Submitted:
23 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Making Agarose Gell of DNA Samples
2.5. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.6. PCR Optimal Conditions
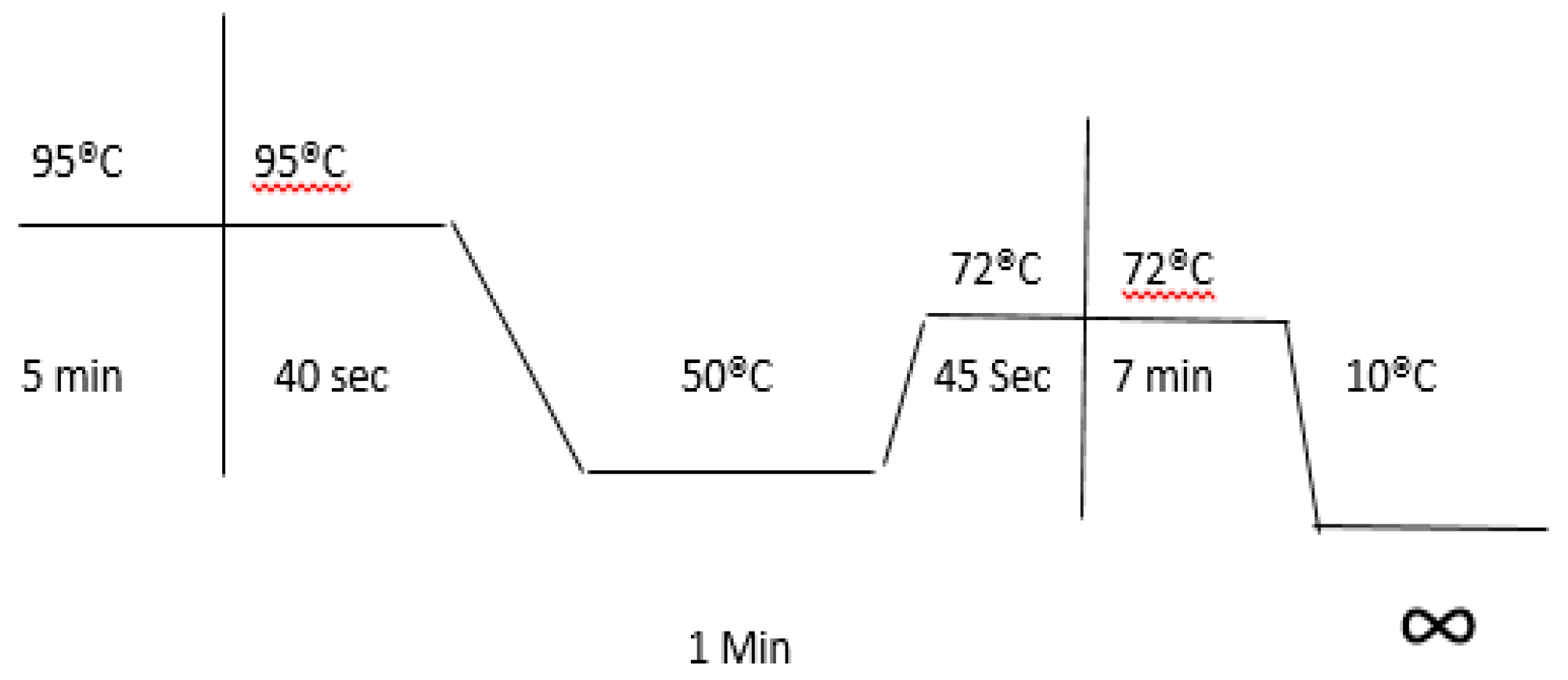
2.7. Amplified Gene Fragment DNA Cleaning from Gel
2.8. Sequencing and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Collection
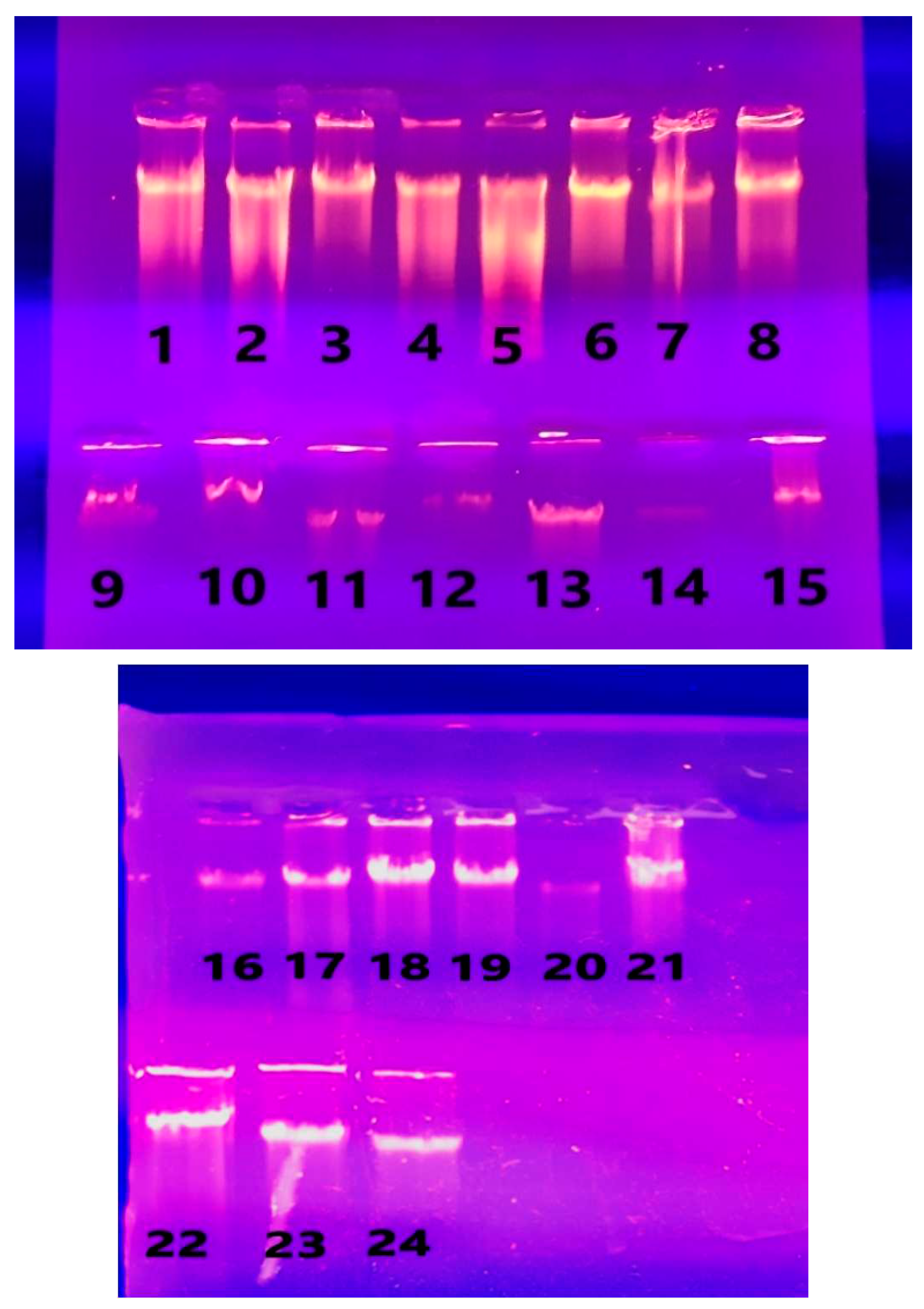
3.2. DNA Extraction
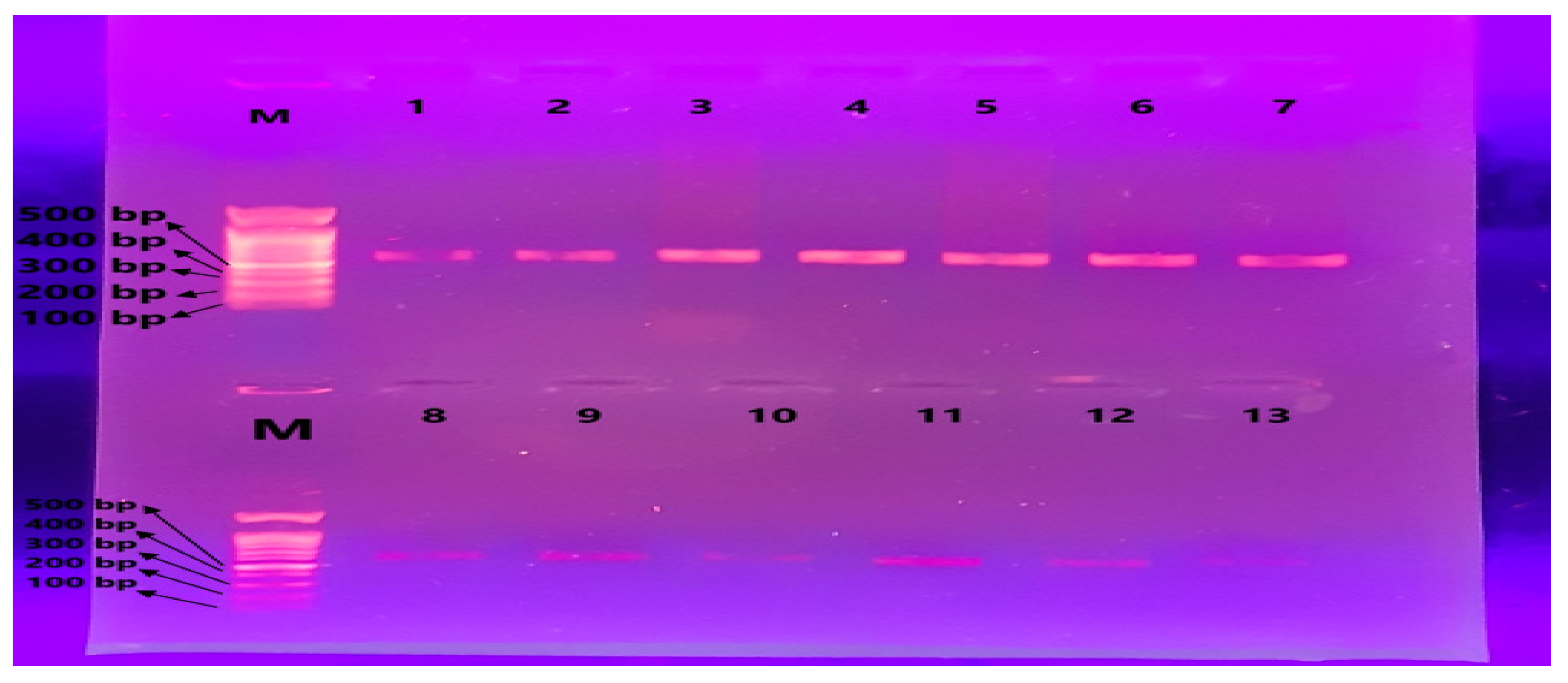
3.3. Amplification of the MT-TL2 Gene
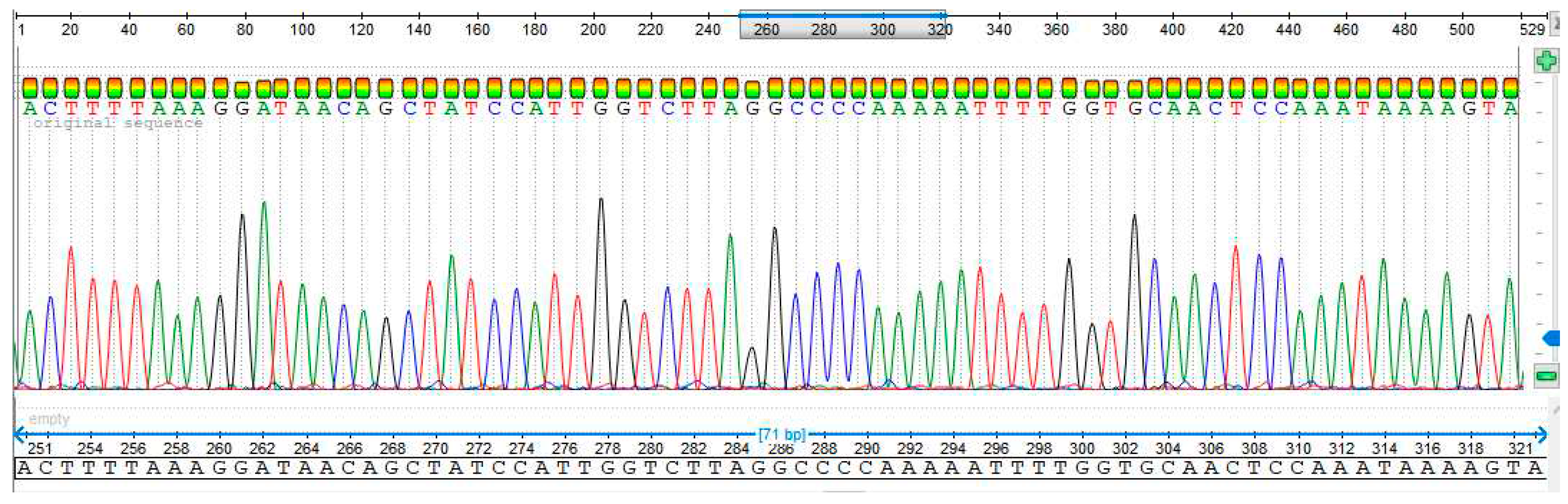
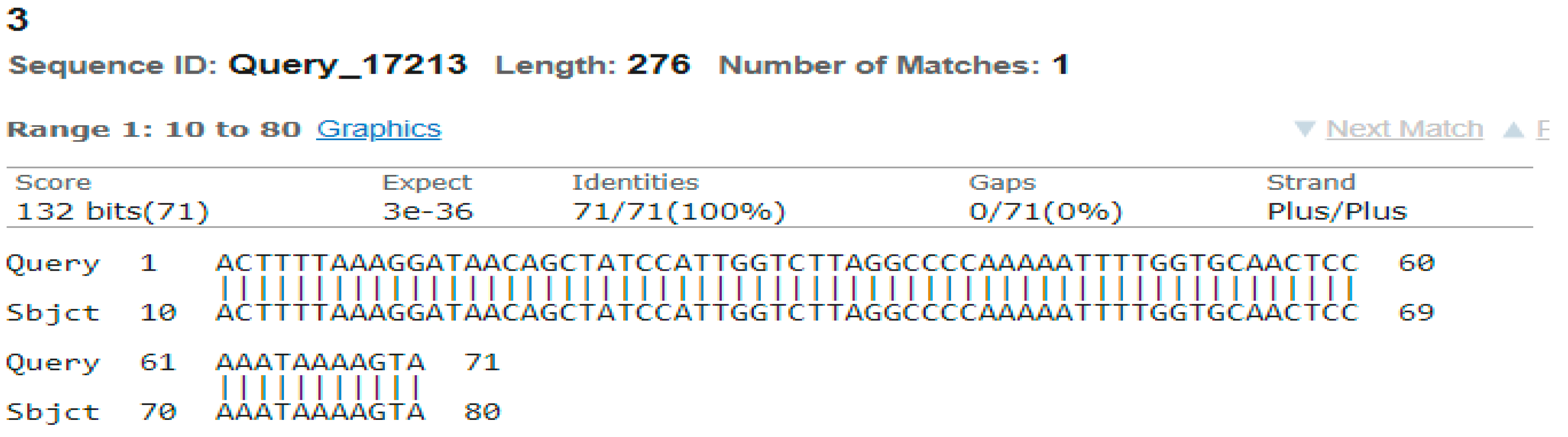
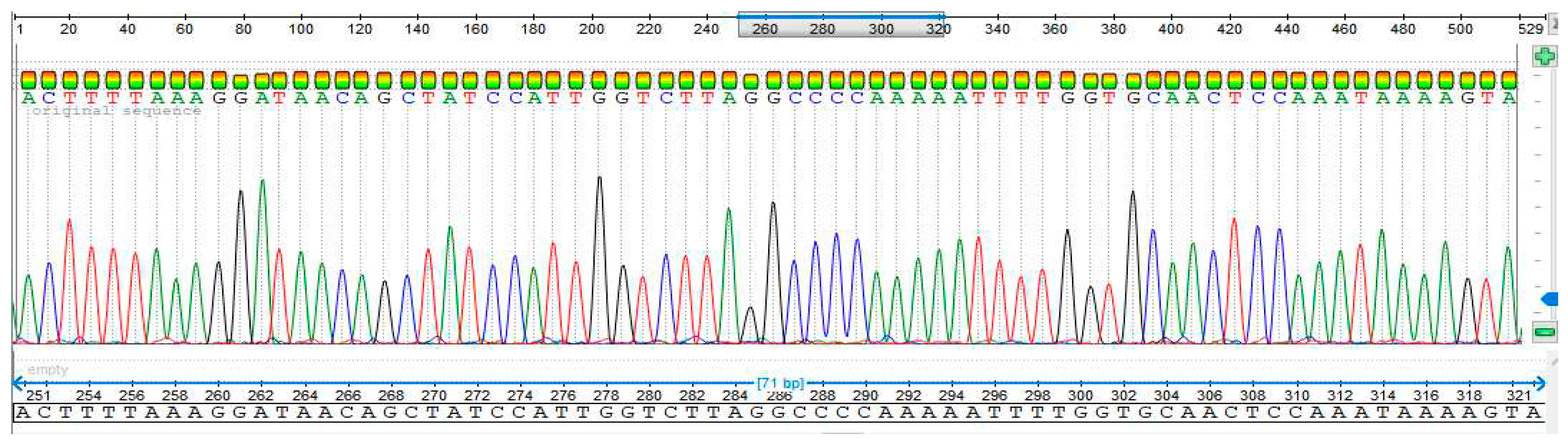
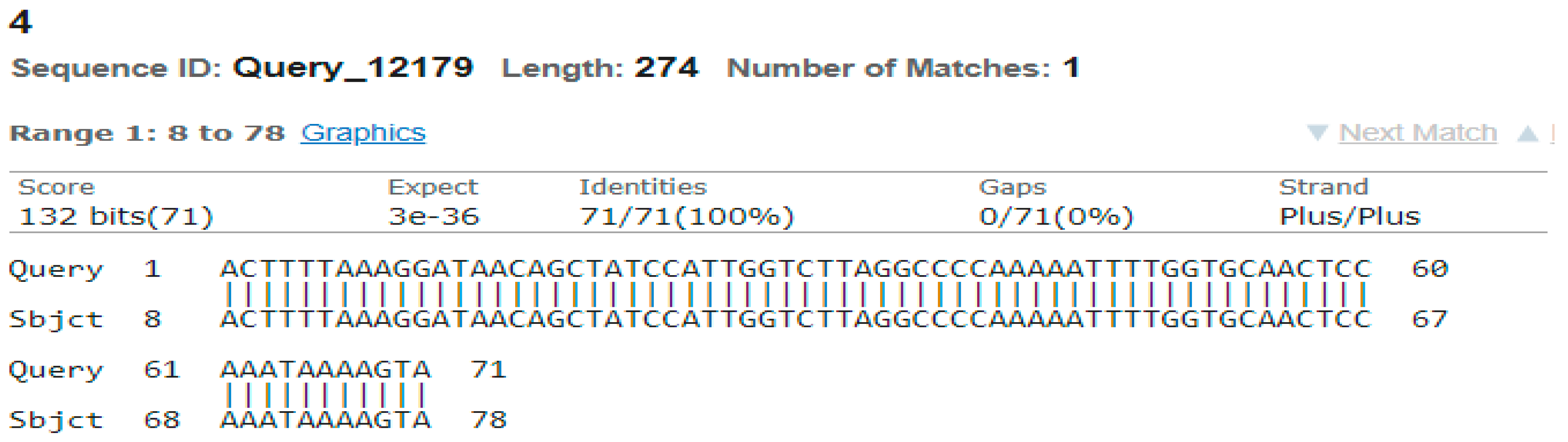
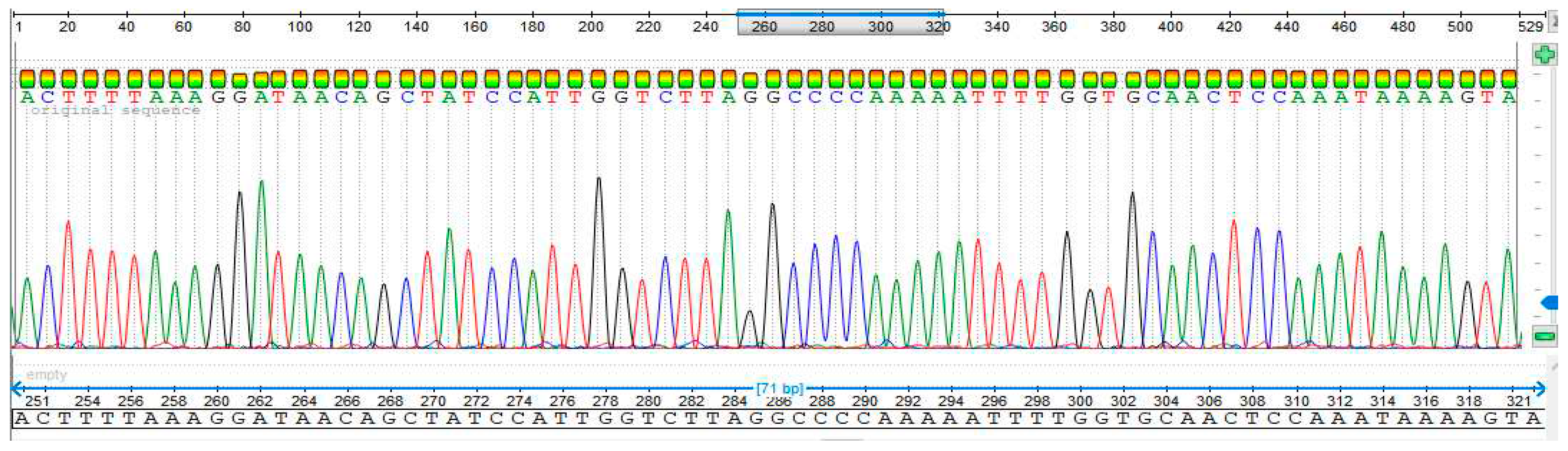
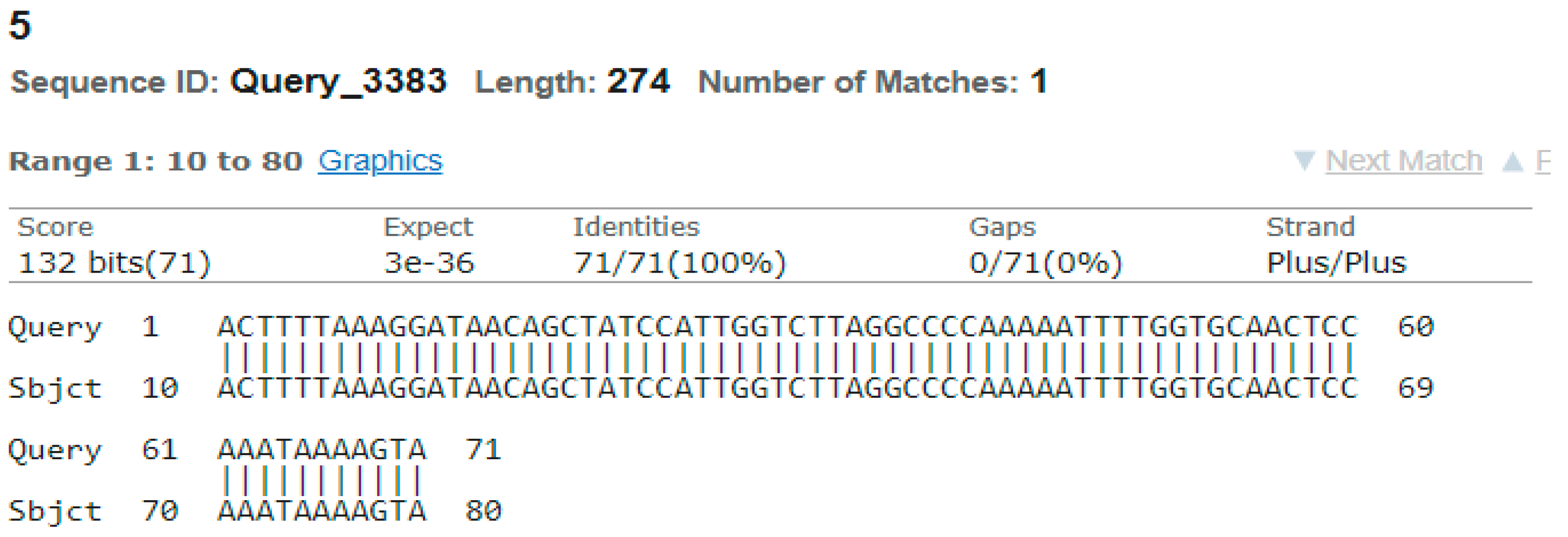
3.4. Sequencing Analysis
- Sample 1
- Sample 2
- Sample 3
- Sample 4
- Sample 5
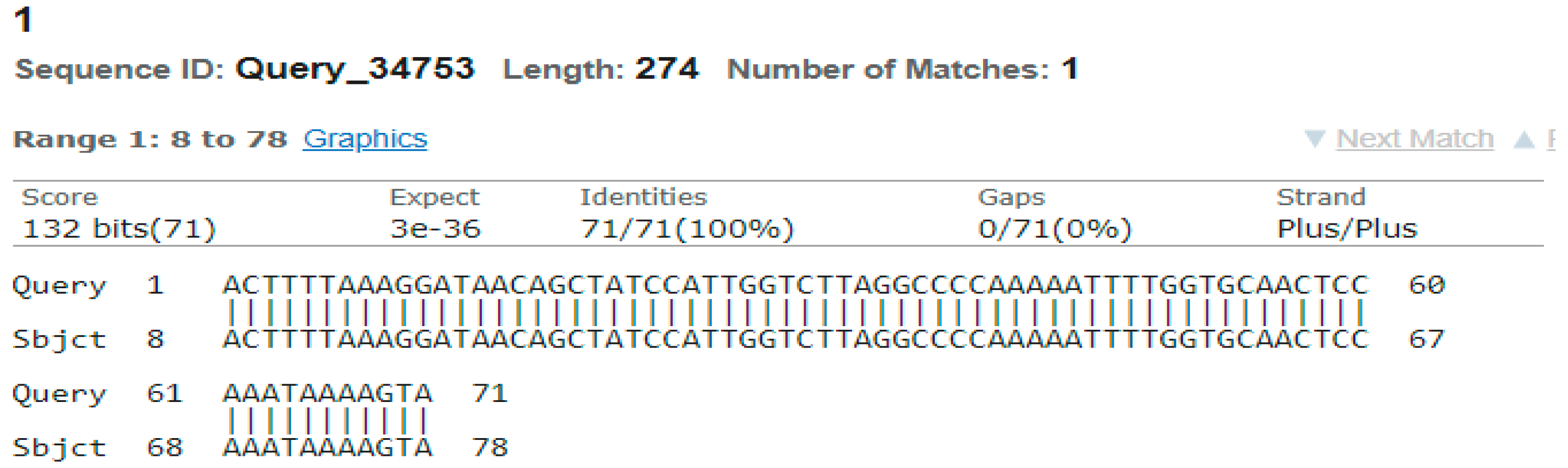

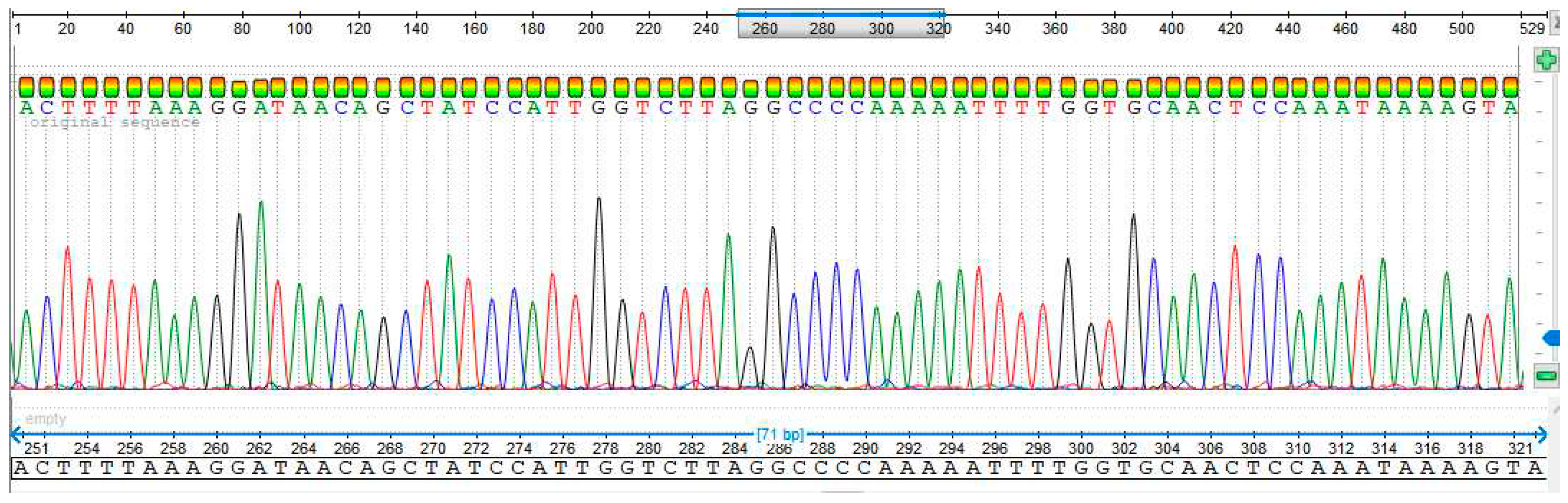
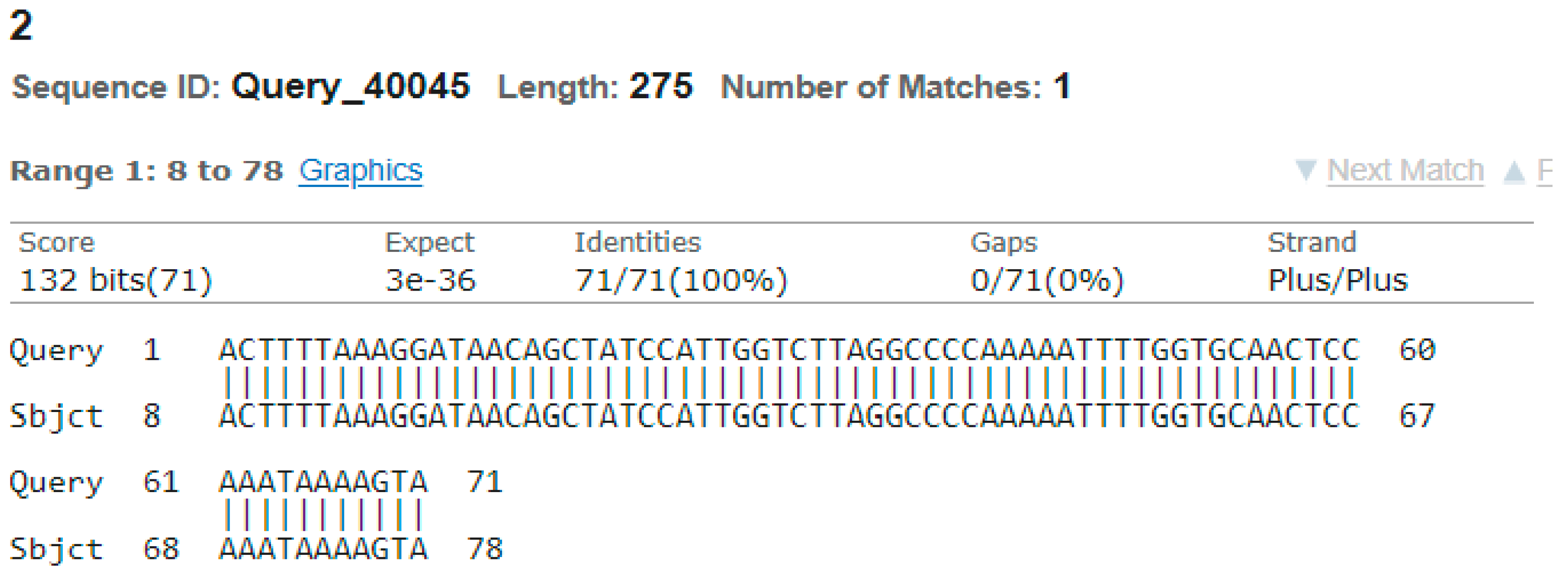





4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Competing interest
Abbreviations
References
- B. I. Bodai and P. Tuso, "Breast cancer survivorship: a comprehensive review of long-term medical issues and lifestyle recommendations," The Permanente Journal, vol. 19, no. 2, p. 48, 2015. [CrossRef]
- N. Giaquinto et al., "Breast cancer statistics, 2022," CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, vol. 72, no. 6, pp. 524-541, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Li et al., "Global burden of female breast cancer: age-period-cohort analysis of incidence trends from 1990 to 2019 and forecasts for 2035," Frontiers in oncology, vol. 12, p. 891824, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Arnold et al., "Current and future burden of breast cancer: Global statistics for 2020 and 2040," The Breast, vol. 66, pp. 15-23, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. B. Claus, J. M. Schildkraut, W. D. Thompson, and N. J. Risch, "The genetic attributable risk of breast and ovarian cancer," Cancer: Interdisciplinary International Journal of the American Cancer Society, vol. 77, no. 11, pp. 2318-2324, 1996. [CrossRef]
- C. Antoniou and D. Easton, "Models of genetic susceptibility to breast cancer," Oncogene, vol. 25, no. 43, pp. 5898-5905, 2006. [CrossRef]
- D. C. Wallace, "Mitochondria and cancer," Nature Reviews Cancer, vol. 12, no. 10, pp. 685-698, 2012. [CrossRef]
- N. Pfanner and A. Geissler, "Versatility of the mitochondrial protein import machinery," Nature reviews Molecular cell biology, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 339-349, 2001. [CrossRef]
- F. Legros, F. Malka, P. Frachon, A. Lombès, and M. Rojo, "Organization and dynamics of human mitochondrial DNA," Journal of cell science, vol. 117, no. 13, pp. 2653-2662, 2004. [CrossRef]
- R. M. Andrews, I. Kubacka, P. F. Chinnery, R. N. Lightowlers, D. M. Turnbull, and N. Howell, "Reanalysis and revision of the Cambridge reference sequence for human mitochondrial DNA," Nature genetics, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 147-147, 1999. [CrossRef]
- E. A. Schon, S. DiMauro, M. Hirano, and R. W. Gilkerson, "Therapeutic prospects for mitochondrial disease," Trends in molecular medicine, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 268-276, 2010. [CrossRef]
- R. Martín-Jiménez, E. Martín-Hernández, A. Cabello, M. T. García-Silva, J. Arenas, and Y. Campos, "Clinical and cellular consequences of the mutation m. 12300G> A in the mitochondrial tRNALeu (CUN) gene," Mitochondrion, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 288-293, 2012. [CrossRef]
- D. Covarrubias, R.-K. Bai, L.-J. C. Wong, and S. M. Leal, "Mitochondrial DNA variant interactions modify breast cancer risk," Journal of human genetics, vol. 53, no. 10, pp. 924-928, 2008. [CrossRef]
- M. Ghaheri, D. Kahrizi, K. Yari, A. Babaie, R. Suthar, and E. Kazemi, "A comparative evaluation of four DNA extraction protocols from whole blood sample," Cellular and Molecular Biology, vol. 62, no. 3, pp. 120-124, 2016.
- G. N. Sharma, R. Dave, J. Sanadya, P. Sharma, and K. Sharma, "Various types and management of breast cancer: an overview," Journal of advanced pharmaceutical technology & research, vol. 1, no. 2, p. 109, 2010.
- F. Bray, J. Ferlay, I. Soerjomataram, R. L. Siegel, L. A. Torre, and A. Jemal, "Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries," CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, vol. 68, no. 6, pp. 394-424, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Ferlay et al., "Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012," International journal of cancer, vol. 136, no. 5, pp. E359-E386, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, E. Mambo, and D. Sidransky, "Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human cancer," Oncogene, vol. 25, no. 34, pp. 4663-4674, 2006. [CrossRef]
- S. U. Haq et al., "Mutation in Mitochondrial MT-TL2 (CUN) Gene and Its Association with Diabetes mellitus in Pakistan," Available at SSRN 3473285, 2019. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



