Submitted:
10 November 2023
Posted:
13 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Microbiota-Based Therapies for Breast Cancer Treatment and Prevention
2.1. Bacterial therapeutics for tumor treatment and immune modulation
2.2. Bacteriotherapy approaches
2.3. Oncolytic virotherapy and phage-based immunotherapies in cancer treatment
2.4. Probiotics and breast cancer pathogenesis
2.5. Microbial polysaccharides
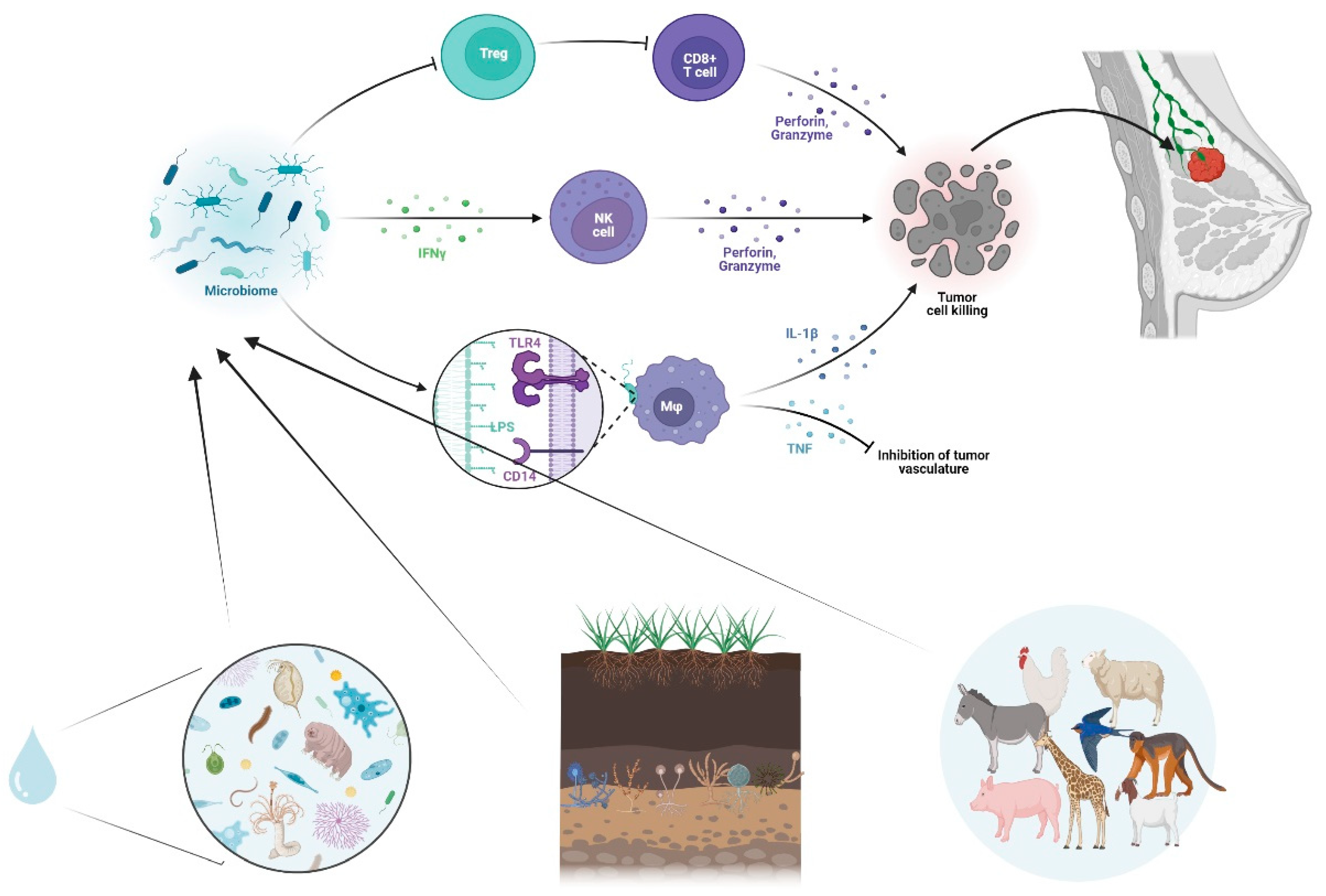
3. Cancer Immunotherapy and Microbiome Immunomodulation
4. Treatment Outcomes and Therapy Resistance
4.1. Radiotherapy
4.2. Chemotherapy
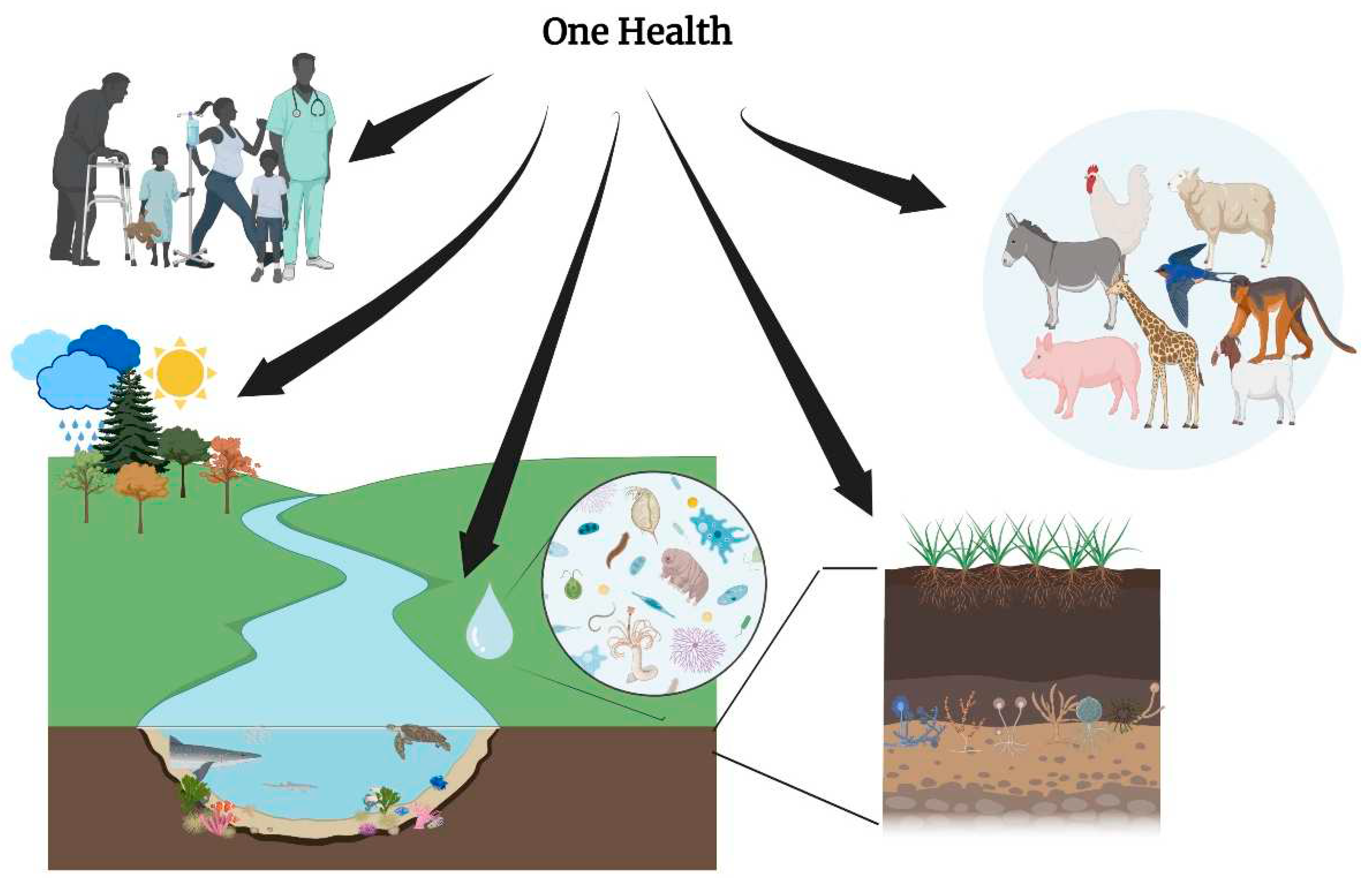
5. Integrating One Health Approach in Cancer Ecology
6. Conclusion
6.1. Integration of microbial therapy within the one health approach
6.2. Regulatory considerations and ethical implications
6.3. Future directions
6.4. Promising avenues for further research and development
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Artusa, V. , Calabrone, L., Mortara, L., Peri, F., Bruno, A.: Microbiota-Derived Natural Products Targeting Cancer Stem Cells: Inside the Gut Pharma Factory. IJMS. 24, 4997 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Xuan, C. , Shamonki, J.M., Chung, A., DiNome, M.L., Chung, M., Sieling, P.A., Lee, D.J.: Microbial Dysbiosis Is Associated with Human Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE. 9, e83744 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Nejman, D. , Livyatan, I., Fuks, G., Gavert, N., Zwang, Y., Geller, L.T., Rotter-Maskowitz, A., Weiser, R., Mallel, G., Gigi, E., Meltser, A., Douglas, G.M., Kamer, I., Gopalakrishnan, V., Dadosh, T., Levin-Zaidman, S., Avnet, S., Atlan, T., Cooper, Z.A., Arora, R., Cogdill, A.P., Khan, M.A.W., Ologun, G., Bussi, Y., Weinberger, A., Lotan-Pompan, M., Golani, O., Perry, G., Rokah, M., Bahar-Shany, K., Rozeman, E.A., Blank, C.U., Ronai, A., Shaoul, R., Amit, A., Dorfman, T., Kremer, R., Cohen, Z.R., Harnof, S., Siegal, T., Yehuda-Shnaidman, E., Gal-Yam, E.N., Shapira, H., Baldini, N., Langille, M.G.I., Ben-Nun, A., Kaufman, B., Nissan, A., Golan, T., Dadiani, M., Levanon, K., Bar, J., Yust-Katz, S., Barshack, I., Peeper, D.S., Raz, D.J., Segal, E., Wargo, J.A., Sandbank, J., Shental, N., Straussman, R.: The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type–specific intracellular bacteria. Science. 368, 973–980 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Dohlman, A.B. , Klug, J., Mesko, M., Gao, I.H., Lipkin, S.M., Shen, X., Iliev, I.D.: A pan-cancer mycobiome analysis reveals fungal involvement in gastrointestinal and lung tumors. Cell. 185, 3807-3822.e12 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Fu, A. , Yao, B., Dong, T., Chen, Y., Yao, J., Liu, Y., Li, H., Bai, H., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., Guo, Y., Li, N., Cai, S.: Tumor-resident intracellular microbiota promotes metastatic colonization in breast cancer. Cell. 185, 1356-1372.e26 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Lakritz, J.R. , Poutahidis, T., Mirabal, S., Varian, B.J., Levkovich, T., Ibrahim, Y.M., Ward, J.M., Teng, E.C., Fisher, B., Parry, N., Lesage, S., Alberg, N., Gourishetti, S., Fox, J.G., Ge, Z., Erdman, S.E.: Gut bacteria require neutrophils to promote mammary tumorigenesis. Oncotarget. 6, 9387–9396 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Liu, M. , Jia, S., Dong, T., Zhao, F., Xu, T., Yang, Q., Gong, J., Fang, M.: Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis of MCF-7 Cells Exposed to 23 Chemicals at Human-Relevant Levels: Estimation of Individual Chemical Contribution to Effects. Environ Health Perspect. 128, 127008 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-Y. , Liu, M.-T., Tao, T., Zhu, X., Fei, F.-Q.: The role of gut microbiota in tumorigenesis and treatment. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 138, 111444 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Roy, S. , Trinchieri, G.: Microbiota: a key orchestrator of cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 17, 271–285 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, A. , Sangwan, N., Jia, M., Liu, C.-C., Keslar, K.S., Downs-Kelly, E., Fairchild, R.L., Al-Hilli, Z., Grobmyer, S.R., Eng, C.: Human breast microbiome correlates with prognostic features and immunological signatures in breast cancer. Genome Med. 13, 60 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Maroof, H. , Hassan, Z.M., Mobarez, A.M., Mohamadabadi, M.A.: Lactobacillus acidophilus Could Modulate the Immune Response Against Breast Cancer in Murine Model. J Clin Immunol. 32, 1353–1359 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G. , Le Noci, V., Ottaviano, E., De Cecco, L., Camisaschi, C., Guglielmetti, S., Di Modica, M., Gargari, G., Bianchi, F., Indino, S., Sartori, P., Borghi, E., Sommariva, M., Tagliabue, E., Triulzi, T., Sfondrini, L.: Reduction of Staphylococcus epidermidis in the mammary tumor microbiota induces antitumor immunity and decreases breast cancer aggressiveness. Cancer Letters. 555, 216041 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z. , Sanchez, A., Shi, Z., Zhang, T., Liu, M., Zhang, D.: Activation of Toll-like Receptor 5 on Breast Cancer Cells by Flagellin Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth. Cancer Research. 71, 2466–2475 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J. , Liao, M., Yao, Z., Liang, W., Li, Q., Liu, J., Yang, H., Ji, Y., Wei, W., Tan, A., Liang, S., Chen, Y., Lin, H., Zhu, X., Huang, S., Tian, J., Tang, R., Wang, Q., Mo, Z.: Breast cancer in postmenopausal women is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Microbiome. 6, 136 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Lakey, J.H., Slatin, S.L.: Pore-Forming Colicins and Their Relatives. In: Van Der Goot, F.G. (ed.) Pore-Forming Toxins. pp. 131–161. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg (2001). 2001. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S. , Kaur, S.: Bacteriocins as Potential Anticancer Agents. Front. Pharmacol. 6, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Baindara, P. , Gautam, A., Raghava, G.P.S., Korpole, S.: Anticancer properties of a defensin like class IId bacteriocin Laterosporulin10. Sci Rep. 7, 46541 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, A. , Hamaji, Y., Sasaki, T., Taniguchi, S., Fujimori, M.: Exogeneous Cytosine Deaminase Gene Expression in Bifidobacterium breve I-53-8w for Tumor-Targeting Enzyme/Prodrug Therapy. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 71, 2921–2926 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.O. , De Carvalho, T.C., Parshikov, I.A., Dos Santos, R.A., Emery, F.S., Furtado, N.A.J.C.: Cytotoxicity of lapachol metabolites produced by probiotics. Lett Appl Microbiol. 59, 108–114 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Karami, P. , Goli, H.R., Abediankenari, S., Chandani, S.R., Jafari, N., Ghasemi, M., Ahanjan, M.: Anti-tumor effects of Bacteroides fragilis and Bifidobacterium bifidum culture supernatants on mouse breast cancer. Gene Reports. 33, 101815 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G. , Le Noci, V., Di Modica, M., Montanari, E., Triulzi, T., Pupa, S.M., Tagliabue, E., Sommariva, M., Sfondrini, L.: The Emerging Role of the Microbiota in Breast Cancer Progression. Cells. 12, 1945 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R. , Lang, T., Yan, W., Zhu, X., Huang, X., Yin, Q., Li, Y.: Gut Microbiota: Influence on Carcinogenesis and Modulation Strategies by Drug Delivery Systems to Improve Cancer Therapy. Advanced Science. 8, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Mendes, I. , Vale, N.: How Can the Microbiome Induce Carcinogenesis and Modulate Drug Resistance in Cancer Therapy? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 24, 11855 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Trivanović, D. , Pavelić, K., Peršurić, Ž.: Fighting Cancer with Bacteria and Their Toxins. Int J Mol Sci. 22, 12980 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Khoshnood, S. , Fathizadeh, H., Neamati, F., Negahdari, B., Baindara, P., Abdullah, M.A., Haddadi, M.H.: Bacteria-derived chimeric toxins as potential anticancer agents. Frontiers in Oncology. 2022; 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, K. , Chakraborty, S., Chen, R., Willcox, M.D., Black, D.S., Walsh, W.R., Kumar, N.: A New Era of Antibiotics: The Clinical Potential of Antimicrobial Peptides. Int J Mol Sci. 21, 7047 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Patyar, S. , Joshi, R., Byrav, D.P., Prakash, A., Medhi, B., Das, B.: Bacteria in cancer therapy: a novel experimental strategy. J Biomed Sci. 17, 21 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Nandi, D. , Parida, S., Sharma, D.: The gut microbiota in breast cancer development and treatment: The good, the bad, and the useful! Gut Microbes. 15, 2221452. [CrossRef]
- Allemailem, K.S. : Innovative Approaches of Engineering Tumor-Targeting Bacteria with Different Therapeutic Payloads to Fight Cancer: A Smart Strategy of Disease Management. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 16, 8159 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. , Wang, C., Shao, Y., Wang, Y., Xing, D., Geng, Z.: Recent advances in bacteria-mediated cancer therapy. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 2022; 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, M.T.-Q. , Qin, Y., You, S.-H., Min, J.-J.: Bacteria-cancer interactions: bacteria-based cancer therapy. Exp Mol Med. 51, 152 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Wei, X. , Du, M., Chen, Z., Yuan, Z.: Recent Advances in Bacteria-Based Cancer Treatment. Cancers (Basel). 14, 4945 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Freedman, J.C. , Shrestha, A., McClane, B.A.: Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin: Action, Genetics, and Translational Applications. Toxins (Basel). 8, 73 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, F. , Bonfim, M., da Silva Vasconcelos Sousa, P., Mengel, J., Ribeiro Castello-Branco, L.R., Pinho, R.T.: Bacillus Calmette–Guérin Immunotherapy for Cancer. Vaccines (Basel). 9, 439 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Nallar, S.C. , Xu, D.-Q., Kalvakolanu, D.V.: Bacteria and genetically modified bacteria as cancer therapeutics: Current advances and challenges. Cytokine. 89, 160–172 (2017). [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, E.F. : The Toxins of William B. Coley and the Treatment of Bone and Soft-Tissue Sarcomas. Iowa Orthop J. 2006; 26, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, N.S. : Engineering the perfect (bacterial) cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 10, 785–794 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M. : Helicobacter pylori CagA and gastric cancer: a paradigm for hit-and-run carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe. 15, 306–316 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Felgner, S. , Kocijancic, D., Frahm, M., Heise, U., Rohde, M., Zimmermann, K., Falk, C., Erhardt, M., Weiss, S.: Engineered Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium overcomes limitations of anti-bacterial immunity in bacteria-mediated tumor therapy. Oncoimmunology. 7, e1382791 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Field, D. , Cotter, P.D., Ross, R.P., Hill, C.: Bioengineering of the model lantibiotic nisin. Bioengineered. 6, 187–192 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.J. , Zhang, L., Janku, F., Collins, A., Bai, R.-Y., Staedtke, V., Rusk, A.W., Tung, D., Miller, M., Roix, J., Khanna, K.V., Murthy, R., Benjamin, R.S., Helgason, T., Szvalb, A.D., Bird, J.E., Roy-Chowdhuri, S., Zhang, H.H., Qiao, Y., Karim, B., McDaniel, J., Elpiner, A., Sahora, A., Lachowicz, J., Phillips, B., Turner, A., Klein, M.K., Post, G., Diaz, L.A., Riggins, G.J., Papadopoulos, N., Kinzler, K.W., Vogelstein, B., Bettegowda, C., Huso, D.L., Varterasian, M., Saha, S., Zhou, S.: Intratumoral injection of Clostridium novyi-NT spores induces antitumor responses. Sci Transl Med. 6, 249ra111 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N. , Gnjatic, S., Sawhney, N.B.: TLR AGONISTS: Are They Good Adjuvants? Cancer journal (Sudbury, Mass.). 16, 382 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L. , Kohlhapp, F.J., Zloza, A.: Erratum: Oncolytic viruses: a new class of immunotherapy drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15, 660–660 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. , Jiang, H., Cheng, L., Liu, R.: The oncolytic herpes simplex virus vector, G47Δ, effectively targets tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Oncology Reports. 35, 1741–1749 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J. , Han, S.-X., Bai, E., Zhou, X., Li, M., Jing, G.-H., Zhao, J., Yang, A.-G., Zhu, Q.: Dose-dependent effect of tamoxifen in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells via stimulation by the ERK1/2 and AKT signaling pathways. Oncology Reports. 29, 1563–1569 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.-G. , Li, J.-J., Hu, P., Lei, L., Wang, J.-N., Liu, R.-B.: An oncolytic herpes simplex virus vector, G47Δ, synergizes with paclitaxel in the treatment of breast cancer. Oncology Reports. 29, 2355–2361 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Soliman, H. , Hogue, D., Han, H., Mooney, B., Costa, R., Lee, M.C., Niell, B., Williams, A., Chau, A., Falcon, S., Soyano, A., Armaghani, A., Khakpour, N., Weinfurtner, R.J., Hoover, S., Kiluk, J., Laronga, C., Rosa, M., Khong, H., Czerniecki, B.: Oncolytic T-VEC virotherapy plus neoadjuvant chemotherapy in nonmetastatic triple-negative breast cancer: a phase 2 trial. Nat Med. 29, 450–457 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P. , Cortes, J., Dent, R., Pusztai, L., McArthur, H., Kümmel, S., Bergh, J., Denkert, C., Park, Y.H., Hui, R., Harbeck, N., Takahashi, M., Untch, M., Fasching, P.A., Cardoso, F., Andersen, J., Patt, D., Danso, M., Ferreira, M., Mouret-Reynier, M.-A., Im, S.-A., Ahn, J.-H., Gion, M., Baron-Hay, S., Boileau, J.-F., Ding, Y., Tryfonidis, K., Aktan, G., Karantza, V., O’Shaughnessy, J.: Event-free Survival with Pembrolizumab in Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 386, 556–567 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Catala, A. , Dzieciatkowska, M., Wang, G., Gutierrez-Hartmann, A., Simberg, D., Hansen, K.C., D’Alessandro, A., Catalano, C.E.: Targeted Intracellular Delivery of Trastuzumab Using Designer Phage Lambda Nanoparticles Alters Cellular Programs in Human Breast Cancer Cells. ACS Nano. 15, 11789–11805 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Dong, X. , Pan, P., Ye, J.-J., Zhang, Q.-L., Zhang, X.-Z.: Hybrid M13 bacteriophage-based vaccine platform for personalized cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials. 289, 121763 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. , Ganguly, S., Tollefsbol, T.O.: Modulating Microbiota as a New Strategy for Breast Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Microorganisms. 10, 1727 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, M.R. , Stephen, T.L., Svoronos, N., Allegrezza, M.J., Tesone, A.J., Perales-Puchalt, A., Brencicova, E., Escovar-Fadul, X., Nguyen, J.M., Cadungog, M.G., Zhang, R., Salatino, M., Tchou, J., Rabinovich, G.A., Conejo-Garcia, J.R.: Microbially Driven TLR5-Dependent Signaling Governs Distal Malignant Progression through Tumor-Promoting Inflammation. Cancer Cell. 27, 27–40 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F. , Jobin, C.: The microbiome and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13, 800–812 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Garrett, W.S. : Cancer and the microbiota. Science. 348, 80–86 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Eslami-S, Z. , Majidzadeh-A, K., Halvaei, S., Babapirali, F., Esmaeili, R.: Microbiome and Breast Cancer: New Role for an Ancient Population. Front. Oncol. 10, 120 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.H. , Michel, C., Bard, J.-M., Dravet, F., Nazih, H., Bobin-Dubigeon, C.: Intestinal Proportion of Blautia sp. is Associated with Clinical Stage and Histoprognostic Grade in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Nutrition and Cancer. 69, 267–275 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.S. , Saeed, A., Baig, M., Asif, N., Masood, N., Yasmin, A.: Anticarcinogenecity of microbiota and probiotics in breast cancer. International Journal of Food Properties. 21, 655–666 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M. , Mahdavi, M., Kheradmand, E., Shahverdi, A.: The Preventive Oral Supplementation of a Selenium Nanoparticle-enriched Probiotic Increases the Immune Response and Lifespan of 4T1 Breast Cancer Bearing Mice. Arzneimittelforschung. 62, 525–531 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Aragón, F. , Carino, S., Perdigón, G., De Moreno De LeBlanc, A.: Inhibition of Growth and Metastasis of Breast Cancer in Mice by Milk Fermented With Lactobacillus casei CRL 431. Journal of Immunotherapy. 38, 185–196 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Chitapanarux, I. , Chitapanarux, T., Traisathit, P., Kudumpee, S., Tharavichitkul, E., Lorvidhaya, V.: Randomized controlled trial of live lactobacillus acidophilus plus bifidobacterium bifidum in prophylaxis of diarrhea during radiotherapy in cervical cancer patients. Radiat Oncol. 5, 31 (2010). [CrossRef]
- Mego, M. , Chovanec, J., Vochyanova-Andrezalova, I., Konkolovsky, P., Mikulova, M., Reckova, M., Miskovska, V., Bystricky, B., Beniak, J., Medvecova, L., Lagin, A., Svetlovska, D., Spanik, S., Zajac, V., Mardiak, J., Drgona, L.: Prevention of irinotecan induced diarrhea by probiotics: A randomized double blind, placebo controlled pilot study. Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 23, 356–362 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, A.A. , Lyra, A., Ouwehand, A.C., Rolny, P., Lindegren, H., Cedgård, L., Wettergren, Y.: Intestinal microbiota is altered in patients with colon cancer and modified by probiotic intervention. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 4, e000145 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Theodoropoulos, G.E. , Memos, N.A., Peitsidou, K., Karantanos, T., Spyropoulos, B.G., Zografos, G.: Synbiotics and gastrointestinal function-related quality of life after elective colorectal cancer resection. Ann Gastroenterol. 2016; 29, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Demers, M. , Dagnault, A., Desjardins, J.: A randomized double-blind controlled trial: Impact of probiotics on diarrhea in patients treated with pelvic radiation. Clinical Nutrition. 33, 761–767 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Österlund, P. , Ruotsalainen, T., Korpela, R., Saxelin, M., Ollus, A., Valta, P., Kouri, M., Elomaa, I., Joensuu, H.: Lactobacillus supplementation for diarrhoea related to chemotherapy of colorectal cancer: a randomised study. Br J Cancer. 97, 1028–1034 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Dizman, N. , Meza, L., Bergerot, P., Alcantara, M., Dorff, T., Lyou, Y., Frankel, P., Cui, Y., Mira, V., Llamas, M., Hsu, J., Zengin, Z., Salgia, N., Salgia, S., Malhotra, J., Chawla, N., Chehrazi-Raffle, A., Muddasani, R., Gillece, J., Reining, L., Trent, J., Takahashi, M., Oka, K., Higashi, S., Kortylewski, M., Highlander, S.K., Pal, S.K.: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab with or without live bacterial supplementation in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomized phase 1 trial. Nat Med. 28, 704–712 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Toi, M. , Hirota, S., Tomotaki, A., Sato, N., Hozumi, Y., Anan, K., Nagashima, T., Tokuda, Y., Masuda, N., Ohsumi, S., Ohno, S., Takahashi, M., Hayashi, H., Yamamoto, S., Ohashi, Y.: Probiotic Beverage with Soy Isoflavone Consumption for Breast Cancer Prevention: A Case-control Study. CNF. 9, 194–200 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Juan, Z. , Chen, J., Ding, B., Yongping, L., Liu, K., Wang, L., Le, Y., Liao, Q., Shi, J., Huang, J., Wu, Y., Ma, D., Ouyang, W., Tong, J.: Probiotic supplement attenuates chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment in patients with breast cancer: a randomised, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial. European Journal of Cancer. 161, 10–22 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, Y. , Basi, A., Fernandez, M.L., Foudazi, H., Bagherzadeh, R., Shidfar, F.: The effects of synbiotics supplementation on reducing chemotherapy-induced side effects in women with breast cancer: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. BMC Complement Med Ther. 23, 339 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M. , Abirami, R.G.: Microbial Polysaccharides - Chemistry and Applications. Journal of Biologically Active Products from Nature. 9, 73–78 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S. , Khalil, A.A., Shaukat, F., Song, Y.: Sources, Extraction and Biomedical Properties of Polysaccharides. Foods. 8, 304 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Lemieszek, M. , Rzeski, W.: Anticancer properties of polysaccharides isolated from fungi of the Basidiomycetes class. wo. 4, 285–289 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Chow, L.W.C. , Lo, C.S.Y., Loo, W.T.Y., Hu, X., Sham, J.S.T.: Polysaccharide Peptide Mediates Apoptosis by Up-regulating p21 Gene and Down-regulating Cyclin D 1 Gene. Am. J. Chin. Med. 31, 1–9 (2003). [CrossRef]
- L.Y. Eliza, W., K. Fai, C., P. Chung, L.: Efficacy of Yun Zhi (Coriolus versicolor) on Survival in Cancer Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. IAD. 6, 78–87 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, E.A.I.F. , Fortes, Z.B., Da Cunha, M.A.A., Sarilmiser, H.K., Barbosa Dekker, A.M., Öner, E.T., Dekker, R.F.H., Khaper, N.: Levan promotes antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in MCF-7 breast cancer cells mediated by oxidative stress. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 102, 565–570 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.N. , Ferronato, M.J., Fermento, M.E., Gandini, N.A., Romero, A.L., Guevara, J.A., Facchinetti, M.M., Curino, A.C.: Antitumoral and antimetastatic activity of Maitake D-Fraction in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 9, 23396–23412 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Kodama, N. , Komuta, K., Nanba, H.: Effect of Maitake ( Grifola frondosa ) D-Fraction on the Activation of NK Cells in Cancer Patients. Journal of Medicinal Food. 6, 371–377 (2003). [CrossRef]
- Alpuim Costa, D. , Nobre, J.G., Batista, M.V., Ribeiro, C., Calle, C., Cortes, A., Marhold, M., Negreiros, I., Borralho, P., Brito, M., Cortes, J., Braga, S.A., Costa, L.: Human Microbiota and Breast Cancer—Is There Any Relevant Link?—A Literature Review and New Horizons Toward Personalised Medicine. Front. Microbiol. 12, 584332 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Laborda-Illanes, A. , Sanchez-Alcoholado, L., Dominguez-Recio, M.E., Jimenez-Rodriguez, B., Lavado, R., Comino-Méndez, I., Alba, E., Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.: Breast and Gut Microbiota Action Mechanisms in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis and Treatment. Cancers. 12, 2465 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. , Bai, J., Ma, C., Wei, J., Du, X.: The Role of Gut Microbiota in Tumor Immunotherapy. Journal of Immunology Research. 2021, 1–12 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Haque, S. , Raina, R., Afroze, N., Hussain, A., Alsulimani, A., Singh, V., Mishra, B.N., Kaul, S., Kharwar, R.N.: Microbial dysbiosis and epigenetics modulation in cancer development – A chemopreventive approach. Seminars in Cancer Biology. 86, 666–681 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Nanda, R. , Chow, L.Q.M., Dees, E.C., Berger, R., Gupta, S., Geva, R., Pusztai, L., Pathiraja, K., Aktan, G., Cheng, J.D., Karantza, V., Buisseret, L.: Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Phase Ib KEYNOTE-012 Study. JCO. 34, 2460–2467 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Adams, S. , Schmid, P., Rugo, H.S., Winer, E.P., Loirat, D., Awada, A., Cescon, D.W., Iwata, H., Campone, M., Nanda, R., Hui, R., Curigliano, G., Toppmeyer, D., O’Shaughnessy, J., Loi, S., Paluch-Shimon, S., Tan, A.R., Card, D., Zhao, J., Karantza, V., Cortés, J.: Pembrolizumab monotherapy for previously treated metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: cohort A of the phase II KEYNOTE-086 study. Annals of Oncology. 30, 397–404 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Dirix, L.Y. , Takacs, I., Jerusalem, G., Nikolinakos, P., Arkenau, H.-T., Forero-Torres, A., Boccia, R., Lippman, M.E., Somer, R., Smakal, M., Emens, L.A., Hrinczenko, B., Edenfield, W., Gurtler, J., Von Heydebreck, A., Grote, H.J., Chin, K., Hamilton, E.P.: Avelumab, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer: a phase 1b JAVELIN Solid Tumor study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 167, 671–686 (2018). [CrossRef]
- AACR Annual Meeting 2017 Online Proceedings and Itinerary Planner | Presentation, https://www.abstractsonline.com/pp8/#!/4292/presentation/1296.
- Emens, L.A. , Adams, S., Loi, S., Schneeweiss, A., Rugo, H.S., Winer, E.P., Barrios, C.H., Dieras, V., de la Haba-Rodriguez, J., Gianni, L., Chui, S.Y., Schmid, P.: IMpassion130: a Phase III randomized trial of atezolizumab with nab-paclitaxel for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC). JCO. 34, TPS1104–TPS1104 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Tolaney, S.M. , Kalinsky, K., Kaklamani, V.G., D’Adamo, D.R., Aktan, G., Tsai, M.L., O’Regan, R., Kaufman, P.A., Wilks, S., Andreopoulou, E., Patt, D.A., Yuan, Y., Wang, G., Xing, D., Kleynerman, E., Karantza, V., Diab, S.: A phase Ib/II study of eribulin (ERI) plus pembrolizumab (PEMBRO) in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (mTNBC) (ENHANCE 1). JCO. 38, 1015–1015 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J. , Cescon, D.W., Rugo, H.S., Nowecki, Z., Im, S.-A., Yusof, M.M., Gallardo, C., Lipatov, O., Barrios, C.H., Holgado, E., Iwata, H., Masuda, N., Otero, M.T., Gokmen, E., Loi, S., Guo, Z., Zhao, J., Aktan, G., Karantza, V., Schmid, P., Luis, F., Gonzalo, G.A., Diego, K., Ruben, K., Matias, M., Mirta, V., Sally, B.-H., Stephen, B., Philip, C., Sherene, L., Dhanusha, S., Andrea, G., Donatienne, T., Carlos, B., Leandro, B., Fabiano, C., Ruffo, D.F.J., Roberto, H., Domicio Carvalho, L., Fernando Cezar Toniazzi, L., Roberto Odebrecht, R., Antonio Orlando, S.N., Felipe, S., David, C., Danielle, C., Cristiano, F., Xinni, S., Joanne, Y., Alejandro, A., Carlos, G., Claudio, S., Cesar, S., Eduardo, Y., Alvaro, G.D., Jesus, S., Petra, H., Zdenek, K., Bohuslav, M., Katarina, P., Jana, P., Vesna, G., Erik, J., Jeanette, J., Soren, L., Tamas, L., Herve, B., Isabelle, D., Anthony, G., Anne-Claire, H.-B., Luis, T., Jens-Uwe, B., Peter, F., Dirk, F., Nadia, H., Jens, H., Anna, K.F.D.S., Christian, K., Sibylle, L., Diana, L., Tjoung-Won, P.-S., Raquel Von, S., Pauline, W., Louis, C., Ava, K., Kai Cheong Roger, N., Peter, A., Tibor, C., Zsuzsanna, K., Laszlo, L., Karoly, M., Gabor, R., John, C., Catherine, K., Seamus, O., Saverio, C., Antonietta, Da., Enrico, R., Tomoyuki, A., Takaaki, F., Kenichi, I., Takashi, I., Yoshinori, I., Tsutomu, I., Hiroji, I., Yoshimasa, K., Koji, M., Yasuo, M., Hirofumi, M., Seigo, N., Naoki, N., Shoichiro, O., Akihiko, O., Yasuaki, S., Eiji, S., Masato, T., Yuko, T., Kenji, T., Koichiro, T., Junichiro, W., Naohito, Y., Yutaka, Y., Teruo, Y., Anita, B., Mastura, M.Y., Angel, G.V., Alejandro, J.R., Jorge, M.R., Flavia, M.-V., Jessica, R.C., Karin, B., Vivianne, T.-H., David, P., Ewa, C., Ewa, N.-Z., Zbigniew, N., Barbara, R., Joanna, S., Cezary, S., Rafal, T., Bogdan, Z., Alexander, A., Natalia, F., Oleg, L., Andrey, M., Vladimir, M., Guzel, M., Jin Hee, A., Seock-Ah, I., Keun Seok, L., Kwong Hwa, P., Yeon Hee, P., Begona, B.D.L.H., Javier, C., Josefina, C.J., Luis, D.L.C.M., Jose, G.S., Maria, G., Esther, H., Esther, Z.A., Chien-Ting, L., Mei-Ching, L., Chiun-Sheng, H., Chao-Jung, T., Ling-Ming, T., Cagatay, A., Gul, B., Irfan, C., Erhan, G., Seyda, G., Nil, M.M., Mustafa, O., Ozgur, O., Sinan, Y., Steve, C., Janine, G., Iain, M., Peter, S., Nicholas, T., Mark, T., Christopher, T., Duncan, W., Hryhoriy, A., Oleksandr, B., Igor, B., Oleksii, K., Olena, K., Hanna, K., Anna, K., Iurii, L., Alla, N., Natalya, O., Olga, P., Andrii, R., Sergii, S., Yaroslav, S., Dmytro, T., Grygorii, U., Ihor, V., Sibel, B., Madhu, C., Michael, C., Patrick, C., Scott, C., Jennifer, D., Keerthi, G., Jeffrey, H., Kent, H., William, I., Randa, L., Janice, L., Raul, M., Susan, M., Rita, N., Ira, O., Coral, O., Timothy, P., Amit, P., Brian, P., Hope, R., Irina, R., Michael, S., Robert, S., Michael, S., Laura, S., Bradley, S., Michaela, T., Frances, V.-A.: Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (KEYNOTE-355): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial. The Lancet. 396, 1817–1828 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Aarnoutse, R. , Ziemons, J., Hillege, L.E., De Vos-Geelen, J., De Boer, M., Bisschop, S.M.P., Vriens, B.E.P.J., Vincent, J., Van De Wouw, A.J., Le, G.N., Venema, K., Rensen, S.S., Penders, J., Smidt, M.L.: Changes in intestinal microbiota in postmenopausal oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients treated with (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy. npj Breast Cancer. 8, 89 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Bilenduke, E. , Sterrett, J.D., Ranby, K.W., Borges, V.F., Grigsby, J., Carr, A.L., Kilbourn, K., Lowry, C.A.: Impacts of breast cancer and chemotherapy on gut microbiome, cognitive functioning, and mood relative to healthy controls. Sci Rep. 12, 19547 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Horigome, A. , Okubo, R., Hamazaki, K., Kinoshita, T., Katsumata, N., Uezono, Y., Xiao, J.Z., Matsuoka, Y.J.: Association between blood omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and the gut microbiota among breast cancer survivors. Beneficial Microbes. 10, 751–758 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Terrisse, S. , Derosa, L., Iebba, V., Ghiringhelli, F., Vaz-Luis, I., Kroemer, G., Fidelle, M., Christodoulidis, S., Segata, N., Thomas, A.M., Martin, A.-L., Sirven, A., Everhard, S., Aprahamian, F., Nirmalathasan, N., Aarnoutse, R., Smidt, M., Ziemons, J., Caldas, C., Loibl, S., Denkert, C., Durand, S., Iglesias, C., Pietrantonio, F., Routy, B., André, F., Pasolli, E., Delaloge, S., Zitvogel, L.: Intestinal microbiota influences clinical outcome and side effects of early breast cancer treatment. Cell Death Differ. 28, 2778–2796 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Okubo, R. , Kinoshita, T., Katsumata, N., Uezono, Y., Xiao, J., Matsuoka, Y.J.: Impact of chemotherapy on the association between fear of cancer recurrence and the gut microbiota in breast cancer survivors. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 85, 186–191 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Martín, B. , Fernández Rodríguez, E.J., Rihuete Galve, M.I., Cruz Hernández, J.J.: Study of Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Women with Breast Cancer. IJERPH. 17, 8896 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.J. , Fletcher, E., Douglas, A., Anderson, E.D.C., McCallum, A., Simpson, C.R., Smith, J., Moger, T.A., Peltola, M., Mihalicza, P., Sveréus, S., Zengarini, N., Campbell, H., Wild, S.H.: Retrospective cohort study of breast cancer incidence, health service use and outcomes in Europe: a study of feasibility. European Journal of Public Health. 28, 327–332 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Jim, H.S.L. , Phillips, K.M., Chait, S., Faul, L.A., Popa, M.A., Lee, Y.-H., Hussin, M.G., Jacobsen, P.B., Small, B.J.: Meta-Analysis of Cognitive Functioning in Breast Cancer Survivors Previously Treated With Standard-Dose Chemotherapy. JCO. 30, 3578–3587 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Wu, D. , Chen, Q., Chen, X., Han, F., Chen, Z., Wang, Y.: The blood–brain barrier: structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 8, 217 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.T. , Ng, T., Shwe, M., Ho, H.K., Foo, K.M., Cham, M.T., Lee, J.A., Fan, G., Tan, Y.P., Yong, W.S., Madhukumar, P., Loo, S.K., Ang, S.F., Wong, M., Chay, W.Y., Ooi, W.S., Dent, R.A., Yap, Y.S., Ng, R., Chan, A.: Association of proinflammatory cytokines and chemotherapy-associated cognitive impairment in breast cancer patients: a multi-centered, prospective, cohort study. Annals of Oncology. 26, 1446–1451 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Shadad, A.K. : Gastrointestinal radiation injury: Symptoms, risk factors and mechanisms. WJG. 19, 185 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.-D. , Kim, H.J., Seo, J.-G., Kang, S.W., Bae, J.-W.: Impact of Pelvic Radiotherapy on Gut Microbiota of Gynecological Cancer Patients Revealed by Massive Pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE. 8, e82659 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Shiao, S.L. , Kershaw, K.M., Limon, J.J., You, S., Yoon, J., Ko, E.Y., Guarnerio, J., Potdar, A.A., McGovern, D.P.B., Bose, S., Dar, T.B., Noe, P., Lee, J., Kubota, Y., Maymi, V.I., Davis, M.J., Henson, R.M., Choi, R.Y., Yang, W., Tang, J., Gargus, M., Prince, A.D., Zumsteg, Z.S., Underhill, D.M.: Commensal bacteria and fungi differentially regulate tumor responses to radiation therapy. Cancer Cell. 39, 1202-1213.e6 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Herranz, M. , Rafail, S., Beghi, S., Gil-de-Gómez, L., Verginadis, I., Bittinger, K., Pustylnikov, S., Pierini, S., Perales-Linares, R., Blair, I.A., Mesaros, C.A., Snyder, N.W., Bushman, F., Koumenis, C., Facciabene, A.: Gut microbiota modulate dendritic cell antigen presentation and radiotherapy-induced antitumor immune response. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 130, 466–479 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Guo, H. , Chou, W.-C., Lai, Y., Liang, K., Tam, J.W., Brickey, W.J., Chen, L., Montgomery, N.D., Li, X., Bohannon, L.M., Sung, A.D., Chao, N.J., Peled, J.U., Gomes, A.L.C., Van Den Brink, M.R.M., French, M.J., Macintyre, A.N., Sempowski, G.D., Tan, X., Sartor, R.B., Lu, K., Ting, J.P.Y.: Multi-omics analyses of radiation survivors identify radioprotective microbes and metabolites. Science. 370, eaay9097 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.L. , Wilson, I.D., Teare, J., Marchesi, J.R., Nicholson, J.K., Kinross, J.M.: Gut microbiota modulation of chemotherapy efficacy and toxicity. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 14, 356–365 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Di Modica, M. , Gargari, G., Regondi, V., Bonizzi, A., Arioli, S., Belmonte, B., De Cecco, L., Fasano, E., Bianchi, F., Bertolotti, A., Tripodo, C., Villani, L., Corsi, F., Guglielmetti, S., Balsari, A., Triulzi, T., Tagliabue, E.: Gut Microbiota Condition the Therapeutic Efficacy of Trastuzumab in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Research. 81, 2195–2206 (2021). [CrossRef]
- One Health, https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/one-health.
- Kleber, K.T. , Iranpur, K.R., Perry, L.M., Cruz, S.M., Razmara, A.M., Culp, W.T.N., Kent, M.S., Eisen, J.A., Rebhun, R.B., Canter, R.J.: Using the canine microbiome to bridge translation of cancer immunotherapy from pre-clinical murine models to human clinical trials. Front. Immunol. 13, 983344 (2022). [CrossRef]
- M. Dujon, A., Brown, J.S., Destoumieux-Garzón, D., Vittecoq, M., Hamede, R., Tasiemski, A., Boutry, J., Tissot, S., Alix-Panabieres, C., Pujol, P., Renaud, F., Simard, F., Roche, B., Ujvari, B., Thomas, F.: On the need for integrating cancer into the One Health perspective. Evolutionary Applications. 14, 2571–2575 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Kattner, P. , Zeiler, K., Herbener, V.J., Ferla-Brühl, K.L., Kassubek, R., Grunert, M., Burster, T., Brühl, O., Weber, A.S., Strobel, H., Karpel-Massler, G., Ott, S., Hagedorn, A., Tews, D., Schulz, A., Prasad, V., Siegelin, M.D., Nonnenmacher, L., Fischer-Posovszky, P., Halatsch, M.-E., Debatin, K.-M., Westhoff, M.-A.: What Animal Cancers teach us about Human Biology. Theranostics. 11, 6682–6702 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Dujon, A.M. , Gatenby, R.A., Bramwell, G., MacDonald, N., Dohrmann, E., Raven, N., Schultz, A., Hamede, R., Gérard, A.-L., Giraudeau, M., Thomas, F., Ujvari, B.: Transmissible Cancers in an Evolutionary Perspective. iScience. 23, 101269 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Epstein, B. , Jones, M., Hamede, R., Hendricks, S., McCallum, H., Murchison, E.P., Schönfeld, B., Wiench, C., Hohenlohe, P., Storfer, A.: Rapid evolutionary response to a transmissible cancer in Tasmanian devils. Nat Commun. 7, 12684 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Kerr, P. , Liu, J., Cattadori, I., Ghedin, E., Read, A., Holmes, E.: Myxoma Virus and the Leporipoxviruses: An Evolutionary Paradigm. Viruses. 7, 1020–1061 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Di Giallonardo, F. , Holmes, E.C.: Viral biocontrol: grand experiments in disease emergence and evolution. Trends in Microbiology. 23, 83–90 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Spernovasilis, N. , Tsiodras, S., Poulakou, G.: Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Diseases: Humankind’s Companions and Competitors. Microorganisms. 10, 98 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Giraudeau, M. , Sepp, T., Ujvari, B., Ewald, P.W., Thomas, F.: Human activities might influence oncogenic processes in wild animal populations. Nat Ecol Evol. 2, 1065–1070 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Sepp, T. , Ujvari, B., Ewald, P.W., Thomas, F., Giraudeau, M.: Urban environment and cancer in wildlife: available evidence and future research avenues. Proc. R. Soc. B. 286, 20182434 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, P.A. , Agnew, D., Keel, M.K., Woolard, K.D.: Cancer in wildlife: patterns of emergence. Nat Rev Cancer. 18, 646–661 (2018). [CrossRef]
- White, J. , Amato, K.R., Decaestecker, E., McKenzie, V.J.: Editorial: Impact of anthropogenic environmental changes on animal microbiomes. Front. Ecol. Evol. 11, 1204035 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Sonnenburg, E.D. , Sonnenburg, J.L.: The ancestral and industrialized gut microbiota and implications for human health. Nat Rev Microbiol. 17, 383–390 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, M.A.M. , Chel, H.M., Thu, M.J., Bawm, S., Htun, L.L., Win, M.M., Oo, Z.M., Ohsawa, N., Lahdenperä, M., Mohamed, W.M.A., Ito, K., Nonaka, N., Nakao, R., Katakura, K.: Anthropogenic interferences lead to gut microbiome dysbiosis in Asian elephants and may alter adaptation processes to surrounding environments. Sci Rep. 11, 741 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Poutahidis, T. , Varian, B.J., Levkovich, T., Lakritz, J.R., Mirabal, S., Kwok, C., Ibrahim, Y.M., Kearney, S.M., Chatzigiagkos, A., Alm, E.J., Erdman, S.E.: Dietary Microbes Modulate Transgenerational Cancer Risk. Cancer Research. 75, 1197–1204 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Kowallik, V. , Das, A., Mikheyev, A.S.: Experimental inheritance of antibiotic acquired dysbiosis affects host phenotypes across generations. Front. Microbiol. 13, 1030771 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Dujon, A.M. , Ujvari, B., Thomas, F.: Cancer risk landscapes: A framework to study cancer in ecosystems. Science of The Total Environment. 763, 142955 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Efird, J.T. , Davies, S.W., O’Neal, W.T., Anderson, E.J.: Animal Viruses, Bacteria, and Cancer: A Brief Commentary. Front. Public Health. 2, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Prüss-Üstün, A. , Wolf, J., Corvalán, C.F., Bos, R., Neira, M.P.: Preventing disease through healthy environments: a global assessment of the burden of disease from environmental risks. World Health Organization, Geneva (2016).
- AbdulRaheem, Y. : Unveiling the Significance and Challenges of Integrating Prevention Levels in Healthcare Practice. J Prim Care Community Health. 14, 21501319231186500 (2023). [CrossRef]
- About: Health promotion and disease prevention through population-based interventions, including action to address social determinants and health inequity, http://www.emro.who.int/about-who/public-health-functions/health-promotion-disease-prevention.html.
- Grenni, P. , Ancona, V., Barra Caracciolo, A.: Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchemical Journal. 136, 25–39 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. , Raguideau, S., Sirén, K., Asnicar, F., Cumbo, F., Hildebrand, F., Segata, N., Cha, C.-J., Quince, C.: Population-level impacts of antibiotic usage on the human gut microbiome. Nat Commun. 14, 1191 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. , Weng, Y., Luo, T., Wang, Q., Yang, G., Jin, Y.: Antimicrobial and the Resistances in the Environment: Ecological and Health Risks, Influencing Factors, and Mitigation Strategies. Toxics. 11, 185 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F. , Péguilhan, R., Turgeon, N., Veillette, M., Baray, J.-L., Deguillaume, L., Amato, P., Duchaine, C.: Quantification of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in clouds at a mountain site (puy de Dôme, central France). Science of The Total Environment. 865, 161264 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.H. , Page, S.W.: Antimicrobial Stewardship in Veterinary Medicine. Microbiol Spectr. 6, 6.3.03 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C. , Loosen, S.H., Joerdens, M.S., Demir, M., Luedde, T., Kostev, K.: Antibiotic therapy is associated with an increased incidence of cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149, 1285–1293 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Ibragimova, S. , Ramachandran, R., Ali, F.R., Lipovich, L., Ho, S.B.: Dietary Patterns and Associated Microbiome Changes that Promote Oncogenesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 725821 (2021). [CrossRef]
- emhj: One Health: perspectives on ethical issues and evidence from animal experiments, http://www.emro.who.int/emhj-volume-18-2012/issue-11/article-15.html.
- Van Herten, J. , Bovenkerk, B., Verweij, M.: One Health as a moral dilemma: Towards a socially responsible zoonotic disease control. Zoonoses and Public Health. 66, 26–34 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Ursell, L.K. , Metcalf, J.L., Parfrey, L.W., Knight, R.: Defining the human microbiome. Nutrition Reviews. 70, S38–S44 (2012). [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.I. , Câtoi, C.: COMPARATIVE ONCOLOGY. In: Comparative Oncology. The Publishing House of the Romanian Academy (2007).
- Dincă, L.C. , Grenni, P., Onet, C., Onet, A.: Fertilization and Soil Microbial Community: A Review. Applied Sciences. 12, 1198 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, M.H. , Sitchenko, K.L., Carpentieri, C., Friedman-Moraco, R.J., Wang, T., Kraft, C.S.: Ethical Considerations in Microbial Therapeutic Clinical Trials. The New Bioethics. 23, 210–218 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G. , Ianiro, G., Ahern, A., Carbone, C., Temko, A., Claesson, M.J., Gasbarrini, A., Tortora, G.: Gut microbiome, big data and machine learning to promote precision medicine for cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17, 635–648 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. , Tan, Q., Fu, Q., Zhou, Y., Hu, Y., Tang, S., Zhou, Y., Zhang, J., Qiu, J., Lv, Q.: Gastrointestinal microbiome and breast cancer: correlations, mechanisms and potential clinical implications. Breast Cancer. 24, 220–228 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Yin, B. , Wang, X., Yuan, F., Li, Y., Lu, P.: Research progress on the effect of gut and tumor microbiota on antitumor efficacy and adverse effects of chemotherapy drugs. Front. Microbiol. 13, 899111 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Poff, A.M. , Ari, C., Seyfried, T.N., D’Agostino, D.P.: The Ketogenic Diet and Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Prolong Survival in Mice with Systemic Metastatic Cancer. PLoS ONE. 8, e65522 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.A. , Blaser, M.J., Caporaso, J.G., Jansson, J.K., Lynch, S.V., Knight, R.: Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat Med. 24, 392–400 (2018). [CrossRef]
- Soto-Pantoja, D.R. , Gaber, M., Arnone, A.A., Bronson, S.M., Cruz-Diaz, N., Wilson, A.S., Clear, K.Y.J., Ramirez, M.U., Kucera, G.L., Levine, E.A., Lelièvre, S.A., Chaboub, L., Chiba, A., Yadav, H., Vidi, P.-A., Cook, K.L.: Diet Alters Entero-Mammary Signaling to Regulate the Breast Microbiome and Tumorigenesis. Cancer Research. 81, 3890–3904 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.-F. , Ou-Yang, F., Li, C.-L., Chen, F.-M., Chuang, C.-H., Kan, J.-Y., Wu, C.-C., Shih, S.-L., Shiau, J.-P., Kao, L.-C., Kao, C.-N., Lee, Y.-C., Moi, S.-H., Yeh, Y.-T., Cheng, C.-J., Chiang, C.-P.: Comprehensive profiles and diagnostic value of menopausal-specific gut microbiota in premenopausal breast cancer. Exp Mol Med. 53, 1636–1646 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Parhi, L. , Alon-Maimon, T., Sol, A., Nejman, D., Shhadeh, A., Fainsod-Levi, T., Yajuk, O., Isaacson, B., Abed, J., Maalouf, N., Nissan, A., Sandbank, J., Yehuda-Shnaidman, E., Ponath, F., Vogel, J., Mandelboim, O., Granot, Z., Straussman, R., Bachrach, G.: Breast cancer colonization by Fusobacterium nucleatum accelerates tumor growth and metastatic progression. Nat Commun. 11, 3259 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Bennet, JustinD., Brinkman, M.: TREATMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS BY IMPLANTATION OF NORMAL COLONIC FLORA. The Lancet. 333, 164 (1989). [CrossRef]
- Mills, H. , Acquah, R., Tang, N., Cheung, L., Klenk, S., Glassen, R., Pirson, M., Albert, A., Hoang, D.T., Van, T.N.: The Use of Bacteria in Cancer Treatment: A Review from the Perspective of Cellular Microbiology. Emergency Medicine International. 2022, 1–6 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z. , Gu, M.-D., Tang, T.: Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Cancer Therapy: Current Knowledge, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Front. Oncol. 12, 891187 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Kasinskas, R.W. , Forbes, N.S.: Salmonella typhimurium Lacking Ribose Chemoreceptors Localize in Tumor Quiescence and Induce Apoptosis. Cancer Research. 67, 3201–3209 (2007). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




