Submitted:
08 November 2023
Posted:
09 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
1. Virus, Cell Culture, and Reagents.
2. Lactate dehydrogenase assay (LDH)

3. Neutral Red assay
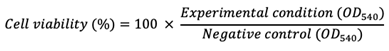
4. Cell infection and treatments with AdipoRon or Adiponectin
5. Flow cytometry and antibody
6. RNA extraction and qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 5’-CAAATTCCATGGCACCGTCA-3’ | 5’-GGAGTGGGTGTCGCTGTTGA-3’ |
| RNAPII | 5'-GAGAGCGTTGAGTTCCAGAACC-3' | 5'-TGGATGTGTGCGTTGCTCAGCA-3' |
| RPLP0 | 5'-AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT-3' | 5’-GGATGGCCTTGCGCA-3' |
| ADIPOR1 | 5’-AGCCTGCGGCTTAATTTGAC-3’ | 5’-CAACTAAGAACGGCCATGCA-3’ |
| ADIPOR2 | 5’-GCAGCCAAGTTTTACCGAAG-3’ | 5’-CACCTCAAATGTGGGCTTTT-3’ |
| CPT1a | 5'-GATCCTGGACAATACCTCGGAG-3' | 5'-CTCCACAGCATCAAGAGACTGC-3' |
| ZIKV-E | 5’-CTGGTCACCTGGGGAAACTA-3’ | 5’- GAGCCTTCTCAAAGCACACC-3’ |
7. Statistical analyses
3. Results
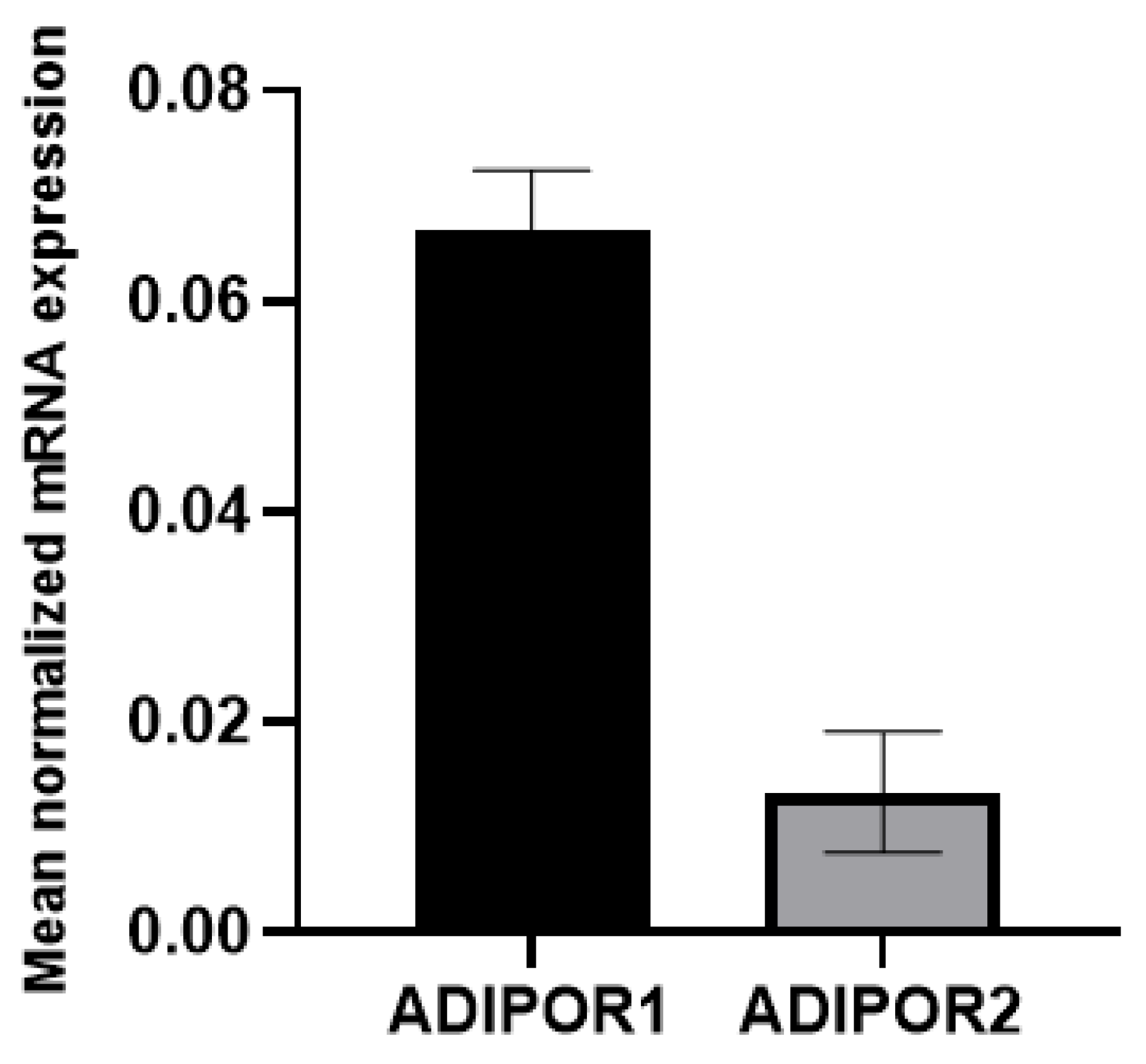
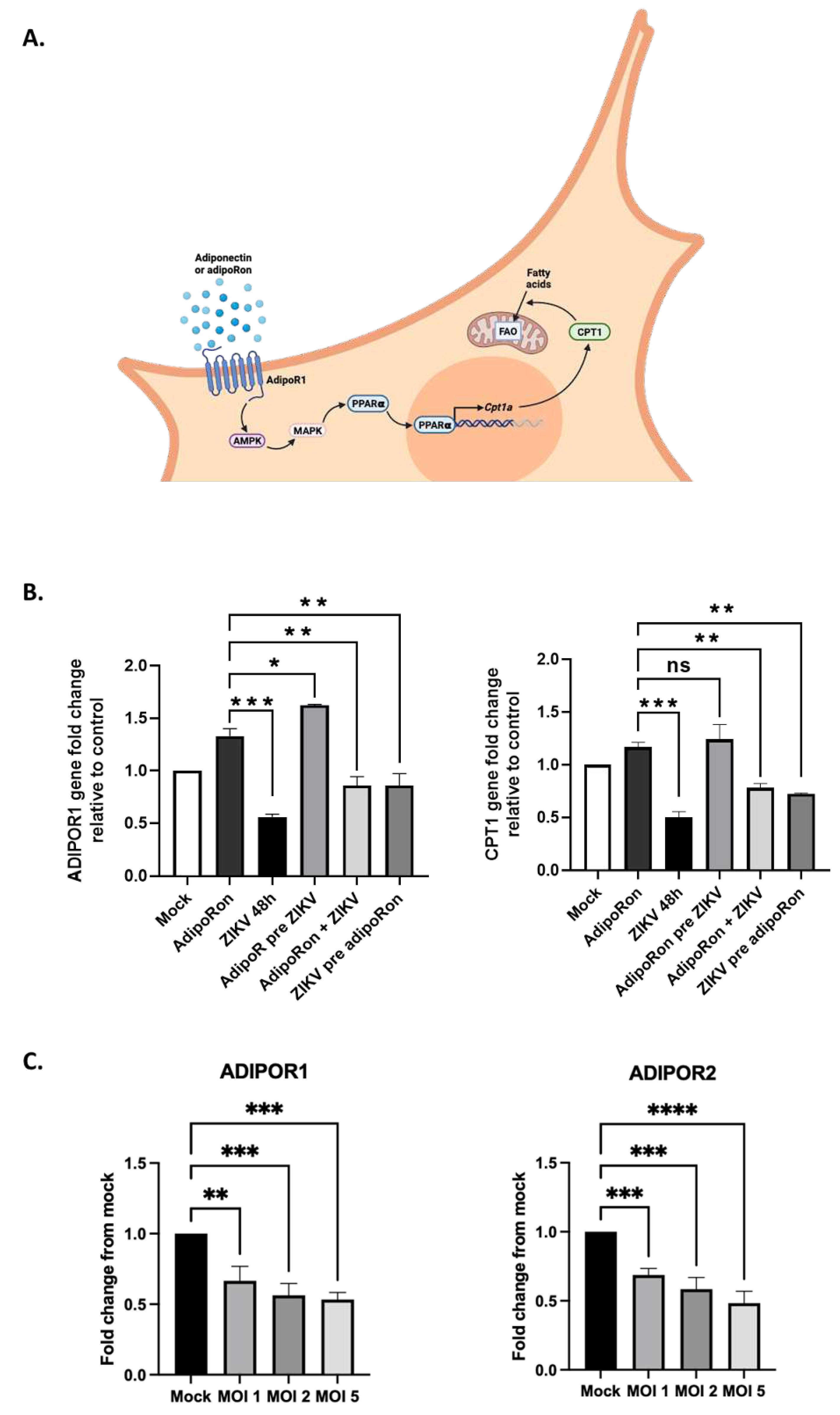
3.1. A549 cells express both adiponectin receptor genes, ADIPOR1 and ADIPOR2
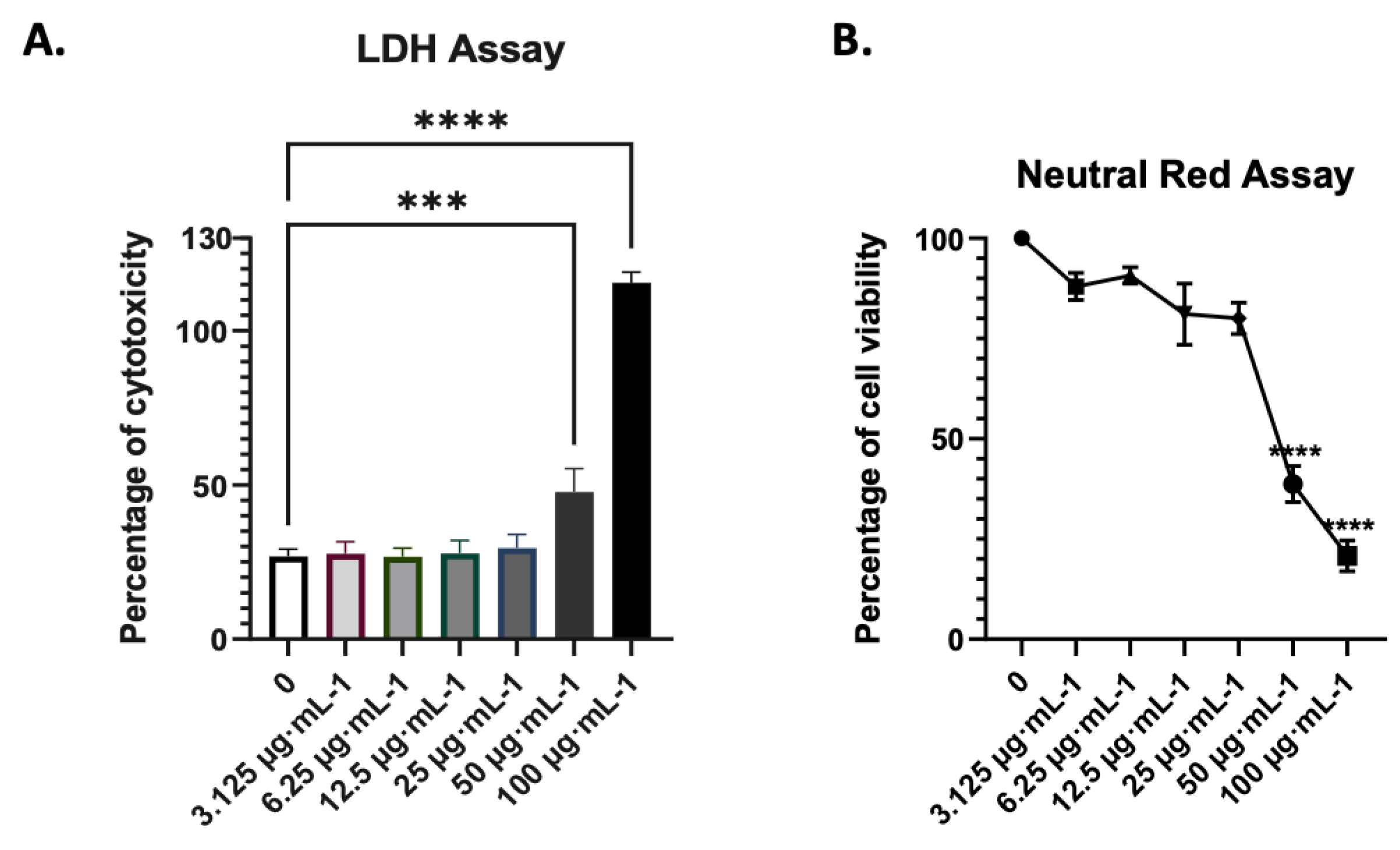
3.2. Assessment of the non-toxic concentration of AdipoRon in A549 cells
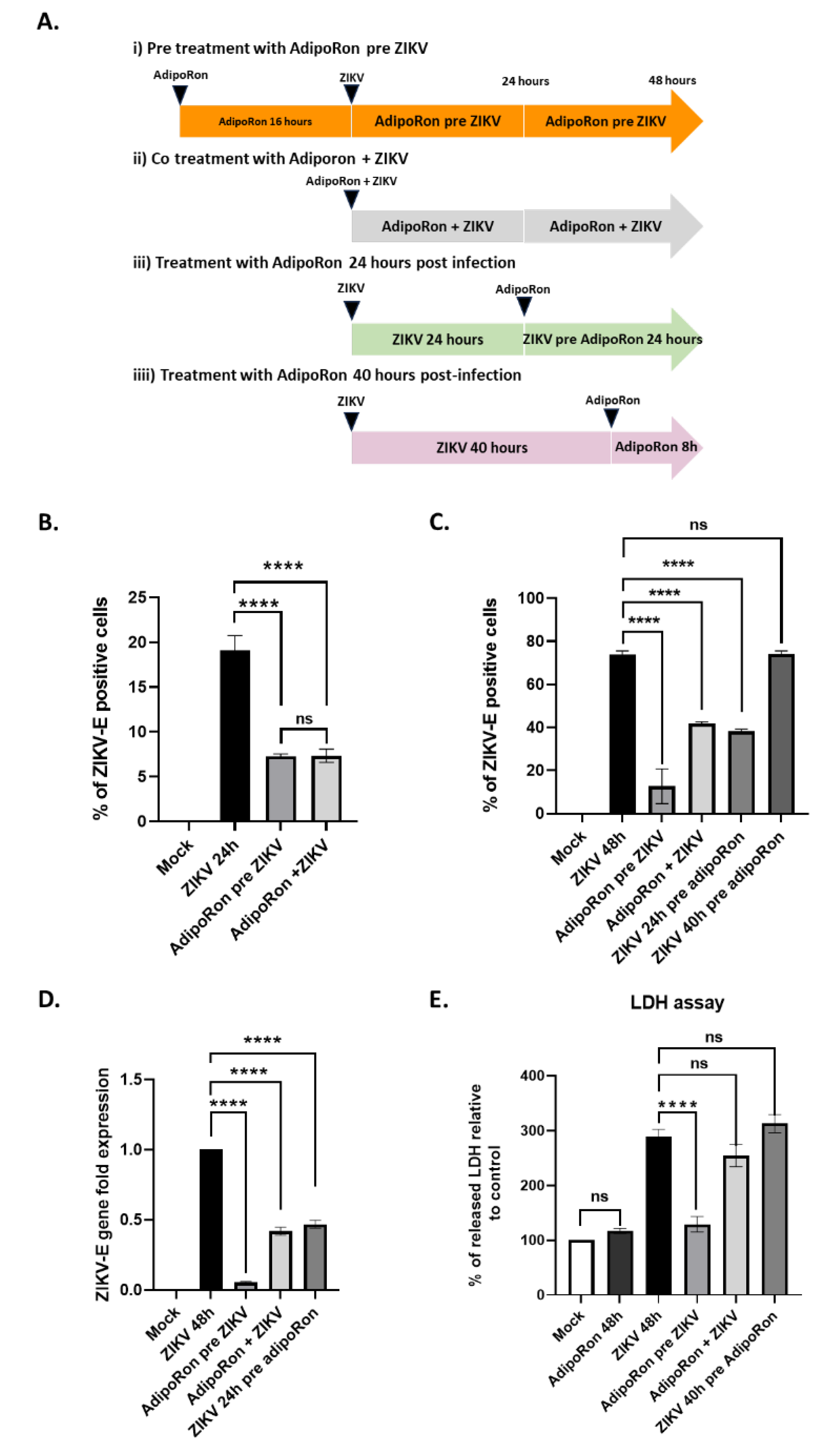
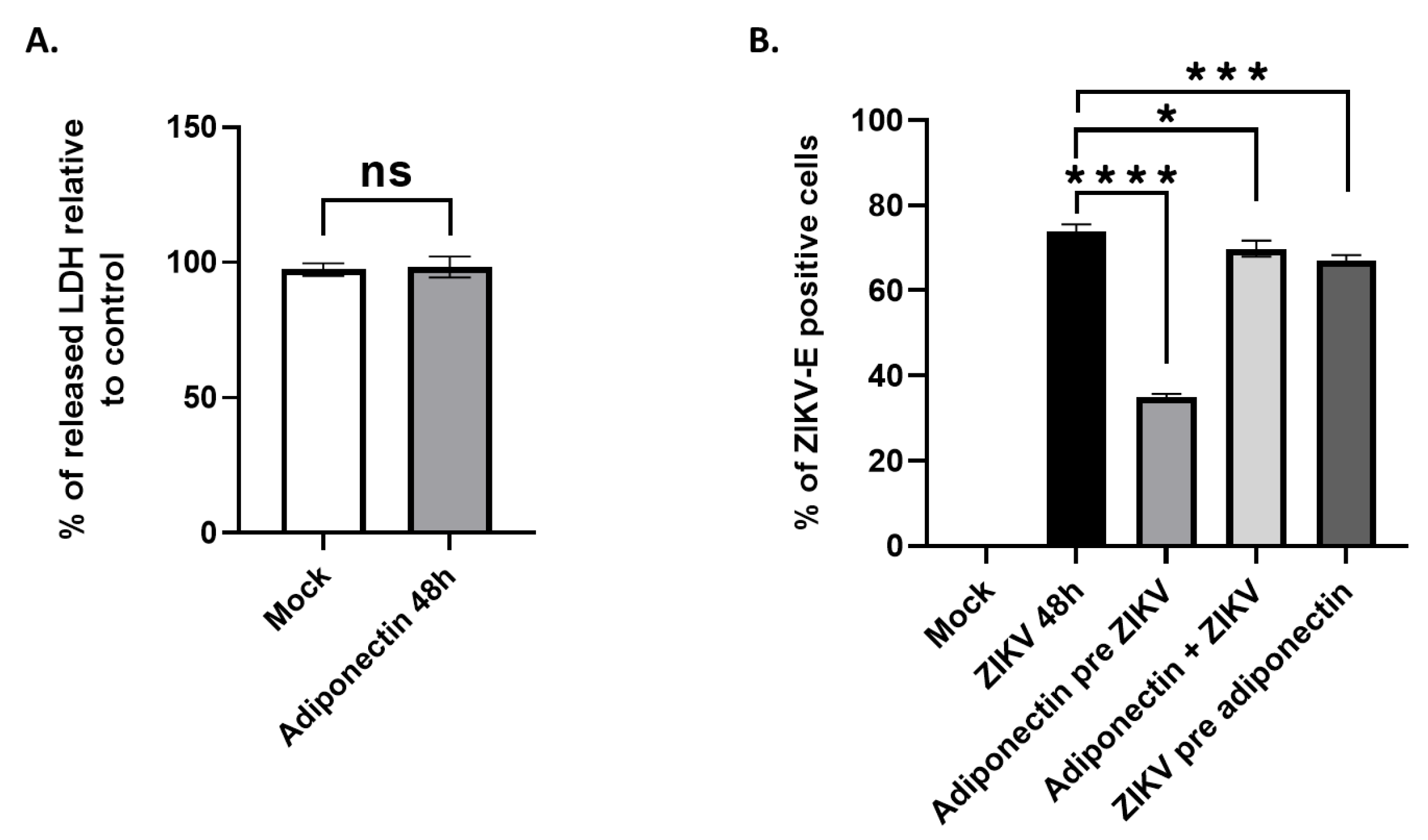
3.3. AdipoRon displays antiviral and cytoprotective effects
3.4. AdipoRon and adiponectin provide anti-ZIKV properties
3.5. ZIKV downregulates ADIPOR1 and CPT1 gene expression
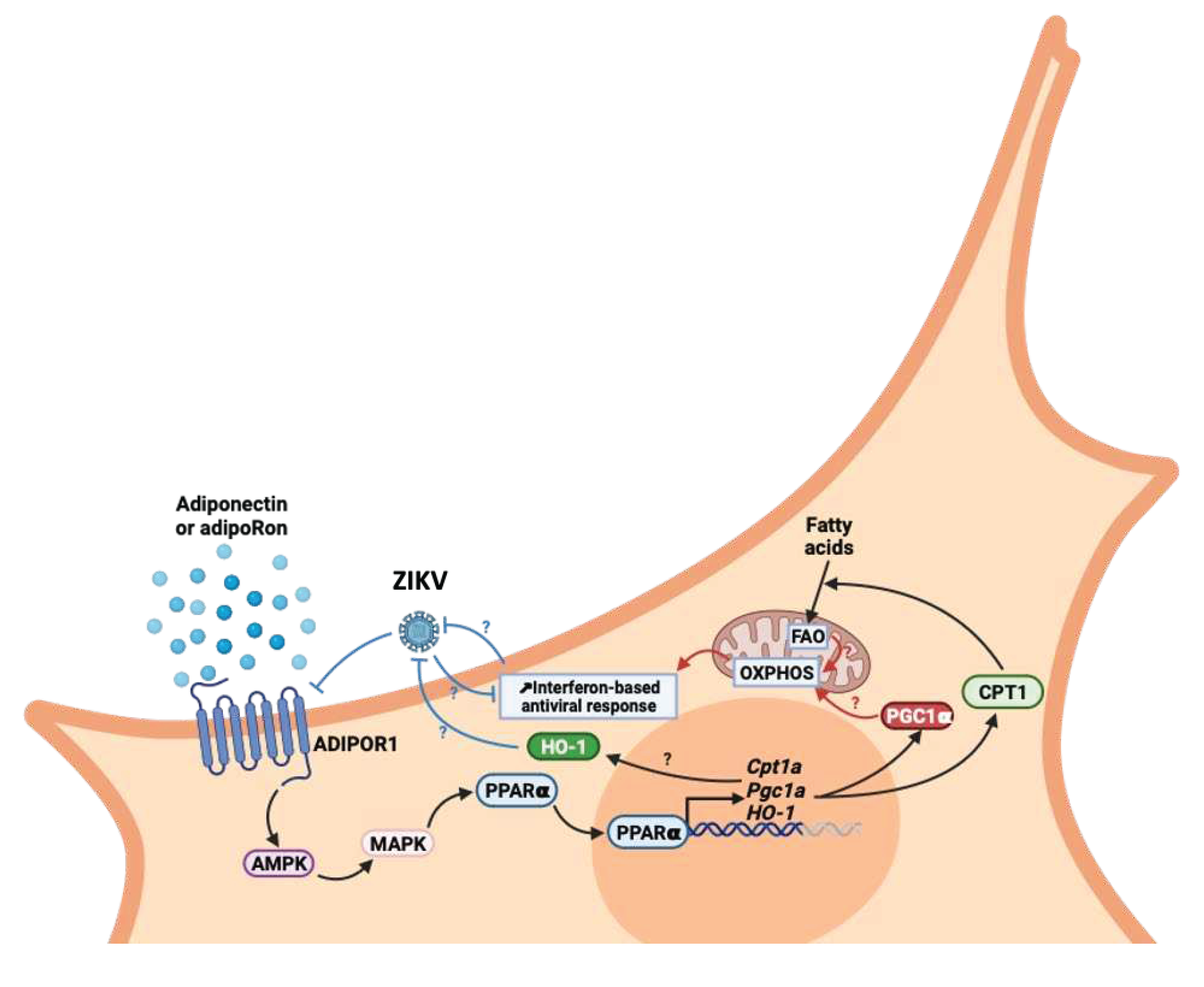
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, B.-H.; Yun, S.-I.; Woolley, M.; Lee, Y.-M. Zika Virus: History, Epidemiology, Transmission, and Clinical Presentation. Journal of Neuroimmunology 2017, 308, 50–64. [CrossRef]
- Gubler, D.J.; Vasilakis, N.; Musso, D. History and Emergence of Zika Virus. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2017, 216, S860–S867. [CrossRef]
- White, M.K.; Wollebo, H.S.; David Beckham, J.; Tyler, K.L.; Khalili, K. Zika Virus: An Emergent Neuropathological Agent. Annals of Neurology 2016, 80, 479–489. [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-I.; Lee, Y.-M. Zika Virus: An Emerging Flavivirus. J Microbiol. 2017, 55, 204–219. [CrossRef]
- Beaver, J.T.; Lelutiu, N.; Habib, R.; Skountzou, I. Evolution of Two Major Zika Virus Lineages: Implications for Pathology, Immune Response, and Vaccine Development. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1640. [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Gubler, D.J.; Schaub, B.; Lanteri, M.C.; Musso, D. An Update on Zika Virus Infection. The Lancet 2017, 390, 2099–2109. [CrossRef]
- Marbán-Castro, E.; Goncé, A.; Fumadó, V.; Romero-Acevedo, L.; Bardají, A. Zika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Their Children: A Review. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2021, 265, 162–168. [CrossRef]
- Runge-Ranzinger, S.; Morrison, A.C.; Manrique-Saide, P.; Horstick, O. Zika Transmission Patterns: A Meta-review. Tropical Med Int Health 2019, 24, 523–529. [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Song, H.; Ming, G. How Does Zika Virus Cause Microcephaly? Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 849–861. [CrossRef]
- Christian, K.M.; Song, H.; Ming, G. Pathophysiology and Mechanisms of Zika Virus Infection in the Nervous System. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 42, 249–269. [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases. IJMS 2020, 21, 1219. [CrossRef]
- Heiker, J.T.; Kosel, D.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Molecular Mechanisms of Signal Transduction via Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors. Biological Chemistry 2010, 391. [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.-S. Assembly of Adiponectin Oligomers. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2014, 15, 125–136. [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Jiang, L.; Xu, F.; Lyu, J.; Jiang, X.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Leak, R.K.; Stetler, R.A.; et al. Adiponectin Ameliorates Hypoperfusive Cognitive Deficits by Boosting a Neuroprotective Microglial Response. Progress in Neurobiology 2021, 205, 102125. [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.-H.; Lam, K.S.-L.; Cheng, O.-Y.; Kwan, J.S.-C.; Ho, P.W.-L.; Cheng, K.K.-Y.; Chung, S.K.; Ho, J.W.-M.; Guo, V.Y.; Xu, A. Adiponectin Is Protective against Oxidative Stress Induced Cytotoxicity in Amyloid-Beta Neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52354. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Wan, R.; Hu, J.; Mattson, M.P.; Spangler, E.; Liu, S.; Yau, S.-Y.; Lee, T.M.C.; Gleichmann, M.; Ingram, D.K.; et al. Adiponectin Protects Rat Hippocampal Neurons against Excitotoxicity. AGE 2011, 33, 155–165. [CrossRef]
- Bloemer, J.; Pinky, P.D.; Govindarajulu, M.; Hong, H.; Judd, R.; Amin, R.H.; Moore, T.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Reed, M.N.; Suppiramaniam, V. Role of Adiponectin in Central Nervous System Disorders. Neural Plasticity 2018, 2018, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.R.; Fasano, R.; Paolisso, G. Adiponectin and Cognitive Decline. IJMS 2020, 21, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Thundyil, J.; Pavlovski, D.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V. Adiponectin Receptor Signalling in the Brain. British J Pharmacology 2012, 165, 313–327. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Liu, M.; Ding, J.; Scherer, P.E.; Liu, F.; Lu, X.-Y. Adiponectin Is Critical in Determining Susceptibility to Depressive Behaviors and Has Antidepressant-like Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2012, 109, 12248–12253. [CrossRef]
- Wędrychowicz, A. Peptides from Adipose Tissue in Mental Disorders. WJP 2014, 4, 103. [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Huo, T.; Guo, F.; Wang, H.; Wei, H.; Yang, Q.; Dong, H.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, L. Globular Adiponectin Elicits Neuroprotection by Inhibiting NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Oxidative Damage in Ischemic Stroke. Neuroscience 2013, 248, 136–144. [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Guo, W.; Zheng, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; et al. Adiponectin Confers Neuroprotection against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through Activating the CAMP/PKA-CREB-BDNF Signaling. Brain Research Bulletin 2018, 143, 145–154. [CrossRef]
- Straub, L.G.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Messengers: Adiponectin. Nat Metab 2019, 1, 334–339. [CrossRef]
- Clain, J.; Couret, D.; Planesse, C.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; Meilhac, O.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Viranaicken, W.; Diotel, N. Distribution of Adiponectin Receptors in the Brain of Adult Mouse: Effect of a Single Dose of the Adiponectin Receptor Agonist, AdipoRON, on Ischemic Stroke. Brain Sciences 2022, 12, 680. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kang, S.M.; Kim, E.; Kim, C.-H.; Song, H.-T.; Lee, J.E. Adiponectin Receptor-Mediated Signaling Ameliorates Cerebral Cell Damage and Regulates the Neurogenesis of Neural Stem Cells at High Glucose Concentrations: An in Vivo and in Vitro Study. Cell Death Dis 2015, 6, e1844–e1844. [CrossRef]
- Nigro, E.; Daniele, A.; Salzillo, A.; Ragone, A.; Naviglio, S.; Sapio, L. AdipoRon and Other Adiponectin Receptor Agonists as Potential Candidates in Cancer Treatments. IJMS 2021, 22, 5569. [CrossRef]
- Formolo, D.A.; Lee, T.H.; Yu, J.; Lin, K.; Chen, G.; Kranz, G.S.; Yau, S.-Y. Increasing Adiponectin Signaling by Sub-Chronic AdipoRon Treatment Elicits Antidepressant- and Anxiolytic-Like Effects Independent of Changes in Hippocampal Plasticity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 249. [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Christie, B.R.; van Praag, H.; Lin, K.; Siu, P.M.-F.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F.; Yau, S. AdipoRon Treatment Induces a Dose-Dependent Response in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. IJMS 2021, 22, 2068. [CrossRef]
- Frumence, E.; Roche, M.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; El-Kalamouni, C.; Nativel, B.; Rondeau, P.; Missé, D.; Gadea, G.; Viranaicken, W.; Desprès, P. The South Pacific Epidemic Strain of Zika Virus Replicates Efficiently in Human Epithelial A549 Cells Leading to IFN-β Production and Apoptosis Induction. Virology 2016, 493, 217–226. [CrossRef]
- Hamel, R.; Dejarnac, O.; Wichit, S.; Ekchariyawat, P.; Neyret, A.; Luplertlop, N.; Perera-Lecoin, M.; Surasombatpattana, P.; Talignani, L.; Thomas, F.; et al. Biology of Zika Virus Infection in Human Skin Cells. J Virol 2015, 89, 8880–8896. [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of Adiponectin Receptors That Mediate Antidiabetic Metabolic Effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.; Cho, J.Y.; Pham, A.; Ramsdell, J.; Broide, D.H. Adiponectin and Functional Adiponectin Receptor 1 Are Expressed by Airway Epithelial Cells in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. The Journal of Immunology 2009, 182, 684–691. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Yang, C.-M.; Chang, J.-F.; Wu, C.-S.; Sia, K.-C.; Lin, W.-N. AdipoR-Increased Intracellular ROS Promotes CPLA 2 and COX-2 Expressions via Activation of PKC and P300 in Adiponectin-Stimulated Human Alveolar Type II Cells. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2016, 311, L255–L269. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, J.-J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.B. Adiponectin Increases Fatty Acid Oxidation in Skeletal Muscle Cells by Sequential Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase, P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, and Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor α. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2562–2570. [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, T.V.B.; Ximenes, R.A. de A.; Miranda-Filho, D. de B.; Souza, W.V.; Montarroyos, U.R.; de Melo, A.P.L.; Valongueiro, S.; de Albuquerque, M. de F.P.M.; Braga, C.; Filho, S.P.B.; et al. Association between Microcephaly, Zika Virus Infection, and Other Risk Factors in Brazil: Final Report of a Case-Control Study. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2018, 18, 328–336. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.K.; Petersen, L.R.; Honein, M.A.; Moore, C.A.; Rasmussen, S.A. Zika Virus as a Cause of Birth Defects: Were the Teratogenic Effects of Zika Virus Missed for Decades? Birth Defects Research 2023, 115, 265–274. [CrossRef]
- Zorrilla, C.D.; García García, I.; García Fragoso, L.; De La Vega, A. Zika Virus Infection in Pregnancy: Maternal, Fetal, and Neonatal Considerations. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2017, 216, S891–S896. [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.L.; Ralston, A. The Fetal Lineage Is Susceptible to Zika Virus Infection within Days of Fertilization. Development 2022, 149, dev200501. [CrossRef]
- Bonifay, T.; Le Turnier, P.; Epelboin, Y.; Carvalho, L.; De Thoisy, B.; Djossou, F.; Duchemin, J.-B.; Dussart, P.; Enfissi, A.; Lavergne, A.; et al. Review on Main Arboviruses Circulating on French Guiana, An Ultra-Peripheric European Region in South America. Viruses 2023, 15, 1268. [CrossRef]
- Noisumdaeng, P.; Dangsagul, W.; Sangsiriwut, K.; Prasertsopon, J.; Changsom, D.; Yoksan, S.; Ajawatanawong, P.; Buathong, R.; Puthavathana, P. Molecular Characterization and Geographical Distribution of Zika Virus Worldwide from 1947 to 2022. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2023, 136, 5–10. [CrossRef]
- Marquine, S.; Durand, G.A.; Modenesi, G.; Khouadhria, S.; Piorkowski, G.; Badaut, C.; Canivez, T.; De Lamballerie, X.; Grard, G.; Klitting, R. Sequence Data From a Travel-Associated Case of Microcephaly Highlight a Persisting Risk Due to Zika Virus Circulation in Thailand. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2023, jiad322. [CrossRef]
- Braga, C.; Martelli, C.M.T.; Souza, W.V.; Luna, C.F.; Albuquerque, M. de F.P.M.; Mariz, C.A.; Morais, C.N.L.; Brito, C.A.A.; Melo, C.F.C.A.; Lins, R.D.; et al. Seroprevalence of Dengue, Chikungunya and Zika at the Epicenter of the Congenital Microcephaly Epidemic in Northeast Brazil: A Population-Based Survey. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2023, 17, e0011270. [CrossRef]
- Aubry, F.; Jacobs, S.; Darmuzey, M.; Lequime, S.; Delang, L.; Fontaine, A.; Jupatanakul, N.; Miot, E.F.; Dabo, S.; Manet, C.; et al. Recent African Strains of Zika Virus Display Higher Transmissibility and Fetal Pathogenicity than Asian Strains. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 916. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.S.; Santos, F.C.P.; Campana, P.R.V.; Costa, V.V.; de Pádua, R.M.; Souza, D.G.; Teixeira, M.M.; Braga, F.C. Natural Products and Derivatives as Potential Zika Virus Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Viruses 2023, 15, 1211. [CrossRef]
- Salampe, M.; Mamada, S.S.; Evary, Y.M.; Mitra, S.; Bin Emran, T.; Harapan, H.; Nainu, F.; Simal-Gandara, J. Promising Marine Natural Products for Tackling Viral Outbreaks:A Focus on Possible Targets and Structure-Activity Relationship. CTMC 2023, 23, 1352–1379. [CrossRef]
- Bernatchez, J.A.; Tran, L.T.; Li, J.; Luan, Y.; Siqueira-Neto, J.L.; Li, R. Drugs for the Treatment of Zika Virus Infection. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 470–489. [CrossRef]
- Martinello, M.; Naggie, S.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Matthews, G.V. Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy for Treatment of Acute and Recent Hepatitis C Virus Infection: A Narrative Review. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2023, 77, S238–S244. [CrossRef]
- Mayberry, J.; Lee, W.M. The Revolution in Treatment of Hepatitis C. Medical Clinics of North America 2019, 103, 43–55. [CrossRef]
- Ng, R.C.-L.; Jian, M.; Ma, O.K.-F.; Bunting, M.; Kwan, J.S.-C.; Zhou, G.-J.; Senthilkumar, K.; Iyaswamy, A.; Chan, P.-K.; Li, M.; et al. Chronic Oral Administration of AdipoRon Reverses Cognitive Impairments and Ameliorates Neuropathology in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Mol Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5669–5689. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y.; Hu, Q.; Cui, W.; Bai, H.; Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Han, L.; et al. Adiponectin/AdiopR1 Signaling Prevents Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Injury after Traumatic Brain Injury in a SIRT3 Dependent Manner. Redox Biology 2022, 54, 102390. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Kinney, B.; Yoo, H. sun; Lee, B.; Schaack, J.; Shao, J. Adiponectin Increases Skeletal Muscle Mitochondrial Biogenesis by Suppressing Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-1. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1463–1470. [CrossRef]
- Majeed, Y.; Halabi, N.; Madani, A.Y.; Engelke, R.; Bhagwat, A.M.; Abdesselem, H.; Agha, M.V.; Vakayil, M.; Courjaret, R.; Goswami, N.; et al. SIRT1 Promotes Lipid Metabolism and Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Adipocytes and Coordinates Adipogenesis by Targeting Key Enzymatic Pathways. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 8177. [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Singh, M.; Porwal, K.; Rajak, S.; Das, N.; Rajput, S.; Trivedi, A.K.; Maurya, R.; Sinha, R.A.; Siddiqi, M.I.; et al. Adiponectin Receptors by Increasing Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Respiration Promote Osteoblast Differentiation: Discovery of Isovitexin as a New Class of Small Molecule Adiponectin Receptor Modulator with Potential Osteoanabolic Function. European Journal of Pharmacology 2021, 913, 174634. [CrossRef]
- Thaker, S.K.; Ch’ng, J.; Christofk, H.R. Viral Hijacking of Cellular Metabolism. BMC Biol 2019, 17, 59. [CrossRef]
- Lebeau, G.; Paulo-Ramos, A.; Hoarau, M.; El Safadi, D.; Meilhac, O.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; Roche, M.; Viranaicken, W. Metabolic Dependency Shapes Bivalent Antiviral Response in Host Cells: The Role of Glutamine; Immunology, 2023;
- Lebeau, G.; El Safadi, D.; Paulo-Ramos, A.; Hoareau, M.; Desprès, P.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; Chouchou, F.; Roche, M.; Viranaicken, W. The Efficient Antiviral Response of A549 Cells Is Enhanced When Mitochondrial Respiration Is Promoted. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1168. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gouilly, J.; Ferrat, Y.J.; Espino, A.; Glaziou, Q.; Cartron, G.; El Costa, H.; Al-Daccak, R.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N. Metabolic Reprogramming by Zika Virus Provokes Inflammation in Human Placenta. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2967. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert-Jaramillo, J.; Purnama, U.; Molnár, Z.; James, W.S. Zika Virus-Induces Metabolic Alterations in Fetal Neuronal Progenitors That Could Influence in Neurodevelopment during Early Pregnancy. Biology Open 2023, 12, bio059889. [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, K.A.; Sanchez, E.L.; Camarda, R.; Lagunoff, M. Dengue Virus Induces and Requires Glycolysis for Optimal Replication. J Virol 2015, 89, 2358–2366. [CrossRef]
- Jordan, T.X.; Randall, G. Flavivirus Modulation of Cellular Metabolism. Current Opinion in Virology 2016, 19, 7–10. [CrossRef]
- Mingo-Casas, P.; Blázquez, A.-B.; Gómez de Cedrón, M.; San-Félix, A.; Molina, S.; Escribano-Romero, E.; Calvo-Pinilla, E.; Jiménez de Oya, N.; Ramírez de Molina, A.; Saiz, J.-C.; et al. Glycolytic Shift during West Nile Virus Infection Provides New Therapeutic Opportunities. J Neuroinflammation 2023, 20, 217. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yu, C.-H.; Jen, C.-Y.; Cheng, C.-F.; Chou, Y.; Chang, C.-C.; Juan, S.-H. Adiponectin-Mediated Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction Protects Against Iron-Induced Liver Injury via a PPARα-Dependent Mechanism. The American Journal of Pathology 2010, 177, 1697–1709. [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.A.; León, M.A.; Céspedes, P.F.; Gómez, R.S.; Canedo-Marroquín, G.; Riquelme, S.A.; Salazar-Echegarai, F.J.; Blancou, P.; Simon, T.; Anegon, I.; et al. Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulates Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Replication and Lung Pathogenesis during Infection. The Journal of Immunology 2017, 199, 212–223. [CrossRef]
- El Kalamouni, C.; Frumence, E.; Bos, S.; Turpin, J.; Nativel, B.; Harrabi, W.; Wilkinson, D.; Meilhac, O.; Gadea, G.; Desprès, P.; et al. Subversion of the Heme Oxygenase-1 Antiviral Activity by Zika Virus. Viruses 2018, 11, 2. [CrossRef]
- Barroso, E.; Eyre, E.; Palomer, X.; Vázquez-Carrera, M. The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β/δ (PPARβ/δ) Agonist GW501516 Prevents TNF-α-Induced NF-ΚB Activation in Human HaCaT Cells by Reducing P65 Acetylation through AMPK and SIRT1. Biochemical Pharmacology 2011, 81, 534–543. [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Hyttinen, J.M.T.; Kaarniranta, K. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibits NF-ΚB Signaling and Inflammation: Impact on Healthspan and Lifespan. J Mol Med 2011, 89, 667–676. [CrossRef]
- Antonia, R.J.; Baldwin, A.S. IKK Promotes Cytokine-Induced and Cancer-Associated AMPK Activity and Attenuates Phenformin-Induced Cell Death in LKB1-Deficient Cells. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaan5850. [CrossRef]
- Stijn, C.M.W.; Kim, J.; Lusis, A.J.; Barish, G.D.; Tangirala, R.K. Macrophage Polarization Phenotype Regulates Adiponectin Receptor Expression and Adiponectin Anti-inflammatory Response. FASEB j. 2015, 29, 636–649. [CrossRef]
- Viola, A.; Munari, F.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Scolaro, T.; Castegna, A. The Metabolic Signature of Macrophage Responses. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1462. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yin, Z.; Qiu, T.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J. Revealing the Characteristics of ZIKV Infection through Tissue-Specific Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis. BMC Genomics 2022, 23, 697. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Dang, J.; Qin, Y.; Lichinchi, G.; Bansal, V.; Rana, T.M. Zika Virus Infection Reprograms Global Transcription of Host Cells to Allow Sustained Infection. Emerging Microbes & Infections 2017, 6, 1–10. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





