Submitted:
15 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
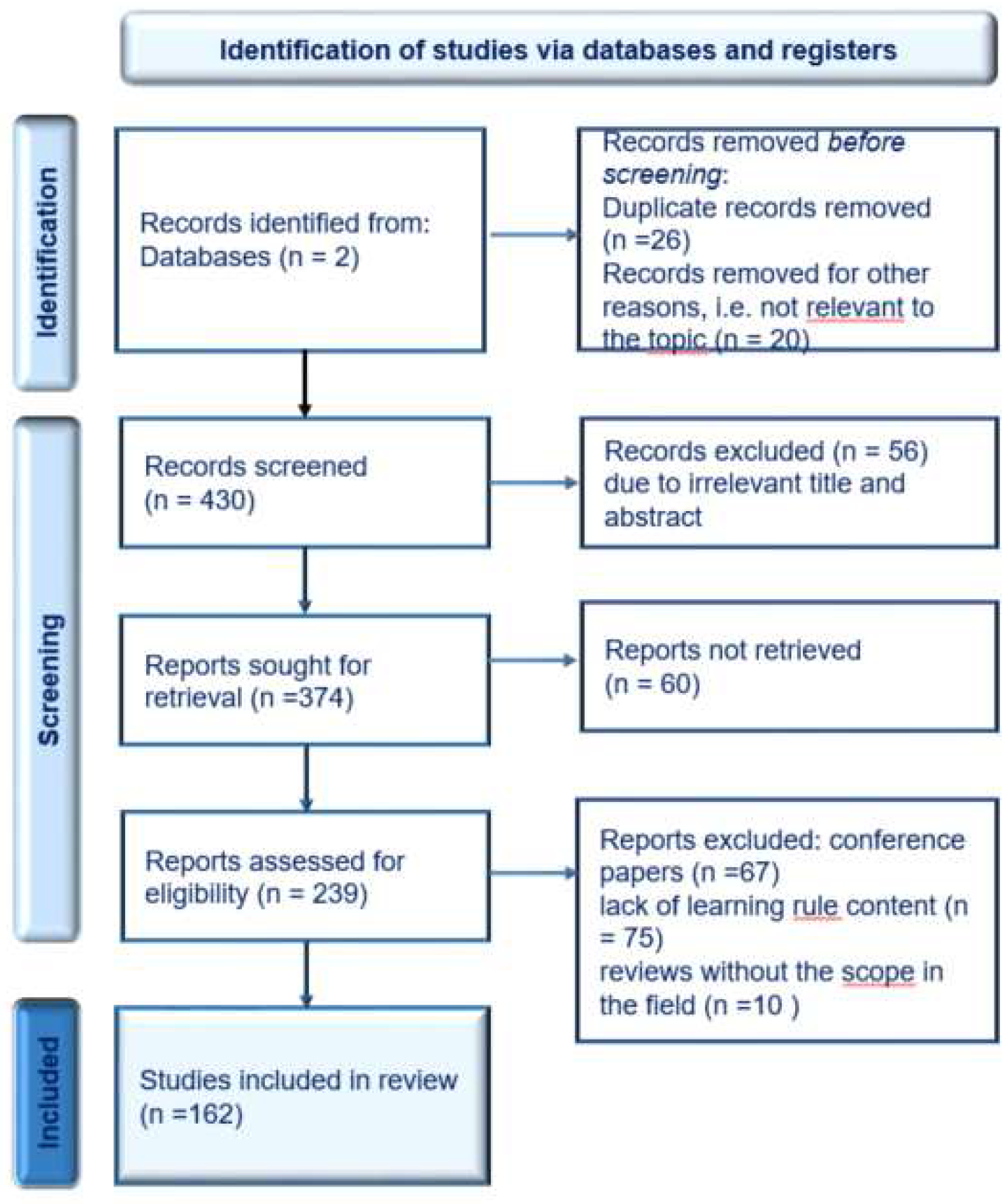
2. Materials and Methods
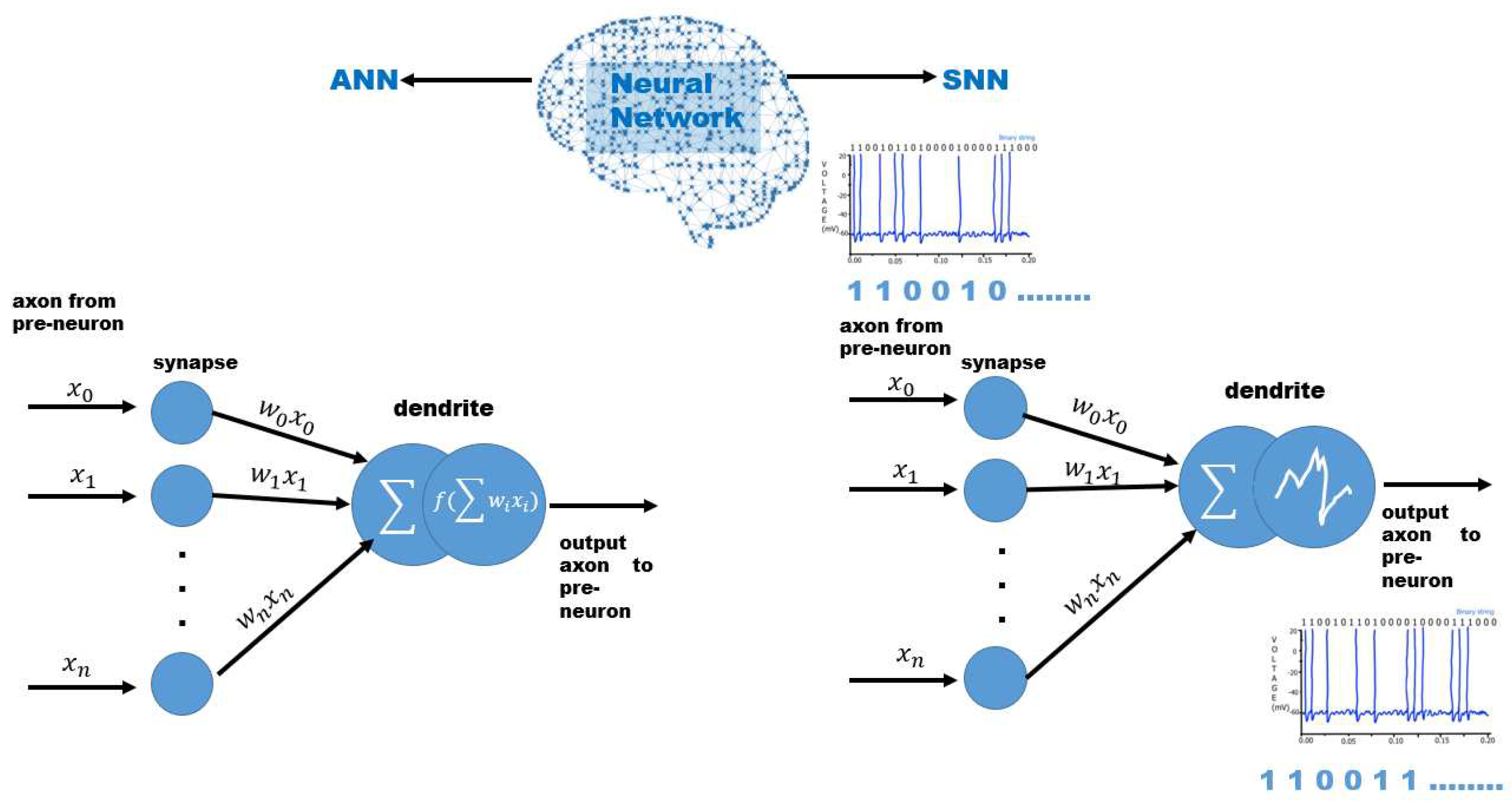
3. Neural communication
4. Taxonomy of neural network applied in the medical image segmentation process
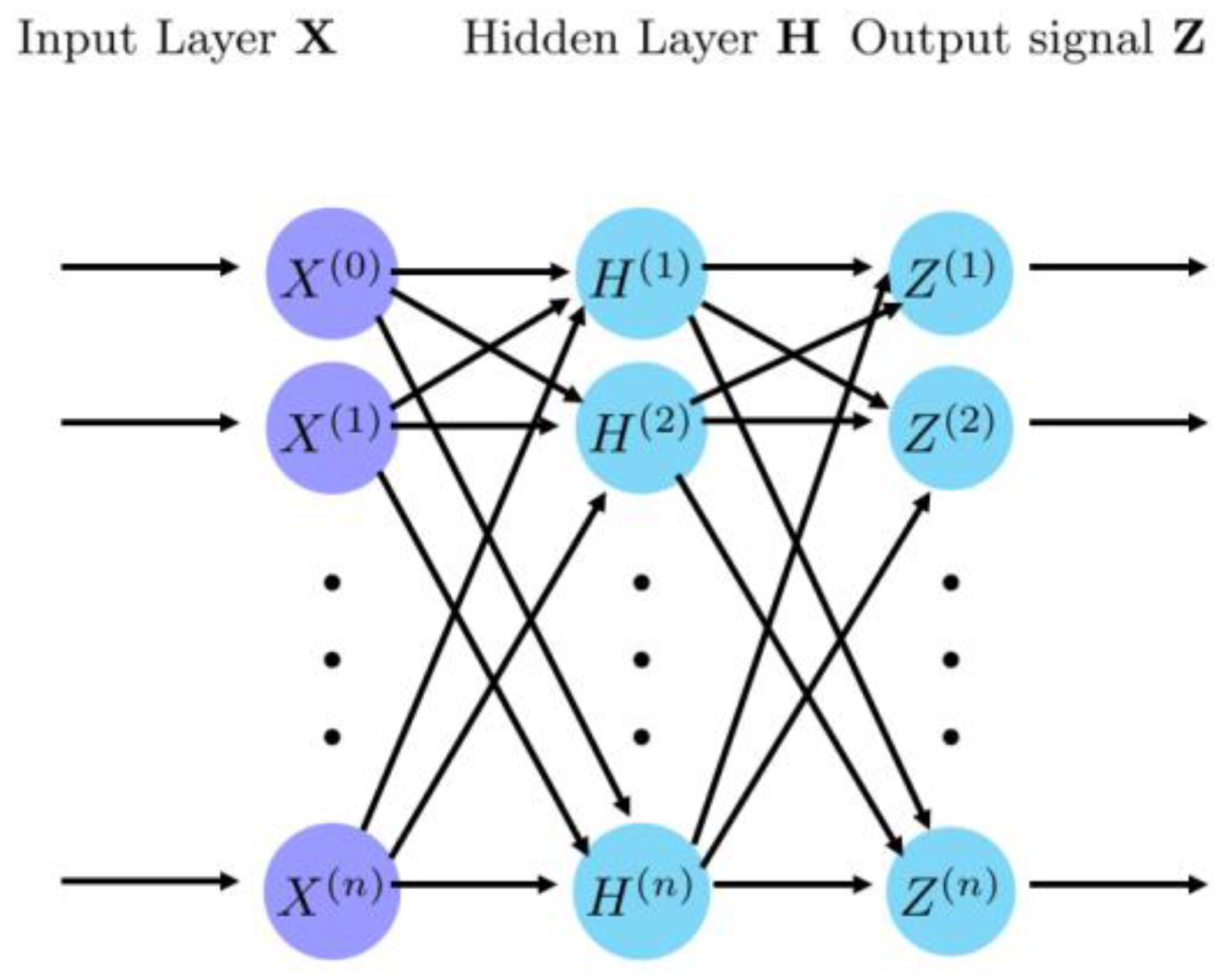
4.1. Convolutional Neural Network
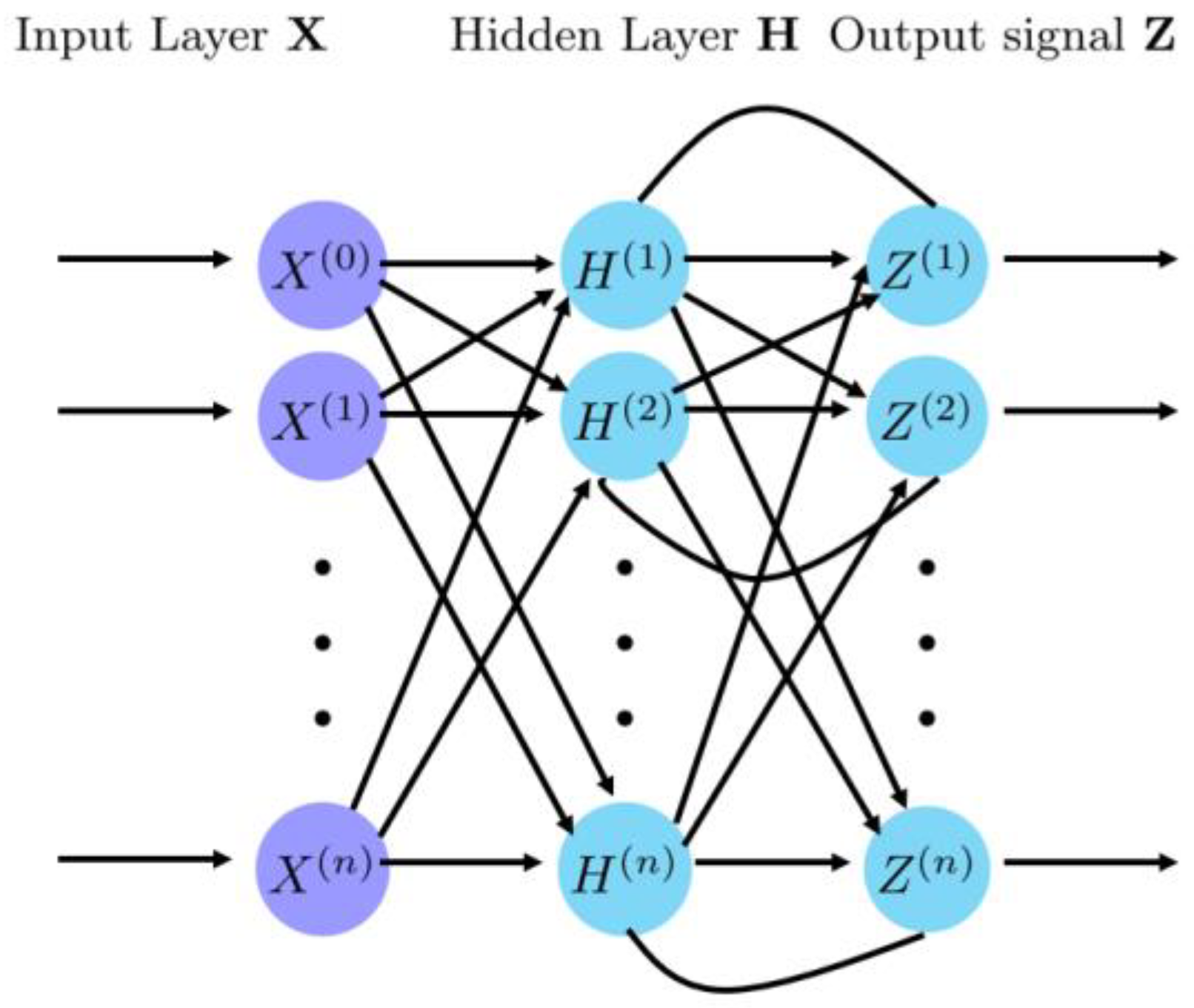
4.2. Recurrent Neural Network
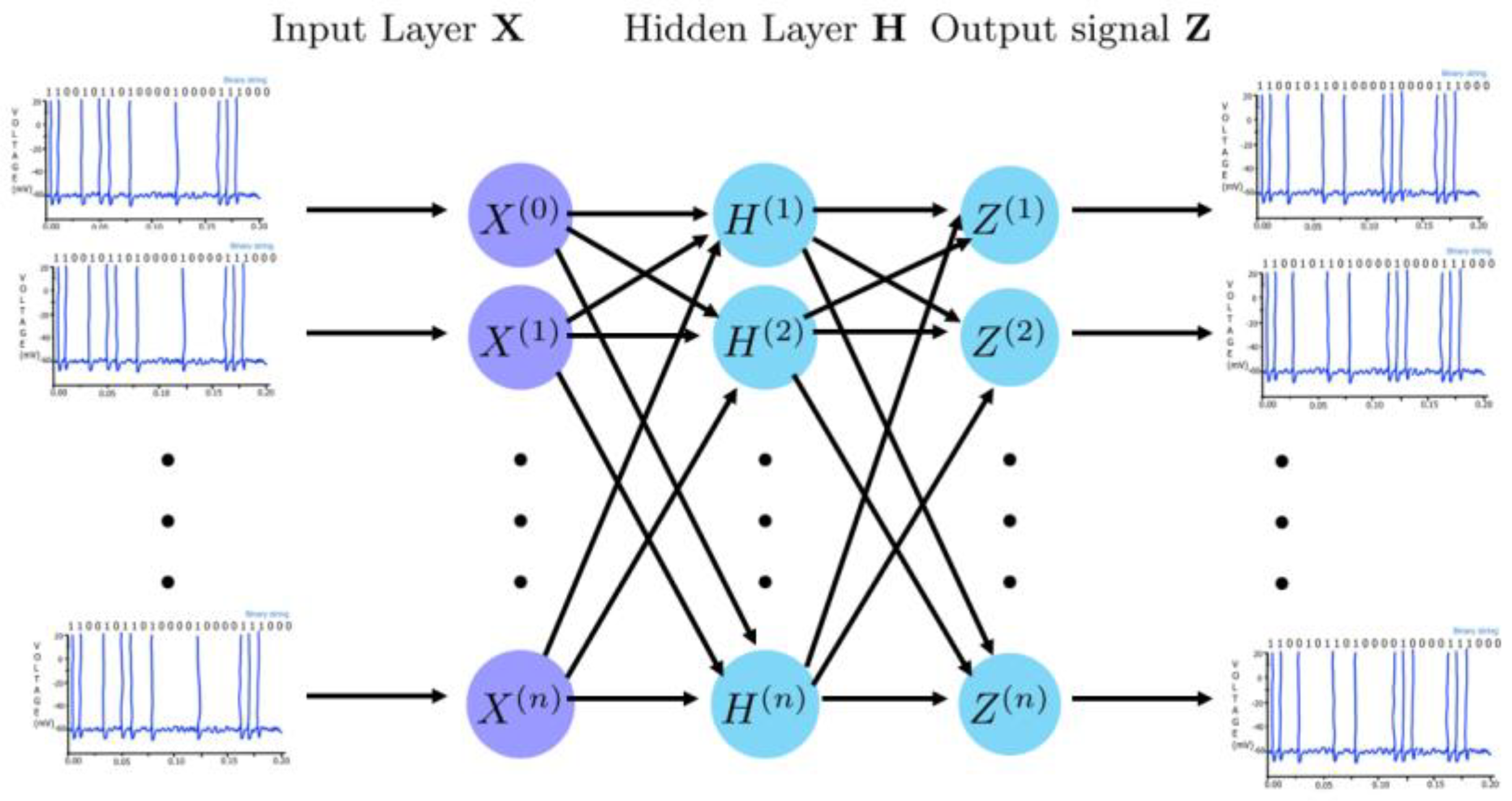
4.3. Spiking Neural Networks
5. Learning algorithms
5.1. Back Propagation Algorithm
5.2. ANN-SNN Conversion
5.3. Supervised Hebbian Learning (SHL)
5.4. Reinforcement Learning with Supervised Models
5.5. Chronotron
5.6. Bio-inspired Learning Algorithms
5.6.1. Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity
5.6.2. Spike-Driven Synaptic Plasticity
5.6.3. Tempotron Learning Rule
6. Neural networks and learning algorithms in the medical image segmentation process
7. Data availability
8. Discussion and conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herculano-Houzel, S. The remarkable, yet not extraordinary, human brain as a scaled-up primate brain and its associated cost. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 2012, 109, pp. 10661-10668. [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Shen, Z. How can artificial neural networks approximate the brain? Front. Psychol. 2023, Jane 9, pp 13:970214. PMID: 36698593; PMCID: PMC9868316. [CrossRef]
- Moscato, V.; Napolano, G.; Postiglione, M. et al. Multi-task learning for few-shot biomedical relation extraction. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023. [Online ahead of print]. Available online. (accessed 21 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Lau, R. Intelligent Metaverse Scene Content Construction. IEEE Access 2023, 11, pp. 76222-76241. [CrossRef]
- López-Ojeda, W.; Hurley, R.A. Digital Innovation in Neuroanatomy: Three-Dimensional (3D) Image Processing and Printing for Medical Curricula and Health Care. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 35, pp. 206-209. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.Y. The Metaverse for Healthcare: Trends, Applications, and Future Directions of Digital Therapeutics for Urology. Int. Neurourol. J. 2023, 27, pp. S3-S12. [CrossRef]
- Pregowska, A.; Osial, M.; Dolega-Dolegowski, D.; Kolecki, R.; Proniewska, K. Information and Communication Technologies Combined with Mixed Reality as Supporting Tools in Medical Education. Electronics 2023, 11, 3778. [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Yan, P. Multi-organ segmentation over partially labeled datasets with multi-scale feature abstraction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, pp. 3619-3629. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Z. An Effective CNN and Transformer Complementary Network for Medical Image Segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 136, 109228. [CrossRef]
- Mazurowski, M.A.; Dong, H.; Gu, H.; Yang, J.; Konz, N.; Zhang, Y. Segment anything model form medical image analysis: An experimental study. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 89 , 102918. [CrossRef]
- Sakshi, S.; Kukreja, V.; Image Segmentation Techniques: Statistical, Comprehensive, Semi-Automated Analysis and an Application Perspective Analysis of Mathematical Expressions. Arch. Computat. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, pp. 457–495. [CrossRef]
- Moztarzadeh, O.; Jamshidi, M.; Sargolzaei, S.; Keikhaee, F.; Jamshidi, A.; Shadroo, S.; Hauer, L. Metaverse and Medical Diagnosis: A Blockchain-Based Digital Twinning Approach Based on MobileNetV2 Algorithm for Cervical Vertebral Maturation. Diagnostics. 2023, 13, 1485. [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Pham, Q.-V.; Pham, M.-T.; Banh, T.-N.; Nguyen, G.-P.; Kim, D.-S. Efficient Real-Time Object Tracking in the Metaverse Using Edge Computing with Temporal and Spatial Consistency. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 71, pp. 341-356. [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Ding, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, H. Self-Supervised Medical Image Denoising Based on WISTA-Net for Human Healthcare in Metaverse. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. pp. 1 -9 2023. [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [CrossRef]
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kirtley, S.; Waffenschmidt, S.; Ayala, A.P.; Moher, D.; Page, M.J.; Koffel, J.B. PRISMA-S: An Extension to the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 39. [CrossRef]
- Adrian, E.D.; Zotterman, Y. The Impulses Produced by Sensory Nerve Endings. J. Physiol. 1926, 61, pp. 465–483. [CrossRef]
- Gerstner, W.; Kistler, W.M.; Naud, R.; Paninski, L. Neuronal Dynamics: From Single Neurons to Networks and Models of Cognition. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2014.
- Rieke, F.; Warland, D.; de Ruyter van Steveninck, R.; Bialek, W. Spikes: Exploring the Neural Code. The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997.
- van Hemmen, J.L.; Sejnowski, T.J. 23 Problems in Systems Neuroscience. Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006.
- Teich, M.C.; Khanna, S.M. Pulse-Number distribution for the neural spike train in the cat's auditory nerve. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 77, pp. 1110–1128. [CrossRef]
- Werner, G.; Mountcastle, V.B. Neural activity in mechanoreceptive cutaneous afferents: stimulus-response relations, Weber Functions, and Information Transmission. J. Neurophysiol. 1965, 28, pp. 359–397. [CrossRef]
- Tolhurst, D.J.; Movshon, J.A.; Thompson, I.D. The dependence of Response amplitude and variance of cat visual cortical neurons on stimulus contrast. Exp. Brain Res. 1981, 41, pp. 414–419. [CrossRef]
- Radons, G.; Becker, J.D.; Dülfer, B.; Krüger, J. Analysis, classification, and coding of multielectrode spike trains with hidden Markov models. Biol. Cybern. 1994, 71, pp. 359–373. [CrossRef]
- de Ruyter van Steveninck, R.R.; Lewen, G.D.; Strong, S.P.; Koberle, R.; Bialek, W. Reproducibility and variability in neural spike trains. Science 1997, 275, pp. 1805–1808. [CrossRef]
- Kass, R.E.; Ventura, V. A spike-train probability model. Neural Comput. 2001, 13, pp. 1713–1720. [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, D. The kinematics of the spike trains. Acta Phys. Pol. B. 2018, 49, pp. 2127–2138. [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. Principles of neurodynamics. Perceptrons and the theory of Bbain mechanisms. Tech. Rep., Cornell Aeronautical Lab Inc, Buffalo, NY, USA, 1961.
- Bu, T.; Fang, W.; Ding, J.; Dai, P.L.; Yu, Z.; Huang, T. Optimal ANN-SNN Conversion for High-Accuracy and Ultra-Low-Latency Spiking Neural Networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.04347, 2023. Available online. (accessed on 13 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Abbott, L.F.; Dayan, P. Theoretical Neuroscience Computational and Mathematical Modeling of Neural Systems, The MIT Press, 2000.
- Yuan, Y.; Gao, R.; Wu, Q.; Fang, S.; Bu, X.; Cui, Y.; Han, C.; Hu, L., Li, X.; Wang, X.; Geng, L.; Liu, W. ACS Sensors 2023, 8 (7), 2646-2655. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh-Dastidar, S.; Adeli, H. Third Generation Neural Networks: Spiking Neural Networks. In Advances in Computational Intelligence; Yu, W.; Sanchez, E.N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009; Volume 116. [CrossRef]
- Lindeberg, T. A time-causal and time-recursive scale-covariant scale-space representation of temporal signals and past time. Biol. Cybern. 2023, 117, pp. 21–59. PMID: 36689001 PMCID: PMC10160219. [CrossRef]
- Rueckauer, B.; Lungu, I.A.; Hu, Y.; Pfeiffer, M.; Liu, S.C. Conversion of Continuous-Valued Deep Networks To Efficient Event-Driven Neuromorphic Hardware. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, T.; Jia, S.; Xu, B. Meta neurons improve spiking neural networks for efficient spatio-temporal learning. Neurocomputing 2023, 531, pp. 217-225. [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE, 1998, 86, pp. 2278-2324.
- Mehrish, A.; Majumder, N.; Bharadwaj, R.; Mihalcea, R.; Poria, S. A review of deep learning techniques for speech processing. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101869. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A. Neural Networks and Deep Learning. Determination Press, 2015; eBook. Available online: NeuralNetworksAndDeepLearning.com (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; et al. Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, pp. 611–629. [CrossRef]
- Sherstinsky, A. Fundamentals of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 2020, 404, 132306. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh-Dastidar, S.; Adeli, H. Spiking neural networks. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2009, 19, pp., 295-308.
- Yamazaki, K.; Vo-Ho, V.K.; Bulsara, D.; Le, N. Spiking Neural Networks and Their Applications: A Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 12,b p. 863. PMID: 35884670; PMCID. [CrossRef]
- Dampfhoffer, A.; et al. Backpropagation-Based Learning Techniques for Deep Spiking Neural Networks: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 1 – 16. [CrossRef]
- Ponulak, F.; Kasinski, A. Introduction to spiking neural networks: Information processing, learning and applications. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2011, 71, pp. 409-33. PMID: 22237491.
- Wu, Y.; et al. Spatio-Temporal Backpropagation for Training High-Performance Spiking Neural Networks. Front Neurosci. 2018, 12, 331. [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Deng, L.; Song, S.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, G.; Zou, Z.; Wu, Z.; He, W.; et al. Towards artificial general intelligence with hybrid Tianjic chip architecture. Nature 2019, 572, pp. 106–111. [CrossRef]
- Rathi, N.; Chakraborty, I.; Kosta, A.; Sengupta, A.; Ankit, A.; Panda, P.; Roy, K. Exploring Neuromorphic Computing Based on Spiking Neural Networks: Algorithms to Hardware. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 243. [CrossRef]
- Rojas, R. The Backpropagation Algorithm. In Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1996; pp. 1-50. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kushwaha, S.; Alarfaj, M.; Singh, M. Comprehensive Overview of Backpropagation Algorithm for Digital Image Denoising. Electronics 2022, 11, 1590. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Khehra, B.S.; Singh, A. Back propagation artificial neural network for diagnosis of heart disease. J. Reliable Intell. Environ. 2023, 9, PP. 57–85. [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.A.; Karlik, B.; Salman, M. S. Back-propagation algorithm with variable adaptive momentum. Knowledge-Based Systems 2016, 114, 79-87. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Khosla, D. Spiking Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Energy-Efficient Object Recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 113, pp. 54–66. [CrossRef]
- Alemanno, F.; Aquaro, M.; Kanter, I.; Barra, A.; Agliari, E. Supervised Hebbian Learning. Europhys. Lett. 2023, 141, 11001. [CrossRef]
- Ponulak, F. ReSuMe—New Supervised Learning Method for Spiking Neural Networks. Technical Report, Technical Report, Poznań University of Technology, Poznań, Poland, 2005. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/ReSuMe-New-Supervised-Learning-Method-for-Spiking-Ponulak/b04f2391b8c9539edff41065c39fc2d27cc3d95a.
- Shrestha, A.; Ahmed, K.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Q. Stable Spike-Timing Dependent Plasticity Rule for Multilayer Unsupervised and Supervised Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14-19 May 2017, pp. 1999–2006. [CrossRef]
- Amato, G.; Carrara, F.; Falchi, F.; Gennaro, C.; Lagani, G. Hebbian Learning Meets Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Image Analysis and Processing – ICIAP 2019; Ricci, E., Rota Bulò, S., Snoek, C., Lanz, O., Messelodi, S., Sebe, N., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11751 pp. 1-14,; Springer: Cham, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Ponulak, F.; Kasinski, A. Supervised learning in spiking neural networks with ReSuMe: sequence learning, classification, and spike shifting. Neural Comput. 2010, 22, pp. 467–510. [CrossRef]
- Florian, R.V. The Chronotron: A Neuron That Learns to Fire Temporally Precise Spike Patterns. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40233. [CrossRef]
- Victor, J.D.; Purpura, K.P. Metric-space analysis of spike trains: theory, algorithms, and applications. Network 1997, 8, pp. 127–164. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.-H.; Zhang, Y.-D. Applicable artificial intelligence for brain disease: A survey. Neurocomputing 2022, 504, pp. 223–239. [CrossRef]
- Markram, H.; Gerstner, W.; Sjöström, P.J. A history of spike-timing-dependent plasticity. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2011, 3, 4,. [CrossRef]
- Merolla, P.A.; et al. A million spiking-neuron integrated circuit with a scalable communication network and interface. Science 2014, 345, pp. 668–673. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Characterization of Generalizability of Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity Trained Spiking Neural Networks. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 695357. [CrossRef]
- Lagani, G.; Falchi, F.; Gennaro, C.; Amato, G. Spiking Neural Networks and Bio-Inspired Supervised Deep Learning: A Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.16235, 2023. Available online. (accessed on 22 October 2023). [CrossRef]
- Gütig, R.; Sompolinsky, H. The tempotron: a neuron that learns spike timing-based decisions. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, pp. 420–428. [CrossRef]
- Cellina, M.; Cè, M.; Alì, M.; Irmici, G.; Ibba, S.; Caloro, E.; Fazzini, D.; Oliva, G.; Papa, S. Digital Twins: The New Frontier for Personalized Medicine? Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7940. [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; He, X.; Li, Z. Digital twin in healthcare: Recent updates and challenges. Digital Health 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Uhl, J.C.; Schrom-Feiertag, H.; Regal, G.; Gallhuber, K.; Tscheligi, M. Tangible Immersive Trauma Simulation: Is Mixed Reality the Next Level of Medical Skills Training? In: Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '23), New York, NY, USA, 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Article 513. [CrossRef]
- Kshatri, S.S.; Singh, D. Convolutional Neural Network in Medical Image Analysis: A Review. Arch Computat Methods Eng . 2023, 30, pp. 2793–2810. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, F.; Xu, L.; Shen, F.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. Multi-Task Refined Boundary-Supervision U-Net (MRBSU-Net) for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Segmentation in Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, pp. 5805-5816. [CrossRef]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Le Folgoc, L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B. et al. Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas. 2018. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999, Availabl. (accessed on 13 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234-241.
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Crimi, A., Bakas, S., Kuijf, H., Menze, B., Reyes, M., eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3-11.
- Alom, M.Z.; Yakopcic, C.; Hasan, M.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. Recurrent residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. J Med Imaging (Bellingham) 2019, 6(1), 014006. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zou, D.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Lu, W.; He, X. Bimodal segmentation and classification of endoscopic ultrasonography images for solid pancreatic tumor. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2023, 83, 104591. [CrossRef]
- Urbanczik, R.; Senn, W. Reinforcement learning in populations of spiking neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 250–252. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Tang, H.; Tan, K. C.; Yu, H. A brain-inspired spiking neural network model with temporal encoding and learning. Neurocomputing 2014, 138, 3-13. [CrossRef]
- Kumarasinghe, K.; Kasabov, N.; Taylor, D. Brain-inspired spiking neural networks for decoding and understanding muscle activity and kinematics from electroencephalography signals during hand movements. Sci. Rep. 2021, pp. 11, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W.B.; et al. Research Progress of spiking neural network in image classification: A Review. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, pp. 19466–19490. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, Z. An Effective CNN and Transformer Complementary Network for Medical Image Segmentation. Pattern Recognition 2023, 136, p. 109228; ISSN 0031-3203. [CrossRef]
- Pregowska, A.; Osial, M.; Dolega-Dolegowski, D.; Kolecki, R.; Proniewska, K. Information and Communication Technologies Combined with Mixed Reality as Supporting Tools in Medical Education. Electronics 2022, 11(22), 3778. [CrossRef]
- Proniewska, K.; Dolega-Dolegowski, D.; Kolecki, R.; Osial, M.; Pregowska, A. Applications of Augmented Reality - Current State of the Art, In The 3D Operating Room with Unlimited Perspective Change and Remote Support. InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023; pp. 1-23.
- Suh, I.; McKinney, T.; Siu, K.-C. Current Perspective of Metaverse Application in Medical Education, Research and Patient Care. Virtual Worlds 2023, 2, pp. 115-128. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. A Review of Deep-Learning-Based Medical Image Segmentation Methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, p. 1224. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, G.-S.; Liao, X.-F.; Yang, G. Global Transformer and Dual Local Attention Network via Deep-Shallow Hierarchical Feature Fusion for Retinal Vessel Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022. PMID: 35984806. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. Available online arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.04306, 2021. Available online. (accessed on 13 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q. Transformers in Medical Image Segmentation: A Review. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2023, 84(12), 104791. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, L.T.; Zhang, Q.; Armstrong, D.; Deen, M.J. Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Image Analysis: State-of-the-Art, Comparisons, Improvement, and Perspectives. Neurocomputing 2021, 444, pp. 92-110. [CrossRef]
- Meta. https://segment-anything.com/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.Y., et al. Segment Anything. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.02643, 2023. Available online: https://segment-anything (accessed on 08 November 2023).
- He, S.; Bao, R.; Li, J.; Stout, J.; Bjornerud, A.; Grant, P.E.; Ou, Y. Computer-Vision Benchmark Segment-Anything Model (SAM) in Medical Images: Accuracy in 12 Datasets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09324, 2023; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.09324 (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, R. Towards Segment Anything Model (SAM) for Medical Image Segmentation: A Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.03678, 2023; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.03678 (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, R.; Fang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y. Medical SAM Adapter: Adapting Segment Anything Model for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv preprint: arXiv:2304.12620, 2023; https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.12620, 2023 (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Yi, Z.; Lian, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Liang, D.; Liu, J. Learning Rules in Spiking Neural Networks: A Survey. Neurocomputing 2023, 531, pp. 163-179; ISSN 0925-2312. [CrossRef]
- Avcı, H.; Karakaya, J. A Novel Medical Image Enhancement Algorithm for Breast Cancer Detection on Mammography Images Using Machine Learning. Diagnostics 2023, 13, p. 348. [CrossRef]
- Ghahramani, M.; Shiri, N. Brain tumour detection in magnetic resonance Imaging using Levenberg–Marquardt backpropagation neural network. IET Image Process. 2023, 17, pp. 88–103. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gajjala, S.; Agrawal, P.; Tison, G. H.; Hallock, L. H.; Beussink-Nelson, L.; Lassen, M. H.; Fan, E.; Aras, M. A.; Jordan. C.; Fleischmann, K. E.; Melisko, M.; Qasim, A.; Shah, S. J.; Bajcsy, R.; Deo, R. C. Fully automated echocardiogram interpretation in clinical practice. Circulation 2018, 138, 1623–1635.
- Sajjad, M.; Khan, S.; Khan M.; Wu, W.; Ullah, A.; Baik,S. W. Multi-grade brain tumor classification using deep CNN with extensive data augmentation. Journal of Computational Science 2021, 30, 174-182. [CrossRef]
- Jun, T.J.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, J.G.; Kweon, J.; Na, W.; Kang, D.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.; Kim, YH. Automated detection of vulnerable plaque in intravascular ultrasound images. Medical & biological engineering & computing 2019, 57(4), 863-876. [CrossRef]
- Ostvik, A.; Smistad, E.; Aase, S. A.; Haugen, B. O.; Lovstakken, L. Real-time standard view classification in transthoracic echocardiography using convolutional neural networks. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 2019, 45, 374–384. [CrossRef]
- Lossau, T.; Nickisch, H.; Wisse, T.; Bippus, R.; Schmitt, H.; Morlock, M.; Grass M. Motion artifact recognition and quantification in coronary CT angiography using convolutional neural networks. Medical image analysis 2019, 52, 68–79. [CrossRef]
- Emad, O.; Yassine, I. A.; Fahmy, A. S. Automatic localization of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI images using deep learning. In Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc, 2015, 683–686. [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Guo, Y.; Gur, Y.; Negahdar, M.; Syeda-Mahmood, T. A Cross-Modality Neural Network Transform for Semi-automatic Medical Image Annotation. In: Ourselin, S.; Joskowicz, L.; Sabuncu, M.; Unal, G.; Wells, W. (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2016. MICCAI 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9901. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Liskowski, P.; Krawiec K. Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2016, 35, 2369-80. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Hassan, S.S.; Wu, J.; et al. Extended reality for biomedicine. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2023, 3, 14. [CrossRef]
- Kakhandaki, N.; Kulkarni, S.B. Classification of Brain MR Images Based on Bleed and Calcification Using ROI Cropped U-Net Segmentation and Ensemble RNN Classifier. Int. J. Inf. Tecnol. 2023, 15, pp. 3405–3420. [CrossRef]
- Manimurugan, S. Hybrid High Performance Intelligent Computing Approach of CACNN and RNN for Skin Cancer Image Grading. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, pp. 579–589. [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Baltes, M.; Abuhajar, N.; Sun, T.; Karanth, A.; Smith, C.D.; Bihl, T.; Liu, J. Spiking Neural Networks Fine-Tuning for Brain Image Segmentation. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, p. 1267639. https://doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1267639.
- Liang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, C.; Zhang, R.; Yue, K.; Li, W.; Li, Y. A Spiking Neural Network Based on Retinal Ganglion Cells for Automatic Burn Image Segmentation. Entropy 2022, 24, 1526. [CrossRef]
- Gilani, S.Q.; Syed, T.; Umair, M. et al. Skin Cancer Classification Using Deep Spiking Neural Network. J Digit Imaging. 2023, 36, pp. 1137–1147. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Parida, P.; Muralibabu, K.; Dash, S. Efficient Simultaneous Segmentation and Classification of Brain Tumors from MRI Scans Using Deep Learning. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering 2023, 43(3), pp. 616-633; ISSN 0208-5216. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Dong, H.; Breast Cancer Recognition Using Saliency-Based Spiking Neural Network. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2022, 2022, 8369368. [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Q.; Luo, K. Artificial intelligence aids in development of nanomedicines for cancer management. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 89, pp. 61-75. [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Halabi, O.; Dakua, S.P.; Padhan, J.; Paul, S.; Palliyali, W. Augmented Reality in Surgical Navigation: A Review of Evaluation and Validation Metrics. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1629. [CrossRef]
- Wisotzky, E.L.; Rosenthal, J-C.; Meij, S.; et al. Telepresence for surgical assistance and training using eXtended reality during and after pandemic periods. J. Telemed. Telecare. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gomez, A.; et al. STTAR: Surgical Tool Tracking Using Off-the-Shelf Augmented Reality Head-Mounted Displays. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Minopoulos, G.M.; Memos, V.A.; Stergiou, K.D.; Stergiou, C.L.; Psannis, K.E. A Medical Image Visualization Technique Assisted with AI-Based Haptic Feedback for Robotic Surgery and Healthcare. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3592. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cairns, B.J.; Li, J.; et al. Generating synthetic mixed-type longitudinal electronic realth records for artificial intelligent applications. Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 98. [CrossRef]
- Pammi, M.; Aghaeepour, N.; Neu, J. Multiomics, artificial intelligence, and precision medicine in perinatology. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 93, pp. 308–315. [CrossRef]
- Vardi, G. On the Implicit Bias in Deep-Learning Algorithms. Commun. ACM. 2023, 66(6), pp. 86–93. [CrossRef]
- PhysioNet. Available online: https://physionet.org/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- National Sleep Research Resource. Available online: https://sleepdata.org/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Open Access Series of Imaging Studies - OASIS Brain. Available online: https://www.oasis-brains.org/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- OpenNeuro. Available online: https://openneuro.org/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Brain Tumor Dataset. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/brain_tumor_dataset/1512427?file=7953679 (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- The Cancer Imaging Archive. Available online: https://www.cancerimagingarchive.net/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- LUNA16. Available online: https://luna16.grand-challenge.org/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- MICCAI 2012 Prostate Challenge. Available online: https://promise12.grand-challenge.org/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- IEEE Dataport. Available online: https://ieee-dataport.org/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- AIMI. Available online: https://aimi.stanford.edu/shared-datasets (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- fastMRI. Available online: https://fastmri.med.nyu.edu/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Available online: http://adni.loni.usc.edu/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Pediatric Brain Imaging Dataset. Available online: http://fcon_1000.projects.nitrc.org/indi/retro/pediatric.html (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- ChestX-ray8. Available online: https://nihcc.app.box.com/v/ChestXray-NIHCC (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Breast Cancer Digital Repository. Available online: https://bcdr.eu/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Brain-CODE. Available online: https://www.braincode.ca/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- RadImageNet. Available online: https://www.radimagenet.com/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- EyePACS. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/kaggle-eyepacs (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Medical Segmentation Decathlon. Available online: http://medicaldecathlon.com/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- DDSM. Available online: http://www.eng.usf.edu/cvprg/Mammography/Database.html (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- LIDC-IDRI. Available online: https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/LIDC-IDRI (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- synapse. Available online: https://www.synapse.org/#!Synapse:syn3193805/wiki/217789 (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Mini-MIAS. Available online: http://peipa.essex.ac.uk/info/mias.html (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Breast Cancer His-to-pathological Data-base (BreakHis). Available online: https://web.inf.ufpr.br/vri/databases/breast-cancer-histopathologi-cal-database-breakhis/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Messidor. Available online: https://www.adcis.net/en/third-party/messidor/ (accessed on 13 November 2023).
- Li, J.; Cheng, Jh.; Shi, Jy.; Huang, F. Brief Introduction of Back Propagation (BP) Neural Network Algorithm and Its Improvement. In Advances in Computer Science and Information Engineering; Jin, D., Lin, S., eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012, 169, pp. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, X.Y.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K. Encoding Real Values into Polychronous Spiking Networks. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Barcelona, Spain, 18-23 July 2010. pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Bohte, S.M.; Kok, J.N.; La Poutre, H. Error-back propagation in temporally encoded networks of spiking neurons. Neurocomputing 2002, 48, pp. 17–37. [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Gupta, M.D. Deep Convolutional Spiking Neural Network Optimized with Arithmetic Optimization Algorithm for Lung Disease Detection Using Chest X-Ray Images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2023, 79, 104197. [CrossRef]
- Kheradpisheh, S.R.; Ghodrati, M.; Ganjtabesh, M.; Masquelier, T. Bio-Inspired unsupervised learning of visual features leads to robust invariant object recognition. Neurocomputing 2016, 205, pp. 382–392. [CrossRef]
- Brader, J.M.; Senn, W.; Fusi, S. Learning real-world stimuli in a neural network with spike-driven synaptic dynamics. Neural Comput. 2007, 19, pp. 2881–2912. [CrossRef]
- Masquelier, T.; Guyonneau, R.; Thorpe, S.J. Competitive STDP-based spike pattern learning. Neural Comput. 2009, 21, pp. 1259–1276. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Delbruck, T.; Pfeiffer, M. Training deep spiking convolutional neural Networks with STDP-based unsupervised pre-training followed by supervised fine-tuning. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, p. 435. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Delbruck, T.; Pfeiffer, M. Enabling Spike-Based Backpropagation for Training Deep Neural Network Architectures. Front Neurosci. 2020, 14, 119. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, L.; Li, G.; Zhu, J.; Shi, L. Direct training for spiking neural networks: Faster, Larger, Better. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019, 33, pp. 1311–1318. [CrossRef]
- Neil, D.; Pfeiffer, M.; Liu, S.-C. Learning to be efficient: algorithms for training low-latency, low-compute deep spiking neural networks. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (SAC '16). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 293–298. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Delbruck, T.; Pfeiffer, M. Training deep spiking neural networks using backpropagation. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 508. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, K.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Pan, G. Bio-Inspired Active Learning Method in spiking neural network. Know.-Based Syst. 2023, 261, C. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Lau, R. Intelligent Metaverse Scene Content Construction. IEEE Access 2023, 11, pp. 76222-76241. [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Bao, R.; Li, J.; Stout, J.; Bjornerud, A.; Grant, P.E.; Ou, Y. Computer-Vision Benchmark Segment-Anything Model (SAM) in Medical Images: Accuracy in 12 Datasets. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2304.09324, 2023; Available online. (accessed on 13 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Himangi; Singla, M. To Enhance Object Detection Speed in Meta-Verse Using Image Processing and Deep Learning. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2023, 11, pp. 176–184. [CrossRef]
- Pooyandeh, M.; Han, K.-J.; Sohn, I. Cybersecurity in the AI-Based Metaverse: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, p. 12993. [CrossRef]
| Network Type | Neuron model | Average Accuracy [%] | Data sets - training/testing/validation sets [%] or training/testing sets [%] | Input parameters | Learning rule | Biological plausibility | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | Perceproton | 99.10 | mammography images lack of information |
mammography images – 33 features extracted by Region of Interest (ROI) | BP | low | [95] |
| CNN | Perceproton | 98.70 | Brain tumor, MRI color images 70/15/15 |
MRI image scan, 12 features (mean, SD, entropy, Energy, contract, homogeneity, correlation, variance, covariance, RMS, skewness, kurtosis) | BP | low | [96] |
| CNN | Perceproton | 93.00 | Echocardiograms 60/40 |
Disease classification, cardiac chamber segmentation, viewpoints classification in echocardiograms | lack of information | low | [97] |
| CNN | Perceproton | 94.58 | brain tumor images 50/25/25 |
brain tumor images | lack of information | low | [98] |
| CNN | Perceproton | 91.10 | IVUS frames, EA after OCT/IVUS registration | IVUS frames, EA after OCT/IVUS registration | lack of information | low | [99] |
| CNN | Perceproton | 98.00 | 2-D ultrasound 49/49/2 |
Classification of the cardiac view into 7 classes | lack of information | low | [100] |
| CNN | Perceproton | 99.30 | coronary cross-sectional images 80/20 |
Detection of motion artifacts in coronary CCTA, classification of coronary cross-sectional images | lack of information | low | [101] |
| CNN | Perceproton | 99.00 | MRI image scan 60/40 |
Bounding box localization of LV in short-axis MRI slices | lack of information | low | [102] |
| CNN and doc2vec | Perceproton | 96.00 | Doppler US cardiac valve images 94/4/2 |
Automatic generation of text for Doppler US cardiac valve images | lack of information | low | [103] |
| Deep CNN + complex data preparation | Perceproton | 97.00 | Vessel segmentation lack of information |
proposing a supervised segmentation technique that uses a deep neural network. Using structured prediction | lack of information | low | [104] |
| CNN and Transformer encoders | Perceproton | 90.70 | Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC), CT image scans from Synapse 60/40 |
CT image scans | BP | low | [105] |
| CNN, and RNN | Perceproton | 95.24 (REs-Net50) 97.18(IncepnetV3) 98.03 (Dense-Net) |
MRI image scan of the brain 80/20 |
MRI image scan of the brain, modality, mask images | BP | low | [106] |
| CNN, and RNN | Perceproton | 95.74 (REs-Net50) 97.14(DarkNet-53) | skin image lack of information |
skin image | BP | low | [107] |
| SNN | LIF | 81.95 | baseline T1-weighted whole brain MRI image scan lack of information |
The hippocampus section of the MRI image scan | ANN-SNN conversion | low | [108] |
| SNN | LIF | 92.89 | burn images lack of information |
256 × 256 burn image encoded into 24 × 256 × 256 feature maps | BP | low | [109] |
| SNN | LIF | 89.57 | skin images (melanoma and non-melanoma) lack of information |
skin images converted into spikes using Poisson distribution | surrogated gradient descent | low | [110] |
| SNN | LIF | 99.60 | MRI scan of brain tumors 80/10/10 |
2D MRI scan of brain tumors | YO-LO-2-based transfer learning | low | [111] |
| SNN | LIF | 95.17 | microscopic images of breast tumor lack of information |
microscopic images of breast tumor | Spike-Prop | low | [112] |
| Database | Data source | Data type | Amount of data | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physionet | [121] | EEG, x-ray images, polysomnographic, |
Auditory evoked potential EEG-Biometric dataset – 240 measurements from 20 subjects The Brno University of Technology Smartphone PPG Database (BUT PPG) – 12 polysomnographic recordings CAP Sleep Database - 108 polysomnographic recordings CheXmask Database: a large-scale dataset of anatomical segmentation masks for chest x-ray images – 676 803 chest radiographs Electroencephalogram and eye-gaze datasets for robot-assisted surgery performance evaluation– EEG from 25 subjects Siena Scalp EEG Database – EEG from 14 subjects |
Publics |
| Physionet | [121] | EEG, x-ray images, polysomnographic, |
Computed Tomography Images for Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection and Segmentation – 82 CT After Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) A multimodal dental dataset facilitating machine learning research and clinic service -574 CBCT images from 389 patients KURIAS-ECG: a 12-lead electrocardiogram database with standardized diagnosis ontology- EEG 147 subjects VinDr-PCXR: An open, large-scale pediatric chest X-ray dataset for interpretation of common thoracic diseases – adult chest radiography (CXR) 9125 subjects VinDr-SpineXR: A large annotated medical image dataset for spinal lesions detection and classification from radiographs - 10466 spine X-ray images from 5000 studies |
Restricted access |
| National Sleep Research Resource | [122] | Polysomnography |
Apnea Positive Pressure Long-term Efficacy Study – 1516 subject Efficacy Assessment of NOP Agonists in Non-Human Primates – 5 subjects Maternal Sleep in Pregnancy and the Fetus – 106 subjects Apnea, Bariatric surgery, and CPAP study – 49 subjects Best Apnea Interventions in Research – 169 subjects Childhood Adenotonsillectomy Trial – 1243 subjects Cleveland Children's Sleep and Health Study – 517 subjects Cleveland Family Study – 735 subjects Cox & Fell (2020) Sleep Medicine Reviews – 3 subjects Heart Biomarker Evaluation in Apnea Treatment – 318 subjects Hispanic Community Health Study / Study of Latinos – 16415 subjects Home Positive Airway Pressure – 373 subjects Honolulu-Asia Aging Study of Sleep Apnea – 718 subjects Learn – 3 subjects Mignot Nature Communications – 3000 subjects MrOS Sleep Study – 2237 subjects NCH Sleep DataBank – 3673 subjects Nulliparous Pregnancy Outcomes Study Monitoring Mothers-to-be – 3012 subjects Sleep Heart Health Study – 5804 subjects Stanford Technology Analytics and Genomics in Sleep – 1881 subjects Study of Osteoporotic Fractures – 461 subjects Wisconsin Sleep Cohort – 1123 subjects |
Publics on request (no commercial use) |
| Open Access Series of Imaging Studies - Oasis Brain | [123] | MRI Alzheimer’s disease | OASIS-1 – 416 subjects OASIS-2 – 150 subjects OASIS-3 – 1379 subjects OASIS-4 – 663 subjects |
Publics on request (no commercial use) |
| openeuro | [124] | MRI, PET, MEG, EEG, and iEEG data (various types of disorders, depending on the database) | 595 MRI public datasets, 23 304 subjects 8 PET public datasets – 19 subjects 161 EEG public dataset – 6790 subjects 23 iEEG public dataset – 550 subjects 32 MEG public dataset – 590 subjects |
Publics |
| brain tumor dataset | [125] | MRI, brain tumor | MRI - 233 subjects | Publics |
| Cancer Ima-ging Ar-chive (TCIA) | [126] | MR, CT, Positron Emission Tomography, Computed Radiography, Digital Radiography, Nuclear Medicine, Other (a category used in DICOM for images that do not fit into the standard modality categories), Structured Reporting Pathology Various | HNSCC-mIF-mIHC-comparison – 8 subjects CT-Phantom4Radiomics – 1 subject Breast-MRI-NACT-Pilot – 64 subjects Adrenal-ACC-Ki67-Seg – 53 subjects CT Lymph Nodes – 176 subjects UCSF-PDGM – 495 subjects UPENN-GBM – 630 subjects Hungarian-Colorectal-Screening – 200 subjects Duke-Breast-Cancer-MRI – 922 subjects Pancreatic-CT-CBCT-SEG – 40 subjects HCC-TACE-Seg – 105 subjects Vestibular-Schwannoma-SEG – 242 subjects ACRIN 6698/I-SPY2 Breast DWI – 385 subjects I-SPY2 Trial – 719 subjects HER2 tumor ROIs – 273 subjects DLBCL-Morphology – 209 subjects CDD-CESM – 326 subjects COVID-19-NY-SBU – 1,384 subjects Prostate-Diagnosis – 92 subjects NSCLC-Radiogenomics – 211 subjects CT Images in COVID-19 – 661 subjects QIBA-CT-Liver-Phantom – 3 subjects Lung-PET-CT-Dx – 363 subjects QIN-PROSTATE-Repeatability – 15 subjects NSCLC-Radiomics – 422 subjects Prostate-MRI-US-Biopsy – 1151 subjects CRC_FFPE-CODEX_CellNeighs – 35 subjects TCGA-BRCA – 139 subjects TCGA-LIHC – 97 subjects TCGA-LUAD – 69 subjects TCGA-OV – 143 subjects TCGA-KIRC – 267 subjects Lung-Fused-CT-Pathology – 6 subjects AML-Cytomorphology_LMU – 200 subjects Pelvic-Reference-Data – 58 subjects CC-Radiomics-Phantom-3 – 95 subjects MiMM_SBILab – 5 subjects LCTSC – 60 subjects QIN Breast DCE-MRI – 10 subjects Osteosarcoma Tumor Assessment – 4 subjects CBIS-DDSM – 1566 subjects QIN LUNG CT – 47 subjects CC-Radiomics-Phantom – 17 subjects PROSTATEx – 346 subjects Prostate Fused-MRI-Pathology – 28 subjects SPIE-AAPM Lung CT Challenge – 70 subjects ISPY1 (ACRIN 6657) – 222 subjects Pancreas-CT – 82 subjects 4D-Lung – 20 subjects Soft-tissue-Sarcoma – 51 subjects LungCT-Diagnosis – 61 subjects Lung Phantom – 1 subject Prostate-3T – 64 subjects LIDC-IDRI – 1010 subjects RIDER Phantom PET-CT – 20 subjects RIDER Lung CT – 32 subjects BREAST-DIAGNOSIS – 88 subjects CT COLONOGRAPHY (ACRIN 6664) – 825 sub-jects |
Publics (Free access, registration required) |
| LUNA16 | [127] | CT, Lung Nodules | LUNA16- 888 CT scans | Publics (Free access to all users) |
| MICCAI 2012 Prostate Challenge | [128] | MRI, Prostate Imaging | Prostate Segmentation in Transversal T2-weighted MR images - Amount of Data: 50 training cases | Publics (Free access to all users) |
| IEEE Dataport | [129] | Ultrasound Images, Brain MRI, Ultra-widefield fluorescein angiography images, Chest X-rays, Mammograms, CT, Lung Image Database Consortium and Image, Thermal Images | CNN-Based Image Reconstruction Method for Ultrafast Ultrasound Imaging: 31,000 images OpenBHB: a Multi-Site Brain MRI Dataset for Age Prediction and Debiasing: >5,000 - Brain MRI. Benign Breast Tumor Dataset: 83 patients - Mammograms. X-ray Bone Shadow Suppression: 4,080 images STROKE: CT series of patients with M1 thrombus before thrombectomy: 88 patients Automatic lung segmentation results Nextmedproject - 718 of the 1012 LIDC-IDRI scans PRIME-FP20: Ultra-Widefield Fundus Photography Vessel Segmentation Dataset -15 images Plantar Thermogram Database for the Study of Diabetic Foot Complications - Amount of data: 122 subjects (DM group) and 45 subjects (control group) |
A part Public and a part restricted (Subscription) |
| AIMI | [130] | Brain MRI studies, Chest X-rays, echocardiograms, CT | BrainMetShare- 156 subjects CheXlocalize: 700 subjects BrainMetShare: 156 subjects COCA - Coronary Calcium and Chest CTs: Not specified CT Pulmonary Angiography: Not specified CheXlocalize: 700 subjects CheXpert: 65,240 subjects CheXphoto: 3,700 subjects CheXplanation: Not specified DDI - Diverse Dermatology Images: Not specified EchoNet-Dynamic: 10,030 subjects EchoNet-LVH: 12,000 subjects EchoNet-Pediatric: 7,643 subjects LERA - Lower Extremity Radiographs: 182 subjects MRNet: 1,370 subjects MURA: 14,863 studies Multimodal Pulmonary Embolism Dataset: 1,794 subjects SKM-TEA: Not specified Thyroid Ultrasound Cine-clip: 167 subjects CheXpert:224,316 chest radiographs of 65,240 subjects |
Publics (Free access) |
| fast MRI | [131] | MRI | fast MRI Knee: 1,500+ subjects fast MRI Brain: 6,970 subjects fast MRI Prostate: 312 subjects |
Publics (Free access, registration required) |
| ADNI | [132] | MRI, PET | Scans Related to Alzheimer's Disease | Publics (Free access, registration required) |
| Pediatric Brain Imaging Dataset | [133] | MRI |
Pediatric Brain Imaging Data-set Over 500 pediatric brain MRI scans | Publics (Free access to all users |
| ChestX-ray8 | [134] | Chest X-ray Images | NIH Clinical Center Chest X-ray Dataset - Over 100,000 images from more than 30,000 subjects |
Publics (Free access to all users) |
| Breast Cancer Digital Repository | [135] | MLO and CC images | BCDR-FM (Film Mammography-based Repository) - Amount of Data: 1010 subjects BCDR-DM (Full Field Digital Mammography-based Repository)Amount of Data: 724 subjects |
Publics (Free access, registration required |
| Brain-CODE | [136] | Neuroimaging | High-Resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Mouse Model Related to Autism - 839 subjects |
Restricted (Application for access is required and Open Data Releases) |
| RadImageNet | [137] | PET, CT, Ultrasound, MRI with DICOM tags | 5 million images from over 1 million studies across 500,000 subjects | Publics subset available; Full dataset licensable; Academic access with restrictions |
| EyePACS | [138] | Retinal fundus images for diabetic retinopathy screening | Images for Training and validation set- 57,146 images Test set - 8,790 images | Available through the Kaggle competition |
| Medical Segmentation Decathlon | [139] | mp-MRI, MRI, CT | 10 data sets Cases (Train/Test) Brain 484/266 Heart 20/10 Hippocampus 263/131 Liver 131/70 Lung 64/32 Pancreas 282/139 Prostate 32/16 Colon 126/64 Hepatic Vessels 303/140 Spleen 41/20 |
Open source license, available for research use |
| DDSM | [140] | Mammography images | 2,500 studies with images, subjects info - 2620 cases in 43 volumes categorized by case type | Publics (Free access) |
| LIDC-IDRI | [141] | CT Images with Annotations | 1018 cases with XML and DICOM files - Images (DICOM, 125GB), DICOM Metadata Digest (CSV, 314 kB), Radiologist Annotations/Segmentations (XML format, 8.62 MB), Nodule Counts by Patient (XLS), Patient Diagnoses (XLS) | Images and annotations are available for download with NBIA Data Retriever, usage under CC BY 3.0 |
| synapse | [142] | CT scans, Zip files for raw data, registration data | CT scans- 50 scans with variable volume sizes and resolutions Labeled organ data -13 abdominal organs were manually labeled Zip files for raw data - Raw Data: 30 training + 20 testing; Registration Data: 870 training-training + 600 training-testing pairs |
Under IRB supervision, Available for participants |
| Mini-MIAS | [143] | Mammographic images | 322 digitized films on 2.3GB 8mm tape - Images derived from the UK National Breast Screening Programme and digitized with Joyce-Loebl scanning microdensitometer to 50 microns, reduced to 200 microns and standardized to 1024x1024 pixels for the database | free for scientific research under a license agreement |
| Breast Cancer Histopathological Database (BreakHis) | [144] | microscopic images of breast tumor | 9,109 microscopic images of breast tumor tissue collected from 82 subjects |
free for scientific research under a license agreement |
| Messidor | [145] | eye fundus color numerical images | 1200 eye fundus color numerical images of the posterior pole | free for scientific research under a license agreement |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





