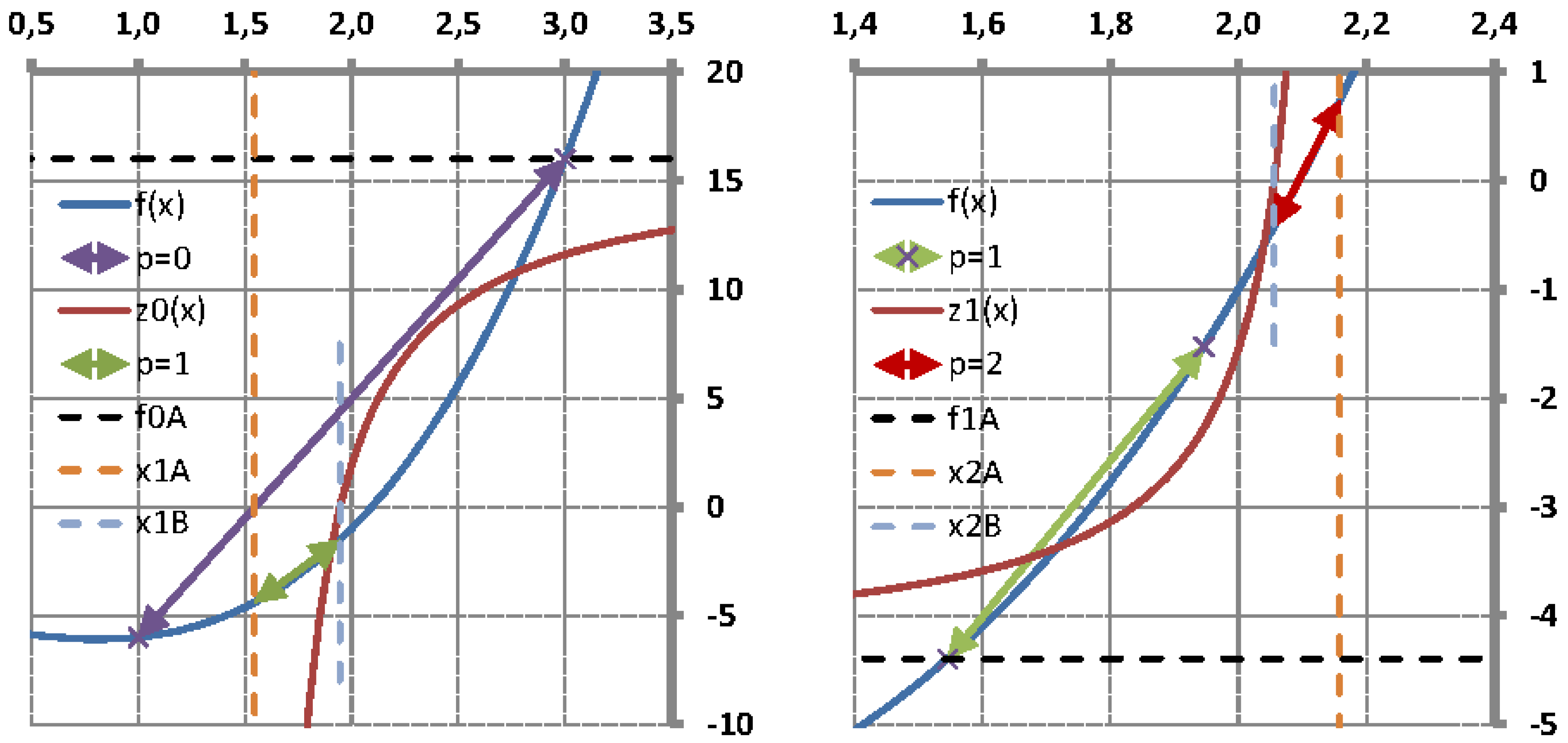
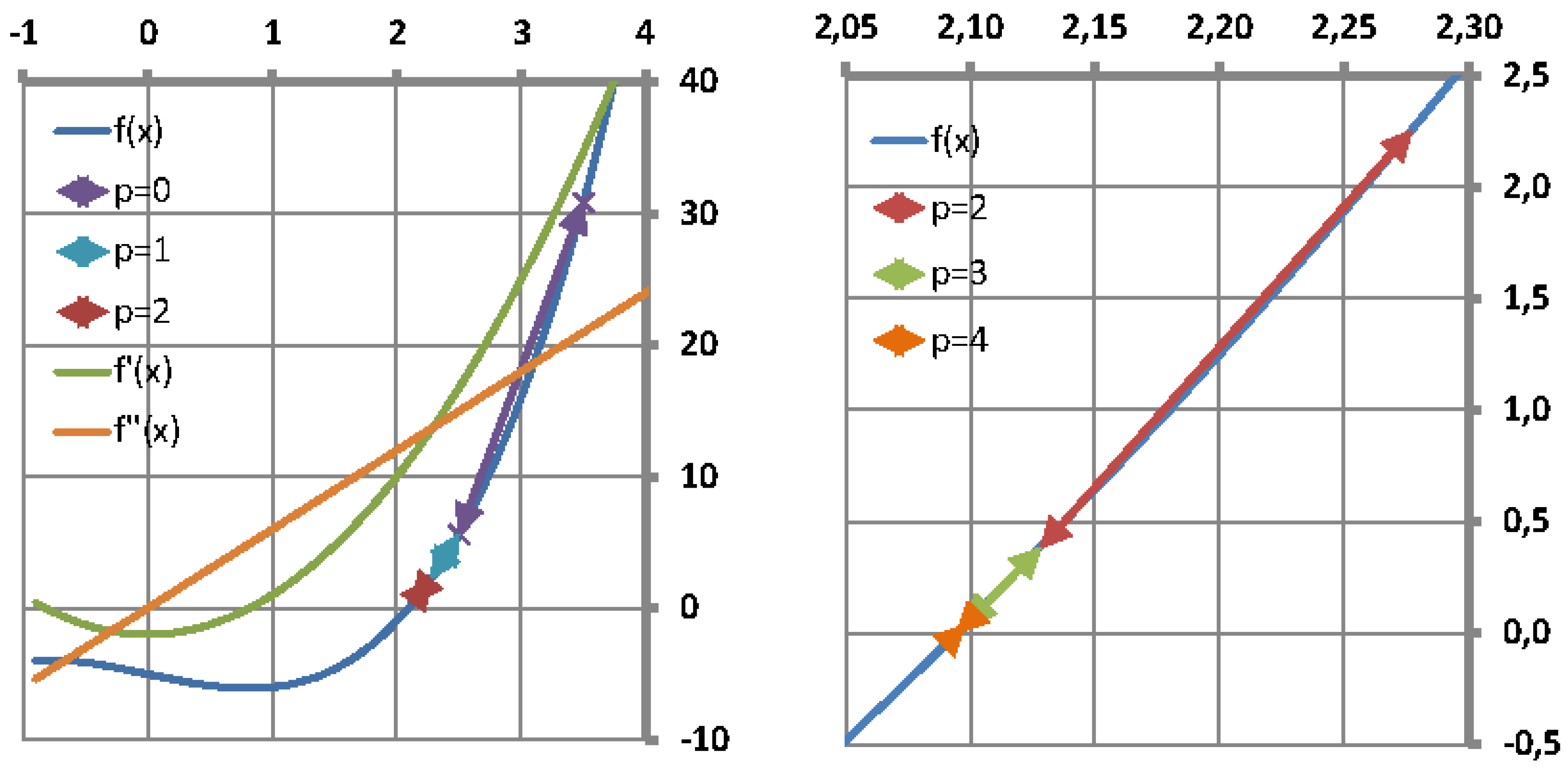
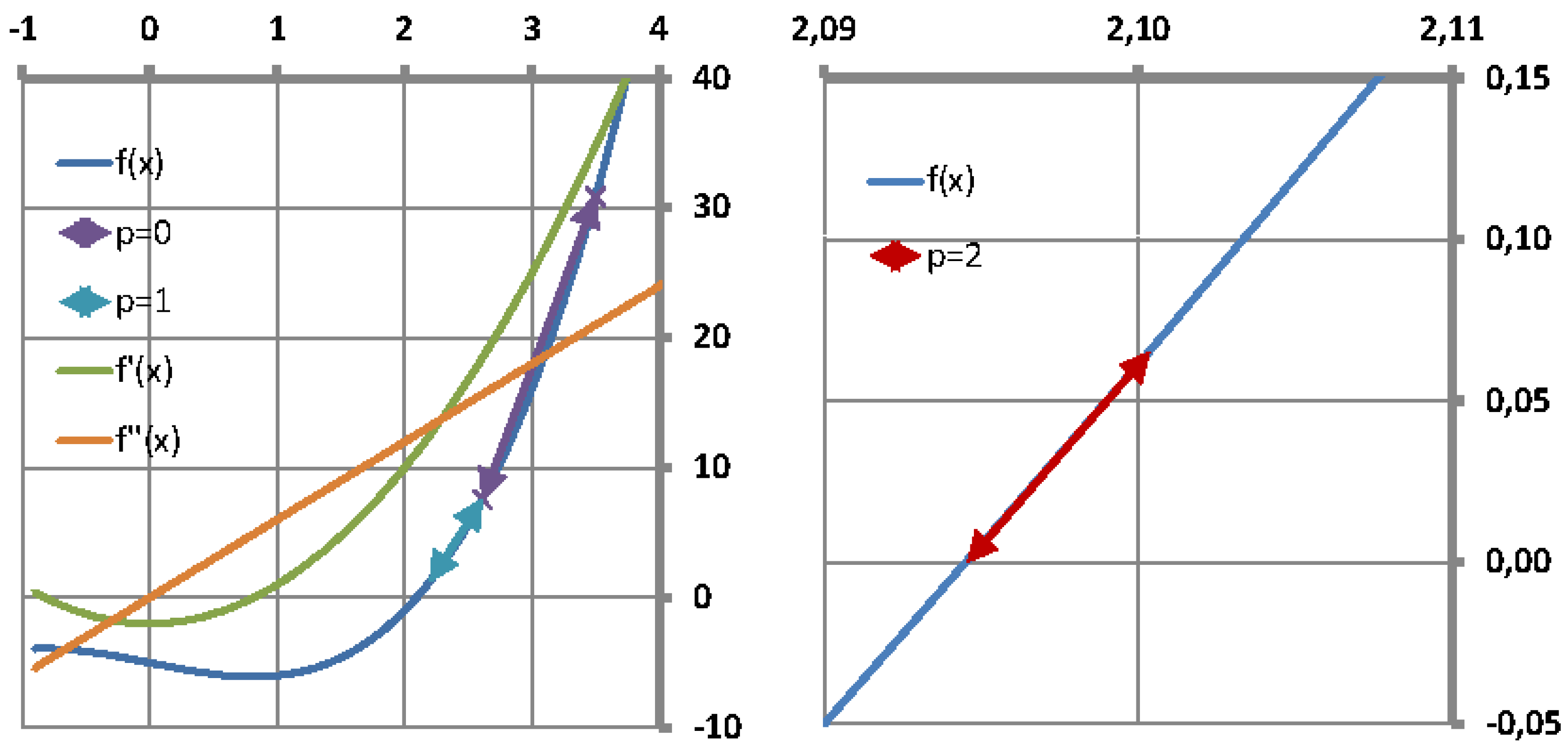
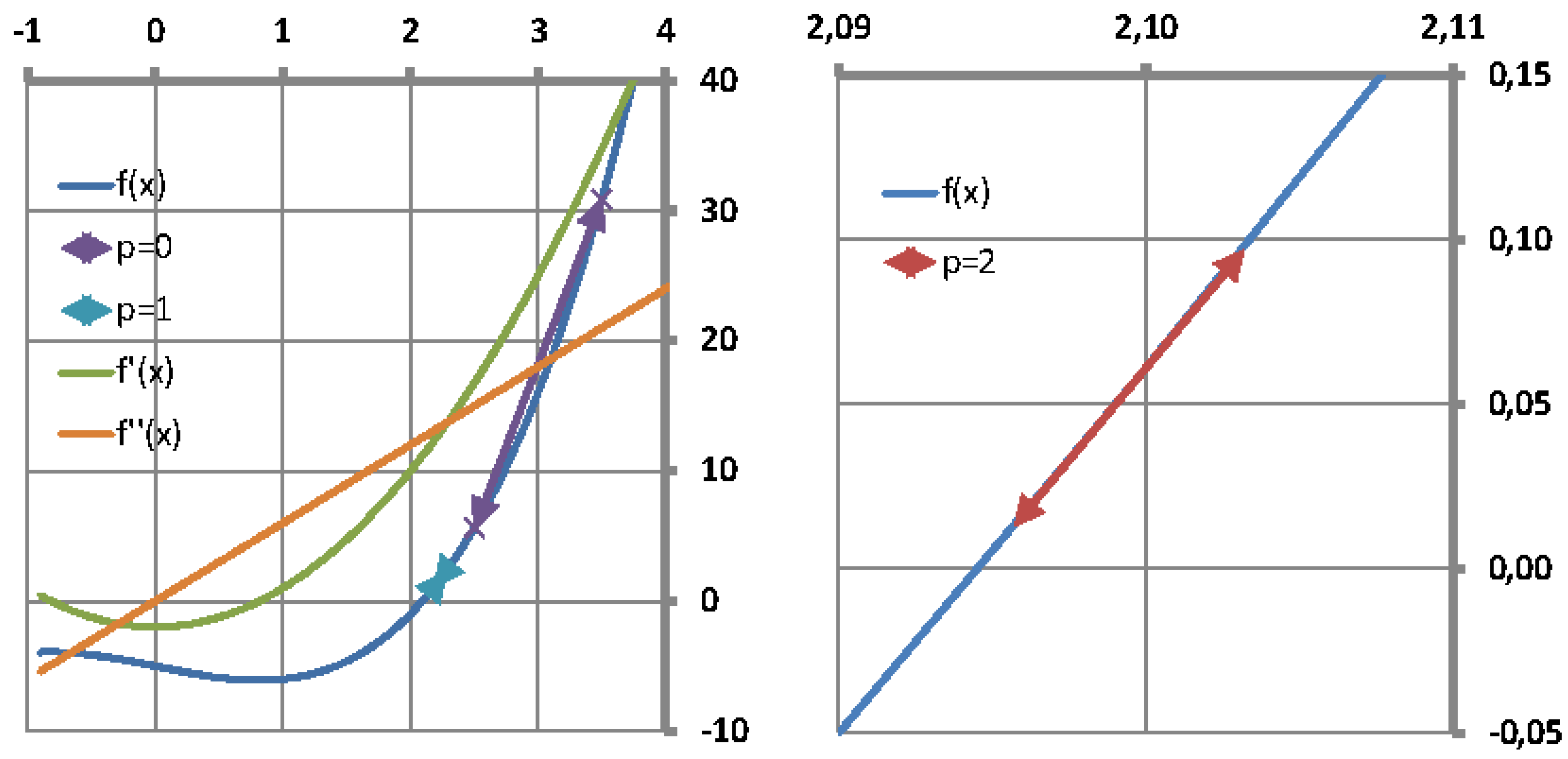
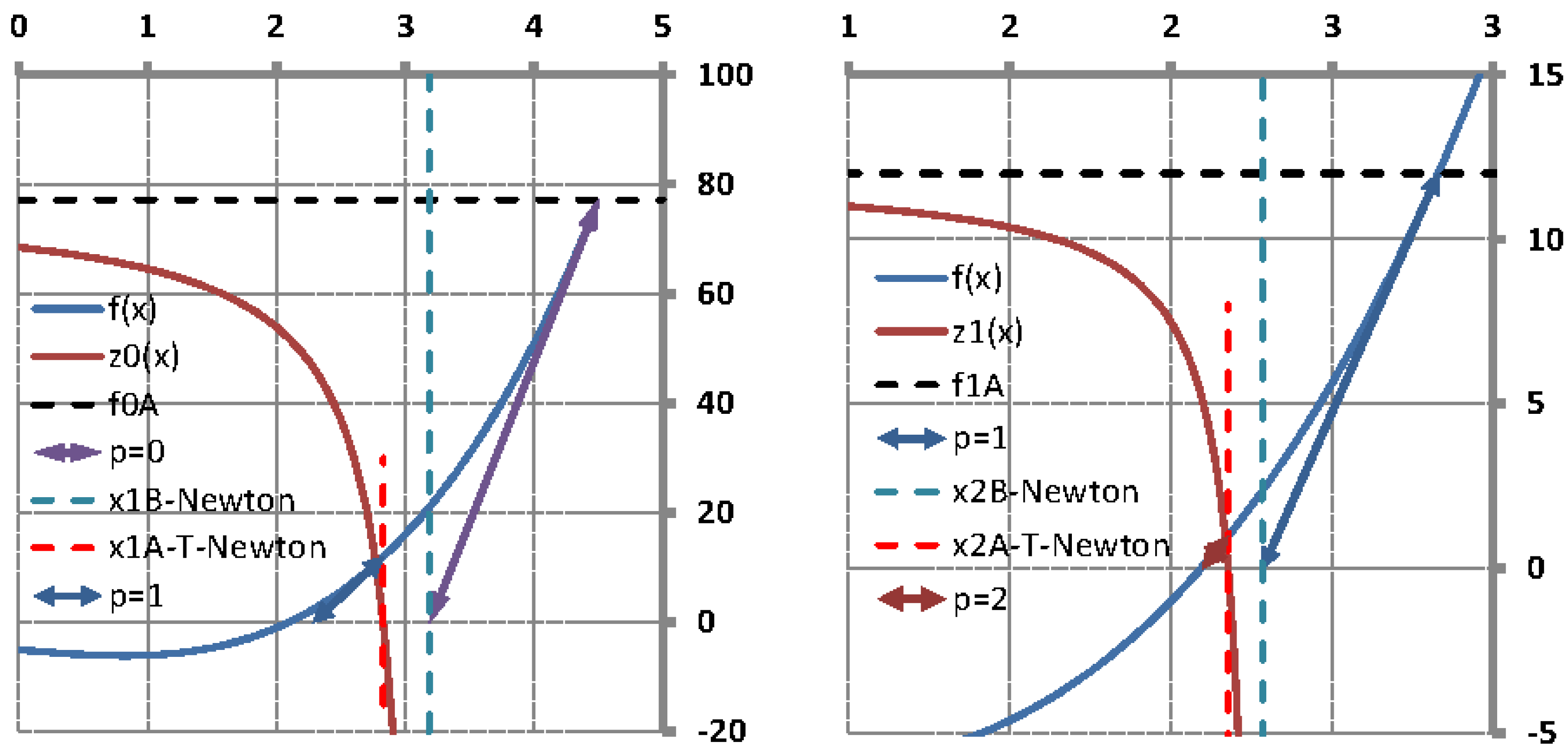
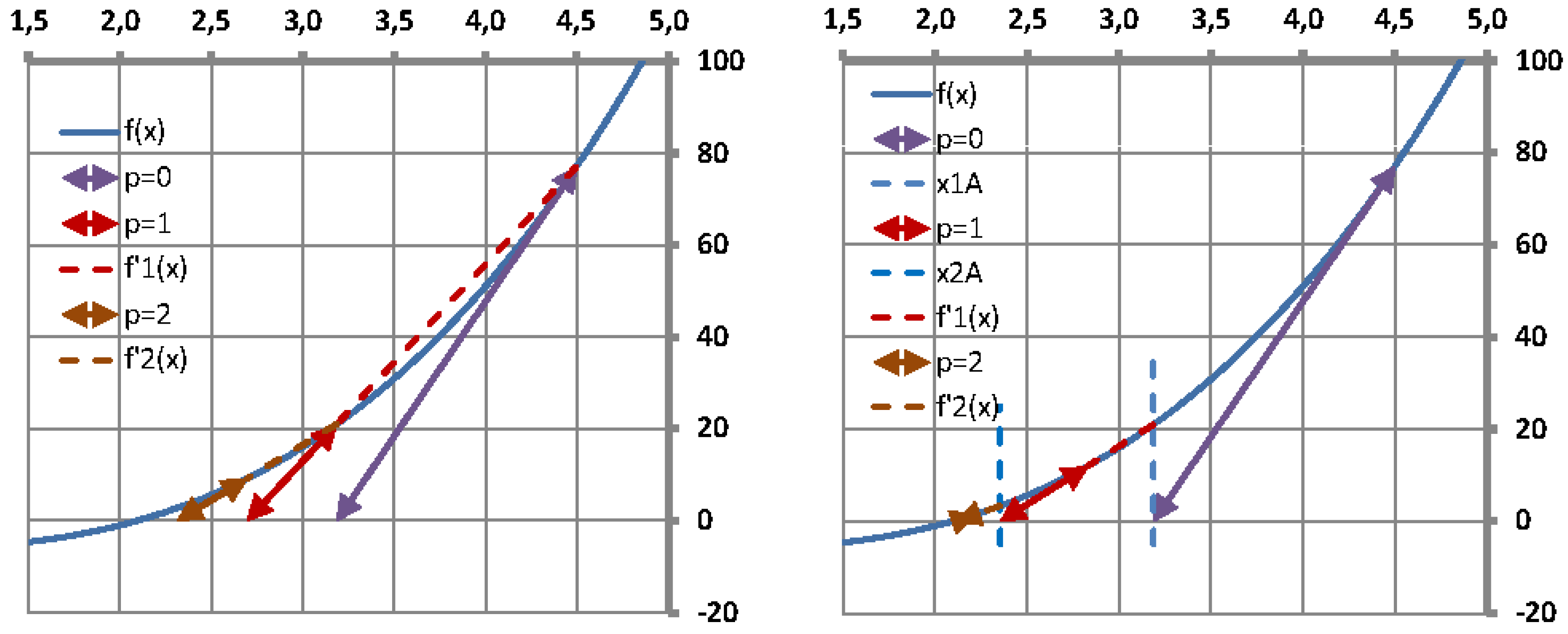
It is well known that the single-variable secant method has asymptotic convergence for sufficiently good initial approximates
and
if
doesn’t vanish in
and
is continuous at least in a neighborhood of the zero
. The super-linear convergence property has also been proved in different ways and it is known that the order of convergence
with asymptotic error constant
The order of convergence of the T-secant method is determined in this section. Let
be the iteration counter and the approximate error be defined in the
iteration as
It follows from Equation (
3.21) and from Definition
7.5 that the error
of the new secant approximate
can be expressed as
It follows from the mean value theorem, that the first factor of right side of Equation (
7.6) can be replaced with
, where
, if
is continuously differentiable on
and
. Let the function
be approximated around the root
by a
order Taylor series expansion as
where
in the remainder term. Since
, it follows from Equation (
7.7) that
Substituting this expression to Equation (
7.6), and since
we get
and
If the series
converges to
, then
and
with increasing iteration counter
, and
It follows from Equation (
4.11) with Definition
7.5 and from the mean value theorem (with
, if
is continuously differentiable on
) that
and the error
of the T-secant approximate
can be expressed as
With the Taylor-series expansion
7.7 for
and
, where
and
in the remainder term, we get
where
and
. If the series
converges to
, then with increasing iteration counter
,
,
,
and
,
, implies that
and
. By substituting
(Equation (
7.14)) into Equation (
7.9) gives
and by re-arranging
with
converges to
,
and the above equation simplifies as
It means that
depends on
and
, and by assuming an asymptotic convergence, a power law relationship
can be established, where
is the asymptotic error constant and
is the convergence rate or also called “convergence order” of the iterative method. It also follows from Equation (
7.20), that
and
Let
be introduced for simplifying purpose, then it follows from Equations (
7.17), (
7.20), (
7.21) and (
7.22) that
where
and
are constants and if the series
converges to
, then with increasing iteration counter
,
. Taking the logarithms of both sides of Equation (
7.23) and dividing by
gives
If
series converges to
, then with increasing iteration counter
,
,
and
and Equation (
7.24) simplifies as
with root (convergence rate of the T-Secant method) :
where
is the convergence rate of the traditional secant method and ’ is the well known golden ratio. It follows from Equation (
7.24) that the actual values
of
depend on the approximate error
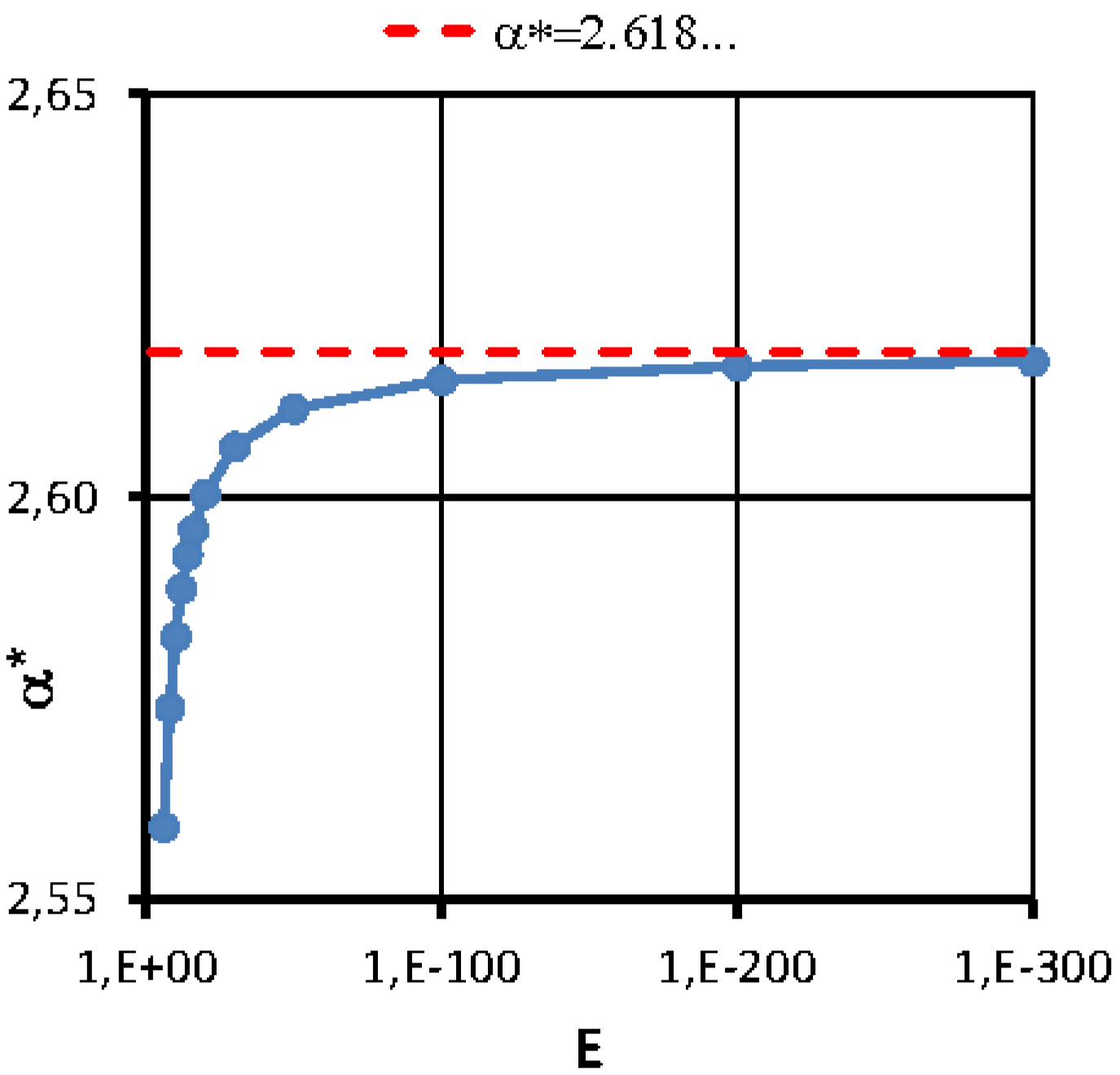
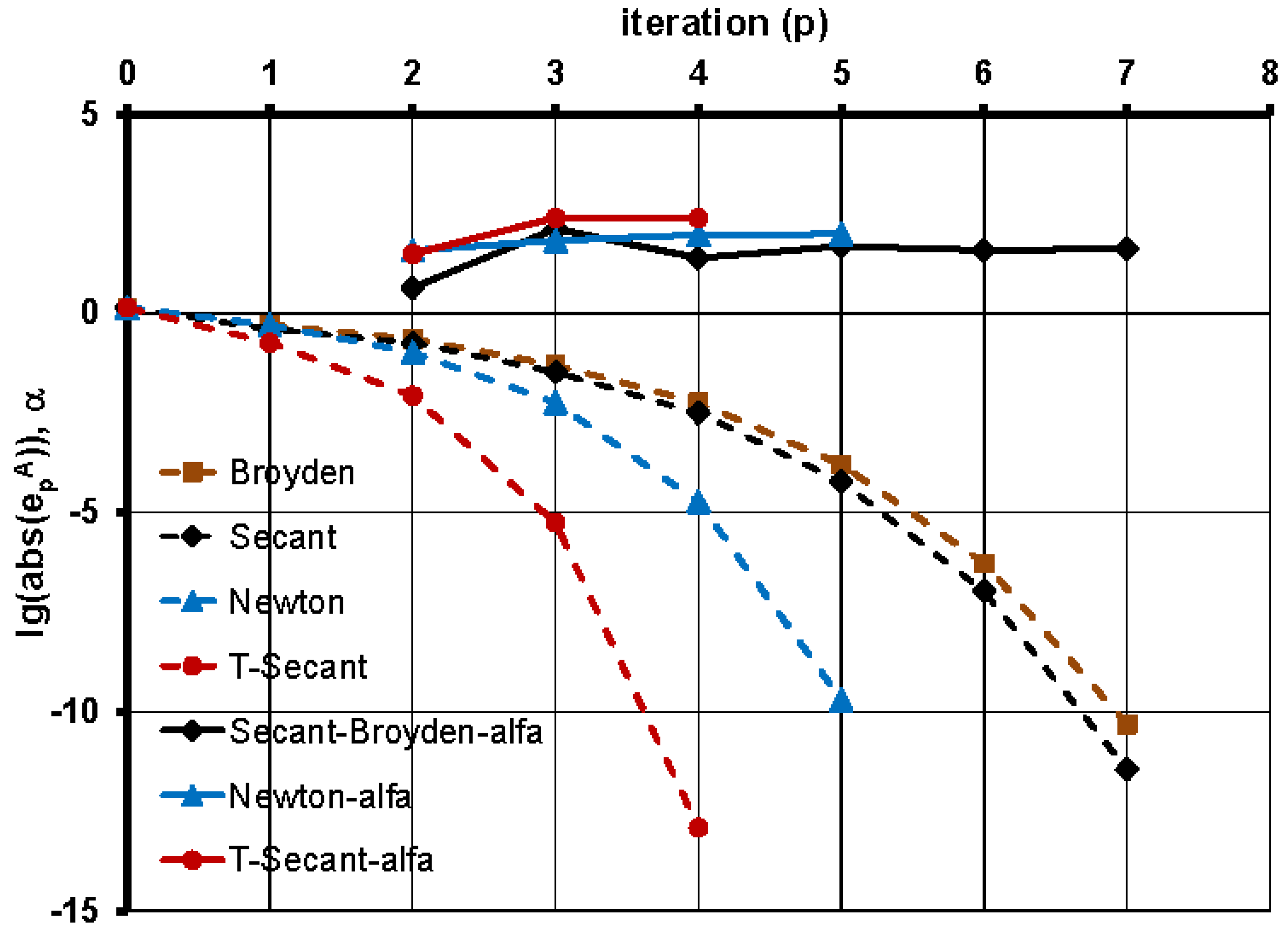
. Convergence rates
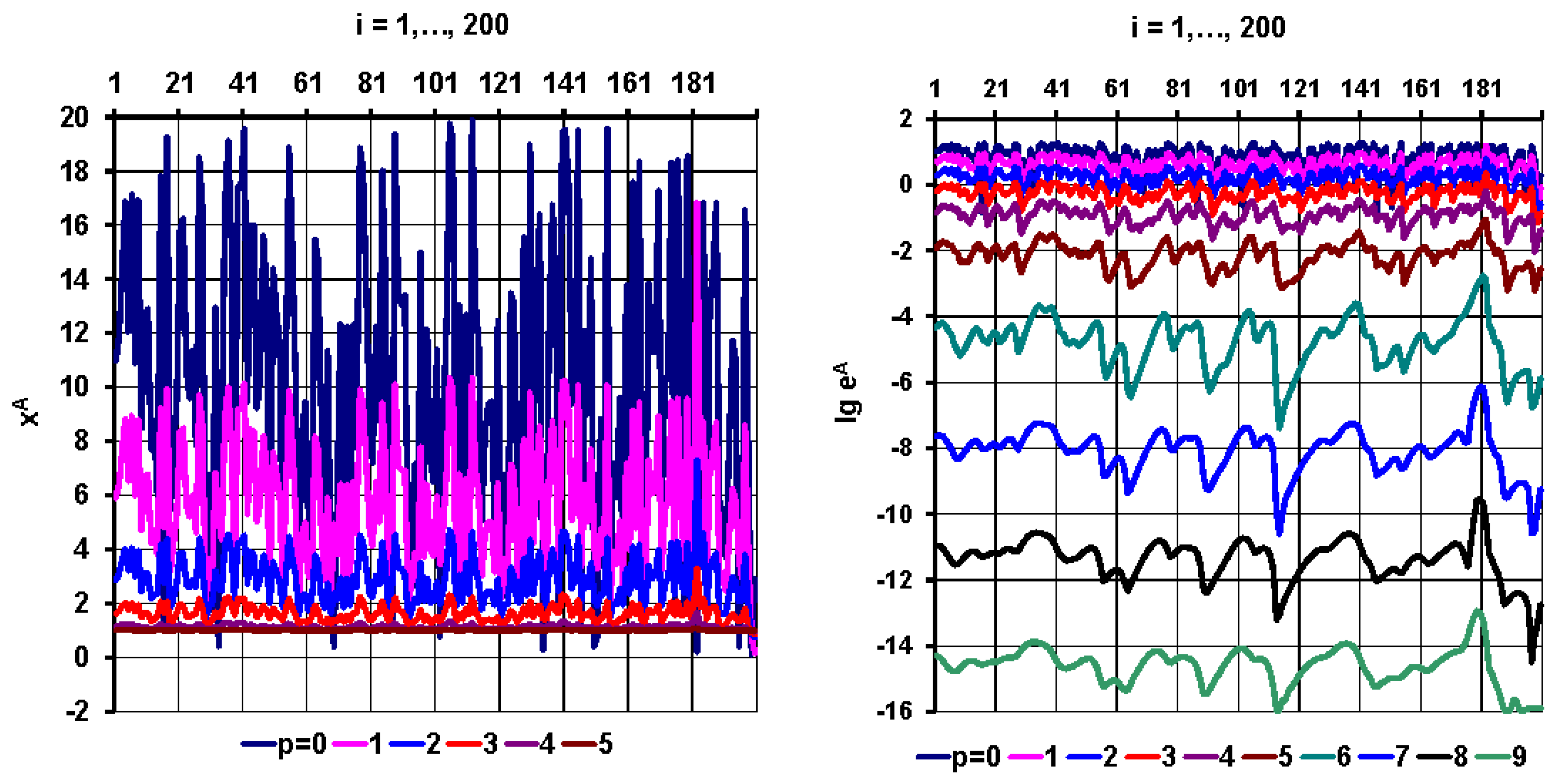
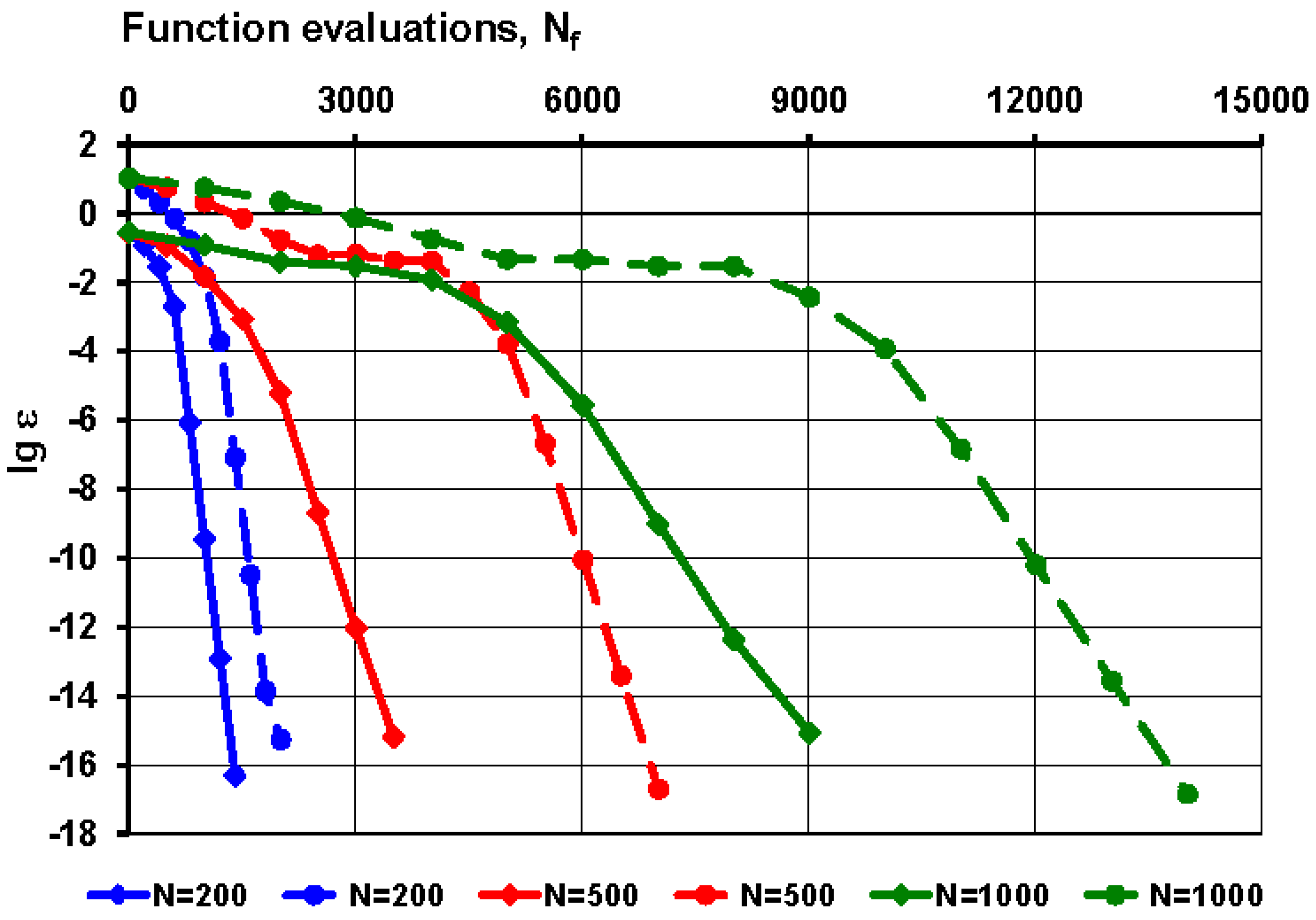
were determined for different
values and shown on
Figure 5. The upper bound
at
is also indicated (horizontal dashed red line).