1. Introduction
Over recent years, pathogenic bacteria's high infection and mortality, especially drug-resistant strains, have severely threatened global human health and livestock breeding [
1,
2]. Various pathogenic bacteria have caused the widespread use of antibiotics. As a result, the abuse of antibiotics triggered the emergence of drug resistance in pathogenic bacteria [
3]. Developing novel antibiotic substances is urgently needed to settle these problems.
Melittin (Mel), a small cationic linear peptide composed of 26 amino acid residues (GIGAVLKVLTTGLPALISWIKRKRQQ-CONH2), is a significant element in the venom of honeybees [
4]. Melittin exhibits a potent antibacterial effect against
S. aureus at concentrations significantly below toxic concentrations. It is effective against planktonic and biofilm-embedded MRSA strains at concentrations ranging from 0.12 to 4 μM [
5]. Therefore, melitin is an up-and-coming candidate for developing new antibiotics to treat pathogenic bacteria infections.
Despite its multiple potential biological activities, the applications of melittin are limited due to its severe hemolytic activity and low proteolytic stability. Melittin resulted in 50% hemolysis of human red blood cells at 2 μM and 100% at 7 μM [
6]. It contains two arginine and three lysine residues sensitive to trypsin, and thus trypsin degrades it rapidly, and nearly no melittin is left after 60 min of incubation [
7].
Multiple strategies have been applied to develop novel antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) with potent antimicrobial activity, lower cytotoxicity, and higher proteolytic stability. The replacement of unnatural amino acids such as D-form and N-methyl amino acids, cyclization, PEG modification, and fatty acid conjugation have been used for precursor modification and construction of antibacterial peptide drugs [
8,
9,
10,
11]. Among them, fatty acid conjugation could significantly tune the antibacterial activity and proteolytic stability of AMPs [
12]. Zhong
et al. showed that conjugated with a fatty acid on the side chain of D-amino acid of Anoplin enhanced antimicrobial potency against multidrug-resistant bacteria [
13]. Liu
et al. reported that fatty acid conjugation with Anoplin developed a series of lipopeptide analogs. The stability of these lipopeptides against trypsin and chymotrypsin degradation was increased by
104~106 times. It was demonstrated that fatty acid conjugation could significantly improve various bioactivities of peptides, including antimicrobial potency and proteolytic stability.
This study used N-terminal fatty acid conjugation to develop novel MDLs with enhanced antimicrobial activity, reduced hemolysis, and resistance toward proteolytic degradation. Furthermore, the mechanism of antimicrobial action of these new MDLs was investigated using membrane permeabilization and LPS/LTA competitive inhibition assay. Overall, our results indicated that the approach of fatty acid conjugation would be a promising method to improve natural melittin's antimicrobial activity and proteolytic stability.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Characterization of MDLs
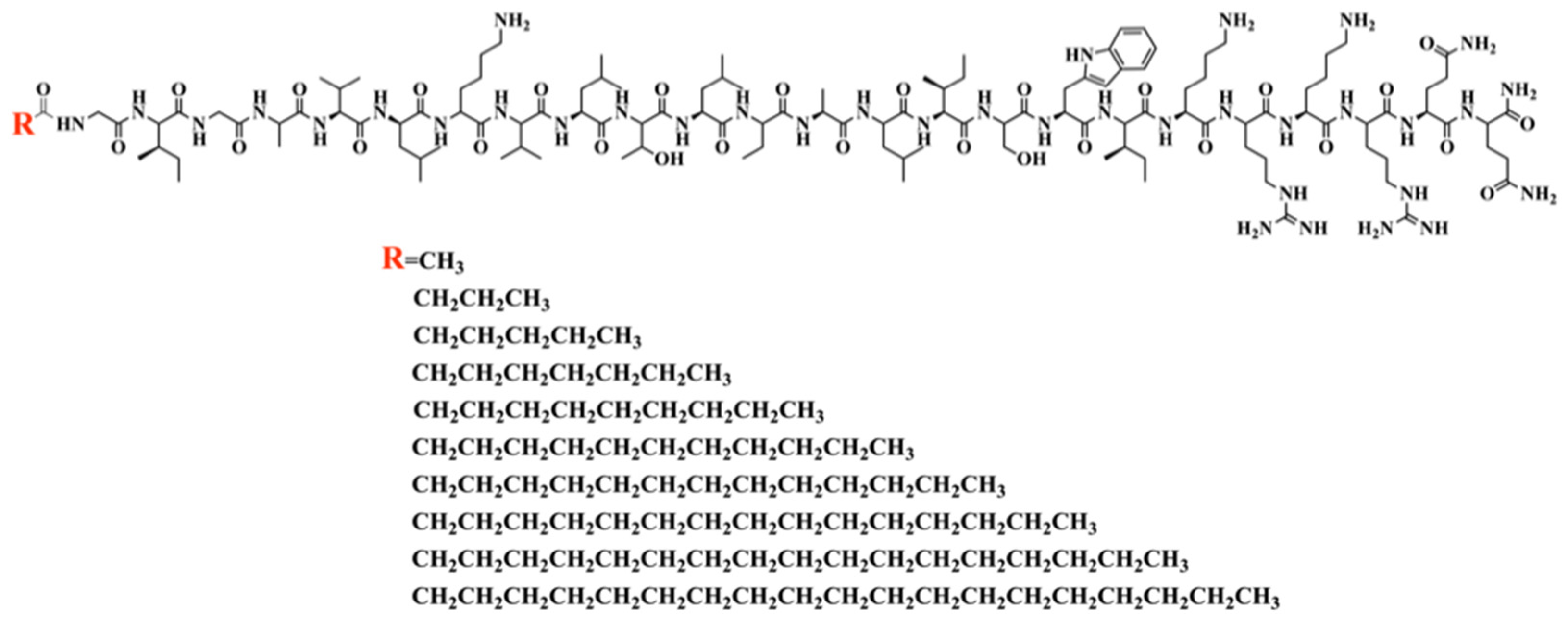
In this study, we aimed to design and synthesize a new series analog of melittin with potent antimicrobial activity, low hemolysis, and high proteolytic stability. Fatty acids of various chain lengths ranging from C2 to C16 were linked to the N-terminal of the melittin sequence. The structural formulas of MDLs were shown in
Figure 1.
All MDLs were synthesized using solid-phase synthesis and characterized by ESI-MS and RP-HPLC. The sequences, molecular weights, and retention time of these MDLs were listed in
Table 1.
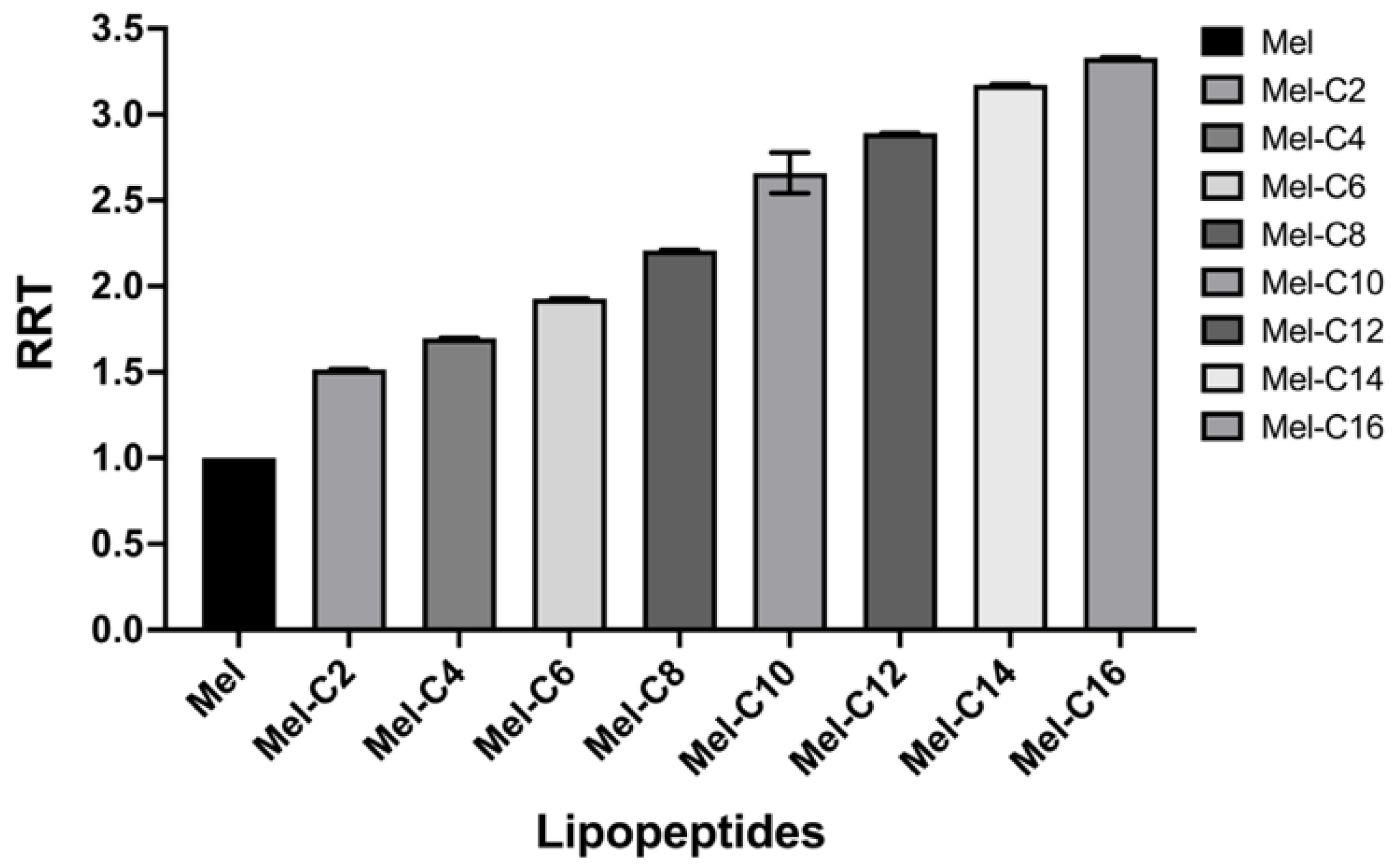
The hydrophobicity, amphipathic, and positive charge distribution of lipopeptides is crucial for these antimicrobial activities [
14]. Among these, hydrophobicity has been deemed essential for promoting hydrophobic interaction with the lipid bilayer, leading to membrane disruption, cytoplasm leakage, and eventual cell death [
15]. Lipopeptides with different peptide sequences and chain lengths usually show different hydrophobicity, generating different retention times (RTs) in the RP-HPLC analysis. The more hydrophobic the lipopeptide, the longer retention time on the column [
16]. The RT of each MDL was recorded and shown in Table. 1 and used to calculate the relative retention time (RRT) with melittin, as exhibited in
Figure 2.
These results indicated that with the longer length of the fatty acid covalently bound to melittin, the RRT of MDLs gradually increased. A similar finding has been reported in a previous study. Liu
et al. designed a series of N-methylated lipopeptides of Anoplin by conjugating fatty acids with various chain lengths (C8~C14), showing that the increase of RRT was associated with the length of fatty acids conjugated [
9].
2.2. The Secondary Structure of MDLs
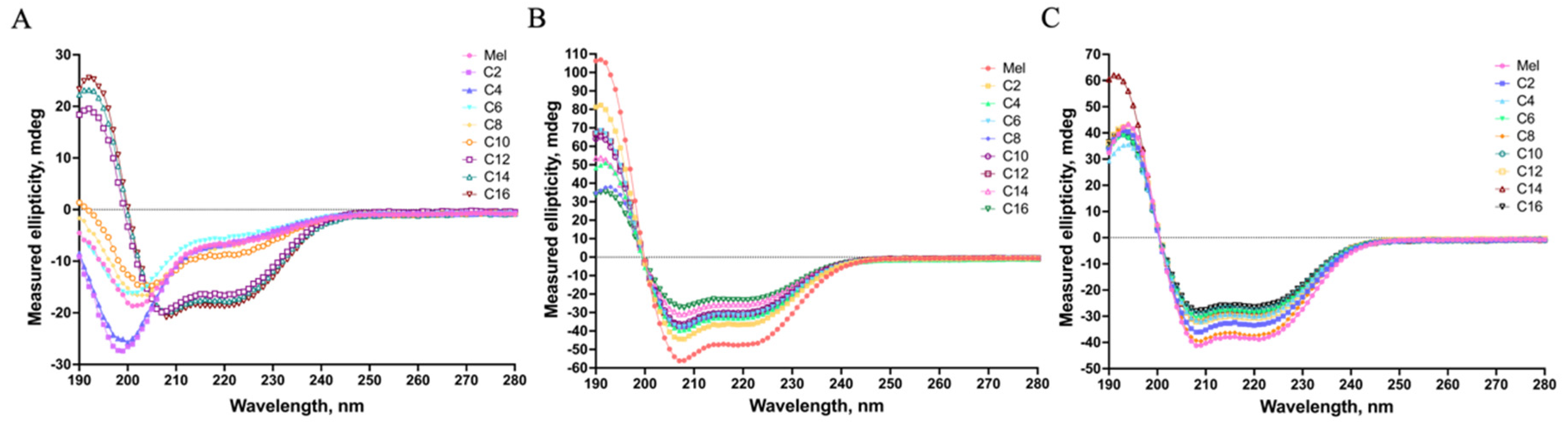
The secondary structure of antimicrobial peptides plays a vital role in their biological activities of disturbing cell membranes [
17]. Herein, the secondary structures of MDLs were determined by CD spectroscopy under different environments and shown in
Figure 3.
The CD spectra shown in
Figure 3A indicated that melittin and the MDLs with C2~C10 tail adopted a definite random-coil conformation in PBS, and the MDLs with C12~C16 tail formed α-helical conformation. This result agreed with an early report that fatty acid conjugation can increase the α-helix content of the lipopeptide structure [
18]. In 50% TFE or 25 mM SDS (
Figure 3B and 3C), the MDLs displayed a typical α-helical conformation, shown by one positive dichroic band at 190 nm and double negative dichroic bands at 208 and 222 nm. To further elaborate the CD data, the contents of α-helix and β-fold were calculated and displayed in
Table 2.
The MDLs exhibited different α-helical contents in 50% TFE. As shown in
Table 2, the α-helical contents of the MDLs were less than that of the parent peptide melittin. Additionally, the α-helical contents of the MDLs tended to decrease with the growth of fatty acid carbon chains. Moreover, in the presence of 25 mM SDS, the α-helical contents tended to decrease with the increased length of the fatty acid chain. In contrast, the β-fold contents of the MDLs showed an increasing trend. A similar finding has been reported in a previous study [
19].
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity in vitro
Recently, multiple studies have found that coupling a fatty acid to antimicrobial peptides could modify both the activity and selectivity of the peptide and the length of the fatty acid was found to be directly correlated to the antimicrobial activity of fatty acid-conjugated antibacterial peptide [
20,
21,
22]. Alexander
et al. detected the antimicrobial activity, structure, and solution assembly properties of peptide AKK conjugated with fatty acids of different carbon chain lengths, and the result showed that the antimicrobial activity of conjugated peptide increased with the fatty acids carbon chain lengths up to 16 carbons [
23]. Here, we designed and synthesized a set of lipopeptides by coupling different lengths of fatty acids to the N-terminus of melittin to reinforce the antimicrobial activity. The antimicrobial efficacy of novel melittin derivatives against both standard and multidrug-resistant strains was assessed, and the results were presented in
Table 3. The result demonstrated that the MDLs exerted broad antimicrobial potency, and fatty acid conjugation leads to a length-dependent antimicrobial activity. When the conjugated fatty acid chain length ranged from 2 to 10 carbons, the MIC values gradually lowered, meaning a remarkable fatty acid chain length-dependent increase in the antimicrobial activity. However, an opposite trend was provided when the conjugated fatty acid chain length was more than 10 carbons. Our results were consistent with the previous report that the reduced antimicrobial activity at longer carbon lengths was primarily due to the self-assembly of the fatty acid-conjugated melittin [
24].
2.5. Hemolytic Assay
Melittin is an amphipathic peptide that can interact with the red blood cell membrane, disrupt phospholipid bilayers, and exert significant hemolytic activity [
25]. Therefore, reducing the hemolysis of melittin is the critical point of its clinical application.
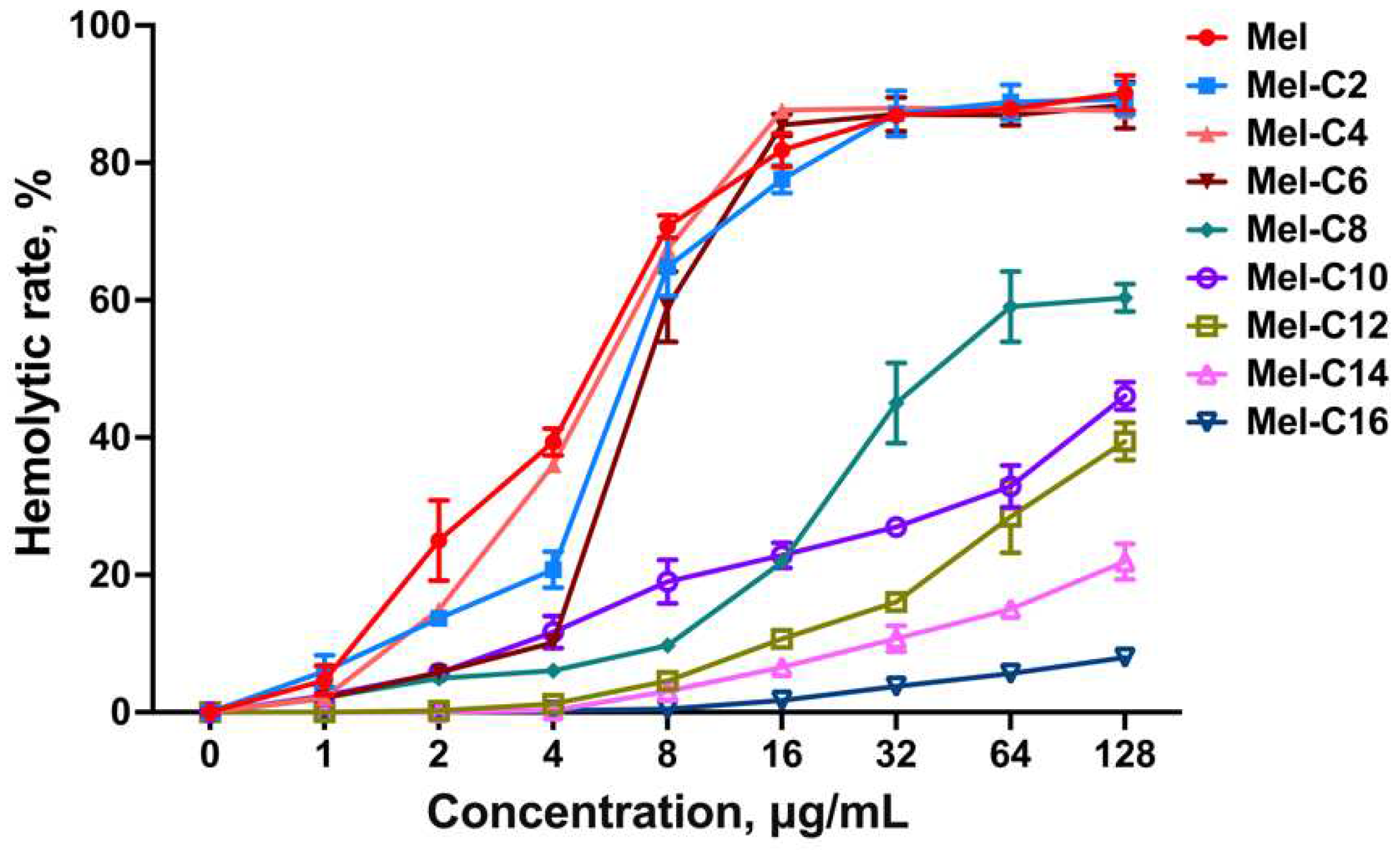
In this study, the hemolytic assay of the MDLs was assessed by measuring the percentage of hemoglobin released from lysed swine erythrocytes after treatment for 1 h, and the result was shown in
Figure 4. The hemolytic activity of the MDLs was associated with the chain length of the coupled fatty acid. Like melittin, when the concentration was over 4 μg/mL, the hemolysis rate of the MDLs with C2~C8 tail rapidly increased. This result agrees with a previous study that fatty acid conjunction can increase the hydrophobicity of AMPs and intensify their membrane interaction and final disruption [
26]. Interestingly, when the length of the carbon chain of the fatty acid exceeded 10, the hemolysis rate of the MDLs showed a decrease with the increase in the length of the fatty acid chain. When the number of carbon in the fatty acid chain reached 16, the lipopeptide did not show hemolysis even at concentrations up to 128 μg/mL. The diminished hemolysis rate is probably attributed to a longer chain length fatty acid promoting lipopeptide self-assembly, which reduces interaction between lipopeptide and erythrocyte membrane.
2.6. Stability Assay
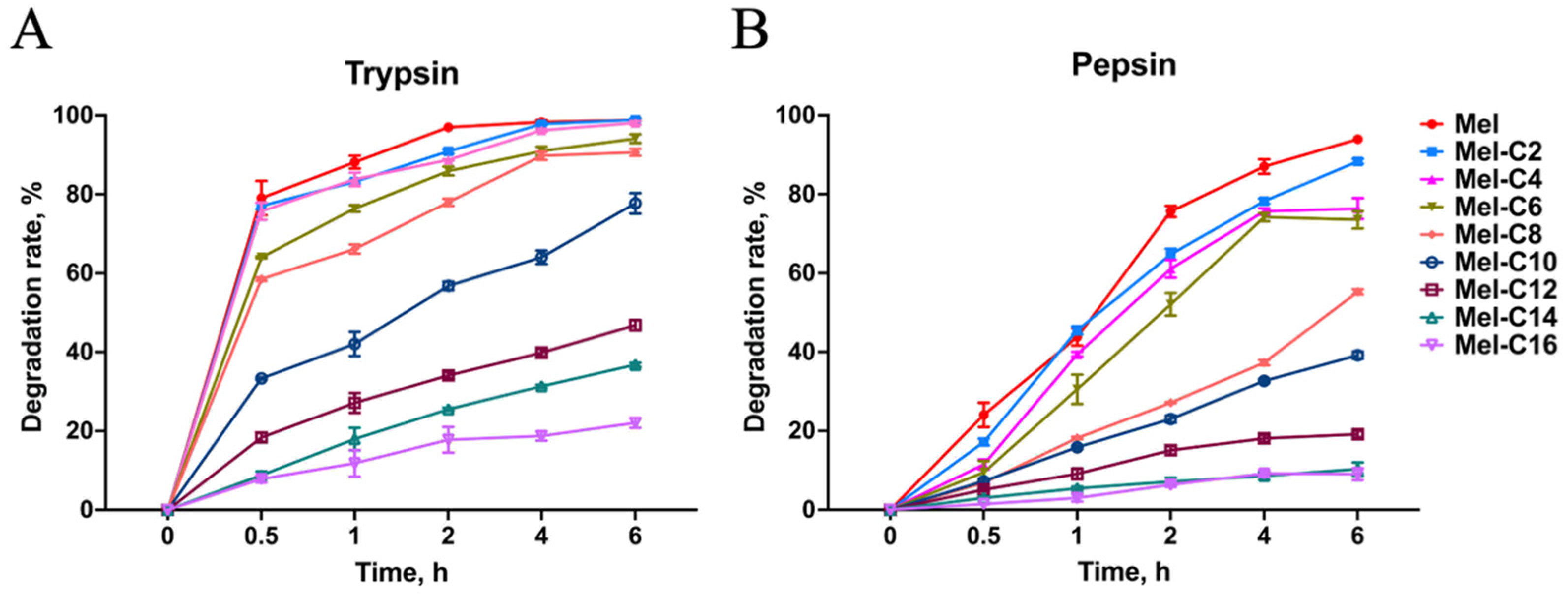
2.6.1. Protease Resistance Assay
Poor protease stability is one of the main factors that have limited melittin's clinical application. Previous research had demonstrated that melittin was digested rapidly by trypsin [
27], and was entirely degraded by pepsin after 2 h of incubation [
28]. In our study, the resistance of the MDLs to protease was examined and shown in
Figure 5.
As shown in
Figure 5A, compared with melittin, the resistance of the MDLs to trypsin was increased slowly with the extension of fatty acid carbon chain length in C2~C10. When the length of the fatty acid carbon chain exceeded 10 carbons, the degradation rate of the MDLs was lower than 40% after being incubated in a trypsin environment for 6 h. By incubation with pepsin (
Figure 5B), the degradation rate of lipopeptides was increased slowly with the extension of fatty acid carbon chain length in C2~C8. When the length of the fatty acid carbon chain exceeded 8 carbons, the degradation rate of lipopeptides was lower than 20% after being incubated in pepsin environment for 6 h. Protease resistance assay results suggested that the conjunction of fatty acids with melittin increased protease stability.
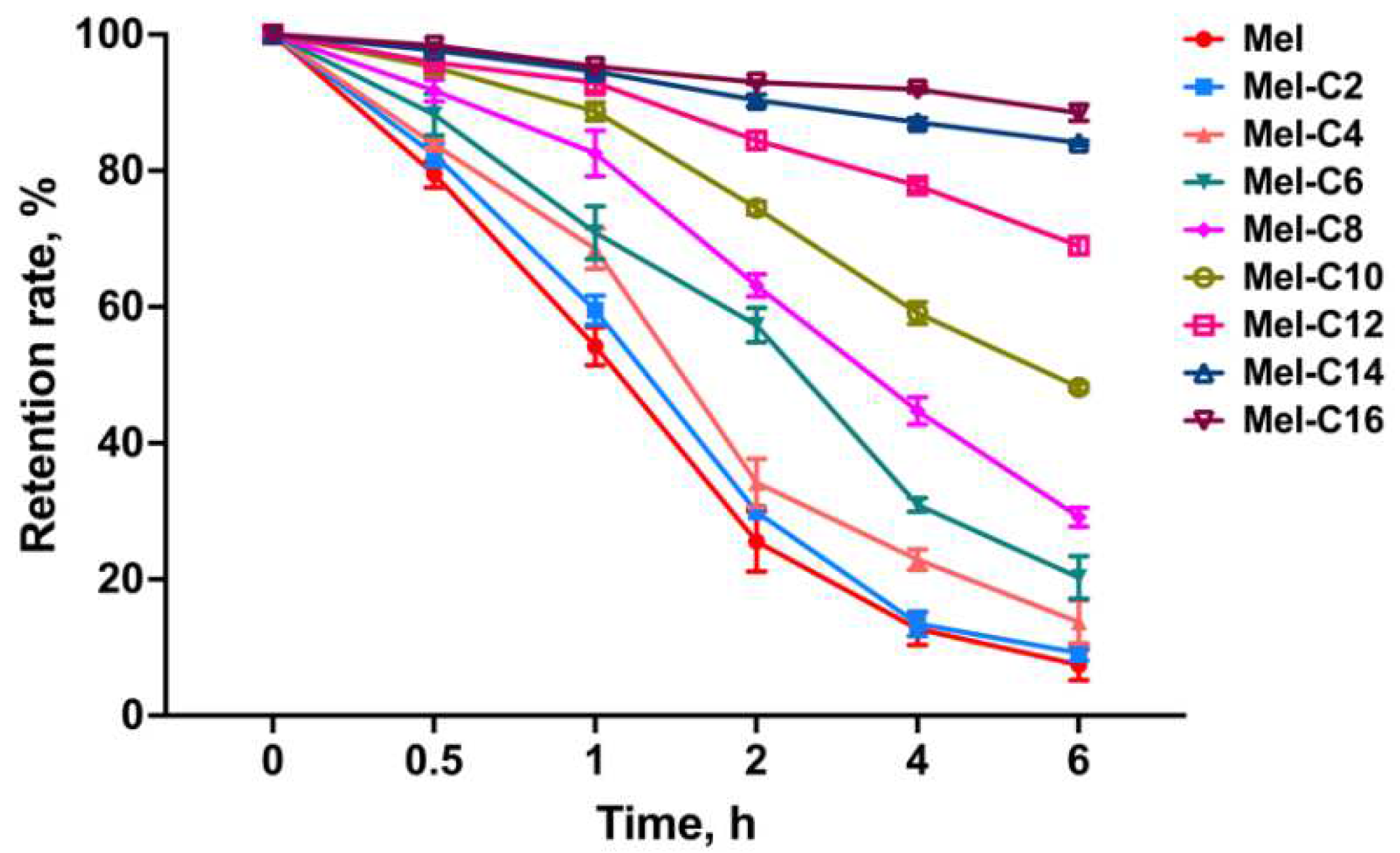
2.6.2. Serum Stability
Melittin was stable in fetal bovine serum, human serum, and human plasma, indicating that melittin could maintain stability in the presence of serum components [
5]. However, binding with serum albumin would weaken the detection of the free MDLs and reduce the antibacterial activity. Here, we evaluated the retention rate of the free MDLs by incubating them with piglet serum and the data exhibited in
Figure 6.
As shown in
Figure 6, with the incubation time prolonged, the retention rate of the MDLs in plasma gradually decreased due to the decrease of free melittin and MDLs after binding with various proteins in plasma. Moreover, the retention rate of the free MDLs gradually increased with the lengthening of the carbon chain of lipopeptides, which was attributed to the fact that fatty acids can prevent the binding of MDLs to proteins in piglet serum and was positively correlated with the length of the carbon chain.
2.6.3. Salt Sensitivity
AMPs realized antimicrobial activity by binding to the negative bacterial membrane through electrostatic interaction [
29]. Body fluids containing high salt concentrations and salt ions under physiological conditions probably affect biological activity.
E. coli ATCC 25922 and
S. aureus ATCC 25923 were treated with the MDLs in the presence of different salts. MIC measurements were used to examine the effects of different physiological salt conditions on antimicrobial activity.
The antimicrobial activity was decreased for most MDLs under salt conditions, with MIC values increasing by 1~8 fold (
Table 4). Compared with K
+, Mg
2+, and Fe
3+, the antimicrobial activity of the MDLs did not reduce remarkably in the presence of Na
+. Given free ions that can impede the electrostatic interaction between AMPs and anionic bacterial membrane due to a charge-shielding effect [
30]. It was not difficult to infer that the monovalent (K
+) and divalent (Mg
2+) ions hindered AMPs binding to bacterial membranes, resulting in decreased antimicrobial activity. Despite the fluctuating MICs in various degrees under physiological salt conditions, the MDLs with C6 and C8 were not wholly inactive. Still, they retained a relatively desirable active state, indicating they tolerated physiological salts.
2.7. The Antimicrobial Mechanisms of the MDLs
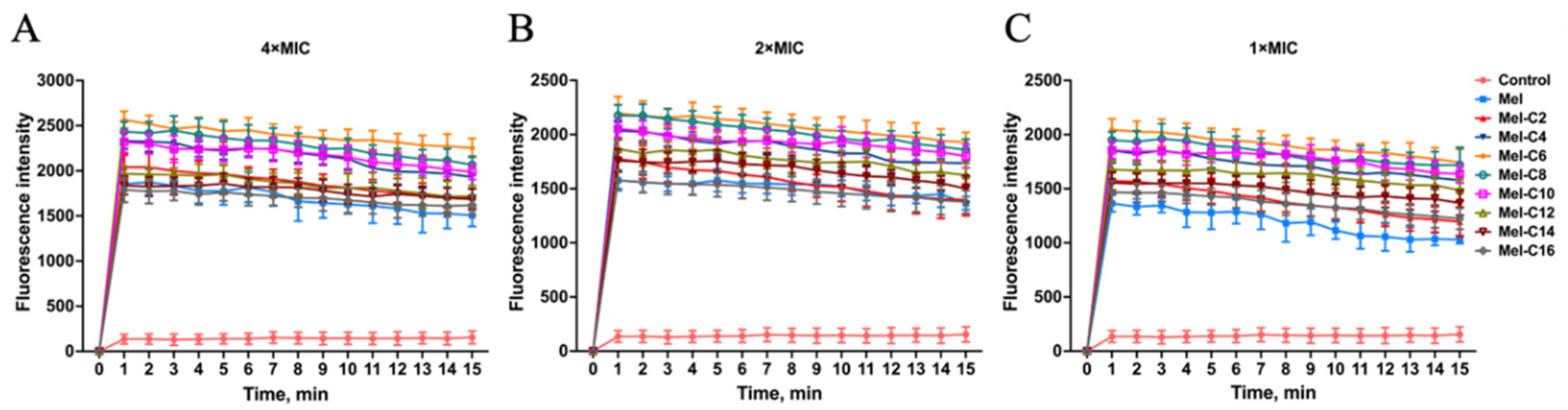
2.7.1. Outer Membrane Permeabilization Assay
The hydrophobic fluorescent probe NPN can be quenched under aqueous conditions, and its fluorescence intensity is enhanced when released into hydrophobic environments [
27]. NPN cannot enter normal bacteria and is taken up once the outer membrane of the bacteria was damaged, leading to an increase in fluorescence intensity. In our study, the ability of the MDLs to permeabilize the outer membrane of
E. coli ATCC 25922 was tested by NPN uptake assays.
As shown in
Figure 7, after incubating with the MDLs, the fluorescence intensity of NPN was increased rapidly in 1 min at concentrations ranging from 1 to 4×MIC and had concentration correlation, which indicated that the MDLs could be able to permeate the outer membrane of
E. coli ATCC 25922 quickly. For all MDLs, the outer membrane permeabilization was higher than melittin at the same concentration.
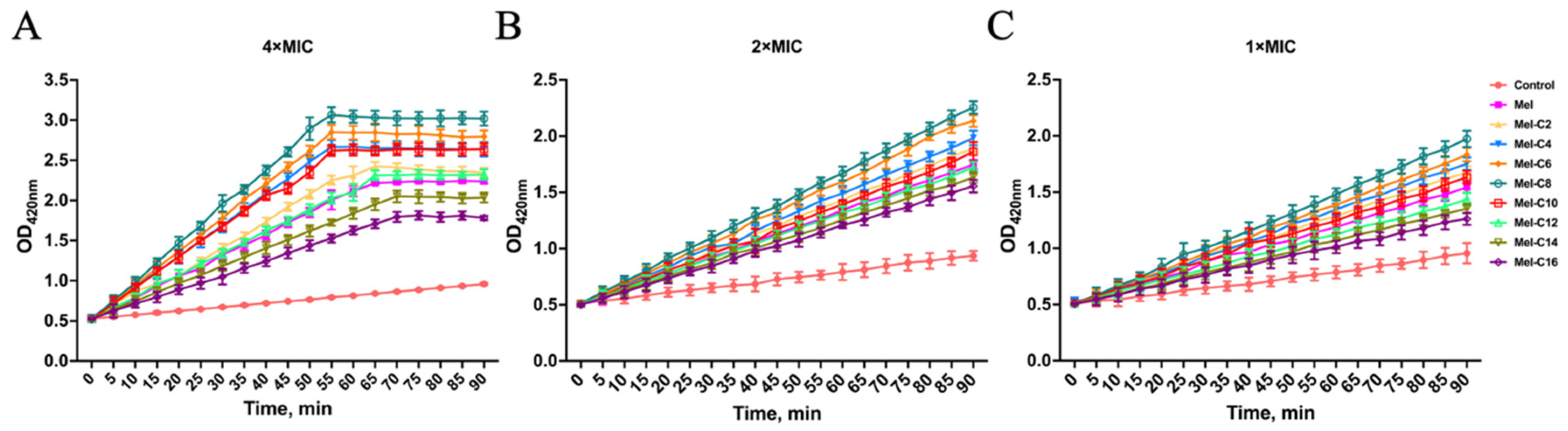
2.7.2. Inner Membrane Permeabilization Assay
The enzyme β-galactosidase is located at the bacterial inner membrane and can decompose the molecule ONPG, a chromogenic mimic of the natural substrate lactose commonly used to detect inner membrane permeabilization.
MDLs were incubated with E. coli ATCC 25922 and penetrated the inner membrane, then the ONPG entered the bacterial cytoplasm and was degraded by β-galactosidase to o-nitrophenol, which were detected at OD420nm by a microplate reader. As shown in
Figure 8, all MDLs increased the inner membrane permeability at 4×MIC. However, the inner membrane permeability of the MDLs was minor compromised at 1×MIC compared to at 4×MIC.
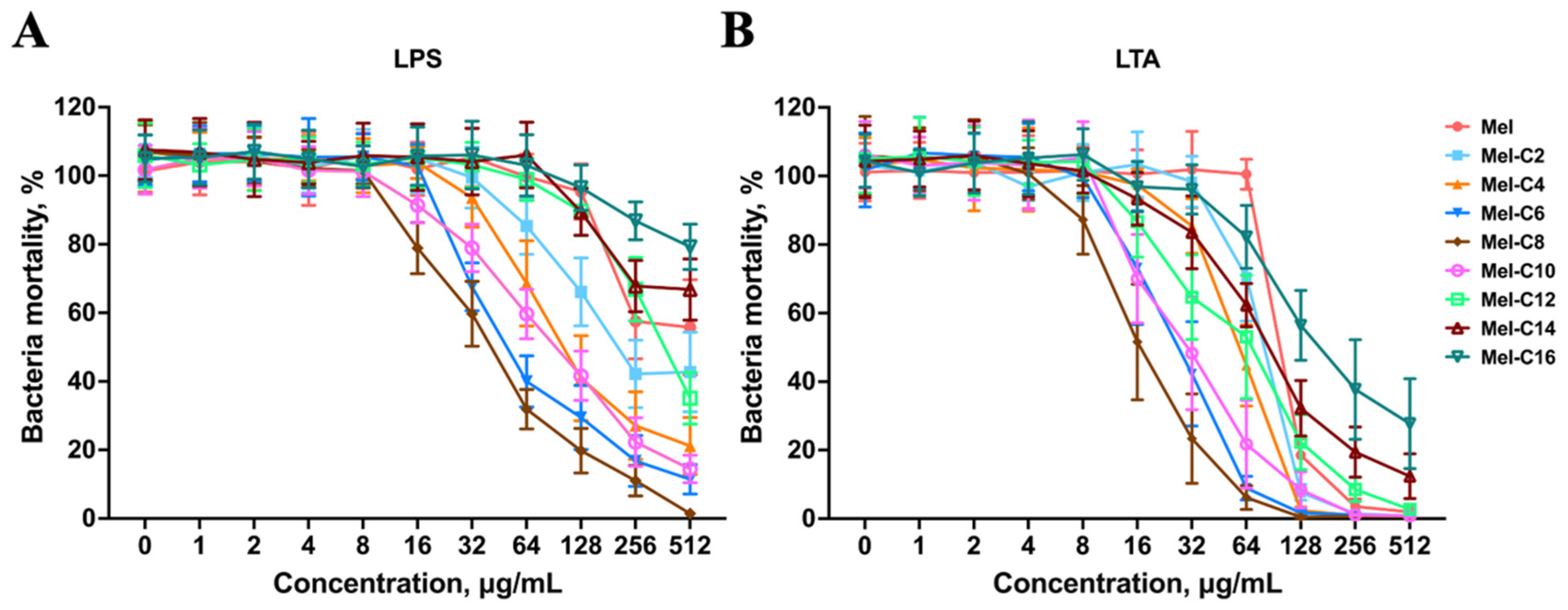
2.7.3. LPS/LTA Competitive Inhibition Assay
LPS and LTA are essential to gram-negative and -positive bacterial membranes, respectively. AMPs with positive charge target and bind to the anionic bacterial membrane surface by electrostatic interaction. The interaction with LPS or LTA is hypothesized to be the first step of lipopeptides to couple on the bacterial membrane.
As shown in
Figure 9, the MDLs could bind to a high concentration of LPS or LTA and exhibit a competitive binding to LTA rather than LPS, implying high membrane selectivity to gram-positive bacterial membranes, which explained the reason new MDLs exerted better antimicrobial activity against gram-positive than gram-negative bacteria. After an initial electrostatic interaction with LPS or LTA, the MDLs were inserted into the bacterial outer and inner lipid membrane and consequently disturbed or destroyed the bacterial membrane, resulting in bacterial death.
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Bacterial Strain
The standard strains Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 43300, Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). Listeria monocytogenes CVCC 3764 and Bacillus cereus CVCC 4101 were obtained from the National Center for Veterinary Culture Collection (CVCC). Shigella castellani CGMCC 1.1869 was obtained from the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The multidrug-resistant strain Escherichia coli was obtained from the research base of Chongqing Academy of Animal Sciences (Chongqing, China). All strains were cultured in nutrient broth overnight at 37 ℃ to a logarithmic growth phase before each experiment.
3.2. Peptide Design, Synthesis, and Analysis
The MDLs in this study were synthesized through solid-phase methods with minor modifications [
31]. Fatty acids (acetic acid, butyric acid, caproic acid, caprylic acid, decylic acid, lauric acid, myristic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, eicosanoic acid) were linked to melittin N-terminus using the same ways as amino acid condensation, respectively. The final MDLs were purified and analyzed by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) on a PrepHT 300SB-C18 column (21.2×250 mm, 7 μm) and a Kromasil-C18 column (4.6×250 mm, 5 μm), respectively. The MDLs identity was confirmed by electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS, SHIMADZU LCMS-2020, SHIMADZU, Japan)
3.3. Hydrophobicity Assay
Each MDL was dissolved and diluted to 0.1 mg/mL in deionized water and then subjected to RP-HPLC on a ChromCore120 C18 column (4.6×250 mm, 5 μm) using 0.1% TFA in water as solvent A and 0.1% TFA in acetonitrile as solvent B. The elution gradient is as follows: 5%B to 90%B over 30 min, 90%B maintained 2 min, and 90%B to 5%B over 1 min. The flow rate was 1 mL/min and measured at 220 nm. The retention time was recorded for each MDL.
3.4. Circular Dichroism (CD) Measurements
The CD spectra of MDLs were measured at 25 ℃ on a CHIRASCAN spectrometer (Applied Photophysics, UK) using a quartz cell with 1.0 mm path length and recording from 180 to 260 nm with a scanning speed of 50 nm/min and the bandwidth was 1 nm to study the relationship between the secondary structures and antimicrobial activity of MDLs. The optical path and slit width were 0.1 cm and 0.1 nm, respectively. The MDLs solutions with a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL were prepared in deionized water to mimic an aqueous environment, 50% TFE to mimic the hydrophobic condition of the microbial membrane, and 25 mM SDS micelles to mimic the negatively charged prokaryotic membrane, respectively. The observed ellipticity was converted to molar ellipticity by using the following equation:
where
[θ] is molar ellipticity (deg·cm2·dmol-1),
is the observed ellipticity corrected for the buffer at a given wavelength (mdeg), MRW is the mean residue molecular weight (molecular weight/number of amino acids),
c is the peptide concentration (mg/mL), and
l is the path length(cm). Assuming lipopeptides were a two-state model, the percentage of α-helix structure of MDLs was calculated using the following equation:
3.5. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Measurements
Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) was determined using the broth microdilution method with a minor modification [
32]. In brief, bacteria (
S. aureus ATCC 43300,
E. faecalis ATCC 29212,
E. coli ATCC 25922,
P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853,
L. monocytogenes CVCC 3764,
B. cereus CVCC 4101,
S. Castellani CGMCC 1.1869, multidrug-resistant strain E. coli) were cultured in Nutrient Broth (NB) medium to logarithmic phase and diluted to 1×10
6 CFU/mL. The MDLs were dissolved to a final concentration of 256~0.25 μg/mL in NB medium by 2-fold dilutions. 50 μL different concentrations of MDLs solution and an equal volume of bacterial suspension were added to a 96-well plate and then incubated at 37 ℃ for 18 h. The minimum concentration of MDLs with no visible growth of bacteria was defined as MIC. Medium-containing bacteria without MDLs were set as the negative control. Each measurement was performed three times independently.
3.6. Hemolytic Activity Assay
The hemolytic activity of the MDLs was evaluated as described before with a minor modification [
33]. Swine erythrocyte was collected by centrifugation at 1000 rpm for 5 min, washed three times, and suspended to a final concentration of 8% vol/vol with PBS. An equal volume of erythrocyte suspension and MDLs solution with various concentrations was mixed in a 96-well plate and incubated for 1 h at 37 ℃. After centrifugation at 1000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was transferred to a 96-well plate. The supernatant's optical density (OD) was measured at 490 nm using a microplate reader (Synergy H1, BioTek, USA). Untreated erythrocytes and erythrocytes treated with 1% Triton X-100 were employed as negative and positive controls, respectively. The hemolysis percentage was calculated from the following equation:
3.7. Stability Assay
3.7.1. Protease Resistance Assay
The resistance of MDLs to trypsin and pepsin was evaluated based on previous studies with minor modifications [
34]. After incubation with trypsin and pepsin, the MDLs degradation was further determined using RP-HPLC analysis to assess the protease's effect on MDLs stability. 500 μg/mL of each MDL was mixed with an equal volume of 0.2 mg/mL of trypsin and pepsin and incubated at 37 °C for 6 h. Aliquots of 50 μL were withdrawn at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 6 h and incubated at 60 °C for 5 min to terminate the reaction. Then, samples were centrifugated at 13,000 rpm for 15 min, and RP-HPLC detected enzymatic digestion of MDLs. Samples were gradient eluted of 5~95% ACN/H2O in 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 1 mL/min within 30 min, and the ultraviolet absorbance was set as 220 nm.
3.7.2. Serum Stability
The serum stability of MDLs was analyzed by RP-HPLC and resistance assay like protease resistance assay. Fresh piglet serum was harvested and incubated with an equal volume of MDLs (500 μg/mL) at 37 °C for 6 h. At 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 6 h, aliquots of samples were withdrawn, and the degradation reaction was terminated by acetonitrile. Then, samples were centrifugated at 13,000 rpm for 15 min, and RP-HPLC analyzed the supernatants.
3.7.3. Salt Sensitivity
MIC determination of S.aureus ATCC 43300 and E. coli ATCC 25922 was performed at physiological salt concentrations (150 mM NaCl, 4.5 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, and 4 mM FeCl3) as described above to evaluate the effect of salt on the bacteriostatic activity of MDLs. The results were detected in triplicate and tested at least twice.
3.8. Antimicrobial Mechanism
3.8.1. Outer Membrane Permeabilization Assay
The outer membrane permeabilization of MDLs was measured using a fluorescent dye NPN assay. Briefly,
E. coli ATCC 25922 was cultured to logarithmic phase in NB medium and diluted to OD600 nm=0.5. After centrifugation at 8500 rpm for 5 min, the bacterial precipitation was washed three times with PBS and suspended with half-volume in the same buffer. The MDLs were dissolved in PBS to final concentrations of 4, 2, and 1×MIC and were added to a 96-well black plate. The bacterial suspension was added after mixing with NPN dye (40 mM). Changes in the fluorescence were recorded using a microplate reader within 15 min (excitation was 350 nm, emission was 420 nm). PBS without MDLs was the negative control, and PBS without the MDLs or bacteria was the blank control. The values were monitored to % NPN uptake using the following equation:
Ft is the fluorescence monitored at different MDLs concentrations; F0 is the initial fluorescence of NPN in the absence of the MDLs, which is the fluorescence of negative control; Fm is the fluorescence monitored when polymyxin B is added. Polymyxin B was used as a positive control.
3.8.2. Inner Membrane Permeabilization Assay
The inner membrane permeabilization of bacteria treated with MDLs was determined by measuring the release activity of bacterial cytoplasm galactosidase utilizing ONPG as a substrate. E. coli ATCC 25922 was cultured in NB medium to logarithmic phase and diluted to OD 420 nm=0.6. Bacteria were harvested by centrifugation at 1500 rpm for 10 min, washed thrice with PBS, and suspended with half-volume in the same buffer. ONPG (30 mM) was added to a 96-well plate with different concentrations of MDLs, and the bacterial suspension was added to finally give MDLs concentrations of 4, 2, and 1×MIC, respectively. PBS without MDLs was used as the negative control, and 1% TritonX-100 was the positive control. OD value at 420 nm detected by a microplate reader indicated inner membrane permeabilization.
3.8.3. LPS/LTA Competitive Inhibition Assay
Newly synthesized MDLs were incubated with lipopolysaccharide or lipoteichoic acid of various concentrations for 30 min at 37 ℃, then incubated with E. coli ATCC 25922 for 18 h, and modulated the final concentration of the MDLs was 1×MIC, the LPS/LTA final concentrations varied from 1 to 512 mg/mL. After incubation, the OD value of bacterial culture suspension was measured by a microplate reader at 600 nm. Three independent experiments were performed in triplicate.
4. Conclusion
In this study, we synthesized a series of new MDLs with an N-terminal fatty acid conjugation approach. Most exerted perfect antimicrobial potential against gram-positive bacteria, including multidrug-resistant strain E. coli. Amongst, C8-Mel presented the highest antimicrobial selectivity with low cytotoxicity and maintained better antimicrobial activity in the presence of physiological salts or serum. Most notably, with the unique membrane mechanisms, all MDLs could bind LPS or LTA, killing bacteria by increasing the permeability of the outer and inner membrane and damaging membrane integrity, leading to intracellular content leakage. Therefore, we provided evidence that the newly designed C6-Mel and C8-Mel, with many preferable advantages, were considered novel antimicrobial candidates for fighting the increasing gram-positive bacterial resistance.
Author Contributions
Data curation, Li Chen; Formal analysis, Sheng Huang and Shan Jiang; Writing – original draft, Sheng Huang and Guoqi Su; Writing – review & editing, Feiyun Yang and Jinxiu Huang.
Funding
This research was financed from the following funds: Special Project for Performance Incentive and Guidance of Research Institutions in Chongqing (21524, cstc2021jxjl80001), Chongqing Natural Science Foundation General Project (CSTC2021jcyj-msxmX0807).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank to Yi Jian from School of Digital Media, Chongqing College of Electronic Engineering for providing figures and tables modifyed assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Reynolds, D.; Burnham, J. P.; Vazquez Guillamet, C.; McCabe, M.; Yuenger, V.; Betthauser, K.; Micek, S. T.; Kollef, M. H., The threat of multidrug-resistant/extensively drug-resistant Gram-negative respiratory infections: another pandemic Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 166. [CrossRef]
- Smith, R. P.; May, H. E.; AbuOun, M.; Stubberfield, E.; Gilson, D.; Chau, K. K.; Crook, D. W.; Shaw, L. P.;
Read, D. S.; Stoesser, N.; Vilar, M. J.; Anjum, M. F., A longitudinal study reveals persistence of antimicrobial
resistance on livestock farms is not due to antimicrobial usage alone. Front Microbiol 2023, 14, 1070340. [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, Y., A systematic review on antibiotics misuse in livestock and aquaculture
and regulation implications in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 798, 149205. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y. Probing Changes in Ca2+-Induced Interaction Forces between Calmodulin and Melittin by Atomic Force Microscopy. Micromachines 2020, 11, 906. [CrossRef]
- Lima, W.G.; de Brito, J.C.M.; Cardoso, V.N.; Fernandes, S.O.A. In-depth characterization of antibacterial activity of melittin against Staphylococcus aureus and use in a model of non-surgical MRSA-infected skin wounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 156, 105592. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.K.; Ahmad, A.; Asthana, N.; Azmi, S.; Srivastava, R.M.; Srivastava, S.; Verma, R.; Vishwakarma, A.L.; Ghosh, J.K. Cell-Selective Lysis by Novel Analogues of Melittin against Human Red Blood Cells and Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 7920–7929. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Jiang, K.; Xie, C.; Zhan, C.; Wang, H.; Lu, W. Co-delivery of paclitaxel and melittin by glycopeptide-modified lipodisks for synergistic anti-glioma therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 13069–13077. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Meng, D. Unnatural amino acids: promising implications for the development of new antimicrobial peptides. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 49, 231–255. [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, N.; Zhong, C.; Zhu, Y.; Gou, S.; Chang, L.; Bao, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J. Effect of N-methylated and fatty acid conjugation on analogs of antimicrobial peptide Anoplin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105453. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Yuan, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, N.; Shan, A. Strategies employed in the design of antimicrobial peptides with enhanced proteolytic stability. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 59, 107962. [CrossRef]
- Grimsey, E.; Collis, D.W.; Mikut, R.; Hilpert, K. The effect of lipidation and glycosylation on short cationic antimicrobial peptides. BBA-Biomembranes 2020, 1862, 183195. [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; He, S.; Yin, K.; Zhang, B.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Pei, N.; Huang, L. Effects of N-terminal modifications on the stability of antimicrobial peptide SAMP-A4 analogues against protease degradation. J. Pept. Sci. 2021, 27, e3352. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Gou, S.; Xie, J.; Yao, J.; Ni, J. Antimicrobial peptides conjugated with fatty acids on the side chain of D-amino acid promises antimicrobial potency against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 141, 105123. [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.-L.; Hu, X.-X.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Yi, H.; Wang, X.-K.; He, Q.-Y.; You, X.-F.; Li, Z.-R. Design, Synthesis, and Bioactivity of Cyclic Lipopeptide Antibiotics with Varied Polarity, Hydrophobicity, and Positive Charge Distribution. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1796–1806. [CrossRef]
- Balleza, D.; Alessandrini, A.; Beltrán García, M. J., Role of Lipid Composition, Physicochemical Interactions, and Membrane Mechanics in the Molecular Actions of Microbial Cyclic Lipopeptides. J Membrane Biol 2019, 252, 131–157. [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, D.; Jaśkiewicz, M.; Bauer, M.; Gołacki, K.; Kamysz, W. Ultrashort Cationic Lipopeptides–Effect of N-Terminal Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Type on Antimicrobial Activity and Hemolysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 257. [CrossRef]
- Jujjavarapu, S.E.; Dhagat, S. In Silico Discovery of Novel Ligands for Antimicrobial Lipopeptides for Computer-Aided Drug Design. Probiotics Antimicro 2017, 10, 129–141. [CrossRef]
- Chu-Kung, A.F.; Bozzelli, K.N.; Lockwood, N.A.; Haseman, J.R.; Mayo, K.H.; Tirrell, M.V. Promotion of Peptide Antimicrobial Activity by Fatty Acid Conjugation. Bioconjugate Chem. 2004, 15, 530–535. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Liu, T.; Gou, S.; He, Y.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J., Design and
synthesis of new N-terminal fatty acid modified-antimicrobial peptide analogues with potent in vitro
biological activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111636. [CrossRef]
- Storck, P.; Umstätter, F.; Wohlfart, S.; Domhan, C.; Kleist, C.; Werner, J.; Brandenburg, K.; Zimmermann,
S.; Haberkorn, U.; Mier, W., Fatty acid conjugation leads to length-dependent antimicrobial activity of a
synthetic antibacterial peptide (Pep19-4LF). Antibiotics 2020, 9, 844. [CrossRef]
- Malina, A.; Shai, Y. Conjugation of fatty acids with different lengths modulates the antibacterial and antifungal activity of a cationic biologically inactive peptide. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 695–702. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, N.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Fatty acid modified-antimicrobial peptide analogues with potent antimicrobial activity and topical therapeutic efficacy against Staphylococcus hyicus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 5845–5859. [CrossRef]
- Chu-Kung, A.F.; Nguyen, R.; Bozzelli, K.N.; Tirrell, M. Chain length dependence of antimicrobial peptide–fatty acid conjugate activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 160–167. [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.-J.; Lin, H.; Caroline, V.; Chew, Y.S.; Pang, L.M.; Aung, T.T.; Li, J.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Tan, D.T.H.; Verma, C.; et al. N-Lipidated Peptide Dimers: Effective Antibacterial Agents against Gram-Negative Pathogens through Lipopolysaccharide Permeabilization. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 6533–6548. [CrossRef]
- Watala, C.; Gwoździński, K. Melittin-induced alterations in dynamic properties of human red blood cell membranes. Chem. Interactions 1992, 82, 135–149. [CrossRef]
- Rounds, T.; Straus, S.K. Lipidation of Antimicrobial Peptides as a Design Strategy for Future Alternatives to Antibiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9692. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xie, C.; Zhang, M.; Wei, X.; Yan, Z.; Ren, Y.; Ying, M.; Lu, W. RGD-modified lipid disks as drug carriers for tumor targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7209–7216. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Tan, P.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, C.; Shan, A.; Li, L. Highly Stabilized α-Helical Coiled Coils Kill Gram-Negative Bacteria by Multicomplementary Mechanisms under Acidic Condition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 22113–22128. [CrossRef]
- Tam, J.P.; Lu, Y.-A.; Yang, J.-L. Correlations of Cationic Charges with Salt Sensitivity and Microbial Specificity of Cystine-stabilized β-Strand Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50450–50456. [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ding, J.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Fan, X.; Shen, Z., Effects of cations and pH on antimicrobial activity of thanatin and s-thanatin against Escherichia coli ATCC25922 and B. subtilis ATCC 21332. Curr Microbiol 2008, 57, 552–557.
- Choi, J.-H.; Lee, T.-K.; Byun, J.-W.; Lee, Y.-S. Preparation of a core–shell type MBHA resin and its application for solid-phase peptide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4272–4275. [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Krochmal, B.; Dudek-Wicher, R. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 165. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Shukla, R.; Kumar, R.; Weingarth, M.; Breukink, E.; Kuipers, O.P. Brevibacillin 2V, a Novel Antimicrobial Lipopeptide With an Exceptionally Low Hemolytic Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 693725. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shang, L.; Yang, G.; Dai, Z.; Zeng, X.; Qiao, S. Biosynthetic Microcin J25 Exerts Strong Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory Activities, Low Cytotoxicity Without Increasing Drug-Resistance to Bacteria Target. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 811378. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).