Submitted:
16 November 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
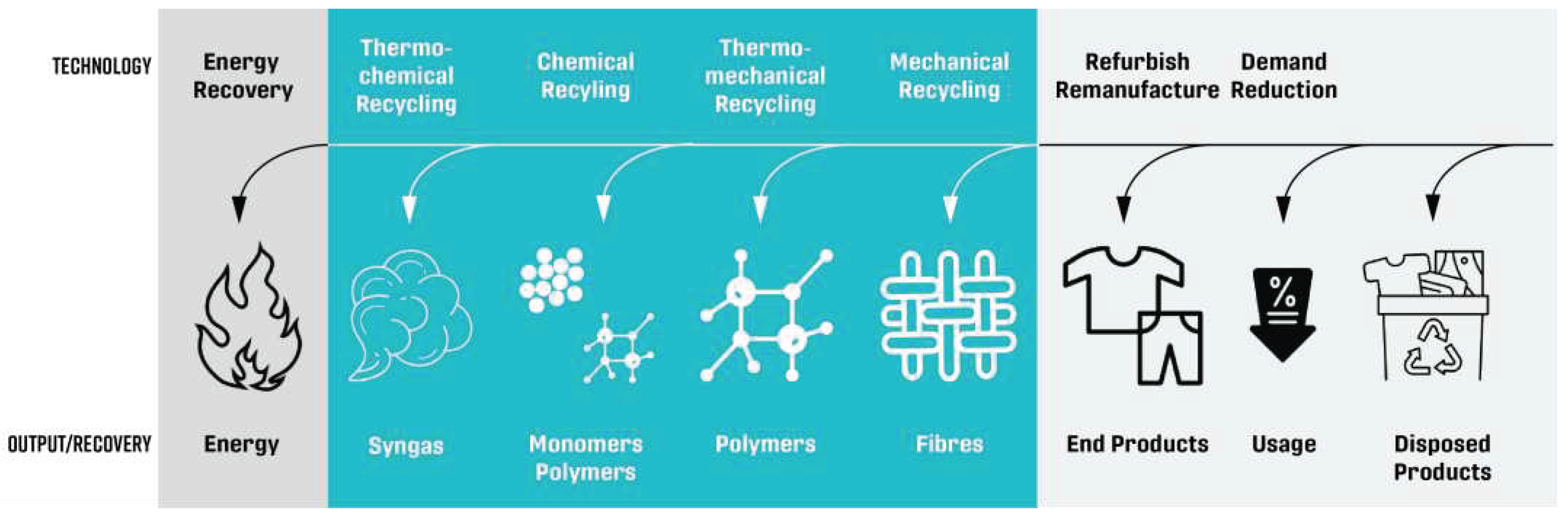
2. Mapping of the textile recycling technologies
3. Current status and prognosis of recycling technology processes
3.1. Mechanical recycling
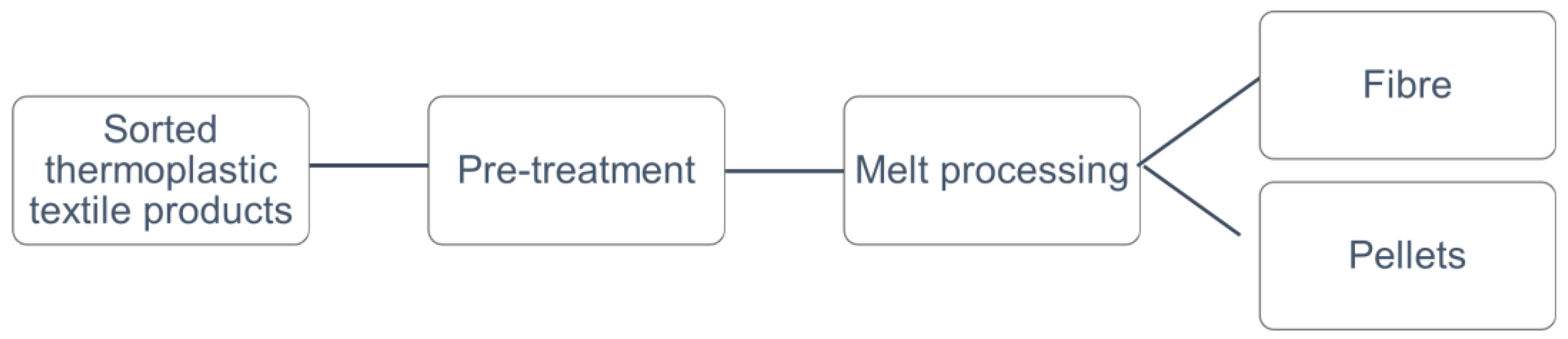
3.2. Thermo-mechanical recycling
- High-level (vacuum) degassing for removal of volatile contaminants and moisture as well as viscosity stabilization for PET.
- High-performance filtration for removal of non-melting particles.
- Solid state or liquid state polymerization units (SSP or LSP) to increase PET intrinsic viscosity (IV).
- Epoxy, e.g. Joncryl ADR grades (BASF)
- Isocyanate, e.g. regular PMDI (Bayer Material Science AG)
- Oxazoline, e.g. Nexamite M992000 (Nexam Chemicals) - contains 1,3-phenylene-bis-oxazoline
- Anhydride, e.g. Nexamite M021200 (Nexam Chemicals) – contains pyromellitic dianhydride
- Others, e.g. Allnico CBC (DSM) – contains carbonylbiscaprolactam
3.3. Chemical recycling
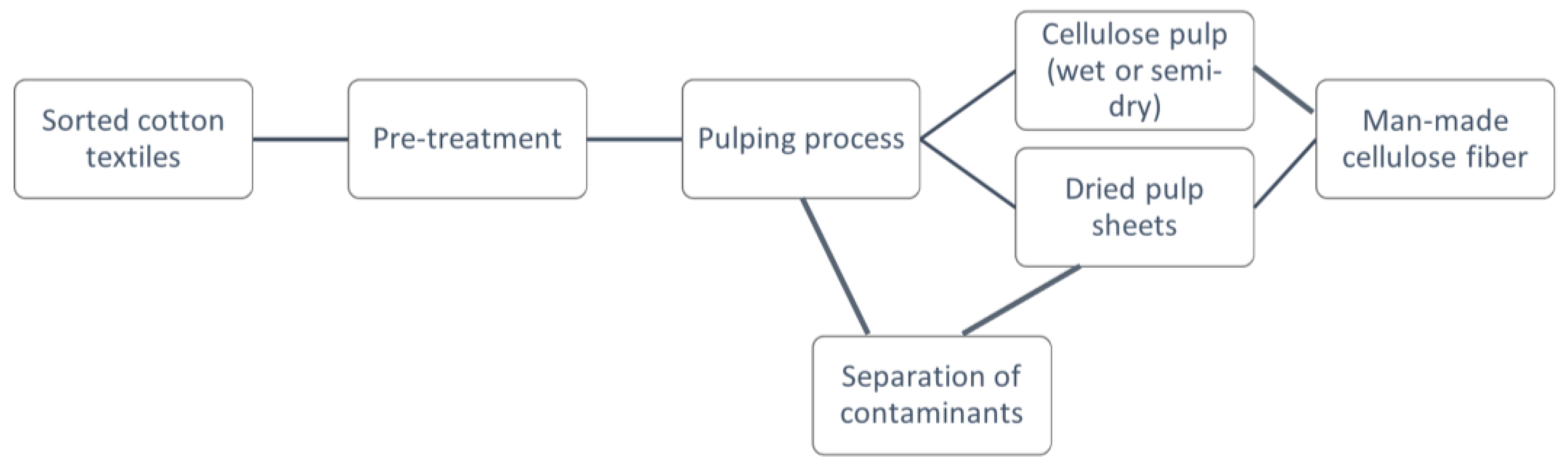
- Polymer recycling of cellulosics via pulping
- Recycling of synthetic and blended textiles
- Monomer recycling of synthetic textiles
3.3.1. Polymer recycling of cellulosic textiles via pulping
3.3.2. Recycling of synthetic and blended textiles
- Solvent-based dissolution followed by filtration to separate materials and extract the desired polymers.
- Hydrothermal processes using a certain combination of water, pressure, temperature and green chemistry to (partially) degrade either cotton or polyester or both.
- Enzymatic process (i.e., biochemical recycling) for degradation of cotton to glucose and/or cellulose powder and recovering polyester.
3.3.3. Monomer recycling of synthetic textiles
- Glycolysis: several demonstration plants constructed and even running
- Methanolysis: first plant in operation, more underway
- Hydrolysis: pilot stage, moving onto industrial/demo stage
3.4. Thermo-chemical recycling (“Thermal depolymerization”)
4. Facilitating technologies
4.1. Automated sorting
4.2. Facilitated disintegration of a textile product
4.2.1. Automatic removal of trims
4.2.2. Yarns for facilitated disassembly
4.2.3. Coating removal and delamination
- Dissolution of the adhesive layer, coating or textile
- Triggerable smart polymer material systems
- Reversible crosslinking-decrosslinking systems
- Supramolecular polymer adhesives
5. Virtual databases and platforms
| Ellie Connect by Ariadne Innovation | |
 |
https://ellieconnect.com/Digital platform to help you find new connections, knowledge and expertise, and use cases for sustainability transformation in and with the textiles & fashion industry. Platform features include:
|
| Reverse Resources | |
 |
https://reverseresources.net/A Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platform to digitise, connect and scale global textile-to-textile recycling. Reverse Recources is a portal to match textile waste with the best possible recycling solutions, enable predictive transparency and build data-driven supply chains. Access point to 4 different types of “roles” on the platform: (i) waste suppliers, (ii) waste handlers, (iii) recyclers, and (iv) brands |
| Refashion Recycle | |
 |
https://recycle.refashion.fr/en/Platform connecting textiles and footwear recycling stakeholders in France and in Europe. It is a tool dedicated to identifying materials from textiles and footwear recycling, to promoting recycling solutions and to connecting stakeholders. In just 3 clicks, professionals are able to obtain in a region of their choice, non-reusable textiles and footwear feedstock potential, recycling solutions and detailed stakeholder profiles corresponding to their request.Free but access is subject to the validation by Refashion depending on the applicant’s motivations. |
| COSH! | |
 |
https://cosh.eco/en Platform providing location-based sustainable shopping advice with more sustainable alternatives to fashion, cosmetics and lifestyle products from local shops and brands. Currently available for Belgium, the Netherlands, Spain and Germany. |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EEA, „Textiles and the environment: the role of design in Europe’s circular economy,” 2022.
- EEA, „Textiles and the environment in a circular economy,” 2019.
- S. Trzepacz, D. B. Lingås, L. Asscherickx, K. Peeters, H. v. Duijn en M. Akerboom, „LCA-based assessment of the management of European used textiles,” Norion Consult, 2023.
- McKinsey, „Scaling textile recycling in Europe - turning waste into value,” McKinsey Apparel, Fashion & Luxury Group, 2022.
- T. Duhoux, E. Maes, M. Hirschnitz-Garbers, K. Peeters, L. Asscherickx, M. Christis, B. Stubbe, P. Colignon, M. Hinzmann en A. Sachdeva, „Study on the technical, regulatory, economic and environmental effectiveness of textile fibres recycling,” European Commission, Brussels, 2021.
- K. J. Nunn.Europe Patent EP 3 845 703 A1, 2021.
- PurFi Global en Concordia Textiles, „Purfi,” 18 July 2023. [Online]. Available: https://purfi.com/.
- Recover Textile Systems, „Recover,” 18 July 2023. [Online]. Available: https://recoverfiber.com/.
- Recover, „Rieter, Recover™ & Polopiqué partner to increase recycled content in the industry,” 8 June 2023. [Online]. Available: https://recoverfiber.com/newsroom/rieter-recover-polopique.
- Natural Fiber Welding, „Clarus®,” 18 July 2023. [Online]. Available: https://clarus.naturalfiberwelding.com/.
- Natural Fiber Welding, „What is CLARUS(r)?,” 11 January 2022. [Online]. Available: https://blog.naturalfiberwelding.com/clarus-natural-fibers-polyester.
- Nouvelles Fibres Textiles, „Textile sorting for circularity,” 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.nouvellesfibrestextiles.com/.
- ITMA Organiser, „The crucial role of cooperation,” 9 June 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.itma.com/blogs/Sustainability-and-Circularity/2023/Recyling/The-crucial-role-of-cooperation.
- Z. Zhoa, Y. Wu, K. Wang, Y. Xia, H. Gao, K. Luo en Z. Cao, „Effect of the Trifunctional Chain Extender on Intrinsic Viscosity, Crystallization Behavior, and Mechanical Properties of Poly(Ethylene Terephtalate),” ACS Omega, vol. 5, pp. 19247-19254, 2020.
- J. Jang, K. Sadeghi en J. Seo, „Chain-Extending Modification for Value-Added Recycled PET: A Review,” Polymer Reviews, vol. 62, nr. 4, pp. 860-889, 2022.
- B. Bimestre en C. Saron, „Chain Extension of Poly(Ethylene Terephtalate) by Reactive Extrusion with Secondary Stabilizer,” Materials Research, vol. 15, nr. 3, pp. 467-472, 2012.
- Infinited Fiber, „Making Infinna™ mainstream – Scaling up the production capacity,” 16 February 2023. [Online]. Available: https://infinitedfiber.com/blog/2023/02/16/making-infinna-mainstream-scaling-up-the-production-capacity/.
- S. Hann en T. Connock, „Chemical Recycling: State of Play,” Eunomia, Bristol, 2020.
- Axens, „Axens, IFPEN and JEPLAN join their forces,” 8 September 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.axens.net/resources-events/news/pr-axens-ifpen-and-jeplan-join-their-forces.
- Noosa, „Noosa the circular fiber,” 18 July 2023. [Online]. Available: http://www.noosafiber.com/index.html.
- Protein Evolution, „Protein Evolution,” 18 July 2023. [Online]. Available: https://protein-evolution.com/.
- P. Biessey, J. Vogel, M. Seitz en P. Quicker, „Plastic Waste Utilization via Chemical Recycling: Approaches, Limitations, and the Challenges Ahead,” Chemie Ingenieur Technik, p. 17, 2023.
- Eastman Chemical Company, „Eastman makes the promise of sustainability a reality with Naia™ Renew,” Kingsport, 2020.
- Terra, „Technical monitoring of optical sorting, recognition and disassembly technologies for textiles at European scale,” Re-_fashion, 2023.
- Wastex, „Textile Sorting Technologies,” 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.wastexrecycling.com.
- Valvan, „Trimclean™ Closing the gap between sorting and recycing,” 26 September 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.valvan.com/uploads/general/VALVAN_trimclean_leaflet-A4_08_lowres.pdf?v=1685433923.
- Resortecs. [Online]. Available: https://resortecs.com/technology/.
- WEAR2GO, „The circular process,” [Online]. Available: https://wear2.com/en/various/the-circular-process/.
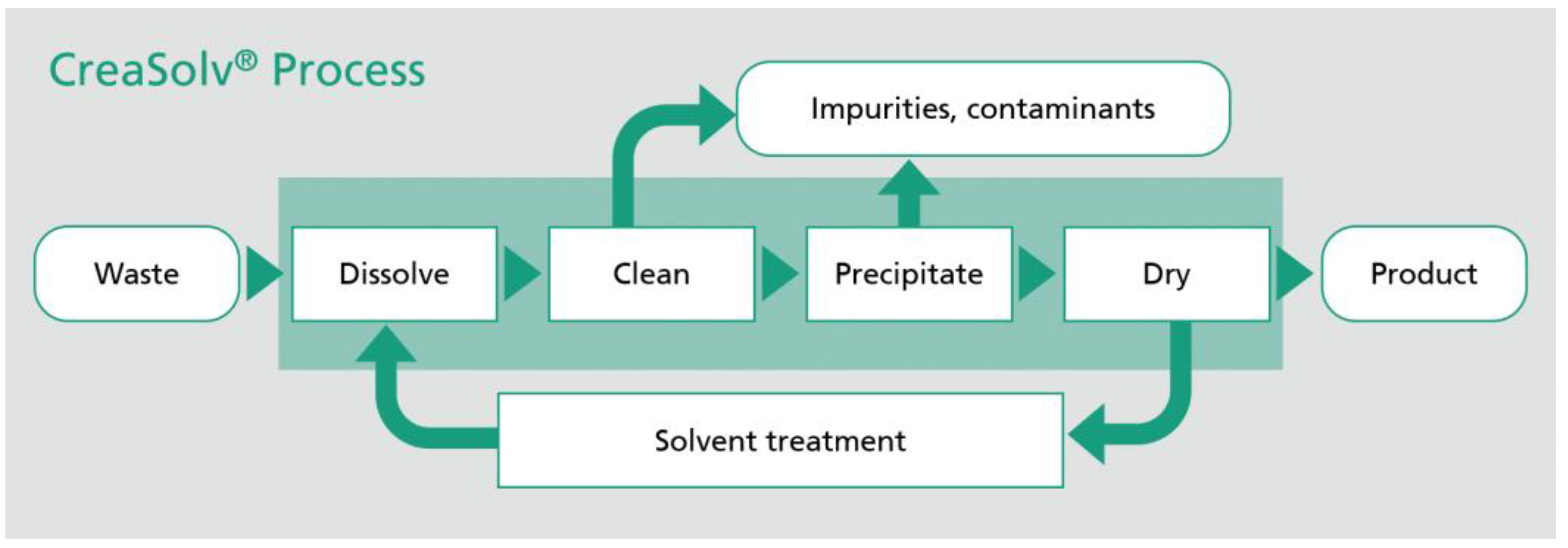
- F. IVV, „Recycling plastics - The CreaSolv® Process,” 26 September 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.ivv.fraunhofer.de/en/forschung/verfahrensentwicklung-polymer-recycling/hochwertiges-kunststoffrecycling.html.
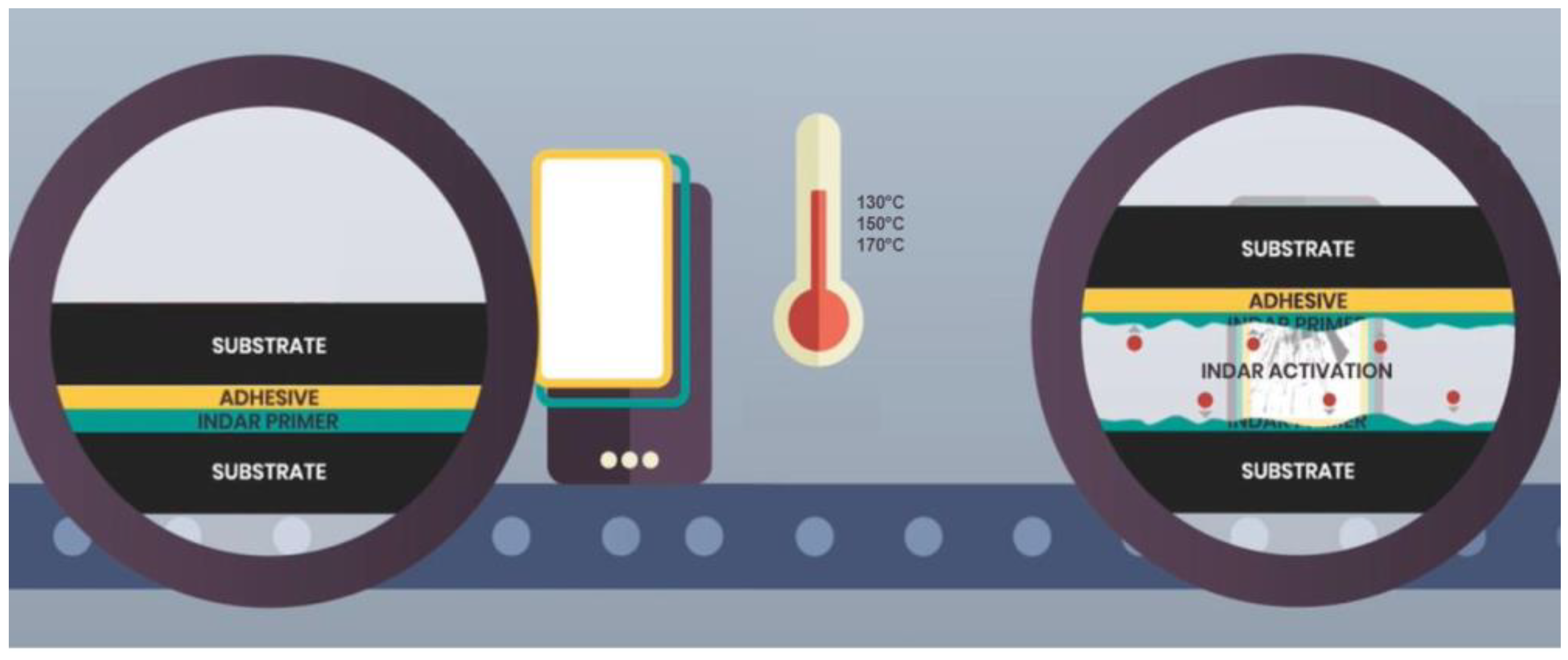
- Rescoll, „INDAR debonding process: structural debondable adhesive used for ground testing of GAIA segments,” 15 July 2011. [Online]. Available: https://rescoll.fr/indar-debonding-process-structural-debondable-adhesive-used-for-ground-testing-of-gaia-segments__trashed/. [Geopend 29 September 2023].
- M. OLIVE, T. BERGARA, J. DI-TOMASO en T. PLOURABOUE, „LATEST ACHIEVEMENTS IN THE FIELD OF ASSEMBLING METALS AND COMPOSITES,” 10 September 2015. [Online]. Available: https://rescoll.fr/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/MMP2015-28-paper.pdf.
- Rescoll.
| 1 | DECOAT was funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 814505 - https://decoat.eu/
|
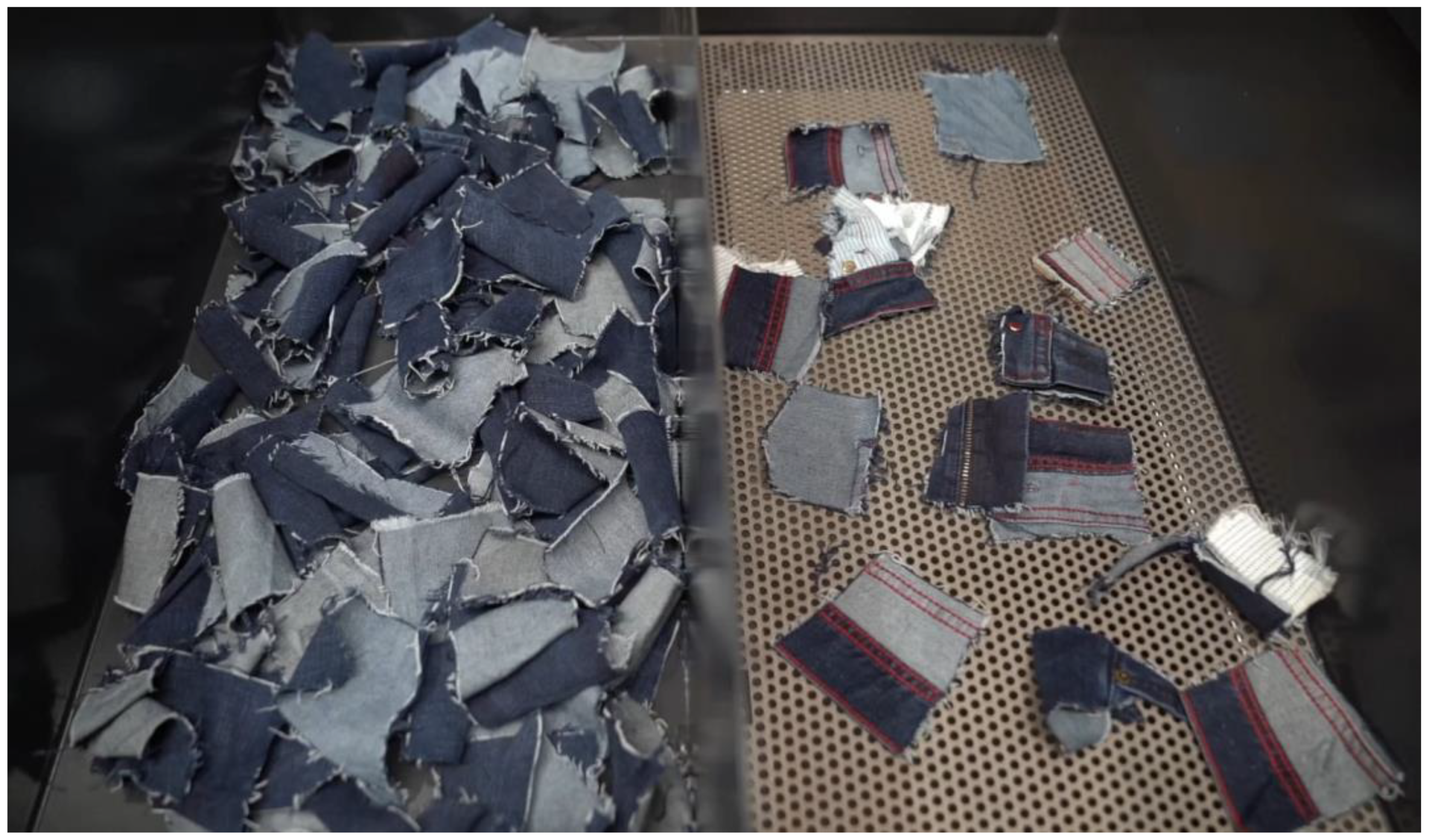
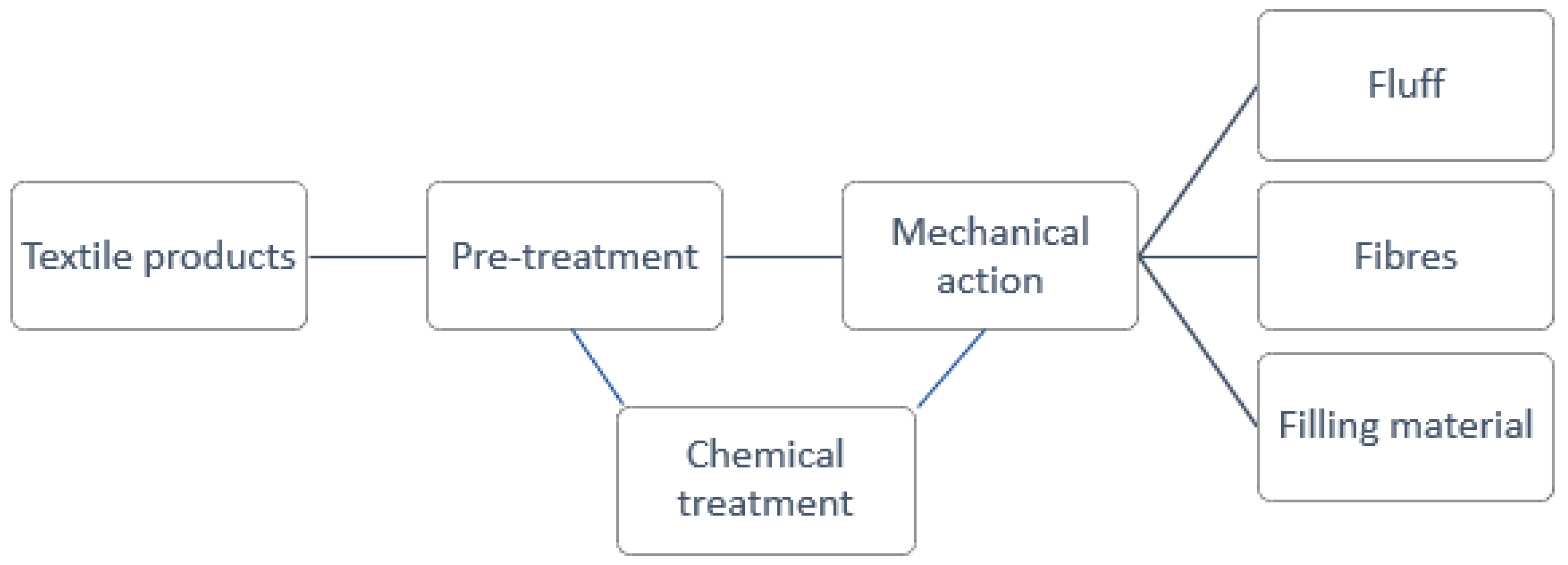



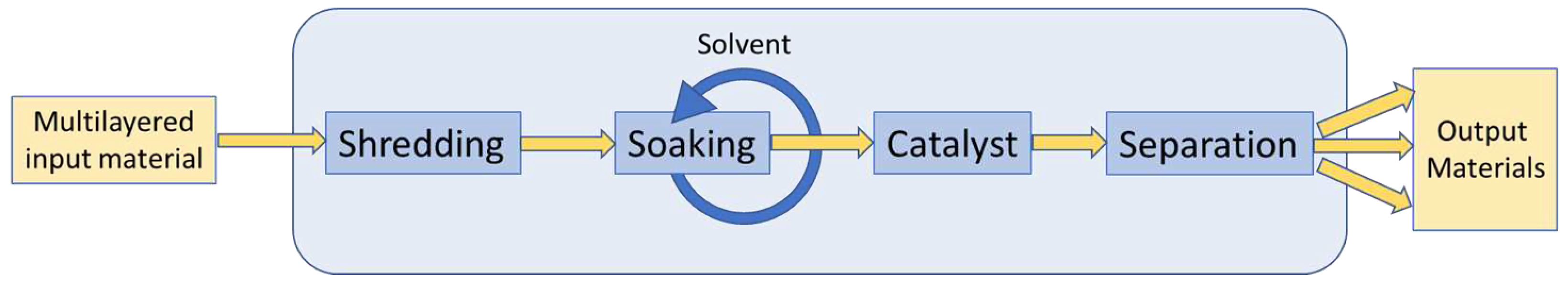
| Mechanical recycling | A process, used in a recycling system, based on physical forces, which may be used in isolation for fabric or fibre recycling or as pre-processing for thermomechanical or chemical and biochemical recycling processes. |
| Thermal recycling | A recycling process based on heating with the aim to recover either polymers or low molecular weight building blocks. Not to be mistaken with thermal recovery, an altogether different process which is not considered a recycling technology by the waste regulation. |
| Thermo-mechanicalrecycling | Process used in a recycling system that melts a polymer, typically employed to permit polymer recycling |
| Thermo-chemicalrecycling | Recycling process using partial oxidation reaction of polymers to produce low molar mass components or heat to degrade polymers to monomers that can be used as feedstock for the chemical industry, with the exclusion of fuels used for energy production or other combustion or energy recovery processes. |
| Chemical recycling | A process using chemical dissolution or chemical reactions which is employed in polymer or monomer recycling. |
| Monomer recycling | System for breaking down polymeric textile materials into their constituent monomers and rebuilding polymeric fibres for new uses |
| Polymer recycling | System for disassembling used fibres, extracting polymers and re-spinning them for new uses |
| COMPANY | TYPE | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|
| Andritz Laroche | Technology development | https://www.andritz.com/products-en/nonwoven-textile/textile-recycling-overview-nonwoven-and-textile |
| Cormatex | Technology development | www.cormatex.it/en |
| Dell’Orco & Villani SRL | Technology development | www.dellorco-villani.it/en/ |
| ALTEX Textil-Recycling GmbH & Co. KG | Recycling (all kinds of natural, synthetic & technical fibres) | www.altex.de |
| Cyclo® | Recycling (cotton) and yarn spinning | https://www.cyclofibers.com/ |
| Derotex NV | Recycling (mainly natural fibres) | www.derotex.be |
| Natural Fiber Welding Clarus | Recycling/material production (natural fibres) | https://clarus.naturalfiberwelding.com/ |
| Nouvelles Fibres Textiles | post-consumer textile sorting and recycling (all kinds of natural and synthetic fibres) | https://www.nouvellesfibrestextiles.com/ |
| Nova Fides | Recycling (wool) | www.novafides.it |
| Procotex SA Corporation NV | Recycling (all kinds of natural, synthetic & technical fibres) | https://en.procotex.com/ |
| Purfi | Recycling (all kinds of natural, synthetic & technical fibres) | https://purfi.com/ |
| Recover | Recycling (cotton fibres) | https://recoverfiber.com/ |
| Säntis Textiles | Recycling (cotton), yarn spinning and weaving | https://www.saentis-textiles.com/ |
| TexloopTM RCotTM | Recycling (cotton) and yarn spinning | https://circularsystems.com/texloop#texloop-summary |
| Usha Yarns LimitedTM | Recycling (cotton, wool, viscose, polyester and blends) and yarn spinning | https://ushayarns.com/ |
| Vanotex NV | Recycling (all kinds of natural & synthetic fibres) | www.vanotex.be |
| COMPANY | TYPE | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|
| BB Engineering | Technology development | https://bbeng.de/en/recycling-2/ |
| Erema | Technology development | https://www.erema.com/en/pet-fibre-recycling/ |
| Gneuss | Technology development | https://www.gneuss.com/en/ |
| NGR | Technology development | https://www.ngr-world.com/ |
| Starlinger | Technology development | https://www.starlinger.com/en/recycling/ |
| Antex | Fibre production and recycling (polyester) | www.antex.net |
| DS Fibres | Fibre production and recycling (polyester, PLA) | www.dstg.com/ds-fibres |
| LoopLife polymers – Despriet Gebroeders | Recycling (PLA & polyolefin textile products) |
http://www.looplife-polymers.eu/drupal/ https://plasticrecyclingdespriet.be/ |
| Vanheede Environment Group (Vanheede Polymers & Compounds) | Waste management and recycling (polyolefin textile products) | https://www.vanheede.com/en/our-treatment/plastic-recycling/ |
| COMPANY + TECHNOLOGY | TYPE | STATUS | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evrnu Nucycl | Technology development/Recycling/ Fibre production | First commercial production facility with capacity of 17 kt/y is due to be completed in 2024. | https://www.evrnu.com/ |
| Ioncell | Technology development | Pilot line (kg scale) operational. Ambition to commercialize the technology in 5-10 years. | https://ioncell.fi/ |
| Saxcell | Technology development and/or recycling | Pilot facility with output of 100 kg pulp/day, target 25 t/y. Cooperation contract with Birla for industrial production of Saxcell fibre | https://saxcell.com/ |
| Birla Cellulose Liva Reviva | Recycling and fibre production | Ambition to scale up the Liva Reviva production to 100 kt/y by 2024/2025. | https://www.birlacellulose.com/ |
| Infinited Fiber Company Infinna® | Recycling and fibre production | Two pilot plants operational since 2018, building a commercial plant of 30 kt/y which is expected to reach full capacity in 2025. | https://infinitedfiber.com/ |
| Lenzing Refibra® | Recycling and fibre production | Lenzing and Södra have set a target of processing 25 kt textile waste per year by 2025. | https://www.lenzing.com/ |
| Renewcell Circulose® | Recycling | Commercial plant of 60 kt/y is running since 2022, expanding to 120 kt/y by 2024. | https://www.renewcell.com/en/ |
| Södra OnceMore® | Recycling andfibre production | Lenzing and Södra have set a target of processing 25 kt textile waste per year by 2025. | https://www.sodra.com/ |
| COMPANY + TECHNOLOGY |
TYPE | STATUS | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polycotton blends – solvent based dissolution | |||
| Worn Again Technologies | Technology development | Pilot line processing 80 kg batches, demonstration plant of 1 kt/y will be online from 2024, commercial plant (50 kt/y) expected by 2027 | https://wornagain.co.uk/ |
| Polycotton blends – hydrothermal processes | |||
| BlockTexx Separation of Fibre Technology |
Technology development/Recycling | Recently commissioned commercial facility operating at 4 kt/y, to be further scaled to 10 kt/y | https://www.blocktexx.com/ |
| Circ | Recycling | Operating a pilot plant with capacity of several tons per day, plans to open its first factory of 65 kt/y capacity in 2025. | https://circ.earth/ |
| HKRITA The Green Machine | Technology development | First industrial scale system operational with capacity of 1.5 t/day | https://www.hkrita.com/en/our-innovation-tech/projects/green-machine-phase-2 |
| Polycotton blends – Enzymatic processes | |||
| HKRITA Textile Waste Recycling by Biological Method (formerly called “the brewery”) | Technology development | Designing and building a pre-industrial scale system |
https://www.innovationhub.hk/article/textile-waste-recycling-by-biological-method https://www.hkrita.com/en/our-innovation-tech/projects/textile-waste-recycling-biological |
| Other materials | |||
| Obbotec-SPEX (solvent-based PP & PE plastics & textiles recycling) |
Technology development/Recycling | Pilot unit commissioned in November 2022, commercial demo plant (app. 10 kt/y) foreseen end 2024. | https://obbotec.com/en/spex-technologie/ |
| PureCycle Technologies (solvent-based PP textiles & plastics recycling) |
Recycling | First commercial plant has just produced the first run of Ultra-Pure Recycled (UPR) resin from post-industrial recycled material at commercial scale, estimated capacity +/- 50 kt/y. | https://www.purecycle.com/ |
| Teijin Aramid (solvent-based aramid recycling) |
Recycling and fibre production | Aim for circular Twaron to be commercially available in 2024, recently performed first industrial-scale production run. | https://www.teijinaramid.com/en/sustainability/recycling-and-circularity/index.html |
| Thai Acrylic Fibre Co. RegelTM (solvent-based acryl recycling) |
Recycling and fibre production | Commercial for larger deniers, now working on achieving finer deniers; | https://regel.world/ |
| COMPANY + TECHNOLOGY |
TYPE | STATUS | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET – glycolysis | |||
| Axens Rewind PET | Technology development | Demonstration plant completed. New units coupled with Toray Films Europe’s polymerization plant with annual production of 30kt/y recycled PET expected by the end of 2025 | https://www.axens.net/markets/plastic-recycling |
| Garbo’s CHEMPET | Technology development | Agreement with Saipem S.p.A. to develop a 45 kt/y industrial plant | https://garbo.it/en/chempet/ |
| Ioniqa Technologies | Technology development | 10 kt/y demonstration plant, announced a partnership to further scale up and commercialize the technology | https://ioniqa.com/ |
| Poseidon Plastics | Technology development/ Recycling | 10 kt/y recycling facility to be built, expected to be available in 2024 | http://poseidonplastics.com/ |
| CuRe Technology | Recycling | Pilot plant with capacity of 20 kg/hr in a continuous process, demonstration plant of 25 kt/y expected by 2025. | https://curetechnology.com/ |
| Eastman Polyester renewal technology | Recycling | Glycolysis plant (capacity unknown) is operational. | https://www.eastman.com/Company/Circular-Economy/Solutions/Pages/Polyester-Renewal.aspx |
| Jeplan BRING Technology | Recycling | 2 kt/y demonstration plant (Kitakyushu Hibikinada Plant) aimed at textile to textile recycling since 2018. | https://www.jeplan.co.jp/en/technology/ |
| PERPETUAL Revalyu | Recycling | Commercial for PET bottle waste (40 t/day), textile recycling still in research phase. |
https://www.perpetual-global.com/ https://www.revalyu.com/ |
| PET – methanolysis | |||
| Loop Industries | Technology development | First commercial manufacturing facility with capacity of 70 kt/y is expected to be completed by the end of 2025. | https://www.loopindustries.com/en |
| RePEaT (joint venture of Itochu, Teijin and JGC) | Technologydevelopment | Unknown | https://repeat-inc.com/en/ |
| Eastman Polyester renewal technology | Recycling | First methanolysis plant is under construction and due to be completed early next year (capacity 110 kt/y). | https://www.eastman.com/Company/Circular-Economy/Solutions/Pages/Polyester-Renewal.aspx |
| Itochu’s RENU technology | Recycling | Commercial plant of 30 kt/y operational (Eunomia) | https://renu-project.com/en |
| Jiaren New materials | Recycling and fibre production | Commercial plant of 25 kt/y and 2nd phase project of 160 kt/y under construction | http://www.jiarenrecycle.com/en/ |
| PET – hydrolysis | |||
| Carbios (enzymatic hydrolysis) | Technology development | Partnership with Indorama Ventures to build 40kt/y PET biorecycling plant, targeted commissioning in 2025. | https://www.carbios.com/en/ |
| DePoly | Technologydevelopment/ Recycling | Pilot plant (50 t/y) operational, are about to build 500 t/y showcase plant (expected to be operational by the end of 2024). | https://www.depoly.co/ |
| Gr3n | Technology development | Working on industrial plant with capacity of 40 kt/y, expected to be operational in 2025 | https://gr3n-recycling.com/ |
| Rittec RevolPET®/RevolTEX® | Technology development | Mini-plant (1kt/y) is being engineered, operation is planned to start by end 2023, pre-industrial plant (up to 20 kt/y) will be engineered in parallel | https://www.rittec.eu/solutions/revolpet-r.html |
| Ambercycle Cycora® (enzymatic hydrolysis) |
Recycling | Scaled from 12 t/y in 2019 to 300 t/y in 2022, exploring the construction and operation of a commercial-scale manufacturing facility | https://www.ambercycle.com/ |
| FENC® TopGreen™ ChemCycle |
Recycling and Fibre production | Unknown | https://www.feg.com.tw/en/news/news_detail.aspx?id=10090 |
| Ineos Infinia | Recycling | Pilot plant, capacity unknown | https://www.ineos.com/businesses/ineos-aromatics/ineos-infinia/ |
| Other materials | |||
| Aquafil’s Econyl (PA6) | Recycling/Fibre production | TRL 9, commercial | https://www.aquafil.com/ |
| Noosa’s NOOCYCLE (PLA, hydrolysis) |
Recycling/ Fibre production | Unknown | http://www.noosafiber.com/ |
| COMPANY + TECHNOLOGY |
TYPE | STATUS | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gasification | |||
| Eastman Carbon Renewal | Recycling | Commercial | https://www.eastman.com/Company/Circular-Economy/Solutions/Pages/Carbon-Renewal.aspx |
| Resonac | Recycling | 195 t/day installation | https://www.resonac.com/ |
| Pyrolysis | |||
| Arcus Greencycling | Technology development | 4 kt/y pilot installation | https://www.arcus-greencycling.com/ |
| Axens Rewind Mix (Purification of pyrolysis oils) | Technology development | Unit of 50 kt/y expected to be operational in 2025 (licensed to Borealis) | https://www.axens.net/markets/plastic-recycling |
| Fuenix | Technology development | Unknown | https://fuenix.com/ |
| Plastic Energy | Technology development/ Recycling | Commercial | https://plasticenergy.com/ |
| Recycling Technologies Plaxx® | Technology development/Recycling | Pilot | https://recyclingtechnologies.co.uk/ |
| CLS-Tex HTEX (hydropyrolysis) | Recycling | Construction of 8 t/day production line started | https://www.cls-tex.nl/cls-inside-workwear-htex |
| GreenMantra Technologies | Recycling | Commercial | https://greenmantra.com/ |
| Hydrothermal liquefaction | |||
| Mura Technology ReNew ELP HydroPRSTM | Technology development | Pilot scale, recycling facility of 20 kt/y under construction, due to launch in 2023. | https://muratechnology.com/renewelp/ |
| Carboliq | Recycling | Semi-industrial pilot plant (200 kg/h), Recycling facility of 10 kt/y expected to be operational by 2025 | https://www.carboliq.com/en/ |
| OMV ReOil 100® | Recycling | Semi-industrial pilot plant (100 kg/h), Start-up of demo-plant of 16 kt/y planned for 2023. | |
| COMPANY + TECHNOLOGY |
TYPE | STATUS | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | |||
| BASF TrinamiX | Technology development | https://trinamixsensing.com/textiles | |
| Gut mIRoGun V4 | Technology development | http://www.gut-stuttgart.de/en/products/mirogun-40-mobile-nir-plastic-detection-from-gut-environmental-technologies.html | |
| Matoha Fabritell | Technology development | https://matoha.com/fabrics-identification | |
| Senorics SenoCorder Solid | Technology development | https://www.senorics.com/ | |
| Spectral Engines Nirone | Technology development | https://shop.spectralengines.com/products/nirone-device-d1-4-d1-7-d2-0-d2-2-d2-5?variant=36643865821349 | |
| Valvan Fibersort | Technology development |
https://www.fibersort.com https://smartfibersorting.com/ |
|
| Lounais-Suomen Jätehuolto Oy (Finland) |
Sorting | https://lsjh.fi/ | |
| TEXAID (Switzerland) | Sorting | https://www.texaid.ch/en/ | |
| Automatic | |||
| HKRITA | Technology development | https://www.hkrita.com/en/our-innovation-tech/projects/smart-garment-sorting-system-for-recycling | |
| Pellenc Mistral+ CONNECT | Technology development | https://www.pellencst.com | |
| PicvisaEcopick, Ecopack, Ecosort Textil | Technology development | https://picvisa.com/en/ | |
| Steinert | Technology development | https://steinertglobal.com | |
| Tomra Autosort | Technology development | https://www.tomra.com/en/solutions/waste-metal-recycling/applications/textiles | |
| Valvan Fibersort | Technology development | https://www.fibersort.com | |
| Wastex – Picvisa | Technology development | https://www.wastexrecycling.com/ | |
| Cetia - Fibersort (France) | Sorting | https://cetia.tech/home-en/ | |
| Coleo Recycling - Picvisa (La Coruña, Spain) | Sorting | 5,000 t/year | https://coleo.es/ |
| LSJH (Finland) | Sorting | Planned for 2025 | https://poistotekstiili.lsjh.fi/en/home/ |
| Salvation Army - Fibersort (Kettering, UK) | Sorting | 500 t/year | https://www.satcol.org/fibersort |
| Soex (Bitterfeld-Wolfen, Germany) | Sorting | https://www.soex.de/en/ | |
| Synergies TLC – Pellenc (France) | Sorting | 3,000 t/year, 25,000 t/year planned for 2025 | https://synergies-tlc.com/ |
| Sysav – Siptex/Tomra (Malmö, Sweden) | Sorting | 24,000 t/year target | https://www.sysav.se/en/siptex/ |
| TEXAID – ReHubs project (Switzerland) | Sorting | 50,000 t/year planned for 2024 | https://www.texaid.ch/en/ |
| COMPANY | TECHNOLOGY | TRL | WEBSITE |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANDRITZ Laroche | Garnetting/tearing lines with integrated automated trim removal | 9 | https://www.andritz.com/products-en/nonwoven-textile/recycling/textile-recycling |
| Dell’Orco & Villani | Garnetting/tearing lines with integrated automated trim removal | 9 | https://www.dellorco-villani.it/en/ |
| Valvan | TrimcleanTM Automatic cutting and trim removal machine | 7 | https://www.valvan.com/en/solutions/textile-sorting-recycling |
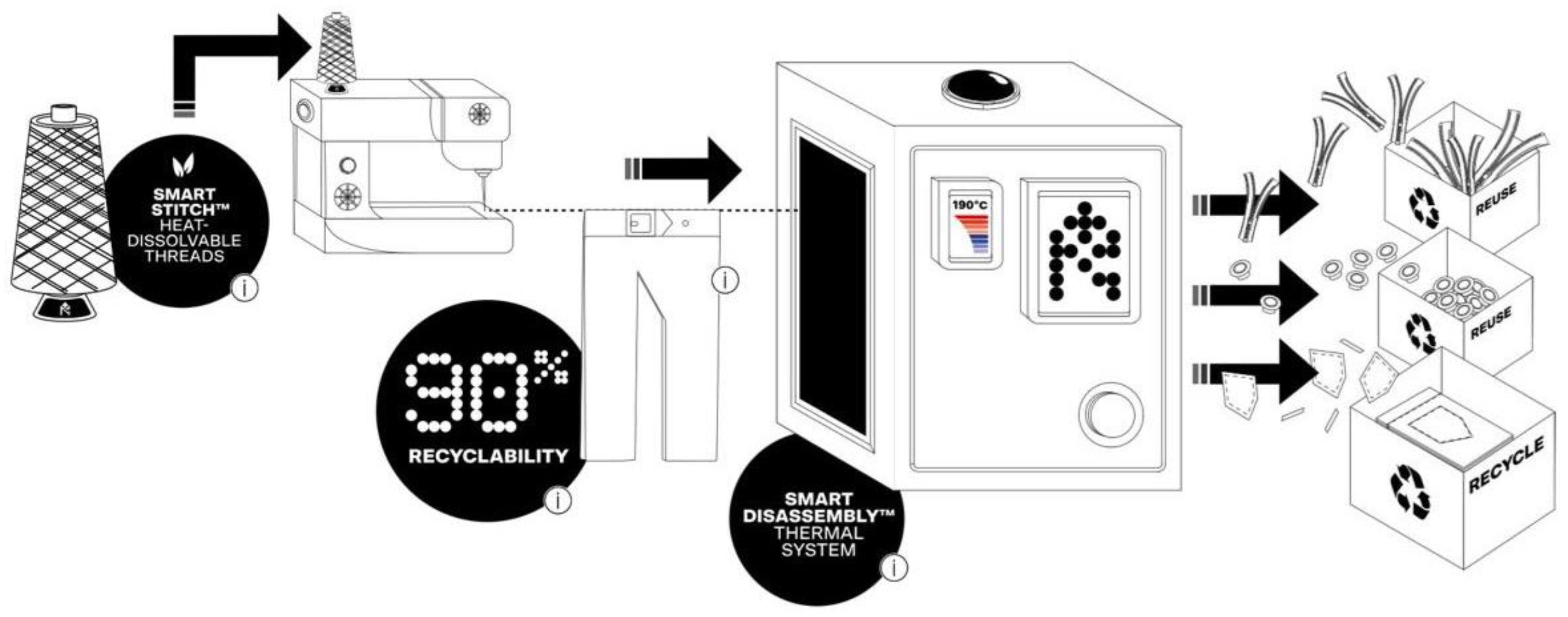
| Resortecs | Smart StitchTM melting threads and Smart DisassemblyTM thermal disassembling ovens | 8 | https://resortecs.com/ |
| Wear2 | Wear2® Ecostitching sewing thread combined with microwave technology for disassembly | 7 | https://wear2.com/en/ |
| Fraunhofer IVV | Creasolv®-adapted process for delamination or dissolution of coatings from PET and PA textile substrates. | 7 | https://www.ivv.fraunhofer.de/en/recycling-environment/recycling-plastics-creasolv.html |
| Rescoll | INDAR Inside® debonding technology | 6 | https://rescoll.fr/rescoll-presents-indar-debonding-primer-a-solution-for-circularity-of-multimaterial-assemblies/ |
| PVC separation | PolySep | 7-8 | https://www.pvcseparation.com/ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





