Submitted:
16 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
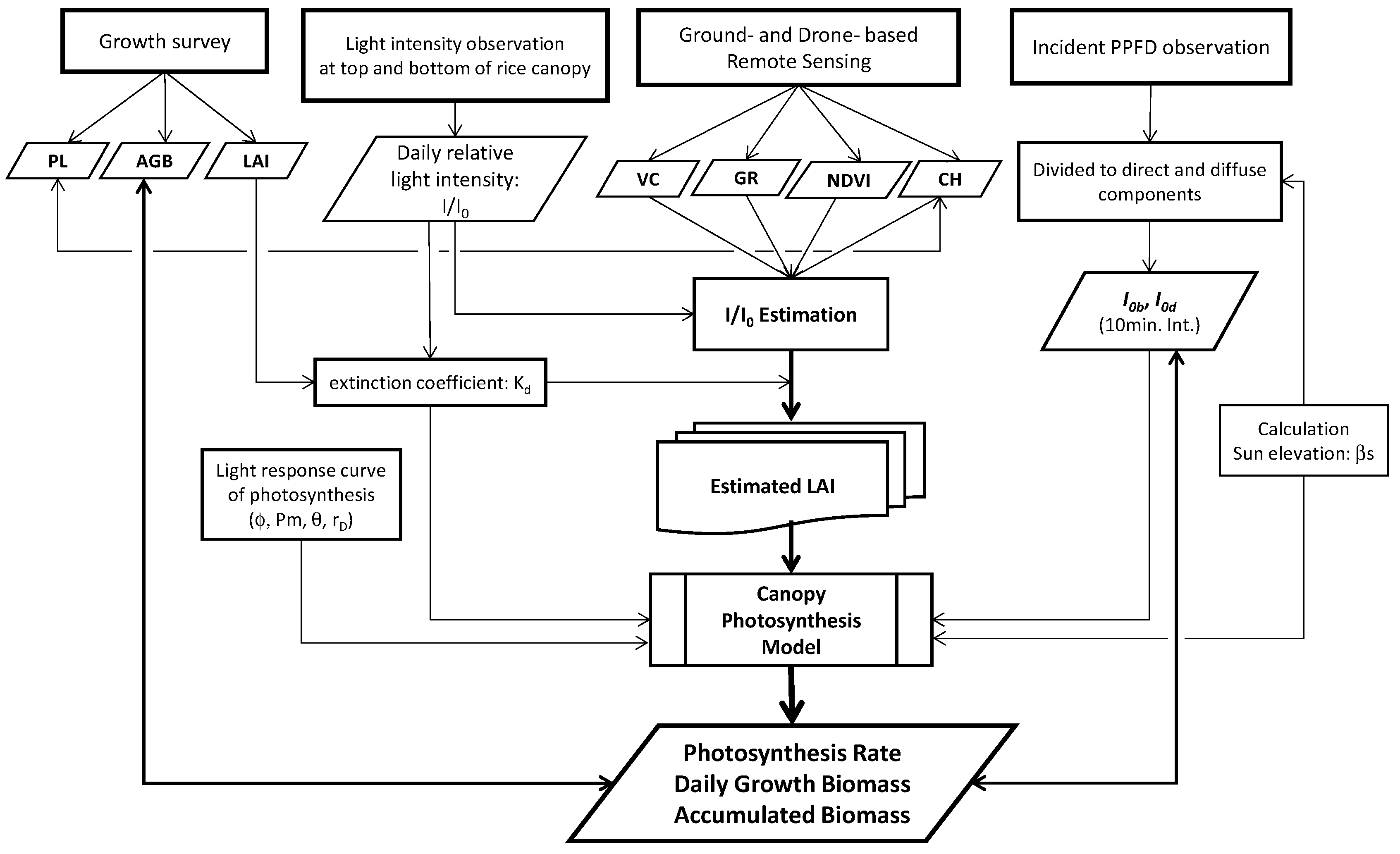
2.1. Model description
2.1.1. Light distribution under canopy
2.1.2. Canopy photosynthesis model
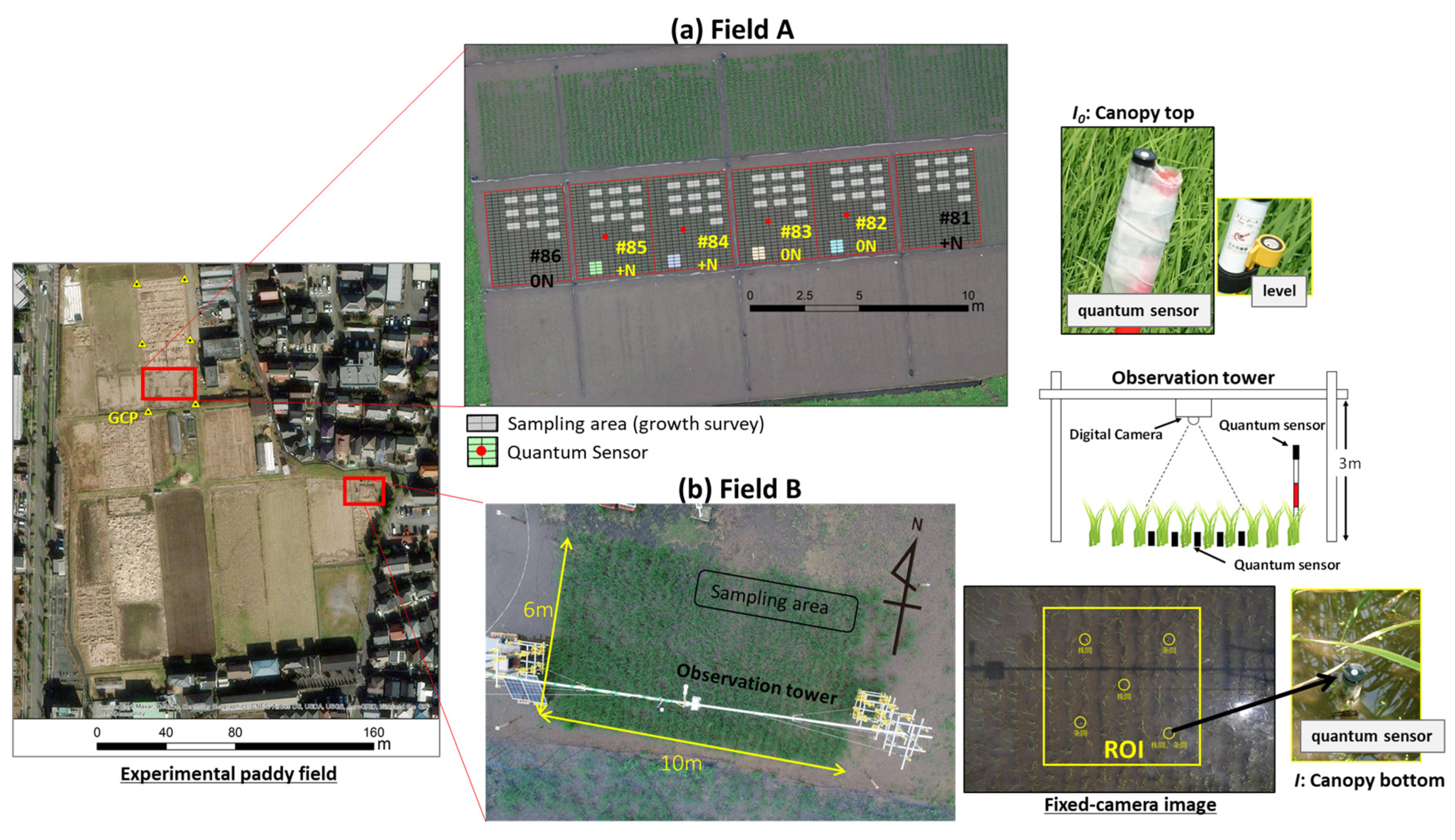
2.2. Experimental site
2.3. Observation data
2.3.1. Relative light intensity under rice canopy
2.3.2. Incident photosynthetic photon flux density
2.3.3. Ground-based remote sensing
2.3.4. UAV-based remote sensing
2.3.5. Rice growth survey
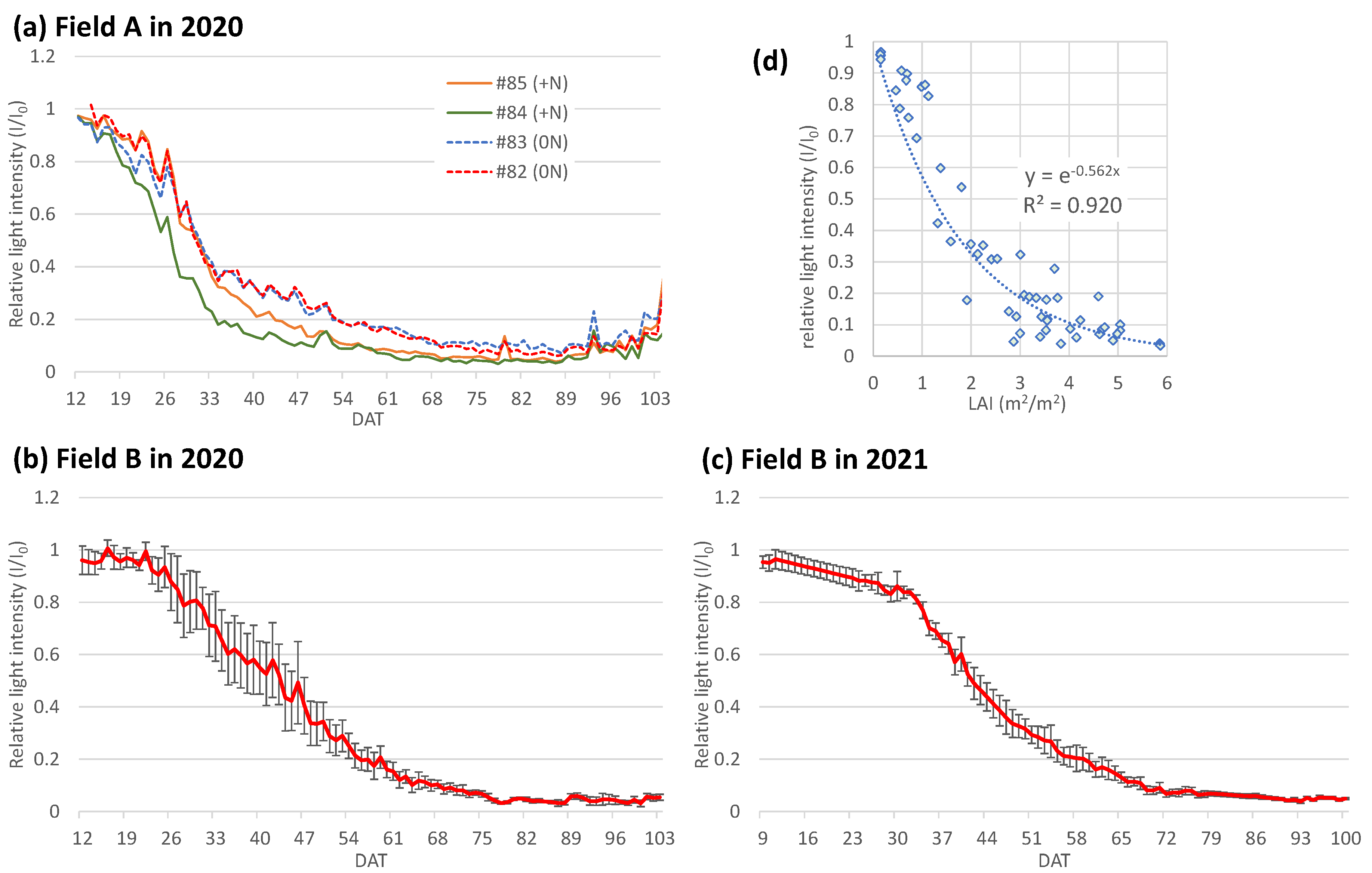
2.4. LAI estimations
2.5. Direct and diffuse components divided from incident global PPFD
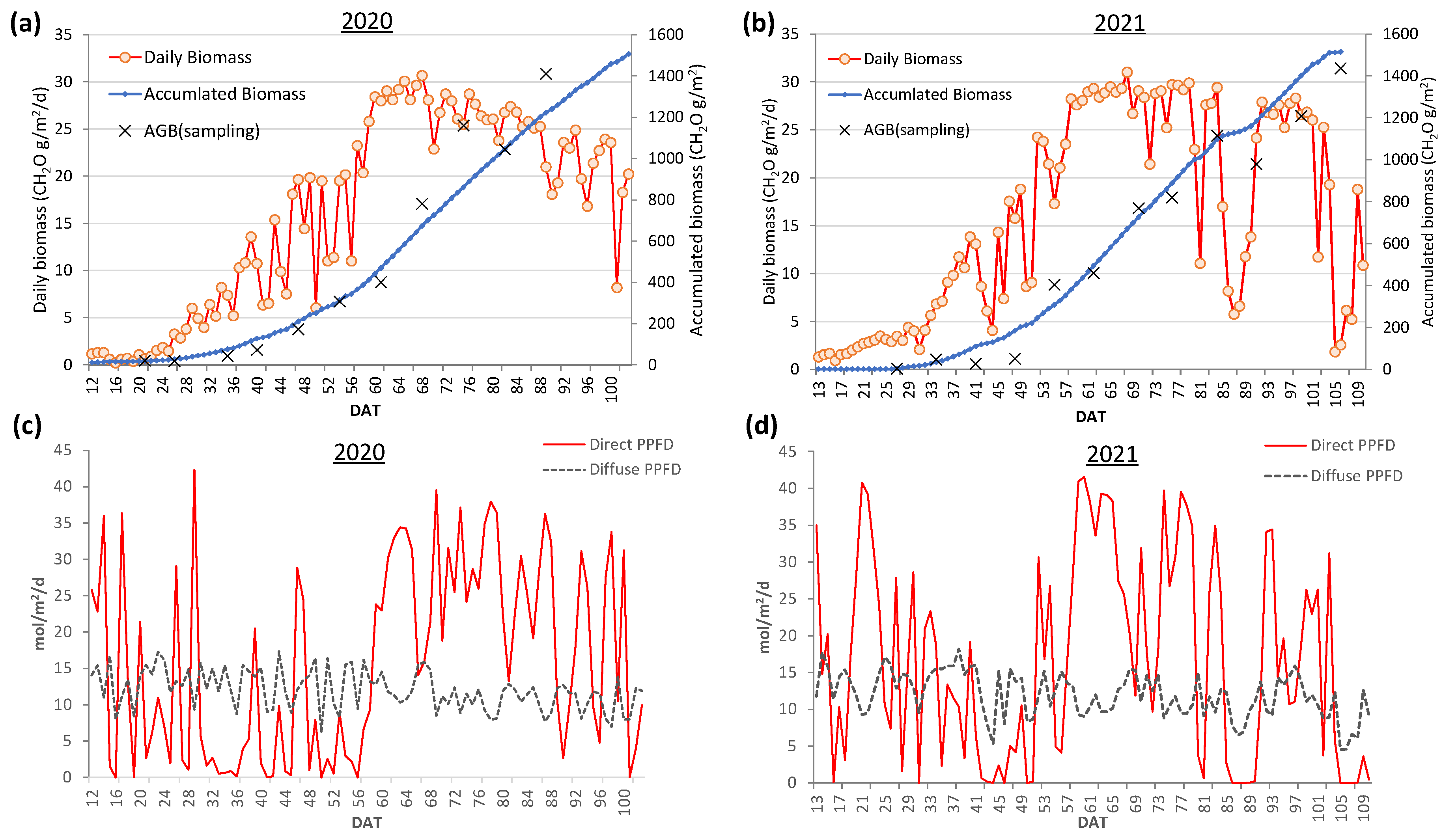
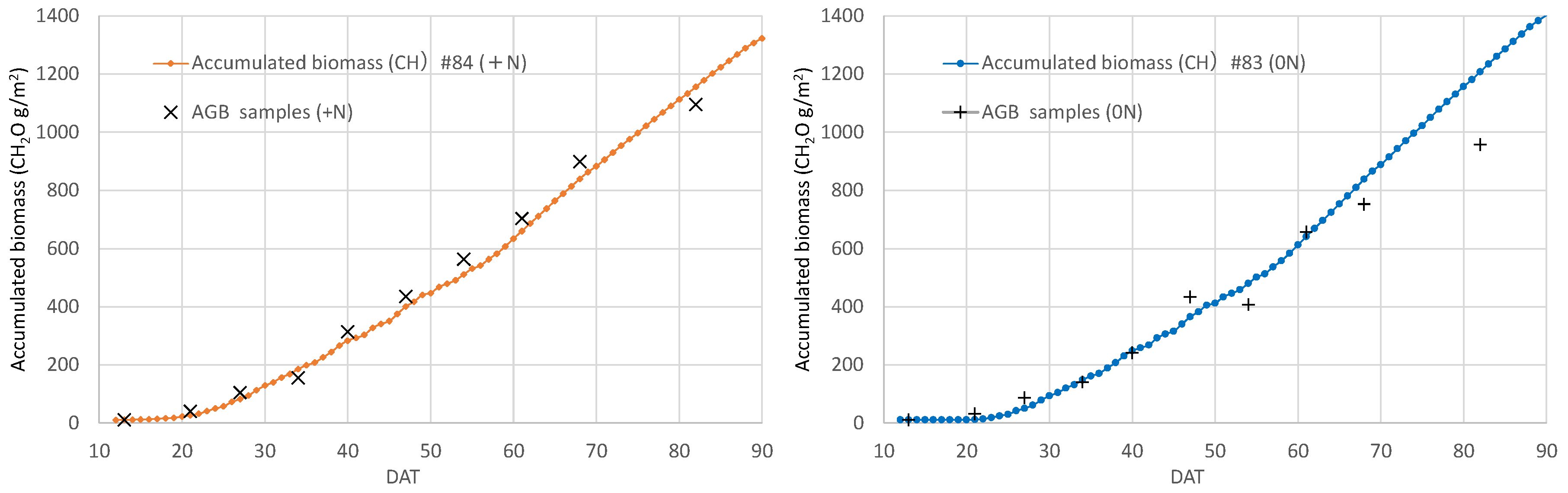
2.6. Estimation of daily growth biomass
3. Results and discussions
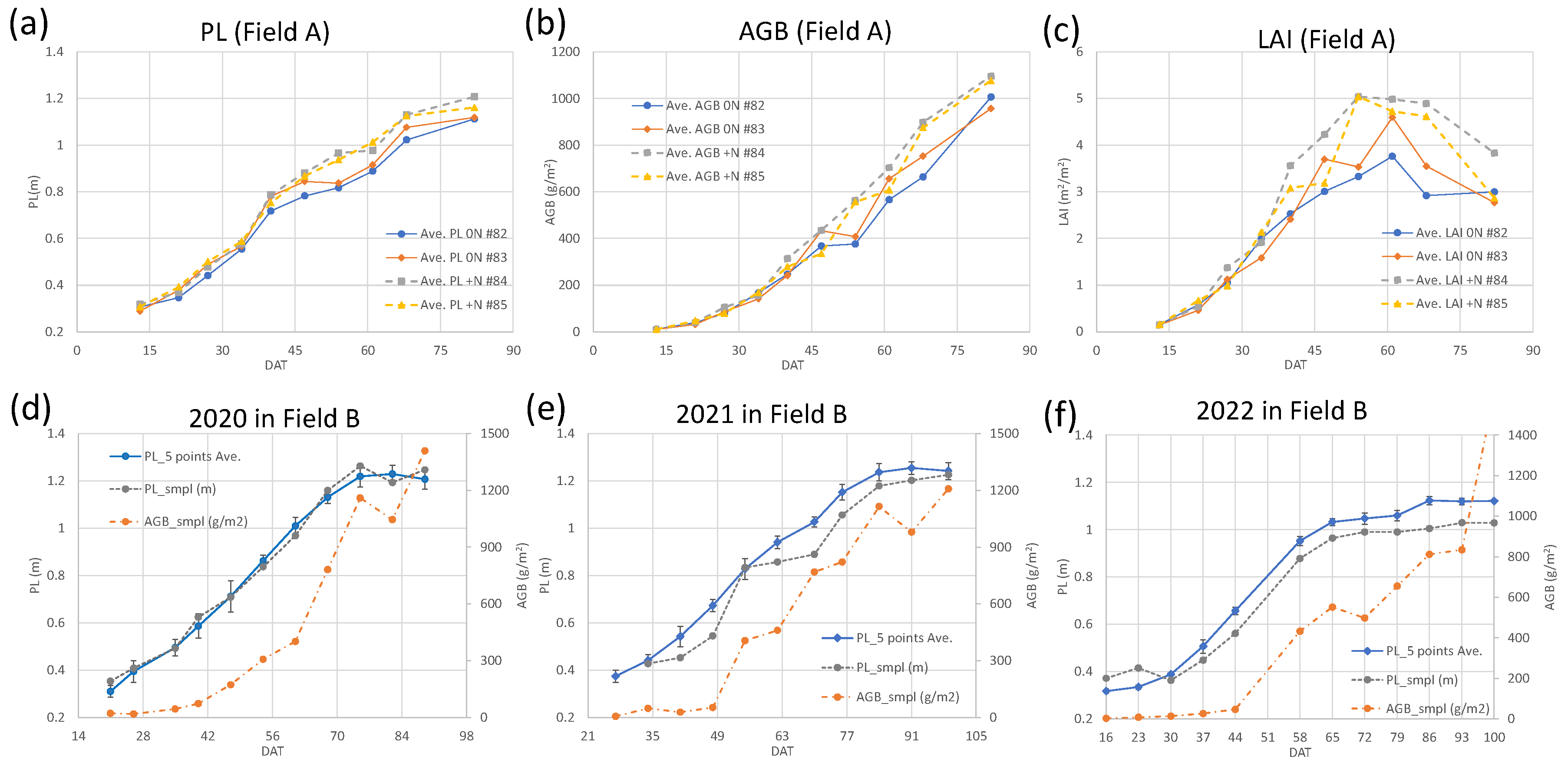
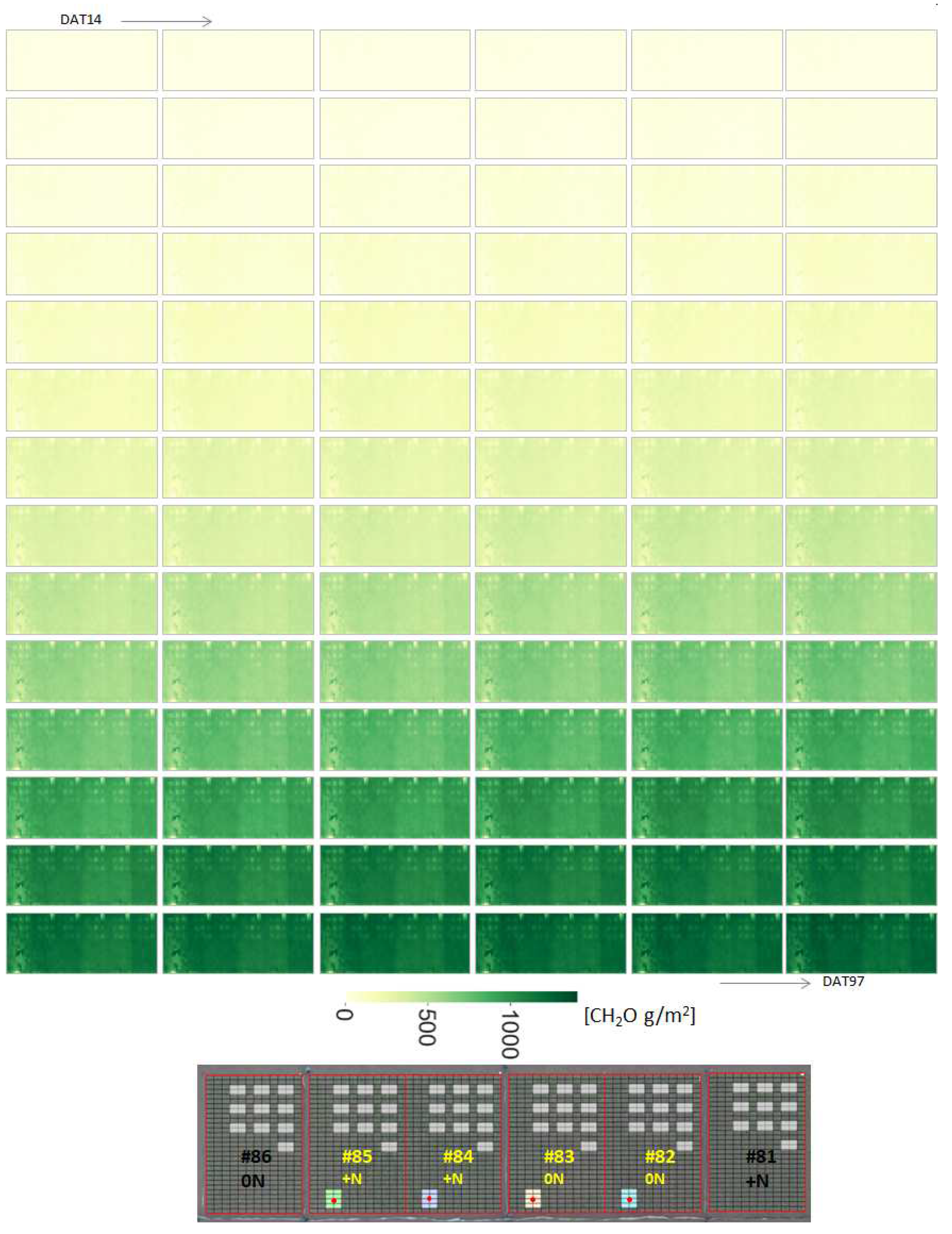
3.1. Rice growth survey
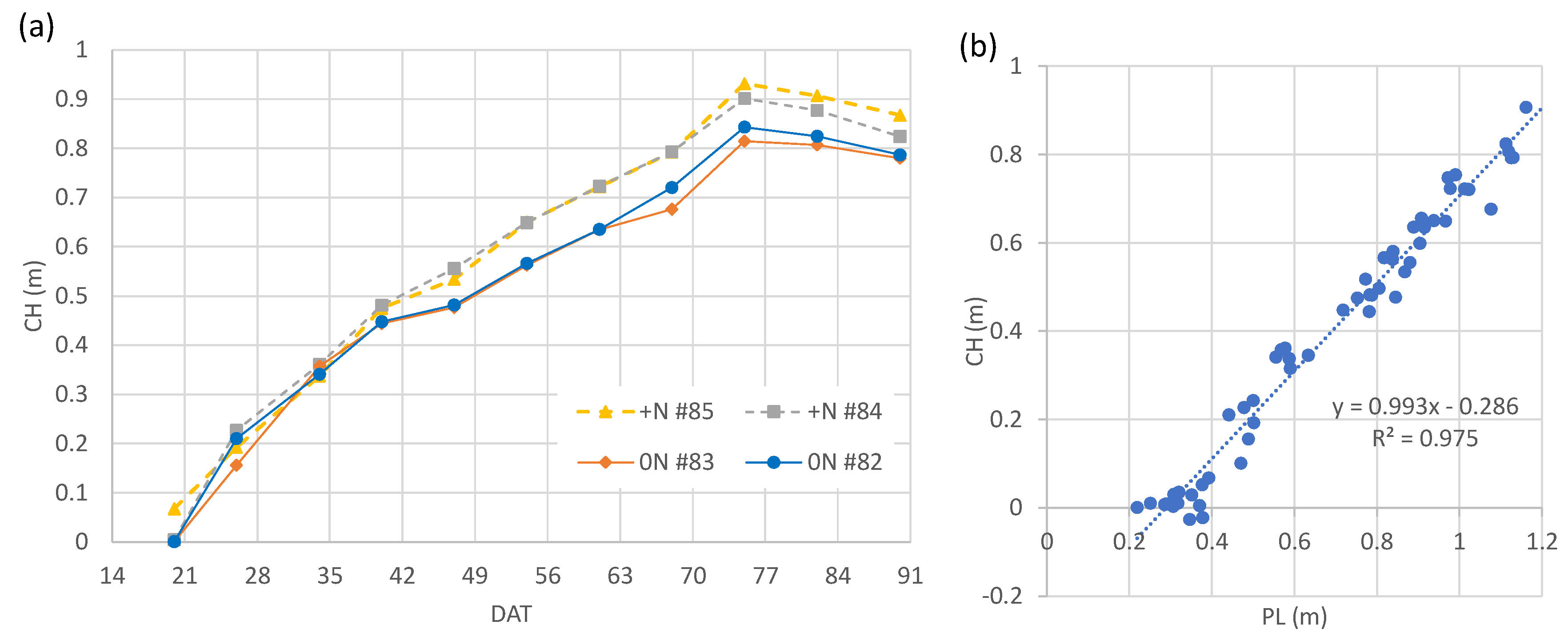
3.2. Weekly change of canopy height calculated from Canopy Surface Models
3.3. Daily change of relative light intensity (I/I0) and the extinction coefficient (Kd)
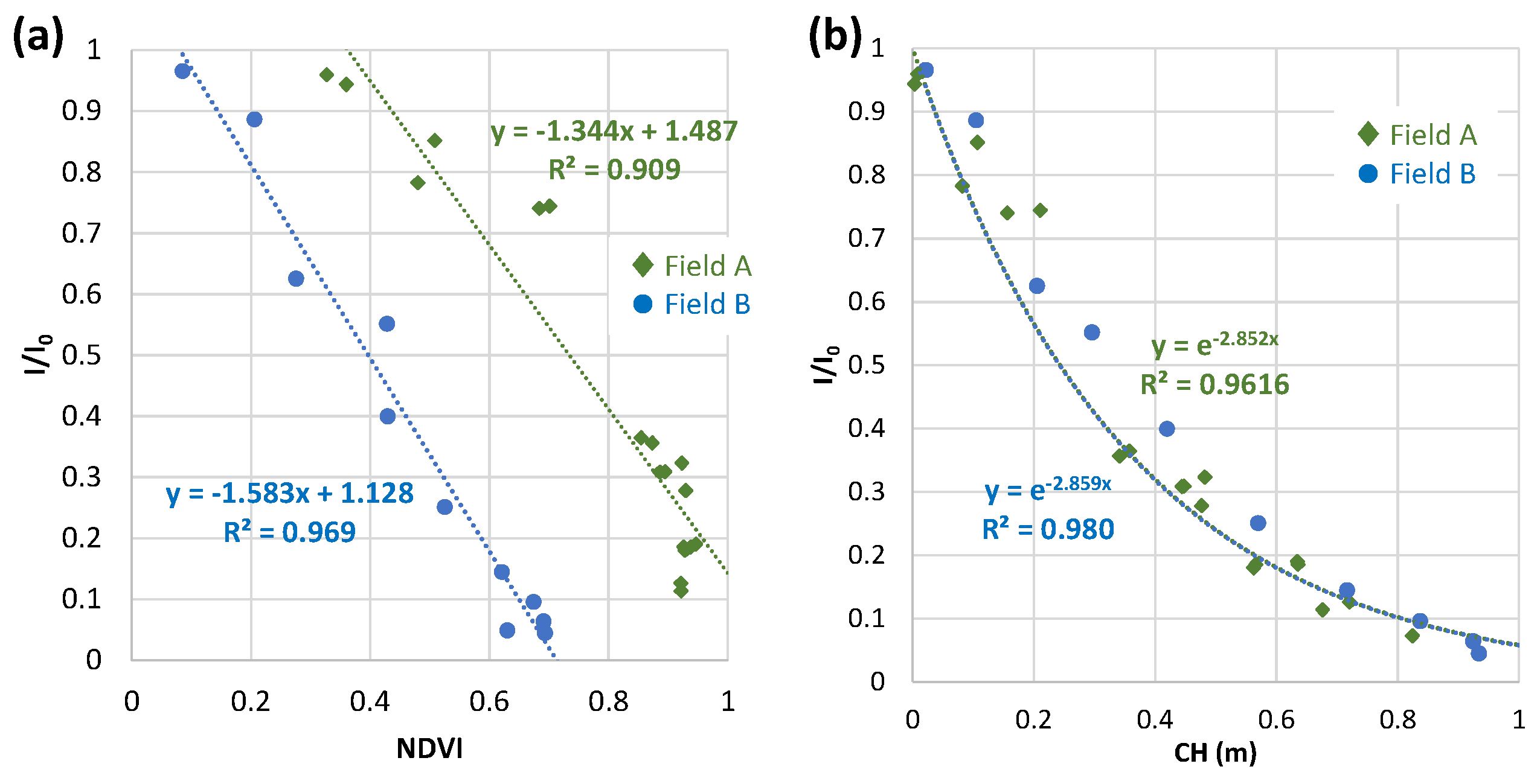
3.4. Relations of relative light intensity with the parameters by ground- and UAV-based observations
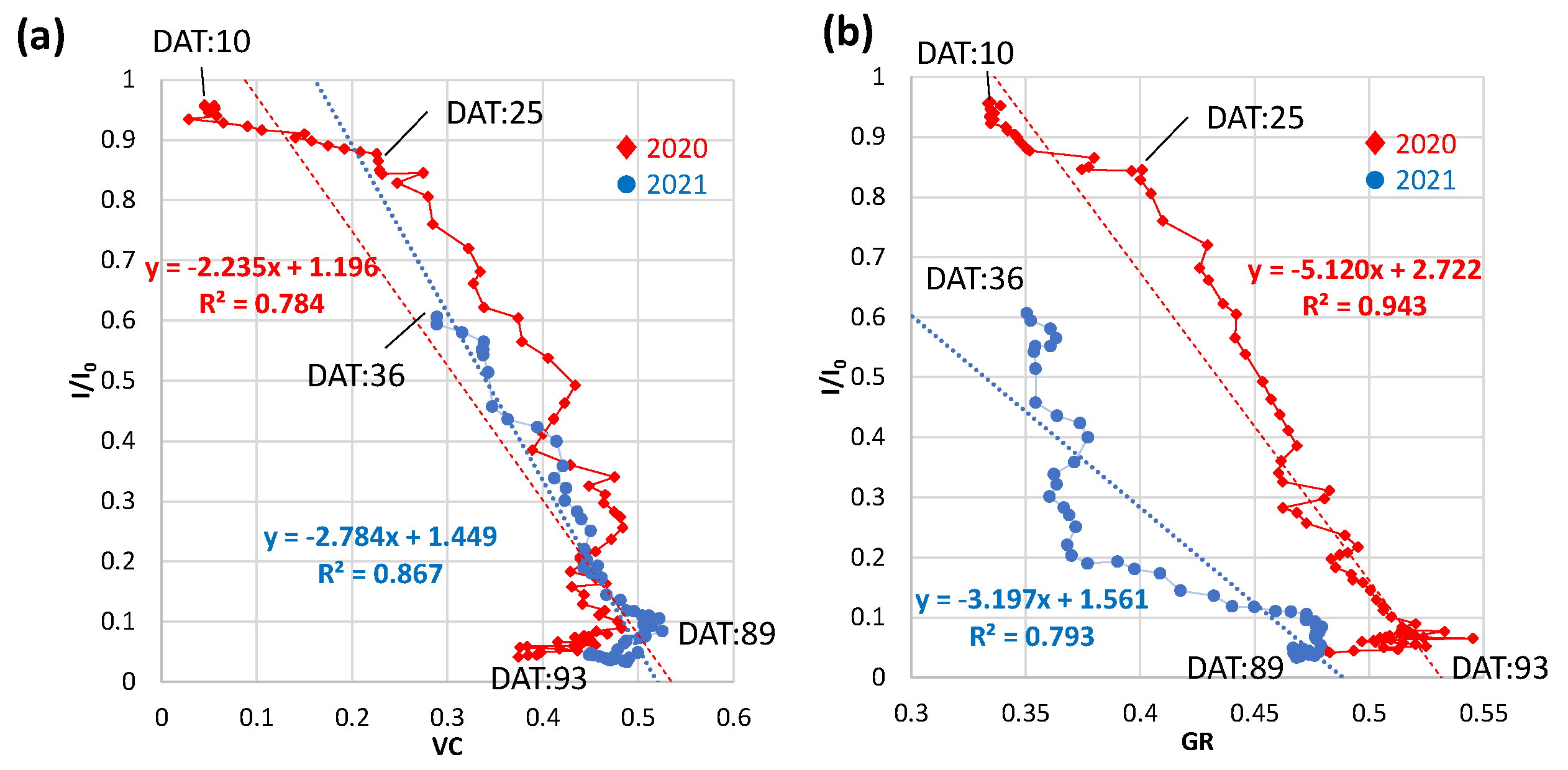
3.4.1. Daily vegetation cover (VC) and green ratio (GR)
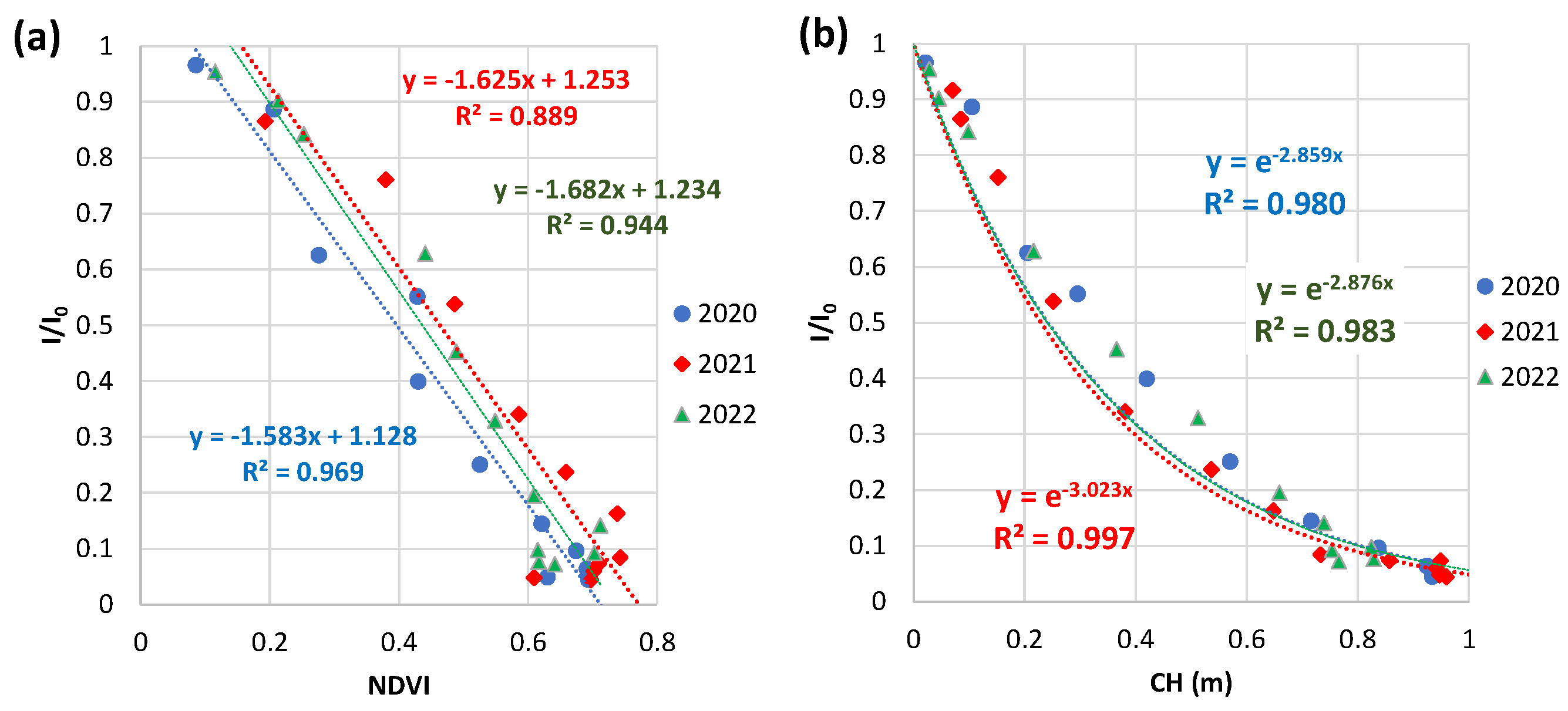
3.4.2. Weekly NDVI and CH at Field B in 2020 to 2022
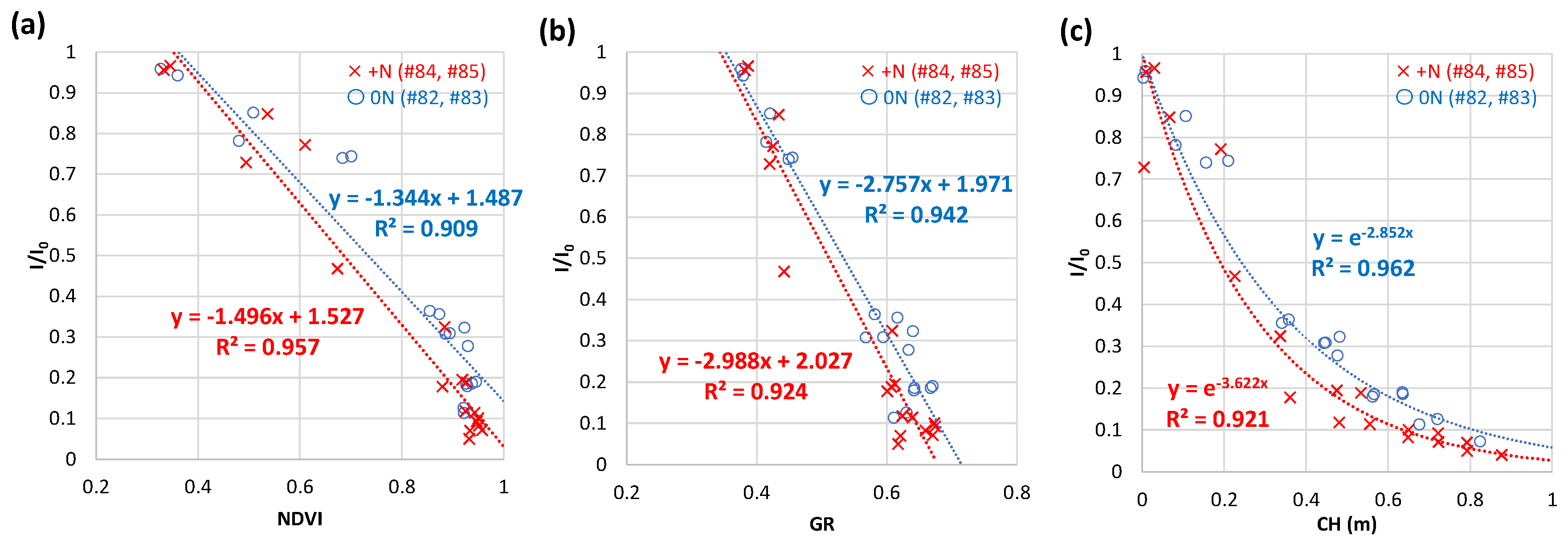
3.4.3. Weekly NDVI and CH by UAV-based observation at field A in 2020
3.4.4. Comparison with field A and field B
3.5. Daily biomass estimation at the field scale
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molotoks, A.; Smith, P.; Dawson, T.P. Impacts of Land Use, Population, and Climate Change on Global Food Security. Food and Energy Security 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP and WHO. 2023. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2023. Urbanization, agrifood systems transformation and healthy diets across the rural–urban continuum. Rome, FAO. [CrossRef]
- FAO. 2020. World Food and Agriculture - Statistical Yearbook 2020. Rome. [CrossRef]
- Alberton, B.; Torres, R. da S.; Cancian, L.F.; Borges, B.D.; Almeida, J.; Mariano, G.C.; Santos, J. dos; Morellato, L.P.C. Introducing Digital Cameras to Monitor Plant Phenology in the Tropics: Applications for Conservation. Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation 2017, 15, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Hu, T.; Yuan, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Song, G. Deep-Learning-Based Rice Phenological Stage Recognition. Remote Sensing 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, W.H.; Steppe, K. Perspectives for Remote Sensing with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Precision Agriculture. Trends in Plant Science 2019, 24, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.B.; Li, Z.L.; Wu, H.; Tang, B.H.; Ma, L.; Zhao, E.; Li, C. Inversion of the PROSAIL Model to Estimate Leaf Area Index of Maize, Potato, and Sunflower Fields from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2014, 26, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, H.B.; Xu, X.Q.; He, J.Y.; Ge, X.K.; Yao, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.X.; Tian, Y.C. Predicting Grain Yield in Rice Using Multi-Temporal Vegetation Indices from UAV-Based Multispectral and Digital Imagery. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2017, 130, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanning, M.; Kühling, I.; Trautz, D.; Jarmer, T. High-Resolution UAV-Based Hyperspectral Imagery for LAI and Chlorophyll Estimations from Wheat for Yield Prediction. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, F.; Ata-UI-Karim, S.T.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, T.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Cao, Q. Combining Color Indices and Textures of UAV-Based Digital Imagery for Rice LAI Estimation. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zermas, D.; Morellas, V.; Mulla, D.; Papanikolopoulos, N. 3D Model Processing for High Throughput Phenotype Extraction – the Case of Corn. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2019, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comba, L.; Biglia, A.; Ricauda Aimonino, D.; Tortia, C.; Mania, E.; Guidoni, S.; Gay, P. Leaf Area Index Evaluation in Vineyards Using 3D Point Clouds from UAV Imagery. Precision Agriculture 2020, 21, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Fang, S.; Gong, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhu, R. Remote Estimation of Grain Yield Based on UAV Data in Different Rice Cultivars under Contrasting Climatic Zone. Field Crops Research 2021, 267, 108148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Gao, D.; Zhao, R.; Tang, W.; An, L.; Li, M.; Sun, H. Improving Estimation of LAI Dynamic by Fusion of Morphological and Vegetation Indices Based on UAV Imagery. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2022, 192, 106603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsi, M. , Saeki, T. Uber den Lichtfaktor in den Pflanzengesellschaften und seine Bedeutung fiir die Stoffproduktion. Jap. J. Bot., 1953, 14, 22–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa1968. 1968.
- Gourdriaan, J. The bare bones of leaf angle distribution in radiation models for canopy photosynthesis and energy exchange. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1988, 43, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anten, N.P.R. Modeling canopy photosynthesis using parameters determined from simple non-destructive measurements. Ecological Research 1997, 12, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, S. Structure of herbaceous plant stands and canopy photosynthesis models. Low Temperature Science, 2009, 67, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Ju, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; He, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Guan, D.; Yan, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Development of a Two-Leaf Light Use Efficiency Model for Improving the Calculation of Terrestrial Gross Primary Productivity. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2013, 173, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Gong, P.; Suyker, A.E.; Si, Y. Effects of the Partitioning of Diffuse and Direct Solar Radiation on Satellite-Based Modeling of Crop Gross Primary Production. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2016, 50, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Oikawa, T. A Simulation Model of the Carbon Cycle in Land Ecosystems (Sim-CYCLE): A Description Based on Dry-Matter Production Theory and Plot-Scale Validation. Ecological Modelling 2002, 151, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Werger, M.J.A. Maximizing Daily Canopy Photosynthesis with Respect to the Leaf Nitrogen Allocation Pattern in the Canopy. Oecologia 1987, 72, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messier, C.; Puttonen, P. Spatial and temporal variation in the Bight environment of developing Scots pine stands: the basis for a quick and efficient method of characterizing Bight. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 1995, 25, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyuki MURAOKA and Naoki KACI ed. The Society for the Study of Species Biology. Introduction to Plant Physiological Ecology, 2005., Bun-ichi So go Shuppan Co. Tokyo. Hiroyuki MURAOKA and Naoki, KACI (Ed.).
- Peprah, C.O.; Yamashita, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sekino, R.; Takano, K.; Katsura, K. Spatio-Temporal Estimation of Biomass Growth in Rice Using Canopy Surface Model from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Remote Sensing 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.H.; Jourdan, R.C. The interrelationship and characteristic distribution of direct, diffuse and total solar radiation. Solar Energy, 1960; 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Orgill, J.F.; Hollands, K.G.T. Correlation equation for hourly diffuse radiation on a horizontal surface. Solar energy 1977, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbs, D.G.; Klein, S.A.; Duffie, J.A. Estimation of the diffuse radiation fraction for hourly, daily and monthly-average global radiation. Solar energy 1982, 28, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacovides, C.P.; Tymvios, F.S.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Kaltsounides, N.A. The Dependence of Global and Diffuse PAR Radiation Components on Sky Conditions at Athens, Greece. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2007, 143, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmura, A.; Dutton, E.G.; Forgan, B.; Fröhlich, C.; Gilgen, H.; Hegner, H.; Heimo, A.; König-Langlo, G.; McArthur, B.; Müller, G.; et al. Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN/WCRP): New Precision Radiometry for Climate Research. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 1998, 79, 2115–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuillier, G.; Hers, M.; Simon, P.C.; Labs, D.; Mandel, H.; Gillotay, D. Observation of the Solar Spectral Irradiance from 200 Nm to 870 Nm during the ATLAS 1 and ATLAS 2 Missions by the SOLSPEC Spectrometer. Metrologia 2003, 35, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Yoshimura, M. Estimation of Global and Diff Use Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density under Various Sky Conditions Using Ground-Based Whole-Sky Images. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohsumi, A. , Hamasaki, A., Nakagawa H., Yoshida, H., Shiraiwa, T., Horie T. A model explaining genotypic and ontogenetic variation of leaf photosynthetic rate in rice (Oryza sativa) based on leaf nitrogen content and stomatal conductance. Annals of Botany. 2007, 99, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkubo, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamori, W.; Adachi, S. Rice Cultivar Takanari Has Higher Photosynthetic Performance Under Fluctuating Light Than Koshihikari, Especially Under Limited Nitrogen Supply and Elevated CO2. Frontiers in Plant Science 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, K.; ookawa, T.; Motobayashi, T.; Hirasawa, T. Quick Estimation of Varietal Differences in Light Extinction Coefficient of the Canopy through the Inclination Angle of Leaf Blade in Rice. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 79(2), 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.K.; Banerjee, S.; Mukkherijee, A.; Nath, R.; Samanta, S. Extinction coefficient and photosynthetically active radiation use efficiency of summer rice as influenced by transplanting dates. Journal of Environmentak Biology, 2018, 39, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Mao, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Duan, F.; Yan, Y. UAV-Based Multispectral Remote Sensing for Precision Agriculture: A Comparison between Different Cameras. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2018, 146, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoj, S.; Igathinathane, C.; Saliendra, N.; Hendrickson, J.; Archer, D. Color Calibration of Digital Images for Agriculture and Other Applications. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2018, 146, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Shinomiya, Y.; Yoshimura, M. Development of Methodology for Plant Phenology Monitoring By Ground-Based Observation Using Digital Camera. ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2019, IV, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ko, J.; Jeong, S.; Yeom, J. min; Kim, H. ok Monitoring Canopy Growth and Grain Yield of Paddy Rice in South Korea by Using the GRAMI Model and High Spatial Resolution Imagery. GIScience and Remote Sensing 2017, 54, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y. Satellite- and Drone-Based Remote Sensing of Crops and Soils for Smart Farming–a Review. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 2020, 66, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dela Torre, D.M.G.; Gao, J.; Macinnis-Ng, C. Remote Sensing-Based Estimation of Rice Yields Using Various Models: A Critical Review. Geo-Spatial Information Science 2021, 24, 580–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, E.; Tasumi, M.; Moriyama, M. Combination of Linear Regression Lines to Understand the Response of Sentinel-1 Dual Polarization SAR Data with Crop Phenology—Case Study in Miyazaki, Japan. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Zhao, J.; Pan, B. Spatio-Temporal Estimation of Rice Height Using Time Series Sentinel-1 Images. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Kumar, L.; Li, Z.; Feng, H.; Xu, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, J. A Review of Data Assimilation of Remote Sensing and Crop Models. European Journal of Agronomy 2018, 92, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Field A | Field B | |
|---|---|---|
| Observation year | 2020 | 2020, 2021, 2022* |
| Relative light intensity (daily) | 4 plots | 5 points |
| Light intensity (10-min) | Downward and upward PPFD (mmol/m2/s) | |
| UAV-based RS (weekly) | CHcsm, GR, NDVI | - |
| Ground-based RS (daily/weekly) | - | VC, GR, NDVI |
| Growth survey (weekly) | PL(m), AGB (g/m2), LAI (m2/m2) | PL(m), AGB (g/m2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





