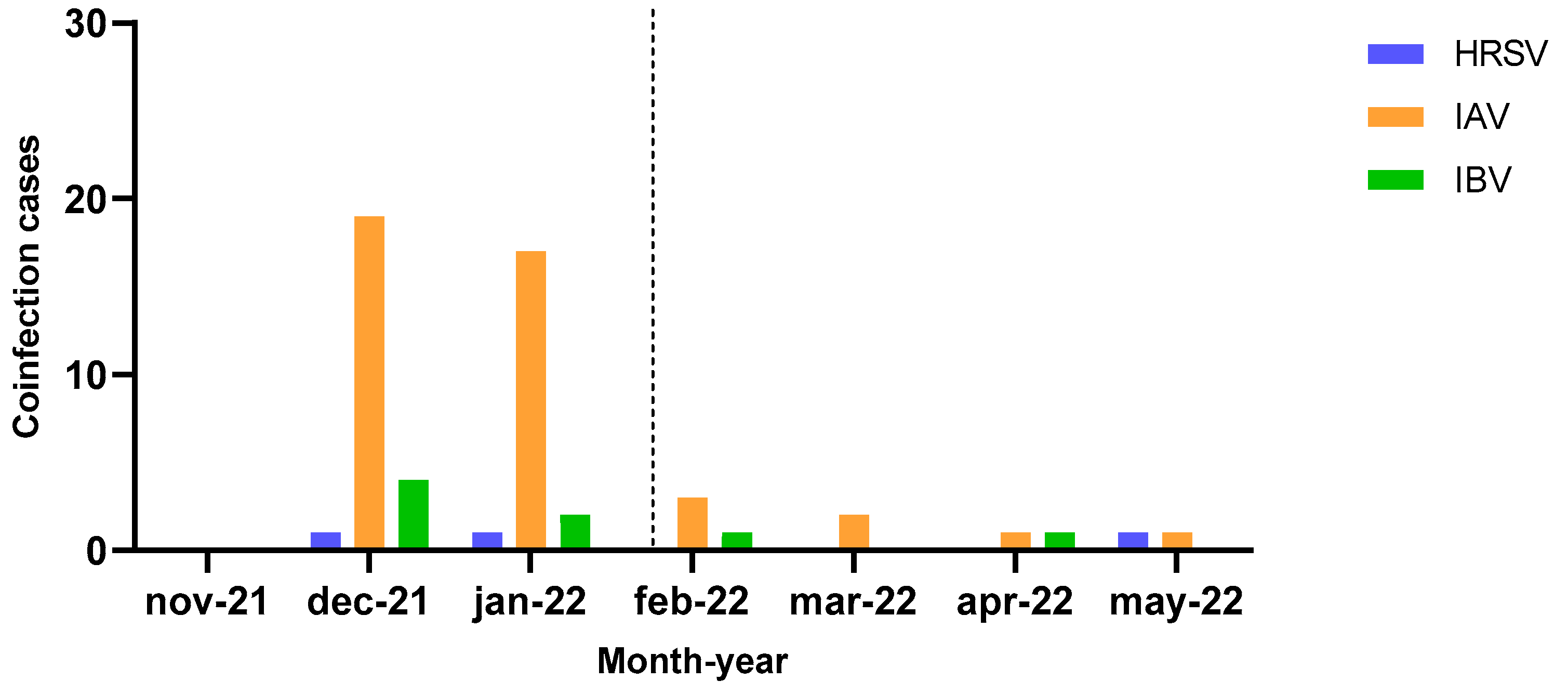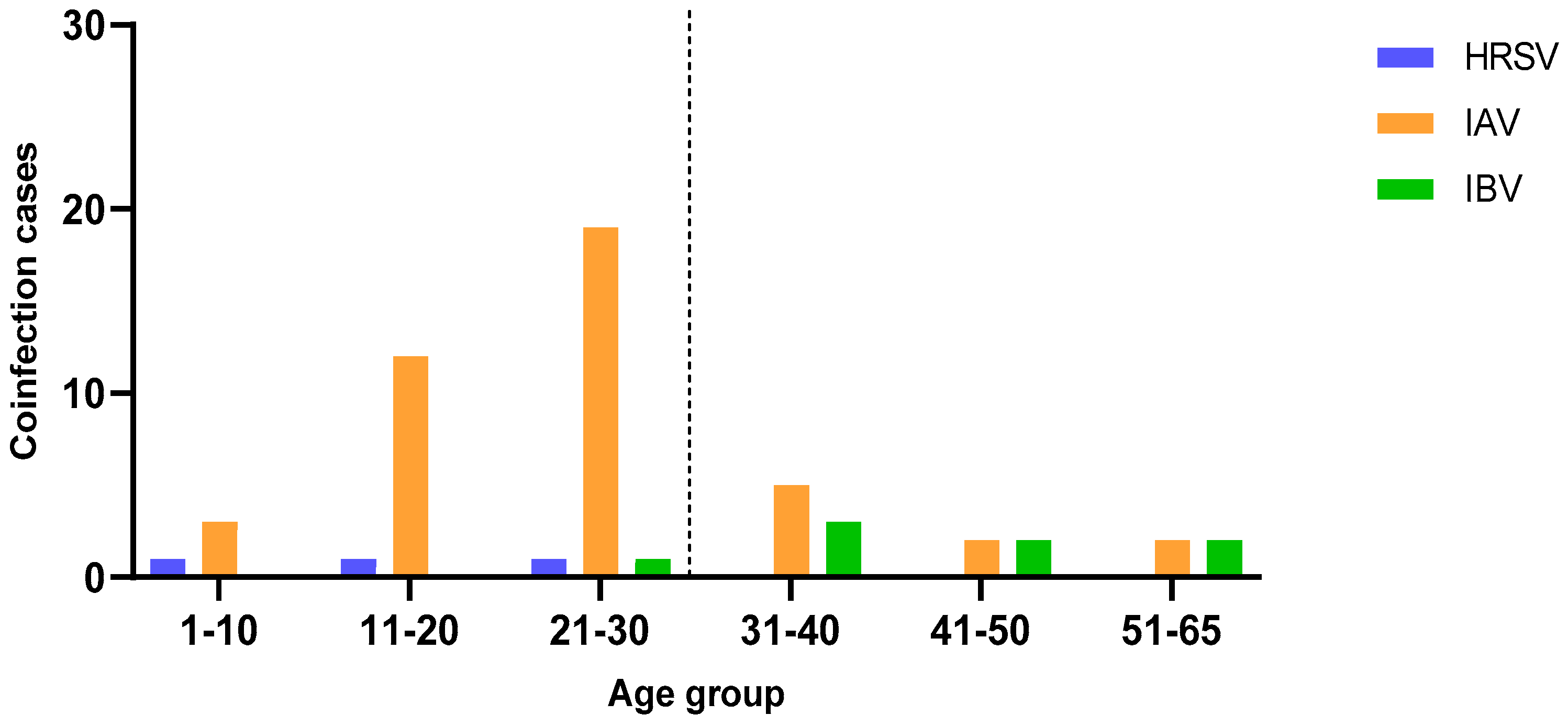1. Introduction
SARS-CoV-2 is a non-segmented, enveloped, positive-sense RNA virus that began its worldwide spread in December 2019 [
1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 pandemic on March 2020. The virus spread all year round, showing peaks in winter and when social containment measures were relaxed [
2]. By contrast, influenza is caused by a segmented, negative-sense RNA virus that gives rise to epidemics, mostly in the winter months. Of the four types of influenza viruses, influenza A (IAV) and B (IBV) are mainly responsible for seasonal influenza. Currently, A/H1N1 and A/H3N2 are the most widespread IAV subtypes circulating in the human population [
3]. Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) is a seasonal negative-sense RNA virus and prominent cause of acute lower respiratory tract infections in young children [
4].
In response to the COVID-19 health emergency and given the absence of specific pharmacological therapies or highly effective vaccines to curb the spread of SARS-CoV-2, many countries adopted non-pharmaceutical mitigation strategies. These strategies included the use of personal protective equipment, implementation of social distancing measures, temporary closure of educational institutions and airports, and mandatory reporting of cases of infection, followed by isolation of affected individuals. This approach passively influenced the seasonal transmission patterns of airborne viruses, including influenza viruses and HRSV [
5,
6].
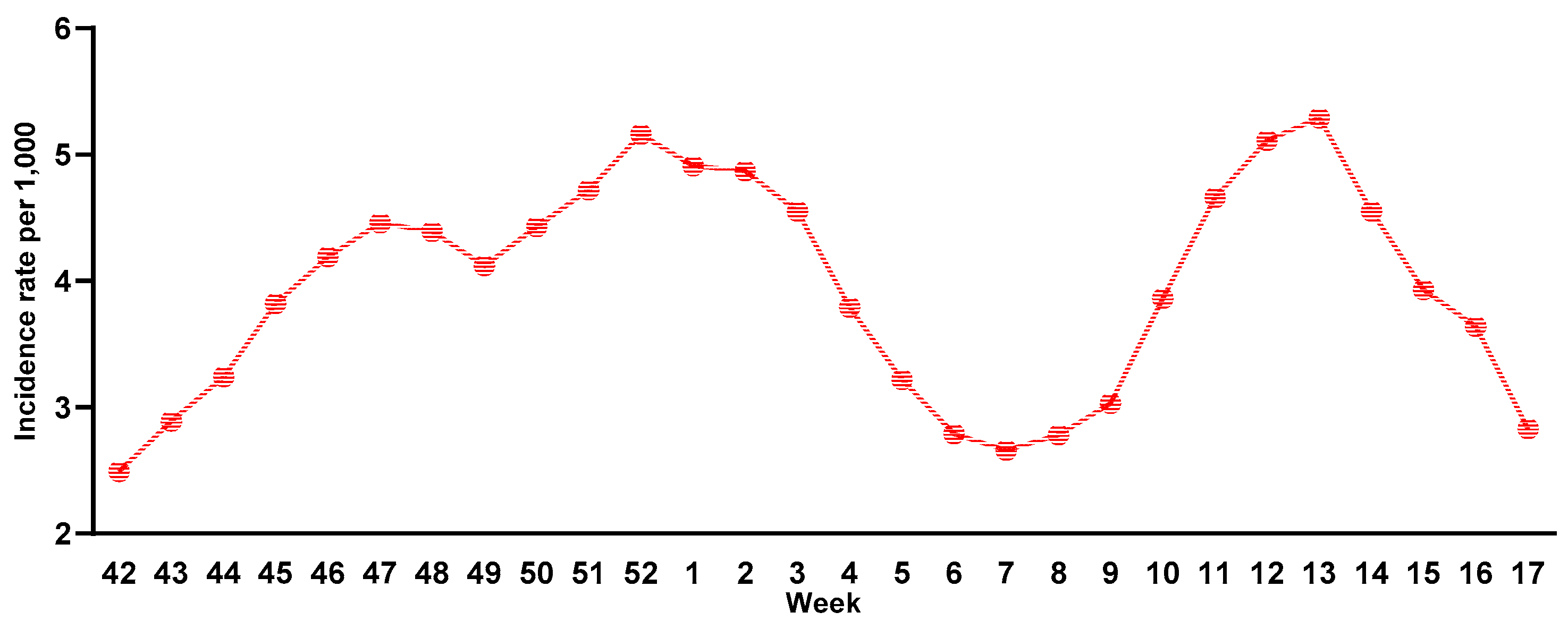
The 2020/2021 influenza season in Italy was characterized by an initial phase of co-circulation of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses, followed by a rapid decline in influenza transmission due to implementation of non-pharmaceutical measures. However, during the 2021/2022 influenza surveillance season (from week 42 of 2021 to week 17 of 2022), an increase in the incidence of influenza was recorded [
7]. The epidemiological curve of influenza cases failed to peak, but showed a bimodal trend at week 52 of 2021 and weeks 12-13 of 2022, when positive samples again rose above the epidemic threshold [
8] (
Figure 1).
An increasing number of studies show that patients affected with COVID-19 may also be coinfected with other respiratory pathogens [
9,
10,
11]. Indeed, the coexistence of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses led to cases of coinfection having more severe symptoms than infections with either virus alone [
12].
The present study, performed during the 2021/2022 influenza season, investigated the prevalence of influenza or HRSV coinfections in SARS-CoV-2-positive subjects in Tuscany (Italy), with the aim of underlining the importance of continuing epidemiological surveillance of other respiratory viruses in addition to SARS-CoV-2.
2. Materials and Methods
Study design
Oropharyngeal swabs were collected during the 2021/2022 influenza surveillance season (from week 46 of 2021 to week 17 of 2022) in Siena, Tuscany (Italy), and stored at -80°C. A total of 940 swabs were selected as having previously tested positive for SARS-CoV-2: 742 collected during the first influenza wave (week 46 of 2021 to week 4 of 2022) and 198 during the second (week 5 to week 17 of 2022). Information on the age and sex of the subject was available for 860 swabs. The median age of subjects was 30 years (range 1-65 years), 422 were male and 438 were female. Swabs were divided by age group as follows: 1-10 years (N=52), 11-20 years (N=146), 21-30 years (N=260), 31-40 years (N=147), 41-50 years (N=125), and 51-65 years (N=130). No information on COVID-19 or influenza vaccination status was available.
Laboratory analysis
Total RNA was extracted from specimens by QIAamp Viral RNA Mini kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction tests (RT-PCR) were performed for IAV, IBV and HRSV with Flu/HRSV kit (Siemens) on nasopharyngeal swabs of subjects who had already tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by COVID-19 HT Screen (Clonit, Abbiategrasso, Italy). At the same time, one-step real-time RT-PCR was performed in a final volume of 25 µL (SuperScript III Platinum One-Step qRT-PCR Kit, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to subtype for pandemic influenza virus A/H1N1 (Flu A/pH1N1) and seasonal influenza virus A/H3N2 (Flu A/H3N2) on samples positive for IAV.
Statistical analysis
The median ages of the total and influenza-positive populations was calculated. The number of SARS-CoV-2/influenza or HRSV coinfection cases by period of collection (first and second influenza waves) and age group (above or below median age, i.e. 30 years) was compared by the Yates corrected chi-square test. Statistical significance was set at p <0.05 (two-tailed test). All statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 6 software.
3. Results
A total of 54 cases (5.7%) of coinfection were detected during the study period: 51 cases (5.4%) of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses (43 for IAV and 8 for IBV) and three cases (0.3%) of SARS-CoV-2 and HRSV. Of the influenza cases, 34 cases of IAV were A/H3N2 subtype while the remaining 9 cases were not attributed to a subtype. The 8 cases of IBV were not subtyped.
As reported in
Figure 2, most coinfections were detected during the first influenza wave (36/43 cases of IAV, 6/8 cases of IBV and 2/3 cases of HRSV), albeit showing no statistically significant difference with respect to the second wave.
For 860 samples, including all those in which an influenza virus or HRSV coinfection was detected, information on the sex and age of the subjects was available.
No significant difference in the distribution of cases by sex was found, while
Figure 3 shows the distribution of coinfection cases by age.
SARS-CoV-2 coinfections with HRSV were only detected in subjects under 30 years of age (median age of positive subjects 14 years), although the difference was not significant. Coinfections with IAV were detected in all age groups, but the prevalence was higher in subjects of 30 years and under (median age of positive subjects 23 years, p=0.0009), while IBV was detected mainly in subjects of 30 years and over (median age of positive subjects 43 years, p=0.0494).
4. Discussion
In December 2019, identification of a new coronavirus in Wuhan, China, demanded a prompt response and global cooperation by health authorities [
6]. The pandemic influenced the seasonal transmission patterns of airborne viruses. SARS-CoV-2 shares transmission through direct contact and airborne contagion as well as symptoms, including fever, cough, sore throat, fatigue, nasal congestion and respiratory distress, with the influenza virus, complicating differentiation of the two infections [
5,
6]. Cases of coinfection with SARS-CoV-2 and influenza proved to have symptoms that were more severe [
12]. After 2019/2020, the incidence of influenza-like illness in Italy declined due to non-pharmaceutical actions imposed for SARS-CoV-2, whereas in the 2021/2022 season, an increase in the incidence of infections caused by influenza viruses was observed, although it did not reach the levels observed before the COVID-19 pandemic. Indeed, the season was characterized by low circulation of influenza, the first cases being reported in week 52 of 2021. Circulation increased from week 8 of 2022, reaching a maximum in week 12 of the same year, when COVID-19 restrictions were relaxed [
13].
In this study, we found a total of three cases of coinfection of SARS-CoV-2 and HRSV and 51 cases of coinfection of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza viruses: 43 cases of IAV and 8 cases of IBV. Ignoring influenza virus type, influenza coinfection cases were detected in 5.4% of the SARS-CoV-2-positive subjects tested in this study, a coinfection rate in line with those reported in other countries [
14,
15,
16].
Among IAV cases, 34 were caused by A/H3N2 subtype, in line with Italian and European data reporting it to be the predominant influenza subtype during the 2021/2022 season [
17,
18].
The majority of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza coinfections were found during the first wave of the influenza season. In a surveillance study conducted on hospitalized subjects in Tuscany during the same season, three cases of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza coinfection were found in March in the second half of the influenza season [
17]. The same study reported two cases of HRSV infection, one of which involved coinfection with SARS-CoV-2. Both cases occurred in subjects aged 30 years or under, in line with the results of our study.
Our study has some limitations: 1) information on vaccination status for COVID-19 and influenza was not available and 2) sequencing of SARS-CoV-2- and influenza-positive samples was not performed.
Given the overlapping symptoms and epidemiology of the influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2, it remains of primary importance to conduct differential diagnosis of these major airborne-transmitted viruses to avert complications related to infection. The use of multiplex RT-PCR tests, as in our study, ensures a timely diagnosis and consequently an appropriate clinical approach to each patient. Despite its limitations, our study underscores the significance of continuous monitoring of the circulation of influenza viruses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M. and G.M.; methodology, I.M.; validation, I.M.; formal analysis, S.M.; investigation, G.M., I.V., L.F., C.B.; resources, C.M.T., I.M., I.V., E.M.; data curation, S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, G.M.; writing—review and editing, S.M.; visualization, S.M.; supervision, I.M.; project administration, I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received funding from the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (PRIN 202022GZEHE_01); EU funding within the NextGenerationEU-MUR PNRR Extended Partnership initiative on Emerging Infectious Diseases (Project no. PE00000007, INF-ACT) and by the EuCARE Project funded by the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Program, Grant Agreement No. 101046016.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zhu. N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang. B.; Song. J.; Zhao. X.; Huang. B.; Shi. W.; Lu. R.; Niu. P.; Zhan. F.; Ma. X.; Wang. D.; Xu. W.; Wu. G.; Gao. G. F.; Tan, W.; & China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team (2020). A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 2020, 382(8). [CrossRef]
- Civil Protection Department. https://mappe.protezionecivile.gov.it/it/mappe-emergenze/mappe-coronavirus/situazione-desktop (accessed on 26/05/2022).
- Krammer. F.; Smith. G.J.D.; Fouchier. R.A.M.; Peiris. M.; Kedzierska. K.; Doherty. P.C.; Palese. P.; Shaw. M.L.; Treanor. J.; Webster.R.G.; García-Sastre. A.. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018, Jun 28;4(1):3.
- Halabi. K.C.; Wang. H.; Leber. A.L.; Sánchez. P.J.; Ramilo, O,; Mejias, A.. Respiratory syncytial virus and SARS-CoV-2 coinfections in children. Pediatr Pulmonol 2022 Dec;57(12):3158-3160. [CrossRef]
- Flerlage. T.; Boyd. D.F.; Meliopoulos. V.; Thomas. P.G.; Schultz-Cherry. S.. Influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2: pathogenesis and host responses in the respiratory tract. Nat Rev Microbiol 2021 Jul;19(7):425-441. [CrossRef]
- Ozaras. R.; Cirpin. R.; Duran. A.; Duman. H.; Arslan O.; Bakcan. Y.; Kaya. M.; Mutlu. H.; Isayeva. L.; Kebanlı. F.; Deger. B.A.; Bekeshev. E.; Kaya. F.; Bilir. S.. Influenza and COVID-19 coinfection: Report of six cases and review of the literature. J Med Virol 2020 Nov;92(11):2657-2665. [CrossRef]
- Istituto Superiore della Sanità, Epicentro. https://www.epicentro.iss.it/influenza/stagione-in-corso (accessed on 01/07/2022).
- Istituto Superiore della Sanità, Epicentro. https://www.epicentro.iss.it/influenza/flunews21-22#epi (accessed on 25/10/2023).
- Bai. L.; Zhao. Y.; Dong. J.; Liang. S.; Guo. M.; Liu. X.; Wang. X.; Huang. Z.; Sun. X.; Zhang. Z.; Dong. L.; Liu. Q.; Zheng. Y.; Niu. D.; Xiang. M.; Song. K.; Ye. J.; Zheng. W.; Tang. Z.; Tang. M.; Zhou. Y.; Shen. C.; Dai. M.; Zhou. L.; Chen. Y.; Yan. H.; Lan. K.; Xu. K.. Coinfection with influenza A virus enhances SARS-CoV-2 infectivity. Cell Res 2021 Apr;31(4):395-403. [CrossRef]
- Burrel. S.; Hausfater. P.; Dres. M.; Pourcher. V.; Luyt. C.E., Teyssou. E.; Soulié. C.; Calvez. V.; Marcelin. A.G.; Boutolleau. D. Co-infection of SARS-CoV-2 with other respiratory viruses and performance of lower respiratory tract samples for the diagnosis of COVID-19. Int J Infect Dis 2021 Jan;102:10-13. [CrossRef]
- Xiaojuan. Z.; Yiyue. G.; Tao. W.; Kangchen. Z.; Yin. C.; Bin. W.; Fengcai. Z.; Baoli Z.; Lunbiao. C.. Co-infection with respiratory pathogens among COVID-2019 cases. Virus Res 2020;285:198005. [CrossRef]
- Uyeki. T. M.; Hui. D. S., Zambon. M.; Wentworth. D. E.; Monto. Arnold. S.. Influenza. Lancet 2022 Aug 27;400(10353):693-706.
- Rapporto Influnet. https://www.iss.it/site/rmi/influnet/pagine/rapportoinflunet.aspx (accessed on 09/02/ 2023).
- Steponavičienė. A.; Burokienė. S.; Ivaškevičienė. I.; Stacevičienė. I.; Vaičiūnienė. D.; Jankauskienė. A.. Influenza and respiratory syncytial virus infections in pediatric patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center experience. Children (Basel) 2023 Jan 7;10(1):126. [CrossRef]
- Trifonova. I.; Christova I.; Madzharova. I.; Angelova. S.; Voleva. S.; Ralitsa. Yordanova.; Tcherveniakova. T.; Krumova. S.; Korsun. N.. Clinical significance and role of coinfections with respiratory pathogens among individual with confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome-2 infection. Front Public Health 2022 Sep 2:10:959319. [CrossRef]
- Saeedeh. E.; Mojtaba. K.; Barat. B.; Nayeb. F.D.; Zahra. N.; Tahereh. N.; Faezeh. S.. The circulation of common respiratory viruses and their co-infection with severe respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 before and after coronavirus disease of 2019 vaccination. Jundishapur J Microbiol 2022 December; 15(12):e133326. [CrossRef]
- Milano. G.; Capitani. E.; Camarri. A.; Bova. G.; Capecchi. P.L.; Lazzeri. G.; Lipari. D., Montomoli. E.; Manini. I,. Surveillance of influenza and other airborne transmission viruses during the 2021/2022 season in hospitalized subjects in Tuscany, Italy. Vaccines (Basel) 2023 Mar 31;11(4):776. [CrossRef]
-
https://www.epicentro.iss.it/influenza/flunews#vir (ultimo accesso 26/05/2022).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).