Submitted:
21 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
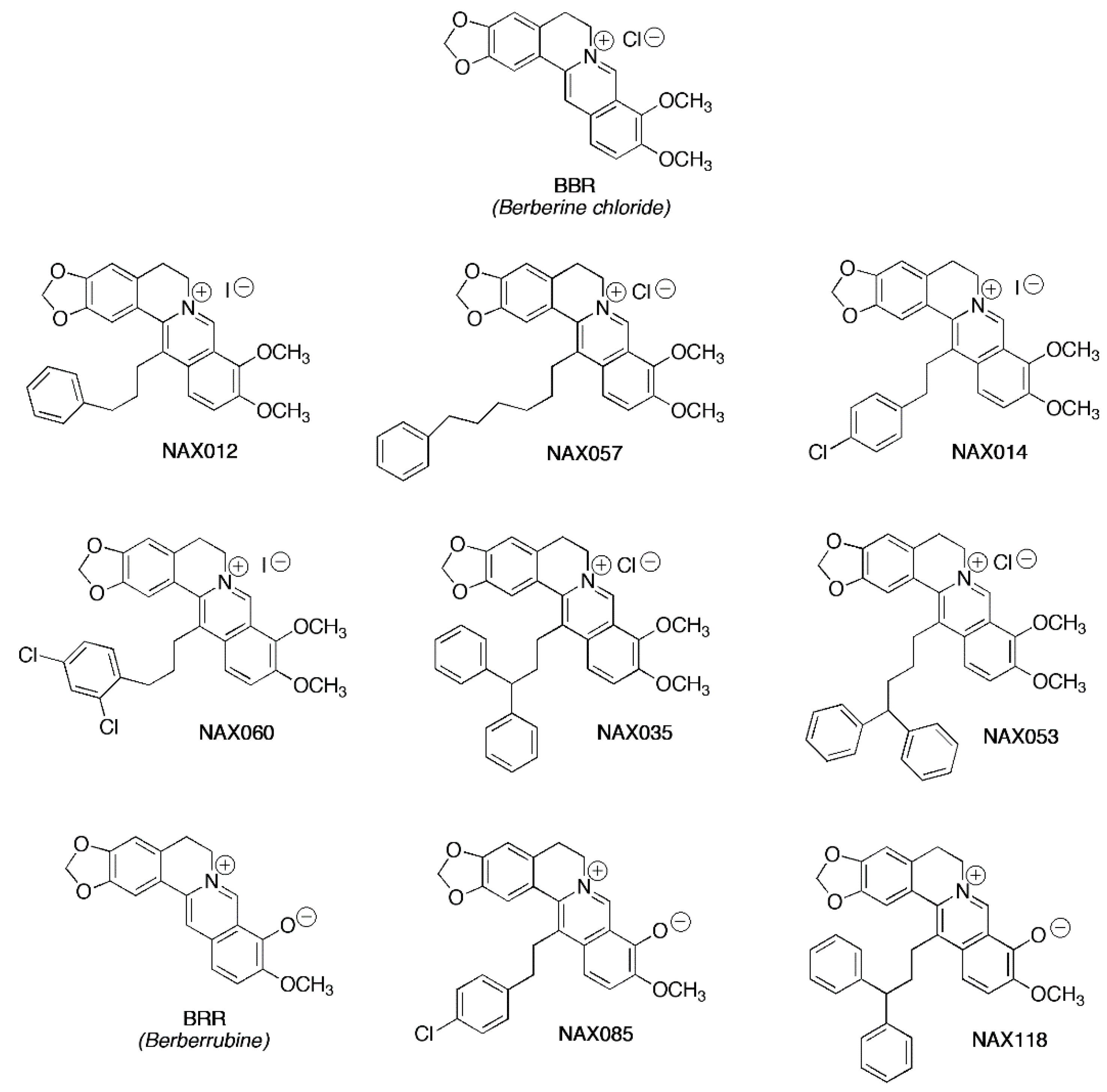
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Drug Treatment
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Quantification of Necrosis/Apoptosis by Flow Cytometry
2.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis on CF33 Cells
2.6. RT-PCR and Semi-Quantitative PCR
2.7. Gel Electrophoresis, Acquisition of Gel Images and Quantitative Analysis
2.8. Ethics Statements
2.9. Zebrafish Housing and Maintenance
2.10. Zebrafish Tg(7xTCF-Xla.-Siam:mCherry) and Tg(Hsa.CTGF:mCherry) Transgenic Lines
2.11. LC50
2.12. In Vivo Drug Treatments
2.13. Microscopy and Image Acquisition
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
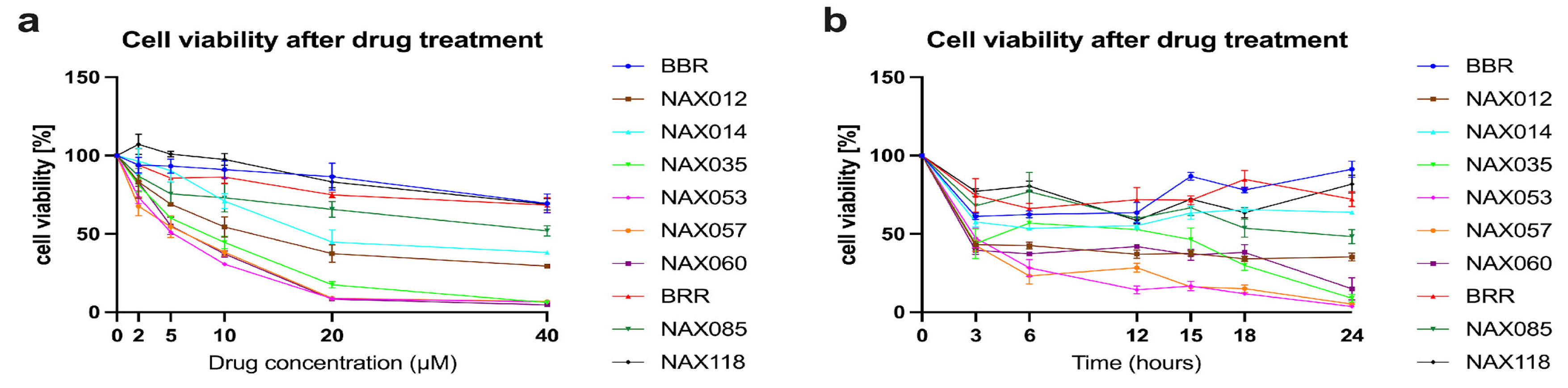
3.1. BBR, BRR, and Analogues Induce a Dose-Dependent Inhibition of Tumor Cell Viability
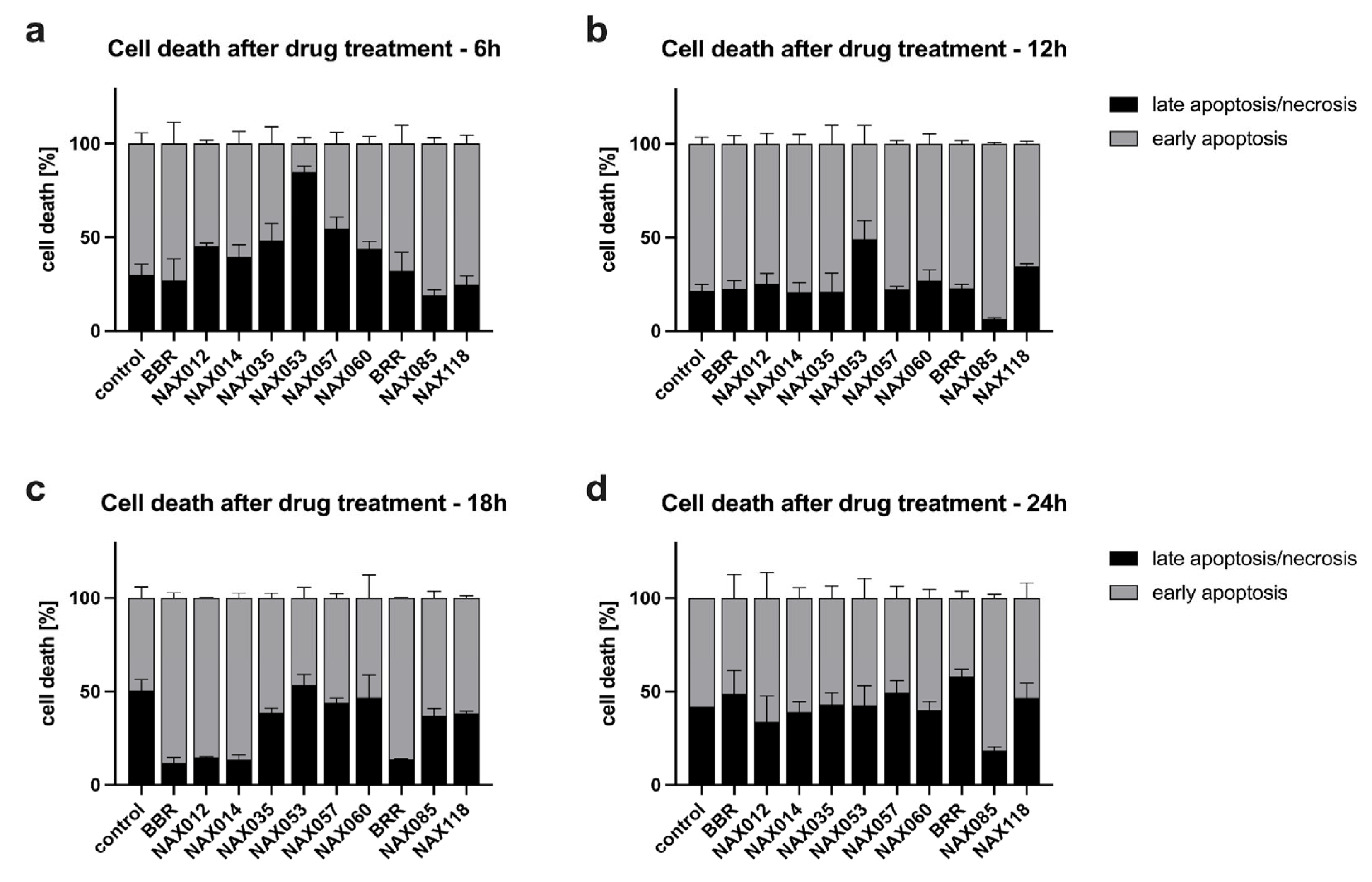
3.2. Induction of Necrosis/Apoptosis in Canine Mammary Tumor Cells by BBR Analogues
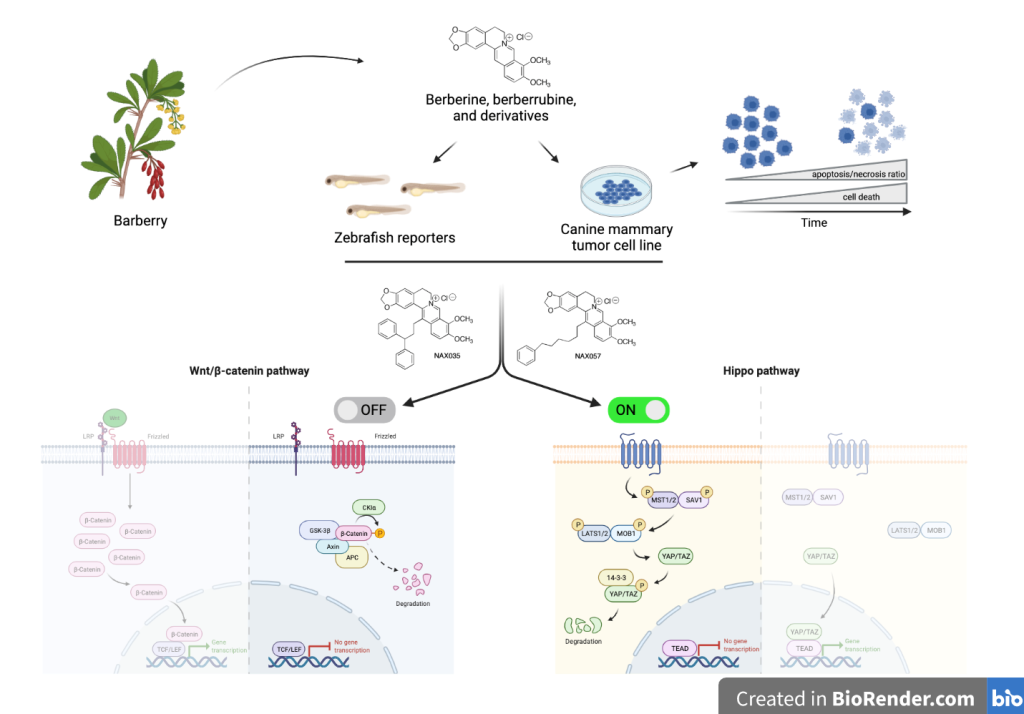
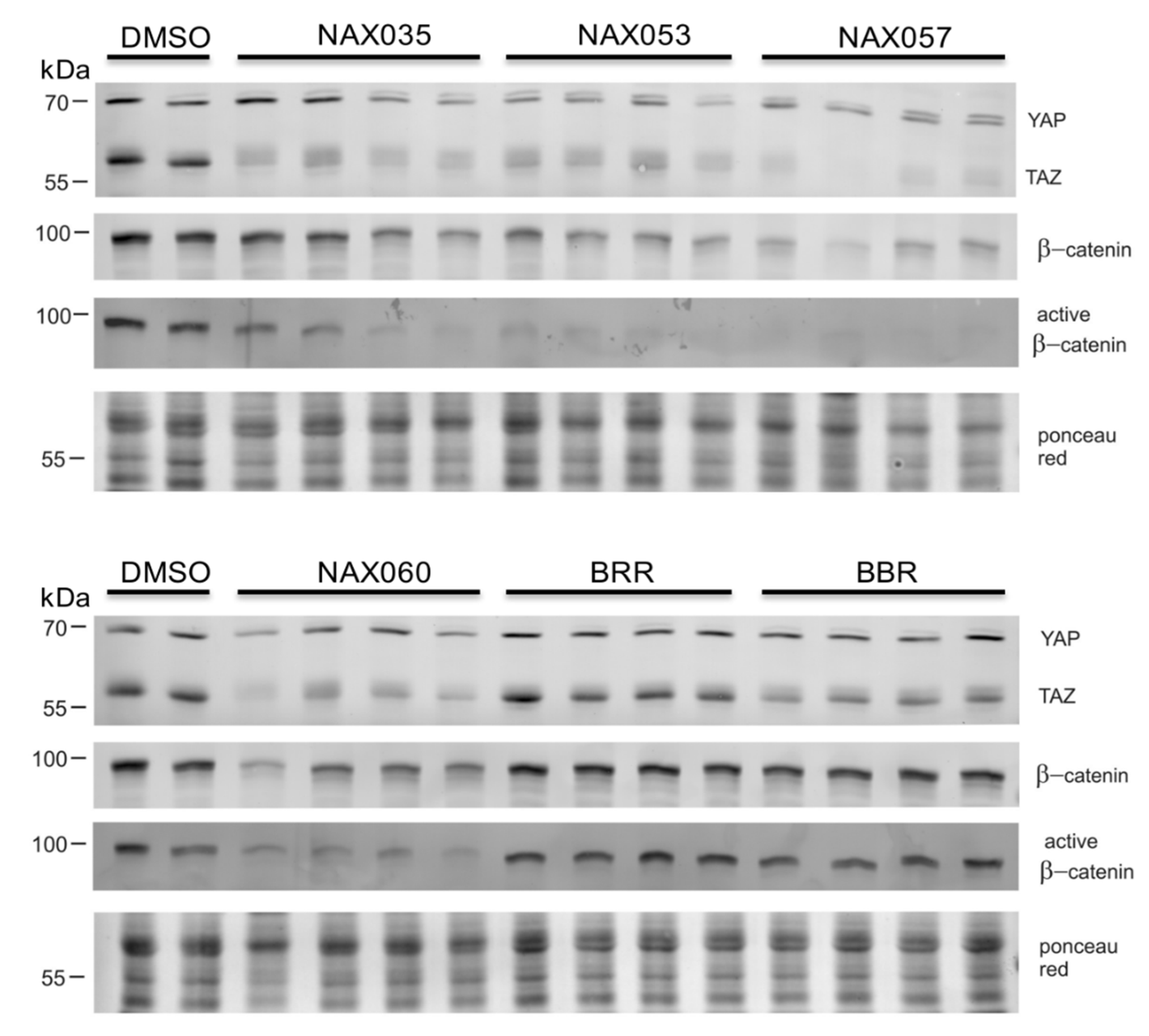
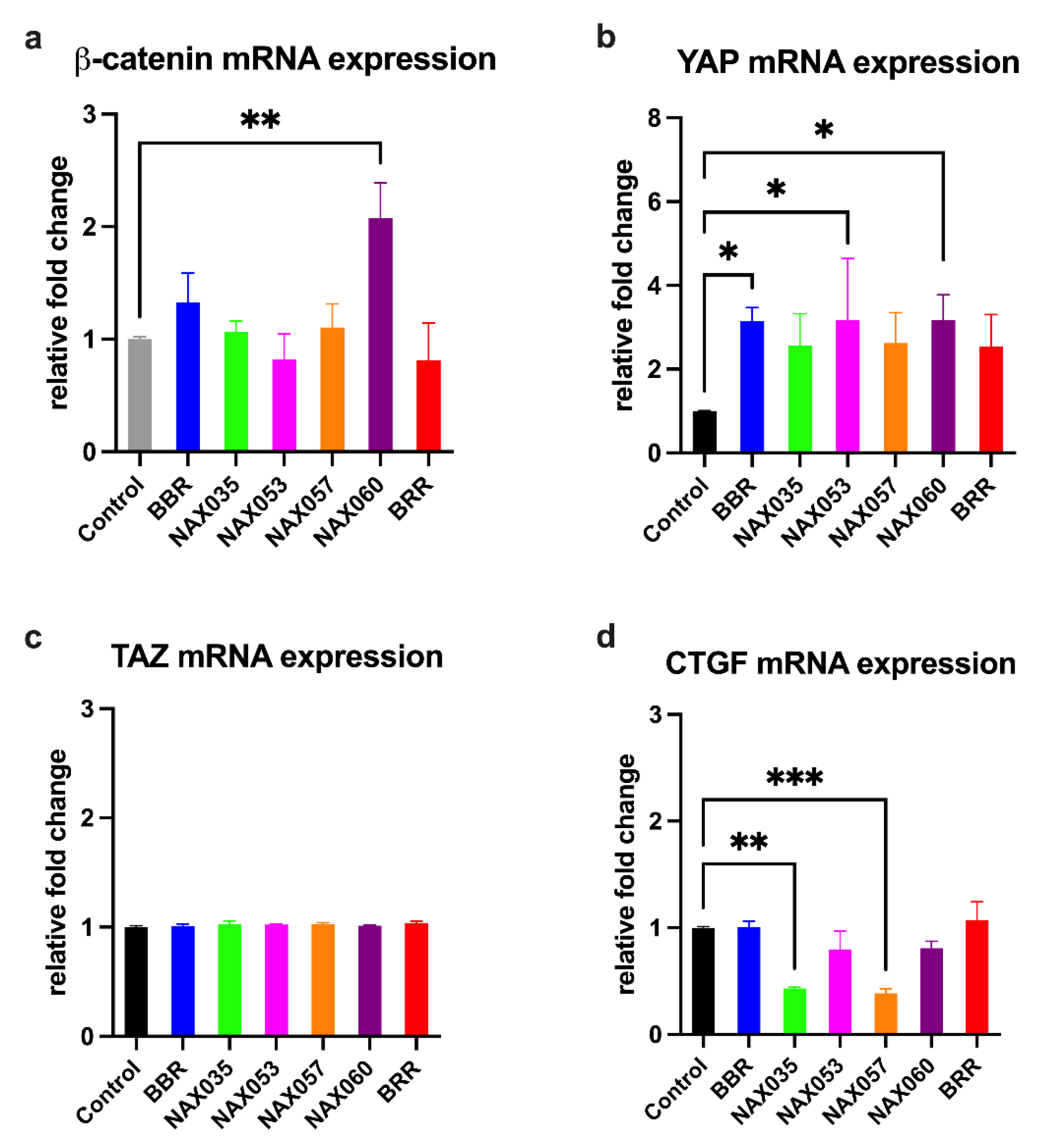
3.3. NAX035, NAX053, NAX057, and NAX060 Induce a Downregulation of Wnt/β-Catenin and an Activation of the Hippo Signaling Pathways in CF33 Cells
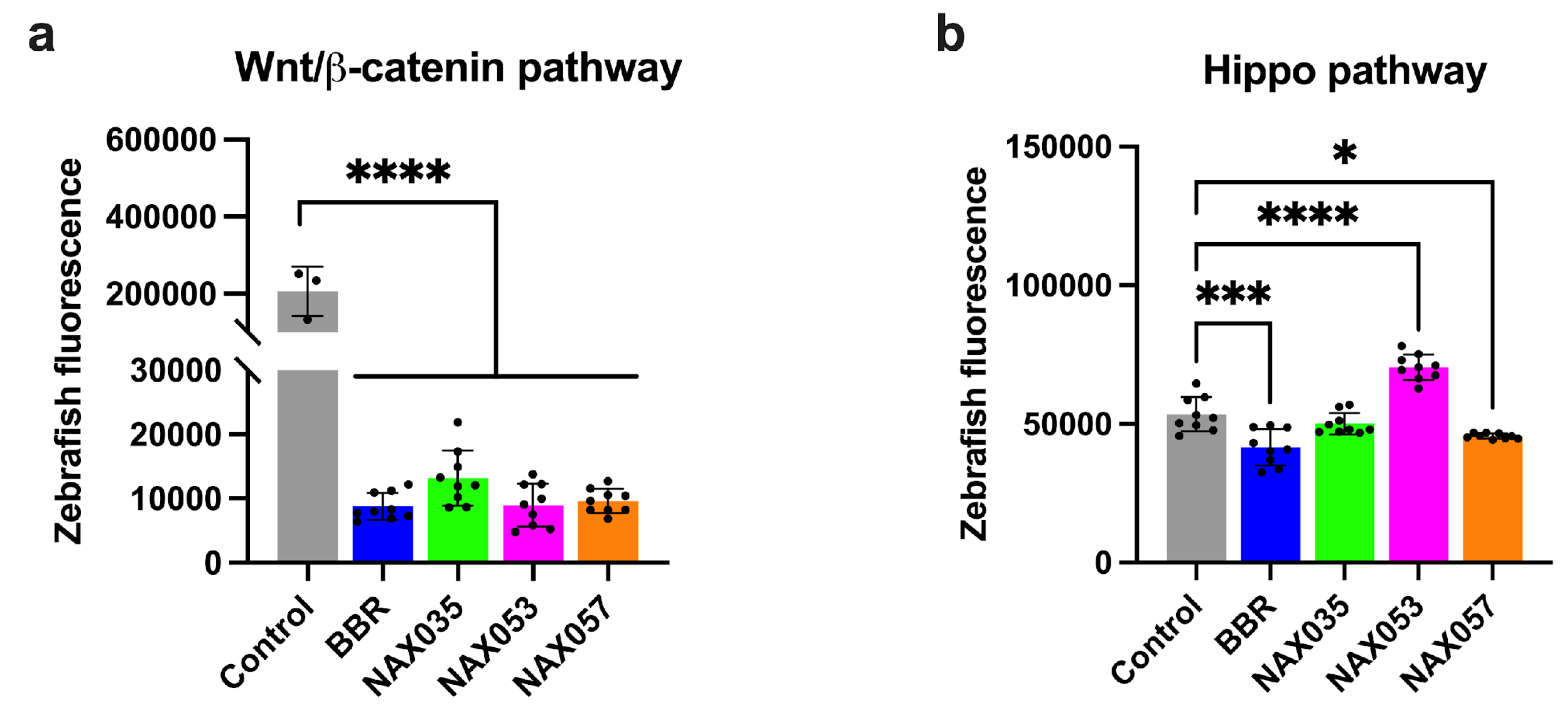
3.4. BBR and NAX057 Reduce the Activity of Wnt/β-Catenin and Activate Hippo Signaling Pathways in Zebrafish Embryos
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Miller, K.D.; Ahmedin, J. Cáncer Statistics. Ca Cáncer Journal 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeg, F.; Anbalagan, M. Breast Cancer Stem Cells and the Challenges of Eradication: A Review of Novel Therapies. Stem Cell Investig 2018, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.B.; O’Hare, M.J.; Stein, R. Models of Breast Cancer: Is Merging Human and Animal Models the Future? Breast Cancer Res 2004, 6, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, P.; Bailey, K.L.; Cartwright, S.B.; Band, V.; Carlson, M.A. Large Animal Models of Breast Cancer. Frontiers in Oncology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N. a. S.; van Wolferen, M.E.; van den Ham, R.; van Leenen, D.; Groot Koerkamp, M.J.A.; Holstege, F.C.P.; Mol, J.A. CDNA Microarray Profiles of Canine Mammary Tumour Cell Lines Reveal Deregulated Pathways Pertaining to Their Phenotype. Anim Genet 2008, 39, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdivia, G.; Alonso-Diez, Á.; Pérez-Alenza, D.; Peña, L. From Conventional to Precision Therapy in Canine Mammary Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2021, 8, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadie, J.; Nguyen, F.; Loussouarn, D.; Peña, L.; Gama, A.; Rieder, N.; Belousov, A.; Bemelmans, I.; Jaillardon, L.; Ibisch, C.; et al. Canine Invasive Mammary Carcinomas as Models of Human Breast Cancer. Part 2: Immunophenotypes and Prognostic Significance. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2018, 167, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-H.; Park, H.-M.; Son, K.-H.; Shin, T.-J.; Cho, J.-Y. Transcriptome Signatures of Canine Mammary Gland Tumors and Its Comparison to Human Breast Cancers. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Nam, A.-R.; Cho, J.-Y. Genome-Wide Methylation Profiling in Canine Mammary Tumor Reveals MiRNA Candidates Associated with Human Breast Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, L.; Devlin, P.; Mckevitt, T.; Rutteman, G.; Argyle, D.J. Telomere Lengths and Telomerase Activity in Dog Tissues: A Potential Model System to Study Human Telomere and Telomerase Biology. Neoplasia 2001, 3, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuten J Donald Tumors in Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Ames: John Wiley and Sons lnc, 2017.
- Jaillardon, L.; Abadie, J.; Godard, T.; Campone, M.; Loussouarn, D.; Siliart, B.; Nguyen, F. The Dog as a Naturally-Occurring Model for Insulin-like Growth Factor Type 1 Receptor-Overexpressing Breast Cancer: An Observational Cohort Study. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restucci, B.; Maiolino, P.; Martano, M.; Esposito, G.; Filippis, D.D.E.; Borzacchiello, G.; Muzio, L.L.O. Expression of B-Catenin, E-Cadherin and APC in Canine Mammary Tumors. Anticancer Research 2007, 27, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Cancers and Targeted Therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-L.; Lin, S.-G.; Mao, Y.-W.; Wu, J.-X.; Hu, C.-D.; Lv, R.; Zeng, H.-D.; Zhang, M.-H.; Lin, L.-Z.; Ouyang, S.-S.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells and Its Effect on Reversing Tumour Drug Resistance by Alkaloids Extracted from Traditional Chinese Medicine. Expert Rev Mol Med 2023, 25, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turashvili, G.; Bouchal, J.; Burkadze, G.; Kolar, Z. Wnt Signaling Pathway in Mammary Gland Development and Carcinogenesis. Pathobiology 2006, 73, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappulli, V.; De Cecco, S.; Trez, D.; Caliari, D.; Aresu, L.; Castagnaro, M. Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and β-Catenin in Feline Mammary Tumours. Journal of Comparative Pathology 2012, 147, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aplin, A.E.; Howe, A.; Alahari, S.K.; Juliano, R.L. Signal Transduction and Signal Modulation by Cell Adhesion Receptors: The Role of Integrins, Cadherins, Immunoglobulin-Cell Adhesion Molecules, and Selectins. Pharmacol Rev 1998, 50, 197–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geyer, F.C.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Savage, K.; Arnedos, M.; Lambros, M.B.; MacKay, A.; Natrajan, R.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Β-Catenin Pathway Activation in Breast Cancer Is Associated with Triple-Negative Phenotype but Not with CTNNB1 Mutation. Modern Pathology 2011, 24, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu de Oliveira, W.A.; El Laithy, Y.; Bruna, A.; Annibali, D.; Lluis, F. Wnt Signaling in the Breast: From Development to Disease. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Saxena, S.; Shrivastava, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.J.; Kumar, A.; Wani, S.A.; Gandham, R.K.; Kumar, N.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling of Spontaneously Occurring Canine Mammary Tumours: Insight into Gene Networks and Pathways Linked to Cancer Pathogenesis. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0208656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Rasotto, R.; Zhang, H.; Pei, S.; Zhou, B.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, D. Evaluation of Expression of the Wnt Signaling Components. Journal of Veterinary Science 2017, 18, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammarco, A.; Gomiero, C.; Sacchetto, R.; Beffagna, G.; Michieletto, S.; Orvieto, E.; Cavicchioli, L.; Gelain, M.E.; Ferro, S.; Patruno, M.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin and Hippo Pathway Deregulation in Mammary Tumors of Humans, Dogs, and Cats. Vet Pathol 2020, 57, 774–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Azzolin, L.; Forcato, M.; Rosato, A.; Frasson, C.; Inui, M.; Montagner, M.; Parenti, A.R.; Poletti, A.; et al. The Hippo Transducer TAZ Confers Cancer Stem Cell-Related Traits on Breast Cancer Cells. Cell 2011, 147, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Song, G. The Hippo Pathway: A Master Regulatory Network Important in Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beffagna, G.; Sacchetto, R.; Cavicchioli, L.; Sammarco, A.; Mainenti, M.; Ferro, S.; Trez, D.; Zulpo, M.; Michieletto, S.; Cecchinato, A.; et al. A Preliminary Investigation of the Role of the Transcription Co-Activators YAP/TAZ of the Hippo Signalling Pathway in Canine and Feline Mammary Tumours. Veterinary Journal 2016, 207, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemette, S.; Rico, C.; Godin, P.; Boerboom, D.; Paquet, M. In Vitro Validation of the Hippo Pathway as a Pharmacological Target for Canine Mammary Gland Tumors. Journal of Mammary Gland Biology and Neoplasia 2017, 22, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, C.; Boerboom, D.; Paquet, M. Expression of the Hippo Signalling Effectors YAP and TAZ in Canine Mammary Gland Hyperplasia and Malignant Transformation of Mammary Tumours. Veterinary and Comparative Oncology 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.-F. Natural Compounds as Anticancer Agents: Experimental Evidence. World J Exp Med 2012, 2, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-W.; Di, Y.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Li, C.G.; Zhou, S.-F. Interaction of Herbal Compounds with Biological Targets: A Case Study with Berberine. ScientificWorldJournal 2012, 2012, 708292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, W. Role of Berberine in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2016, 12, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W. Non-Coding RNAs and Berberine: A New Mechanism of Its Anti-Diabetic Activities. Eur J Pharmacol 2017, 795, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Baggioni, A. Berberine and Its Role in Chronic Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 2016, 928, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, S. Berberine and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Concise Review. Pharmacol Res 2016, 113, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillhon, M.; Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Berberine: New Perspectives for Old Remedies. Biochem Pharmacol 2012, 84, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpaoli, E.; Arcamone, A.G.; Buzzetti, F.; Lombardi, P.; Salvatore, C.; Provinciali, M. Antitumor Effect of Novel Berberine Derivatives in Breast Cancer Cells. Biofactors 2013, 39, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Lombardi, P.; Tillhon, M.; Scovassi, A.I. Berberine, an Epiphany Against Cancer. Molecules 2014, 19, 12349–12367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; You, D.; Jeong, Y.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, J.E. Berberine Down-Regulates IL-8 Expression through Inhibition of the EGFR/MEK/ERK Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 50, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Khalil, A.A.; Imran, M.; Shah, Z.A.; Emran, T.B.; Mitra, S.; Khan, Z.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; et al. Berberine as a Potential Anticancer Agent: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, B.; Cao, H.; Xu, X.; Ruan, H.; Yi, T.; Tan, L.; Qu, R.; Song, G.; et al. Berberine Potently Attenuates Intestinal Polyps Growth in ApcMin Mice and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis Patients through Inhibition of Wnt Signalling. J Cell Mol Med 2013, 17, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpaoli, E.; Damiani, E.; Orlando, F.; Lucarini, G.; Bartozzi, B.; Lombardi, P.; Salvatore, C.; Geroni, C.; Donati, A.; Provinciali, M. Antiangiogenic and Antitumor Activities of Berberine Derivative NAX014 Compound in a Transgenic Murine Model of HER2/Neu-Positive Mammary Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, L.; Kothandan, G.; Manoharan, R. Berberine and Emodin Abrogates Breast Cancer Growth and Facilitates Apoptosis through Inactivation of SIK3-Induced MTOR and Akt Signaling Pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2020, 1866, 165897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, M.; Kitaguchi, D.; Morinami, S.; Kurashiki, Y.; Hashida, H.; Miyata, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Sakai, M.; Murata, N.; Tanaka, S. Berberine-Induced Nucleolar Stress Response in a Human Breast Cancer Cell Line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 528, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinozzi, S.; Colliva, C.; Camborata, C.; Roberti, M.; Ianni, C.; Neri, F.; Calvarese, C.; Lisotti, A.; Mazzella, G.; Roda, A. Berberine and Its Metabolites: Relationship between Physicochemical Properties and Plasma Levels after Administration to Human Subjects. J Nat Prod 2014, 77, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, A.; Ikekawa, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Shirakawa, S.; Iigo, M. Antitumor Activity of Berberrubine Derivatives. Gan 1976, 67, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ikekawa, T.; Ikeda, Y. Antitumor Activity of 13-Methyl-Berberrubine Derivatives. J Pharmacobiodyn 1982, 5, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.A.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Muller, M.T.; Chung, I.K. Induction of Topoisomerase II-Mediated DNA Cleavage by a Protoberberine Alkaloid, Berberrubine. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 16316–16324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.Y.; Saha, U.; Fiorillo, G.; Lombardi, P.; Kumar, G.S. Calorimetric Insights into the Interaction of Novel Berberrubine Derivatives with Human Telomeric G-Quadruplex DNA Sequence. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry 2018, 132, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, P.; Buzzetti, F.; Arcamone, A.G. Benzoquinolizinium Salt Derivatives as Anticancer Agents 2011.
- Albring, K.F.; Weidemüller, J.; Mittag, S.; Weiske, J.; Friedrich, K.; Geroni, M.C.; Lombardi, P.; Huber, O. Berberine Acts as a Natural Inhibitor of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling--Identification of More Active 13-Arylalkyl Derivatives. Biofactors 2013, 39, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Tillhon, M.; Parks, M.; Dutto, I.; Prosperi, E.; Savio, M.; Arcamone, A.G.; Buzzetti, F.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Multiple Effects of Berberine Derivatives on Colon Cancer Cells. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 924585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guamán Ortiz, L.M.; Croce, A.L.; Aredia, F.; Sapienza, S.; Fiorillo, G.; Syeda, T.M.; Buzzetti, F.; Lombardi, P.; Scovassi, A.I. Effect of New Berberine Derivatives on Colon Cancer Cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2015, 47, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierpaoli, E.; Fiorillo, G.; Lombardi, P.; Salvatore, C.; Geroni, C.; Piacenza, F.; Provinciali, M. Antitumor Activity of NAX060: A Novel Semisynthetic Berberine Derivative in Breast Cancer Cells. BioFactors 2018, 44, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, S.L.; Follo, M.Y.; Steelman, L.S.; Lertpiriyapong, K.; Cocco, L.; Ratti, S.; Martelli, A.M.; Candido, S.; Libra, M.; Murata, R.M.; et al. Abilities of Berberine and Chemically Modified Berberines to Inhibit Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Adv Biol Regul 2019, 71, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnoi, K.; Ke, R.; Saini, K.S.; Viswakarma, N.; Nair, R.S.; Das, S.; Chen, Z.; Rana, A.; Rana, B. Berberine Represses β-Catenin Translation Involving 4E-BPs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Mol Pharmacol 2021, 99, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpaoli, E.; Piacenza, F.; Fiorillo, G.; Lombardi, P.; Orlando, F.; Salvatore, C.; Geroni, C.; Provinciali, M. Antimetastatic and Antitumor Activities of Orally Administered NAX014 Compound in a Murine Model of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchetto, R.; Testoni, S.; Gentile, A.; Damiani, E.; Rossi, M.; Liguori, R.; Drögemüller, C.; Mascarello, F. A Defective SERCA1 Protein Is Responsible for Congenital Pseudomyotonia in Chianina Cattle. Am J Pathol 2009, 174, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of Embryonic Development of the Zebrafish. Dev Dyn 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sert, N.P. du; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0: Updated Guidelines for Reporting Animal Research. PLOS Biology 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, E.; Ozhan-Kizil, G.; Mongera, A.; Beis, D.; Wierzbicki, C.; Young, R.M.; Bournele, D.; Domenichini, A.; Valdivia, L.E.; Lum, L.; et al. In Vivo Wnt Signaling Tracing through a Transgenic Biosensor Fish Reveals Novel Activity Domains. Dev Biol 2012, 366, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astone, M.; Lai, J.K.H.; Dupont, S.; Stainier, D.Y.R.; Argenton, F.; Vettori, A. Zebrafish Mutants and TEAD Reporters Reveal Essential Functions for Yap and Taz in Posterior Cardinal Vein Development. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 10189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmickiene, I.; Atkocius, V.; Aleknavicius, E.; Ostapenko, V. Impact of Season of Diagnosis on Mortality among Breast Cancer Survivors. J Cancer Res Ther 2018, 14, S1091–S1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhid, L.; Corzo-Martínez, M.; Torres, C.; Vázquez, L.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T.; Ramírez de Molina, A. Improving In Vivo Efficacy of Bioactive Molecules: An Overview of Potentially Antitumor Phytochemicals and Currently Available Lipid-Based Delivery Systems. J Oncol 2017, 2017, 7351976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anis, K.V.; Rajeshkumar, N.V.; Kuttan, R. Inhibition of Chemical Carcinogenesis by Berberine in Rats and Mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 2001, 53, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.-G.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wu, S.-X.; Zhou, D.-D.; Yang, Z.-J.; Saimaiti, A.; Zhao, C.-N.; Shang, A.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Gan, R.-Y.; et al. Anticancer Effects and Mechanisms of Berberine from Medicinal Herbs: An Update Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Long, Y.; Ni, L.; Yuan, X.; Yu, N.; Wu, R.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y. Anticancer Effect of Berberine Based on Experimental Animal Models of Various Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefidabi, R.; Mortazavi, P.; Hosseini, S. Antiproliferative Effect of Berberine on Canine Mammary Gland Cancer Cell Culture. Biomedical Reports 2017, 6, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Jing, Z.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, J.; Cao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, P.; Mao, W. Berberine Activates Caspase-9/Cytochrome c-Mediated Apoptosis to Suppress Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2017, 95, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, A.; Abdelhamed, S.; Yagita, H.; Inoue, H.; Yokoyama, S.; Hayakawa, Y.; Saiki, I. Berberine Enhances Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand-mediated Apoptosis in Breast Cancer. Oncology Letters 2013, 6, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.; You, D.; Jeong, Y.; Jeon, M.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, J.E. Berberine Suppresses Cell Motility Through Downregulation of TGF-Β1 in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 2018, 45, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnam, K.C.; Ellutla, M.; Bodduluru, L.N.; Kasala, E.R.; Uppulapu, S.K.; Kalyankumarraju, M.; Lahkar, M. Preventive Effect of Berberine against DMBA-Induced Breast Cancer in Female Sprague Dawley Rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2017, 92, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, E.; Pierpaoli, E.; Orlando, F.; Donati, A.; Provinciali, M. Sidestream Dark Field Videomicroscopy for in Vivo Evaluation of Vascularization and Perfusion of Mammary Tumours in HER2/Neu Transgenic Mice. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 2015, 42, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Hu, P.; Wang, X.; Kuang, C.; Xiang, Q.; Yang, F.; Xiang, J.; Zhu, S.; Wei, L.; Zhang, J. Tumor Suppressor Berberine Binds VASP to Inhibit Cell Migration in Basal-like Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45849–45862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marverti, G.; Ligabue, A.; Lombardi, P.; Ferrari, S.; Monti, M.G.; Frassineti, C.; Costi, M.P. Modulation of the Expression of Folate Cycle Enzymes and Polyamine Metabolism by Berberine in Cisplatin-Sensitive and -Resistant Human Ovarian Cancer Cells. International Journal of Oncology 2013, 43, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q. Apoptosis, Autophagy, Necroptosis, and Cancer Metastasis. Mol Cancer 2015, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Yu, H.-Z.; Huang, S.-M.; Zheng, Y.-L. P53, Bcl-2 and Cox-2 Are Involved in Berberine Hydrochloride-Induced Apoptosis of HeLa229 Cells. Mol Med Rep 2016, 14, 3855–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Li, L.; Zou, X.; Xu, L.; Yi, P. Berberine Attenuated Proliferation, Invasion and Migration by Targeting the AMPK/HNF4α/WNT5A Pathway in Gastric Carcinoma. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Dian, L.; Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Zheng, M.; Wang, J.; Drobot, L.; Horak, I. Berberine Alkaloids Inhibit the Proliferation and Metastasis of Breast Carcinoma Cells Involving Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and EMT. Phytochemistry 2022, 200, 113217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-Y.; Shi, C.-J.; Fu, W.-M.; Zhang, J.-F. Berberine Inhibits Tumour Growth in Vivo and in Vitro through Suppressing the LincROR-Wnt/β-Catenin Regulatory Axis in Colorectal Cancer. J Pharm Pharmacol 2023, 75, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Peng, W.W.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, L. β-Catenin Correlates with the Progression of Colon Cancers and Berberine Inhibits the Proliferation of Colon Cancer Cells by Regulating the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Gene 2022, 818, 146207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Dannappel, M.; Wan, C.; Firestein, R. Transcriptional Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guan, K.-L. Hippo Signaling in Embryogenesis and Development. Trends Biochem Sci 2021, 46, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calses, P.C.; Crawford, J.J.; Lill, J.R.; Dey, A. Hippo Pathway in Cancer: Aberrant Regulation and Therapeutic Opportunities. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Mina, M.; Armenia, J.; Chatila, W.K.; Luna, A.; La, K.C.; Dimitriadoy, S.; Liu, D.L.; Kantheti, H.S.; Saghafinia, S.; et al. Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell 2018, 173, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, B. The Regulation and Function of YAP Transcription Co-Activator. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica 2014, 47, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-L.; Li, Q.-Y.; Jin, M.-J.; Lu, C.-F.; Mu, Z.-Y.; Xu, W.-Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.-Y. A Review: Hippo Signaling Pathway Promotes Tumor Invasion and Metastasis by Regulating Target Gene Expression. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2021, 147, 1569–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.S.; Jiang, J. Hippo-Independent Regulation of Yki/Yap/Taz: A Non-Canonical View. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2021, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Ma, H.; Yao, J. The Anti-Cancer Mechanisms of Berberine: A Review. Cancer Manag Res 2020, 12, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Shao, R. Cyclizing-Berberine A35 Induces G2/M Arrest and Apoptosis by Activating YAP Phosphorylation (Ser127). Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 2018, 37, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Siegel, P.M.; Shu, W.; Drobnjak, M.; Kakonen, S.M.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Guise, T.A.; Massague, J. A Multigenic Program Mediating Breast Cancer Metastasis to Bone. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 537–549. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-C.; Shih, J.-Y.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Su, J.-L.; Lin, B.-Z.; Chen, S.-T.; Chau, Y.-P.; Yang, P.-C.; Kuo, M.-L. Connective Tissue Growth Factor and Its Role in Lung Adenocarcinoma Invasion and Metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004, 96, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebolledo, D.L.; Acuña, M.J.; Brandan, E. Role of Matricellular CCN Proteins in Skeletal Muscle: Focus on CCN2/CTGF and Its Regulation by Vasoactive Peptides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer F (5’-3’) | Primer R (5’-3’) | Amplicon length (pb) | Number of cycles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTB | TGGCACCACACCTTCTACAA | CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG | 182 | 25 |
| β-catenin | ACACGTGCAATCCCTGAACT | CACCATCTGAGGAGAACGCA | 138 | 26 |
| TAZ | TCCAATCACCAGTCCTGCAT | AGCTCCTTGGTGAAGCAGAT | 125 | 28 |
| YAP | CCCAGACTACCTTGAAGCCA | CTTCCTGCAGACTTGGCATC | 107 | 28 |
| CTGF | CGACTGGAAGACACGTTTGG | AGGAGGCGTTGTCATTGGTA | 136 | 27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





