1. Introduction
Plastic basically a simulated polymer catches some other chemicals to provide better redaction known as the nature of petrochemical which hold plasticity and molecular mass (Costa et al. 2016). Nowadays plastics are more available comparatively other chemicals and the process of manufacturing products, long durability, simple weight and obviously cost effective is the main reason behind increasing the use plastic in society (Andrady and Neal 2009; Cauwenberghe et al. 2015). Plastic debris, which can be found on land as well as in the ocean, has been a major environmental concern in recent years. However, because of its effects on aquatic organisms and human health, tiny plastic particles known as microplastic have recently come to light as a hazardous contaminant (Cole et al. 2011). Microscopic pieces of plastic debris that contaminate the environment are called microplastics, or MPs. Plastic particles less than five millimeters are referred to as micro-plastic. Scientists have been studying the possible risks associated with MPs since they first discovered them in the waters in the early 1970s. One of the most concerning challenges facing the world today is the widespread perception of MPs debris in aquatic ecosystems. Depending on the manner in which they are produced, microplastics can be categorized as primary or secondary substances.
Primary MPs particles are deliberately manufactured smaller than 5 mm in order to be used in industrial applications (ceiling liquids used in oil and gas exploration) or personal care products (toothpaste, body washes, and facial cleansers). These products can be released into the environment directly through spills, sewage discharge, and industrial and domestic effluents, or indirectly through run-off. Based on the chemical composition, Primary microplastics are derived from the unintentional release of intermediate plastic feedstock, such as mermaid tears and pellets. They can also be produced as byproducts of industrial production, dust and fiber emissions, and the degradation of plastic materials (GESAMP 2015). Primary microplastic pellets are lipophilic, which means they easily absorb toxic and hazardous substances from nearby marine water on their surface. They contain polythene (PE), polystyrene (PS), polypropylene (PP), and polyolefin particles. The surface of the collected pellets from the marine environment contained a variety of hydrophobic and aromatic chemicals, including dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) (Cauwenberghe et al. 2015). There have been reports of high PCB concentrations on polypropylene pellets on beaches in Bangladesh (Ryan, 2013) and Japan (Mato et al. 2001). The reports of plastic pellet availability from beaches in Belgium (Claessens et al. 2011), India (Jayasiri, 2013), and Singapore (NG & Oberd 2006) showed the wide dispersion of these microscopic microplastics.
According to Cole et al. (2011) and Eriksen et al. (2013), secondary MPs are the main cause of micro-plastic pollution in aquatic environments. They are created when larger plastic particles that are already present in the environment gradually deteriorate due to UV radiation (photo-oxidation), mechanical transformation (such as wave abrasion), and biological degradation by microorganisms. When compared to other types of plastic litter, nano-plastics (1-3 nm) have mostly unknown toxicological properties and fates. Micro-plastics in the environment can further degrade into these particles (da Costa et al, 2016). Nanoplastics are released when synthetic fibers break down while washing garments and when plastic products like expanded polystyrene break down quickly due to mechanical friction. The reduced size of these nanoplastics and the high ratio of volume to surface area make them vincible to ingestion by the major consumers of the food chain such as corals, phytoplankton and zooplankton.
MPs are dispersed diversely in different stratum of the aquatic environment (water surface, water column, and sediment) due to their wide range of shapes (e.g. spheres, fiber, film, irregular) and densities influencing their availability and affects on most of the organism extent to aquatic ecosystem. The use of MPs in industry and daily life are widespread because of their lightweight, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Since 1950, the plastics sector has experienced tremendous growth, with global output reaching 320 million tons in 2017 (Plastics Europe, 2018) and projected to reach 33 billion tons by 2050 (Rochman et al., 2013). The advantages of plastics include their lightweight, durability, and resistance to corrosion. However, a huge amount of MPs particles are released into aquatic and terrestrial environments because of their extensive use, high-level production, rapid disposal, and recalcitrance where they will persist for a long time (Sunny et al., 2021a). Most plastics are transported via rivers, which causes a large amount of plastic waste to end up in the world's oceans (Horton et al. 2017). Furthermore, a variety of aquatic organisms can be absorb micro-plastics due to their small size and immense specific surface area. This could result in harmful consequences that could propagate up the food chain (Sunny et al., 2021b; Islam et al., 2023). Through the food chain, MPs have an impact on a multitude of life forms, including higher-order species like humans, birds, and mammals, as well as the ecosystem's regular functioning. Among several aquatic organisms, it has been documented that amphibians, copepods, lungworms, barnacles, mussels, decapod crustaceans, gulls, fish, and turtles consume MPs (Sunny, 2017, Abbasi et al. 2018). Along with oxidative stress and neurotoxicity, harmful effects on growth, reproduction, and survival have been shown (Wang et al. 2019a). Moreover, MPs interact with different heavy metals and organic contaminants which enhance the enhance the impacts of toxicity. Therefore, along with the physical toxicity, chemical and metal-based toxicity are also identified with MPs which increases the potential pernicious effects of MPs to a greater extent. Endurance of micro plastics and resistance against labefaction and waste of the plastic annihilation is a great challenge in present condition [Sivan 2011]. Perhaps recycling is identified as the best solutions but at the same time plastic debris throw into landfill apparently takes long lasting in the decomposition which ultimately found a major problem [Cole et al. 2011].
Being a pressing problem and the fastest-growing source of pollution, it is now a top priority for environmental concerns. The current assessment may help pave the way for additional research in this field. Growing global awareness of MPs pollution has given scientists international opportunities and avenues for investigation. This review aims to provide a critical understanding of the ingestion of microplastics (MPs) by aquatic biota. It will cover various aspects such as the current global plastic situation, the routes that MPs take in the aquatic environment, the eco-toxicological effects of MPs, the interactions that MPs have with other contaminants, and the effects that these interactions have on aquatic organisms in the aquatic environment.
2. Methods
“Plastic pollution’ or ‘plastic contamination’ or ‘microplastic pollution and fish’ or ‘plastic waste management” were the basic term used in search of conducting and exploring from the internationally published articles, journals and scientific literature. When gathering data on plastic pollution in freshwater and marine environments from different sources, these are the websites that should be highlighted in particular.
- ➢
- ➢
- ➢
- ➢
- ➢
- ➢
At the same time, inquiring some other search engines like goggle and others for gathering local information regarding pelagic biota, fresh water and aquatic environment so on without facing any restriction in connection to year of publication. Owning to some limitation of the number of published studies, we included partial matches, scientific reports, conference papers, reviews, unpublished reports, opinion papers (no field-data), thesis and other publications in the grey literature.
Principally, the study trying to incorporated the data depending on the types of plastics, microplastics, aquatic environment such as fresh and marine water, distribution of MPs, environmental fate of MPs, affect of MPs on human health and finally the pernicious effect on aquatic food system.
3. Results
3.1. Global Status of Microplastic
Plastics production increased dramatically in 2010 from 1.5 million tons in 1950 to 250 million tons, and it is estimated that this amount will reach 33 billion by 2050 (Rochman et al. 2013).The increase occurred suddenly. The location, depth, fixity habitat, geography, and other factors all influence the variations in microplastics. The world's rivers discharge between 1.1 and 2.41 million tons of plastic annually into the ocean. Of these, the twenty most polluting rivers in Asia account for over two thirds (67%) of the total annual input, covering 2.2% of the world's surface area and housing 21% of the world's population (Lebreton et al. 2017). Since suspended particles can remobilize to the water column by resuspension, bioturbation, or hydrodynamic phenomena after falling to sediments, it is important to observe the behavior of microplastics in marine environments from a dynamic and ever-changing standpoint. Scientists estimate that, if plastic pollution is not removed by 2050, there will be more plastic in marine environments than fish. Large plastic polymer components found in the natural environment are used in the industrial sectors, as shown in Table I.
Table 1.
The application of plastics and their major components.
Table 1.
The application of plastics and their major components.
| Micro plastic |
Application |
Density in natural environment (g/cm3) |
References |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) |
Water and soft drink bottles, food jar |
1.38-1.39 |
Sailaja et al, (2018); Sharma and Chatterjee, (2017) |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
Cables, plumbing pipes |
1.20-1.45 |
| High-density polyethylene (HDPE) |
Shampoo bottles, packaging |
0.94-0.98 |
| Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) |
Grocery bags, packaging |
0.93-0.97 |
| Polypropylene (PP) |
Medicine bottles and caps, chips packs |
0.89-0.91 |
| Polystyrene (PS) |
Disposal cups, cutlery, packaging foam |
1.04-1.11 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) |
Food packaging, electronic and defense gadgets |
1.2-1.22 |
| Polyamide (PA) |
Fishing nets, clothing, ropes |
1.13-1.5 |
Plastic polymers likes PS, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and polyethylene terephthalate holding distinctive gravity > 1 are commonly accumulated in the benthos because PP and PE with appointed gravity < 1 levitates on the surface of water. Massive PE and PP is identified as primary source of microplastic in the surface water bodie (Reisser et al. 2013).
3.1.1. Different Types of Micro-Plastics Studied in Field and Laboratory
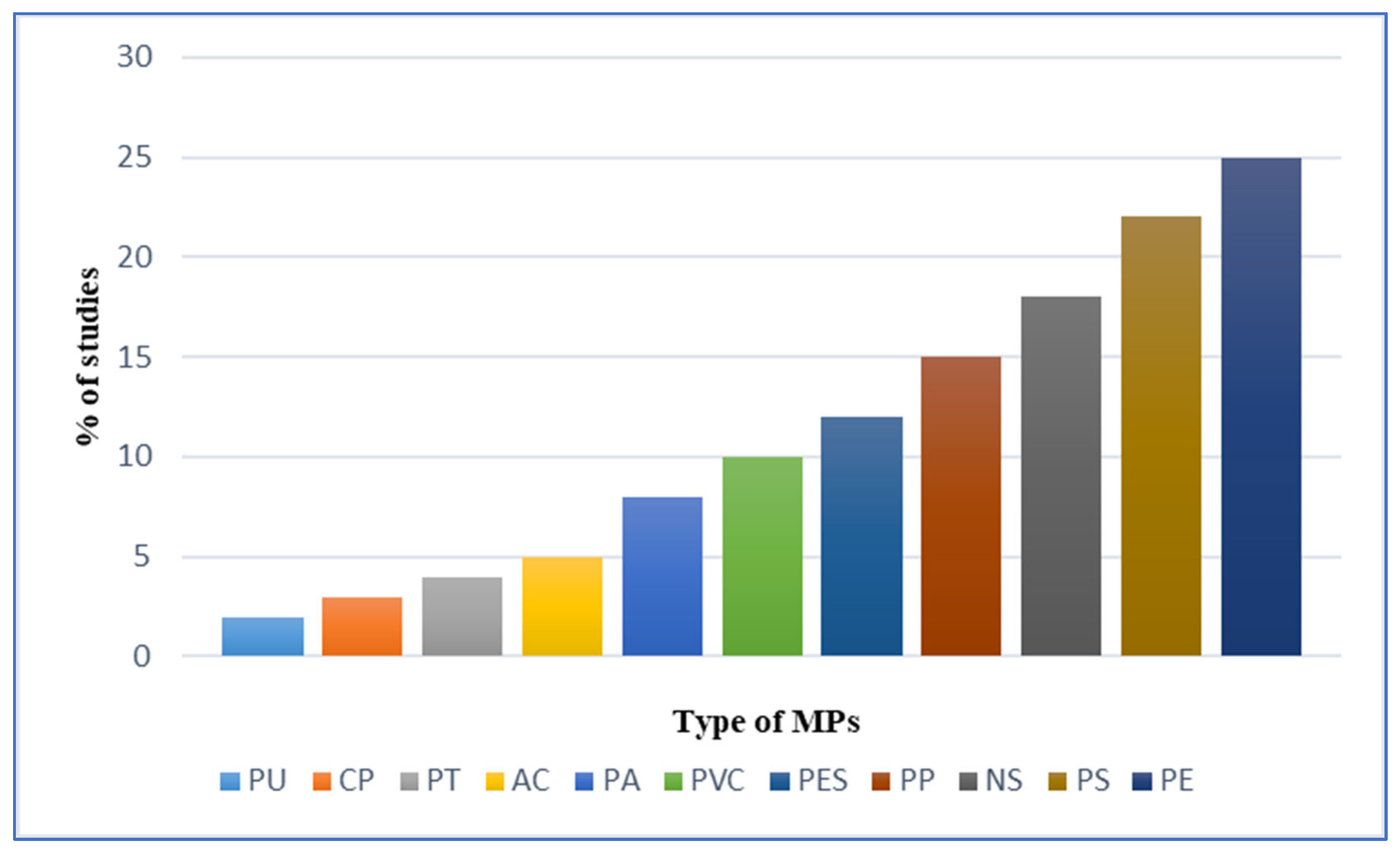
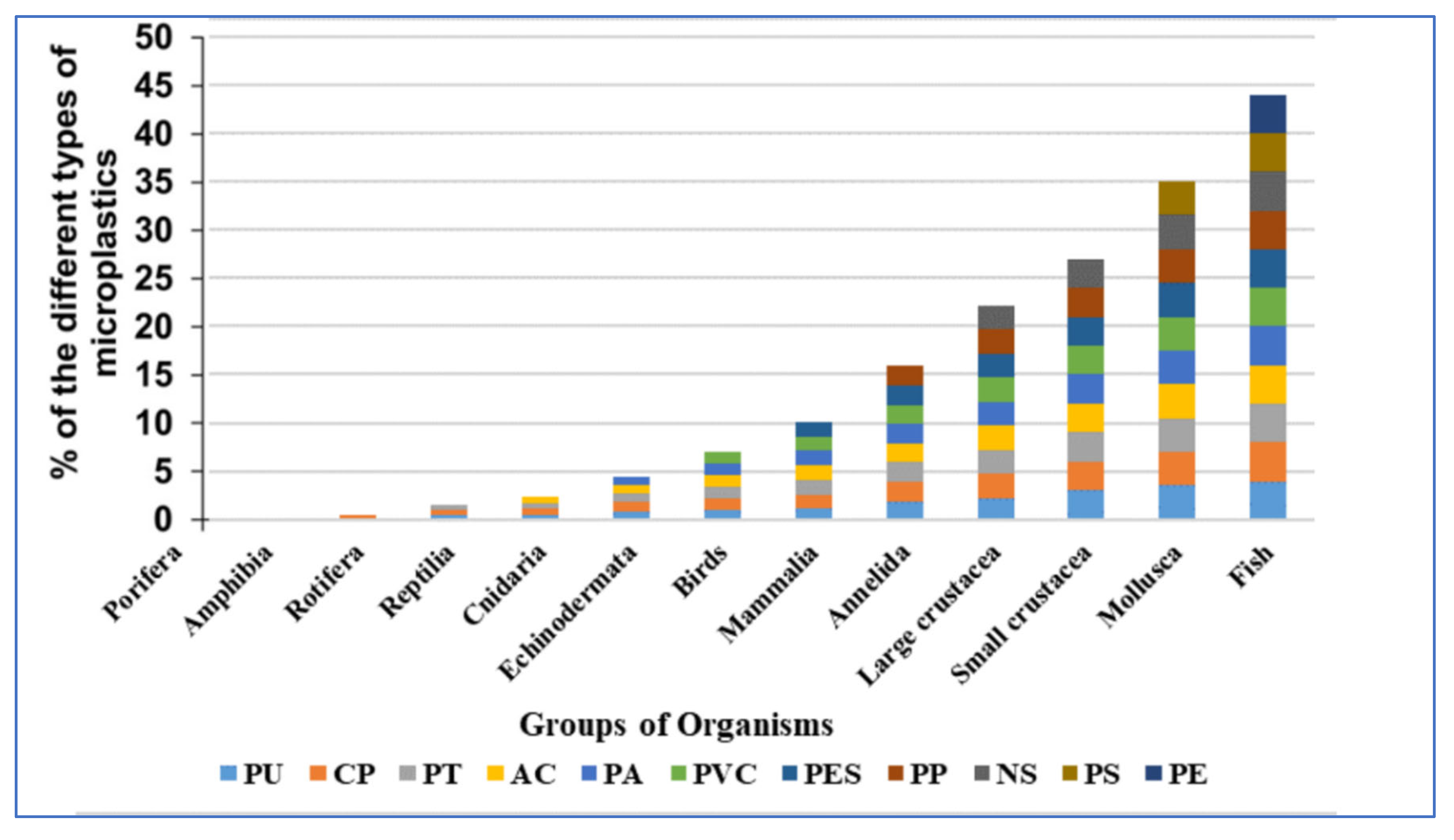
In the field and laboratory studies (
Figure 1), fish were the most frequently studied group of organisms, followed by crustaceans (21% for large and small crustaceans combined), molluscs (14%), annelid worms (6%), mammalia and birds (5%) (
Figure 2), and there were relatively few studies of other organism groups. The most common types of micro-plastics that are reported are PE (23%) and PS (22%), followed by NS (15%), PP (12%), PES (9%), PVC (8%), PA (7%), and AC (5%), etc.
About 12% polyethylene was identified in the fish which was the most common type of MP studied in fishes. Ingestion of PE by pelagic and benthic fish took place due to its widespread presence in both water column and sediments or lack of selectivity however it was less commonly reported in other groups of organisms like mollusks, small crustaceans, and annelids
(Lusher et al. 2013). (
Figure 2). Fish and small crustaceans have been reported to effects PS in these studies (
Figure 2) although crustaceans have been shown to have the ability to distinguish live particles from inert ones, e.g. algae and PS beads
(Poulet and Marsot, 1978). The PS fragments were reported to adhere with the dead copepods which could contribute to vertical transport of this type of MP
(Cole et al, 2013).
Aquatic species are potentially sensitive to these acquiring pollutants due to the vast spectrum of physicochemical properties and the widespread distribution of MPs in aquatic environments (Lusher et al., 2013). When animals are exposed to MPs, they may absorb them through their digestive tract and gills (de Sá et al. 2015; Watts et al. 2014). The ingestion may result by ingesting organisms of lower trophic levels harboring these particles, such as plankton containing MPs, or from an incapacity to distinguish MPs from prey (de Sá et al., 2015). (Fendall and Sewell, 2009). MPs have the ability to cling directly to living things (Cole et al., 2013).
3.2. Distribution of Micro-Plastics in Aquatic Environment
Going back to the last couple of years, separate ubiquitous reports and surveys have been informed about the appearance of floating microbeads and microplastics in various waterfalls around the whole world (Cozar et al. 2014; Eriksen et al. 2014; Reisser et al. 2015). The floating microplastics and microbeads are considered as a serious threat to North Atlantic region especially in Northern Hemisphere subtropical gyres (Li et al. 2016). The North Pacific central belt where first identified the drastic concentrations of micro plastics (Moore et al. 2001) and then generated the term ‘marine debris patches’ (Kaiser 2010; Zhang et al. 2010). Nearly 22.290 tonnes of floating plastic offal (> 33.000 particles km−2) were gather in the North Pacific subtropical gyre showed Law et al. (2010) in his studies whereas found PP, PE, plastic slices, narrow plastic films and pellets. Somewhere about 270.000 tons of MPs was found in the past 5 years in South Pacific, North Pacific, South Indian, South Atlantic and North Atlantic seas whereby almost five subtropical gyres along the Bay of Bengal, the Mediterranean Sea and costal Australia (Eriksen et al. 2014). Therefore the aquatic environment polluted because of diversified MPs offal (Barnes et al. 2009) bases on the split anthropogenic actions, unfavorable strong currents, velocity of winds and landfall geology.
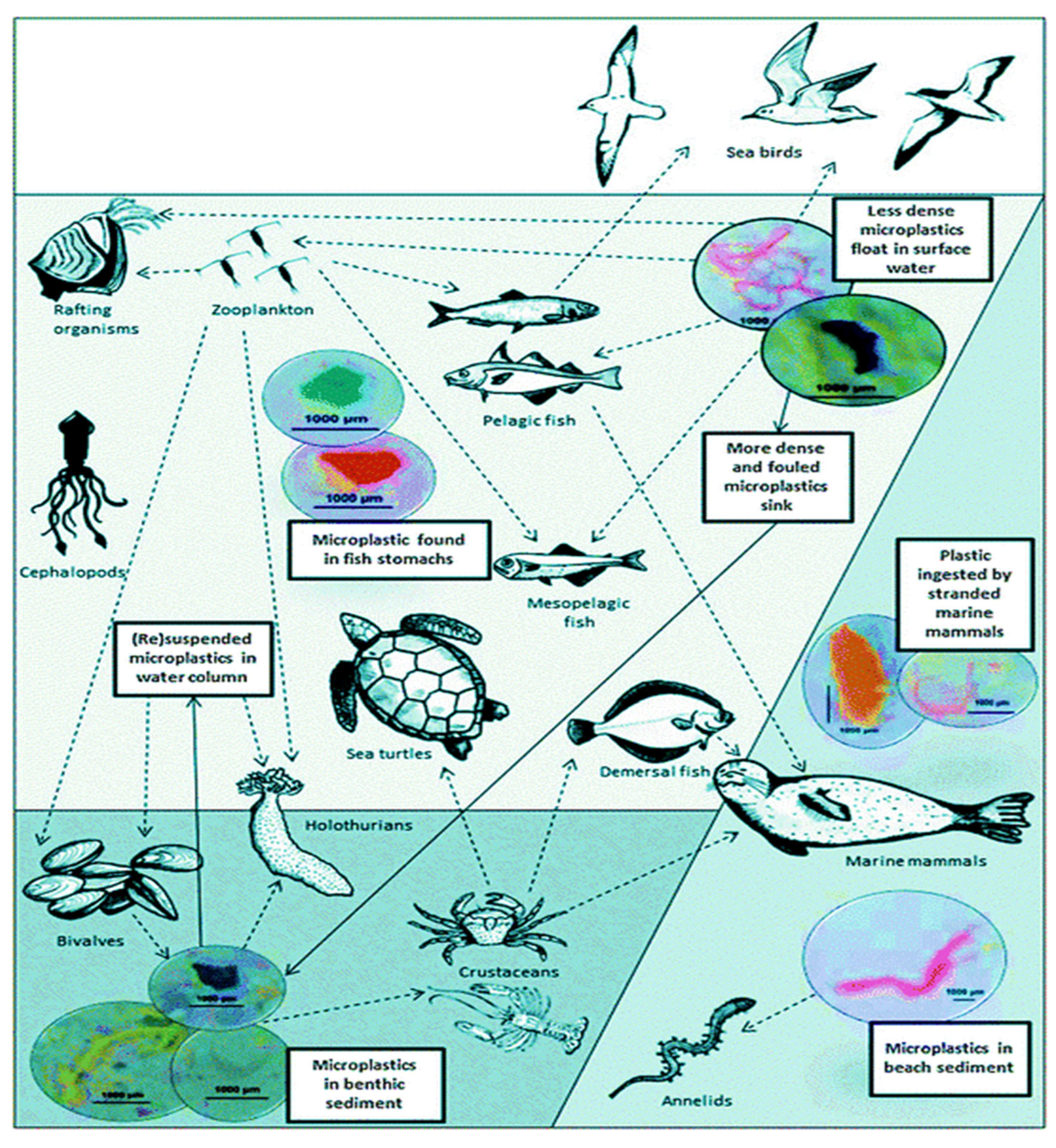
In the Bay of Bengal, Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean wherein mentioned gruesome affluence of plastic garbage due to manmade and natural factors. Basically, plastic industry and industrial activities were greatly built in coastal areas and their industrial waste sometimes directly gone to seas water due to lack of their own waste management system. Furthermore, absorption and ingestion of micro-plastics by primary trophic level organisms e.g. phytoplankton and zooplankton could be a pathway into the food chain (
Bhattacharya et al. 2010). Due to their tendency to migrate during the day, many zooplankton species may be a vector for the spread of microplastic pollution to deeper water columns and their occupants. This could occur by fecal pellets sinking to the seafloor or predation
(Wright et al. 2013a). According to field observations, fur seals (
Arctocephalus spp.) have microplastics in their scat
(Eriksson et al. 2003). Microplastics were found in the gut and haemolymph of shore crabs (
Carcinus maenas) in feeding experiments
(Farrell and Nelson, 2013). The presence of MPs was also found in some commercially important fish, mollusks, and crustaceans that humans consume, raising concerns about exposure as well as trophic transfer to humans
(Galloway, 2015; Hasan et al., 2023). The following (
Figure 3) illustrates the trophic transmission of MPs and their interactions in the marine environment.
3.3. Effect of MPs in Aquatic Food System
Numerous studies have documented the presence of microplastics in aquatic environments. These microplastics are bioavailable to a variety of organisms that hold various positions in aquatic food webs, including fish, corals, mollusks, annelid worms, zooplanktons, sea urchins, and echinoderms (Browne et al. 2008; de Sá et al. 2015; Islam et al., 2023). When these nonbiodegradable materials are ingested by aquatic organisms and bioaccumulate in the food chain, they move up the trophic scale (Gregory 1996; Carpenter and Smith 1972, Desforges et al. 2014). A number of organisms, including seabirds, turtles, crustaceans, and fish, have already been shown to be negatively impacted by microplastics, including clogged digestive tracts, stunted feeding, imbalanced hormonal secretion, delayed ovulation, and decreased fertility (Azzarello and Vleet 1987; McCauley and Bjorndal 1999; Wright et al. 2013; Derraik 2002; Cole et al. 2011, Van Cauwenberghe and Janssen, 2014). Aquatic organism mortality is a long-standing consequence of microplastics in the food chain (Derraik 2002; Wright et al. 2013).
3.3.1. Plankton
Phytoplankton produce their food by the presence of CO2 and sunlight through photosysnthesis but due to omnipresent nature of microplastics, they penetrates in to their cell wall by phagocytosis which reduces their chlorophyll concentrations in the green algae (Nerland et al. 2014; Kuddus et al., 2020; Kuddus et al., 2022). These phytoplanktons are consumed by zooplankton which serves as a key component in aquatic food system. The bioavailability of microplastic in the zooplankton act as a key transfer routes of microplastic to the higher trophic levels (Cozar et al. 2014). Since many species with distinct life cycles feed zooplankton, this process can transfer microplastics to higher trophic levels, which in turn impacts the aquatic ecosystem (Wirtz 2012; Hasan et al., 2023). Various investigations have demonstrated that fifteen distinct taxa of zooplankton, spanning from copepods to jellyfish, have assimilated microplastic latex particles (less than 5 mm) by filter feeding (Frost 1977; Hart 1991; Wilson 1973; Cole et al. 2013). When polystyrene microplastics are consumed by zooplankton, they remain in the gut for up to 7 days, while for shore crabs (Carcinus maenus), this retention period can reach up to 14 days. This can cause disruptions to the zooplanktons' feeding and digestion processes as the microplastics either pass through the gut or clog or accumulate in the digestive tract (Watts et al. 2014; Cole et al. 2013). Marine organisms that are benthic and pelagic can access microplastics when zooplankton ingests them as faecal pellets (Setala et al. 2014).
3.3.2. Benthic Organism
About 98% of the marine biota is made up of the benthic population, and Nerland et al. (2014) reported the evidence of consumption of microplastics by benthic invertebrate. Blue mussels in the North Sea region of Germany absorbed microplastics measuring approximately 0.36 ± 0.07 particles g−1 (wet weight), whereas 33.5% of the microplastic particles were taken by North Pacific barnacles (van Cauwenberghe and Janssen 2014; Goldstein and Goodwin 2013). Due to the omnivorous eating habits, lobsters (Nephrops norvegicus) in the Clyde Bay on Scotland's west coast were found to have microplastics (< 5 mm) in their gut area (Murray and Cowie 2011). The ingestion of a high concentration of microplastics, particularly polystyrene, by the benthic worm (Arenicola marina), a significant component of marine food chains, leads to a decrease in both feeding ability and weight (Wright et al. 2013; Besseling et al. 2013).
3.3.3. Fish
The most common ways that MPs are exposed to the environment are by direct ingestion as food or ingestion of MPs by mistake as prey. Plastic polymers like PS, polyamide, polyester, and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) were reported in pelagic feeding fish species in the English Channel (Lusher et al. 2013; Sazzad et al., 2023). Evidence of microplastic was found in 30% of the individual fish species (Possatto et al. 2011; Lusher et al. 2013). MPs have been found to have an impact on some planktivorous fish and the bottom-feeding fish like Gerreidae in a tropical estuary in northeast Brazil and the North Pacific Central Gyre, respectively (Ramos et al. 2012). In addition, 83% of the Norway lobsters were discovered to have microfibre infections (Murray and Cowie 2011). Smaller MPs can be expelled from fish by natural feces, while larger-sized MP beads remain in the fish's stomach for a longer period of time and are therefore thought to be more detrimental to the marine fish ecosystem (Dos Santos and Jobling 1992). Fish that have an accumulation of large MPs get malnourished and starve to death (Boerger et al. 2010).
3.3.4. Marine Mammals and Turtles
There have been reports of MPs affecting marine mammals (including sea turtles, whales, seals, bears, and sealions) and turtles in many countries worldwide (Derraik 2002; Meaza et al. 2020). Sea turtles in Brazil have been observed to accumulate MPs in their digestive tracts (Nerland et al. 2014). Due to their high lipid and fat content, some filter-feeding mammals, such as baleen whales, were particularly vulnerable to microplastic contamination, which eventually accumulated in their stomach and intestine. In fact, recent reports of stranded whale deaths have been linked to a significant accumulation of microplastic debris in these organisms' guts (Fossi et al. 2012; Sharma and Chatterjee 2017). Harbour seals, scat of fur seals, and Hooker's sea lions have been reported to accumulate microplastics in their stomach and intestine (Bravo Rebolledo et al. 2013; Goldsworthy et al. 1997; McMahon et al. 1999). Despite the fact that polar bears can consume microplastics, no studies on this subject have been released as of yet.
3.3.5. Sea Birds
Due to the habit of feeding from the sea surface, seabirds (including albatrosses, shearwaters, petrels, and northern fulmars) have been found to accumulate microplastics in their stomachs and digestive systems, which are found in the form of inductrial pellets (Ryan 1987; Robards et al. 1995; Blight and Burger 1997; Vlietstra and Parga 2002). Many seabirds are also able to eliminate microplastics from their digestive tracts through regurgitation, despite the fact that younger seabirds were more exposed to microplastic contamination during the feeding process, which resulted in starvation and loss of fitness (Lindborg et al. 2012; Kuhn and van Franeker 2012; Tanaka et al. 2013).
Table 2.
Eco-toxicological effects of MPs across several groups of organisms.
Table 2.
Eco-toxicological effects of MPs across several groups of organisms.
| Classes |
MPs type |
Effects |
Ref. |
| Fish |
PE |
↓ Total protein, globulin, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels
↑ Mortality
↑ CYP P450
↓ AChE activity
↓ Predatory performance
↓ Predatory efficiency |
Oliveira et al. 2013; Haghi and Banaee, 2017; Mazurais et al. 2015; de Sá et al. 2015 |
| PS |
↓ Body length
↓ Larval locomotion
↓ AChE activity
↑Alterations of metabolic profiles
↑Lipid and energy metabolism disturbed
↑Inflammations and lipid accumulation in the liver
↓ Activity
↑ Weight loss in the brain
↓ Water in the brain |
Chen et al. 2017a; Lu et al. 2016; Mattsson et al. 2017 |
| PVC |
↑ Peroxidase activity and skin mucus
↑ Phagocytic capacity
↑ genes related to stress
↑ Structural alterations of the Distal intestine
↓ The regular structure of serosa, |
Peda et al. 2016; Espinosa et al. 2017 |
| Crustacean |
PE |
↑ Mortality
↓ Reproduction
↓ Growth |
Au et al. 2015 |
| PS |
↑ Mortality
↓ Survival
↓ Fecundity
↓ Ingestion rates
↓ Hemolymph sodium ions
↑ Hemolymph calcium ions
↑ Oxygen consumption |
Lee et al. 2013; Watts et al. 2016; Cole et al, 2013 |
| PP |
↓ Feeding rate
↓ Body mass
↓ Metabolic rate
↑ Mortality
↓ Growth
↓ Weight |
Au et al. 2015; Welden and Cowie, 2016 |
| |
PVC |
↑ Mortality
↓ Settlement |
Li et al. 2016 |
| PES |
↑ Mortality
↓ Settlement
↓ Wet weight gain |
Li et al. 2016; Jemec et al. 2016; Straub et al. 2017 |
| PA |
↓ Assimilation efficiency |
Blarer and Burkhardt-Holm, 2016 |
| AC |
↑ Immobilization |
|
| Mollusks |
PE |
↑ Energy consumption
↑ MPs accumulation
↓ AChE and Catalase activities
↓ Lysosomal integrity
↓ the gene involved in immunity |
Van Cauwenberghe et al. 2015; von Moos et al. 2012; Avio et al. 2015; Détrée and Gallardo-Escárate, 2017 |
| PS |
↑ Maintenance costs
↓ Oocyte number
↓ Sperm velocity
↓ Filtering activity
↓ Phagocytic activity
↑ Apoptotic processes |
Sussarellu et al. 2016 |
| Annelida |
PE |
↑ Energy consumption
↓ Protein content |
Van Cauwenberghe et al. 2015 |
| PS |
↓ Feeding activity |
Besseling et al. 2013 |
| PVC |
↓ Energy reserves
↓ Feeding activity
↑ Phagocytic activity
↑ Inflammatory response
↓ Lipid reserves
↑ MPs retention
↑ Oxidative stress |
Browne et al. 2013 |
| Echinoderms |
PE |
↑ Anomalous larvae development |
Nobre et al. 2015 |
| PS |
↓ Fertilization rate
↓ Growth
↑ Larval development abnormalities
↑ Oxidative stress
↑ MPs accumulation
↑ Malformations
↑ Disruption of cell membrane |
Martinez-Gomez et al. 2017 |
| Rotifers |
PS |
↓ Growth rate
↓ Fecundity
↓ Lifespan
↑ Reproduction time |
Jeong et al. 2016 |
3.4. Interactive Eco-Toxicological Effects of MPs with Other Contaminants
The circumstance in which organisms are simultaneously exposed to many pollutants in the environment has led to a great deal of research on the combined beneficial and detrimental effects of MPs with other environmental toxins, as indicated in (
Table 3).
In these studies, the combined effects of MPs and legacy pollutants (POPs, endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), metals, antibiotics, and herbicides were investigated. The legacy POPs included polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and dichlorodiphenyltrichlorotetraethanes (DDT and breakdown products). The metals included nickel, silver, and chromium VI. The effects of MPs with endocrine-disrupting substances including pharmaceutical 17α-ethinylestradiol and Bisphenol-A, pesticide paraquat, and antibiotics like cephalaxin and triclosan were also recorded in this study. The following summarizes MPs' interactions with other pollutants and their ecotoxicological effects (
Table 3).
3.5. Effect of MP on Human Health
Eating seafood, including shellfish, as well as non-seafood items like beef, honey, and salt exposes one's diet to plastic, and this is probably the most well-known way for consumers to be exposed (Bari et al., 2023, Faruk et al., 2023). According to several recent studies, there is plastic debris in tap and bottled water that is intended for human consumption worldwide. This debris can be harmful to our bodies by causing oxidative stress, genotoxicity, and inflammation (Kelly and Wright, 2017).
The first documented instances of direct interactions between plastic nanoparticles and brain tissue were discovered in 2017, when it was discovered that fish with plastic nanoparticle contamination had behavioral problems and brain damage (Mattsson et al. (2017). Despite the fact that the study was conducted on fish, exposure to plastic particles can seriously harm humans (Tufael et al., 2023). According to certain research, nanoplastic particles have the ability to move from the gut to the lymphatic system in several animals and may pierce deeply into organ tissue (Brennecke et al. 2015). Plastics are known to contain common chemical additives that provide them durability, plasticity, and stability in the heat, but they are also known to be endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), which can lead to immunological disorders, hormone-related cancers, delayed or accelerated puberty in females, imbalances in sex ratios, and disruptions in infertility cycles (Bergman et al. 2013). Organisms should be concerned about even low levels of exposure to endocrine-disrupting substances; animal experiments have revealed worrying side effects such as immune system and thyroid dysfunction (Gallo et al. 2018).
3.6. Micro-Plastics Pollution in the Context of Bangladesh
Being an expanding country, the usage of plastic materials has increased, endangering biodiversity and the environment. The absence of a suitable recycling unit and a waste management system is making this worse. The single-use food packaging system and a lack of public awareness are also responsible for the rise in plastic pollution (Haque et al., 2017). The primary plastic pollution materials found in metropolitan areas include polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), polypropylene (PP), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) (Shimo, 2014). According to Uddin et al. (2018), due to the low cost of polythene bags and the absence of substitute materials, 35% of customers in the Mymensingh Sadar upazilla used 5–10 plastic bags per week, while 65% of shopkeepers used 50–100 plastic bags per week. But in 2002, the Bangladeshi government outlawed the production, advertising, and use of polyethylene packets thinner than 55 μm (Bangladesh Environment Conservation Act, 1995). The legislature enacted the Mandatory Jute Packaging Act. 2010 in 2010, which mandated the use of jute fiber instead of polythene bags when bundling items. However, despite this legislation, polythene is still produced, traded, and used extensively throughout the nation due to its poor enforcement and lack of reasonably priced, environmentally friendly alternatives. The overall quantity of plastic garbage dumped in landfills in Bangladesh's main city, Dhaka, as well as smaller cities, has risen many times over. The primary cause of microplastic (MP) pollution in Bangladesh's aquatic and terrestrial habitats is the unregulated use of plastic and microbeads in personal care products. Both plastic producers and consumers are still unaware of the harmful effects of these recently identified micropollutants. Here are some concerning data on Bangladesh's plastic pollution (Waste Concern, 2014):
In Bangladesh, about 3,000 tonnes of plastic debris is generated every day.
Among total generated waste, about 8% comprises of plastic debris which is about 800,000 tonnes numerically.
About 14 million pieces of polythene bags are used every day in Dhaka city which ultimately end up in rivers and the ocean.
Every day about 73,000 tonnes of plastic waste end up in the Bay of Bengal through the Padma, Jamuna, and Meghna rivers.
Around 250 tonnes of non-recyclable plastic products are sold in old Dhaka every month.
The growth of bio-waste production is 5.2% while plastic waste comprises of 7.5%.
In 2015, the Environment and Social Development Organization (ESDO) carried out a primary study on the extent of microplastic (MP) pollution in Bangladesh's three notable urban communities (Dhaka, Chittagong, and Sylhet) (ESDO, 2016). The study found that MPs are present in 60 commonly used cosmetic products in Bangladesh (face wash, detergent, body wash, nail polish, toothpaste, face and body scrub), and approximately 8000 billion microbeads are released into the surrounding water bodies each month (about 7000 billion in Dhaka, approximately 1000 billion in Chittagong, and 200 billion in Sylhet). They also reported that about 92% of retailers were not aware of plastic pollutation while about 40% remained conscious about selling those products. The majority of users of these products with microbeds were found to be females (ages 20 to 29). Of all the other products, face washes were the most frequently used, and 95% of users were unaware of the negative effects that microbeads have on the environment and human health, while 92% of retailers chose to ignore these concerns (ESDO, 2016).
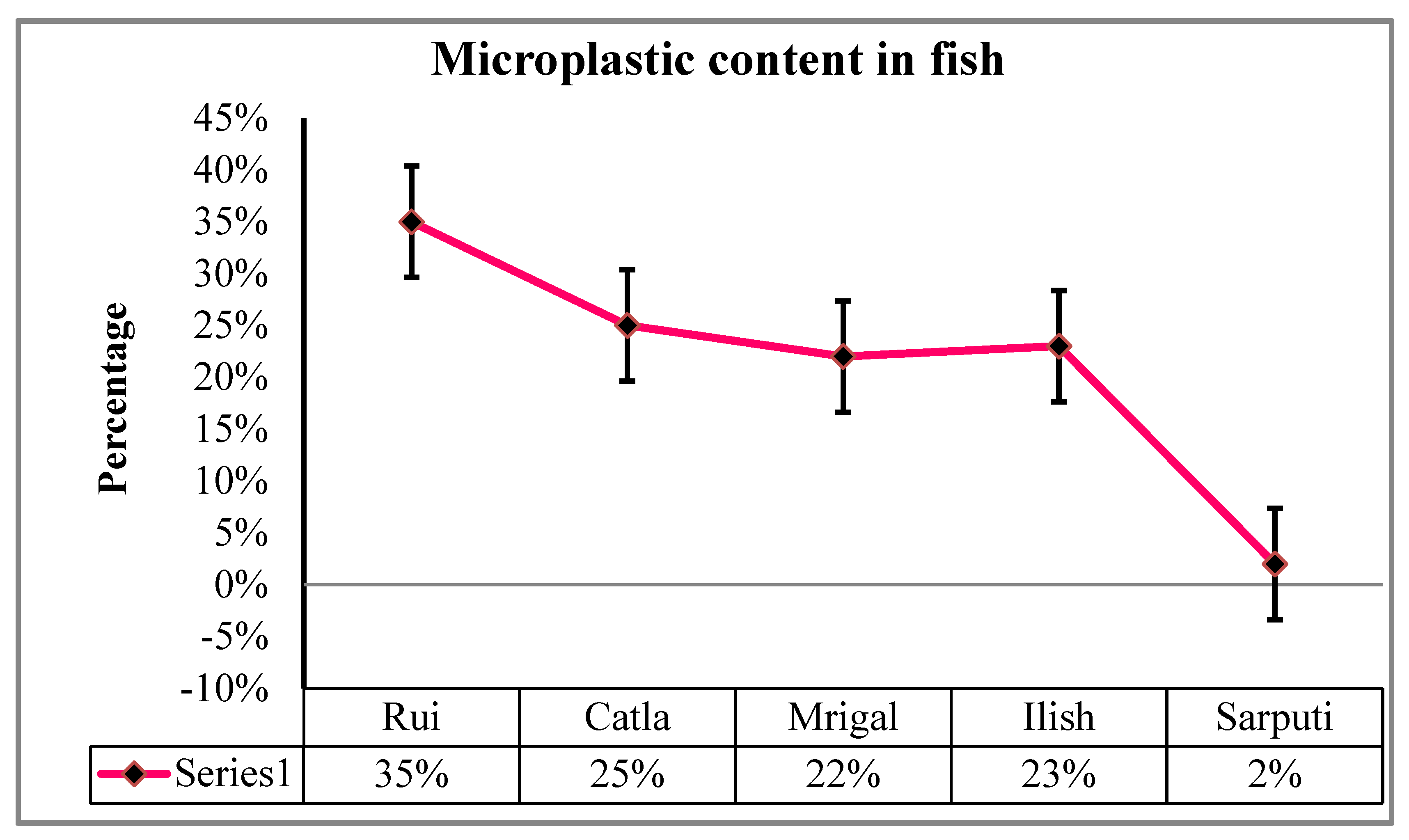
In order to assess the level of water pollution, they collected 100 fish samples from five different species: Rui (
Labeo rohita), Catla (
Gibelion catla), Mrigal (
Cirrhinus mrigala), Ilish (
Tenualosa ilisha), and Sarpunti (
Puntius sarana). They found that larger fish, like Rui, were more contaminated with micro-plastics than smaller fish, like Sarpunti (
Figure 4). The largest percentage of MPs (61%) was found in Dhaka city, while the lowest percentage (8%), was found in Sylhet. Fish from the Buriganga River and Dhaka City lakes (40%) have higher levels of microbeads in their respiratory systems and guts than fish from the nearby rivers (ESDO, 2016). Among all the fish species under investigation, demersal fish (
Mystus vittatus) had the highest MPs, with 73.3% of the samples taken from freshwater fish (Parvin et al. 2021).
All the plastic debris eventually washes away into the Bay of Bengal as wetlands, lakes, ponds, and rivers are continuously contaminated with MPs and thereby affecting the marine lives and biodiversity which ultimately distribute into the humans and animals through the food web. A recent study found 443 MP item in three marine fishes explicitly pink Bombay-duck (Harpadon nehereus), white Bombay-duck (H. translucens) and gold-stripe sardine (Sardinella gibbosa) collected from the Northern Bay of Bengal at Bangladesh (Hossain et al. 2019). The coastal population of Bangladesh was 70.9 million in 2016 where the average waste generation rate was 0.43 kg/person per day of which 8% of this was plastic waste (Jambeck et al. 2015).
3.7. Mitigation Measures
An effective understanding between scientists and policy makers can contribute to the comprehensive mitigation of MPs in the environment. In response to tackle this emerging issue several mitigating measures have been identified. These included reducing plastic sources, reusing waste, composting and recycling, energy generation from waste conversion and management systems for debris at access water points and land. These measures are essential and control regulations, and overlap with the opposing adversary to avoid plastic debris from entering the wetland.
3.7.1. Ban and Restriction
A notable example of this kind of cooperation is the legislation that forbids plastic microbeads, as studies have demonstrated that it is possible to simply halt the release of microbeads, hence lowering the risk to marine life. To lessen the amount of plastic waste that accumulates, governments all over the world have devised strategic plans to outlaw the use and sale of plastic bags as well as the inclusion of microplastics in products. Across Asia, Africa, America, Europe, and Oceania, at least thirty nations have either completely or partially outlawed the use of plastic bags. In 2002, Bangladesh became the pioneer country to outlaw polythene bags, with subsequent countries including China, Eritrea, Mali, Mauritania, and South Africa. As of 2019, microbead-containing natural health products and over-the-counter medications are prohibited in Canada. A total ban on the supply of lightweight plastic bags at grocery store checkouts has been enforced by France.
According to Kibria (2017), a number of actions can be taken to lessen the risks and threats posed by plastic waste, including managing waste; lowering the generation of waste (e.g., recycling); halting the rise in single-use plastics through legislation, levy, or tax increase; educating the public through behavior-modifying education and outreach programs; and gathering and disposing of outdated or abandoned nets for recycling. In Bangladesh, post-consumer waste management and recycling are the significant operations that are currently carried out by the informal sector (Amin, 2017). Yasmin and Rahman (2017) estimated that Dhaka City generates 124 tons of recyclable plastic garbage per day, of which 103 tons are recycled, or 83% of the waste is recycled. Although Bangladesh has enacted legislation to preserve the environment and manage garbage, the National Environmental Policy of 2013 acknowledged the 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) approach as a suitable waste management plan. However, the strategy has not been effectively implemented. On the other hand, teaching about environmental issues in schools may facilitate the Bangladeshi government's 3Rs policy (Amin, 2017). Politicians as well as entrepreneurs in the plastics industry need to raise public awareness and offer alternatives to plastic shopping bags (Shariq, 2011).
3.7.2. Microplastc Regulations
Solutions for reducing MPs in the environment may come from a sustained collaboration between science and policy. Furthermore, new scientific knowledge may facilitate the conduct of research important to policymakers and scientists. A few of the legislation that are discussed in this paper are the outcome of the cooperation between scientists and legislators, which helped to create improvements aimed at mitigating the effects of MPs. A notable example of this kind of cooperation is the legislation that forbids plastic microbeads, as studies have demonstrated that microbead release can be easily controlled, reducing the damage to marine life. Consequently, the US, Canada, the EU, and Australia have all introduced legislation to outlaw this source of plastic contamination (Rochman et al. 2016). Certain manufacturers have consented to remove plastic microbeads from their goods on a voluntary basis in response to this regulation (Schnurr et al. 2018).
A notable example of this kind of cooperation is the legislation that forbids plastic microbeads, as studies have demonstrated that it is possible to simply halt the release of microbeads, hence lowering the risk to marine life. In a variety of applications, such as personal care products and abrasives, scientists have recently developed biodegradable cellulose microbeads from a sustainable source that show promise as a replacement for persistent plastic microbeads (Coombs Obrien et al. 2017). This could eventually be required by law. Operation Clean Sweep, launched by the plastics industry to lessen the loss of plastic pellets to the environment, was a response from both industry and policy to address the issue following reports of plastic pellets in the oceans, on beaches, and in seabirds' digestive tracts (Rochman et al. 2016). Thus, further research on MPs is needed in order to create and put into practice efficient management plans. In order to combat plastic pollution and manage MPs without causing harm to the environment, one effective and safe course of action is the biodegradation of plastic polymers by certain organisms like bacteria, fungi, and mealworms. According to a recent study by Bombelli et al. (2017), the wax moth Galleria mellonella larvae quickly biodegraded PE to produce ethylene glycol. Similar to this, earthworm (Lumbricus errestris) gut-derived bacteria and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) MP particles degraded (Lwanga et al. 2018). Because of this, there is a great deal of optimism about the application of organisms that consume plastic in waste management. Most importantly, governments must provide funding for additional research and inventions aimed at discovering species capable of decomposing plastic more effectively. All of these tactics work together to lessen the impact of MPs in both terrestrial and aquatic habitats. Throughout the supply chain, industry is essential to the mitigation of MPs. IKEA is one company that has incorporated the EPR strategy into its business model by encouraging material reuse and recycling across its supply chain (INGKA Holding 2017). Furthermore, 1 million shoes manufactured from plastic waste were sold by Adidas in 2017—that's the same as 16.5 million plastic bottles and 14.3 t of nylon gill nets (Kharpal 2018). Reducing the use of plastic can also be accelerated by improving circular economy concepts like recycling and waste management plans, which will have significant direct and indirect socioeconomic and environmental effects. Mitigating plastic pollution by cleaning up the coast and the ocean are crucial, urgent actions that are required to contribute to the reduction of marine plastic pollution. If implemented and managed appropriately, plastic bag bans can effectively reduce the misuse of single-use plastic and, in turn, mitigate plastic and microplastic pollution (Schnurr et al. 2018). Furthermore, in order to enable recycling, plastics manufacturers need to make sure that their products are properly labeled and standardized. Additionally, raising awareness of MPs issues through campaigns and teaching people about their own duty to minimize plastic and MPs pollution by choosing to reject, reduce, reuse, and recycle plastics is being done through universities, schools, organizations, and networks. Children who receive educational interventions (such as teaching about marine trash) indicate higher levels of awareness, consequences perception, and self-reported action (Hartley et al. 2015).
3.8. Knowledge Gaps
Bangladesh still lacks sufficient research on the effects of MPs contamination on the terrestrial and aquatic biota. Subsequent investigations may concentrate on the measurement and description of plastics in freshwater and estuary environments, in addition to the influence of plastics on planktons, mollusks, freshwater fish, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Future research issues could also include the effects of plastics on the food chain, the transmission route, and the physiology of organisms affected by microplastics. The government and people of Bangladesh must act swiftly to address the actual danger that micropollutants pose to the ecosystem and biodiversity of the Bay of Bengal and the surrounding coastal areas. They also need to take the necessary actions to prevent the use of plastics and products containing microbeads, as well as the massive amounts of refuse that are being disposed of into the environment. Nonetheless, several studies have been conducted about the prevalence and dispersion of microplastics on the beaches and coastlines of India, Bangladesh's neighbor (Desforges et al. 2014; Van Cauwenberghe and Janssen, 2014).
4. Conclusions
In the modern world, it is undeniable that MPs occur and accumulate in aquatic environments. It's also clear that a wide variety of organisms come into contact with these particles, and that this interaction could have a variety of negative effects that put people, animals, and ecosystems at risk. Certain developing nations lack established laws and regulations to prevent microplastic pollution, despite being the primary source of plastic pollution in freshwater and marine environments. Although the deleterious effect of MPs is well known but the global plastic production is alarmingly rising. If plastic manufacture continues, the aquatic ecology will be irreversibly destroyed, and many fragile aquatic creatures will become extinct in the near future. So, in order to make the earth a better place for our generation, we urgently need to stop using plastic. It will be impossible to eliminate the usage of plastic if the general public remains unconcerned. The appropriate steps should be taken by the government to guarantee that the regulations controlling the use of plastic are faithfully carried out. Studies on the contamination caused by microplastics in Bangladesh are confined to marine rather than freshwater areas. Consequently, given the importance of freshwater systems and fisheries to a large number of people in Bangladesh, current research should focus on the effects of plastic pollution on humans, freshwater species, and marine organisms. The industries that produce plastics should be proactive in managing their end-of-life goods. They can utilize biodegradable polymers, which will break down into smaller pieces over time due to microbial (fungal and bacterial) decomposition, hence extending the plastics' longevity in the environment. Besides industrial plastic pollution should be reduced by recycling or upgrading of plastic litter. Recently, plastic materials can be converted into usable smaller fragments for the manufacture of new petrochemicals by tertiary recycling techniques. More reviews on plastic pollution should be published and detail research should be carried out so that people can have the awareness related to this future threat.
References
- Abbasi, S., Soltani, N., Keshavarzi, B. (2018). Micro-plastics in different tissues of fish and prawn from the Musa Estuary, Persian Gulf. Chemosphere 205, 80-87. [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.N., 2017. Country chapter state of the 3Rs in Asia and the Pacific-Malaysia. United Nations Cent. Reg. Dev 1–64.
- Andrady AL, Neal MA (2009) Applications and societal benefits of plastics. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364:1977–1984. [CrossRef]
- Au, S.Y., Bruce, T. F., Bridges, W. C., Klaine, S. J. (2015). Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposure. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 34, 2564-2572. [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G., Gorbi, S., Milan, M., Benedetti, M., Fattorini, D., D'Errico, G., Pauletto, M., Bargelloni, L., Regoli, F. (2015). Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from micro-plastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 198, 211–222. [CrossRef]
- Azzarello MY, Vleet ES (1987) Marine birds and plastic pollution. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 37:295–303.
- Bangladesh Environment Conservation Act. Act No. 1 of 1995. pp. 153–166. 1995. [cited 2020 June 18]. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bangladesh_Environment_ Conservation Act.
- Bari, K. F., Salam, M. T., Hasan, S. E., & Sunny, A. R. (2023). Serum zinc and calcium level in patients with psoriasis. Journal of Knowledge Learning and Science Technology ISSN: 2959-6386 (online), 2(3), 7-14. [CrossRef]
- Barnes DKA, Galgani F, Thompson RC, BarlazM (2009) Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364:1985–1998. [CrossRef]
- Bergman, Å., Heindel, J. J., Jobling, S., Kidd, K., Zoeller, T. R., & World Health Organization. (2013). State of the science of endocrine disrupting chemicals 2012: summary for decision-makers.
- Besseling, B.,Wegner, A., Foekema, E.M., Heuvel-Greve, M.J., Koelmans, A.A. (2013). Effects of microplastic on fitness and PCB bioaccumulation by the lugworm Arenicola marina (L.) environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 593–600. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P., Turner, J. P., & Ke, P.-C. (2010). Physical adsorption of charged plastic nanoparticles affects algal photosynthesis. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 114(39), 16556–16561. [CrossRef]
- Blarer, P., Burkhardt-Holm, P. (2016). Microplastics affect assimilation efficiency in the freshwater amphipod Gammarus fossarum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 23 (23), 23522-23532. [CrossRef]
- Blight LK, Burger AE (1997) Occurrence of plastic particles in seabirds from the eastern North Pacific. Mar Pollut Bull 34:323–325. [CrossRef]
- Boerger CM, Lattin GL, Moore S, Moore CJ (2010) Plastic ingestion by planktivorous fishes in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Mar Pollut Bull 60:2275–2778. [CrossRef]
- Bravo Rebolledo EL, van Franeker JA, Jansen OE, Brasseur SM (2013) Plastic ingestion by harbour seals (Phoca vitulina) in The Netherlands. Mar Pollut Bull 67:200–202. [CrossRef]
- Brennecke, D., Ferreira, E.C., Costa, T.M.M., Appel, D., Gama, B.A.P., Lenz,M. (2015). Ingested micro-plastics (b100 μm) are translocated to organs of the tropical fiddler crab Uca rapax. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 96, 491–495. [CrossRef]
- Browne MA, Dissanayake A, Galloway TS, Lowe DM, Thompson RC (2008) Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis. Environ Sci Technol 42:5026– 5031. [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A., Niven, S.J., Galloway, T.S., Rowland, S.J., Thompson, R.C. (2013). Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms, reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 23 (23), 2388–2392. [CrossRef]
- Carpenter EJ, Smith K (1972) Plastics on the Sargasso Sea surface. Science 175:1240–1241. [CrossRef]
- Cauwenberghe LV, Devriese L, Galgani F, Robbens J, Janssen CR (2015) Microplastics in sediments: a review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Mar Environ Res 111:5–17. [CrossRef]
- Chakma, S., Paul, A. K., Rahman, M. A., Hasan, M. M., Sazzad, S. A. & Sunny, A. R. (2022). Climate Change Impacts and Ongoing Adaptation Measures in the Bangladesh Sundarbans. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology and Fisheries. 1;26(2):329-48. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q., Gundlach, M., Yang, S., Jiang, J., Velki, M., Yin, D., Hollert, H. (2017a). Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of micro-plastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafish larvae locomotor activity. Sci. Total Environ. 584-585, 1022–1031. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q., Yin, D.Q., Jia, Y.L., Schiwy, S., Legradi, J., Yang, S.Y., Hollert, H. (2017b). Enhanced uptake of BPA in the presence of nanoplastics can lead to neurotoxic effects in adult zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 609, 1312–1321. [CrossRef]
- Claessens M, De Meester S, Van Landuyt L, De Clerck K, Janssed RC (2011) Occurence and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments along the Belgian coast. Mar Pollut Bull 62:2199–2204. [CrossRef]
- Cole, M., Lindeque, P., Halsband, C., Galloway, T.S. (2011). Micro-plastics as contaminants in the marine environment: a review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 62, 2588–2597. [CrossRef]
- Cole,M., Lindeque, P., Fileman, E., Halsband, C., Goodhead, G., Moger, J., Galloway, T.S. (2013). Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47 (12), 6646–6655. [CrossRef]
- Costa JP, Santos PSM, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos T (2016) (Nano) plastics in the environment—sources, fates and effects. Sci Total Environ 567:15–26. [CrossRef]
- Cozar A, Echevarria F, González-Gordillo JI, Irigoien X, Ubeda B, Hernandez-Leon S, Palma AT, Navarro S, Garcia-de-Lomas J, Ruiz A, Fernandez-depuelles ML, Duarte CM (2014) Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:10239–10244. [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J.P., Santos, P.S., Duarte, A.C., Rocha-Santos, T., 2016. (Nano) plastics in the environment–sources, fates and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 566, 15–26. [CrossRef]
- de Sá L.C., Oliveira M., Ribeiro F, Rocha T.L., Futter M.N. (2018) Studies of the effects of micro-plastics on aquatic organisms: what do we know and where should we focus our efforts in the future? Sci Total Environ 645:1029–1039. [CrossRef]
- de Sá, L.C., Luís, L.G., Guilhermino, L. (2015). Effects of micro-plastics on juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps): confusion with prey, reduction of the predatory performance and efficiency, and possible influence of developmental conditions. Environ. Pollut. 196, 359–362. [CrossRef]
- Derraik JGB (2002) The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 44:842–852. [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.P.W., Galbraith, M., Dangerfield, N., Ross, P.S. (2014). Widespread distribution of micro-plastics in subsurface seawater in the NE Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 79, 94–99. [CrossRef]
- Détrée, C., Gallardo-Escárate, C. (2017). Polyethylene microbeads induce transcriptional responses with tissue-dependent patterns in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. J. Molluscan. Stud. 83, 220-225. [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos J, JoblingM(1992) A model to describe gastric evacuation in cod (Gadus morhua L.) fed natural prey. ICES J Mar Sci 49:145– 154. [CrossRef]
- Eriksen M, Laurent CML, Henry SC, Thiel M, Moore CJ, Borerro JC, Galgani F, Ryan PG, Reisser J (2014) Plastic pollution in the World’s oceans: more than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS One. [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M., Mason, S., Wilson, S. (2013). Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 77 (1-2), 177-182. [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C., & Burton, H. (2003). Origins and biological accumulation of small plastic particles in fur seals from Macquarie Island. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 32, 380–384. [CrossRef]
- ESDO (Environment and Social Development Association). Study Report: Microbeads! Unfold Health Risk and Environmental Pollutant. (2016). [cited 2020 June 18]. Available from: http:// esdo.org/wp-content/uploads/Microbeads-final-report-10.11.16-1.pdf.
- Espinosa, C., Cuesta, A., Esteban, M.A. (2017). Effects of dietary polyvinylchloride microparticles on general health, immune status and expression of several genes related to stress in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 68, 251-259. [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P., & Nelson, K. (2013). Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environmental Pollution, 177, 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Faruk, O., Hasan, S. E., Jubayer, A., Akter, K., Al Shiam, S. A., Rahman, K., & Ali, M. Y. (2023). Microbial Isolates from Urinary Tract Infection and their Antibiotic Resistance Pattern in Dhaka city of Bangladesh. Journal of Knowledge Learning and Science Technology ISSN: 2959-6386 (online), 2(3), 76-87. [CrossRef]
- Fendall, L.S., Sewell, M.A. (2009). Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: micro-plastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 58, 1225–1228. [CrossRef]
- Fonte, E., Ferreira, P., Guilhermino, L. (2016). Temperature rise and micro-plastics interact with the toxicity of the antibiotic cefalexin to juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps): post-exposure predatory behaviour, acetylcholinesterase activity and lipid peroxidation. Aquat. Toxicol. 180, 173–185. [CrossRef]
- Fossi MC, Panti C, Guerranti C, Coppola D, Giannetti M, Marsili L, Minutoli R (2012) Are baleen whales exposed to the threat of microplastics? A case study of the Mediterranean fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus). Mar Pollut Bull 64:2374–2379. [CrossRef]
- Frost BW (1977) Feeding behavior of Calanus pacificus in mixtures of food particles. Limnol Oceanogr 22:472–491. [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F., Fossi, C., Weber, R., Santillo, D., Sousa, J., Ingram, I., & Romano, D. (2018). Marine litter plastics and micro-plastics and their toxic chemicals components: the need for urgent preventive measures. Environmental Sciences Europe, 30, 1-14.
- Galloway, T. S. (2015). Micro- and nano-plastics and human health. In M. Bergmann, L. Gutow, M. Klages (Eds.), Marine anthropogenic litter, (pp. 347–370). Springer, Berlin.
- GESAMP (2015). Sources, fate and effects of microplastics in the marine environment: a global assessment. In: Kershaw PJ (ed) (IMO/FAO/ UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP/UNDP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection). Rep Stud GESAMP No. 90, pp 96.
- Goldstein M, Goodwin D (2013) Gooseneck barnacles (Lepas spp.) ingest microplastic debris in the North Pacific subtropical gyre. Peer J. [CrossRef]
- Goldsworthy SD, Hindell MA, Crowley HM (1997) Diet and diving behaviour of sympatric fur seals Arctocephalus gazella and A. tropicalis at Macquarie Island. In: Hindell M, Kemper C (eds) Marine mammal research in the Southern Hemisphere, Status, ecology and medicine, vol vol. 1. Surrey Beatty & Sons, New South Wales, Australia, pp 151–163.
- Gregory MR (1996) Plastic ‘scrubbers’ in hand cleansers: a further (and minor) source for marine pollution identified. Mar Pollut Bull 32: 867–871. [CrossRef]
- Haghi, B. N., Banaee, M. (2017). Effects of micro-plastic particles on paraquat toxicity to common carp (Cyprinus carpio): biochemical changes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 14 (3), 521-530. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M. R., Hossain, M. M., Islam, M. S., Sunny, A. R., Ferdous, J., Chowdhury, M. Z. A., Maria, A. M., Sarder, A. A. H... & Sultana, A. (2023). Seasonal Variation of Quality and the Total Viable Count of Lean and Fatty Fish. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology & Fisheries, 27(5).
- Horton, A.A., Walton, A., Spurgeon, D.J., Lahive, E., Svendsen, C. (2017). Microplastics in freshwater and terrestrial environments: evaluating the current understanding to identify the knowledge gaps and future research priorities. Sci. Total Environ. 586, 127–141. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M. S., Sobhan, F., Uddin, M. N., Sharifuzzaman, S. M., Chowdhury, S. R., Sarker, S., & Chowdhury, M. S. N. (2019). Microplastics in fishes from the Northern Bay of Bengal. Science of The Total Environment, 690, 821-830. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S., 2011. Prospects and challenges of plastic industries in Bangladesh. J. Chem. Eng 26, 16–21. [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Sunny, A.R.; Sazzad, S.A.; Amith, D.; Nazmul, H., Koushikur, R.; Faruque, M.M.; Ashrafuzzaman, M.; Prodhan, S.H. (2023). Environmental Jeopardy and Coping Strategies of the Small-scale Fishers in the Bangladesh Sundarbans: The Precedent of the World’s Largest Mangrove. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology & Fisheries, 27(6).
- Jambeck, J., Geyer, R.,Wilcox, C., Siegler, T.R., Perryman, M., Andrady, A., Narayan, R., Law, K.L., 2015. Plasticwaste inputs fromland into the ocean. Science 347, 3–6. https://doi. org/10.1126/science.1260352.
- Jayasiri HB, Purushothaman CS, Vennila A (2013) Quantitative analysis of plastic debris on recreational beaches in Mumbai, India. Mar Pollut Bull 77:107–112. [CrossRef]
- Jemec, A., Horvat, P., Kunej, U., Bele, M., Krzan, A. (2016). Uptake and effects of microplastic textile fibers on freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna. Envron. Pollut. 219, 201-209. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.B., Won, E.J., Kang, H.M., Lee, M.C., Hwang, D.S., Hwang, U.K., Zhou, B., Souissi, S., Lee, S.J., Lee, J.S., (2016). Microplastic size-dependent toxicity, oxidative stress induction and and p-JNK and p-p38 activation in the Monogonont rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 50 (16), 8849–8857. [CrossRef]
- Kaiser J (2010) The dirt on ocean garbage patches. Science 328:1506. [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R., Syberg, K., Shashoua, Y., Bury, N.R. (2015). Influence of polyethylene microplastic beads on the uptake and localization of silver in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 206, 72-79. [CrossRef]
- Kibria, G., 2017. Plastic Waste, Plastic Pollution-A Threat to All Nations Low-carbon Economic & Sustainable Development Pathways View Project. , pp. 17–19 https://doi. org/10.13140/RG.2.2.11169.51048.
- Kim, D., Chae, Y., An, Y.J. (2017). Mixture Toxicity of Nickel and Microplastics with Different Functional Groups on Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51 (21), 12852-12858. [CrossRef]
- Kuddus, M. A., Datta, G. C., Miah, M. A., Sarker, A. K., Hamid, S. M. A., & Sunny, A. R. (2020). Performance study of selected orange fleshed sweet potato varieties in north eastern bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol, 5, 673-682. [CrossRef]
- Kuddus, M. A., Sunny, A. R., Sazzad, S. A., Hossain, M., Rahman, M., Mithun, M. H., ... & Raposo, A. (2022). Sense and Manner of WASH and Their Coalition with Disease and Nutritional Status of Under-five Children in Rural Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study. Frontiers in Public Health, 10, 890293. [CrossRef]
- Kuhn S, van Franeker JA (2012) Plastic ingestion by the northern fulmar (Fulmarus glacialis) in Iceland. Mar Pollut Bull 64:1252–1254. [CrossRef]
- Law KL, Morèt-Ferguson S, Maximenko N, Proskurowski G, Peacock EE, Hafner J, Reddy CM (2010) Plastic accumulation in the North Atlantic subtropical gyre. Science 329:1185–1888.
- Lebreton, L.C.M., Van Der Zwet, J., Damsteeg, J.W., Slat, B., Andrady, A., Reisser, J., 2017. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nat. Commun. 8, 1–10. https://doi. org/10.1038/ncomms15611.
- Lee, K.W., Shim, W.J., Kwon, O.Y., Kang, J.H., (2013). Size-dependent effects of micro polystyrene particles in the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47 (19), 11278–11283. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N., Qu, X.Y., Su, L., Zhang, W.W., Yang, D.Q., Kolandhasamy, P., Li, D.J., Shi, H.H. (2016). Microplastics in mussels along the coastal waters of China. Environ. Pollut. 214, 177-184. [CrossRef]
- Lindborg VA, Ledbetter JF,Walat JM, Moffett C (2012) Plastic consumption and diet of glaucous-winged gulls (Larus glaucescens). Mar Pollut Bull 64:2351–2356. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.F., Zhang, Y., Deng, Y.F., Jiang, W., Zhao, Y.P., Geng, J.J., Ding, L.L., Ren, H.Q. ( 2016). Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50 (7), 4054-4060. [CrossRef]
- Luis, L., Ferreira, P., Fonte, E., Oliveira, M., Guilhermino, L. (2015). Does the presence of micro-plastics influence the acute toxicity of chromium(VI) to early juveniles of the common goby (Pomatoschistus microps)? A study with juveniles from two wild estuarine populations. Aquat. Toxicol. 164, 163–174. [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L., McHugh, M., Thompson, R.C. (2013). Occurrence of micro-plastics in the gastrointestinaltract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 67, 94–99. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.N., Huang, A.N., Cao, S.Q., Sun, F.F., Wang, L.H., Guo, H.Y., Ji, R. (2016). Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ. Pollut. 219, 166-173. [CrossRef]
- Mandatory Jute Packaging Act. (2010). [cited 2020 June 18]. Available from: http://motj.portal.gov.bd/sites/default/files/files/motj.portal.gov.bd/law/de00c47c_82e0_4eca_a5a9_ f77cbd6c92ec/25september13.pdf.
- Martinez-Gomez, C., Leon, V.M., Calles, S., Gomariz-Olcina, M., Vethaak, A.D. (2017). The adverse effects of virgin microplastics on the fertelization and larval development of sea urchins. Mar. Environ. Res. 130, 69-76. [CrossRef]
- Mato Y, Isobe T, Takada H, Kanehiro H, Ohtake C, Kaminuma T (2001) Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ Sci Technol 35:318–324. [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, K., Johnson, E. V., Malmendal, A., Linse, S., Hansson, L. A., & Cedervall, T. (2017). Brain damage and behavioural disorders in fish induced by plastic nanoparticles delivered through the food chain. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 11452. [CrossRef]
- Mazurais, D., Emande, B., Quazuguel, P., Severe, A., Huelvan, C., Madec, L., Mouchel, O., Soudant, P., Robbens, J., Huvet, A., Zambonino-Indante, J. (2015). Evaluation of the impact of polyethylene microbeads ingestion in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 112 (Part A), 78–85. [CrossRef]
- McCauley SJ, Bjorndal KA (1999) Conservation implications of dietary dilution from debris ingestion: sublethal effects in post hatchling loggerhead sea turtles. Conserv Biol 13:925–929. [CrossRef]
- McMahon CR, Hooley D, Robinson S (1999) The diet of itinerant male Hooker’s sea lions, Phocarctos hookeri, at sub-Antarctic Macquarie Island. Wildl Res 26:839–846. [CrossRef]
- Meaza I, Toyoda JH, Wise JP Sr. Microplastics in Sea Turtles, Marine Mammals and Humans: A One Environmental Health Perspective. Front Environ Sci. 2020 Feb;8:575614. Epub 2021 Feb 16. PMID: 34765609; PMCID: PMC8579821. [CrossRef]
- Moore CJ,Moore SL, Leecaster MK,Weisberg SB (2001) A comparison of plastic and plankton in the North Pacific central gyre. Mar Pollut Bull 42:1297–1300. [CrossRef]
- Murray F, Cowie PR (2011) Plastic contamination in the decapod crustacean Nephrops norvegicus. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1207–1217. [CrossRef]
- Nerland IL, Halsband C, Allan I, Thomas KV (2014) Microplastics in marine environments: occurrence, distribution and effects project no. 14338 report no. 6754-2014 Oslo.
- Ng KL, Obbard JP (2006) Prevalence of microplastics in Singapore’s coastal marine environment. Mar Pollut Bull 52:761–767. [CrossRef]
- Nobre CR, Santana MFM, Maluf A. (2015). Assessment of microplastic toxicity to embryonic development of the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Mar Pollut Bull 92, 99-104. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M., Ribeiro, A., Hylland, K., Guilhermino, L. (2013). Single and combined effects of microplastics and pyrene on juveniles (0+ group) of the common goby Pomatoschistus microps (teleostei: gobiidae). Ecol. Indic. 34, 641-647. [CrossRef]
- Parvin, F., Jannat, S., & Tareq, S. M. (2021). Abundance, characteristics and variation of microplastics in different freshwater fish species from Bangladesh. Science of The Total Environment, 784, 147137. [CrossRef]
- Paul-Pont, I., Lacroix, C., Fernandez, C.G., Hegaret, H., Lambert, C., Le Goic, N., Frere, L., Cassone, A.L., Sussarellu, R., Fabioux, C., Guyomarch, J., Albentosa, M., Huvet, A., Soudant, P. (2016). Exposure of marine mussels Mytilus spp. to polystyrene micro-plastics: toxicity and influence on fluoranthene bioaccumulation. Environ. Pollut. 216, 724–737. [CrossRef]
- Peda, C., Caccamo, L., Fossi, M.C., Gai, F., Andaloro, F., Genovese, L., Perdichizzi, A., Romeo, T., Maricchiolo, G. (2016). Intestinal alterations in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax (Linnaeus, 1758) exposed to microplastics: Preliminary results. Environ. Pollut. 212, 251-256. [CrossRef]
- Plastics Europe, (2018). Plastics-the Facts 2018. An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data.
- Possatto FE, Barletta M, Costa MF, Ivar do Sul JA, Dantas DV (2011) Plastic debris ingestion by marine catfish: an unexpected fisheries impact. Mar Pollut Bull 62:1098–1102. [CrossRef]
- Poulet, S.A., Marsot, P. (1978). Chemosensory grazing by marine calanoid copepods (Arthropoda: Crustacea). Science 200, 1403–1405. [CrossRef]
- Ramos JAA, Barletta M, Costa MF (2012) Ingestion of nylon threads by Gerreidae while using a tropical estuary as foraging grounds. Aquat Biol 17:29–34.
- Reisser J, Shaw J, Wilcox C, Hardesty BD, Proiett M, Thums M, Pattiaratchi C (2013) Marine plastic pollution in waters around Australia: characteristics, concentrations, and pathways. PLoS One 8. [CrossRef]
- Reisser J, Slat B, Noble K, du Plessis K, EppM, ProiettiM, de Sonneville J, Becker T, Pattiaratchi C (2015) The vertical distribution of buoyant plastics at sea: an observational study in the North Atlantic gyre. Biogeosciences 12:1249–1256. [CrossRef]
- Rist, S.E., Assidqi, K., Zamani, N.P., Appel, D., Perschke, M., Huhn, M., Lenz, M. (2016). Suspended micro-sized PVC particles impair the performance and decrease survival in the Asian green mussel Perna viridis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 111 (1–2), 213–220. [CrossRef]
- Robards MD, Piatt JF, Wohl KD (1995) Increasing frequency of plastic particles ingested by seabirds in the subarctic North Pacific. Mar Pollut Bull 30:151–157. [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M., Browne, M.A., Halpern, B.S. (2013). Classify plastic waste as hazardous. Nature 494 (7436), 169-171. [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M., Kurobe, T., Flores, I., The, S.J. (2014). Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbed chemical pollutants from the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 493, 656-661. [CrossRef]
- Ryan PG (1987) The incidence and characteristics of plastic particles ingested by seabirds. Mar Environ Res 23:175–206. [CrossRef]
- Sailaja R.R.N., Kaushik C., Deepthi M.V., Pratik R., Ameen Khan M. (2018). Challenges and opportunities - plastic waste management in India; Retrived from http://www.teriin.org/ sites/default/files/2018-06/plastic-wastemanagement_0.pdf; last accessed on June 22. Setälä, O., Fleming-Lehtinen, V., Lehtiniemi, M. (2014). Ingestion and transfer ofmmicro-plastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 185, 77–83.
- Sazzad, S. A., Billah, M., Sunny, A. R., Anowar, S., Pavel, J. H., Rakhi, M. S., ... & Al-Mamun, M. A. (2023). Sketching Livelihoods and Coping Strategies of Climate Vulnerable Fishers. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology & Fisheries, 27(4). [CrossRef]
- Setala O, Fleming-Lehtinen V, Lehtiniemi M (2014) Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ Pollut 185: 77–83. [CrossRef]
- Sharma S., and Chatterjee S. (2017). Microplastic pollution, a threat to marine ecosystem and human health: a short review. Environ Sci Pollut Res., 24:21530–21547. [CrossRef]
- Sivan A (2011) New perspectives in plastic biodegradation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:422–426. [CrossRef]
- Sleight, V.A., Bakir, A., Thompson, R.C., Henry, T.B. (2017). Assessment of micro-plasticsorbed contaminant bioavailability through analysis of biomarker gene expression in larval zebrafish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 116 (1–2), 291–297. [CrossRef]
- Straub, S., Hirsch, P.E., Burkhardt-Holm, P. (2017). Biodegradable and petroleum-based microplastics do not differ in their ingestion and excretion but in their biological effects in the freshwater invertebrate Gammarus fossarum. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 14 (7), 774. [CrossRef]
- Sunny, A. R., Mithun, M. H., Prodhan, S. H., Ashrafuzzaman, M., Rahman, S. M. A., Billah, M. M., ... & Hossain, M. M. (2021b). Fisheries in the context of attaining Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Bangladesh: COVID-19 impacts and future prospects. Sustainability, 13(17), 9912. [CrossRef]
- Sunny, A.R. (2017). Impact of oil Spill in the Bangladesh Sundarbans. InternationalJournal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies, 5 (5): 365-368.
- Sunny, A.R.; Sazzad, S.A.; Datta, G.C.; Sarker, A.K.; Ashrafuzzaman, M. & Prodhan, S.H. (2021a). Assessing impacts of COVID-19 on aquatic food system and small-scale fisheries in Bangladesh. Marine Policy, 126: 104422. [CrossRef]
- Sussarellu R., Suquet, M., Thomas, Y., Lambert, C., Fabioux, C., Pernet, M.E.J., Le Goic, N., Quillien, V., Mingant, C., Epelboin, Y., Corporeau, C., Guyomarch, J., Robbens, J., Paul-Pont, I., Soudant, P., Huvet, A. (2016). Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113 (9), 2430-2435. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka K, Takada H, Yamashita R, Mizukawa K, Fukuwaka MA, Watanuki Y (2013) Accumulation of plastic-derived chemicals in tissues of seabirds ingesting marine plastics. Mar Pollut Bull 69: 219–222. [CrossRef]
- Tosetto, L., Brown, C., Williamson, J.E. (2016). Micro-plastics on beaches: ingestion and behavioural consequences for beachhoppers. Mar. Biol. 163 (10), 199. [CrossRef]
- Tufael, Hasan, S.E.; Jubayer, A.; Akter, K.; Akter, A.; Akter, F.; Shiam, S.A.A & Sunny, A.R. (2023). Effects of Nigella Sativa and Syzygium Cumini Seed Extracts on Blood Glucose Levels in Swiss Albino Mice. Journal of Knowledge Learning and Science Technology ISSN: 2959-6386 (online), 2(3), 53-62. [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.V., Claessens, M., Vandegehuchte, M.N. (2015). Micro-plastics are taken up by mussels (Mytilus edulis) and lugworms (Arenicola marina) living in natural habitats. Environ. Pollut. 199, 10–17. [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.V., Janssen, C.R. (2014). Micro-plastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 193, 65–70. [CrossRef]
- Vlietstra LS, Parga JA (2002) Long-term changes in the type, but not amount, of ingested plastic particles in short-tailed shearwaters in the southeastern Bering Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 44:945–955. [CrossRef]
- von Moos N., Burkhardt-Holm P., Kӧhler A. (2012). Uptake and Effects of Microplastics on Cells and Tissue of the Blue Mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an Experimental Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46 (20), 11327−11335. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Wang, M.X., Ru, S.G. (2019a). High levels of microplastic pollution in the sediments and benthic organisms of the South Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total Environ. 651, 1661-1669. [CrossRef]
- Waste Concern. (2014). [cited 2020 June 18]. Available from: http://wasteconcern.org/wpcontent/ uploads/2016/05/Waste-Data-Base_2014_Draft-Final.pdf.
- Watts, A.J.R., Lewis, C., Goodhead, R.M., Beckett, S.J., Moger, J., Tyler, C.R., Galloway, T.S. (2014). Uptake and retention of micro-plastics by the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48 (15), 8823–8830. [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.R., Urbina, M.A., Corr, S., Lewis, C., Galloway, T.S. (2015). Ingestion of plastic microfibers by the crab Carcinus maenas and its effect on food consumption and energy balance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 (24), 14597–14604. [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.J.R., Urbina, M.A., Goodhead, R., Moger, J., Lewis, C., Galloway, T.S. (2016). Effect of microplastic on the gills of the shore Crab Carcinus maenas. Environ. Sci. Technol. 50 (10), 5364-5369. [CrossRef]
- Welden, N.A.C., Cowie, P.R. (2016). Long-term microplastic retention causes reduced body condition in the langoustine, Nephrops norvegicus. Environ. Pollut. 218, 895-900. [CrossRef]
- Wilson DS (1973) Food size selection among copepods. Ecology 54: 909–914. [CrossRef]
- Wirtz KW (2012) Who is eating whom? Morphology and feeding type determine the size relation between planktonic predators and their ideal prey. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 445:1–12. [CrossRef]
- Wright SL, Rowe D, Thompson RC, Galloway TS (2013). Microplastic ingestion decreases energy reserves in marine worms. Curr Biol 23: 1031–1033. [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. L., & Kelly, F. J. (2017). Plastic and human health: a micro issue? Environmental science & technology, 51(12), 6634- 6647. [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. L., Thompson, R. C., & Galloway, T. S. (2013a). The physical impacts of micro-plastics on marine organisms: A review. Environmental Pollution, 178, 483–492. [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, S., Rahman, M.I., 2017. A review of solid waste management practice in Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Prot. Policy 5, 19. https://doi.org/ 10.11648/j.ijepp.20170502.11.
- Zhang Y, Zhang YB, Feng Y, Yang XJ (2010). Reduce the plastic debris: a model research on the great Pacific ocean garbage patch. Adv Mater Res 116:59–63. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).