Submitted:
16 November 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We modify the traditional LSTM by adding a de-trending operation for nonstationary data;
- We propose to use the diffusion graph convolution to extract the spatial correlations in the air quality data from multi-sites;
- We propose two different models based on the LS-deGCN to predict air quality at multi-sites and evaluate them on the air quality data in the city of Chengdu and the other data from seven major cities.
2. Literature Review
3. Proposed Models
3.1. Problem and Research Gap
3.2. Nonstationary Diffusion Convolutional LSTM
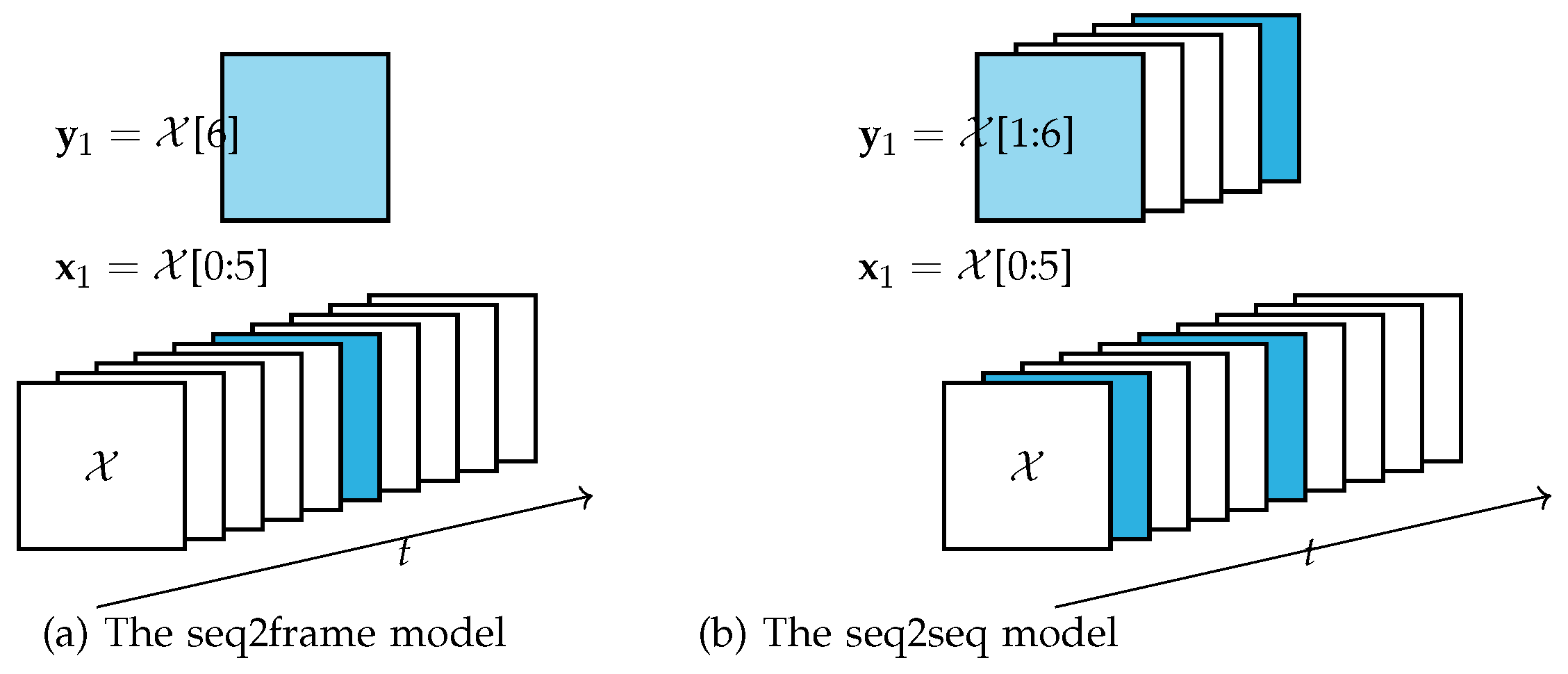
3.3. Two new models
3.4. Selection of tuning parameters l and
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Baselines
- Linear regression: This is one of the most commonly used approaches to modeling the relationship between a dependent variable y and covariates .
- Support vector regression: Equipped with a radial basis kernel, it extends linear regression by controlling how much error in regression is acceptable.
- LSTM sequence-to-scalar (seq2scalar): Samples under this model are constructed in the same way as those under the seq2seq model. The difference is that we take the target y as one of the nine pollutants one by one; that is, we need to train nine separate models for the nine pollutants.
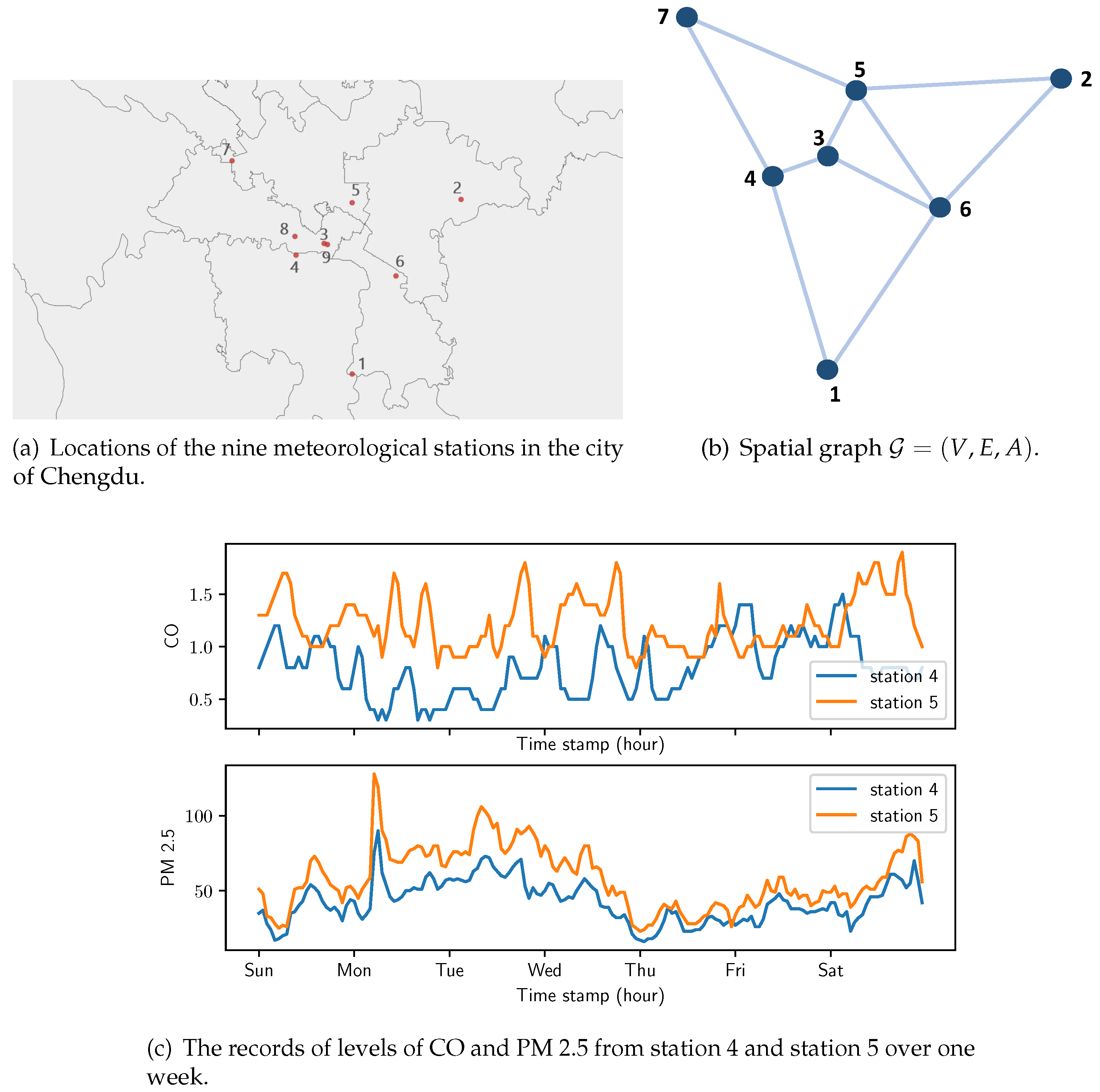
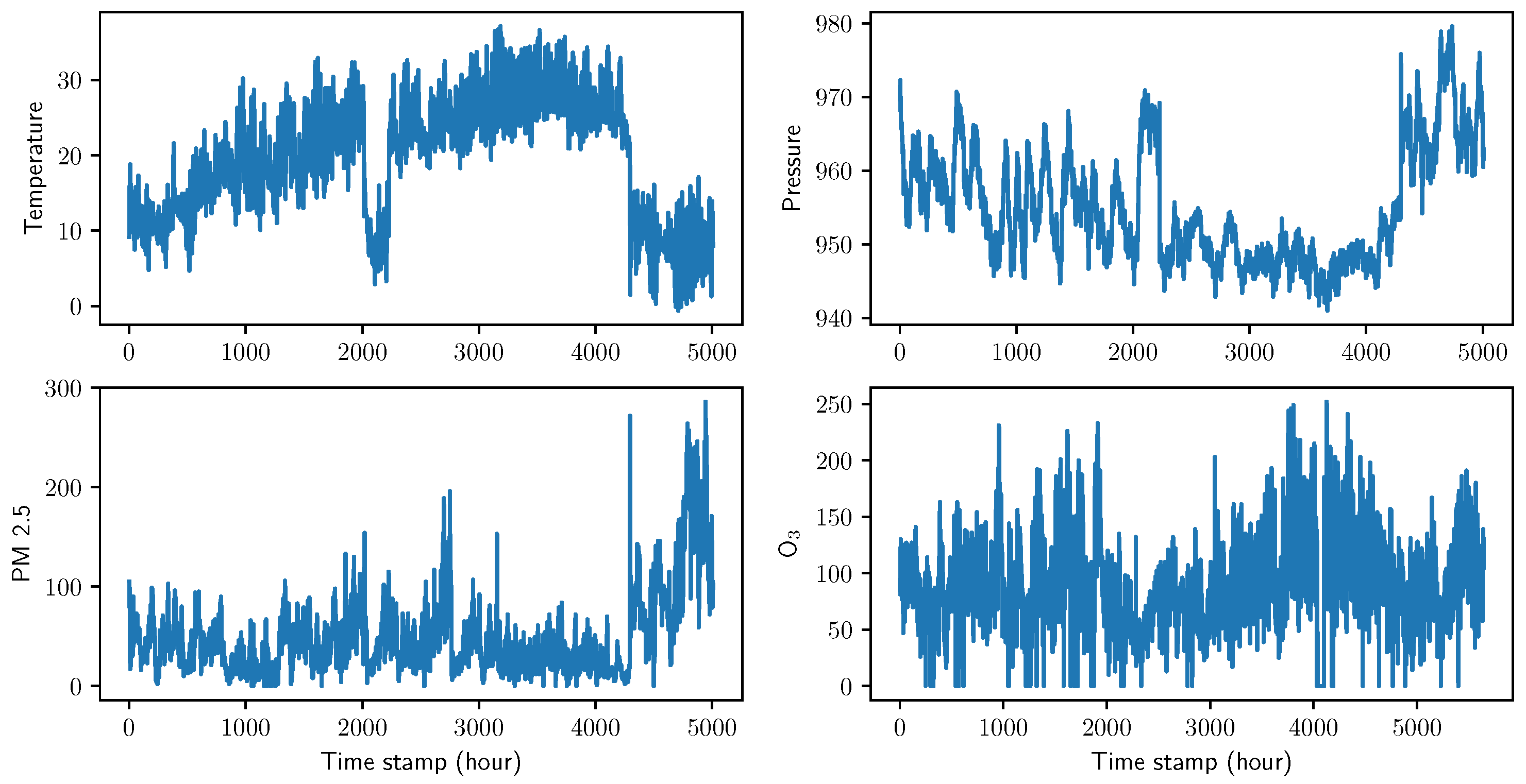
4.2. Data description and preprocessing
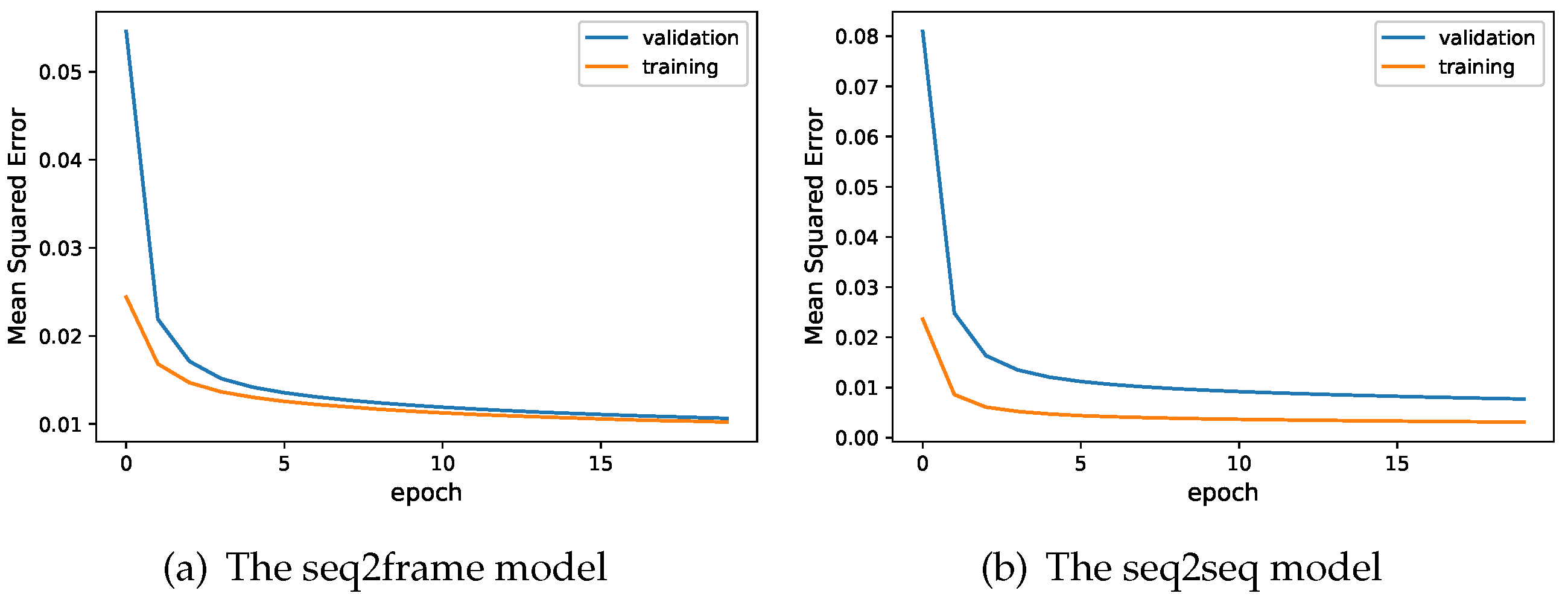
4.3. Training
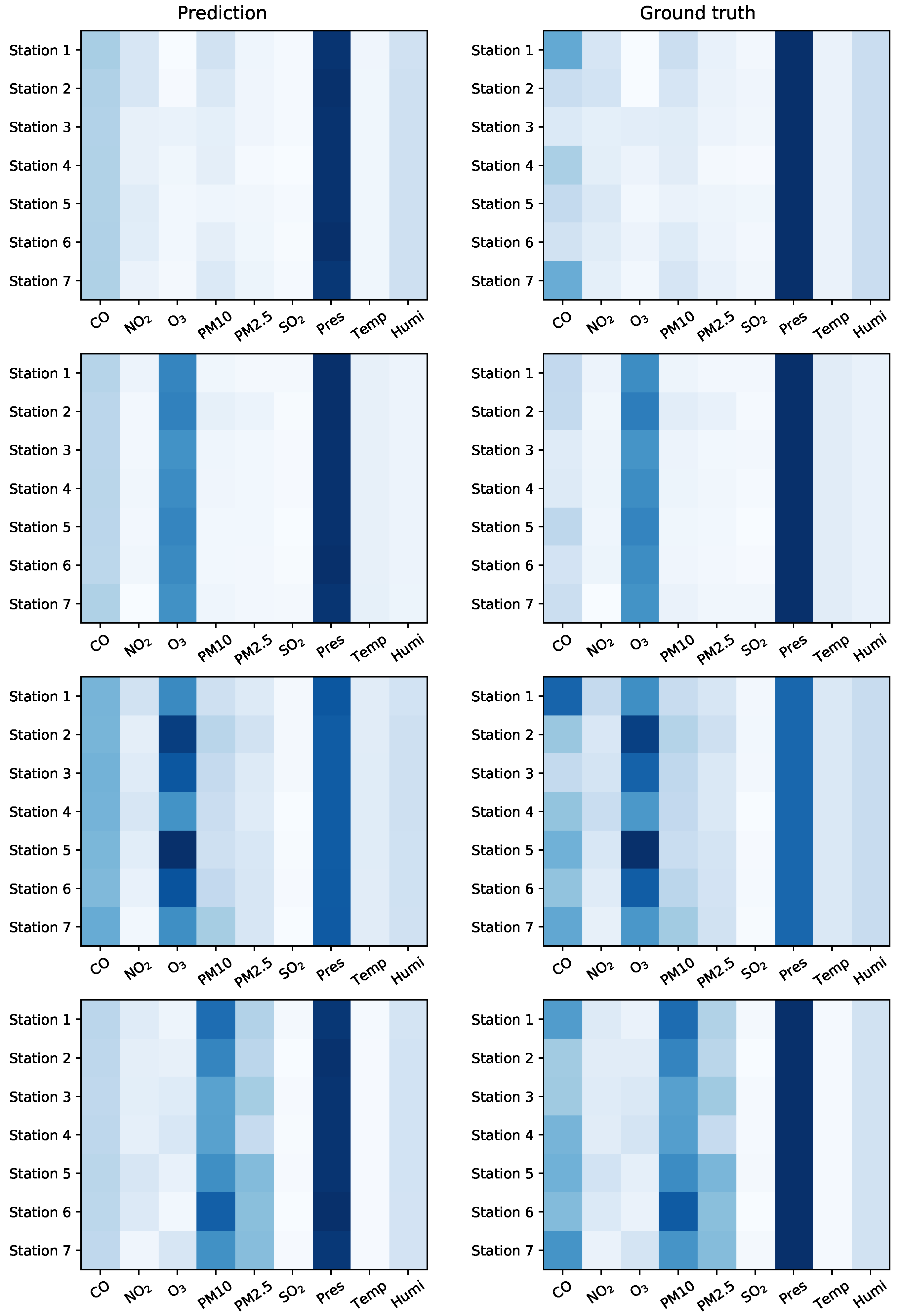
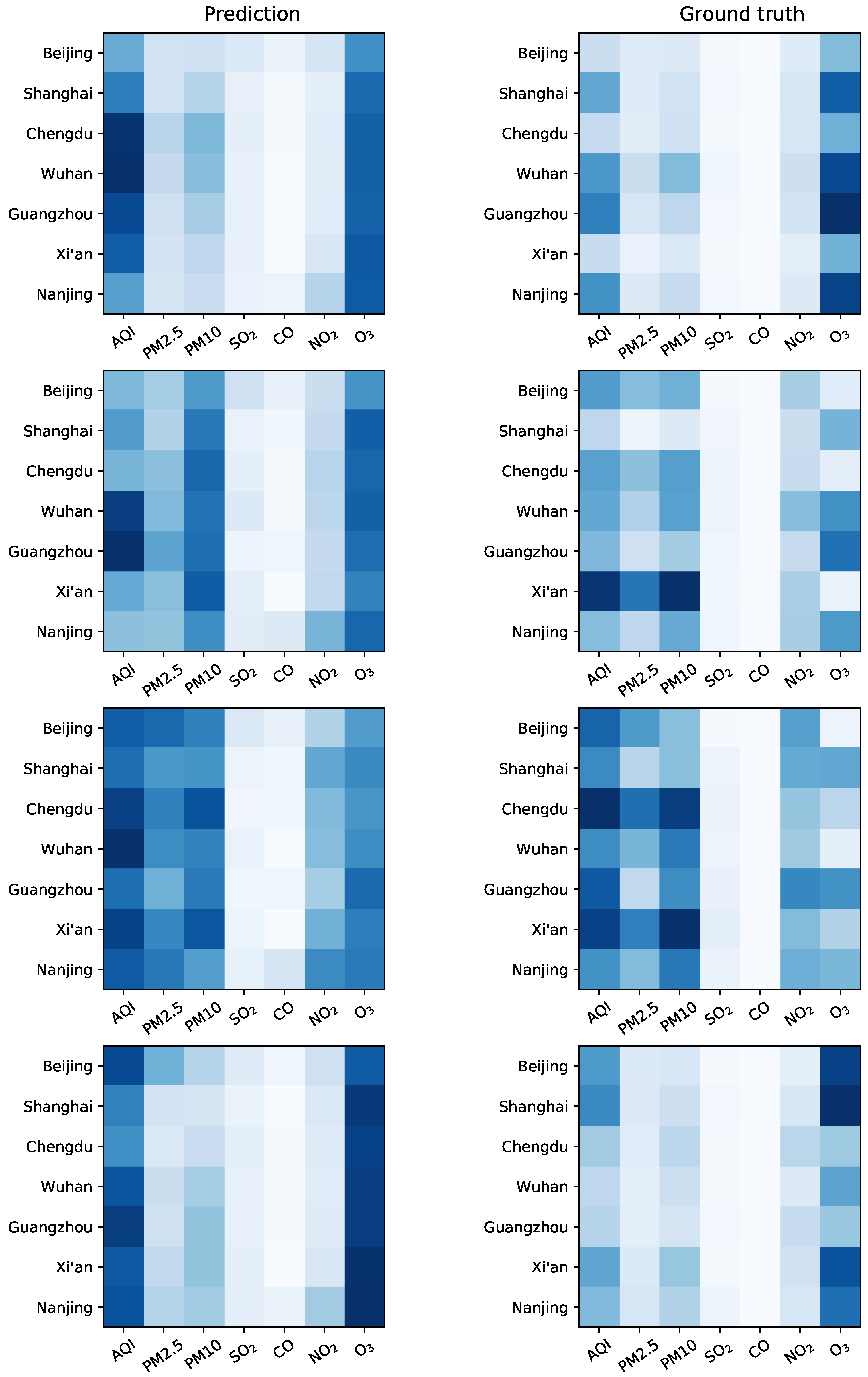
4.4. Visualization of predictions
4.5. Evaluation with three metrics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| LS-deGCN | Long-short de-trending graph convolutional network |
| NLP | Natural language processing |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| RMSE | Root mean squared error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
References
- Ayturan, Y.A.; Ayturan, Z.C.; Altun, H.O. Air pollution modelling with deep learning: A review. International Journal of Environmental Pollution and Environmental Modelling 2018, 1, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, B.; Dong, A.; He, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, S.X. Cautionary tales on air-quality improvement in Beijing. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2017, 473, 20170457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Wang, T.; Song, G.; Hu, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Deep air learning: Interpolation, prediction, and feature analysis of fine-grained air quality. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2018, 30, 2285–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Sun, C.; Li, V.O. Granger causality based air quality estimation with spatio-temporal (ST) heterogeneous big data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS); 2015; pp. 612–617. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Sun, C.; Li, V.O. An extended spatio-temporal Granger causality model for air quality estimation with heterogeneous urban big data. IEEE Transactions on Big Data 2017, 3, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Kuo, P.H. A deep CNN-LSTM model for particulate matter (PM2. 5) forecasting in smart cities. Sensors 2018, 18, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Yao, X.; Cui, S.; Hu, Y.; You, C.; Chi, T. Long short-term memory neural network for air pollutant concentration predictions: Method development and evaluation. Environmental Pollution 2017, 231, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Q.; Hou, J.; Feng, X.; Karimian, H.; Lin, S. A spatiotemporal prediction framework for air pollution based on deep RNN. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2017, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, G. A deep spatial-temporal ensemble model for air quality prediction. Neurocomputing 2018, 314, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhourong, C.; Hao, W.; Yeung, D.; Wong, W.; Woo, W. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 2015; pp. 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, R.; Shahabi, C.; Liu, Y. Diffusion Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network: Data-Driven Traffic Forecasting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR ’18); 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Deodatis, G. Non-stationary stochastic vector processes: seismic ground motion applications. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics 1996, 11, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Long, M.; Wang, J.; Yu, P.S. Memory In Memory: A predictive neural network for learning higher-order nonstationarity from Spatio-temporal dynamics. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2019; pp. 9154–9162. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yan, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Forecasting PM2.5 concentration using spatio-temporal extreme learning machine. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), 2016 15th IEEE International Conference on. IEEE; 2016; pp. 950–953. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaemi, Z.; Alimohammadi, A.; Farnaghi, M. LaSVM-based big data learning system for dynamic prediction of air pollution in Tehran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 2018, 190, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.C.; Binaykia, A.; Chang, P.C.; Tiwari, M.K.; Tsao, C.C. Urban air quality forecasting based on multi-dimensional collaborative support vector regression (svr): A case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Shijiazhuang. PLOS One 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Sahu, S.K. A Bayesian spatiotemporal model to estimate long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution at coarser administrative geographies in England and Wales. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society) 2018, 181, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Raischel, F.; Lind, P.G. Air quality prediction using optimal neural networks with stochastic variables. Atmospheric Environment 2013, 79, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancofiore, F.; Busilacchio, M.; Verdecchia, M.; Tomassetti, B.; Aruffo, E.; Bianco, S.; Di Tommaso, S.; Colangeli, C.; Rosatelli, G.; Di Carlo, P. Recursive neural network model for analysis and forecast of PM10 and PM2. 5. Atmospheric Pollution Research 2017, 8, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, İ.; Şimşek, M.U.; Özdemir, S. A deep learning model for air quality prediction in smart cities. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data). IEEE; 2017; pp. 1983–1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Computation 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 2014; pp. 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Lin, T.; Lu, Y. An interpretable LSTM neural network for autoregressive exogenous model. In Proceedings of the Workshop of International Conference on Learning Representations; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wilson, T.; Tan, P.N.; Hatami, P.; Luo, L. MUSCAT: Multi-scale spatio-temporal learning with application to climate modeling. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence; 2018; pp. 2912–2918. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T.; Tan, P.N.; Luo, L. A low rank weighted graph convolutional approach to weather prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. IEEE; 2018; pp. 627–636. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, R.; Shahabi, C.; Liu, Y. Diffusion convolutional recurrent neural network: data-driven traffic forecasting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Mansimov, E.; Salakhudinov, R. Unsupervised learning of video representations using LSTMs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning; 2015; pp. 843–852. [Google Scholar]
- Shuman, D.I.; Narang, S.K.; Frossard, P.; Ortega, A.; Vandergheynst, P. The emerging field of signal processing on graphs: Extending high-dimensional data analysis to networks and other irregular domains. IEEE signal processing magazine 2013, 30, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Datasets | Description |
|---|---|
| Training | Data from January 1, 2013 to December 31, 2015 |
| Validation | Data from January 1, 2016 to June 1, 2016 |
| Testing | The remaining data |
| Models | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 24 | Linear regression | 1.78 | 1.82 | 2.23 |
| Support vector regression | 1.61 | 1.93 | 1..98 | |
| LSTM seq2scalar | 1.04 | 1.12 | 1.25 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2frame | 0.58 | 0.78 | 1.1 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2seq | 0.56 | 0.77 | 0.87 | |
| = 48 | Linear regression | 1.67 | 1.79 | 2.03 |
| Support vector regression | 1.52 | 1.76 | 1.95 | |
| LSTM seq2scalar | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.95 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2frame | 0.45 | 0.62 | 0.67 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2seq | 0.39 | 0.56 | 0.57 |
| Models | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 24 | Linear regression | 0.5634 | 0.5367 | 0.5278 |
| Support vector regression | 0.5763 | 0.5598 | 0.5557 | |
| LSTM seq2scalar | 0.7021 | 0.7167 | 0.7198 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2frame | 0.7234 | 0.7545 | 0.7517 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2seq | 0.7365 | 0.7652 | 0.7482 | |
| = 48 | Linear regression | 0.5612 | 0.5423 | 0.5186 |
| Support vector regression | 0.5834 | 0.5654 | 0.5521 | |
| LSTM seq2scalar | 0.6825 | 0.7212 | 0.7237 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2frame | 0.7235 | 0.7866 | 0.7655 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2seq | 0.7655 | 0.8123 | 0.7785 |
| Models | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| = 24 | Linear regression | 0.0175 | 0.0211 | 0.0234 |
| Support vector regression | 0.0158 | 0.0147 | 0.0186 | |
| LSTM seq2scalar | 0.0148 | 0.0167 | 0.0166 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2frame | 0.0092 | 0.0091 | 0.0101 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2seq | 0.0077 | 0.0089 | 0.0093 | |
| = 48 | Linear regression | 0.0178 | 0.0198 | 0.0211 |
| Support vector regression | 0.0153 | 0.0132 | 0.0201 | |
| LSTM seq2scalar | 0.0136 | 0.0142 | 0.0154 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2frame | 0.0080 | 0.0079 | 0.0091 | |
| Nonstationary LS-deGCN seq2seq | 0.0071 | 0.0078 | 0.0083 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





