Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
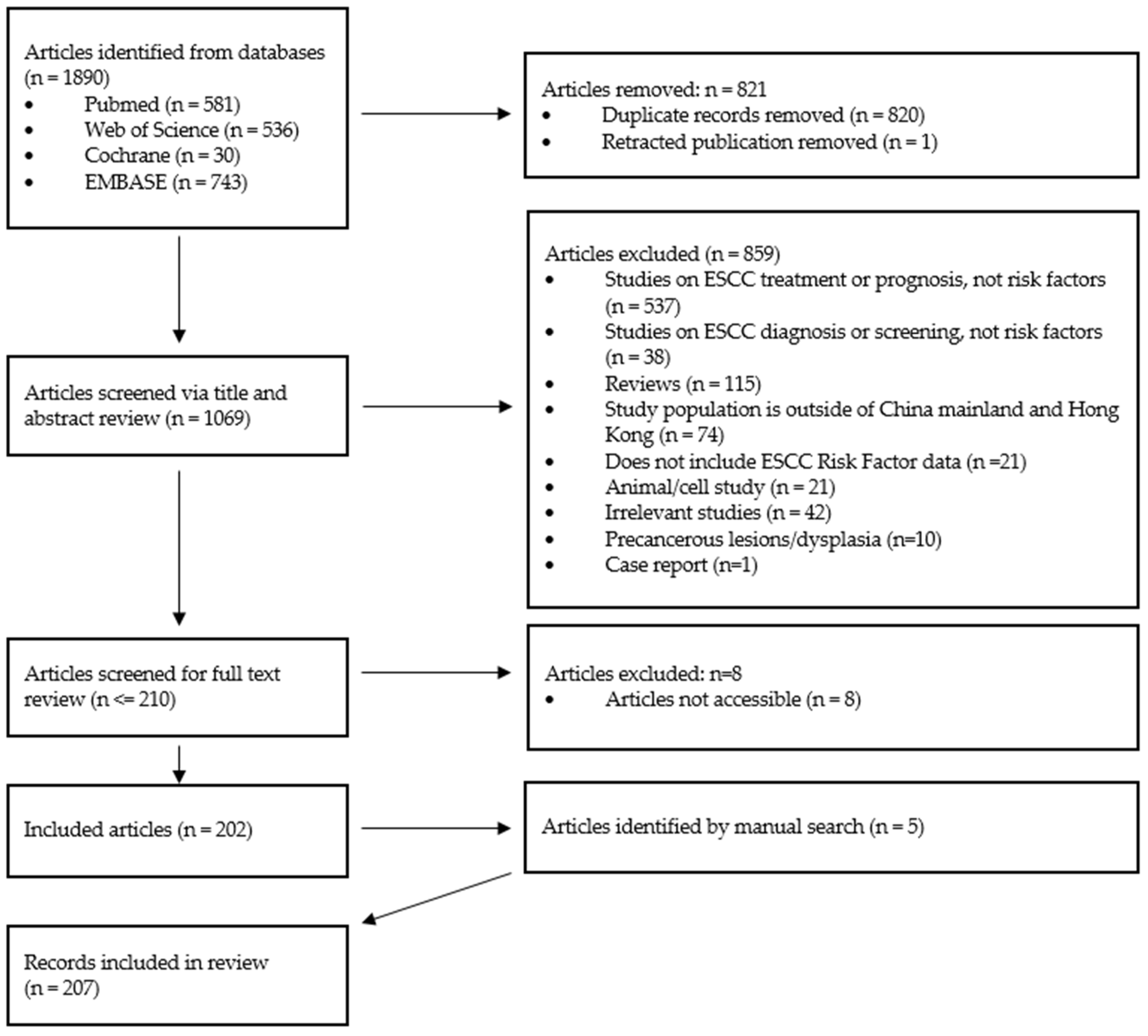
3. Results
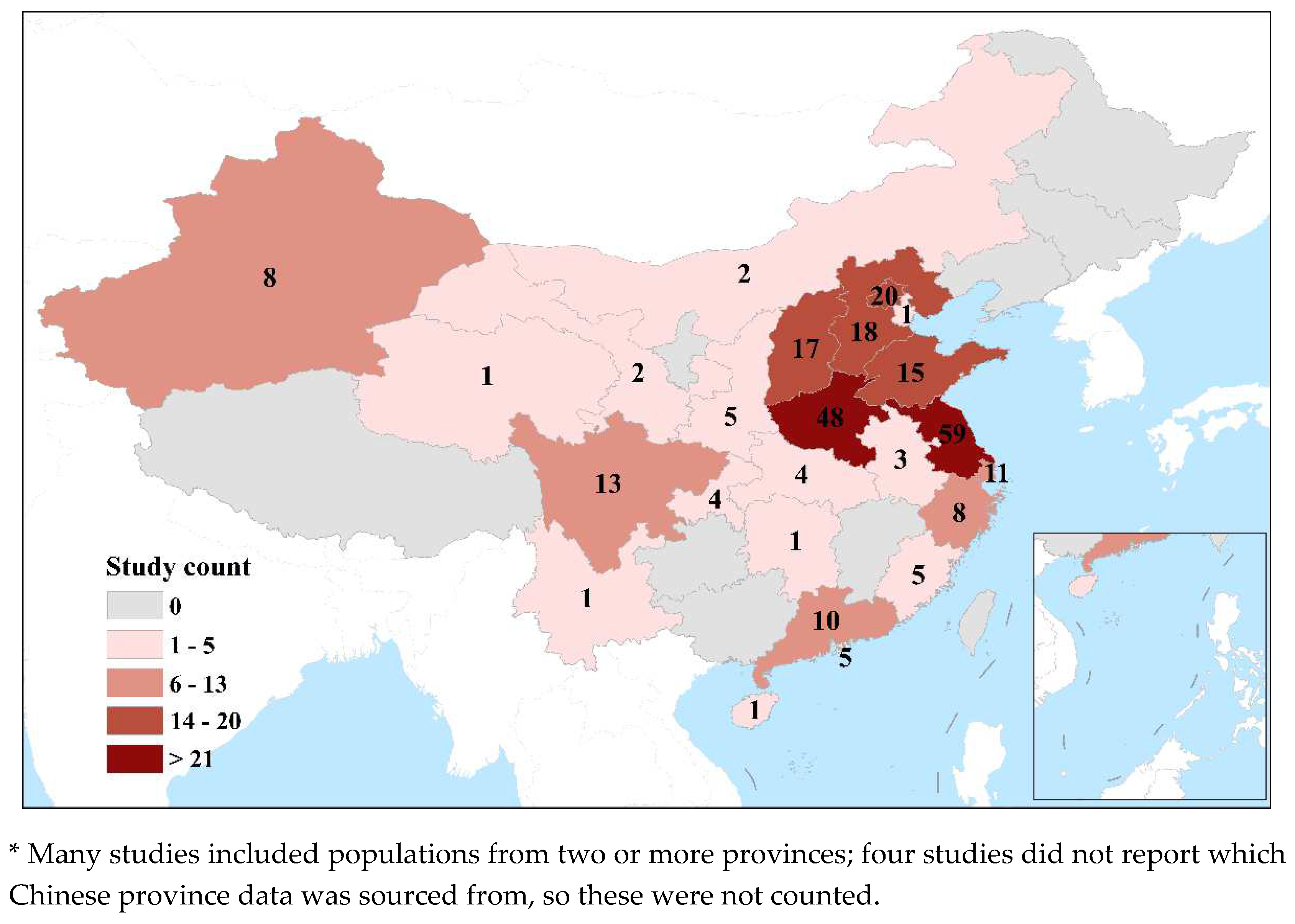
3.1. Study characteristics
3.2. Study type
Genetic
Gene-environment interactions
Family history
HPV
Helicobacter pylori
Alcohol and smoking
Pickled vegetable consumption
Salted meat consumption
Tea type consumption
Fresh fruit and vegetable consumption
Other dietary factors
Dietary behavior
Oral Health
Environmental factors
Socioeconomic status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global Surveillance of Trends in Cancer Survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of Individual Records for 37 513 025 Patients Diagnosed with One of 18 Cancers from 322 Population-Based Registries in 71 Countries. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, N.; Kelly, R.J. The Management of Localized Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Western Approach. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, D.M.; Ferlay, J.; Curado, M.-P.; Bray, F.; Edwards, B.; Shin, H.-R.; Forman, D. Fifty Years of Cancer Incidence: CI5 I-IX. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yin, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mortality, Morbidity, and Risk Factors in China and Its Provinces, 1990-2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2019, 394, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Totsuka, Y.; Shan, B.; Wang, C.; Wei, W.; Qiao, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Inoue, M.; Tanaka, H.; He, Y. Esophageal Cancer in High-Risk Areas of China: Research Progress and Challenges. Ann. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; He, J. Patterns and Trends in Esophageal Cancer Incidence and Mortality in China: An Analysis Based on Cancer Registry Data. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2023, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan — a Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. 2016, 5. 5. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Xiong, H.; Qiu, H.; Fu, Q.; Chen, B.; Hu, G.; Yuan, X. Association of P53 and MDM2 Polymorphisms with Risk of Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Related Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC). Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Ning, T.; Ke, Y. P53 Codon 72 Polymorphism and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2008, 47, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Hu, N.; Hyland, P.L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Yu, K.; Su, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, L.M.; Chanock, S.J.; et al. Genetic Variants in DNA Repair Pathway Genes and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Gastric Adenocarcinoma in a Chinese Population. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Tan, W.; Zhang, S. P53 Gene Codon 72 Polymorphism and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case/Control Study in a Chinese Population. Esophagus 2008, 21, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Qiu, H.; Huang, L.; Xiong, H.; Yuan, X. Combined Effects of Leukocyte Telomere Length, P53 Polymorphism and Human Papillomavirus Infection on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Han Chinese Population. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Song, W.; Zhang, B.; Borjigin, B. Association of TP53 Codon 72 Genotype Polymorphism and Environmental Factors with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Mongolian Population of the Chinese Region of Inner Mongolia. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Mu, L.N.; Lu, H.; Lu, Q.Y.; You, N.C.Y.; Yu, S.Z.; Le, A.D.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.F.; Marshall, J.; et al. Dietary Selenium Intake and Genetic Polymorphisms of the GSTP1 and P53 Genes on the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2006, 15, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Ning, T.; Chen, Z.; Xu, C. Association of Genetic Polymorphisms in MDM2, PTEN and P53 with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Hum Genet 2012, 57, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Tong, L.; Wei, J.; Pan, W.; Li, L.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, C.; Yang, M. The ALDH7A1 Genetic Polymorphisms Contribute to Development of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 12665–12670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Runli, J.; Wei, X.; Lili, G.; Linyan, C.; Yamei, R.; Ruitao, W.; Zhengyun, Z.; Baiqing, L.; Xia, S. Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and ALDH2 and ADH1B Polymorphisms in Chinese Females. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 2065–2068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; You, N.C.; Lu, H.; Mu, L.N.; Lu, Q.Y.; Yu, S.Z.; Le, A.D.; Marshall, J.; Heber, D.; Zhang, Z.F. Dietary Selenium Intake, Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 and X-Ray Repair Cross-Complementing 1 Genetic Polymorphisms, and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer 2006, 106, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.Z.; Chen, H.M.; Qi, Z.; Guo, Q.H. Genetic Polymorphisms in Cytochrome P4502E1, Alcohol and Aldehyde Dehydrogenases and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Gansu Chinese Males. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, C.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, X.; Qing, T.; Gao, P.; Shi, L.; Fan, M.; Cheng, H.; et al. Alcohol Intake Interacts with Functional Genetic Polymorphisms of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (ALDH2) and Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH) to Increase Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer Risk. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, Y.; Miao, X.; Tan, W.; Wei, Q.; et al. Identification of Genetic Variants in Base Excision Repair Pathway and Their Associations with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4378–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhou, R.M.; Wan, L.L.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Dong, X.J. Polymorphisms of the DNA Repair Gene Xeroderma Pigmentosum Groups A and C and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Population of High Incidence Region of North China. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2008, 134, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Fu, C.; Wang, J.; Xue, H.; Xu, B. Interaction between XRCC1 Polymorphisms and Intake of Long-Term Stored Rice in the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.X.; Dai, L.P.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xie, W. Association of Polymorphisms in X-Ray Repair Cross Complementing 1 Gene and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 509215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Du, J.; Shi, M.; Jin, G.; Yang, M. Short Leukocyte Telomere Length, Alone and in Combination with Smoking, Contributes to Increased Risk of Gastric Cancer or Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Miao, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Xiong, P.; Liang, G.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; et al. Significant Increase in Risk of Gastroesophageal Cancer Is Associated with Interaction between Promoter Polymorphisms in Thymidylate Synthase and Serum Folate Status. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Luo, G. j; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhang, D. q; Chen, J. m; Chen, X. b; Li, Z. d; Zhao, Q. Interaction between Alcohol Consumption and CYP 2C19 Gene Polymorphism in Relation to Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cheng, H.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhuang, M.; Lu, M.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Family History of Esophageal Cancer Increases the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, J.Y.; Fan, J.H.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R. Family History and Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer in the Linxian General Population. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 605106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wen, X.D.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, N.; Wen, D.G. Younger Age of Onset and Multiple Primary Lesions Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cases with a Positive Family History of the Cancer Suggests Genetic Predisposition. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2014, 127, 2779–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. The Absence of Human Papillomavirus in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in East China. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Q.; Liang, M.; Zheng, S.; Li, X.L.; Lu, X.; Sheyhidin, I. Viral Load of HPV 16/18 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Three Ethnic Groups Living in Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, Z.; Weiss, N.S.; Madeleine, M.M.; Liu, F.; Tian, X.; Song, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Human Papillomavirus Infection and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2012, 21, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhang, D.K.; Lam, K.Y.; Ma, L.; Ngan, H.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Tsao, S.W. Prevalence of HPV Infection in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Patients and Its Relationship to the P53 Gene Mutation. Int J Cancer 1997, 72, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Hu, G.; Yuan, X. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2013, 26, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehryar, M.M.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, H.W.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.T. Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus in Esophageal Carcinoma in Tangshan, China. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 2905–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Hu, S.P.; Lu, L.C.; Tang, C.Z.; Kuang, Z.S.; Zhong, S.P.; Zeng, Y. Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Esophageal Carcinoma. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 68, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.X.; Tsao, S.W.; Poon, C.S.P.; Wang, L.D.; Wong, Y.C.; Cheung, A.L.M. Viral Load of HPV in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 103, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.F.; Roth, M.J.; Wei, W.Q.; Abnet, C.C.; Chen, F.; Lu, N.; Zhao, F.H.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, G.Q.; Taylor, P.R.; et al. No Association between HPV Infection and the Neoplastic Progression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Result from a Cross-Sectional Study in a High-Risk Region of China. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuyama, K.; Castillo, A.; Aguayo, F.; Sun, Q.; Khan, N.; Koriyama, C.; Akiba, S. Human Papillomavirus in High- and Low-Risk Areas of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Br J Cancer 2007, 96, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Wei, S.; Xiong, H.; Fu, X.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Yuan, X.; et al. HPV Seropositivity Joints with Susceptibility Loci Identified in GWASs at Apoptosis Associated Genes to Increase the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC). BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Xu, Z.; Hang, D.; Guo, F.; Abliz, A.; Weiss, N.S.; Xi, L.; Liu, F.; Ning, T.; Pan, Y.; et al. Anti-HPV-E7 Seropositivity and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Population in China. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamangar, F.; Qiao, Y.L.; Schiller, J.T.; Dawsey, S.M.; Fears, T.; Sun, X.D.; Abnet, C.C.; Zhao, P.; Taylor, P.R.; Mark, S.D. Human Papillomavirus Serology and the Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cancers: Results from a Cohort in a High-Risk Region in China. Int J Cancer 2006, 119, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.S.; Tian, D.P.; Guan, X.Y.; Yun, H.; Wang, H.T.; Xiao, Y.; Bi, C.; Ying, S.; Su, M. Esophageal Intraepithelial Invasion of Helicobacter Pylori Correlates with Atypical Hyperplasia. Int J Cancer 2014, 134, 2626–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Xing, L.; Shen, H.; Cui, J.; Mi, J.; Wang, J.; Misumi, J.; Hang, X. Serum Pepsinogens and Helicobacter Pylori Are Not Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Area in China. Tumori 2013, 99, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Sun, G.; Tang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Gao, W.; Cox, S.B.; Wang, J.S. Etiological Study of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in an Endemic Region: A Population-Based Case Control Study in Huaian, China. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekheden, I.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Jin, L.; Lu, M.; Ye, W. Gastric Atrophy and Its Interaction with Poor Oral Health Elevate the Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Region of China: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.S.; Kamangar, F.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R.; Liang, H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Liu, B.; Fan, J.H.; Abnet, C.C. Serum Pepsinogens and Risk of Gastric and Oesophageal Cancers in the General Population Nutrition Intervention Trial Cohort. Gut 2009, 58, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mao, B.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Rui, J.; Chen, G. A118G Polymorphism in μ-Opioid Receptor Gene and Interactions with Smoking and Drinking on Risk of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Clin Lab Anal 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Xu, B.; Rao, J.Y.; Shen, H.B.; Xue, H.C.; Jiang, Q.W. Diet Habits, Alcohol Drinking, Tobacco Smoking, Green Tea Drinking, and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Chinese Population. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007, 19, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M, W.; JK, Z.; ZF, Z.; RQ, H.; J, Y.; JY, Z.; XS, W.; XF, Z.; AM, L.; P, van’ t V. ; et al. Smoking and Alcohol Drinking Increased the Risk of Esophageal Cancer among Chinese Men but Not Women in a High-Risk Population. Cancer Causes Control CCC 2011, 22, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.Y.; Tan, W.; Song, N.; Lin, D.X. Ser326Cys Polymorphism in hOGG1 Gene and Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Int J Cancer 2001, 95, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Feng, J.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y.; Ji, C.; Cheng, M.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, H. Genetic Variant of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2014, 18, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, N.; Wakai, T.; Wei, L.; He, Y.; Kumagai, N.; Kitsu, K.; Wang, S.; Akazawa, K. Effect of the Interaction between the Amount and Duration of Alcohol Consumption and Tobacco Smoking on the Risk of Esophageal Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, N.; Wakai, T.; Akazawa, K.; Ling, Y.; Wang, S.; Shan, B.; Okuhara, Y.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Kataoka, H. Heavy Alcohol Intake Is a Risk Factor for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma among Middle-Aged Men: A Case-Control and Simulation Study. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Hu, A.; Hu, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y. Comparison of Lifestyle and Living Environment among High Risk Immigrant and Low Risk Host Residents: Implications for Esophageal Cancer Etiology. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 11, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.E.; Chen, H.F.; Hu, Z.J.; Shi, X.S. Independent and Combined Effects of Environmental Factors and CYP2C19 Polymorphisms on the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Fujian Province of China. BMC Med. Genet. 2015, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, G.D.; Sun, X.D.; Abnet, C.C.; Fan, J.H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Dong, Z.W.; Mark, S.D.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R. Prospective Study of Risk Factors for Esophageal and Gastric Cancers in the Linxian General Population Trial Cohort in China. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, I.T.S.; Christiani, D.C. Consumption of Salted Meat and Its Interactions with Alcohol Drinking and Tobacco Smoking on Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, J.P.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, R.B.; Jiang, M.; Song, Q.K. Increased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Associated with Frequent and Long-Term Consumption of Salted Meat and Salted Fat. J Int Med Res 2019, 47, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, H.; Plymoth, A.; Jin, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Ye, W. Very Hot Tea Drinking Increases Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk in a High-Risk Area of China: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 10, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Xu, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, X. Tea Drinking and the Risk of Esophageal Cancer: Focus on Tea Type and Drinking Temperature. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 29, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, N.; Han, X.; Giffen, C.; Ding, T.; Goldstein, A.M.; Taylor, P.R. Jasmine Tea Consumption and Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer in China. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 20, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, N.; Han, X.Y.; Ding, T.; Giffen, C.; Goldstein, A.M.; Taylor, P.R. Risk Factors for Esophageal and Gastric Cancers in Shanxi Province, China: A Case-Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011, 35, e91–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Lao, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, Q.; Su, X.; Tak-Sun Yu, I. Dietary Patterns and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Case-Control Study in a Rural Population. Clin Nutr 2017, 36, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X.; Song, J.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z. Dietary Fatty Acid Patterns and Risk of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.X.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Xie, P.; Wang, S.; Yan, L.; Xing, X.; Lu, J.; Tse, L.A.; Wang, H.H.X.; et al. Dietary Intake of Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Is Related to the Reduced Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.L.; Yang, L.; Su, M.; Wang, S.K.; Yin, H.; Wang, J.S.; Sun, G.J. Vitamin D3 and Beta-Carotene Deficiency Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma - Results of a Case-Control Study in China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Tse, L.A.; Xing, X.; Lin, S.; Zhao, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, C.X.; Liu, X. Dietary Flavonoid Intake and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Qu, C.; He, Y.; Song, Q. Peanut Consumption Associated with a Reduced Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study in a High-Risk Area in China. Thorac Cancer 2018, 9, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, J.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Z.; Tang, X.; Rao, W.; Hu, Z. Dietary Inflammatory Nutrients and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.S.; Tang, L.; Sun, G.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.S. Mycotoxin Exposure Is Associated with Increased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Huaian Area, China. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, B.; Guan, S.; An, D.; Cheng, Y. Dinner-to-Bed Time and Post-Dinner Walk: New Potential Independent Factors in Esophageal Cancer Development. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, C.L.; Song, Q.K.; Deng, Y.M.; Qu, C.X.; Li, J. Association between Dietary Behavior and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Yanting. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2014, 15, 8657–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.P.; Nie, G.J.; Chen, M.J.; Yaz, T.Y.; Guli, A.; Wuxur, A.; Huang, Q.Q.; Lin, Z.G.; Wu, J. Hot Food and Beverage Consumption and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study in a Northwest Area in China. Med. Baltim. 2017, 96, e9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Yang, A.; Xing, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Lu, H.; Han, J. Association of Alcohol Consumption before a Meal with the Risk of Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 12, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Poor Oral Health Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma - a Population-Based Case-Control Study in China. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Winckler, B.; Lu, M.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Oral Microbiota and Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Area of China. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0143603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Lu, M.; Ye, W.; Jin, L.; Suo, C.; Chen, X. Association of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma With the Interaction Between Poor Oral Health and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Regulating Cell Cycles and Angiogenesis: A Case-Control Study in High-Incidence Chinese. Cancer Control 2022, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Xie, S.; Li, W.; Ran, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.; Zuo, X.; Tian, L. Association of Wheat Chaff Derived Silica Fiber and Esophageal Cancer in North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zuo, X.; Tian, L. A Possible Role of Biogenic Silica in Esophageal Cancer in North China? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 8340–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, J.; Gu, Y.; Pan, E.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, R.; et al. Urinary Exposure of N-Nitrosamines and Associated Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a High Incidence Area in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Yang, X.; Suo, C.; Yuan, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lu, M.; Chen, X.; Ye, W. Socioeconomic Status Is Inversely Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk: Results from a Population-Based Case-Control Study in China. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6911–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, B.J.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G.L. Tumor-Suppressor Functions of the TP53 Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 Mutations in Human Cancers: Origins, Consequences, and Clinical Use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.; Nakagawara, A. Role of P53 in Cell Death and Human Cancers. Cancers 2011, 3, 994–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cao, J.; Topatana, W.; Juengpanich, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Shen, J.; Cai, L.; Cai, X.; Chen, M. Targeting Mutant P53 for Cancer Therapy: Direct and Indirect Strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol.J Hematol Oncol 2021, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H.E.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Hasan, A.; Caceci, T.; Pozzoli, G.; Morrione, A.; Giordano, A.; Cenciarelli, C. P53 Signaling in Cancer Progression and Therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ke, Y. Precision Screening for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Ershow, A.G.; Chen, Z.J.; Wacholder, S.; Li, G.Y.; Guo, W.; Li, B.; Blot, W.J. A Case-Control Study of Cancer of the Esophagus and Gastric Cardia in Linxian. Int. J. Cancer 1989, 43, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricker, A.R.; Preussmann, R. Carcinogenic N-Nitrosamines in the Diet: Occurrence, Formation, Mechanisms and Carcinogenic Potential. Mutat. Res. 1991, 259, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer List of Classifications by Cancer Sites with Sufficient or Limited Evidence in Humans, IARC Monographs Volumes 1–134.
- Claeys, L.; Romano, C.; De Ruyck, K.; Wilson, H.; Fervers, B.; Korenjak, M.; Zavadil, J.; Gunter, M.J.; De Saeger, S.; De Boevre, M.; et al. Mycotoxin Exposure and Human Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burd, E.M. Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Cancer. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervical Cancer Available online:. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- Farhadi, M.; Tahmasebi, Z.; Merat, S.; Kamangar, F.; Nasrollahzadeh, D.; Malekzadeh, R. Human Papillomavirus in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Esophagus in a High-Risk Population. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnet, C.C.; Qiao, Y.L.; Mark, S.D.; Dong, Z.W.; Taylor, P.R.; Dawsey, S.M. Prospective Study of Tooth Loss and Incident Esophageal and Gastric Cancers in China. Cancer Causes Control 2001, 12, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search terms |
|---|---|
| Pubmed | ("risk factor" OR "risk factors") AND ("esophageal squamous cell carcinoma" OR "oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma" OR "esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma" OR "oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma") AND ("China" or "Chinese") Filters: Human, English |
| Web of Science | ("risk factor" OR "risk factors") AND ("esophageal squamous cell carcinoma" OR "oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma" OR "esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma" OR "oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma") AND ("China" or "Chinese") |
| Cochrane trials | All text: (risk factor OR risk factors) AND (China OR Chinese) AND (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma OR esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma) Filters: English, Human |
| Embase | All text: (risk factor OR risk factors) AND (China OR Chinese) AND (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma OR esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma) Filters: English, Human, has an abstract, and exported only articles. Selected exclusions: conference abstracts, reviews, articles in press, preprints |
| Study Group | Count (n = 207) |
|---|---|
| Genetic | 129 (62.3%) |
| Diet/dietary habits | 22 (10.6%) |
| HPV | 19 (9.2%) |
| Other | 11 (5.3%) |
| Gene-environ. interaction | 10* (4.8%) |
| Multiple risk factors | 6 (2.9%) |
| Oral Health | 5 (2.4%) |
| Family history | 3 (1.4%) |
| H. pylori | 2** (1.0%) |
| Study population ethnicity | Count (n = 207) |
| Not reported | 138 (66.7%) |
| Han | 66 (31.9%) |
| Kazakh | 2 (1%) |
| Uyghur, Kazakh, or Han | 1 (0.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





