Submitted:
20 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
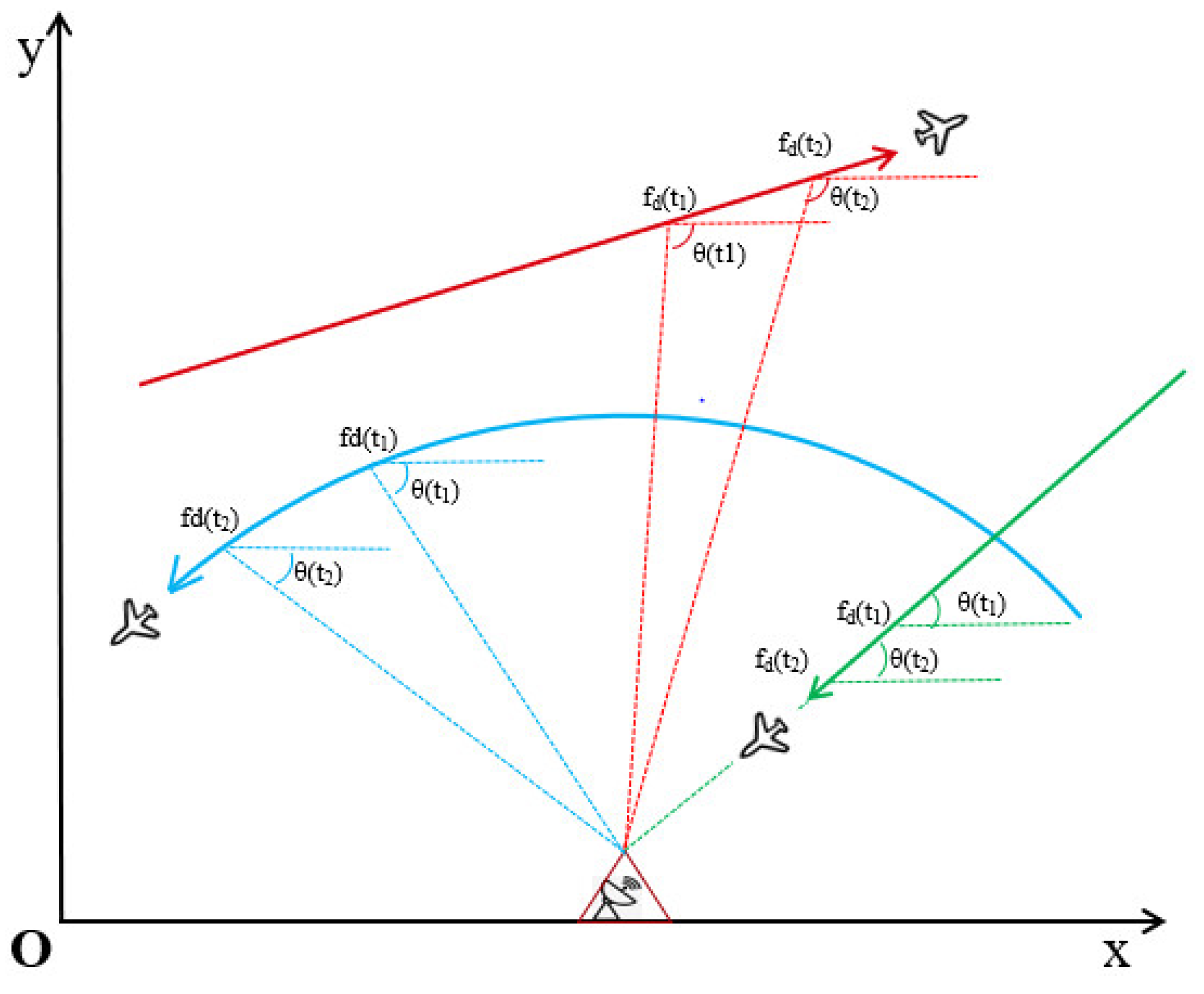
2. Problem Formulation
3. The Model for Maneuvering Target Tracking
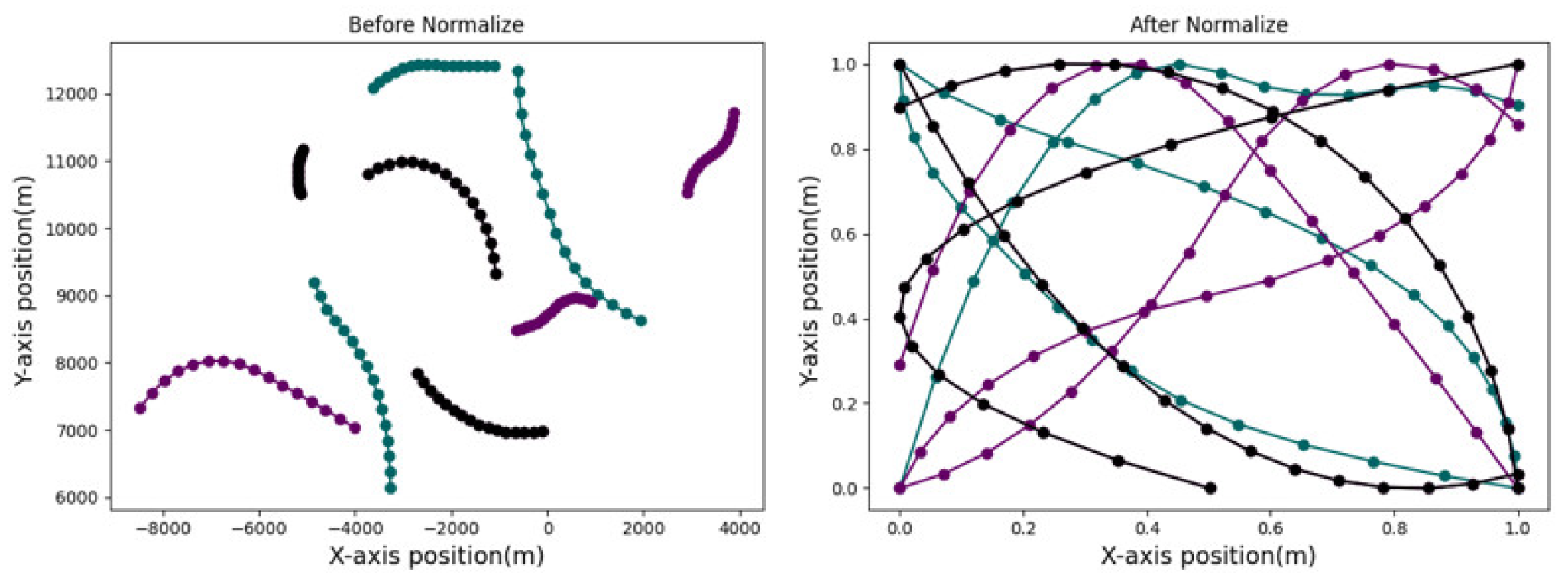
3.1. Normalization Methods
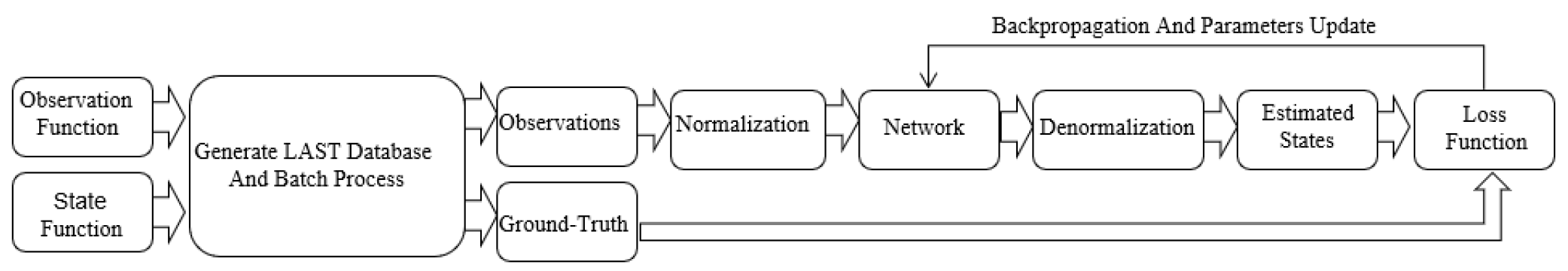
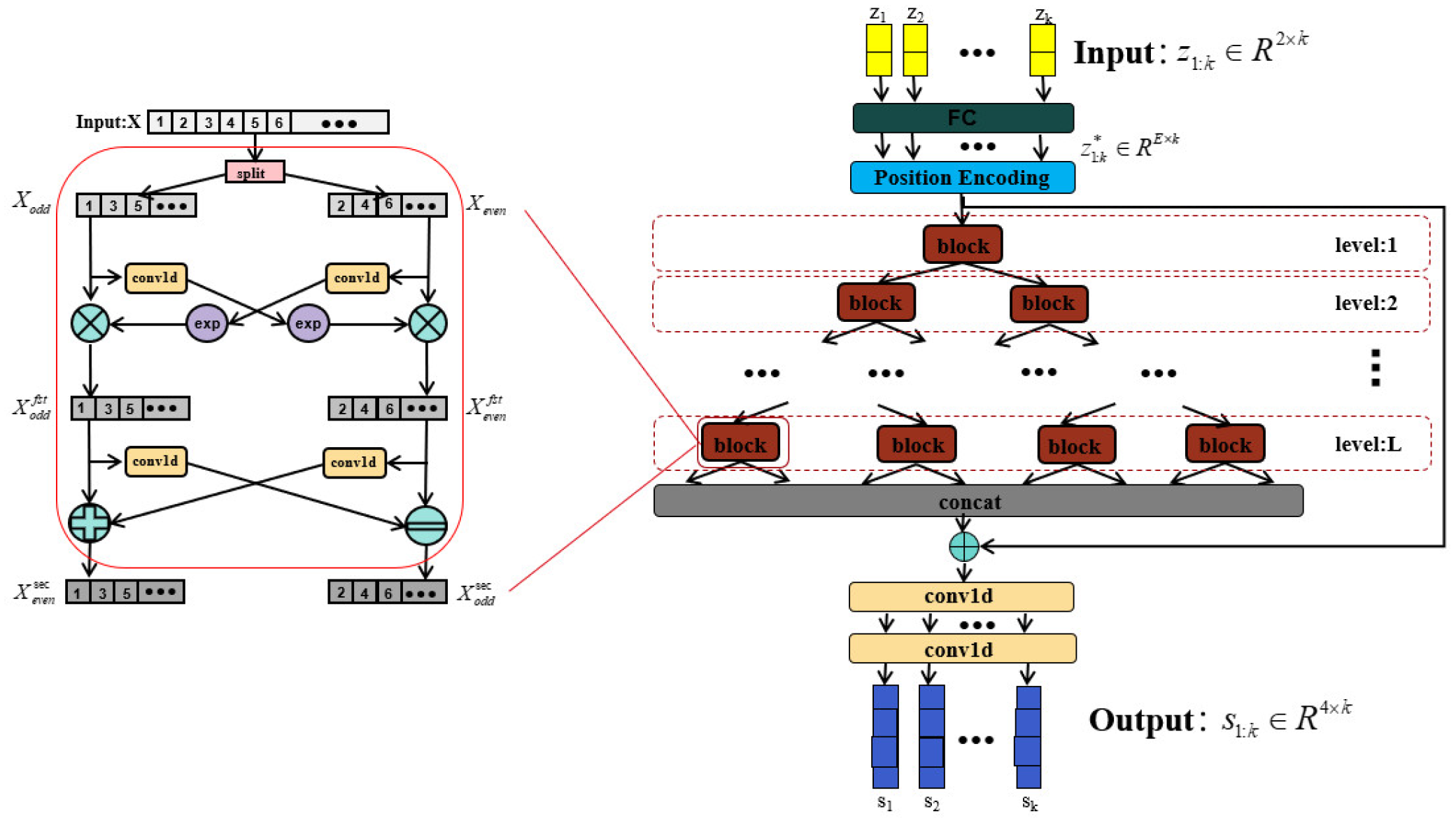
3.2. Proposed Model
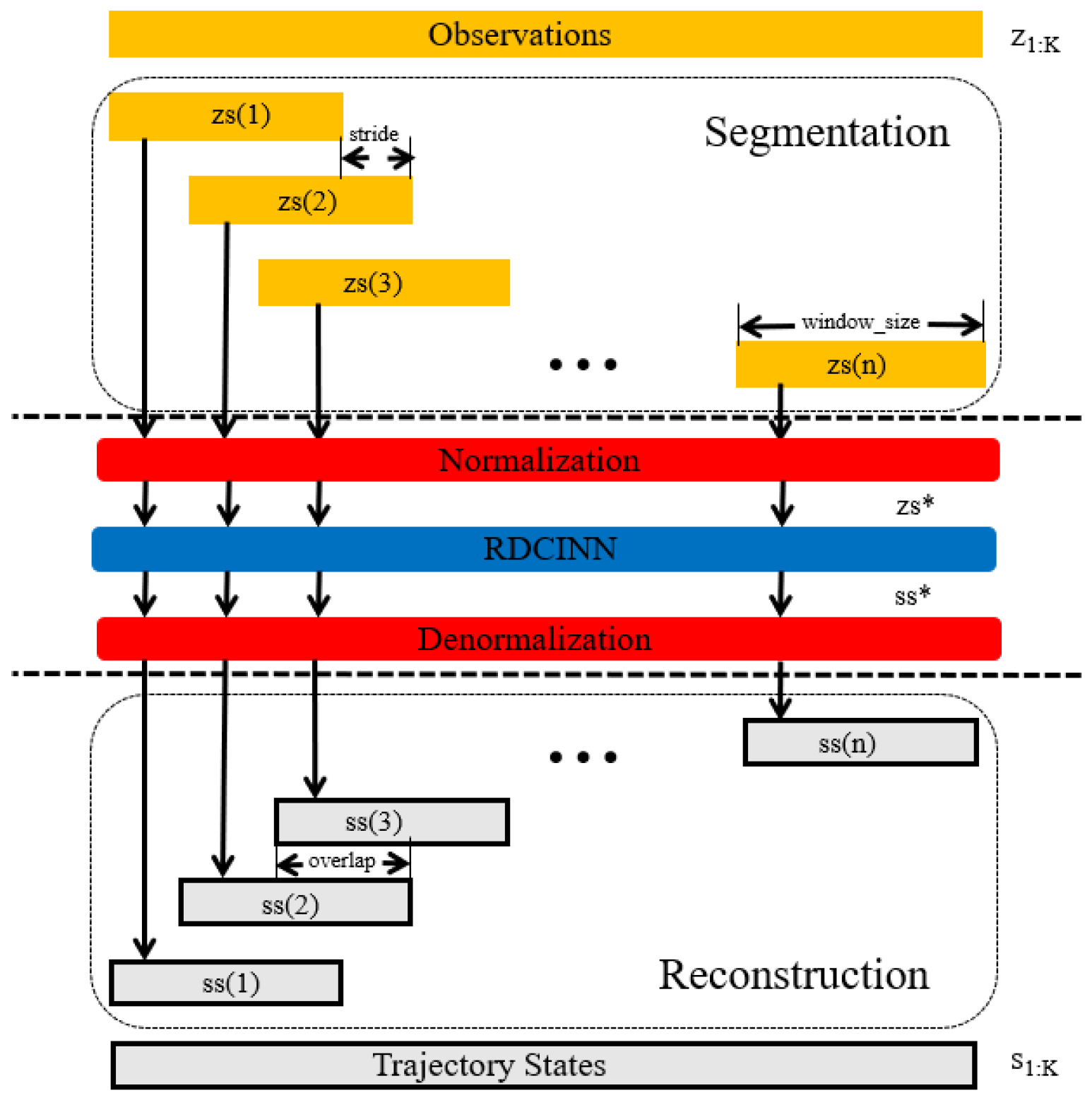
3.3. Test Reorganization Phase
4. Simulation Experiments
4.1. Parameter Setting Details
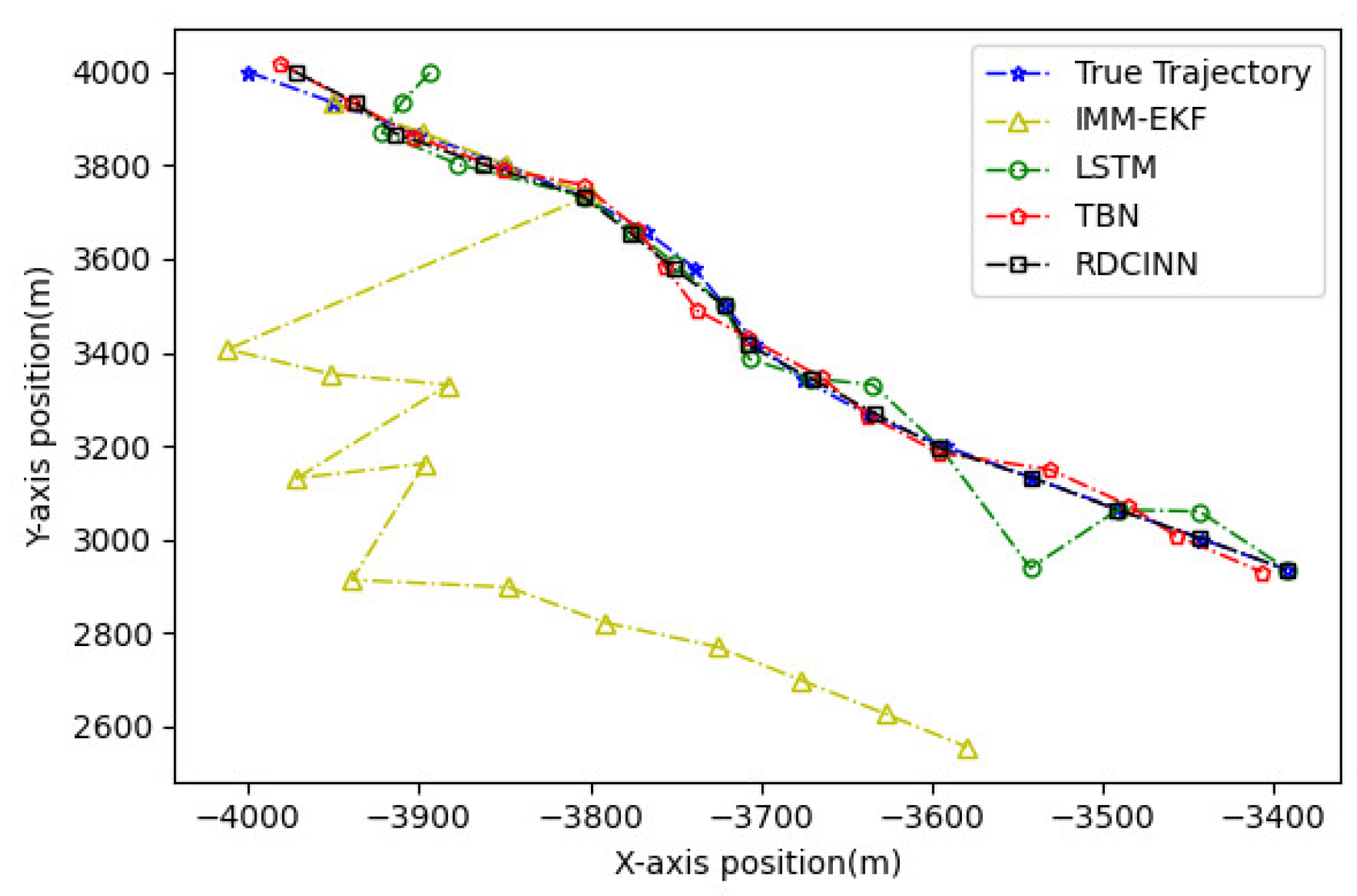
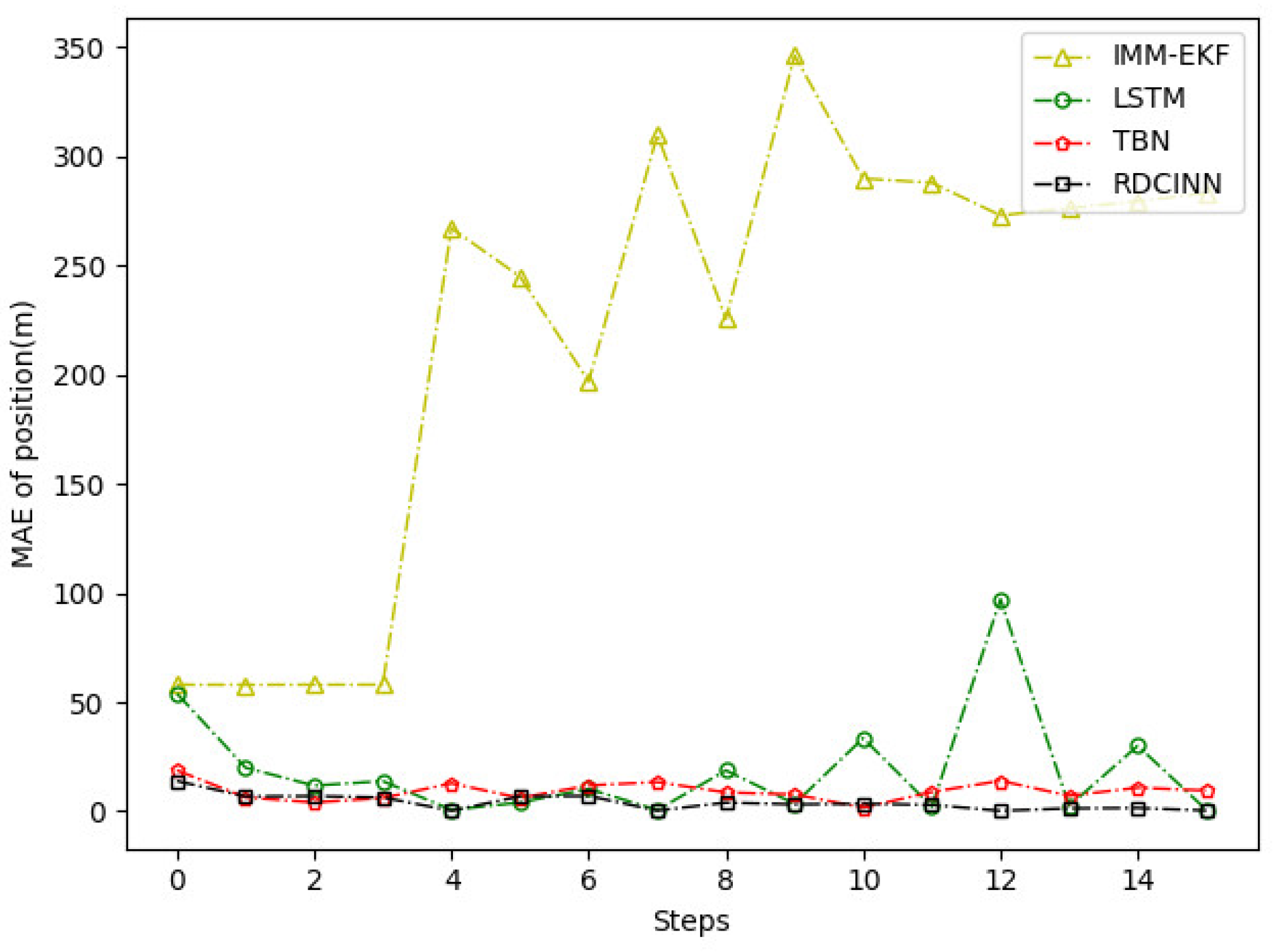
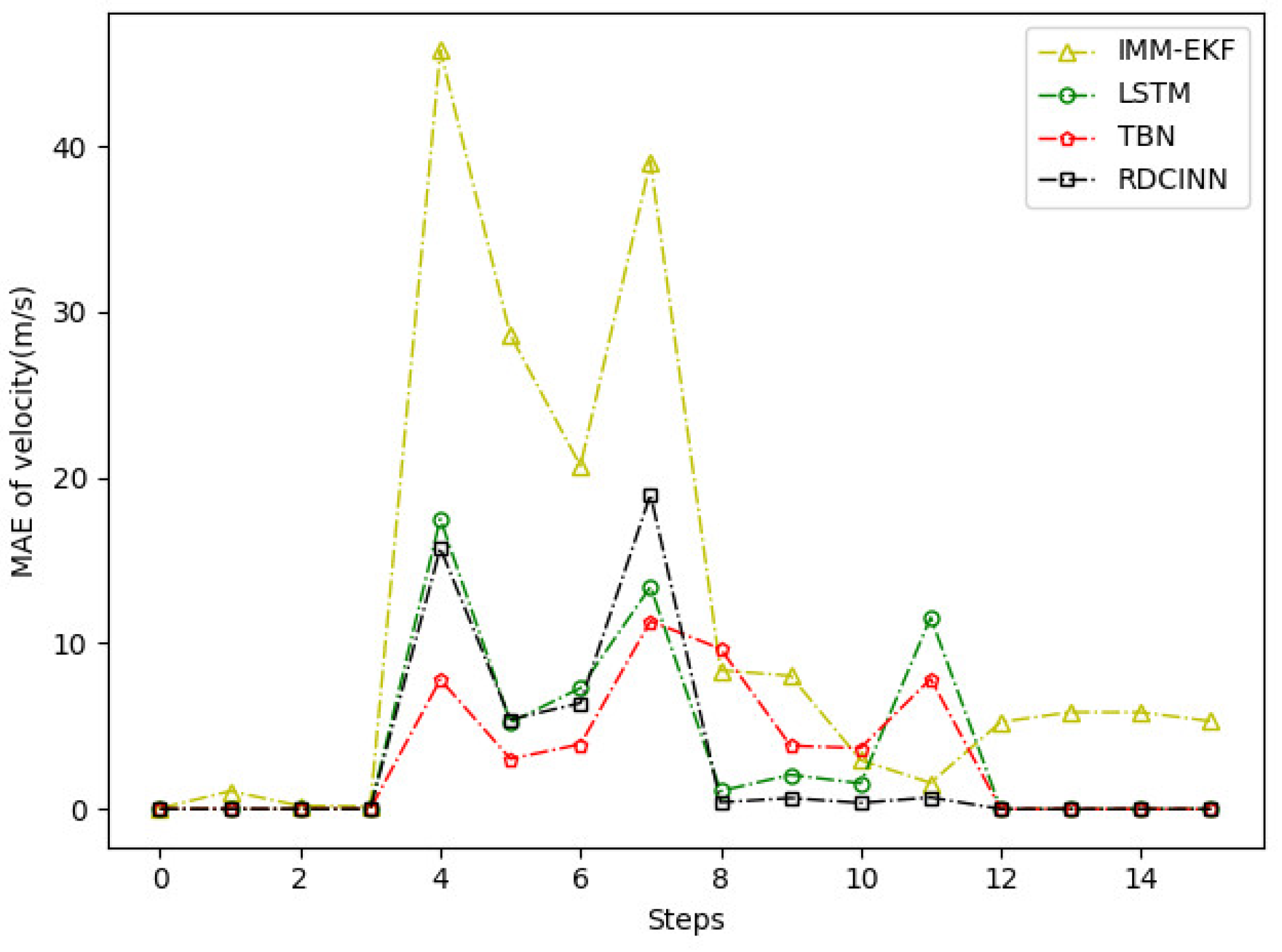
4.2. Experimental Results
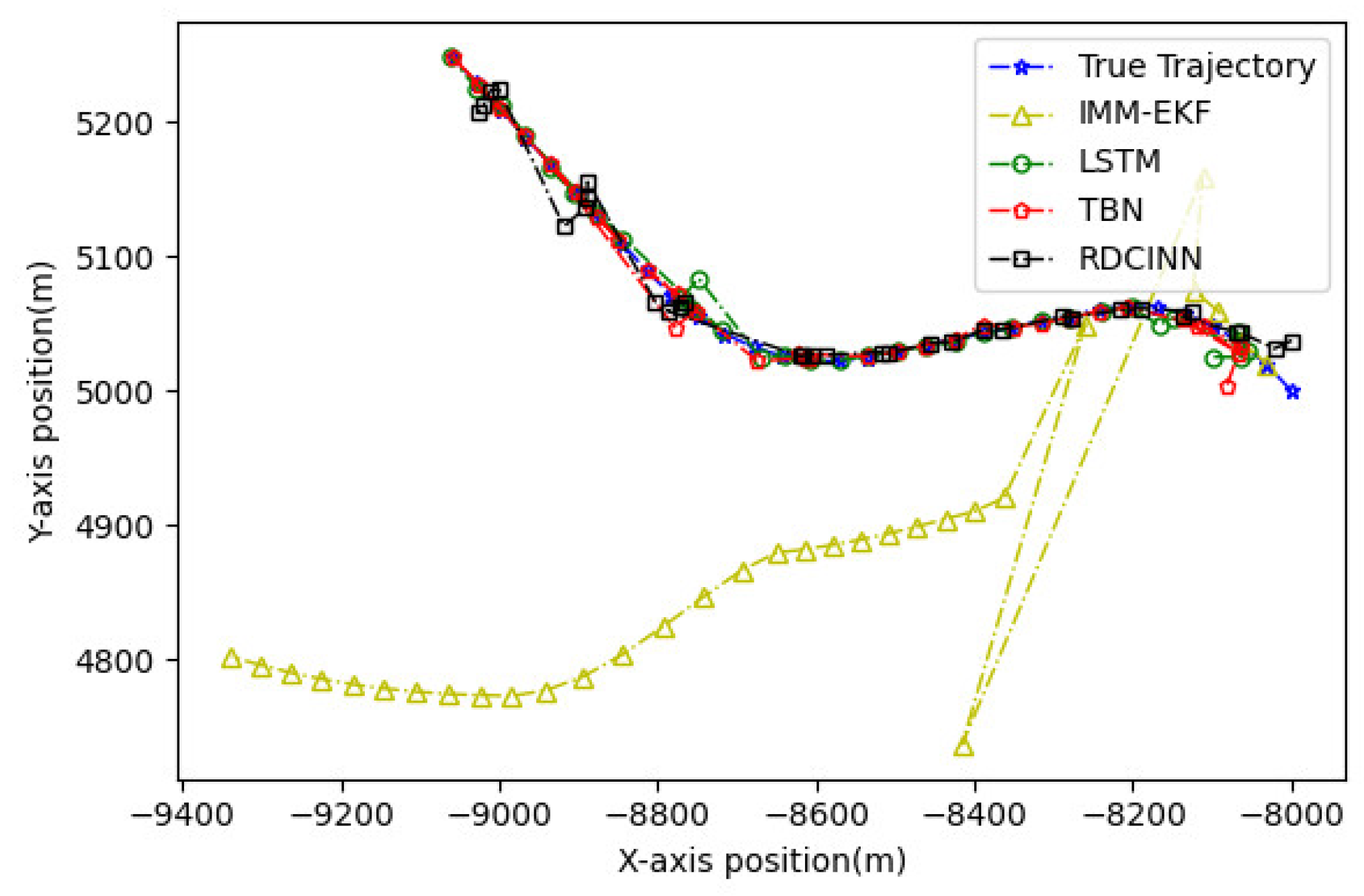
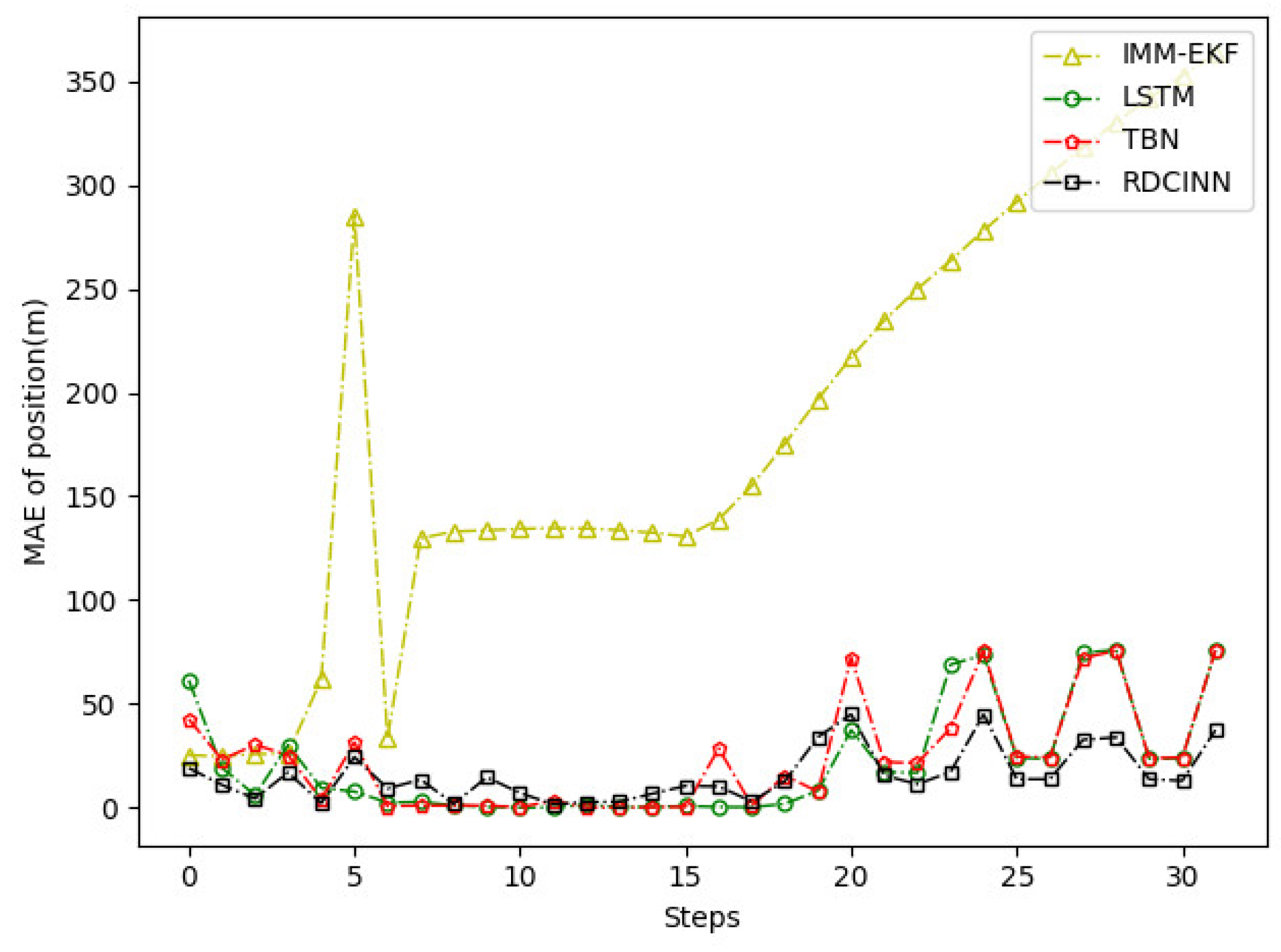
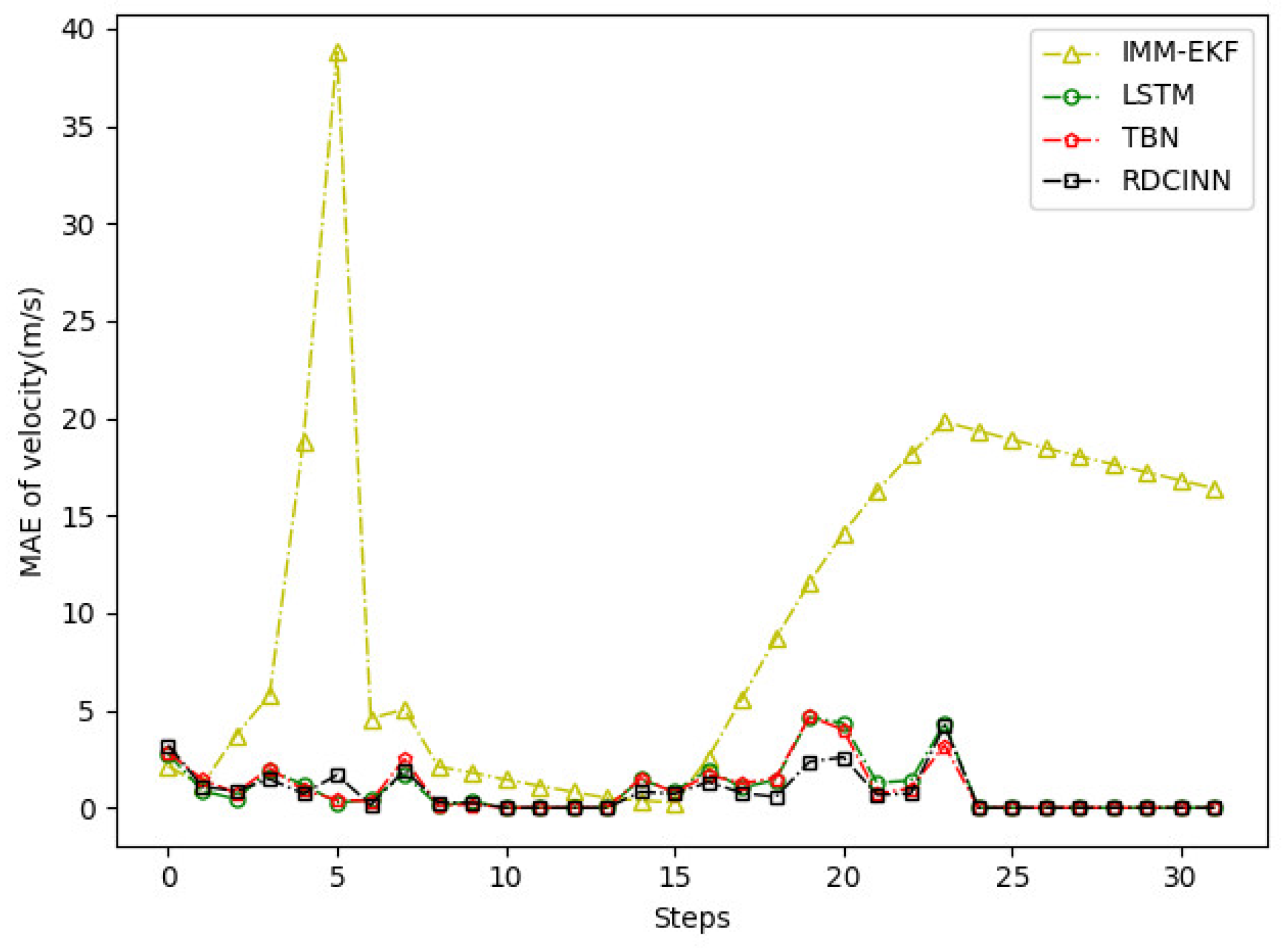
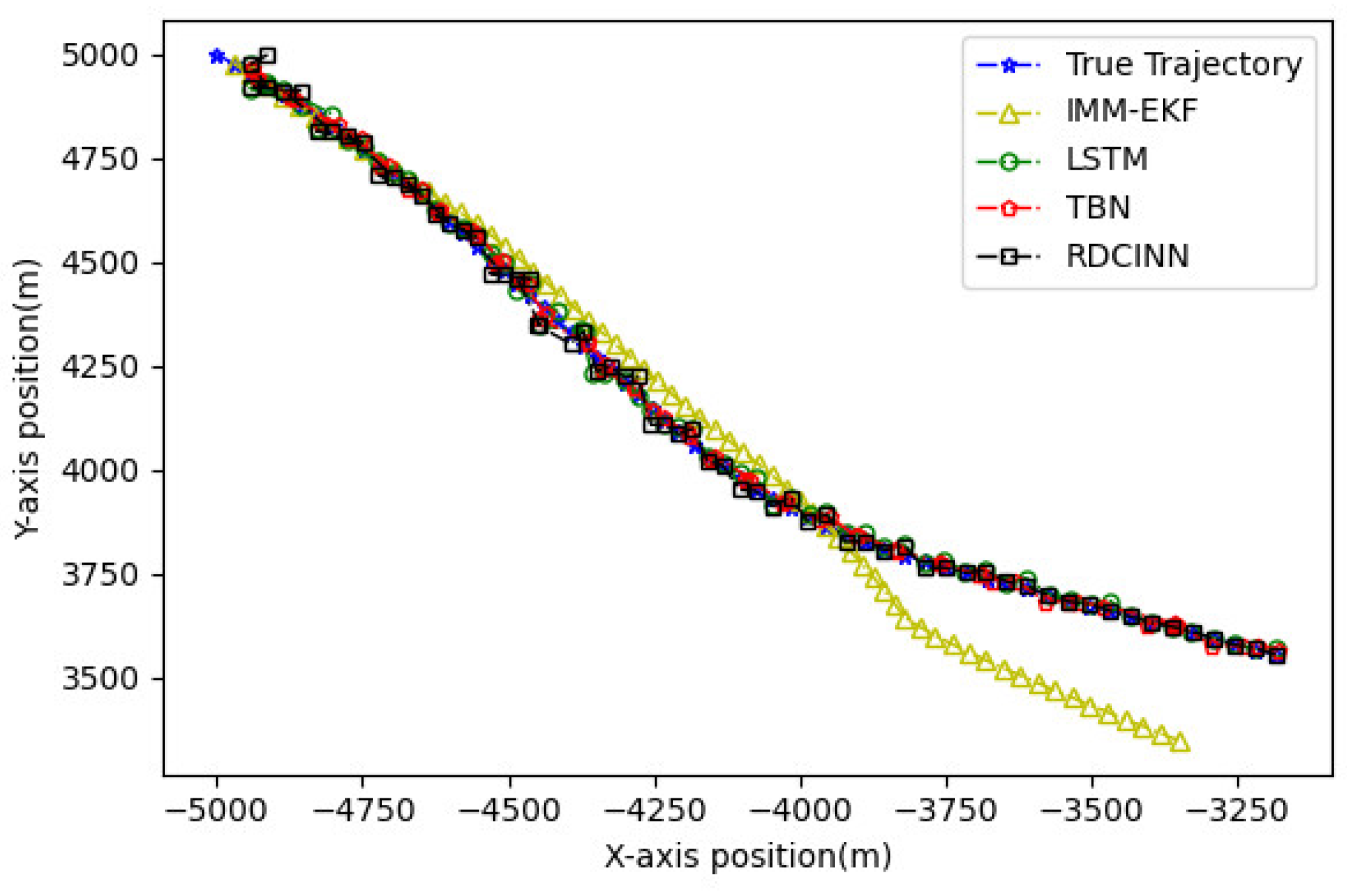
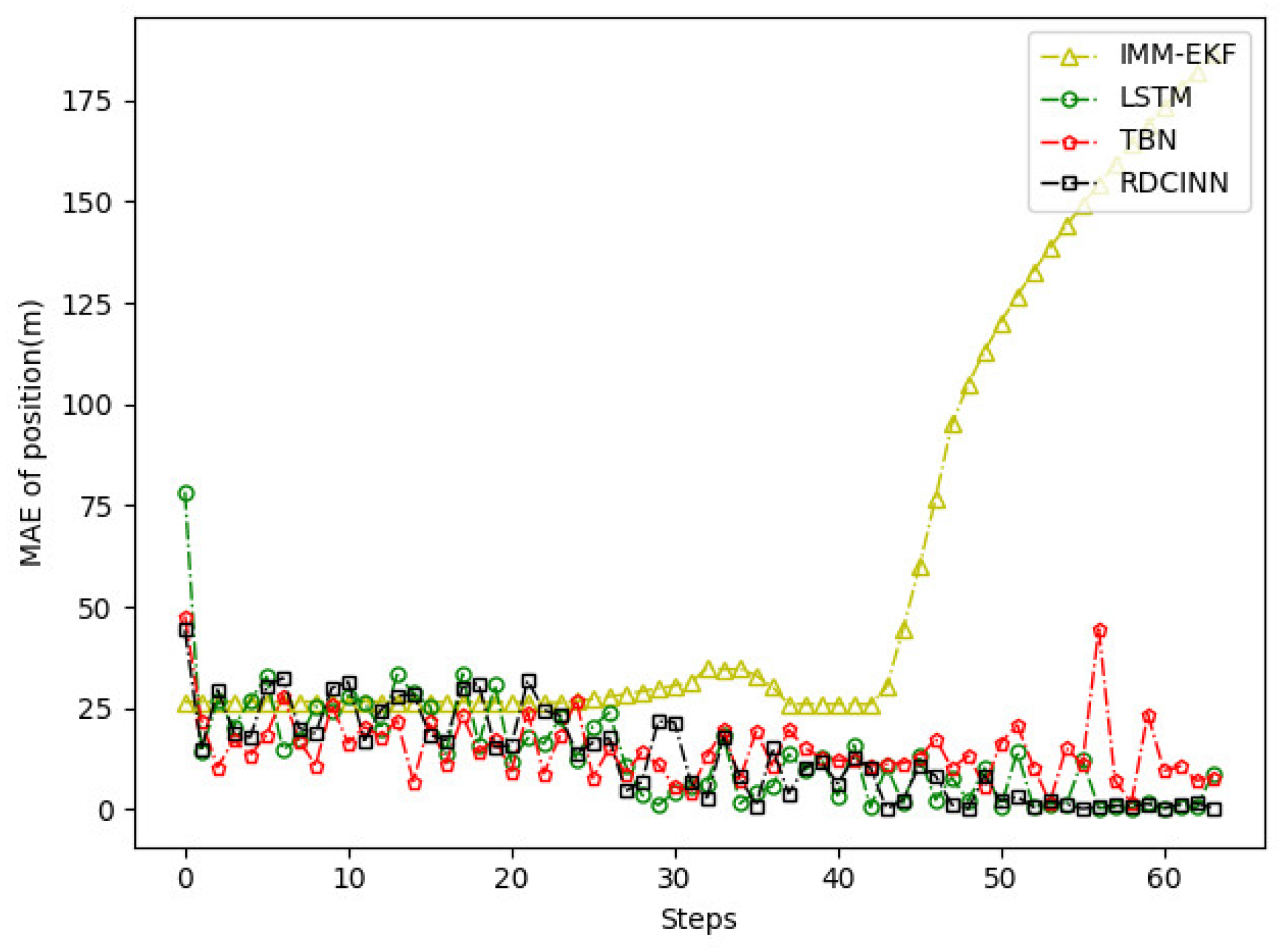
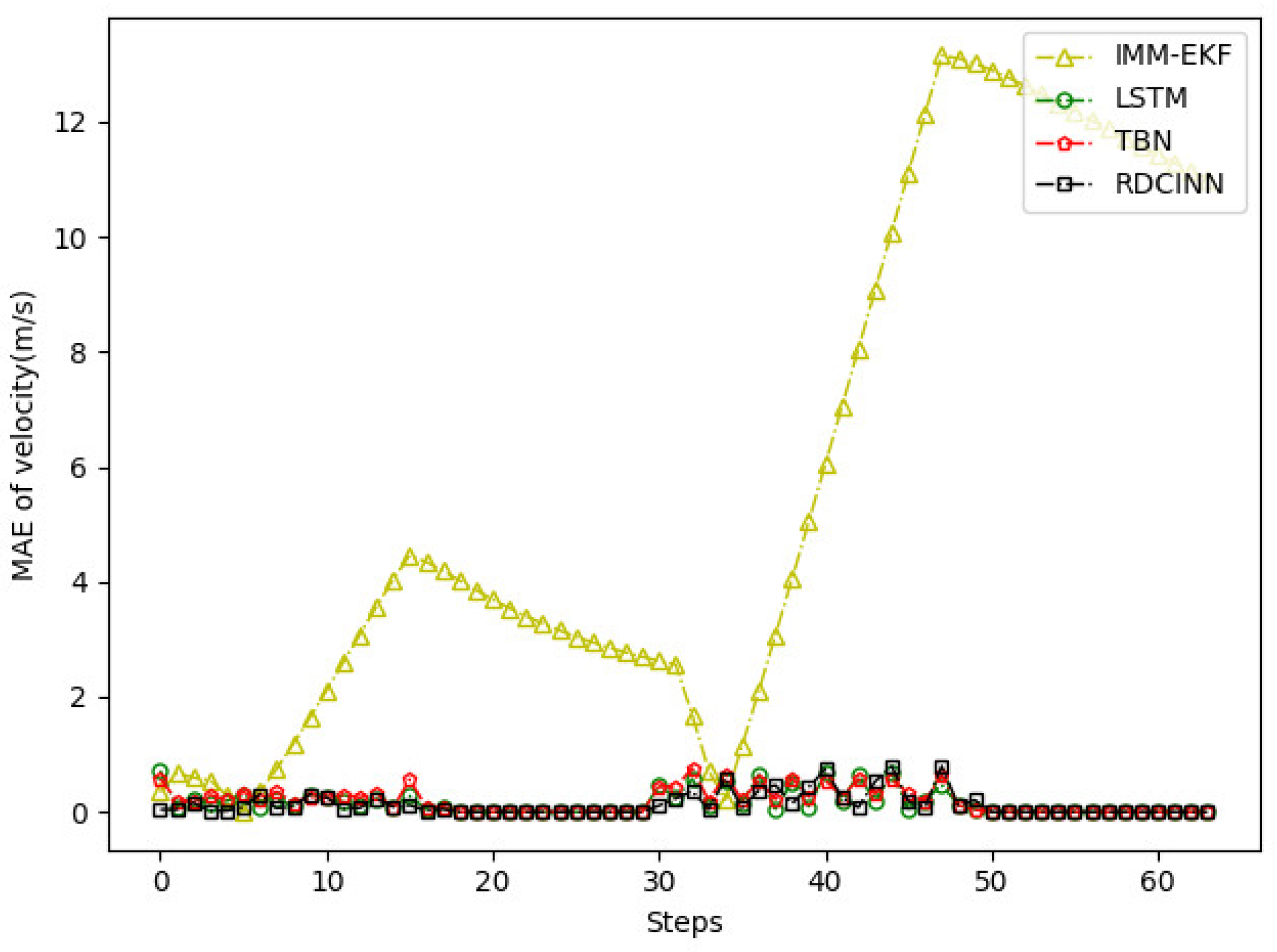
5. Conclusions
Funding
References
- Chunlai Y, U. Research on key technologies of single-station passive positioning and tracking using spatial frequency domain information. 2008.
- Aidala, V.J. Kalman Filter Behavior in Bearings-Only Tracking Applications. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1979, AES-15, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazek, J.; Jiranek, J.; Bajer, J. Indoor passive positioning technique using ultrawide band modules. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Military Technologies (ICMT). IEEE; 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, K. Passive localization of frequency-agile radars from angle and frequency measurements. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1999, 35, 1129–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Tian, S.; Mao, X. Target Locating and Tracking Based on the Azimuth and the Change Rate of Doppler Frequency. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Intelligent Automation Conference. Springer Singapore; 2018; pp. 719. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lv, K.; Liu, M. Maneuvering Target Passive Tracking Algorithm Based on Doppler Frequency Rate and Azimuth. Command. Control. Simul. 2018, 40, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Li, X. Passive multi-sensor maneuvering target tracking based on UKF-IMM algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2009 WASE International Conference on Information Engineering. IEEE; 2009; Volume 2, pp. 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.F.; Gu, X.F.; Wang, H.N. Design and comparison of two MM algorithms for strong maneuvering target tracking. J. Syst. Simul. 2009, 21, 965–968. [Google Scholar]
- Blom HA, P.; Bar-Shalom, Y. The interacting multiple model algorithm for systems with Markovian switching coefficients. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1988, 33, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuli, G.; Wu, H.; Cheng, T.; Huang, S. Tracking maneuvering target on airport surface based on IMM-UKF algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Optoelectronics and Image Processing. IEEE; 2010; Volume 2, pp. 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Pang, F.; Liang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Improved interactive multiple model filter for maneuvering target tracking. In Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control Conference. IEEE; 2014; pp. 7312–7316. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Xing, J.; Ma, Z.; Sha, J.; Meng, X. Improved IMM algorithm for nonlinear maneuvering target tracking. Procedia Eng. 2012, 29, 4117–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Dang, L.M.; Lee, S.; Han, D.; Moon, H. Multiple object tracking in deep learning approaches: A survey. Electronics 2021, 10, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Deep learning for natural language processing: advantages and challenges. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2018, 5, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Shengli, W.; Dingbao, X. Radar track prediction method based on BP neural network. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8051–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yan, J.; Zhou, S.; Chen, B.; Liu, H. Long short-term memory-based recurrent neural networks for nonlinear target tracking. Signal Process. 2019, 164, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, M. DeepMTT: A deep learning maneuvering target-tracking algorithm based on bidirectional LSTM network. Inf. Fusion 2020, 53, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yu, H.; Du, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J. DeepGTT: A general trajectory tracking deep learning algorithm based on dynamic law learning. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2021, 15, 1125–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X. Transformer-Based Maneuvering Target Tracking. Sensors 2022, 22, 8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.P.; He, Y. Transformer-based tracking Network for Maneuvering Targets. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). IEEE; 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling. arxiv preprint 2018, arXiv:1803.01271. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zeng, A.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.; Lai, Q.; Ma, L.; Xu, Q. Scinet: Time series modeling and forecasting with sample convolution and interaction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 5816–5828. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, M. A Kalman estimation based rao-blackwellized particle filtering for radar tracking. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 8162–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Bar-Shalom, Y. Design of interacting multiple model algorithm for tracking in air traffic control systems. Proceedings of 32nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. IEEE; 1993; pp. 906–911. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Müller, M.; Rios, A.; Sennrich, R. Why self-attention? a targeted evaluation of neural machine translation architectures. 2018. [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Value |
| Distance Range | [926m,18520m] |
| Angle Range | [-180o,180o] |
| Velocity Range | [-340m/s,340m/s] |
| Turn Rate () | [-10o/s,10o/s] |
| The Standard Deviation of Acceleration Noise () | [8m/s2,13m/s2] |
| The Standard Deviation of Azimuth Noise () | [1o,1.8o] |
| The Standard Deviation of Doppler Noise () | 1m/s |
| Sampling Time Interval(T) | 1s |
| MAE of Position(m) | MAE of Velocity(m) | |
| LSTM | 58.73 | 8.84 |
| TBN | 44.16 | 6.82 |
| RDCINN | 42.76 | 6.35 |
| MAE of Position(m) | MAE of Velocity(m) | |
| IMM+EKF | 219.53 | 11.17 |
| LSTM | 18.92 | 3.73 |
| TBN | 9.21 | 3.19 |
| RDCINN | 4.07 | 3.04 |
| MAE of Position(m) | MAE of Velocity(m) | |
| IMM+EKF | 184.08 | 10.25 |
| LSTM | 21.56 | 1.02 |
| TBN | 24.01 | 0.99 |
| RDCINN | 15.66 | 0.82 |
| MAE of Position(m) | MAE of Velocity(m) | |
| IMM+EKF | 60.82 | 5.73 |
| LSTM | 13.65 | 0.16 |
| TBN | 15.02 | 0.19 |
| RDCINN | 13.33 | 0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





