Submitted:
19 November 2023
Posted:
20 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
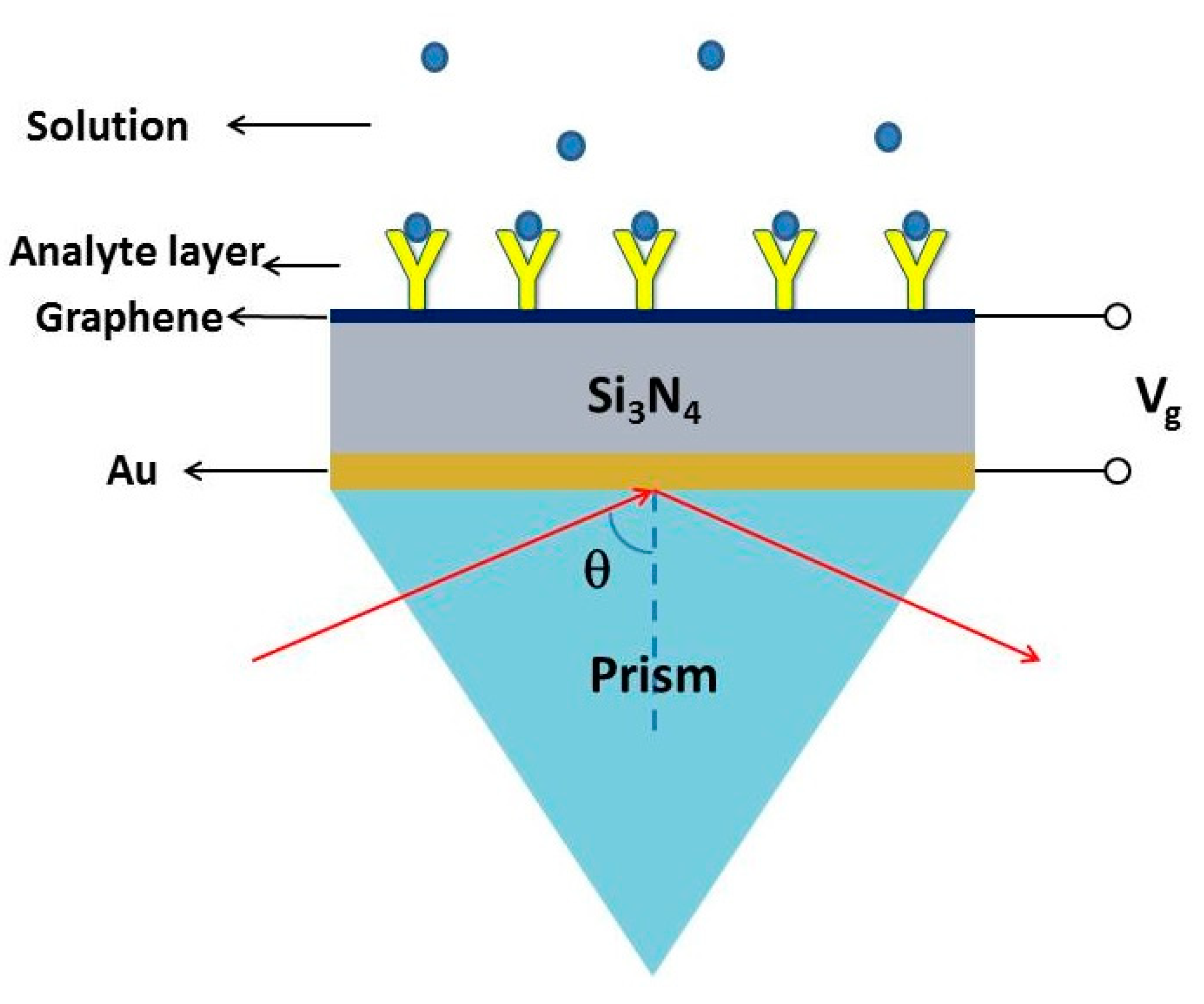
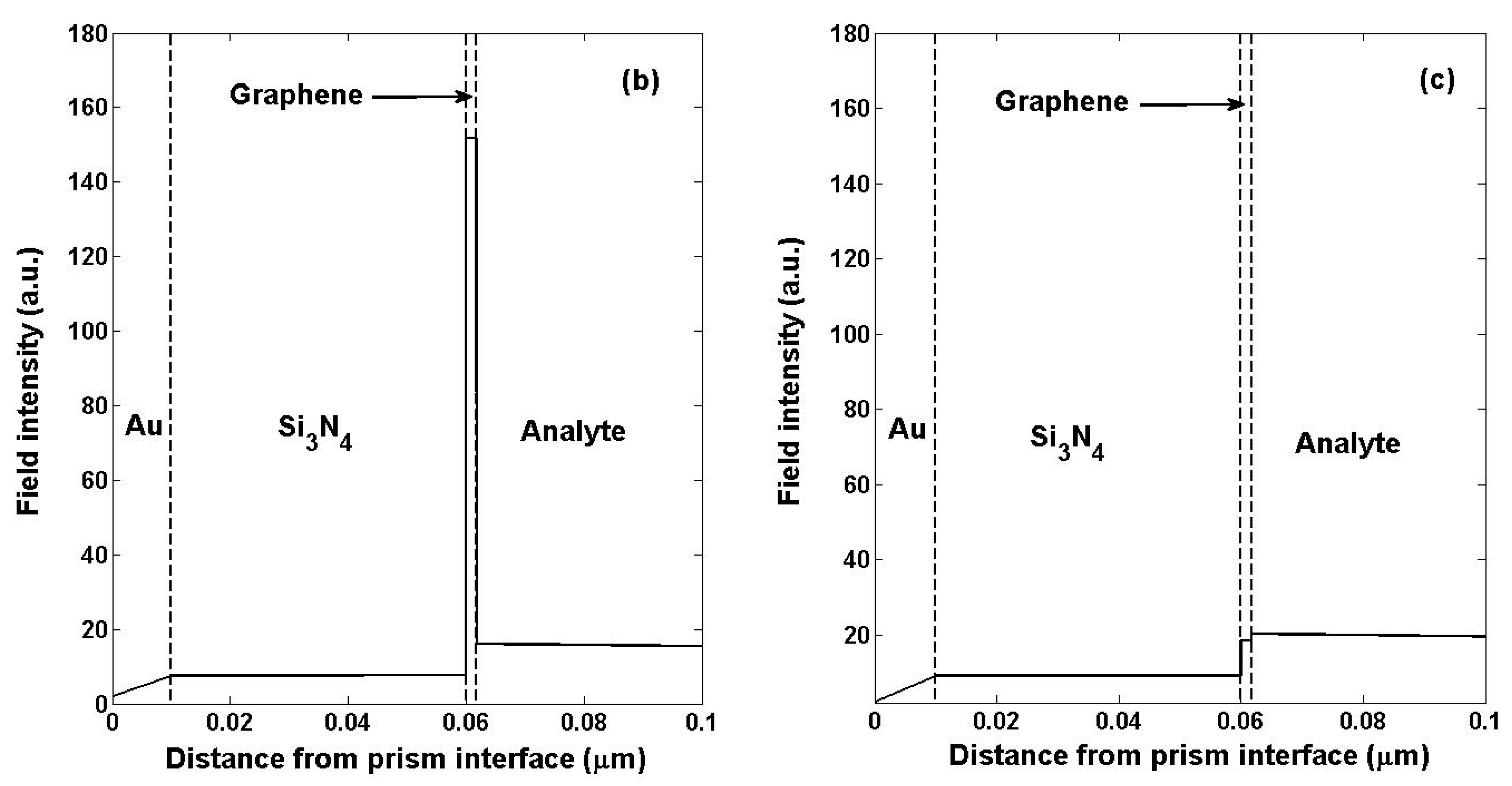
2. Structure Design and Physical Mechanism
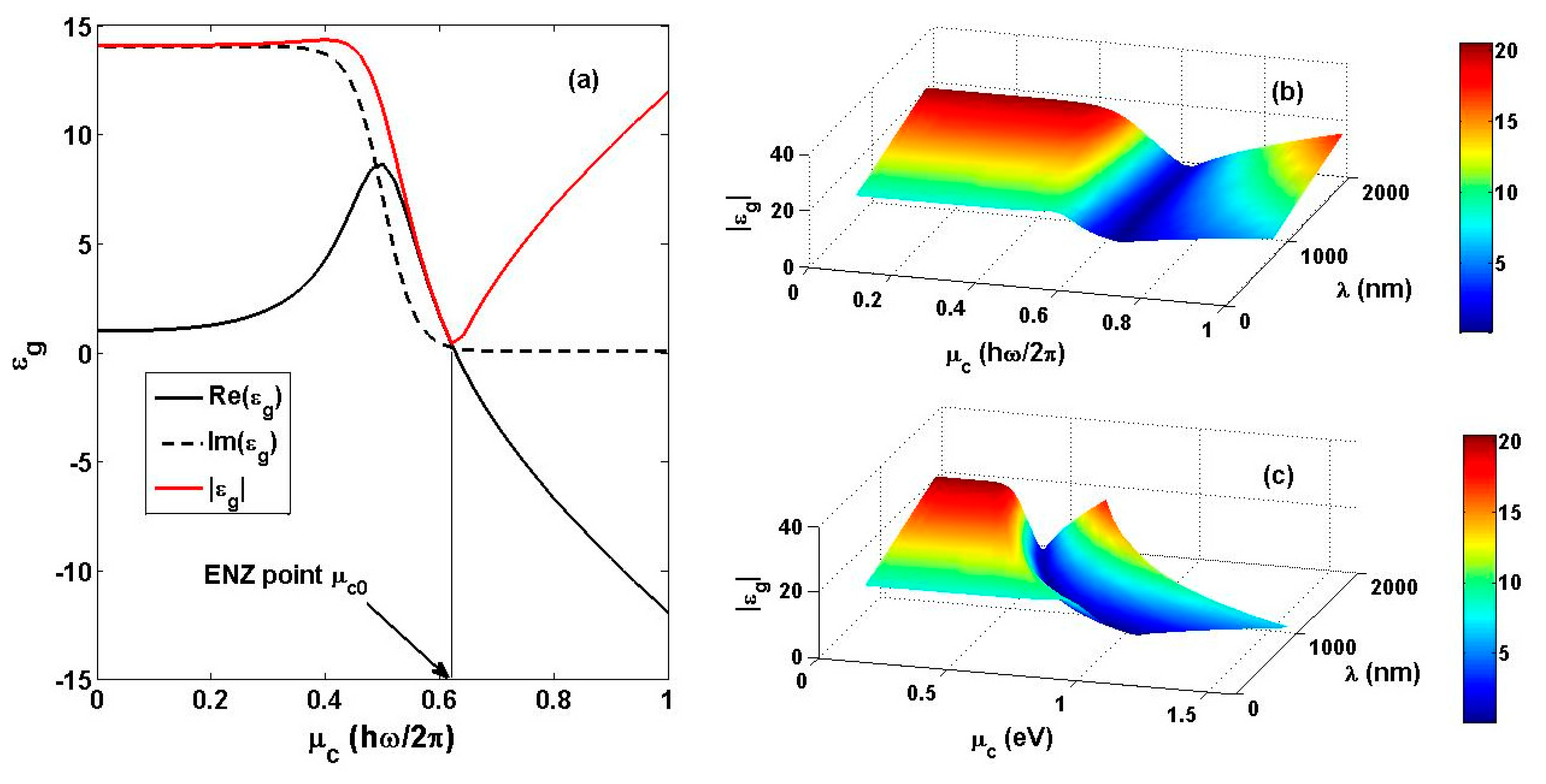
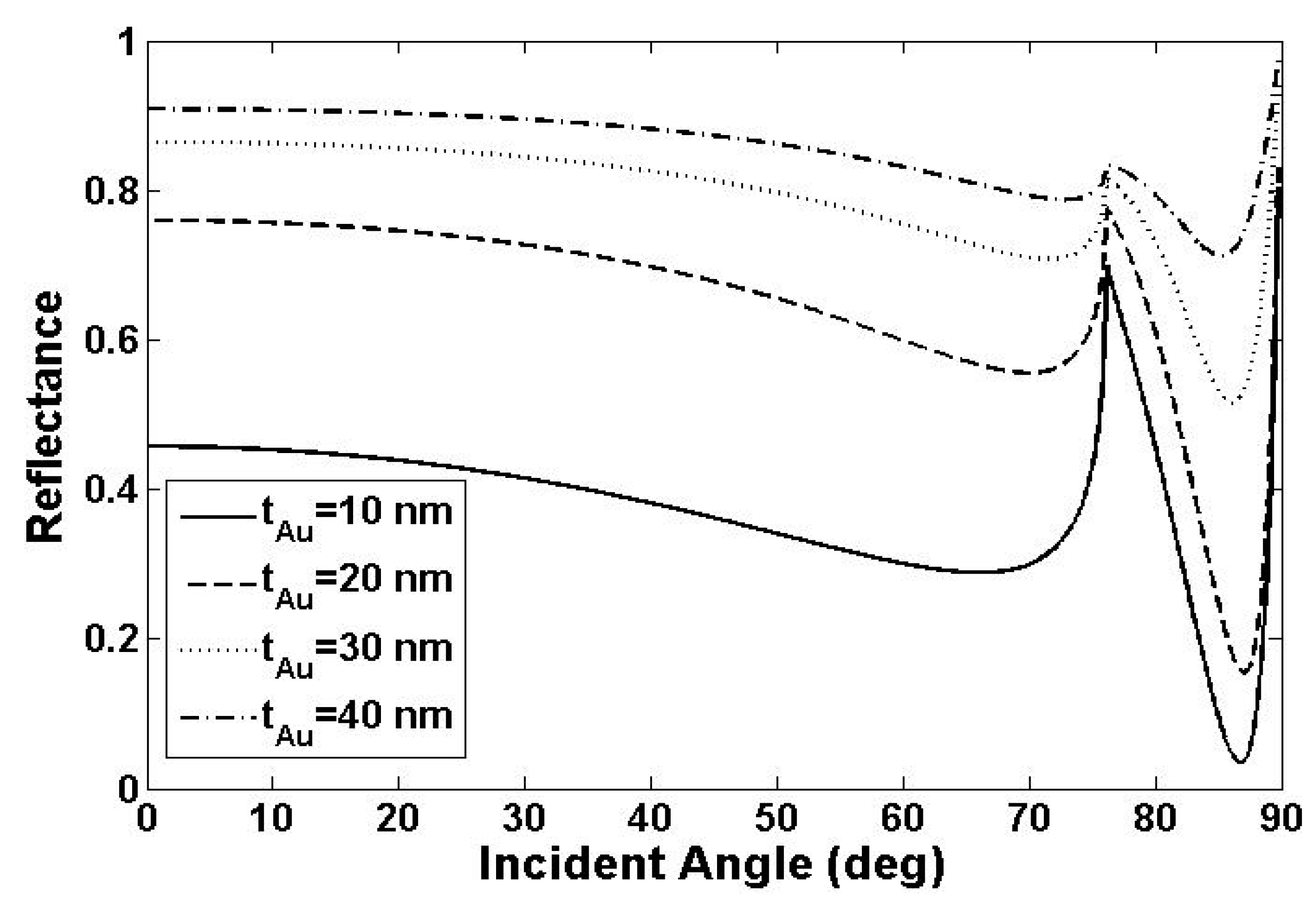
3. Numerical Method and Optimal Consideration
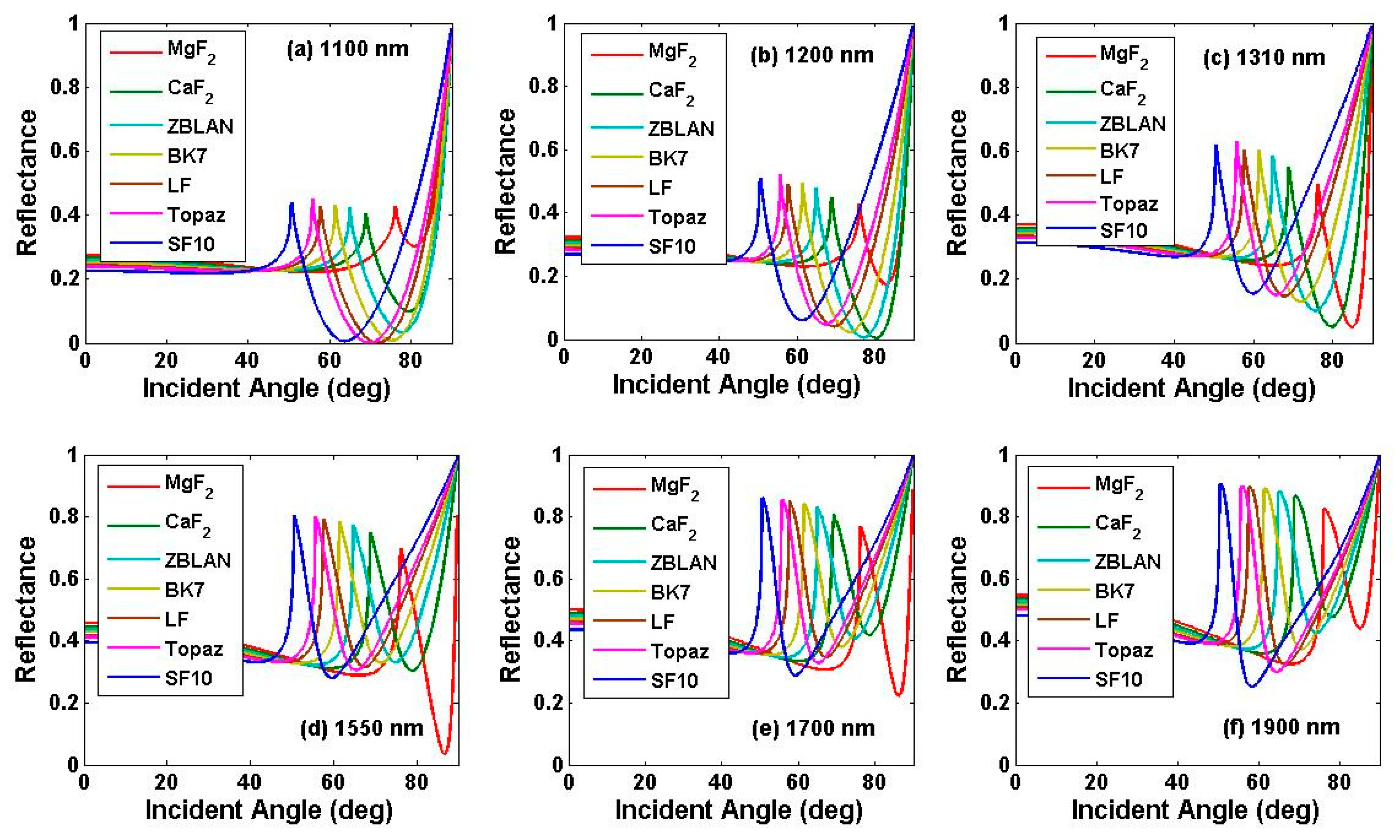
4. Sensing Performance Based on Wavelength Interrogation Mode
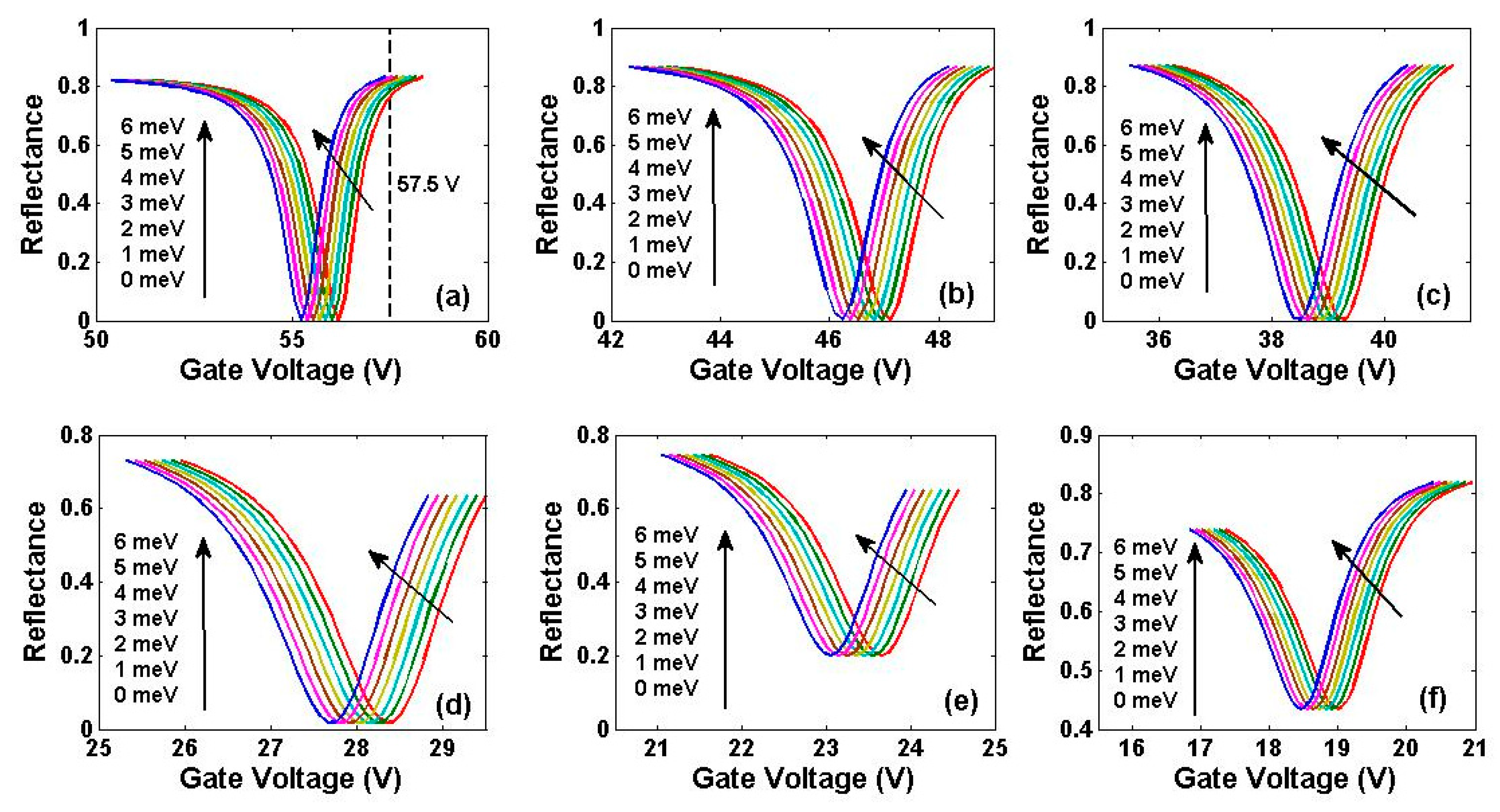
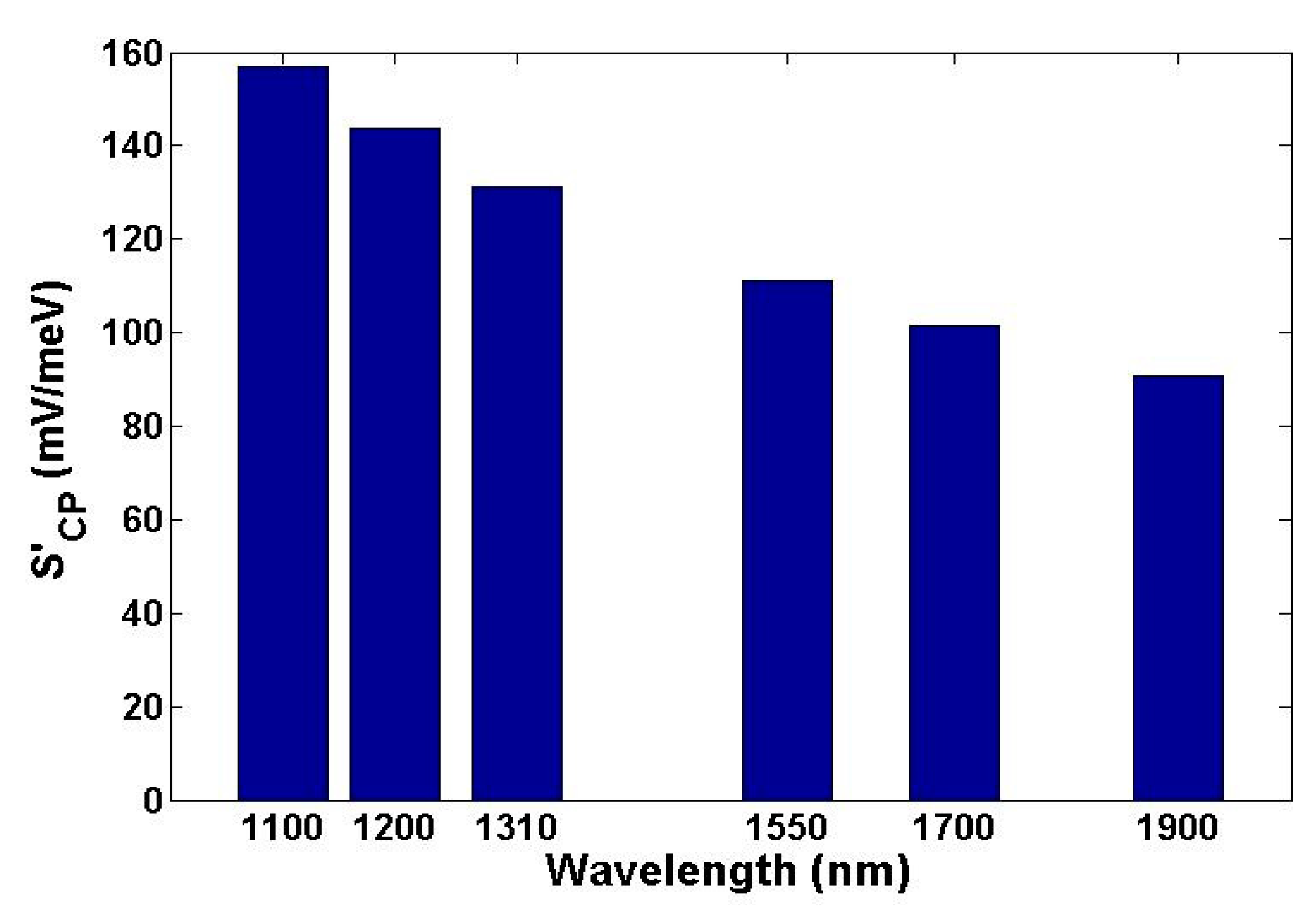
5. Sensing Performance Based on Gate Voltage Interrogation Mode
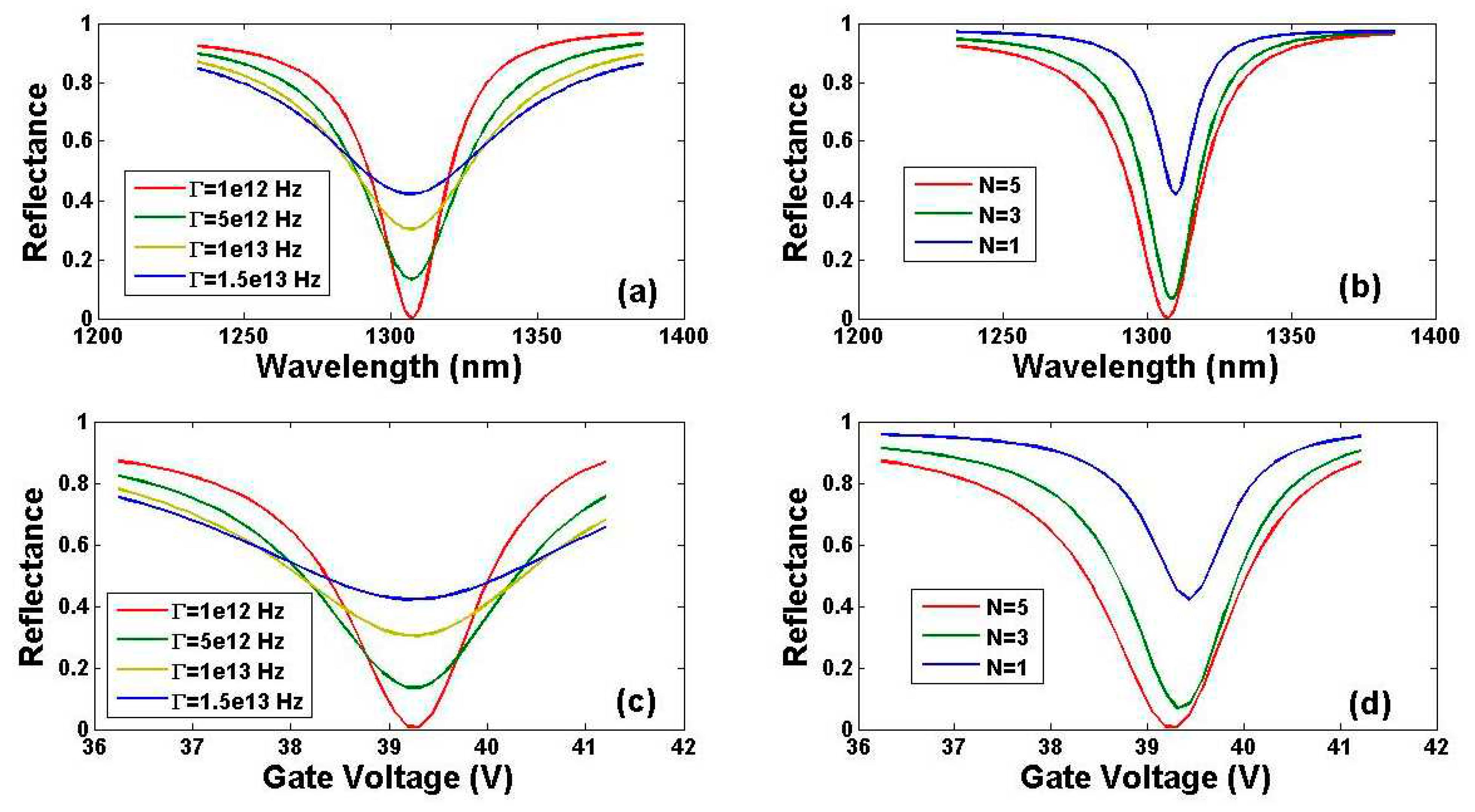
6. Discussion on the Influence of the Quality and the Atom layer Number of the Graphene Film on the Sensing Performance
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Si3N4 layer thickness | 50 nm | 60 nm | 70 nm | 80 nm | 90 nm | 100 nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 nm | optimal prism | LF | LF | LF | Topaz | Topaz | Topaz |
| resonance angle | 71.7° | 73.4° | 75.2° | 75.3° | 77.2° | 78.9° | |
| 1200 nm | optimal prism | CaF2 | ZBLAN | ZBLAN | BK7 | BK7 | BK7 |
| resonance angle | 80.3° | 78.9° | 80.7° | 79.7° | 81.6° | 83° | |
| 1310 nm | optimal prism | MgF2 | CaF2 | CaF2 | CaF2 | ZBLAN | ZBLAN |
| resonance angle | 84.9° | 81.8° | 83.7° | 85° | 84.1° | 85.4° | |
| 1550 nm | optimal prism | MgF2 | MgF2 | MgF2 | CaF2 | CaF2 | CaF2 |
| resonance angle | 86.8° | 87.7° | 87.3° | 84.9° | 86.9° | 87.9° | |
| 1700 nm | optimal prism | MgF2 | MgF2 | MgF2 | MgF2 | CaF2 | CaF2 |
| resonance angle | 86.2° | 87.9° | 88.5° | 87.7° | 85.3° | 87.3° | |
| 1900 nm | optimal prism | MgF2 | MgF2 | MgF2 | MgF2 | MgF2 | CaF2 |
| resonance angle | 85.1° | 86.8° | 88.5° | 89° | 88.1° | 85° | |
References
- Homola, J. Present and future of surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2003, 377, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, P.K.; Umar, A.; Lohia, P.; Albargi, H.; Castaneda, L. Dwivedi, D.K. 2D nanomaterial-based surface plasmon resonance sensors for biosensing applications. Micromachines, 2020, 11, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Chu, H.S.; Koh, W.S.; Li, E.P. Highly sensitive graphene biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt. Express, 2010, 18, 14395–14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.M.; Guo, J.; Wang, Q.K.; Lu, S.B.; Dai, X.Y.; Xiang, Y.J.; Fan, D.Y. Sensitivity enhancement by using few-layer black phosphorus-graphene/TMDCs heterostructure biochemical sensor. Sens. Actuators B, 2017, 249, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Huo, Y.Y.; Jiang, S.Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Ning, T.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, W.Y.; Man, B.Y. Theoretical design of a surface plasmon resonance sensor with high sensitivity and high resolution based on graphene-WS2 hybrid nanostructure and Au-Ag bimetallic film. RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 47177–47182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, J.B.; Prajapati, Y.K.; Singh, V.; Saini, J.P. Sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensor based on graphene-MoS2 hybrid structure with TiO2-SiO2 composite layer. Appl. Phys. A, 2015, 121, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.N.; Chen, S.J.; Lin, C.Y. Sensitivity improvement of a surface plasmon resonance sensor based on two-dimensional materials hybrid structure in visible region: a theoretical study. Sensors, 2020, 20, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.J.; Pagneux, Q.; Larroulet, I.; Serrano, A.Y.; Pesquera, A.; Zurutuza, A.; Mandler, D.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Label-free femtomolar cancer biomarker detection in human serum using graphene-coated surface plasmon resonance chips. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 89, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Chen, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Hu, S.Q.; Luo, Y.H.; Dong, J.L.; Zhu, W.G.; Qiu, W.T.; Guan, H.Y.; Lu, H.H.; Yu, J.H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z. Plasmonic interface modified with graphene oxide sheets overlayer for sensitivity enhancement. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 34916–34923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.M.; Kang, L.X.; Chen, M.W.; Coquet, P.; Yong, K.T. Heterolayered films of monolayer WS2 nanosheets on monolayer graphene embedded in poly(methyl methacrylate) for plasmonic biosensing. ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2020, 3, 10446–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.X.; Chong, Y.; Zhang, P.H.; Ma, J.M.; Li, D.C. A D-shaped fiber SPR sensor with a composite nanostructure of MoS2-graphene for glucose detection. Talanta, 2020, 219, 121324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Nong, J.P.; Mei, Y.H.; Zhong, C.Y.; Lan, G.L.; Hu, W.H. Single-layer graphene-coated gold chip for enhanced SPR imaging immunoassay. Sens. Actuators B, 2018, 273, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.Z.; Song, H.; Zhao, W.M.; Jing, J.Y. A dual channel self-compensation optical fiber biosensor based on coupling of surface palsmon polariton. Opt. Laser Technol., 2020, 124, 106002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorodko, O.; Spadavecchia, J.; Serrano, A.Y.; Larroulet, I.; Pesquera, A.; Zurutuza, A.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Highly sensitive detection of DNA hybridization on commercialized graphene-coated surface plasmon resonance interfaces. Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 11211–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Cai, H.Y.; Qiao, X.; Wang, X.P. High-performance polarization control modulated surface plasmon resonance sensor based on monolayer graphene/Au-NPs architecture for detection of DNA hybridization. Meas. Sci. Technol., 2019, 30, 125701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.Y.; Liang, W.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Sun, Y.H.; Xiang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Dai, Z.G.; Duo, Y.H.; Wu, L.M.; Qi, K.; Shivananju, B.N.; Zhang, L.J.; Cui, X.Q.; Zhang, H.; Bao, Q.L. Ultrasensitive detection of miRNA with an antimonene-based surface plasmon resonance sensor. Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.M.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lu, M. D.; Bi, S.; Jing, Z.G.; Yu, Q.X.; Peng, W. Label-free near-infrared plasmonic sensing technique for DNA detection at ultralow concentrations. Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 2000763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Q.X.; Peng, W. Self-referencing SPR biosensing with an ultralow limit-of-detection using long-wavelength excitation. Sens. Actuators B, 2021, 327, 128935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.L.; Liu, Y.N.; Chang, S.S.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, J.H. Surface plasmonic sensors: sensing mechanism and recent applications. Sensors, 2021, 21, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorenko, A.N.; Polini, M.; Novoselov, K.S. Graphene plasmons. Nat. Photonics, 2012, 6, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablan, M.; Soljacic, M.; Buljan, H. Plasmons in graphene: fundamental properties and potential applications. Proc. IEEE, 2013, 101, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Geng, B.S.; Horng, J.; Girit, C.; Martin, M.; Hao, Z.; Bechtel, H.A.; Liang, X.G.; Zettl, A.; Shen, Y.R.; Wang, F. Graphene plasmonics for tunable terahertz metamaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2011, 6, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.G.; Li, X.S.; Chandra, B.; Tulevski, G.; Wu, Y.Q.; Freitag, M.; Zhu, W.J.; Avouris, P.; Xia, F.N. Tunable infrared plasmonic devices using graphene/insulator stacks. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2012, 7, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.Y.; Thongrattanasiri, S.; Schlather, A.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Ajayan, P.M.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J.; Abajo, F.J.G. de Gated tenability and hybridization of localized plasmons in nanostructured graphene. ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 2388–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, V.W.; Jang, M.S.; Sherrott, M.; Lopez, J.J.; Atwater, H.A. Highly confined tunable mid-infrared plasmonics in graphene nanoresonators. Nano Lett., 2013, 13, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Z.; Rodin, A.S.; Andreev, G.O.; Bao, W.; Mcleod, A.S.; Wagner, M.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhao, Z.; Thiemens, M.; Dominguez, G.; Fogler, M.M.; Castro Neto, A.H.; Lau, C.N.; Keilmann, F.; Basov, D.N. Gate-tuning of graphene plasmons revealed by infrared nano-imaging. Nature, 2012, 487, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.N.; Badioli, M.; Alonso-Gonzalez, P.; Thongrattanasiri, S.; Huth, F.; Osmond, J.; Spasenovic, M.; Centeno, A.; Pesquera, A.; Godignon, P.; Elorza, A.Z.; Camara, N.; Abajo, F.J.G.de; Hillenbrand, R.; Koppens, F.H.L. Optical nano-imaging of gate-tunable graphene plasmons. Nature, 2012, 487, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abajo, F.J.G. de Graphene plasmonics: challenges and opportunities. ACS Photonics, 2014, 1, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.D.; Abajo, F.J.G. de Nonlinear graphene nanoplasmonics. Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Li, T.; Almdal, K.; Mortensen, N.A.; Xiao, S.S.; Ndoni, S. Experimental demonstration of graphene plasmons working close to the near-infrared window. Opt. Lett., 2016, 41, 5345–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.R.; Diankov, G.; Dai, H.J. Narrow graphene nanoribbons from carbon nanotubes. Nature, 2009, 458, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Wang, X.R.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S.W.; Dai, H.J. Chemically derived, ultrasmooth graphene nanoribbon semiconductors. Science, 2008, 319, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranzo, D.A.; Nanot, S.; Dias, E.J.C.; Epstein, I.; Peng, C.; Efetov, D.K.; Lundeberg, M.B.; Parret, R.; Osmond, J.; Hong, J.Y.; Kong, J.; Englund, D.R.; Peres, N.M.R.; Koppens, F.H.L. Probing the ultimate plasmon confinement limits with a van der Waals heterostructure. Science, 2018, 360, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.G.; Li, Z.Q.; Li, X.S.; Zhu, W.J.; Avouris, P.; Xia, F.N. Infrared spectroscopy of tunable dirac terahertz magneto-plasmons in graphene. Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 3766–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, N.; Roulleau, P.; Roche, B.; Hashisaka, M.; Hibino, H.; Petkovic, I.; Glattli, D.C. Resonant edge magnetoplasmons and their decay in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2014, 113, 266601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, G.X.; Wang, L.; Goldflam, M.D.; Wagner, M.; Fei, Z.; Mcleod, A.S.; Liu, M.K.; Keilmann, F.; Ozyilmaz, B.; Castro Neto, A.H.; Hone, J.; Fogler, M.M.; Basov, D.N. Ultrafast optical switching of infrared plasmon polaritons in high-mobility graphene. Nat. Photonics, 2016, 10, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, S. A.; Ziegler, K. New electromagnetic mode in graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2007, 99, 016803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakil, A.; Engheta, N. Transformation optics using graphene. Science, 2011, 332, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, D.; Limaj, O.; Janner, D.; Etezadi, D.; Abajo, F.J.G. de Mid-infrared plasmonic biosensing with graphene. Science, 2015, 349, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R. B. A theoretical design of evanescent wave biosensors based on gate-controlled graphene surface plasmon resonance. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.L.; Shu, J.; Qiu, C.Y.; Xu, Q.F. Excitation of plasmonic waves in graphene by guided-mode resonance. ACS Nano, 2012, 6, 7806–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.L.; Yan, W.; Jepsen, P.U.; Hansen, O.; Mortensen, N.A.; Xiao, S.S. Experimental observation of plasmons in a graphene monolayer resting on a two-dimensional subwavelength silicon grating. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 102, 131101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C. H. Analysis of surface plasmon excitation at terahertz frequencies with highly dopted graphene sheets via attenuated total reflection. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, 101, 111609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purkayastha, A.; Srivastava, T.; Jha, R. Ultrasensitive THz-plasmonics gaseous sensor using doped graphene. Sens. Actuators B, 2016, 227, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhong, S.C.; Yao, H.Z.; Cui, D.X. Tunable ultrasensitive terahertz sensing based on surface plasmon polariton of doped monolayer graphene. Phys. Status Solidi A, 2017, 214, 1600550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhong, S.C.; Shen, Y.C.; Yu, Y.J.; Cui, D.X. Terahertz phase jumps for ultra-sensitive graphene plasmon sensing. Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 22466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziolkowski, R.W. Propagation in and scattering from a matched metamaterial having a zero index of refractive. Phys. Rev. E, 2004, 70, 046608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engheta, N. Pursuing near-zero response. Science, 2013, 340, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberal, I.; Engheta, N. Near-zero refractive index photonics. Nat. Photonics, 2017, 11, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.J.; Neumayer, D.; Perebeinos, V.; Avouris, P. Silicon nitride gate dielectrics and band gap engineering in graphene layers. Nano Lett., 2010, 10, 3572–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Diaz, J.S.; Moldovan, C.; Capdevila, S.; Romeu, J.; Bernard, L.S.; Magrez, A.; Lonescu, A.M.; Perruisseau-Carrier, J. Self-biased reconfigurable graphene stacks for terahertz plasmonics. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, Y.C.; Luo, Y.H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.F.; Liu, G.S.; Yu, J.H. Near-infrared tunable surface plasmon resonance sensor based on graphene plasmons via electrostatic gating control. RSC Adv., 2021, 11, 37559–37567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Jeong, H.; Park, N.H.; Yim, W.; Kim, M.H.; Park, J.K.; Son, S. Bae, S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.; Ahn, Y.H.; Ahn, K.J.; Hong, B.H.; Park, J.Y.; Rotermund, F.; Yeom, D. Active control of all-fibre graphene devices with electrical gating. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, D.; Tittl, A.; Limaj, O.; Abajo, F.J.G.de; Pruneri, V.; Altug, H. Double-layer graphene for enhanced tunable infrared plasmonics. Light-Sci. Appl., 2017, 6, e16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, M.; Neumaier, D.; Schall, D.; Otto, M.; Matheisen, C.; Giesecke, A. L.; Sagade, A.A.; Kurz, H. Experimental verification of electro-refractive phase modulation in graphene. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.H.; Dong, H.Z.; Wei, Y.Y.; Luo, Y.H.; Zhong, Y.C. Qiu, W.T.; Dong, J.L.; Lu, H.H.; Guan, H.Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Zhu, W.G.; Chen Z. Theoretical investigation of optical modulators based on graphene-coated side-polished fiber. Opt. Express, 2018, 26, 13759–13772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshginqalam, B.; Ahmadi, M.T.; Ismail, R.; Sabatyan, A. Graphene/graphene oxide-based ultrasensitive surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Plasmonics, 2017, 12, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Diaz, J.S.; Esquius-Morote, M.; Perruisseau-Carrier, J. Plane wave excitation-detection of non-resonant plasmons along finite-width graphene strips. Opt. Express, 2013, 21, 24856–24872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, G.W. Dyadic Green’s functions and guided surface waves for a surface conductivity model of graphene. J. Appl. Phys., 2008, 103, 064302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, K.; Okawachi, Y.; Lamont, M.R.E.; Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M. Broadband mid-infrared frequency comb generation in a Si3N4 microresonator. Opt. Lett., 2015, 40, 4823–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliaev, L.Y.; Shkondin, E.; Lavrinenko, A.V.; Takayama, O. Optical, structural and composition properties of silicon nitride films deposited by reactive radio-frequency sputtering, low pressure and plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films, 2022, 763, 139568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.C.; Shi, Y.M.; Huang, W.; Chen, P.; Li, L.J. Electrical detection of DNA hybridization with single-base specificity using transistors based on CVD-grown graphene sheets. Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, N.; Berry, V. Graphene-based single-bacterium resolution biodevice and DNA transistor: interfacing graphene derivatives with nanoscale and microscale biocomponents. Nano Lett., 2008, 8, 4469–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipova, H.; Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance sensing of nucleic acids: a review. Anal. Chim. Acta, 2013, 773, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artyukhin, A.B.; Stadermann, M.; Friddle, R.W.; Stroeve, P.; Bakajin, O.; Noy, A. Controlled electrostatic gating of carbon nanotube FET devices. Nano Lett., 2006, 6, 2080–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.S.; Li, S.L.; Miyazaki, H.; Sato, S.; Hayashi, K.; Yamada, A.; Yokoyama, N.; Tsukagoshi, K. Origin of the relatively low transport mobility of graphene grown through chemical vapor deposition. Sci. Rep., 2012, 2, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Chiang, W.Y.; Su, Y.H.; Hofmann, M.; Hsieh, Y.P. Solid-diffusion-facilitated cleaning of copper foil improves the quality of CVD graphene. Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.H.; Guo, Y.X.; Qi, Z.K.; Xie, K.; Zhang, R.X.; Xia, Y.M.; Chen, C.; Zeng, H.L.; Cui, P.; Ji, H.X.; Qin, S.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y. Elimination of grain boundaries in graphene growth on a Cu-Ni alloyed substrate by chemical vapor deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125, 18217–18224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.T.; Sohn, M.K.; Park, H.J.; Huang, J.S.; Subramanian, K.R.V.; Kang, D.J. Universal 2D material film transfer using a novel low molecular weight polyvinyl acetate. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 534, 147650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xia, J.L.; Tao, N.J. Ionic screening of charged-impurity scattering in graphene. Nano Lett., 2009, 9, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, M.; Sorianello, V.; Midrio, M.; Koppens, F.H.L.; Huyghebaert, C.; Neumaier, D.; Galli, P.; Templ, W.; D’Errico, A.; Ferrari, C. Graphene-based integrated photonics for next-generation datacom and telecom. Nat. Rev. Mater., 2018, 3, 392–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Bakharev, P.V.; Wang, Z.J.; Biswal, M.; Yang, Z.; Jin, S.W.; Wang, B.; Park, H.J.; Li, Y.Q.; Qu, D.S.; Kwon, Y.W.; Chen, X.J.; Lee, S.H.; Willinger, M.G.; Yoo, W.J.; Lee, Z.H.; Ruoff, R.S. Large-area single-crystal AB-bilayer and ABA-trilayer graphene grown on a Cu/Ni(111) foil. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2020, 15, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
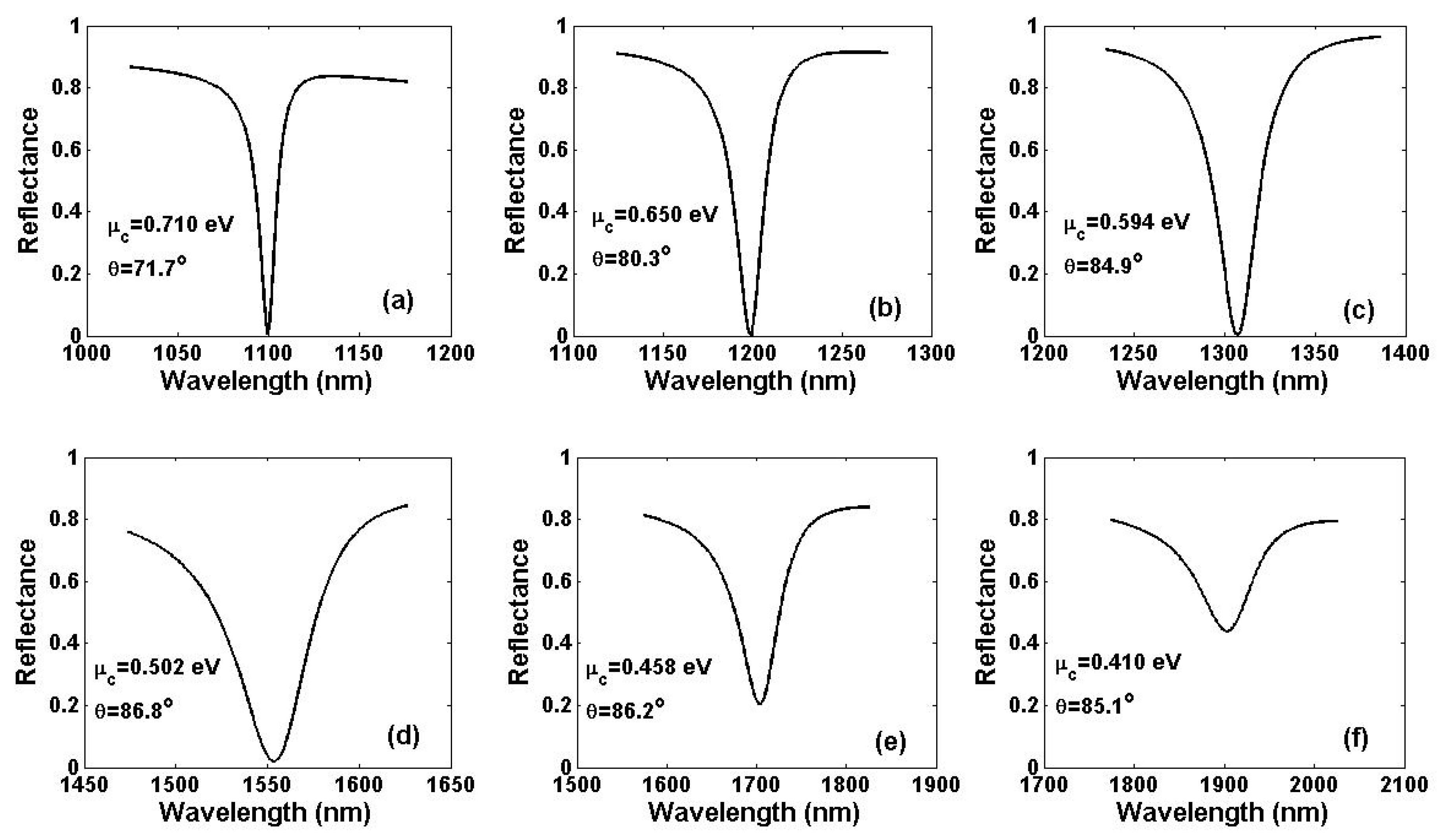

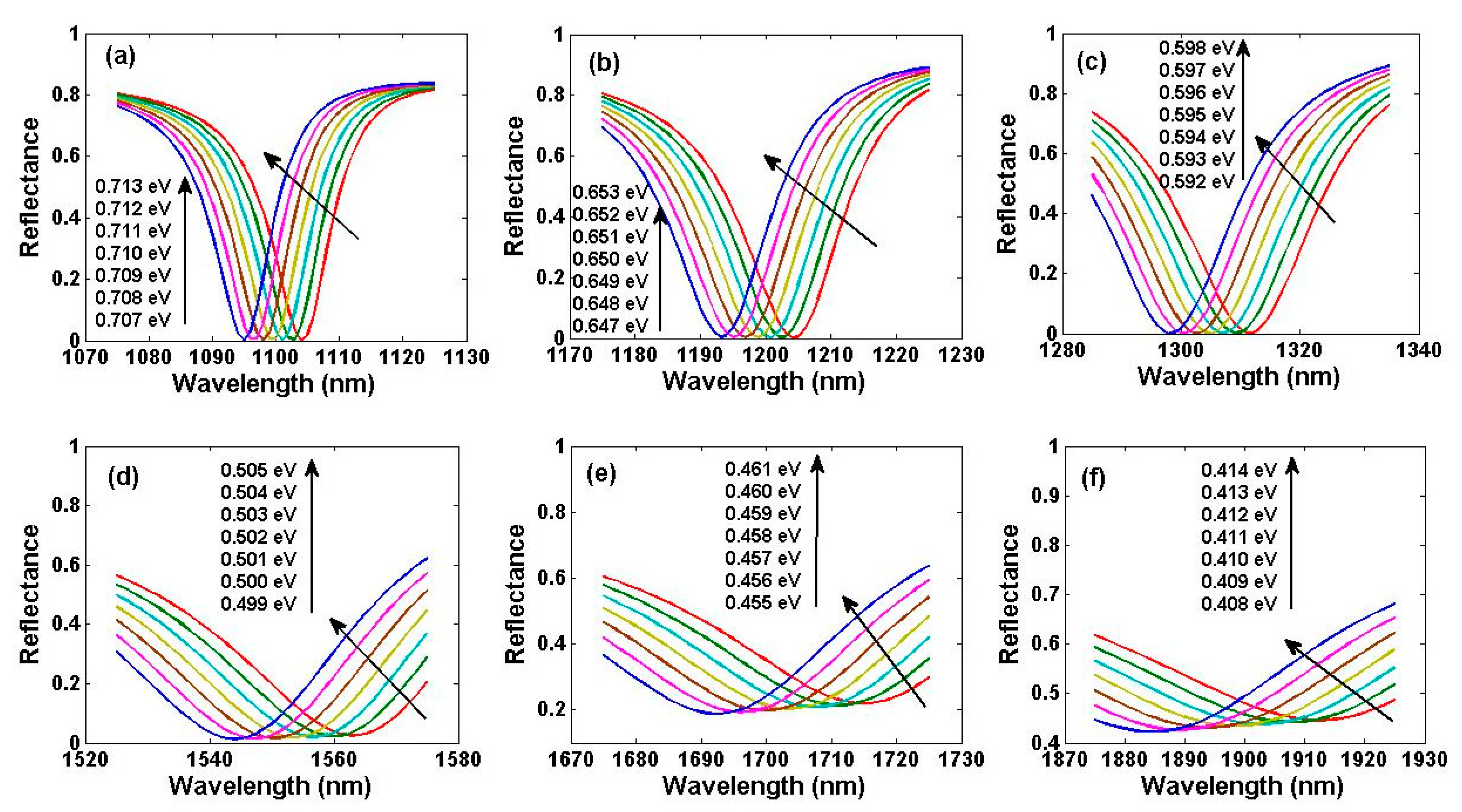
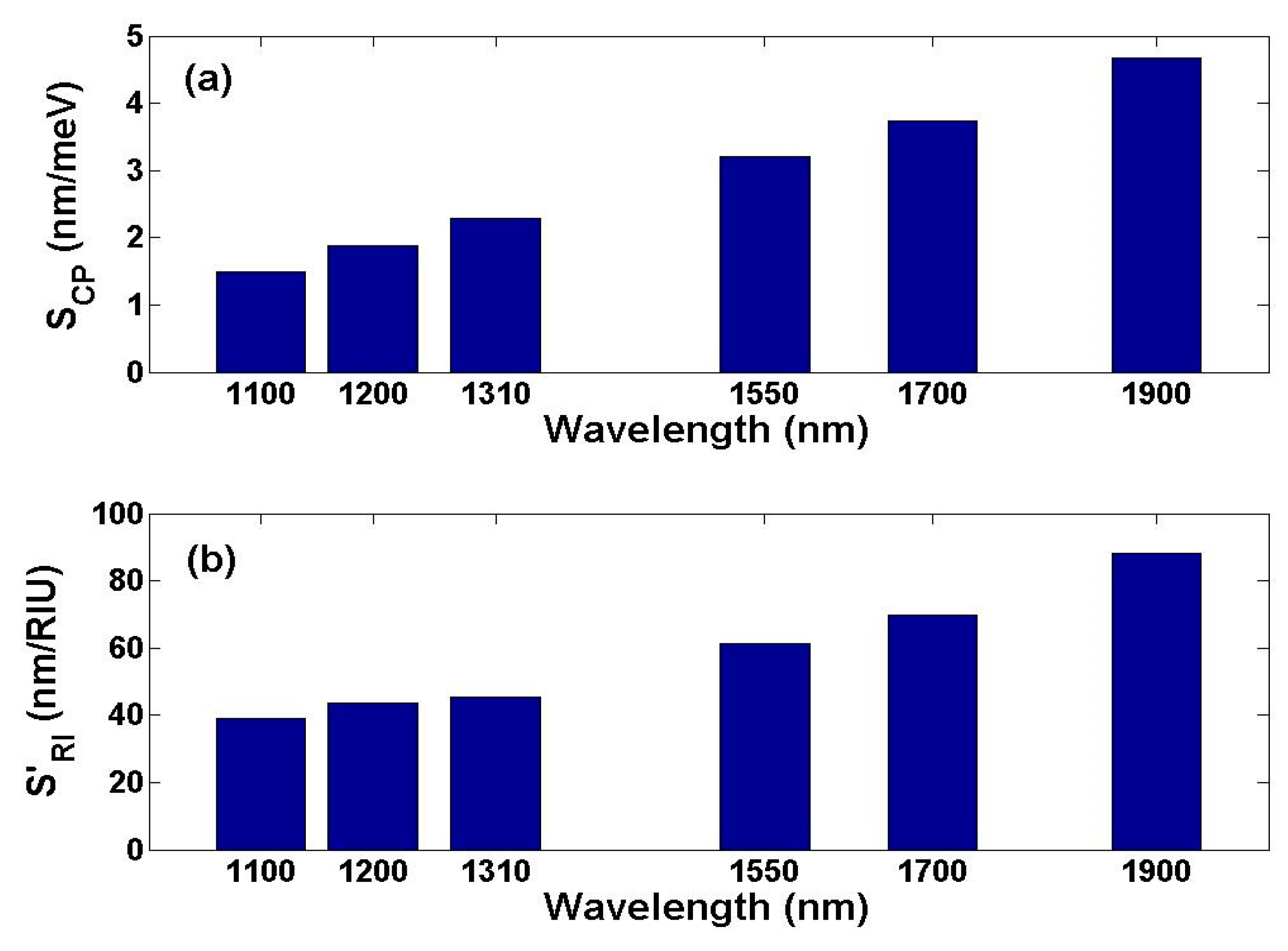
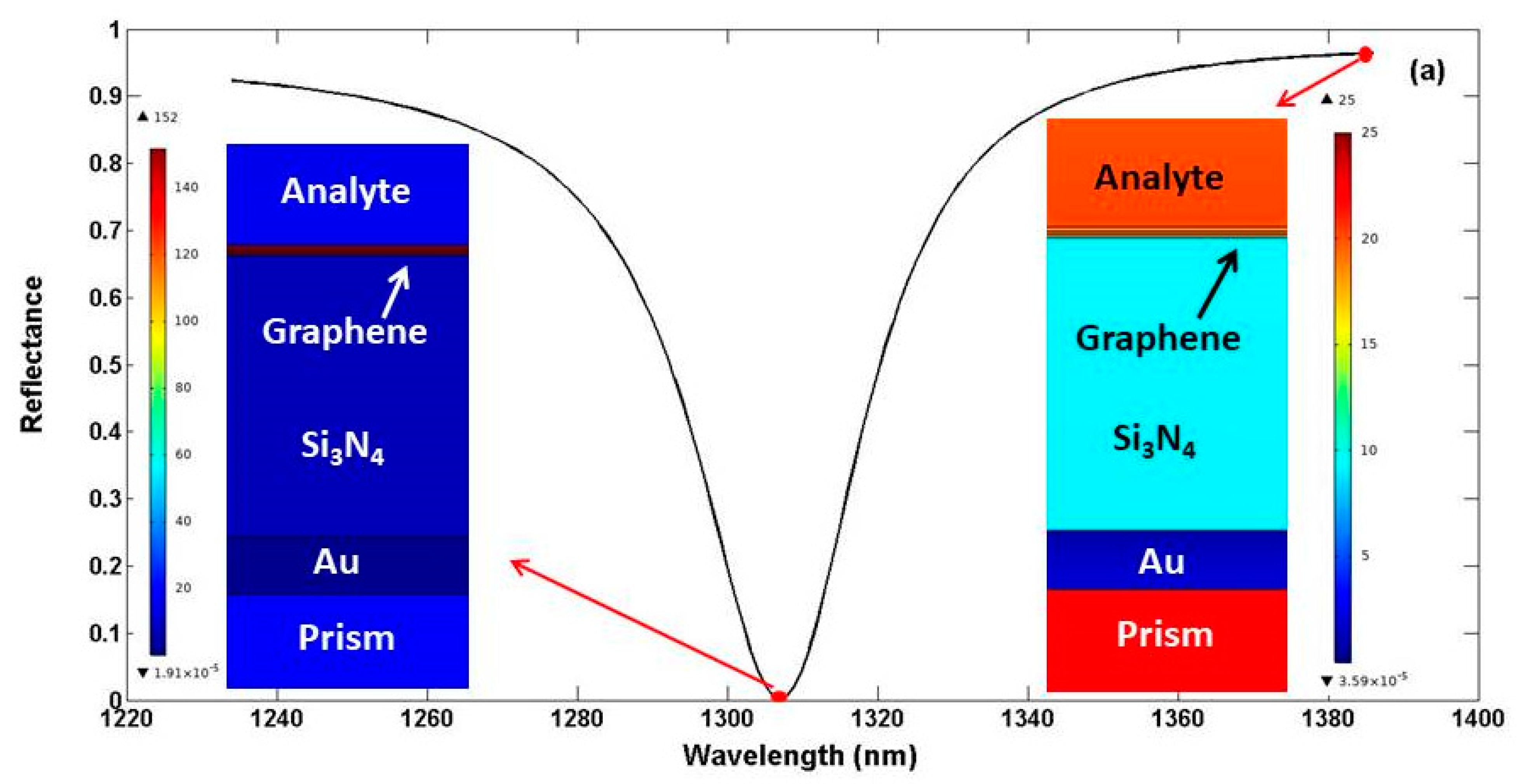
| λ(nm) | 760 | 850 | 980 | 1100 | 1200 | 1310 | 1550 | 1700 | 1900 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μc0(eV) | 1.037 | 0.923 | 0.798 | 0.709 | 0.649 | 0.594 | 0.502 | 0.458 | 0.410 |
| μcPR(eV) | 1.037 | 0.923 | 0.798 | 0.710 | 0.650 | 0.594 | 0.502 | 0.458 | 0.410 |
| Vg(V) | 119.6 | 94.8 | 70.9 | 56.2 | 47.1 | 39.4 | 28.2 | 23.5 | 18.9 |
| SPR structure | Theoretical/experimental | LOD | FWHM | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBAK1/Au film/graphene/AuNSs | experimental | 0.5 fM | - | 14 |
| K9/Au film/graphene/AuNPs | experimental | 0.5 fM | - | 15 |
| K9/Au film/antimonene/AuNRs | experimental | 10 aM | - | 16 |
| K9/AuNT array/AuNPs | experimental | 1.2 aM | 114.471 nm | 17 |
| K9/Au film/GO-AuNPs | experimental | 0.2 fM | - | 18 |
| MgF2/Au film/Si3N4/graphene | theoretical | <4.27 fM | 78.4 nm | this work |
| LF/Au film/Si3N4/graphene | theoretical | <21.66 aM | 1158 mV | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




