1. Introduction
In recent years, the demand for bone replacement materials used in the treatment of bone diseases has increased due to ongoing aging of the population. To date, β-tricalcium phosphate (β-Ca
3(PO
4)
2: β-TCP) has been employed clinically for this purpose because this material shows excellent biocompatibility along with a high degree of biosorption and can replace autologous bone when implanted in a bone defect [
1,
2,
3]. Even so, β-TCP has inferior osteogenic potential and lacks mechanical strength compared with autogenous bone. As an example, in the case that raw β-TCP powder is prepared via a solid phase reaction and subsequently sintered for 24 h at 1100 °C, which is below the alpha-beta transition temperature, grain growth can occur without an increase in density. The result is a body exhibiting approximately 80% sintering with a bending strength in the range of 40-60 MPa [
4]. It has been reported that sintered bodies having greater density and with bending strengths in the range of 150-200 MPa can be obtained by adding a trace oxide to prevent the crystal transition when sintering at high temperatures of 1150 to 1250 °C [
5]. However, the incorporation of these transition inhibitors may form a substitution-type solid solution with the oxide of β-TCP, thus suppressing the original solubility of β-TCP and resulting in reduced biosorption. It has also been demonstrated that densification can be promoted by hot pressing [
6,
7], hot isostatic pressing [
8,
9] and spark plasma sintering [
10], although the necessary equipment is expensive to purchase and to operate. The present work prepared composite sintered bodies in which nanoparticles were dispersed to generate a secondary phase [
11]. Specifically, colloidal silica (SiO
2) was added to β-TCP powder in the form of nanoparticles with the aim of improving the sintering characteristics and mechanical strength of the material.
Silicon is known to be essential for the growth and development of bone and cartilage [
12] and is found at concentrations on the order of 100 ppm in bone and ligaments and 200-600 ppm in cartilage and other connective tissues [
13]. The localized concentration of this element at active calcareous sites in the bones of young mice has also been noted, where it is involved in the early stages of biomineralization [
14].
Another approach to producing high-density, high-strength sintered bodies is to utilize very finely powdered raw materials. Therefore, the present study also assessed the use of the polymerized complex method. In this process, metal ions are complexed after which carboxyl and hydroxyl groups present in the complex are dehydrated and condensed by heating to prepare a polymeric gel in which metal ions are coordinated [
15]. This technique allows metal ions to be incorporated at an atomic level of dispersion and also permits the homogeneous dispersion of trace amounts of various additives. In addition, powders can be prepared rapidly and at low temperatures by sintering these gel precursors and hence the synthesis of raw material particles is facile [
16,
17].
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of β-TCP
Calcium nitrate tetrahydrate (Ca(NO3)2·4H2O, 99.0%, Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemicals Corporation, Osaka, Japan) and 2-phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTC, 50% in water, K-I Kasei, Tokyo, Japan) were used as the Ca and P sources, respectively. A calcium nitrate solution was initially prepared by dissolving 21.98 g of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O in 50 ml of pure water with stirring. This solution was subsequently added to 33.02 g of the PBTC solution to prepare a mixture having a Ca/P molar ratio of 1.50. This mixed solution was subsequently heated with magnetic stirring at 150 °C for 3 h using a hot plate. The gel-like material obtained from the resulting dehydration-condensation polymerization was then transferred to a crucible and dried at 180 °C and 300 °C for 24 h and 10 h, respectively, to prepare the β-TCP precursor. This precursor was then calcined by heating to 900 °C at a rate of 5 °C·min-1 and held at that temperature for 6 h under atmospheric air.
The samples produced in this manner were assessed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a MiniFlex600 diffractometer (Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan) and by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy (FT-IR-4200, Jasco, Tokyo, Japan). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM; VE-7800, KEYENCE, Tokyo, Japan) was also used to observe the shapes and diameters of the particles comprising these materials while the particle size distributions were ascertained using a laser diffraction particle size analyzer (MT3300EXII, MicrotracBEL Corp., Osaka, Japan).
2.2. Preparation and evaluation of sintered bodies
Fumed colloidal silica (SiO2; particle size: 12 nm, Strem Chemicals Inc., Newburyport, USA) was added to the raw β-TCP powder at 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 wt% by external blending followed by mixing in ethanol for 12 h using alumina spheres. The external blending refers to the mixing ratio (wt%) in which the weight of the raw material is 100. After removing the ethanol with a rotary evaporator, the milled powder was mixed with a 2 wt% polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemicals Corporation, Osaka, Japan), added at 8 wt%, and with deionized water, also added at 8 wt%, in a plastic bag. The resulting mixture was subsequently passed through a Teflon sieve having 200 μm pores. Kerosene (Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemicals Corporation, Osaka, Japan) was then added to the material at 5 wt% followed by thorough mixing in a plastic bag. The resulting mixture was placed in a cylindrical (11 mm dia.) mold forming machine (CDM-5M, Riken Kiki Corp., Tokyo, Japan) and subjected to a uniaxial pressure of 120 MPa for 1 min. This process generated a compact having a diameter of 11.0 mm and a thickness of 2.0 mm that was vacuum-sealed in a plastic bag using a vacuum packaging machine (V-280A, Tosei Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The compact was then subjected to cold isostatic pressing (CIP) at 200 MPa for 10 min, employing an LCP-80-200A device (NPA System, Tokyo, Japan). The compacts produced in this manner were sintered at 200 °C for 5 h, 500 °C for 5 h and 1120 °C for 24 h, applying a temperature ramp of 3 °C·min-1 between each temperature and under atmospheric air. The sintered bodies were analyzed by XRD and FTIR spectroscopy. In addition, the lattice constants of these specimens were determined along with sintering ratios and linear shrinkage rates. The lattice constants were obtained using the silicon internal standard method. Porosity and bulk density were ascertained using the Archimedes method and microstructural observations of the sintered bodies were performed by field emission (FE) SEM (JSM-IT-800, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), Electron probe microanalysis (EPMA, EPMA-1720, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) data were acquired and microstructural observations and elemental mapping were performed using scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM, TalosF200X, FEI Company Japan Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Finally, three-point bending tests were carried out to assess mechanical strength with an Autograph AGS-X instrument (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of β-TCP as a starting material
The sample generated by calcination of the precursor gel synthesized using the polymerized complex method with heating at 900 °C was found to comprise a single β-TCP phase based on analyses by XRD and FTIR spectroscopy. The particle morphology and particle size distribution of this material were also examined.
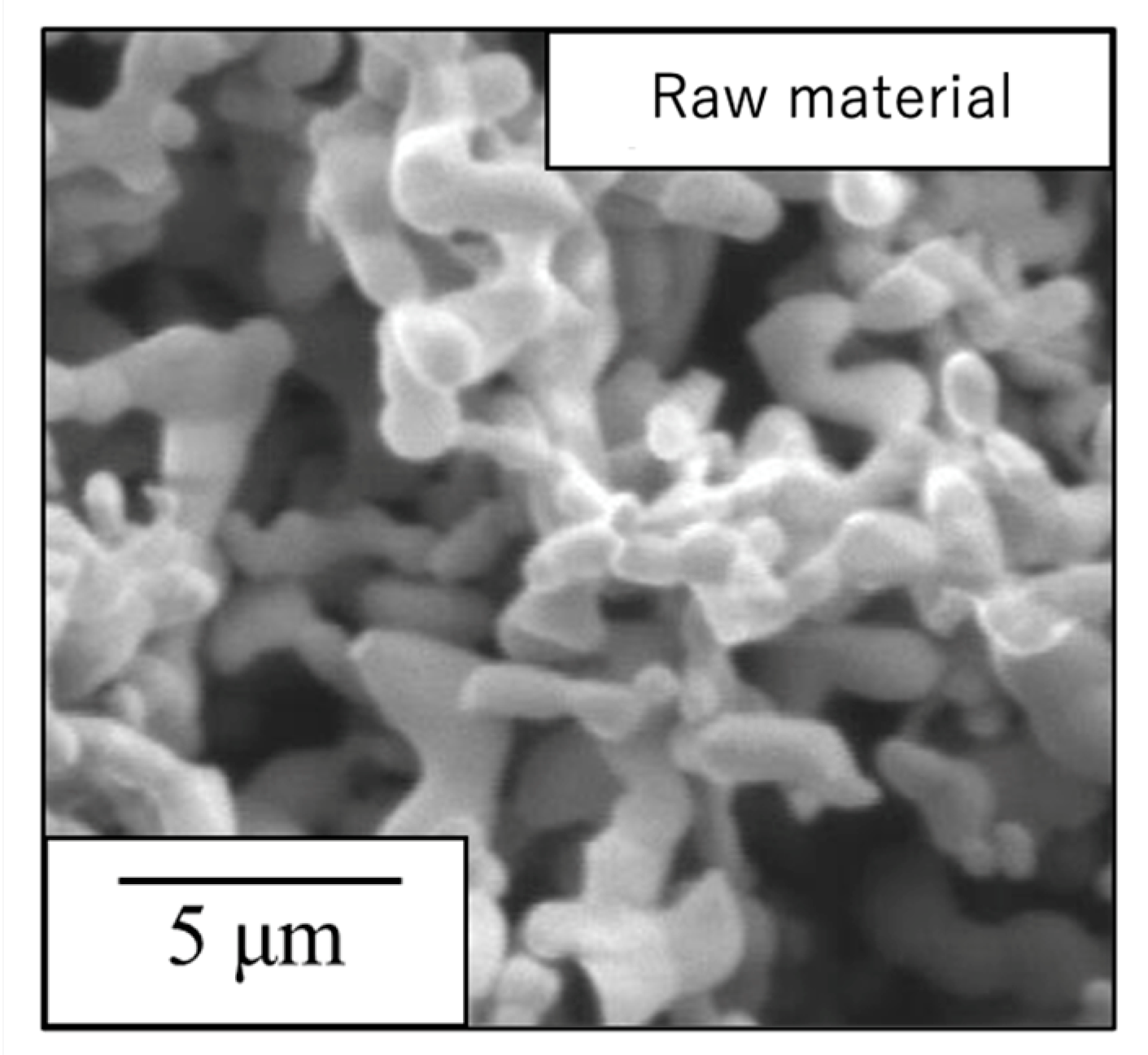
Figure 1 presents an SEM image of this β-TCP specimen after calcination while
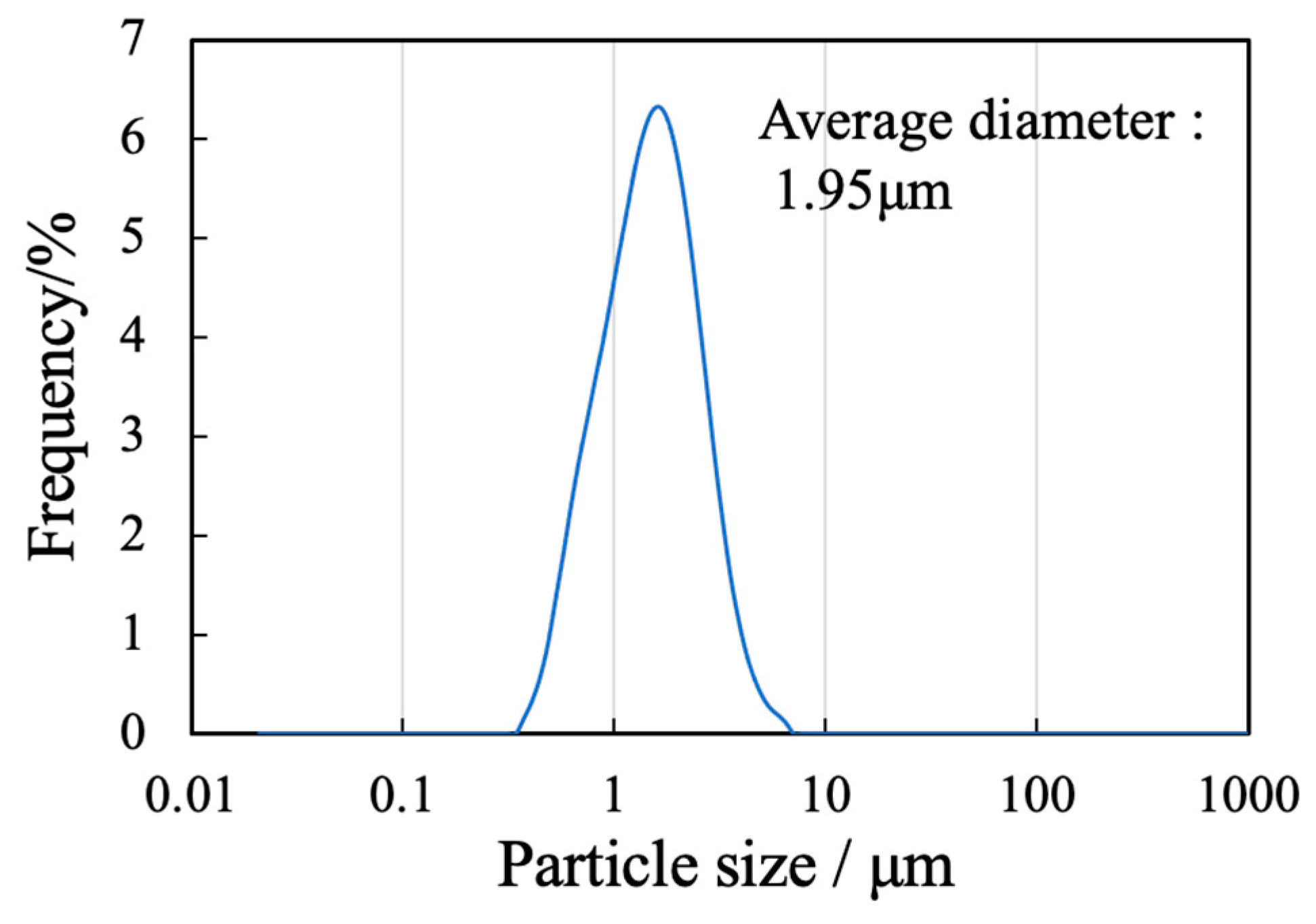
Figure 2 shows the particle size distribution data acquired after ball-milling of the precursor gel. The SEM image indicates narrow particles with sizes in the range of 2-5 µm. The size distribution of the particles obtained by ball milling ranged from 0.3 to 5 μm with a median diameter of 1.95 μm. These results indicate that the starting material for the sintered bodies (that is, the β-TCP powder) consisted of fine particles having a relatively narrow range of sizes and an average size of less than 2 μm.
3.2. Preparation and evaluation of β-TCP composite sintered bodies containing SiO2
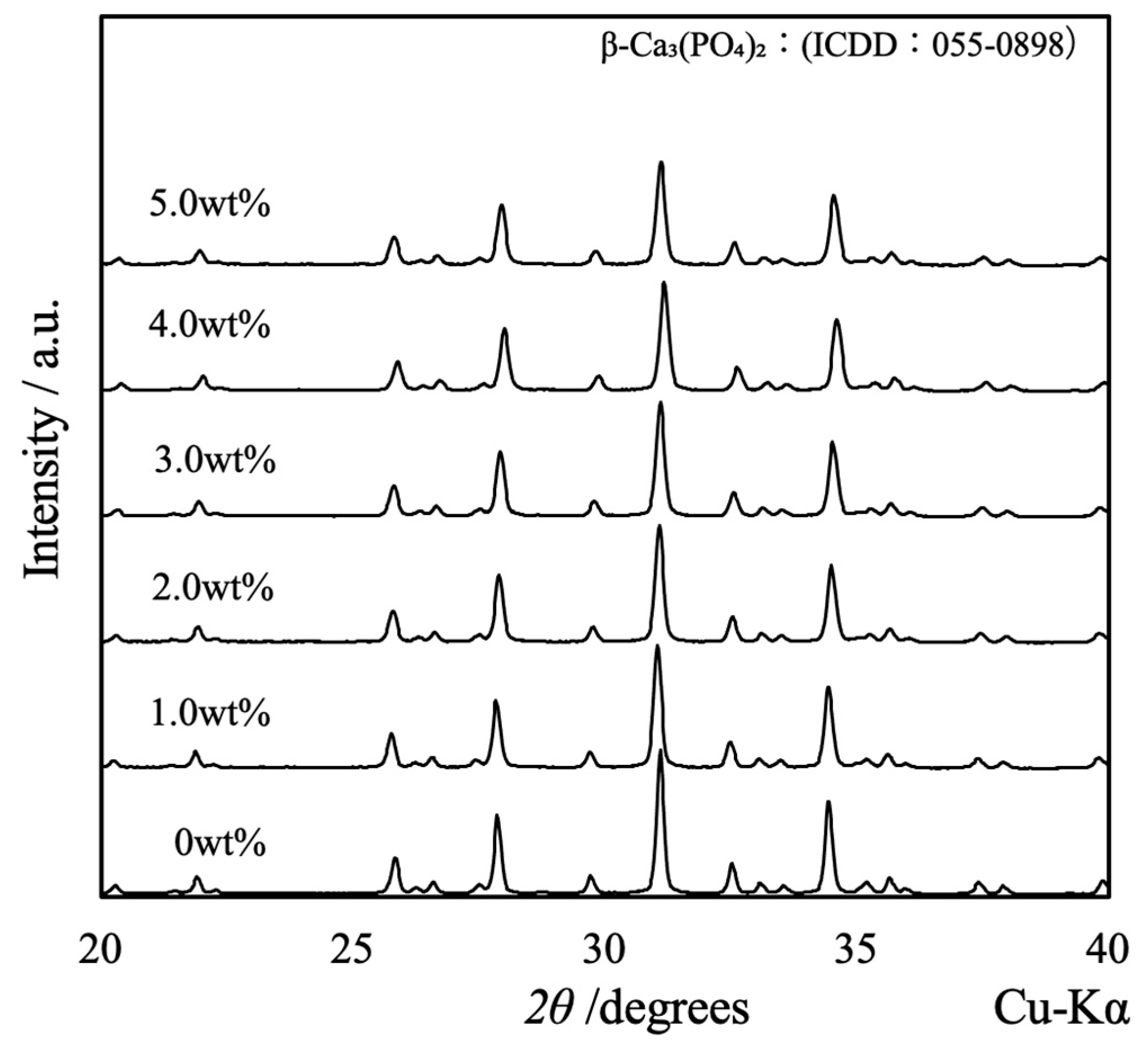
Figure 3 shows the XRD patterns acquired from the β-TCP composite sintered bodies in which varying concentrations of SiO
2 nanoparticles were dispersed. The peaks generated by each specimen were consistent with those of β-TCP (ICDD no. 055-0898), indicating that all samples had the same crystal structure as β-TCP [
18]. Because the patterns of these sintered bodies were not modified, it appears that the SiO
2 did not form a solid solution within the β-TCP crystal structure. Furthermore, no peaks related to SiO
2 or various by-products were obtained, presumably because of the low concentration or amorphous nature of the SiO
2. Interestingly, the XRD pattern generated by a specimen containing 10 wt% SiO
2 contained peaks attributed to cristobalite (ICDD no. 001-043, data not shown). This result suggests that the SiO
2 nanoparticles added at lower concentrations were also changed to cristobalite upon heating.
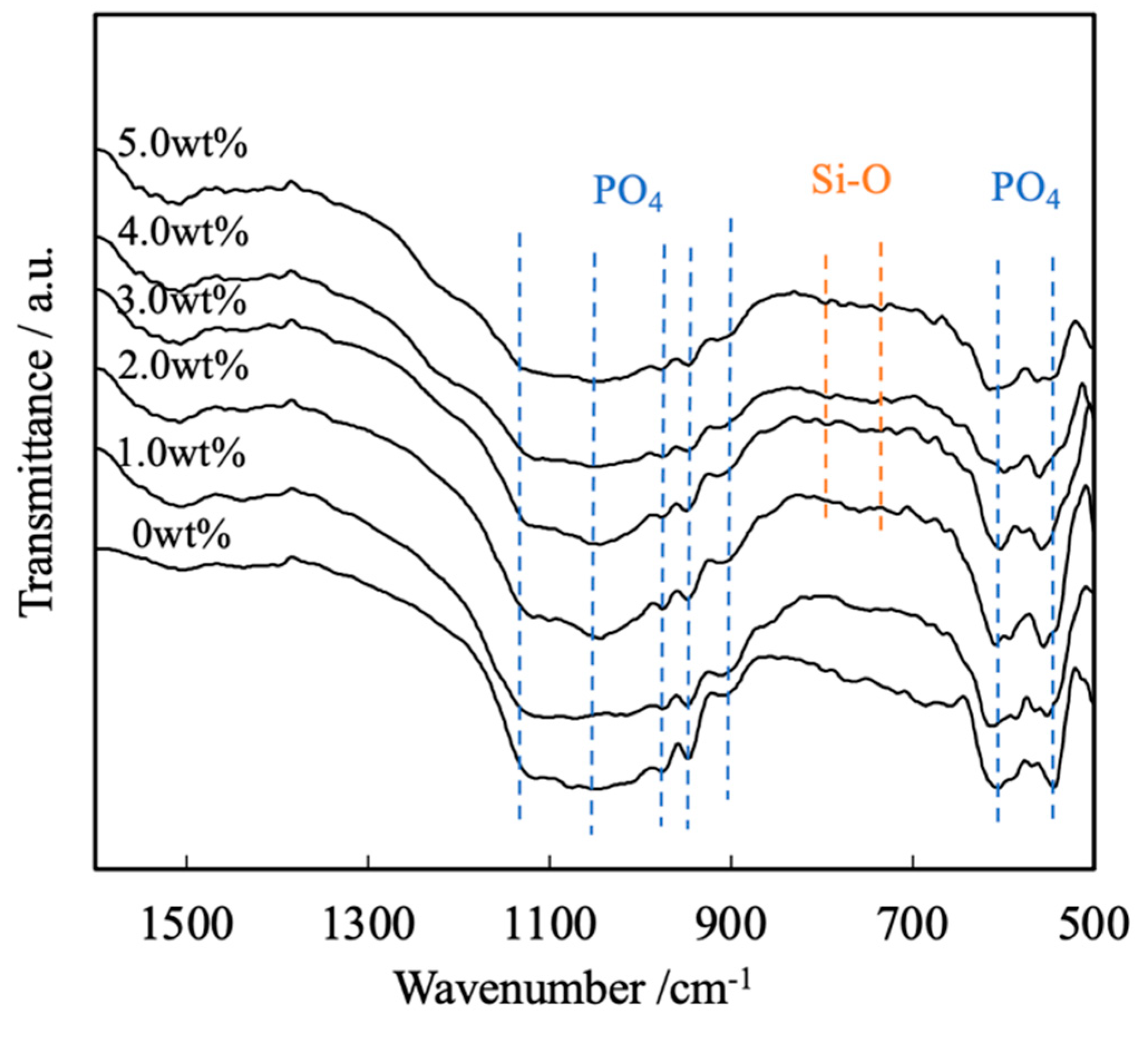
Figure 4 presents the FTIR spectra of these same sintered bodies. Each of these spectra contains peaks ascribed to the bending and stretching vibrations of PO
4 groups (attributed to the presence of calcium phosphate) within the ranges of 550 to 605 cm
-1 and 905 to 1120 cm
-1, respectively. In contrast, there are no peaks related to by-products such as hydroxyapatite or Ca
2P
2O
7. Peaks are also present in the range of 1000 to 1100 cm
-1 because of the inverse symmetry vibrations of Si-O-Si groups in SiO
2. Note that these peaks are not evident because they overlap with the peaks attributed to the stretching vibrations of PO
4 groups. Less intense peaks related to Si-O-Si symmetric vibrations are also apparent at 800 and 855 cm
-1, suggesting the presence of SiO
2[
19,
20].
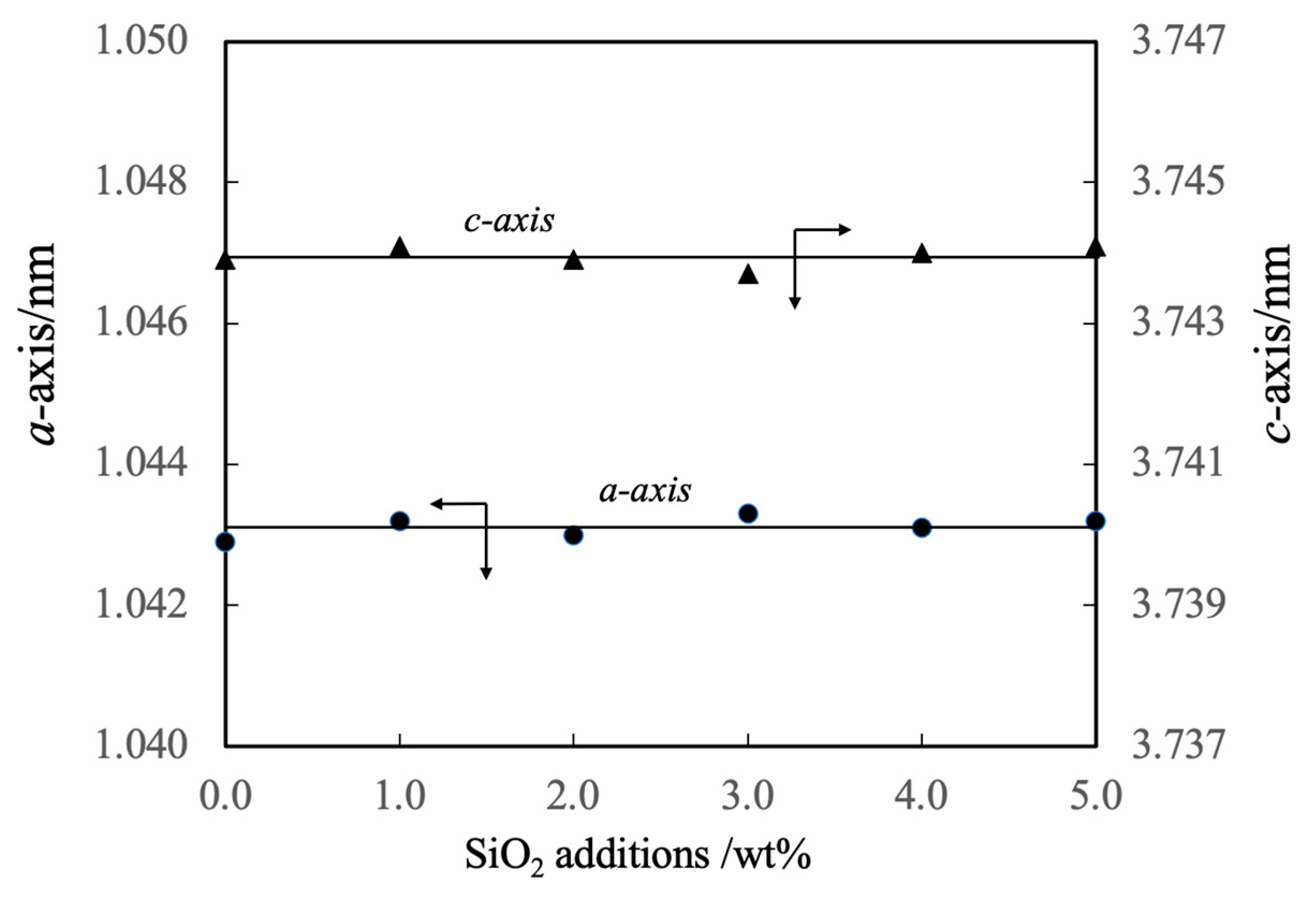
The lattice constants of these specimens are summarized in
Figure 5. These values indicate that the complexed SiO
2 did not form a solid solution with the β-TCP. However, it should be noted that the authors previously prepared β-TCP in which silicon ions were substituted at phosphorus sites [
21]. Although the composition of the β-TCP was not modified upon adding SiO
2 in the present work, prior work demonstrated that the increased negative charge resulting from the replacement of PO
43- with SiO
44- ions was compensated for by the incorporation of Ca
2+ ions. Hence, the Ca/P molar ratio was increased above the stoichiometric value of 1.50. In the present study, it is appears that silicon ions were not substituted into the β-TCP lattice because cations were not available to compensate for the associated change in charge.
3.3. Evaluations of physical properties
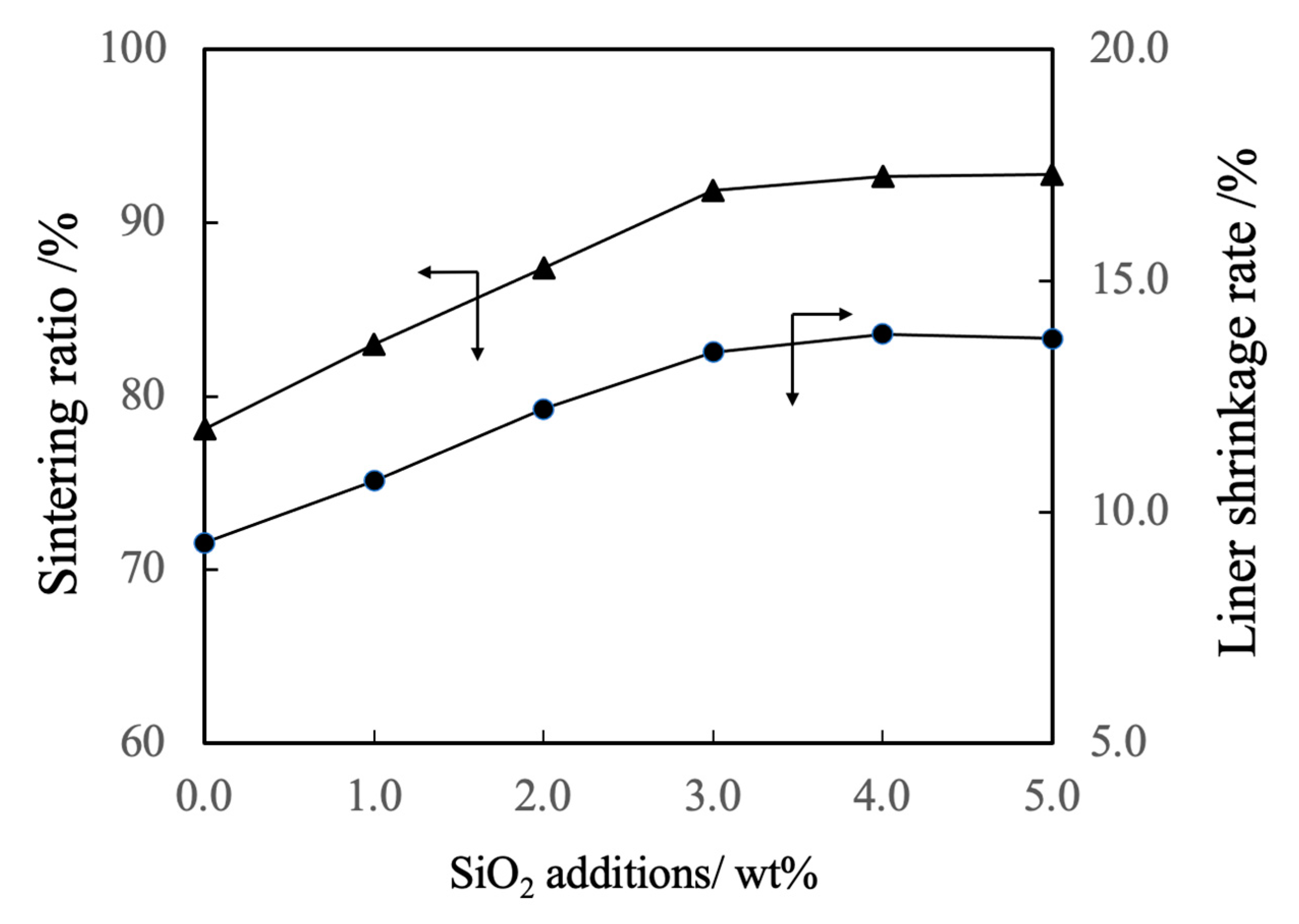
Figure 6 shows the linear shrinkage and sintering ratio (that is, relative density) of the various sintered bodies. The linear shrinkage of the pure β-TCP was 9.3% whereas this value was approximately 13% at a SiO
2 addition level of 3.0 wt% and did not change with the incorporation of higher concentrations of SiO
2. The greater linear shrinkage observed with increases in SiO2 addition can be attributed to densification of the material. The sintered bodies containing 3.0 wt% SiO
2 showed a sintering ratio of 93% whereas the sintering ratio for the β-TCP was 78%. Hence, the sintering ratio also increased along with the SiO
2 content.
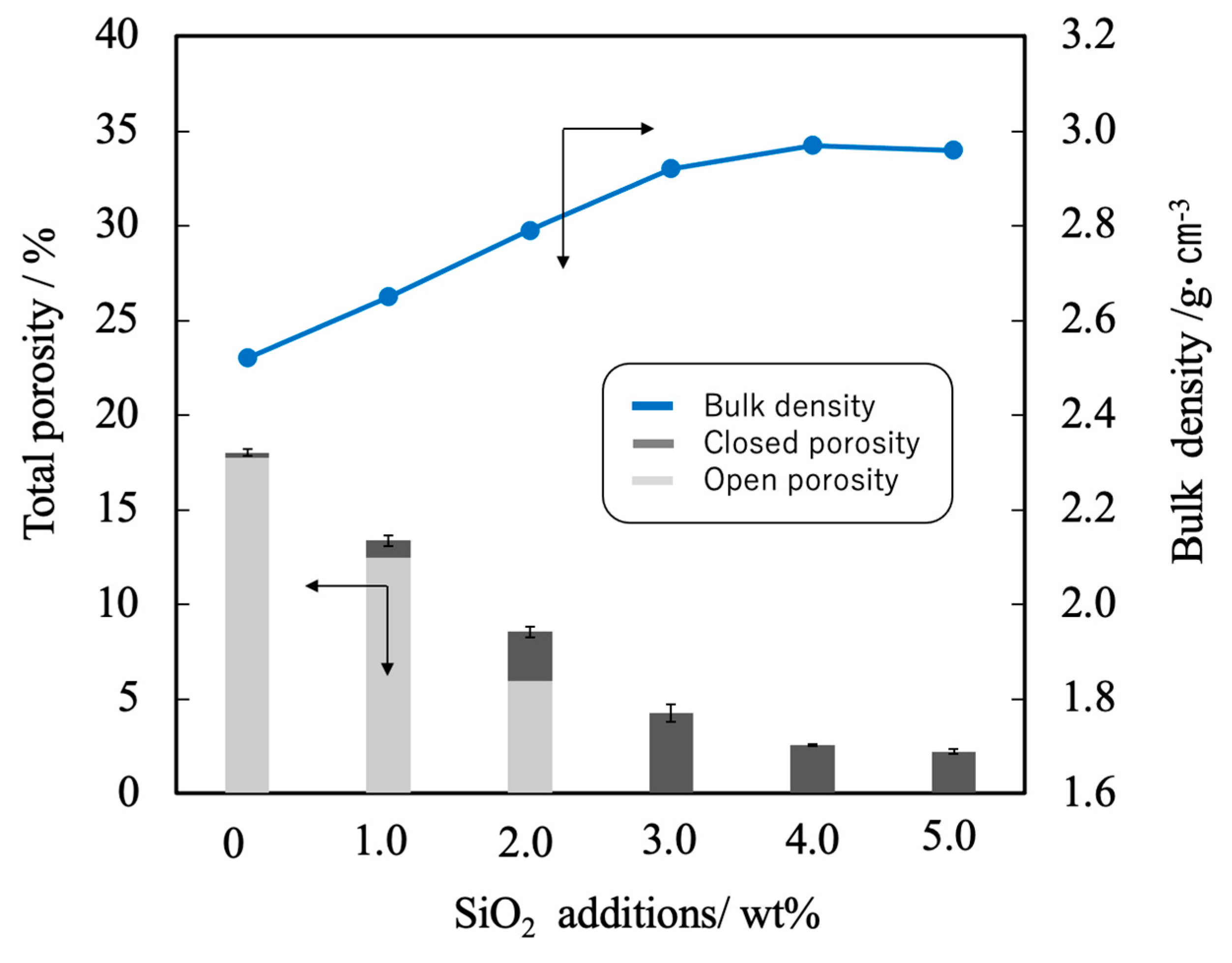
Figure 7 summarizes the porosity and bulk density values for sintered bodies. The bulk density of the β-TCP was 2.54, in agreement with the linear shrinkage and sintering ratio. In contrast, the bulk densities of the sintered bodies containing 3.0 wt% or more SiO
2 were in the range of 2.95 to 2.98 g·cm
-3 (compared with a theoretical density of 3.07 g·cm
-3). These data demonstrate that the bulk density was increased with increases in SiO
2 content in this range. Conversely, the open porosity values of the sintered bodies decreased with increasing SiO
2 addition up to 2 wt% whereas the closed porosity values decreased with SiO
2 addition above 3 wt%. The decrease in open porosity indicates that the sintering characteristics of the material were improved.
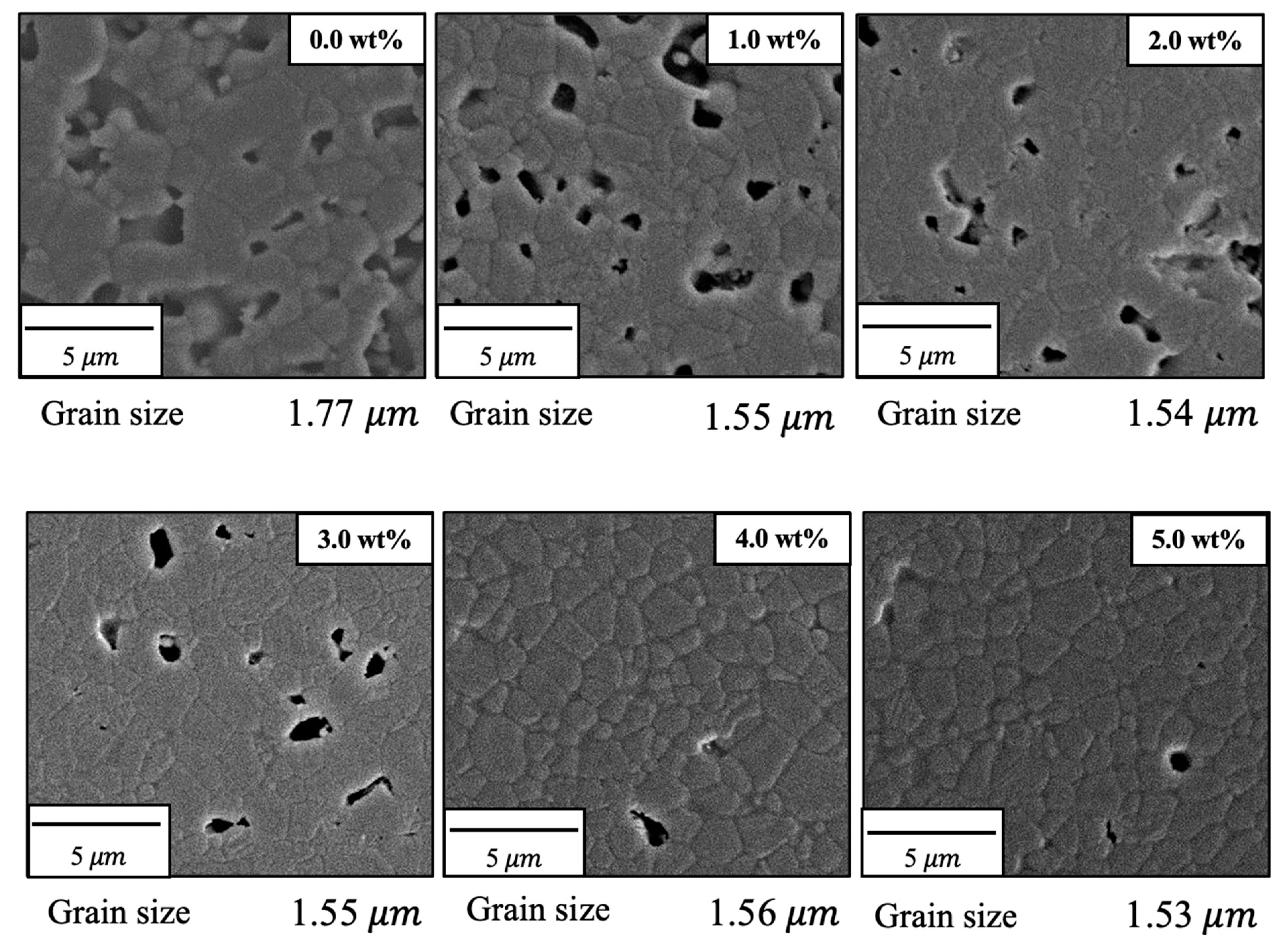
Figure 8 shows FE-SEM images of the various specimens. The particle sizes obtained from these images using the intercept method [
22] are also provided in the figure. On this basis, it is apparent that both porosity and particle size were decreased with increases in the concentration of SiO
2. These images are in agreement with the earlier porosity data because the open pores on the surfaces of the sintered bodies were similar to those measured by the Archimedes method as described above. The grains in the pure sintered material were approximately 1.7 μm in size whereas SiO
2 addition decreased this value to approximately 1.5 μm. These results confirm that bulk density, sintering ratio, and linear shrinkage increase with increasing SiO
2 content, while porosity and grain size decrease with increasing SiO
2 content. Hence, the sintered bodies became denser with SiO
2 addition. This effect is thought to be due to reduced diffusion of the β-TCP as a consequence of the SiO
2, which suppressed grain growth and promoted densification through grain microstructural reconstruction.
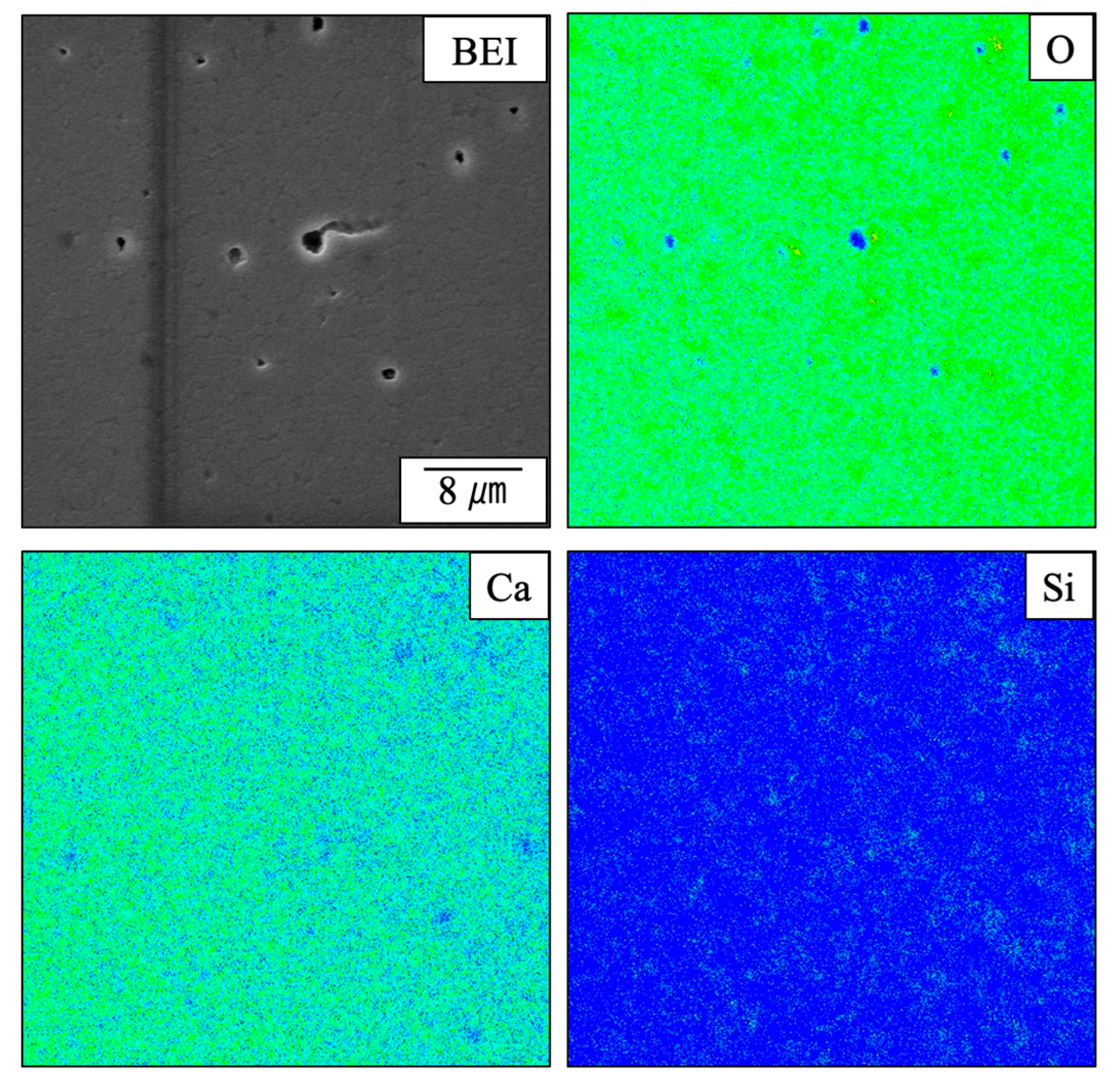
Figure 9 provides elemental mapping images of a sintered specimen containing 4.0 wt% SiO
2 as acquired using EMPA. These images demonstrate that O was primarily absent around the pore openings while Si was more homogeneously dispersed. It can also be seen that Ca was absent at the locations at which Si was present. These results provide more evidence that a solid solution was not formed between the β-TCP and SiO
2 but rather that these materials existed as separate phases. However, it is not possible to determine from these images whether the SiO
2 was located within the grains or at the grain boundaries.
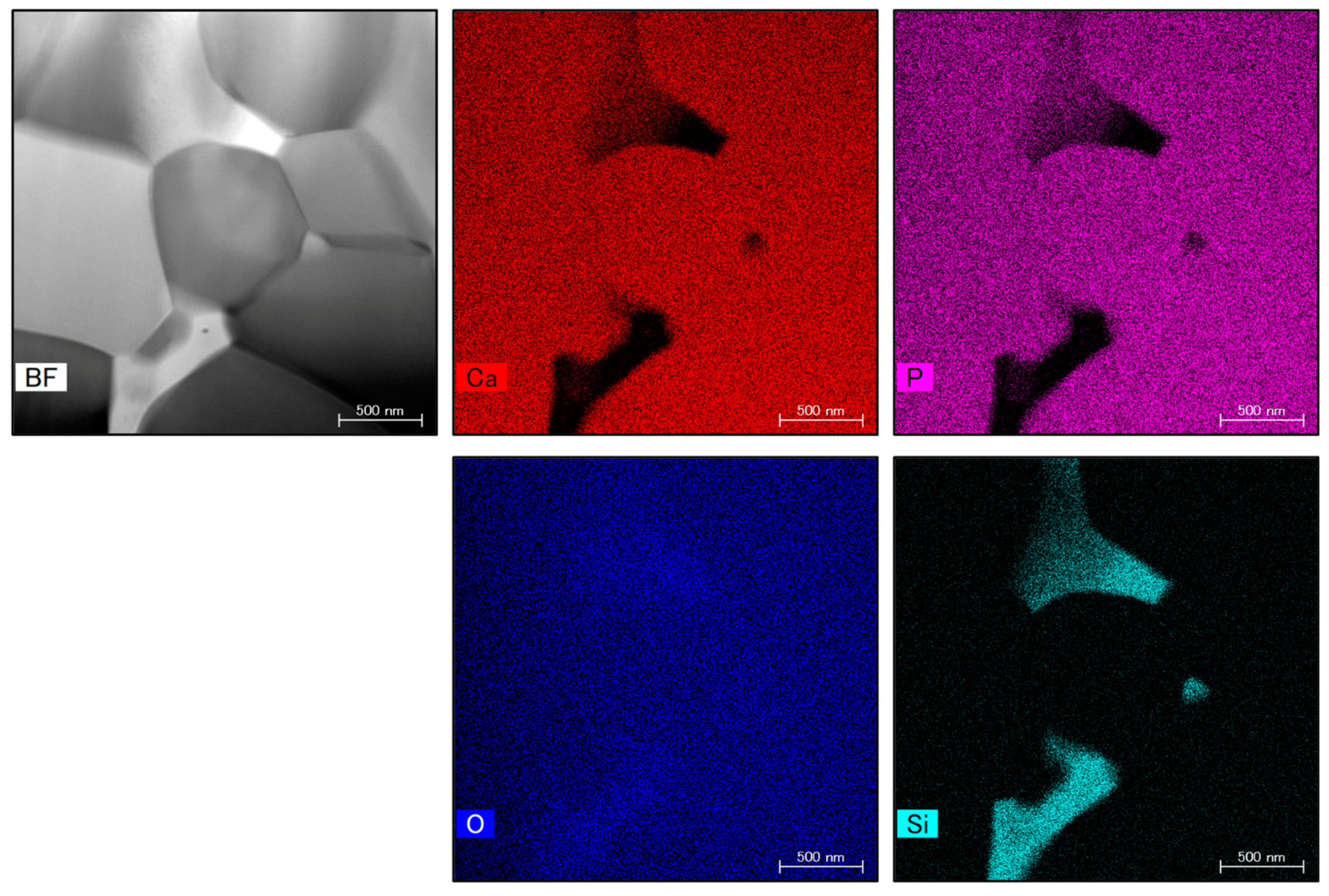
Figure 10 presents STEM images showing the microstructure and elemental mapping of the 4.0 wt% SiO
2 specimen. The SiO
2 nanoparticles were found to have sizes of 100 to 500 nm and to be situated at the intersections between grain boundaries.
3.4. Mechanical strength assessments
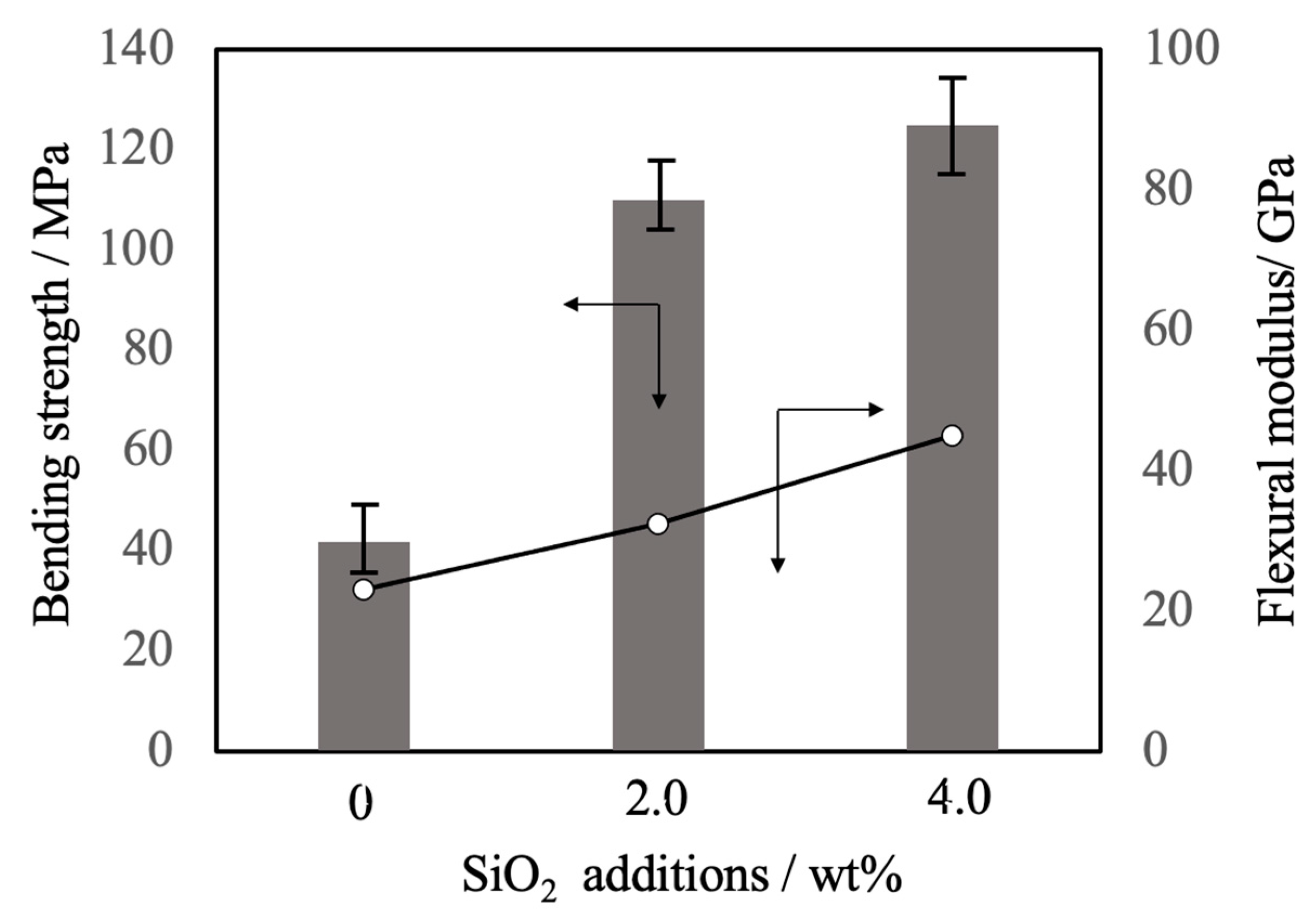
Figure 11 summarizes the three-point bending strength and flexural modulus values obtained for the sintered bodies. The average strength value for the pure β-TCP was 42 MPa while the specimens containing 2.0 and 4.0 wt% SiO
2 had strengths of 110 and 125 MPa, respectively. These increases in strength are attributed to densification and possibly to the suppression of crack propagation by SiO
2 nanoparticles at the intersections between grain boundaries. The addition of these SiO
2 nanoparticles resulted in higher values of mechanical strength that were more than comparable to those of β-TCP sintered bodies produced using the hot press technique [
10]. In particular, the hot-pressed specimens showed a higher sintering ratio than those obtained in this study, suggesting that the improvement of mechanical strength observed in this study was largely due to the dispersion effect of the nanoparticles. SEM observations of the fractured surfaces of the sintered bodies without SiO
2 nanoparticles showed grain boundary fractures that promoted crack propagation. Following the addition of SiO
2 nanoparticles, crack propagation occurred via intragrain or grain boundary fractures.
4. Conclusions
Composite sintered bodies comprising silicon dioxide nanoparticles dispersed in the microstructures of β-TCP were fabricated. Nano-sized colloidal silica was used as the silicon dioxide component in these materials. This silicon dioxide was well-dispersed as secondary phase particulates that suppressed grain growth in the sintered bodies and promoted densification by increasing shrinkage. However, substitution to form a solid solution with β-TCP was not observed even upon heating at 1120 °C. This lack of substitution likely can be attributed to the absence of free calcium ions required for charge compensation. Silicon dioxide was found to be present as 100-500 nm nanoparticles near the intersections of grain boundaries. Sintered bodies with 4.0 wt% SiO2 exhibited bending strengths comparable to that of cortical bone and hence could possibly be used as a bone filling material.
Author Contributions
K.H., M.O. and H.S. initiated the project. K.H. wrote the paper. M.O. produced all of the figures. All authors participated in the discussion and interpretation of the results. All authors edited and proofread the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dorozhkin, S.V., Bioceramics of calcium orthophosphates, Biomaterials, 2010, 31, 1465–1485. [CrossRef]
- Bohner, M.; Santoni, B.L.G.; Döbelin, N. β-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta Biomater., 2020, 113, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giannoudis, P.V.; Dinopoulos, H.; Tsiridis, E., Bone substitutes: an update, Injury, 2005, 36, S20–S27. [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, T.; Umegaki, T.; Yamashita, K. , Effects of additives on sintering and some properties of calcium phosphates with various Ca/P ratios, J. Mater. Sci., 1991, 26, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, H.A.; Kalita, S.J. , Influence of oxide-based sintering additives on densification and mechanical behavior of tricalcium phosphate (TCP), J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med., 2007, 18, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Kondo, N.; Kita, H.; Mitamura, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Toda, Y. , Effect of substitutional monovalent and divalent metal ions on mechanical properties of beta-tricalcium phosphate, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2005, 88, 2315–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, R.; Ohashi, K.; Yoshida, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Shibata, H.; Meguro, T.; Fukuyama, S.; Hashimoto, K., Effect of vanadium ion addition on sintering of β-tricalcium phosphate by hot pressing, Phosphorus Research Bulletin, 2012, 26, 4–5. [CrossRef]
- Boilet, L.; Descamps, M.; Rguiti, E.; Tricoteaux, A.; Lu, J.; Petit, F.; Lardot, V.; Cambier, F.; Leriche, A. , Processing and properties of transparent hydroxyapatite and β-tricalcium phosphate obtained by HIP process, Ceram. Int., 2013, 39, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateescu, M.; Rguitti, E.; Ponche, A.; Descamps, M.; Anselme, K., Biomimetic evaluation of β-tricalcium phosphate prepared by hot isostatic pressing, Biomatter, 2012, 2, 103–11. [CrossRef]
- Kawagoe, D.; Ioku, K.; Fujimori, H.; Goto, S. , Transparent β-tricalcium phosphate ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering, J. Ceram. Soc. Japan, 2004, 112, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niihara, K. , New design concept of structural ceramics - ceramic nanocomposite, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn, 1991, 99, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugdaohsingh, R. , Silicon and bone health, J. Nutr. Health Aging, 2007, 11, 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, K. , A bound form of Si in glycosaminoglycans and polyuronides, Proc. Natl.Acad.Sci., 1973, 70, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, E.M., Silicon: a possible factor in bone calcification, Science, 1970, 167, 279–280. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Yoshida, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Toda, Y. , Preparation of beta-tricalcium phosphate by chelate reaction of calcium ion with phosphonic acid, Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn, 2010, 34, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakihana, M. , Sol-gel preparation of high temperature superconducting oxides, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Tech., 1996, 6, 7–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M., Feature and importance of solution processing for ceramics-nano-particles, thin films, thick films, patterns and bulks, Journal of MMIJ, 2009, 125, 381–388. [CrossRef]
- Yashima, M.; Sakai, A.; Kimiyama, T.; Hoshikawa, A. , Crystal structure analysis of β-tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2 by neutron powder diffraction, J. Solid State Chem., 2003, 175, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitarz, M.; Handke, M.; Mozgawa, W. , Identification of silicooxygen rings in SiO2 based on IR spectra, Spectrochim. Part A, 2000, 56, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Lee, K.; Lin, Y.; Lan, X.; Huang, L. , Effects of surface-active substances on acid–base indicator reactivity in SiO2 gels, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2003, 320, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Imai, T.; Shibata, H., Preparation of silicon-substituted beta-tricalcium phosphate by the polymerized complex method, Phosphorus Research Bulletin, 2023, 39, 14–22. [CrossRef]
- Abrams, H., Grain size measurement by the intercept method, Metallography, 1971, 4, 59–78. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).