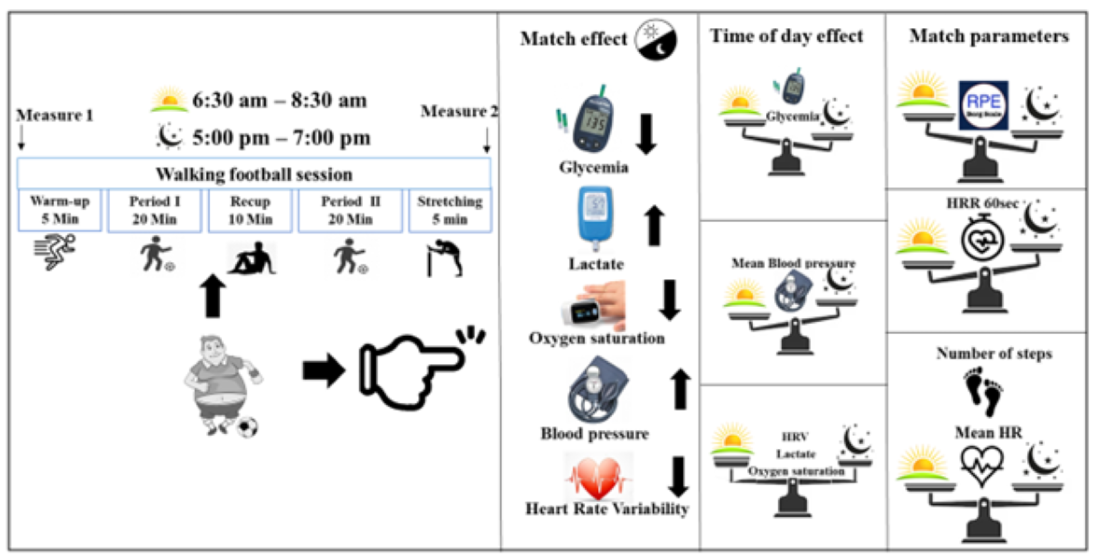
1. Introduction
Obesity often associated with sedentary behavior[
1,
2], is associated with elevated risk of diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases, and cancers [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. This chronic disorder is currently ranked in the 5th highest global public health problem and is responsible for 4.8% of deaths worldwide [
7]. Mainly, Tunisian statistics indicate a prevalence of 26.2% for obesity [
8]. Particularly, obesity is associated with circadian misalignment which can be explained by social jet lag and erratic lifestyle [
9]. Indeed, the circadian clock system is involved in controlling the biology of adipose tissue, energy metabolism, and physiological responses to exercise [
10]. Due to its chronobiotic effects, exercise can induce phase shift in the circadian rhythmicity of supra-chiasmatic nucleus [
11,
12], which could lessen the harmful effects of circadian misalignment [
13,
14], and increases the activation of metabolic pathways and systemic energy homeostasis in skeletal muscle [
15]. Moreover, exercise is effective to improve hunger suppression as a result of change in energy balance [
16]. For these reasons, regular physical activity is strongly encouraged in order to minimize the consequences of obesity and to fight against other cardiovascular and metabolic disorders [
17]. In this context, recreational team sports, particularly football, have emerged as cost-effective interventions promoting cardiometabolic health [
18,
19,
20,
21]. Walking football (WF), a variant introduced in 2011, is a feasible and sustainable exercise intervention. Research suggests its potential to enhance participants’ body composition and physical fitness [
22,
23] , alongside contributing positively to mental well-being [
24,
25,
26].
Mainly, recent studies have shown that timing exercises can have a greater physiological and molecular response, promoting chronobiological homeostasis and treating conditions like obesity [
12,
27]. Understanding exercise (i.e., WF) timing is crucial for robust evidence backing guidelines and clinical recommendations.
Regarding cardiovascular responses, previous studies have shown that exercise in the afternoon or in the evening presents a greater glucose reduction from the morning [
28,
29]. Moreover, it has been shown that an engagement in 60 minutes of endurance exercise during evening led to a significant increase in growth hormone, and blood adrenaline immediately after exercise, compared to morning exercise [
30]. Otherwise, previous studies suggested that moderate intensity aerobic exercise does not change heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) during 24-h recovery independently of time-of-day (TOD) [
31].
Despite substantial evidence of the positive impact of physical exercise, whatever its intensity and type, on reducing mortality risk [
32,
33] knowledge is limited regarding the relationship between recreational exercise (e,i, WF) at different TOD and health risks [
34].
Recognizing this gap, our focus in this study was on assessing physiological responses and physical performance during a single walking football match conducted at different TOD, specifically among individuals with higher body weight. This exploration aims to contribute valuable insights to recommendations on the how and when of exercise, especially in the context of higher weight individuals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
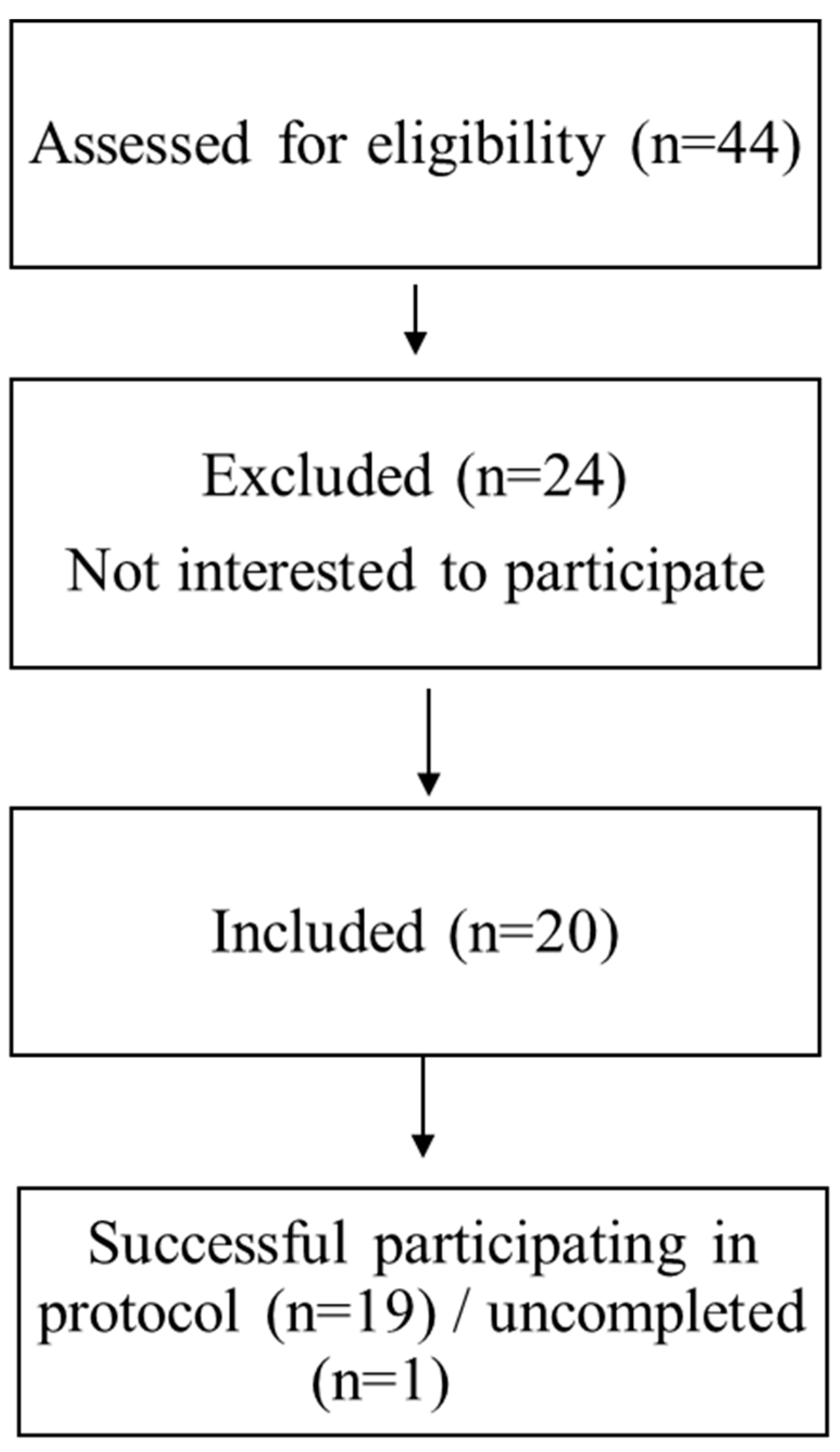
Nineteen men volunteered to participate in this study (
Figure 1). They were recruited based on: (i) they were overweight / obese (BMI> 25 kg/m2), (ii) over 30 years old, and [
35] they did not have any injuries nor any cardiovascular, respiratory, or neurological diseases. Answers to the Horne & Ostberg [
36] questionnaire categorized subjects as “moderately evening” (n = 9) or “intermediate” (n = 8) or “moderately morning” (n = 2) chronotypes.
The characteristics of the present study participants are presented in
Table 1. The participants gave written informed consent to participate in the experiment after receiving a de-tailed description of the possible risks and discomforts related to the experimental procedures. All procedures were approved by the local ethics committee (personal protection committee - CPP SUD, Sfax, Tunisia) and registered in the Pan African Clinical Trial Registry (Trial ID: PACTR202203813725635). This study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figure 1.
Flow chart of participants’ recruitment.
Figure 1.
Flow chart of participants’ recruitment.
Table 1.
Participants Anthropometric Characteristics.
Table 1.
Participants Anthropometric Characteristics.
| Age |
44.89±6.51 |
| Height (cm) |
173.16±4.31 |
| Weight (kg) |
100.16±13.47 |
| BMI (kg/m2) |
33.16±4.75 |
| Fat mass (kg) |
33.79±10.19 |
| Lean mass (kg) |
66.37±4.67 |
| Body water (kg) |
47.55±6.99 |
2.2. Experimental design
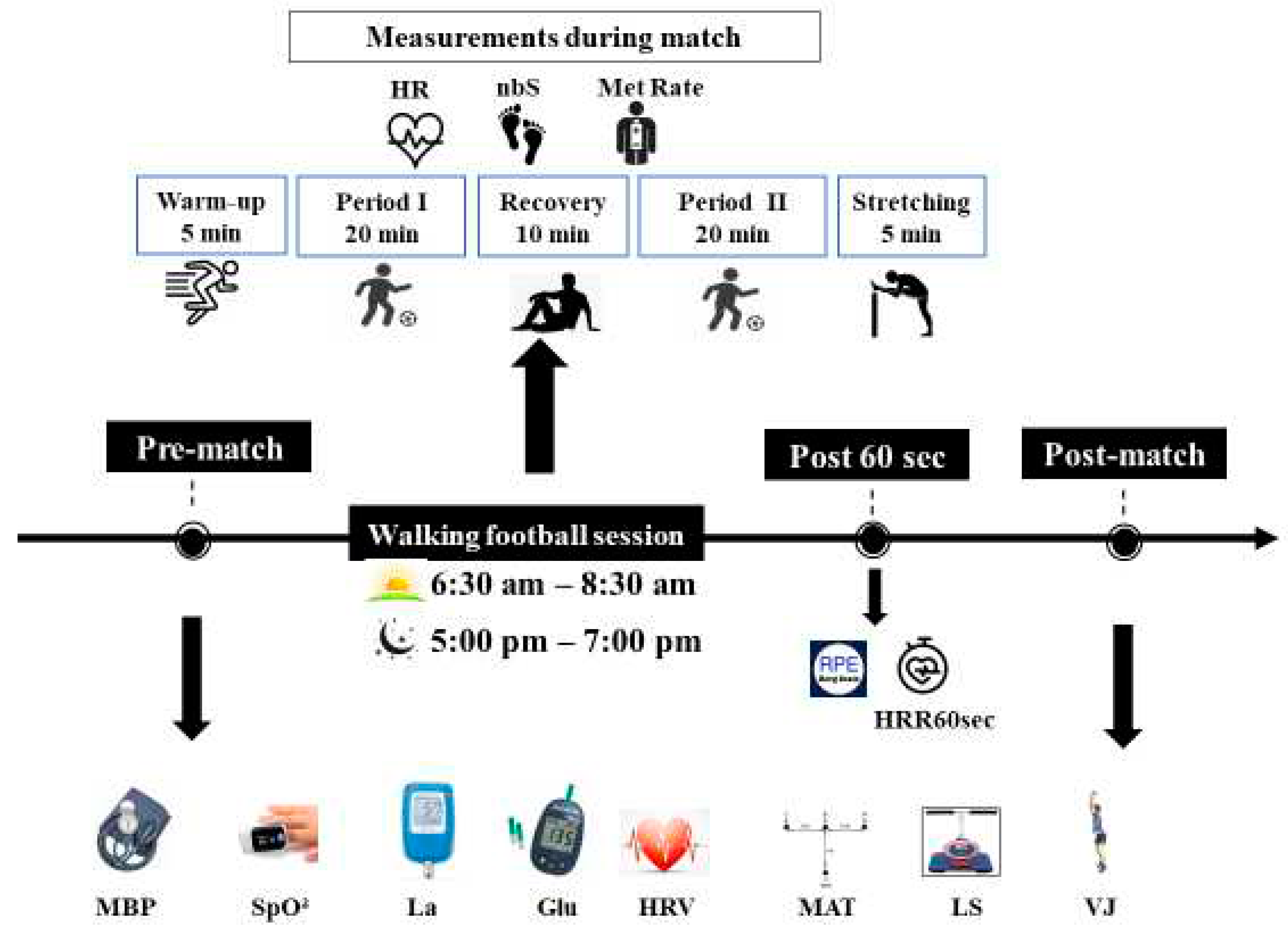
The experimental design consisted in playing 5 vs 5 matches on a 30-45m wide and 45-60m long field at two different times of day. Participants were familiarized with the WF practice (3 familiarization sessions) before the start of the experimental sessions. Each WF session began with warm-up of 10-minute, and then participants played two 20-minute periods interspersed with a 10-minute passive recovery. The WF session then ended with 5 minutes of stretching (
Figure 2).
Participants have performed two walking football matches (WFM), in a randomized order, over 2 days with only one test session per day, allowing a recovery period of 7 days in between. The morning session was conducted between 6:30 am and 8:30 am and the evening one was conducted between 5:00 pm and 7:00 pm. HR recovery after 1 min (HRR60s) and RPE score have been recorded only after the WFM. Moreover, selected physiological parameters and physical performances have been assessed before and after the WFM (
Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Experimental protocol. HRV: Heart Rate Variability; MBP: Mean blood pressure; SpO²: Oxygen saturation; La: Blood lactate; Gl: Glycemia; MAT: Modified Agility T-Test; VJ: Vertical jump height; LS: Lumbar Strength; nbS: Number of steps; HR: heart rate; Met Rate: Expenditure of Energy; HRR60s: Heart rate of recovery after 60 second; RPE: rating of perceived exertion; ↓: measurement.
Figure 2.
Experimental protocol. HRV: Heart Rate Variability; MBP: Mean blood pressure; SpO²: Oxygen saturation; La: Blood lactate; Gl: Glycemia; MAT: Modified Agility T-Test; VJ: Vertical jump height; LS: Lumbar Strength; nbS: Number of steps; HR: heart rate; Met Rate: Expenditure of Energy; HRR60s: Heart rate of recovery after 60 second; RPE: rating of perceived exertion; ↓: measurement.
2.3. Measurements
Physiological parameters
A digital scale was used to measure body weight with accuracy of 0.1 kg (Tanita TBF 401, Tanita Corp., Japan), and a stadiometer was used to measure height with accuracy of 0.1 cm (Holtain, Crymych, Dyfed, UK). Measured anthropometric parameters were: fat mass (FM), lean body mass (LBM), and total body water (TBW).
The systolic and diastolic BP was measured with a stethoscope (MissouriR) and a manual aneroid sphygmomanometer (MissouriR) with a precision of 2 mmHg. Measure was taken in a seated position after 10 minutes of rest, 3 times at intervals of one minute. MBP was calculated with a standard formula as follows:
The result was taken as the mean value of the three measures.
We have used a HR sensor (Mooky center technology, HR5) synchronized with an ActiGraph GT3X (Actigraph, Pensacola, FL, USA) to record the HR and RR intervals. The HR sensor was placed on the chest, and the triaxial accelerometer in the non-dominant wrist which calibrated and synchronized to record HR, R-R-intervals and triaxial accelerations at 100 Hz. R-R-intervals have been recorded using a modified protocol of Kammoun et al [
23]. Then RR data. csv files were exported from Actilife 6 (version 6.13.7) app and then processed by Kubios HRV Premium Software (version 3.5). The option “automatic method” was used to correct the RR series [
38]. During the analyses, data sets with artefacts >3% were removed from consideration [
39]. All HRV measurements are presented in the table below (
Table 2).
To measure SpO2 levels a pulse oximeter finger probe (HOL_MD300C15D) was applied to the left hand's ring finger.
The levels of blood lactate [La] were assessed using the Lactate Pro 2 electrochemical method portable blood lactate meter (Arkray, Kioto, Japan), point-of-care analyzer that functions through enzymatic amperometric detection. When blood sample interacts with the reagent on the test strip, it generates a slight electrical current corresponding to the [La]. The device gauges this current slight electrical and computes the [La]. It only requires 0.3 μl of whole-blood sample and takes 15 sec to measure the lactate value.
Glycemia [Gl] was assessed using the blood glucose test meter (Accu-Chek Active, Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). The measurement utilized an electrochemical method, involving a small blood sample taken from the tip of the index finger. Glucose in the blood reacts with an enzyme electrode containing glucose oxidase which fixed on the strips and calculates the glucose level in the blood [
40].
The Modified Agility T-Test (MAT) was used, as previously described [
41], to assess the speed with directional changes such as multidirectional sprinting, left and right shuffling, and backpedaling.
The Takei Vertical Jump Meter (Takei Jump-MD TKK5406) was used to evaluate the explosive strength of the leg muscles. Three attempts were made to jump from the standing position without recoil, and the highest score was recorded after this trial was adopted [
42,
43].
The measure of the static strength of back muscles was assessed with a Takei back muscle dynamometer (Takei 516489, Japan) with a dial range from 0 to 300 kgs. The description of realization was detailed in the study of [
23]. Three trials were conducted following the demonstration and the familiarization trial, with a pausing for 2 minutes in between each trial. Maximal strength for the three trials was used.
The ActiGraph GT3X (Actigraph, Pensacola, FL, USA) accelerometer was used to measure the nbS and energy expenditure (Met rate) of the subjects during the WFM. The accelerometers' initial data were collected at a sampling frequency of 30 Hz. The accelerometer was initialized before each test session. Participants wore GT3X activity monitors on their non-dominant arm (Actigraph, Pensacola, FL, USA). Actilife 6 (version 6.13.7) was used to download and analyse the GT3X data. The WFM data of nbS were downloaded to a computer at 60s intervals and predicted Expenditure Energy (METs) was obtained by Freedson’s prediction equation [
44].
HR data. csv files were exported from Actilife 6 (version 6.13.7), then Excel software was used to extract and evaluate HR beats (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). HR data from the WFM were expressed as mean HR and max HR. We also extracted the mean HR after 1 minute from the WFM (HRR60s).
Participants rated their subjective level of exertion for physical exercise using the Borg CR10 RPE scale, which has values ranging from 0 (no effort) to 10 (maximal effort [
45].
2.4. Sample size calculation
The study design was a controlled parallel trial, with realization of all of the experimental conditions in the same period to minimize the effects of external conditions. Furthermore, the minimum required sample size was calculated using the G*power software (version 3.1.9.6; Kiel University, Kiel, Germany). We set α and power (1-β) values at 0.5 and 0.9 respectively. The sample size of the study was calculated, a priori, based on the study of Brito et al. [
46]. To achieve the desired power, data from 16 participants would be sufficient to minimize the risk of incurring a type 2 statistical error. Twenty volunteers have been included to accommodate any potential dropouts during the experiments. Finally, we completed the experimentation with 19 participants, as one individual sustained an injury and did not complete the study.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Values are reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD). SPSS version 25 for Windows (SPSS Inc, Chicago, Il, USA) used to performed data analyses. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to determine if the data were normally distributed. Two-way analysis of variance was used to determine differences between experimental conditions (2 times-of-day (Morning and evening) × 2 Time-points: Before and after the WFM). The Bonferroni post-hoc test was applied when a significant difference was found. However, when the normality was failed, a Wilcoxon test was used to compare between all conditions and to determine the interaction TOD × delta change match (After – before Match). To estimate the meaningfulness of significant findings, the effect sizes were calculated as partial eta-squared (ηp2) for the ANOVA. Small, moderate, and large effect sizes were represented by ηp2 values of 0.01, 0.06, and 0.13 respectively. For nbS, mean HR, Met Rate, HR max, HRR60s, and RPE, we have used the paired student t-test when data were normally distributed, to analyze the effect of TOD (Morning versus Evening). The Wilcoxon test has been used for non-parametric data. Cohen's d test was utilized to determine effect sizes, with values typically interpreted as follows: a small effect (0.2), a medium effect (0.5), and a large effect (0.8) or higher [
47].
3. Results
3.1. HRV
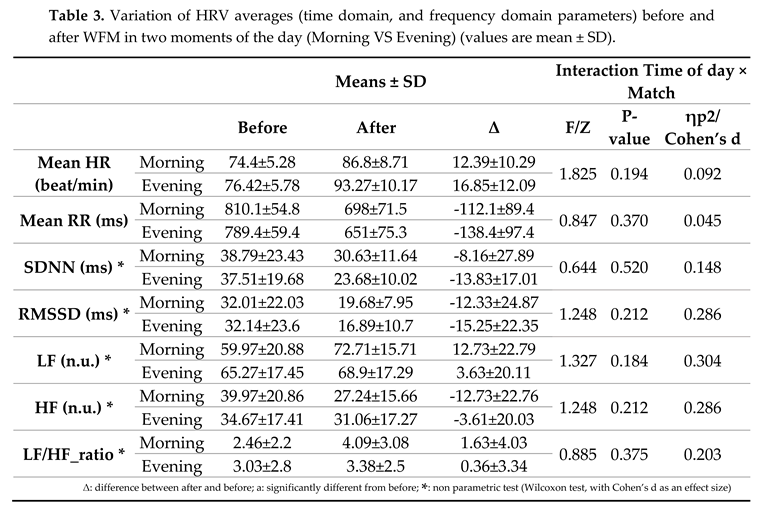
The
Table 2 displays the statistical results of the diurnal variation of HRV data (time domain, and frequency domain parameters) before and after WFM.
Statistical analyses revealed no significant interaction (TOD × match) for HR and mean RR, RMSSD and SDNN. A significant
For the frequency parameters no significant interaction (TOD × match) for LF, HF and HF/LF ratio.
3.2. Physiological parameters
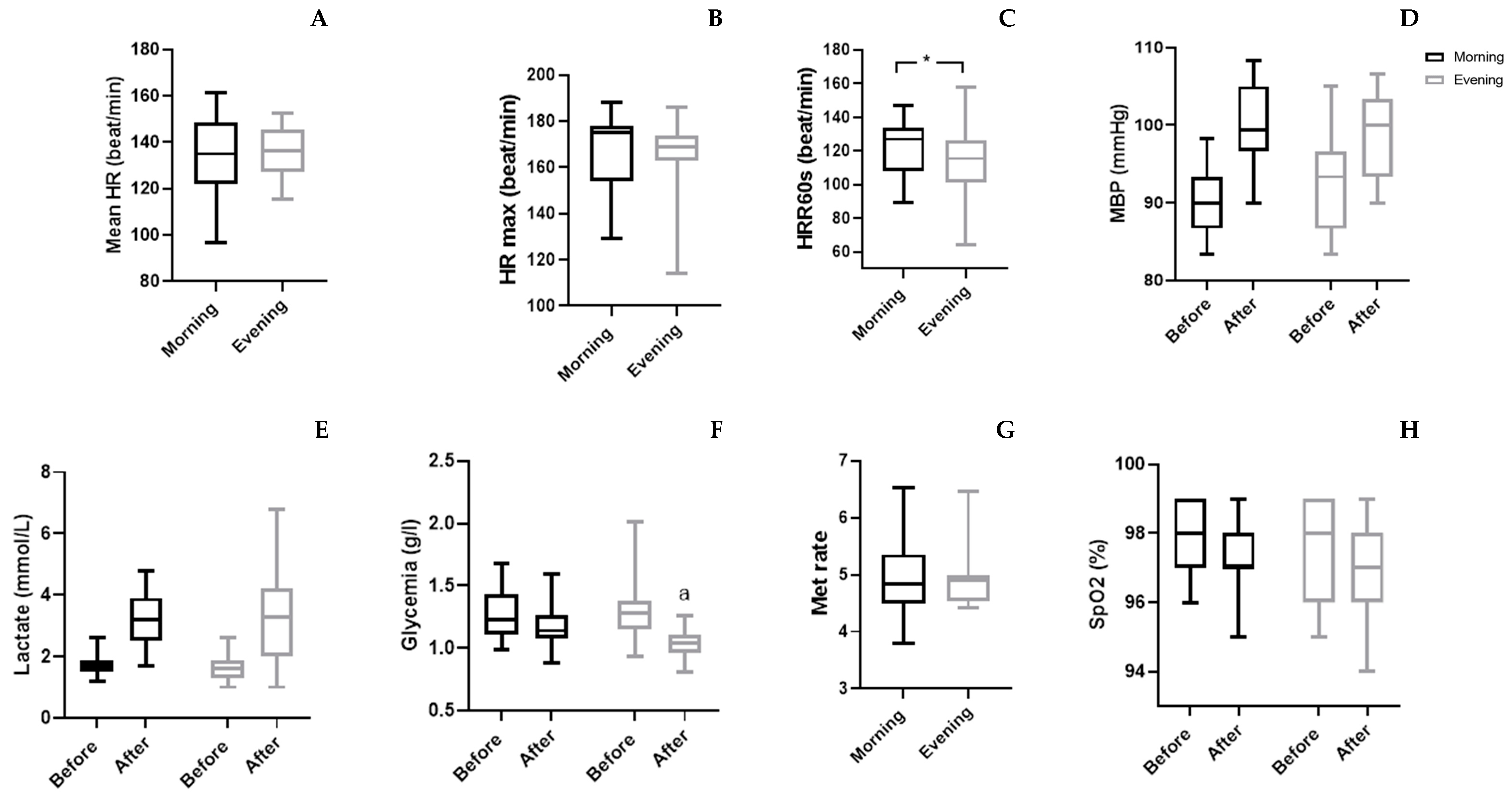
The physiological parameters (
Table 4 and
Figure 3), statistical analyses showed a significant interaction (TOD × match) only for [Gl] (p=0.039; ES=0.21) and MBP (p=0.007; ES=0.34). The Wilcoxon test revealed that [Gl] was decreased only in the evening after WFM (p=0.001), while MBP did not showed any significant change. There was no significant TOD × match interaction of [La] and SpO
2.
3.3. Physical parameters
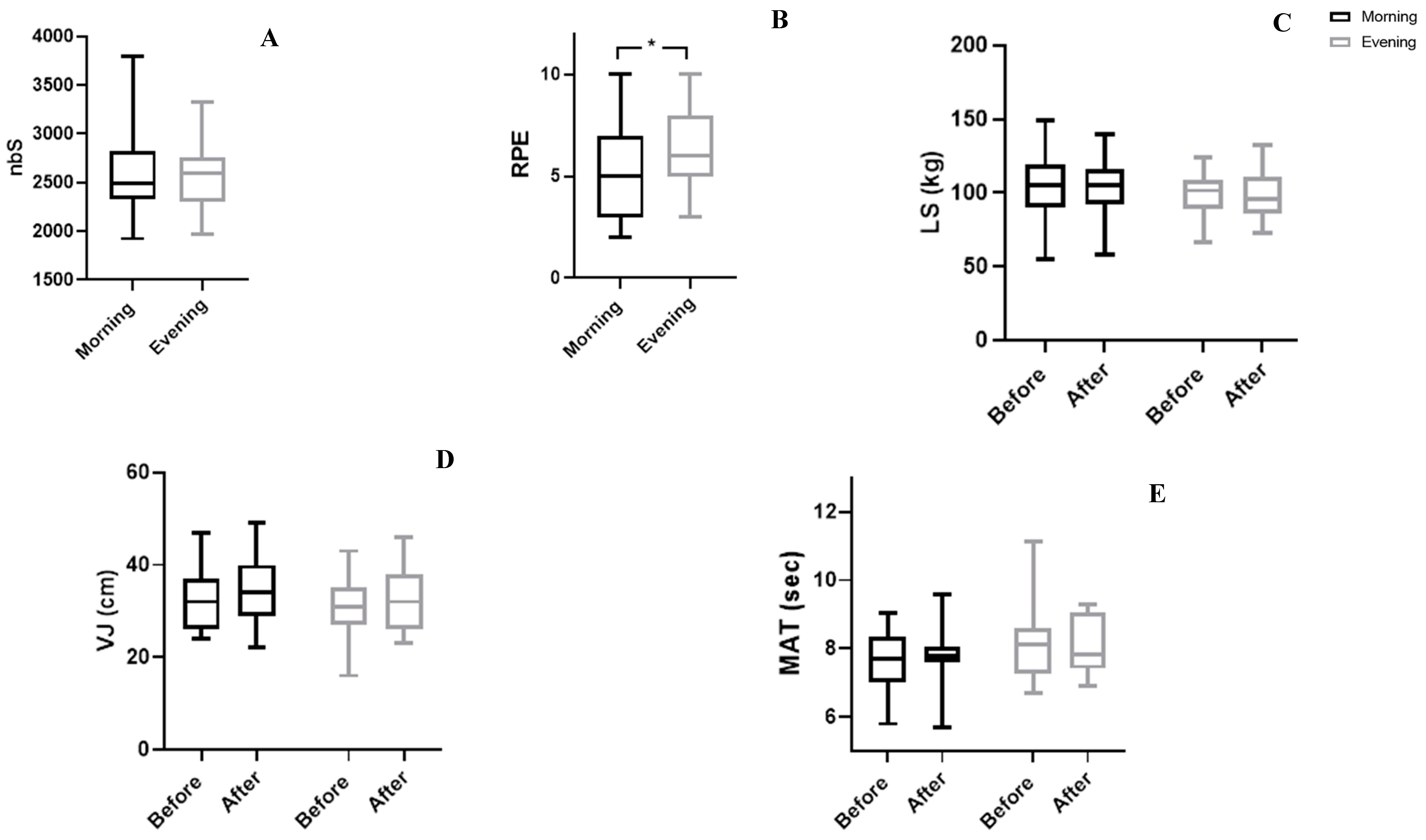
As showed in
Table 4 and
Figure 4, no significant interaction (TOD × Match) was observed for physical parameters, especially VJ, MAT, and LS.
Table 4.
Diurnal variation of physiological and physical parameters, before and after WFM (values are mean ± SD).
Table 4.
Diurnal variation of physiological and physical parameters, before and after WFM (values are mean ± SD).
| |
|
Means ± SD |
Interaction TOD × Match |
| Parameters |
TOD |
Δ |
F/Z |
P-value |
ηp2/ Cohen’s d |
| MBP (mmHg) |
Morning |
9.88±5.33 |
9.275 |
0.007 |
0.340 |
| Evening |
5.61±6.94 |
|
SpO2 (%)*
|
Morning |
-0.74±1.24 |
0.659 |
0.510 |
0.151 |
| Evening |
-1.11±1.91 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) |
Morning |
1.48±0.95 |
0.310 |
0.585 |
0.017 |
| Evening |
1.63±1.13 |
| Glycemia (g/l) |
Morning |
-0.08±0.2 |
4.960 |
0.039 |
0.216 |
| Evening |
-0.27±0.29 |
| MAT (s) * |
Morning |
0.08±0.48 |
1.087 |
0.277 |
0.249 |
| Evening |
-0.17±0.84 |
| LS (Kg) |
Morning |
-0.71±21.87 |
0.003 |
0.955 |
0.000 |
| Evening |
-0.71±13.08 |
| VJ (cm) |
Morning |
2±3.42 |
0.018 |
0.894 |
0.001 |
| Evening |
1.84±4.52 |
| Δ: difference between after and before; VJ: Vertical
Jump; MAT: Modified agility test; LS: Lumber strength; SpO2: Oxygen
saturation; MBP: Mean blood pressure; Lactate; Glycemia; *: non parametric test (Wilcoxon
test, with Cohen’s d as an effect size)
|
3.4. Match parameters
Statistics analyzes showed that no significant difference was observed between the two TOD (
Table 5 and
Figure 4 and Figure 5) in nbS (p=0.54, d=0.17), mean HR (p=0.40, d=0.19), Met Rate (p=0.18, d=0.08), and HR max (p=0.60, d=0.03). But HRR60s from the end of the match and RPE presented a remarkable difference between the evening and morning. Where the HR decreased quickly in the evening compared to the morning (p=0.048, d=0.47). Also, RPE was lower in the morning compared to the evening (p=0.04; d=0.47).
Table 5.
Match parameters results (Mean±SD).
Table 5.
Match parameters results (Mean±SD).
| Parameters |
t/Z |
p |
Confidence interval -95% |
Confidence interval 95% |
Cohen’s d |
| RPE |
-2.22 |
0.04 |
-2.05 |
-0.06 |
0.47 |
| nbS |
-0.63 |
0.54 |
-281.95 |
153.06 |
0.17 |
| Met Rate* |
1.33 |
0.18 |
- |
- |
0.08 |
| Mean HR (beat/min) |
-0.86 |
0.40 |
-9.43 |
3.96 |
0.19 |
| HR max* (beat/min) |
0.52 |
0.60 |
- |
- |
0.03 |
| HRR60s* (beat/min) |
2.29 |
0.048 |
0.073 |
16.091 |
0.47 |
| nbS: Number of steps; Mean HR: Mean heart rate; Met
Rate: Expenditure of Energy; HR max: maximal Heart rate HRR60s: Heart rate of
recovery after 60 second; RPE: rating of perceived exertion in the morning
and in the evening.
*
: non parametric test.
|
Figure 3.
Group means and standard deviation of physiological parameters. A: Mean HR: Mean heart rate; B: HR max: maximal Heart rate; C: HRR60s: Heart rate of recovery after 60 second; D: MBP: Mean blood pressure; E: Lactate; F: Glycemia; G: Met Rate: Expenditure of Energy; H: SpO2: Oxygen saturation; a: significantly from before at p<0.05.
Figure 3.
Group means and standard deviation of physiological parameters. A: Mean HR: Mean heart rate; B: HR max: maximal Heart rate; C: HRR60s: Heart rate of recovery after 60 second; D: MBP: Mean blood pressure; E: Lactate; F: Glycemia; G: Met Rate: Expenditure of Energy; H: SpO2: Oxygen saturation; a: significantly from before at p<0.05.
Figure 4.
Group means and standard deviation of physical parameters. A: nbS: Number of steps; B: RPE: rating of perceived exertion C: LS: Lumber strength; D: VJ: Vertical Jump; E: MAT: Modified agility test, a: significantly from before; *: significantly different at p<0.054.
Figure 4.
Group means and standard deviation of physical parameters. A: nbS: Number of steps; B: RPE: rating of perceived exertion C: LS: Lumber strength; D: VJ: Vertical Jump; E: MAT: Modified agility test, a: significantly from before; *: significantly different at p<0.054.
4. Discussion
To the best of the researchers’ knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the diurnal fluctuation of physiological responses and physical performance, using biosensors, before and after practicing WFM in higher weight individuals.
Despite the numerous beneficial effects of regular physical activity practice [
48], acute strenuous exercise was associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events [
1,
4]. Therefore, it is crucial to thoroughly investigate these exercise-related factors to maximize the benefits of exercise and prevent the occurrence of ischemic events, especially in obese and overweight individuals. Monitoring cardiometabolic parameters using Sophisticated sensors that offer digital health biomarkers (e.g., HR, HRV, HRR60s, glycemia and SpO
2) is essential for maintaining overall health.
In this context, HRV is a useful tool in assessing the risk of cardiac events and in evaluating the advantages and disadvantages linked to physical exercise [
49]. Indeed, persons living with obesity showed a decrease in HRV, indicating an alteration in cardiac autonomic function [
50], due to predominance of sympathetic tone [
51]. Moreover, the importance of HR assessment in the recovery phase as predictor of mortality has been taken into consideration [
52].
According to previous recommendations, individuals should aim for 100 steps per minute while walking to achieve reasonable cadence for moderate intensity exercise [
53]. Current wearable devices can measure and quantify the number of steps which indicate the varying levels of daily activity. Therefore, it was crucial to examine the nbS walked during a WFM to gain insights into the intensity of this activity. For this reason, we used the accelerometer (Actigraph, GTX3) to measure the nbS and to determine the energy expenditure (met rate) during the WFM.
4.1. Physiological parameters
Our investigation revealed a lack of significant interaction between TOD and the WFM for time domain parameters including Mean RR, SDNN and RMSSD. This finding aligns with a prior study that found no significant differences in RMSSD before and after a 30-minute recovery period in the morning, afternoon, and night in sedentary healthy men after 35 minutes of cycling [
31]. However, another study conducted in men with pre-hypertension displayed a slower RMSSD30s recovery after maximal exercise performed in the evening compared to the morning [
46]. These variations underscore the intricate relationship between TOD, exercise, and autonomic nervous system responses, suggesting that the impact may be context-dependent and influenced by individual health status.
Same, frequency domain parameters did not show any significant interaction TOD × match. Accordingly, previous research concluded that cardiac autonomic control remained constant across the different TOD, as indicated by HRV analysis, during the 24-hours period following moderate aerobic exercise in sedentary subjects [
31,
54]. HRV can be affected by many factors including physical activity independently of TOD.
In the present study, HRV biomarkers were influenced by the WFM. Indeed, after ceasing exercise, both HR and HRV exhibit a time-dependent recovery, ultimately reverting to their pre-exercise [
55]. Limited studies have examined how exercise intensity and duration affect HRV during the first 10 minutes of recovery after workout. In this sense, Michael et al. [
56] suggest that exercise intensity might have a subtle effect on HRV recovery, especially during the first hour after exercise. Notably, another study found that higher exercise intensity resulted in slower recovery of HR and HRV [
56]. In conclusion, TOD did not affect HR and HRV recovery after WFM.
In this current investigation, a significant interaction TOD × match was observed for MBP. WFM induced increase of MBP was more pronounced in the morning compared to the evening. Accordingly, a prior study has reported elevated MBP in the morning compared to the evening after exercise in normotensive males [
57]. In contrast, another study in healthy subjects showed no significant changes in BP after walking and running exercises [
58]. Moreover, previous research did not found significant differences in HR and BP values between morning and evening after a 30-minute cycling session [
57]. According to Whelton et al[
59], BP variability is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Additionally, earlier studies have indicated that forearm blood flow after exercise reached its highest in the afternoon (at 3 pm to 7 pm) [
60]. Moreover, compared to morning exercise (at 8 am), another study found a progressive increase in systemic vascular resistance after afternoon exercise (at 4 pm) [
61]. These observations explain the faster decease in BP in the afternoon, which support our findings.
Although, we did not find any significant interaction TOD x match for HRV parameters, the present findings showed that HRR60s was lower in the evening from the morning. These results can be explained by the findings of Molina et al [
62], which indicated no significant correlation between HRR with HRV in supine position, during the 1
st minute after exercise. Lower HRR60s values in the evening can be explained by the function of sympathetic activity which rose in the morning and reached its lowest during the evening [
63]. Previous studies have also indicated that cardiovascular responses to exercises are TOD dependent [
34]. According to previous research, the most markedly peaks in catecholamine reactivity around 9h00 am and 9h30 pm, decline in vagal activity around 9h00 am and faster recovery of systolic BP after exercise in the late afternoon (around 5h00 pm) compared to the early morning (8h30) [
64].
Otherwise, means of [La] levels increased after the WFM at both morning and evening sessions. This finding is consistent with a previous study that evaluated [La] level before and after WFM in older individuals, revealing a significant increase around 157% post-session [
65]. This highlights the high intensity of WFM, as evidenced by the comparatively high post session [La] concentration. These findings suggest that WF practice places a significant demand on the glycolytic pathway in addition to the aerobic ones.
Our results showed a significant interaction TOD × match for [Gl] levels. The decrease in [Gl] levels after the WFM was higher in the evening than in the morning. This aligns with previous studies that reported reduced [Gl] levels after evening exercise of similar intensity [
66,
67]. Furthermore, catecholamine are the main hormones whose concentrations increase markedly during exercise [
68], lay a pivotal role in elevating lipolysis and glycogenolysis [
69]. Additionally, during exercise muscle fibers produced IL-6 [
70], enhancing both [Gl] uptake and fat oxidation [
71,
72]. Notably, it has been indicated that catecholamines and IL-6 exhibit fluctuations throughout the day, with higher levels observed in the evening compared to the morning [
69]. The above-mentioned mechanisms could support the greater blood [Gl] control and insulin sensitivity after evening exercise is more than morning one [
28,
73].
4.2. Physical parameters
There was no significant interaction TOD × match for the physical parameters measured in the present study. MAT did not reveal any notable differences despite suggestions that multidirectional activities might be beneficial [
74]. An anterior study reported an average of 100 changes in direction and 45 accelerations and decelerations at a speed of 1.5 m/s² during a WFM [
65]. A systematic review suggests that anaerobic power (ei., jump height) peak in the afternoon [
75]. However, in our current study, we did not observe a significant interaction TOD × match. It appears that the duration of the WFM has suppressed the impact of TOD on physical performance (MAT, LS and VJ).
the present study is the first to consider the nbS taken during a WFM among higher weight men. Our statistical results did not reveal any TOD effect on the nbS. During the WFM, participants achieved an average of 2546.94±412.37 steps in the morning and 2611.38±356.34 steps in the evening. These findings align with another study, which indicated that obese men normally walk at a rhythm around of 63.8 steps/min [
76]. According to previous recommendations, individuals should aim for 100 steps per minute while walking to stimulate moderate intensity [
53]. Therefore, participating in WFM can assist high weight men in meeting the daily step count recommendations and enable them to achieve the required amount of moderate-to-vigorous intensity activity.
4.3. Match parameters
HR max and mean HR recorded during the WFM did not change across TOD. Previous study found that there is no significant difference between morning and evening in mean HR and HR max in healthy subject during a progressive cycling exercise [
77].
Higher HRmax and mean HR values are in line with findings of previous studies on recreational small-sided football training [
19] and WF sessions [
65] in elderly men. Furthermore, according to Harper et al. [
65], WF sessions exhibit a relative intensity of 90% VO
2peak in elderly. Indeed, WF has been classified as an intermittently vigorous-intensity exercise in elderly [
78]. The present findings support the claim that football-based training at these intensities has major positive effects on the cardiovascular system [
19].
4.4. RPE
The present study revealed that RPE values were significantly lower in the morning compared to the evening. The RPE values obtained during the WFM indicated a moderate (≥4) to very hard intensity (≥7) level. These RPE values are similar to those reported in a prior study conducted on WF in older adults [
78]. To improve and maintain cardiorespiratory and musculoskeletal capacity, the American college of sports medicine suggests practicing moderate intensity exercises corresponding to RPE =13 (equivalent of %HRmax = 64-76% and%V̇O2max 46-63%) [
79]. Based on our findings, WF can be considered a safe activity that has the potential to improve the cardiorespiratory and metabolic health of individuals living obesity.
The present study presents some limits: Firstly, the participant pool was limited in number. Secondly, the demographic characteristics are not well detailed (there are huge differences between the patients). Lastly a single session is not enough, more sessions are needed to confirm the results.
5. Conclusions
The application of digital biomarkers for monitoring health status during WFM has been shown to be an effective and insightful approach. Notably, our study revealed a lack significant diurnal variation in physiological parameters (HRV, lactate, and SpO2) and physical performance.
However, specific metrics, such as HRR60s and MBP were significantly lower in the evening compared with morning. The reduction in [Gl] levels was greater in the evening compared to the morning. Overall, the safety of WF practice in higher weight men has been demonstrated. Furthermore, it appears that practicing WF in the evening is safer, as indicated by HRR60, [Gl], and MBP findings.
As we move forward, future studies should focus on investigating the effects of long-term WF practice, particularly concerning cardiovascular health and metabolism. A more extensive exploration of these aspects will contribute valuable insights for optimizing the health benefits of walking football, especially for individuals with higher body weight.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.H. and S.H.; methodology, S.H. and N.K. writing—original draft preparation, S.H., O.H.; S.T.; data analysis, S.H..; writing—review and editing, S.H.., S.T.., O.H., H.C. and T.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures were approved by the local ethics committee (personal protection commit-tee - CPP SUD, Sfax, Tunisia) and registered in the Pan African Clinical Trial Registry (Tri-al ID: PACTR202203813725635). This study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets examined in this study can be obtained from the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude for the cooperation of all the volunteers who took part in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lavie, C.J. , et al., Sedentary Behavior, Exercise, and Cardiovascular Health. Circ Res 2019, 124, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, S., A. Hebestreit, and W. Ahrens, [Physical activity and obesity]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2012, 55, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, U.E. , et al., Prevention of chronic disease in the 21st century: elimination of the leading preventable causes of premature death and disability in the USA. Lancet 2014, 384, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, G.F. , et al., Promoting Physical Activity and Exercise: JACC Health Promotion Series. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018, 72, 1622–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, H.W. , 3rd, et al., The pandemic of physical inactivity: global action for public health. Lancet 2012, 380, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnurr, T.M. , et al., Evidence for shared genetics between physical activity, sedentary behaviour and adiposity-related traits. Obes Rev 2021, 22, e13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.F. , et al., The impact of changing the prevalence of overweight/obesity and physical inactivity in Australia: An estimate of the proportion of potentially avoidable cancers 2013-2037. International Journal of Cancer 2019, 144, 2088–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministère de la, S. , Rapport de l’enquête national THES-2016 - Ministère de la santé publique. 2016.
- Mota, M.C. , et al., Social jetlag and metabolic control in non-communicable chronic diseases: a study addressing different obesity statuses. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serin, Y. and N. Acar Tek, Effect of Circadian Rhythm on Metabolic Processes and the Regulation of Energy Balance. Ann Nutr Metab 2019, 74, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, Y. , et al., Impairment of Circadian Rhythms in Peripheral Clocks by Constant Light Is Partially Reversed by Scheduled Feeding or Exercise. Journal of Biological Rhythms 2015, 30, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P. , et al., Exercise time cues (zeitgebers) for human circadian systems can foster health and improve performance: a systematic review. BMJ open sport & exercise medicine 2018, 4, e000443. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, A.M. , et al., Voluntary scheduled exercise alters diurnal rhythms of behaviour, physiology and gene expression in wild-type and vasoactive intestinal peptide-deficient mice. The Journal of Physiology 2012, 590, 6213–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilski, J. , et al., Effects of time of day and the wingate test on appetite perceptions, food intake and plasma levels of adipokines. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology: An Official Journal of the Polish Physiological Society 2016, 67, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Egan, B. and J.R. Zierath, Exercise metabolism and the molecular regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation. Cell Metab 2013, 17, 162–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceylan, H.İ., Ö. Saygın, and Ü. Özel Türkcü, Assessment of acute aerobic exercise in the morning versus evening on asprosin, spexin, lipocalin-2, and insulin level in overweight/obese versus normal weight adult men. Chronobiology International 2020, 37, 1252–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, V.A. , et al., Effects of aerobic training intensity on resting, exercise and post-exercise blood pressure, heart rate and heart-rate variability. J Hum Hypertens 2010, 24, 175–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krustrup, P. , et al., Recreational soccer is an effective health-promoting activity for untrained men. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2009, 43, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangsbo, J. , et al., Executive summary: Football for health - prevention and treatment of non-communicable diseases across the lifespan through football. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports 2014, 24, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, T.R. , et al., The Effects of 52 Weeks of Soccer or Resistance Training on Body Composition and Muscle Function in +65-Year-Old Healthy Males--A Randomized Controlled Trial. PloS One 2016, 11, e0148236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, M.T. , et al., Effect of team sports and resistance training on physical function, quality of life, and motivation in older adults. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports 2017, 27, 852–864. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, J.T., S. Bruce-Low, and L. Sammut, The impact of 12 weeks walking football on health and fitness in males over 50 years of age. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammoun, N. , et al., Effects of Walking Football During Ramadan Fasting on Heart Rate Variability and Physical Fitness in Healthy Middle-Aged Males. Am J Mens Health 2022, 16, 15579883221103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamont, E. , et al., Qualitative investigation of the role of collaborative football and walking football groups in mental health recovery. Mental Health and Physical Activity 2017, 12, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P. , et al., Walking football as sustainable exercise for older adults - A pilot investigation. Eur J Sport Sci 2017, 17, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, G. , et al., Recruiting Older Men to Walking Football: A Pilot Feasibility Study. Explore (NY) 2019, 15, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, B.M. and J.R. Zierath, Circadian rhythms and exercise - re-setting the clock in metabolic disease. Nature Reviews. Endocrinology 2019, 15, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savikj, M. , et al., Afternoon exercise is more efficacious than morning exercise at improving blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomised crossover trial. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moholdt, T. , et al., The effect of morning vs evening exercise training on glycaemic control and serum metabolites in overweight/obese men: a randomised trial. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 2061–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K. and M.A. Febbraio, Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012, 8, 457–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodel, E. , et al., Different times of day do not change heart rate variability recovery after light exercise in sedentary subjects: 24 hours Holter monitoring. Chronobiol Int 2017, 34, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lear, S.A. , et al., The effect of physical activity on mortality and cardiovascular disease in 130 000 people from 17 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries: the PURE study. Lancet 2017, 390, 2643–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, T. , et al., Wearable-device-measured physical activity and future health risk. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H. , et al., Associations of timing of physical activity with all-cause and cause-specific mortality in a prospective cohort study. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, B.J. , et al., Sport and Exercise Clinical Profile of Commotio Cordis: An Under Appreciated Cause of Sudden Death in the Young During Sports and Other Activities. Perspectives in Male Psychology 2011, 10, 91-108-120. [Google Scholar]
- Horne, J.A. and O. Ostberg, A self-assessment questionnaire to determine morningness-eveningness in human circadian rhythms. International Journal of Chronobiology 1976, 4, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coats, A.J. , et al., Systemic and forearm vascular resistance changes after upright bicycle exercise in man. J Physiol 1989, 413, 289–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipponen, J.A. and M.P. Tarvainen, A robust algorithm for heart rate variability time series artefact correction using novel beat classification. J Med Eng Technol 2019, 43, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarvainen, J.A.L. Accuracy of Kubios HRV software respiratory rate estimation algorithms. Accuracy of Kubios HRV Software Respiratory Rate Estimation Algorithms 2022, 2022-07-02.
- Feldman, B. , Electrochemistry Encyclopedia -- Electrochemical blood glucose test. 2009.
- Sassi, R.H. , et al., Relative and absolute reliability of a modified agility T-test and its relationship with vertical jump and straight sprint. J Strength Cond Res 2009, 23, 1644–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, D.L. , et al., Reliability of vertical jump performance evaluated with contact mat in elderly women. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging 2013, 33, 288–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. , et al., Constructing an index of physical fitness age for Japanese elderly based on 7-year longitudinal data: sex differences in estimated physical fitness age. Age (Dordr) 2012, 34, 203–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedson, P.S., E. Melanson, and J. Sirard, Calibration of the Computer Science and Applications, Inc. accelerometer. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 1998, 30, 777–781. [Google Scholar]
- Shariat, A. , et al., Borg CR-10 scale as a new approach to monitoring office exercise training. Work 2018, 60, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L. , et al., Time of day affects heart rate recovery and variability after maximal exercise in pre-hypertensive men. Chronobiol Int 2015, 32, 1385–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. , A power primer. Psychological Bulletin 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piercy, K.L. and R.P. Troiano, Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans From the US Department of Health and Human Services. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2018, 11, e005263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessa, F. , et al., Heart rate variability as predictive factor for sudden cardiac death. Aging (Albany NY) 2018, 10, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidan-Yaylali, G. , et al., The Association between Central Adiposity and Autonomic Dysfunction in Obesity. Med Princ Pract 2016, 25, 442–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza-Salinas, A. , et al., Autonomic function and its relationship with central obesity and hemodynamic variables in obese and overweight adults. Nutr Hosp 2022, 39, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hautala, A.J. , et al., Heart rate recovery after maximal exercise is associated with acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene polymorphism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006, 291, H459–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor-Locke, C. , et al., How fast is fast enough? Walking cadence (steps/min) as a practical estimate of intensity in adults: a narrative review. Br J Sports Med 2018, 52, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecanha, T. , et al., 24-h cardiac autonomic profile after exercise in sedentary subjects. Int J Sports Med 2014, 35, 245–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stanley, J., J. M. Peake, and M. Buchheit, Cardiac Parasympathetic Reactivation Following Exercise: Implications for Training Prescription. Sports Medicine 2013, 43, 1259–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, S. , et al., Submaximal exercise intensity modulates acute post-exercise heart rate variability. European Journal of Applied Physiology 2016, 116, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H. , et al. Effects of time of day on post-exercise blood pressure: circadian or sleep-related influences? Chronobiol Int 2008, 25, 987-98.
- Nóbrega, T.K.S.d. et al., Caminhada/corrida ou uma partida de futebol recreacional apresentam efetividade semelhante na indução de hipotensão pós-exercício. Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte 2013, 19, 31–34.
- Whelton, P.K. , et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, M., F. W. Zechman, and R.E. Smith, Circadian variation in human peripheral blood flow levels and exercise responses. Journal of Applied Physiology 1968, 25, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H. , et al., The acute post-exercise response of blood pressure varies with time of day. European Journal of Applied Physiology 2008, 104, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, G.E. , et al., Post-exercise heart-rate recovery correlates to resting heart-rate variability in healthy men. Clinical Autonomic Research 2016, 26, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheer, F.A.J.L. , et al., Impact of the human circadian system, exercise, and their interaction on cardiovascular function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010, 107, 20541–20546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J. , et al., The circadian system modulates the rate of recovery of systolic blood pressure after exercise in humans. Sleep 2020, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, L.D. , et al., The Physiological, Physical, and Biomechanical Demands of Walking Football: Implications for Exercise Prescription and Future Research in Older Adults. J Aging Phys Act 2019, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, C. , et al., Effects of arm exercise on serum glucose response in type 2 DM patients. J Nurs Res 2002, 10, 187–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, C., C. T. Ku, and W.H. Huang, Establishment of a predictive model of serum glucose changes under different exercise intensities and durations among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Nurs Res 2003, 11, 287–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-K. , et al., Chrono-exercise: Time-of-day-dependent physiological responses to exercise. Sports Medicine and Health Science 2023, 5, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zouhal, H. , et al., Catecholamines and the Effects of Exercise, Training and Gender. Sports Medicine 2008, 38, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, Nolan J. , et al., Global Phosphoproteomic Analysis of Human Skeletal Muscle Reveals a Network of Exercise-Regulated Kinases and AMPK Substrates. Cell Metabolism 2015, 22, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingsgaard, H. , et al., Interleukin-6 regulates pancreatic α-cell mass expansion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, 13163–13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellingsgaard, H. , et al., Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nature Medicine 2011, 17, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-K. , et al., Late-afternoon endurance exercise is more effective than morning endurance exercise at improving 24-h glucose and blood lipid levels. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2022, 13, 957239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L. , et al., EFFECTS OF SLACKLINE TRAINING ON POSTURAL CONTROL, JUMP PERFORMANCE, AND MYOELECTRICAL ACTIVITY IN FEMALE BASKETBALL PLAYERS. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 2016, 30, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaier, R. et al., Diurnal Variation in Maximum Endurance and Maximum Strength Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2022, 54, 169-180.
- Tudor-Locke, C. , et al., Accelerometer profiles of physical activity and inactivity in normal weight, overweight, and obese U.S. men and women. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2010, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, T. , et al., Time-of-Day Effect on Cardiac Responses to Progressive Exercise. Chronobiology International 2011, 28, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P. , et al., Walking football as sustainable exercise for older adults - A pilot investigation. European Journal of Sport Science 2017, 17, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, C.E. , et al., American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2011, 43, 1334–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).