Submitted:
05 November 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
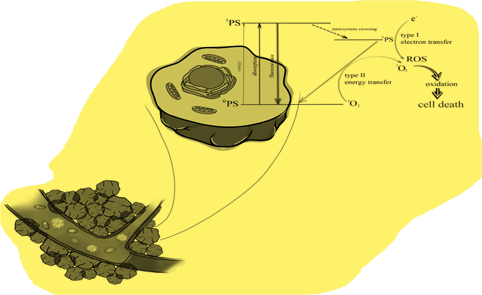
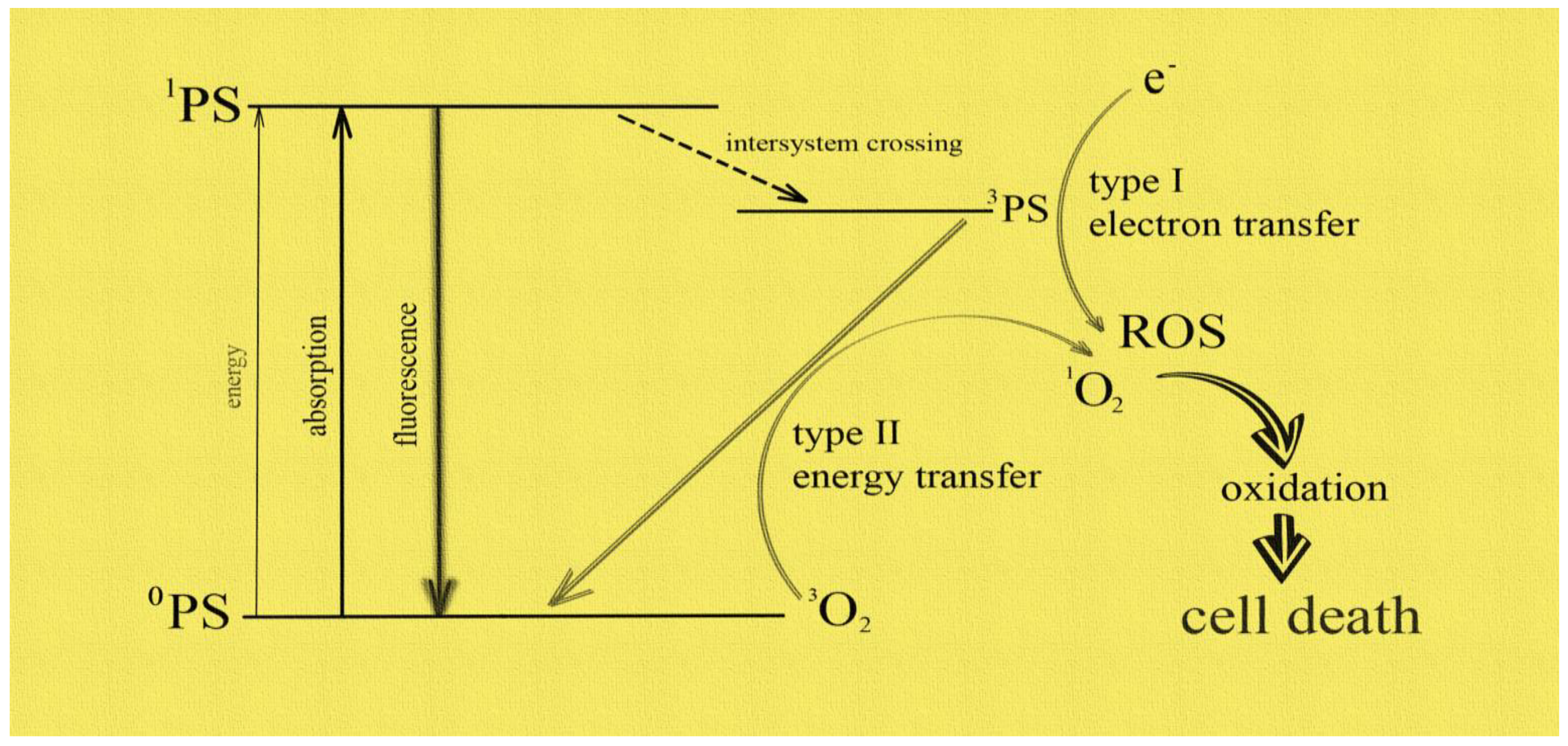
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
3. Literature review
3.1. Esophageal cancer
3.2. Stomach cancer
3.3. Colon cancer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattiuzzi C, Lippi G. Current Cancer Epidemiology. J Epidemiol Glob Health 2019, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F. Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2014, 23, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander S, Lander E, Gibson MK. Esophageal Cancer: Overview, Risk Factors, and Reasons for the Rise. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 9 October 2023.
- Kuipers EJ, Grady WM, Lieberman D, Seufferlein T, Sung JJ, Boelens PG, van de Velde CJ, Watanabe T. Colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong Y: Gao H, Qi Q, Liu X, Li J, Gao J, Li P, Wang Y, Du L, Wang C. High fat diet, gut microbiome and gastrointestinal cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5889–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumo Xie, Lishuo Shi, Xiaosheng He, Yanxin Luo, Gastrointestinal cancers in China, the USA, and Europe. Gastroenterology Report 2021, 9, 91–104. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas G, Krasna M. Overview of esophageal cancer. Ann Cardiothorac Surg 2017, 6, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang FL, Yu SJ. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J Surg 2018, 41, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li J, Xu J, Zheng Y, Gao Y, He S, Li H, Zou K, Li N, Tian J, Chen W, He J. Esophageal cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors and screening. Chin J Cancer Res 2021, 33, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 2003, 349, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short MW, Burgers KG, Fry VT. Esophageal Cancer. Am Fam Physician 2017, 95, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gastric cancer Elizabeth C Smyth, MD Magnus Nilsson, PhD Heike I Grabsch, PhD Nicole CT van Grieken, PhD Florian Lordick, MD.
- Ilic M, Ilic I. Epidemiology of stomach cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2022, 28, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem E, Sagaert X, Topal B, Haustermans K, Prenen H. Gastric cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzo Catalano, Roberto Labianca, Giordano D. Beretta, Gemma Gatta, Filippo de Braud, Eric Van Cutsem, Gastric cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 2009, 71, 127–164. [Google Scholar]
- Mármol I, Sánchez-de-Diego C, Pradilla Dieste A, Cerrada E, Rodriguez Yoldi MJ. Colorectal Carcinoma: A General Overview and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikbakht HA, Hassanipour S, Shojaie L, Vali M, Ghaffari-Fam S, Ghelichi-Ghojogh M, Maleki Z, Arab-Zozani M, Abdzadeh E, Delam H, Salehiniya H, Shafiee M, Mohammadi S. Survival Rate of Colorectal Cancer in Eastern Mediterranean Region Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Control 2020, 27, 1073274820964146. [Google Scholar]
- Haraldsdottir S, Einarsdottir HM, Smaradottir A, Gunnlaugsson A, Halfdanarson TR. Krabbamein í ristli og endaþarmi [Colorectal cancer - review]. Laeknabladid 2014, 100, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cappell, M.S. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and management of colon cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2008, 37, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicki, T.; Ruszkowska, M.; Danielewicz, A.; Niedźwiedzka, E.; Arłukowicz, T.; Przybyłowicz, K.E. A Review of Colorectal Cancer in Terms of Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Development, Symptoms and Diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaukat, A., Levin, T.R. Current and future colorectal cancer screening strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022, 19, 521–531.
- Rkein AM, Ozog DM. Photodynamic therapy. Dermatol Clin 2014, 32, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, K.; Aihara, Y.; Oda, Y.; Fukui, A.; Tsuzuk, S.; Saito, T.; Nitta, M.; Muragaki, Y.; Kawamata, T. Photodynamic therapy for malignant brain tumors in children and young adolescents. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 957267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, L.I.N.; Hassan, S.A.B.; Alshadidi, A.A.F.; Rangaiah, G.C.; Divakar, D.D. Short-term influence of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy as an adjuvant to mechanical debridement in reducing soft-tissue inflammation and subgingival yeasts colonization in patients with peri-implant mucositis. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 42, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Pallares, P.; Navarro-Bielsa, A.; Almenara-Blasco, M.; Gracia-Cazaña, T.; Gilaberte, Y. Photodynamic Therapy, a successful treatment for granular parakeratosis. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 42, 103562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiades-Armenakas, M. Laser-mediated photodynamic therapy. Clin. Dermatol. 2006, 24, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski S, Knap B, Przystupski D, Saczko J, Kędzierska E, Knap-Czop K, Kotlińska J, Michel O, Kotowski K, Kulbacka J. Photodynamic therapy - mechanisms, photosensitizers and combinations. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 106, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis P, Berg K, Cengel KA, Foster TH, Girotti AW, Gollnick SO, Hahn SM, Hamblin MR, Juzeniene A, Kessel D, Korbelik M, Moan J, Mroz P, Nowis D, Piette J, Wilson BC, Golab J. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: an update. CA Cancer J Clin 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarranz A, Jaén P, Sanz-Rodríguez F, Cuevas J, González S. Photodynamic therapy of cancer. Basic principles and applications. Clin Transl Oncol 2008, 10, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C. Kübler, Photodynamic therapy. Medical Laser Application 2005, 20, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Triesscheijn M, Baas P, Schellens JH, Stewart FA. Photodynamic therapy in oncology. Oncologist 2006, 11, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano T, Wang KK. Photodynamic Therapy for Gastrointestinal Cancer. Photochem Photobiol 2020, 96, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, H. Photodynamic therapy in gastrointestinal cancer: a realistic option? Drugs Aging 2000, 16, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qumseya BJ, David W, Wolfsen HC. Photodynamic Therapy for Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Carcinoma. Clin Endosc 2013, 46, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber J, Herman M, Kessel D, Fromm D. Photodynamic treatment of neoplastic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. Recent advances in techniques and results. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2000, 385, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip AG, Clichici S, Daicoviciu D, Olteanu D, Mureşan A, Dreve S. Photodynamic therapy--indications and limits in malignant tumors treatment. Rom J Intern Med. 2008, 46, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Gao S, Liang S, Ding K, Qu Z, Wang Y, Feng X. Specific cellular accumulation of photofrin-II in EC cells promotes photodynamic treatment efficacy in esophageal cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2016, 14, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao SG, Wang LD, Feng XS, Qu ZF, Shan TY, Xie XH. [Absorption and elimination of photofrin-II in human immortalization esophageal epithelial cell line SHEE and its malignant transformation cell line SHEEC]. Ai Zheng 2009, 28, 1248–1254. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen P, de Rooij FW, van Velthuysen ML, Edixhoven A, van Hillegersberg R, Tilanus HW, Wilson JH, Siersema PD. Biochemical basis of 5-aminolaevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX accumulation: a study in patients with (pre)malignant lesions of the oesophagus. Br J Cancer 1998, 78, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi Y, Zhang B, Feng X, Qu F, Wang S, Wu L, Wang X, Liu Q, Wang P, Zhang K. Apoptosis and autophagy induced by DVDMs-PDT on human esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2018, 24, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Zhao P, Chen F, Li L, Luo R. Effect and mechanism of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy in esophageal cancer. Lasers Med Sci 2011, 26, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apoptosis associated with esophageal adenocarcinoma: influence of photodynamic therapy.
- Chen XH, Luo RC, Li LB, Ding XM, Lv CW, Zhou XP, Yan X. [Mechanism of photodynamic therapy against human esophageal carcinoma xenografts in nude mice]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2009, 29, 2222–2224. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li L, Song D, Qi L, Jiang M, Wu Y, Gan J, Cao K, Li Y, Bai Y, Zheng T. Photodynamic therapy induces human esophageal carcinoma cell pyroptosis by targeting the PKM2/caspase-8/caspase-3/GSDME axis. Cancer Lett 2021, 520, 143–159, Erratum in: Cancer Lett 2022, 525, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue Q, Wang P, Wang X, Zhang K, Liu Q. Targeted inhibition of p38MAPK-enhanced autophagy in SW620 cells resistant to photodynamic therapy-induced apoptosis. Lasers Med Sci 2015, 30, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip YT, Davis RJ. Signal transduction by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)--from inflammation to development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1998, 10, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N, Zhou HF. Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2015, 35, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Puente Y, Zapata-Benavides P, Tari AM, López-Berestein G. Bcl-2-related antisense therapy. Semin Oncol 2002, 29 (Suppl. 11), 71–76.
- Weng C, Li Y, Xu D, Shi Y, Tang H. Specific cleavage of Mcl-1 by caspase-3 in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in Jurkat leukemia T cells". J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10491–10500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala A, Muñoz MF, Argüelles S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi M, Taghizadeh S, Kaviani E, Vakili O, Taheri-Anganeh M, Tahamtan M, Savardashtaki A. Caspase-3: Structure, function, and biotechnological aspects. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 2022, 69, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel P, Harrison L. Tumor hypoxia: causative factors, compensatory mechanisms, and cellular response. The Oncologist 2004, 9 (Suppl. 5), 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan J, Li S, Meng Y, Liao Y, Jiang M, Qi L, Li Y, Bai Y. The influence of photodynamic therapy on the Warburg effect in esophageal cancer cells. Lasers Med Sci 2020, 35, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Cai L, He J, Li X, Li L, Chen X, Lan P. Influence and mechanism of 5-aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy on the metastasis of esophageal carcinoma. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2017, 20, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Y, Sui H, Jiang C, Li S, Han Y, Huang P, Du X, Du J, Bai Y. Dihydroartemisinin Increases the Sensitivity of Photodynamic Therapy Via NF-κB/HIF-1α/VEGF Pathway in Esophageal Cancer Cell in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018, 48, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P. VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology 2005, 69 (Suppl. 3), 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahopoulos, S.A. Aberrant control of NF-κB in cancer permits transcriptional and phenotypic plasticity, to curtail dependence on host tissue: molecular mode. Cancer Biology & Medicine 2017, 14, 254–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou JH, Du XX, Jia de X, Wu CL, Huang P, Han Y, Sui H, Wei XL, Liu L, Yuan HH, Zhang TT, Zhang WJ, Xie R, Lang XH, Liu T, Jiang CL, Wang LY, Bai YX. Dihydroartemisinin accentuates the anti-tumor effects of photodynamic therapy via inactivation of NF-κB in Eca109 and Ec9706 esophageal cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014, 33, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa H, Ito H, Terasaki M, Matano D, Taninaka A, Shigekawa H, Matsui H. Nitric oxide regulates the expression of heme carrier protein-1 via hypoxia inducible factor-1α stabilization. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0222074. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo JO, Lim YC, Kim YM, Ha KS. Differential cytotoxic responses to low- and high-dose photodynamic therapy in human gastric and bladder cancer cells. J Cell Biochem 2011, 112, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou GJ, Huang ZH, Yu JL, Li Z, Ding LS. [Effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy on human gastric cancer xenografts in nude mice in vivo]. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 2008, 11, 580–583. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Takahira K, Sano M, Arai H, Hanai H. Apoptosis of gastric cancer cell line MKN45 by photodynamic treatment with photofrin. Lasers Med Sci. 2004, 19, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Ewetse MP, Ma C, Pu W, Xu B, He P, Wang Y, Zhu J, Chen H. The "Light Knife" for Gastric Cancer: Photodynamic Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu Y, Xu B, Xiang L, Ding T, Wang N, Yu R, Gu B, Gao L, Maswikiti EP, Wang Y, Li H, Bai Y, Zheng P, Ma C, Wang B, Wang X, Zhang T, Chen H. Photodynamic therapy improves the outcome of immune checkpoint inhibitors via remodelling anti-tumour immunity in patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2023, 26, 798–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao Y, Cao Y, Chen Y, Wu L, Hang H, Jiang C, Zhou X. B2M gene expression shapes the immune landscape of lung adenocarcinoma and determines the response to immunotherapy. Immunology 2021, 164, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue Q, Wang X, Wang P, Zhang K, Liu Q. Role of p38MAPK in apoptosis and autophagy responses to photodynamic therapy with Chlorin e6. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2015, 12, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng CL, Lin HC, Chiang WL, Shih YH, Chiang PF, Luo TY, Cheng CC, Shieh MJ. Anti-angiogenic treatment (Bevacizumab) improves the responsiveness of photodynamic therapy in colorectal cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2018, 23, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg RC, Messmann H, Schlottmann K, Endlicher E, Seeger S, Schölmerich J, Knuechel R. Intracellular localization is a cofactor for the phototoxicity of protoporphyrin IX in the gastrointestinal tract: in vitro study. Photochem Photobiol 2003, 78, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siboni G, Weitman H, Freeman D, Mazur Y, Malik Z, Ehrenberg B. The correlation between hydrophilicity of hypericins and helianthrone: internalization mechanisms, subcellular distribution and photodynamic action in colon carcinoma cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2002, 1, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orenstein A, Kostenich G, Roitman L, Shechtman Y, Kopolovic Y, Ehrenberg B, Malik Z. A comparative study of tissue distribution and photodynamic therapy selectivity of chlorin e6, Photofrin II and ALA-induced protoporphyrin IX in a colon carcinoma model. Br J Cancer 1996, 73, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg RC, Messmann H, Rauch J, Seeger S, Knuechel R. Metabolic characterization of tumor cell-specific protoporphyrin IX accumulation after exposure to 5-aminolevulinic acid in human colonic cells. Photochem Photobiol 2002, 76, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra LE, Porcal GV, Macor LP, Ponzio RA, Spada RM, Lorente C, Chesta CA, Rivarola VA, Palacios RE. Metallated porphyrin-doped conjugated polymer nanoparticles for efficient photodynamic therapy of brain and colorectal tumor cells. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2018, 13, 605–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng JH, Shi D, Zhao Y, Chen ZL. [Role of calcium signal in apoptosis and protective mechanism of colon cancer cell line SW480 in response to 5-aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy]. Ai Zheng 2006, 25, 683–688. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y, Hu LL. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med 2020, 19, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar]
- Šemeláková M, Mikeš J, Jendželovský R, Fedoročko P. The pro-apoptotic and anti-invasive effects of hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy are enhanced by hyperforin or aristoforin in HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cells. J Photochem Photobiol B 2012, 117, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu Y, Yao Y, Wang L, Chen H, Tan N. Hyaluronic Acid Coated Liposomes Co-Delivery of Natural Cyclic Peptide RA-XII and Mitochondrial Targeted Photosensitizer for Highly Selective Precise Combined Treatment of Colon Cancer. Int J Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 4929–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan CM, Lo PC, Yeung SL, Ng DK, Fong WP. Photodynamic activity of a glucoconjugated silicon(IV) phthalocyanine on human colon adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 2010, 10, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risheng Ye, Yi Zhang, Amy S. Lee ; The ER Chaperone GRP78 and Cancer, Protein Misfolding Disorders. A Trip into the ER 2009, 1, 47.
- Gariboldi MB, Ravizza R, Baranyai P, Caruso E, Banfi S, Meschini S, Monti E. Photodynamic effects of novel 5,15-diaryl-tetrapyrrole derivatives on human colon carcinoma cells. Bioorg Med Chem 2009, 17, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamse H, Houreld NN. Genetic Aberrations Associated with Photodynamic Therapy in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrehman G, Xv K, Li Y, Kang L. Effects of meta-tetrahydroxyphenylchlorin photodynamic therapy on isogenic colorectal cancer SW480 and SW620 cells with different metastatic potentials. Lasers Med Sci 2018, 33, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang G, Liu Z, Xiong L, Chen X, Li Q, Huang H, Lin L, Miao X, Ma L, Chen W, Wen Y. [Role of PpIX-based photodynamic therapy in promoting the damage and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cell and its mechanisms]. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2017, 42, 874–881. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shahzidi S, Stokke T, Soltani H, Nesland JM, Peng Q. Induction of apoptosis by hexaminolevulinate-mediated photodynamic therapy in human colon carcinoma cell line 320DM. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2006, 25, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali SM, Olivo M. Bio-distribution and subcellular localization of Hypericin and its role in PDT induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Int J Oncol 2002, 21, 531–540. [Google Scholar]
- Matroule JY, Carthy CM, Granville DJ, Jolois O, Hunt DW, Piette J. Mechanism of colon cancer cell apoptosis mediated by pyropheophorbide-a methylester photosensitization. Oncogene 2001, 20, 4070–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Arnaiz C, Acuña MI, Busto N, Echevarría I, Martínez-Alonso M, Espino G, García B, Domínguez F. Thiabendazole-based Rh(III) and Ir(III) biscyclometallated complexes with mitochondria-targeted anticancer activity and metal-sensitive photodynamic activity. Eur J Med Chem 2018, 157, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang X, Zhang A, Qiu X, Yang K, Zhou H. The IL-12 family cytokines in fish: Molecular structure, expression profile and function. Dev Comp Immunol 2023, 141, 104643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili A, Makowski M, Switaj T, Nowis D, Wilczynski GM, Wilczek E, Chorazy-Massalska M, Radzikowska A, Maslinski W, Biały L, Sienko J, Sieron A, Adamek M, Basak G, Mróz P, Krasnodebski IW, Jakóbisiak M, Gołab J. Effective photoimmunotherapy of murine colon carcinoma induced by the combination of photodynamic therapy and dendritic cells. Clin Cancer Res 2004, 10, 4498–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogno IS, Gilardi P, Comini L, Núñez-Montoya SC, Cabrera JL, Rivarola VA. Natural photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy: In vitro activity against monolayers and spheroids of human colorectal adenocarcinoma SW480 cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2020, 31, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinkowska E, Ziółkowski P, Pacholska E, Latos-Grazyński L, Chmielewski P, Radzikowski C. The new sensitizing agents for photodynamic therapy: 21-selenaporphyrin and 21-thiaporphyrin. Anticancer Res 1997, 17, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar]
- TLuo M, Ji J, Yang K, Li H, Kang L. The role of autophagy in the treatment of colon cancer by chlorin e6 photodynamic therapy combined with oxaliplatin. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2022, 40, 103082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necrotic and apoptotic features of cell death in response to Foscan photosensitization of HT29 monolayer and multicell spheroids.
- Pansa MF, Lamberti MJ, Cogno IS, Correa SG, Rumie Vittar NB, Rivarola VA. Contribution of resident and recruited macrophages to the photodynamic intervention of colorectal tumor microenvironment. Tumour Biol 2016, 37, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz P, Szokalska A, Wu MX, Hamblin MR. Photodynamic therapy of tumors can lead to development of systemic antigen-specific immune response. PLoS One 2010, 5, e15194. [Google Scholar]
- Na TY, Schecterson L, Mendonsa AM, Gumbiner BM. The functional activity of E-cadherin controls tumor cell metastasis at multiple steps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 5931–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma H, Yang K, Li H, Luo M, Wufuer R, Kang L. Photodynamic effect of chlorin e6 on cytoskeleton protein of human colon cancer SW480 cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2021, 33, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wufuer R, Ma HX, Luo MY, Xu KY, Kang L. Downregulation of Rac1/PAK1/LIMK1/cofilin signaling pathway in colon cancer SW620 cells treated with Chlorin e6 photodynamic therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2021, 33, 102143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobre M, Boscencu R, Neagoe IV, Surcel M, Milanesi E, Manda G. Insight into the Web of Stress Responses Triggered at Gene Expression Level by Porphyrin-PDT in HT29 Human Colon Carcinoma Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan Z, Liu C, Sun Y, Li Y, Wu H, Ma S, Shang J, Zhan Y, Yin P, Gao F. Bufalin exacerbates Photodynamic therapy of colorectal cancer by targeting SRC-3/HIF-1α pathway. Int J Pharm 2022, 624, 122018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West CM, Moore JV. Mechanisms behind the resistance of spheroids to photodynamic treatment: a flow cytometry study. Photochem Photobiol 1992, 55, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez ME, Catrinacio C, Ropolo A, Rivarola VA, Vaccaro MI. A novel HIF-1α/VMP1-autophagic pathway induces resistance to photodynamic therapy in colon cancer cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2017, 16, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid M, Zadeh LR, Baradaran B, Molavi O, Ghesmati Z, Sabzichi M, Ramezani F. Up-down regulation of HIF-1α in cancer progression. Gene 2021, 798, 145796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberti MJ, Pansa MF, Vera RE, Fernández-Zapico ME, Rumie Vittar NB, Rivarola VA. Transcriptional activation of HIF-1 by a ROS-ERK axis underlies the resistance to photodynamic therapy. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0177801. [Google Scholar]
- Wang HP, Hanlon JG, Rainbow AJ, Espiritu M, Singh G. Up-regulation of Hsp27 plays a role in the resistance of human colon carcinoma HT29 cells to photooxidative stress. Photochem Photobiol 2002, 76, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurászová K, Mikeš J, Halaburková A, Jendželovský R, Fedoročko P. YM155, a small molecule inhibitor of survivin expression, sensitizes cancer cells to hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2016, 15, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendzelovský R, Mikes J, Koval’ J, Soucek K, Procházková J, Kello M, Sacková V, Hofmanová J, Kozubík A, Fedorocko P. Drug efflux transporters, MRP1 and BCRP, affect the outcome of hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy in HT-29 adenocarcinoma cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2009, 8, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkiss SF, Grahn MF, Williams NS. Haematoporphyrin derivative--photodynamic therapy of colorectal carcinoma, sensitized using verapamil and adriamycin. Surg Oncol 1996, 5, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaburková A, Jendželovský R, Kovaľ J, Herceg Z, Fedoročko P, Ghantous A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate photodynamic therapy in colon cancer cells marked by chromatin-mediated epigenetic regulation of CDKN1A. Clin Epigenetics 2017, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu K, Yao H, Wen Y, Zhao H, Zhou N, Lei S, Xiong L. Functional role of a long non-coding RNA LIFR-AS1/miR-29a/TNFAIP3 axis in colorectal cancer resistance to pohotodynamic therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2018, 1864 Pt B, 2871–2880. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo M, Yang X, Chen HN, Nice EC, Huang C. Drug resistance in colorectal cancer: An epigenetic overview. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2021, 1876, 188623. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson N, Kruger CA, Abrahamse H. Targeted photodynamic therapy as potential treatment modality for the eradication of colon cancer and colon cancer stem cells. Tumour Biol 2017, 39, 1010428317734691. [Google Scholar]
- Lin S, Lei K, Du W, Yang L, Shi H, Gao Y, Yin P, Liang X, Liu J. Enhancement of oxaliplatin sensitivity in human colorectal cancer by hypericin mediated photodynamic therapy via ROS-related mechanism. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2016, 71, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan Z, Fan G, Wu H, Liu C, Zhan Y, Qiu Y, Shou C, Gao F, Zhang J, Yin P, Xu K. Photodynamic therapy synergizes with PD-L1 checkpoint blockade for immunotherapy of CRC by multifunctional nanoparticles. Mol Ther 2021, 29, 2931–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleban J, Mikes J, Horváth V, Sacková V, Hofmanová J, Kozubík A, Fedorocko P. Mechanisms involved in the cell cycle and apoptosis of HT-29 cells pre-treated with MK-886 prior to photodynamic therapy with hypericin. J Photochem Photobiol B 2008, 93, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
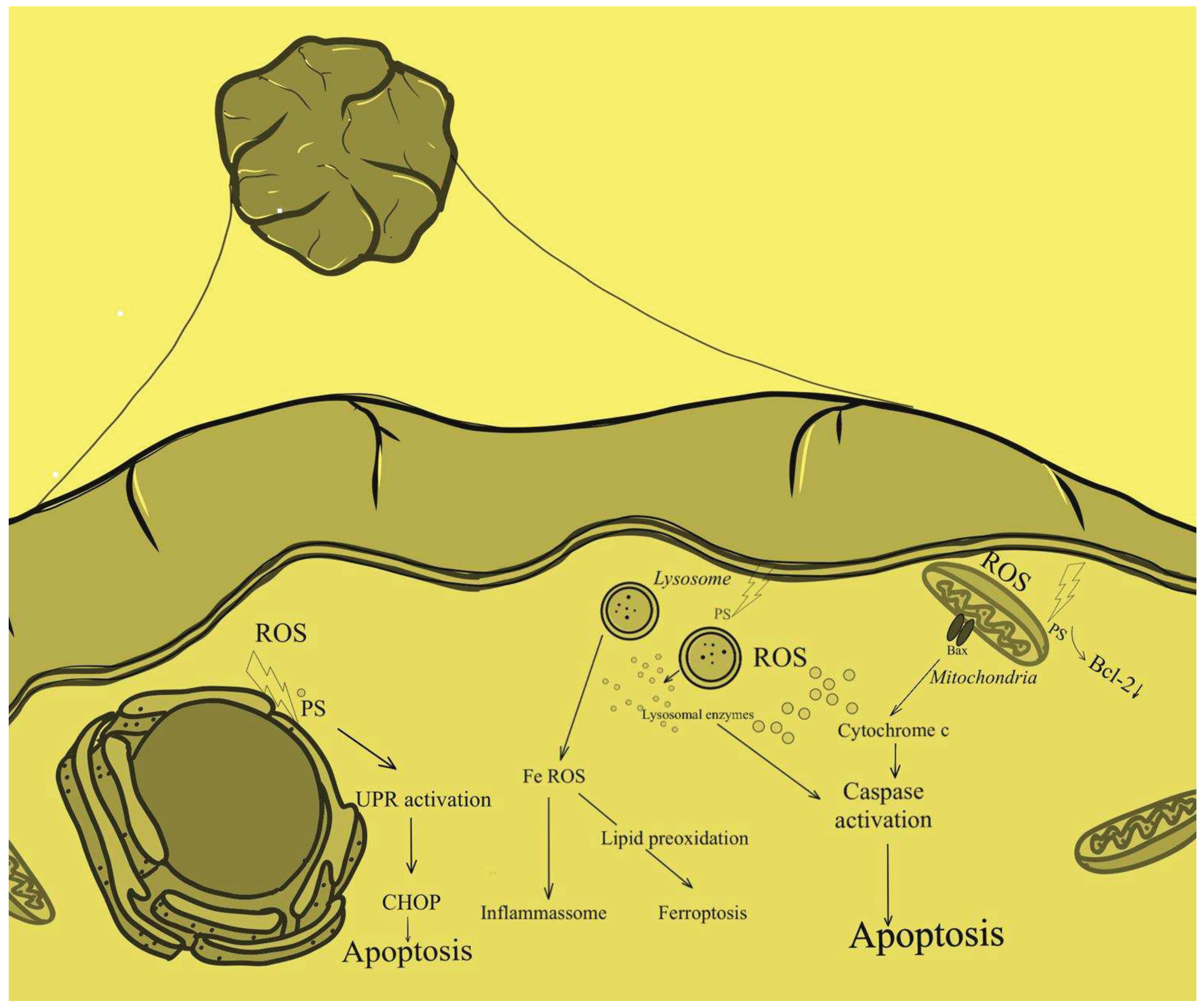
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




