Submitted:
07 November 2023
Posted:
08 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
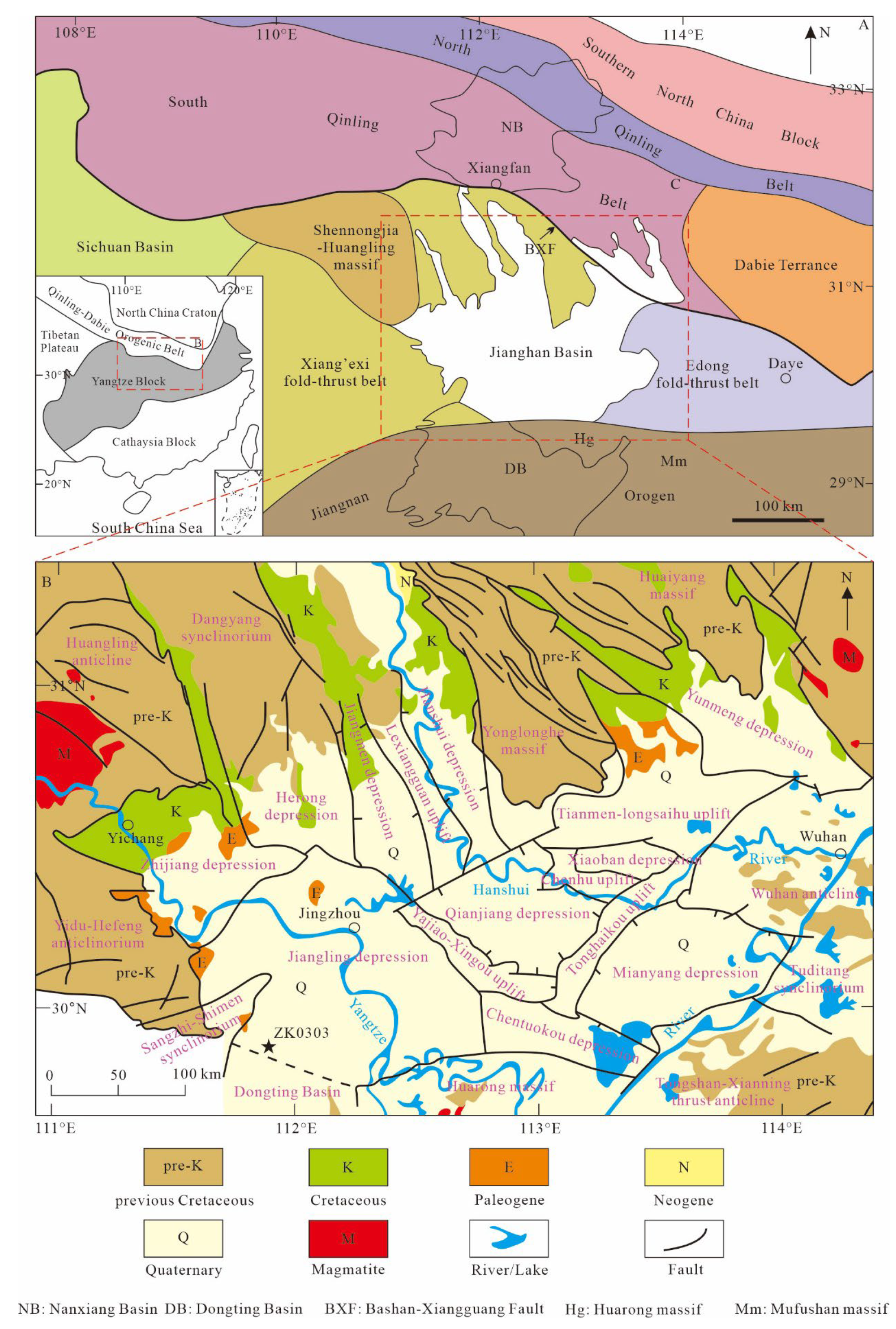
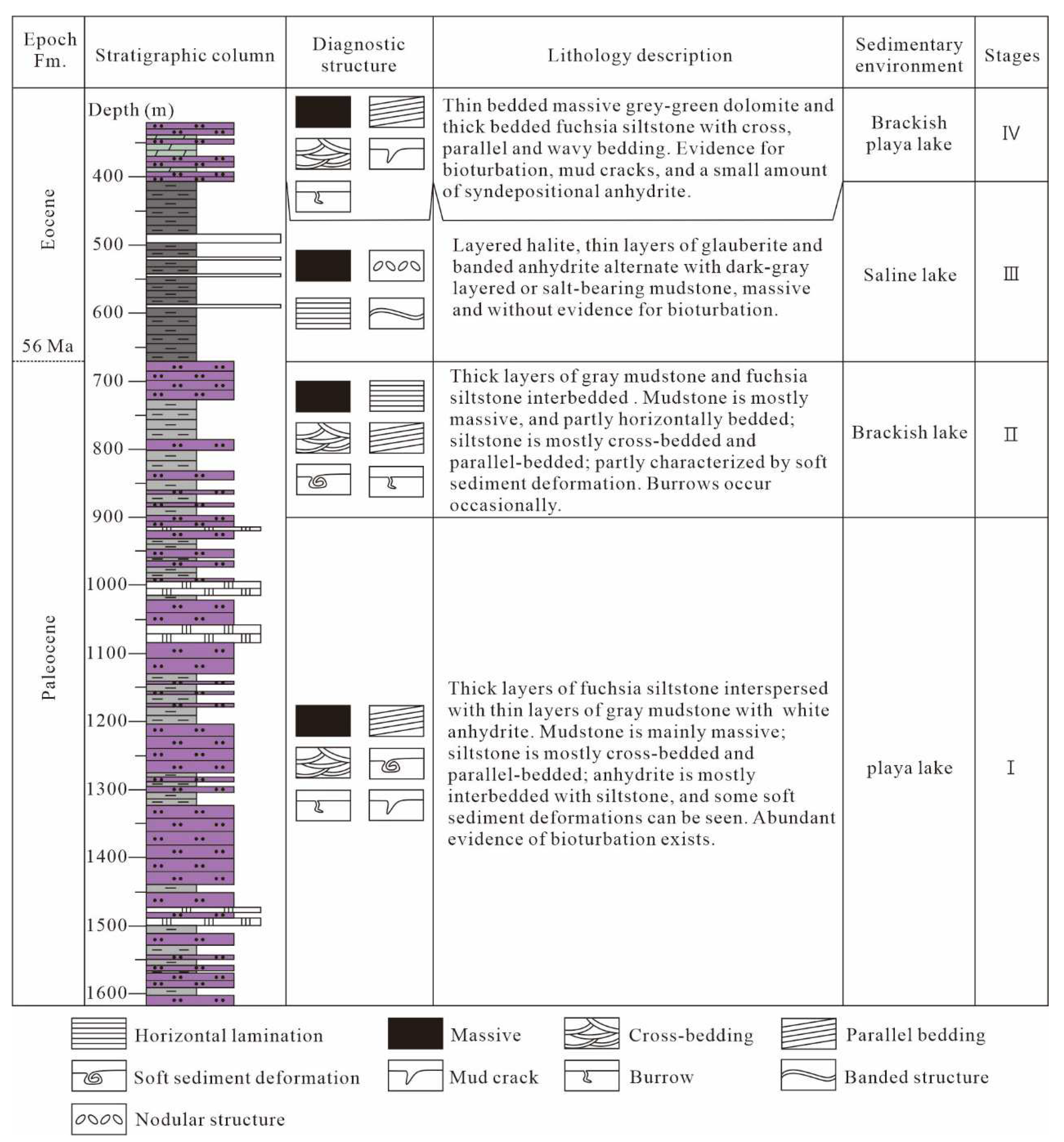
2. Geological Setting
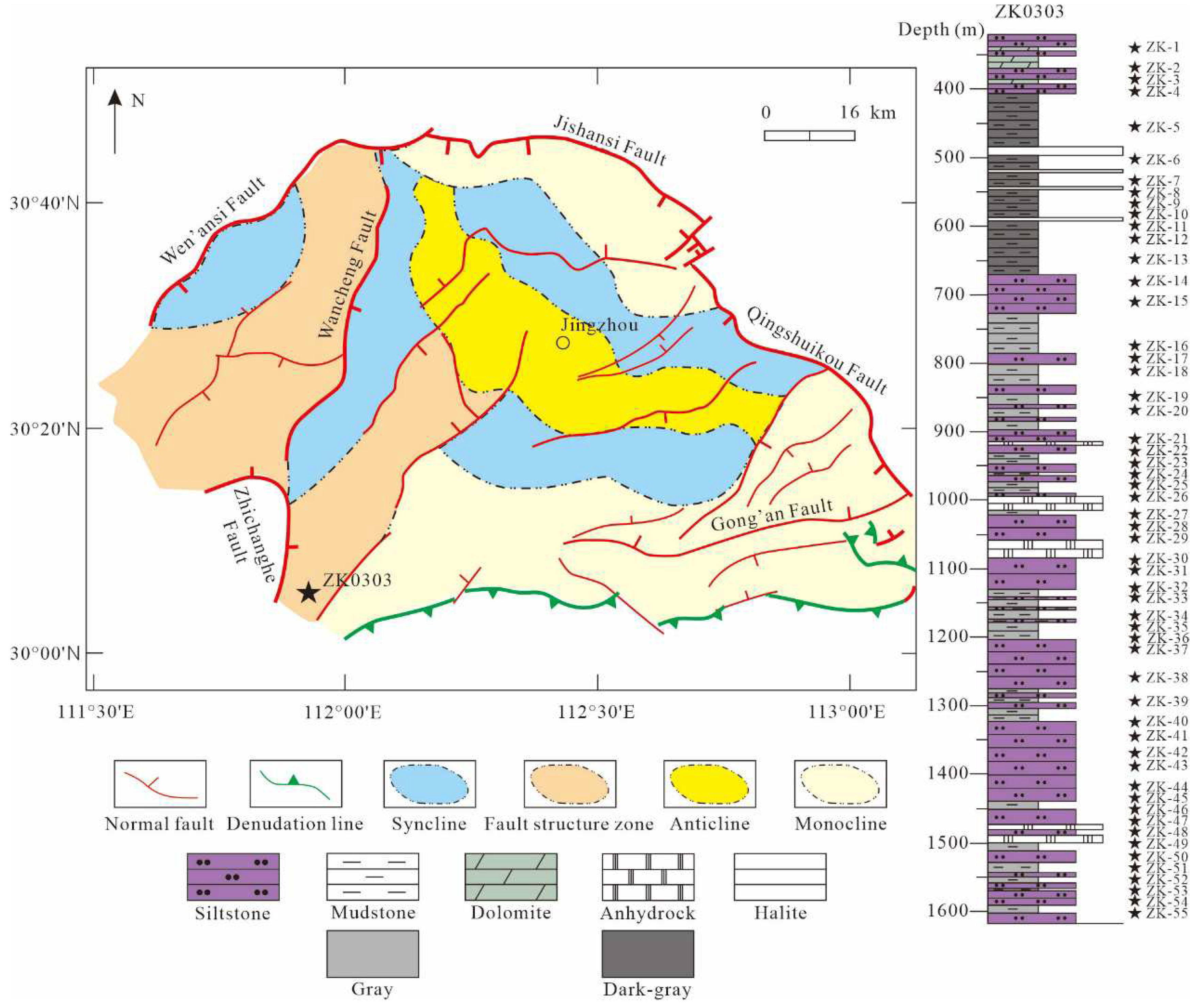
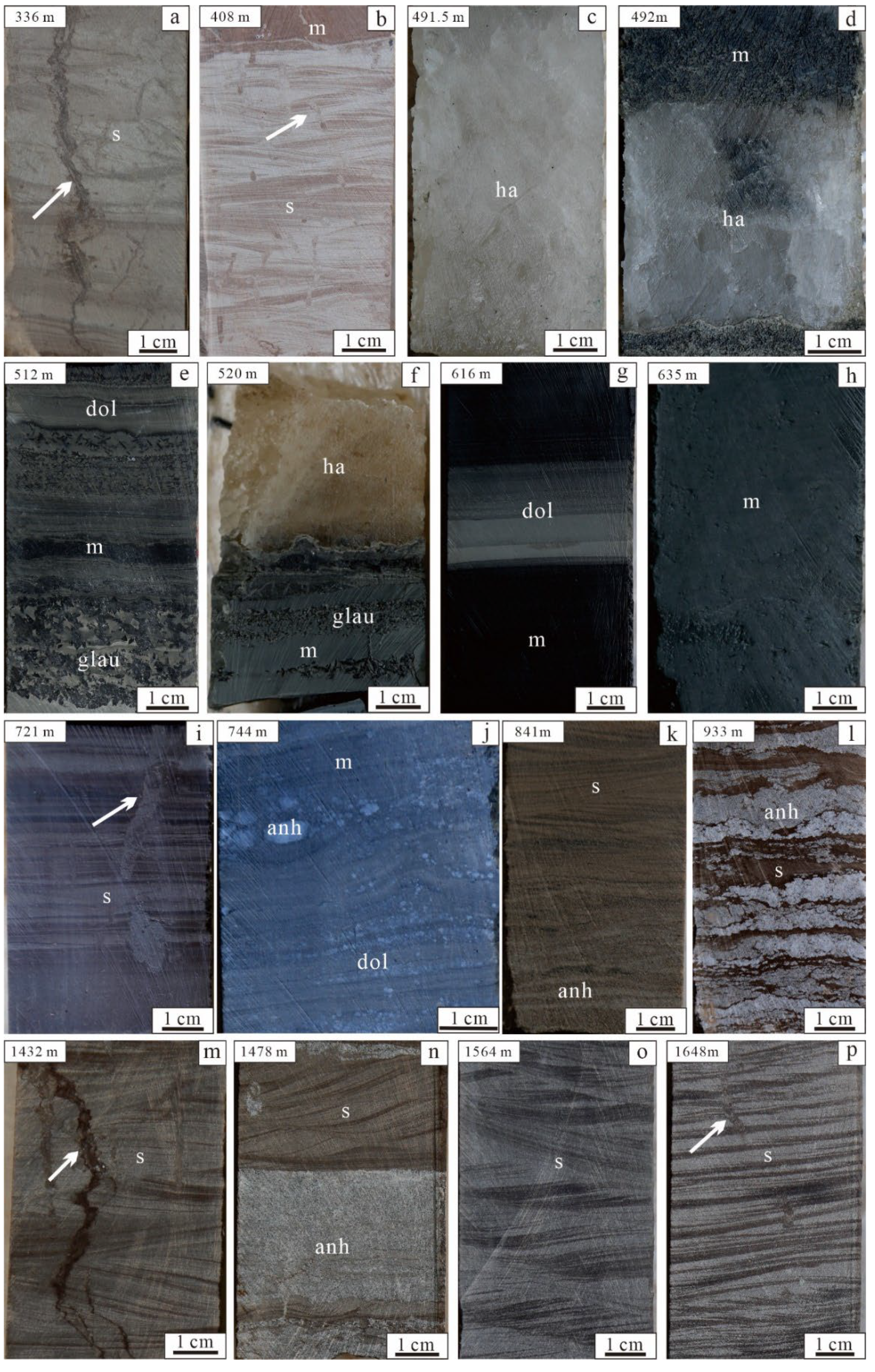
3. Sampling and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Major Elements Geochemistry
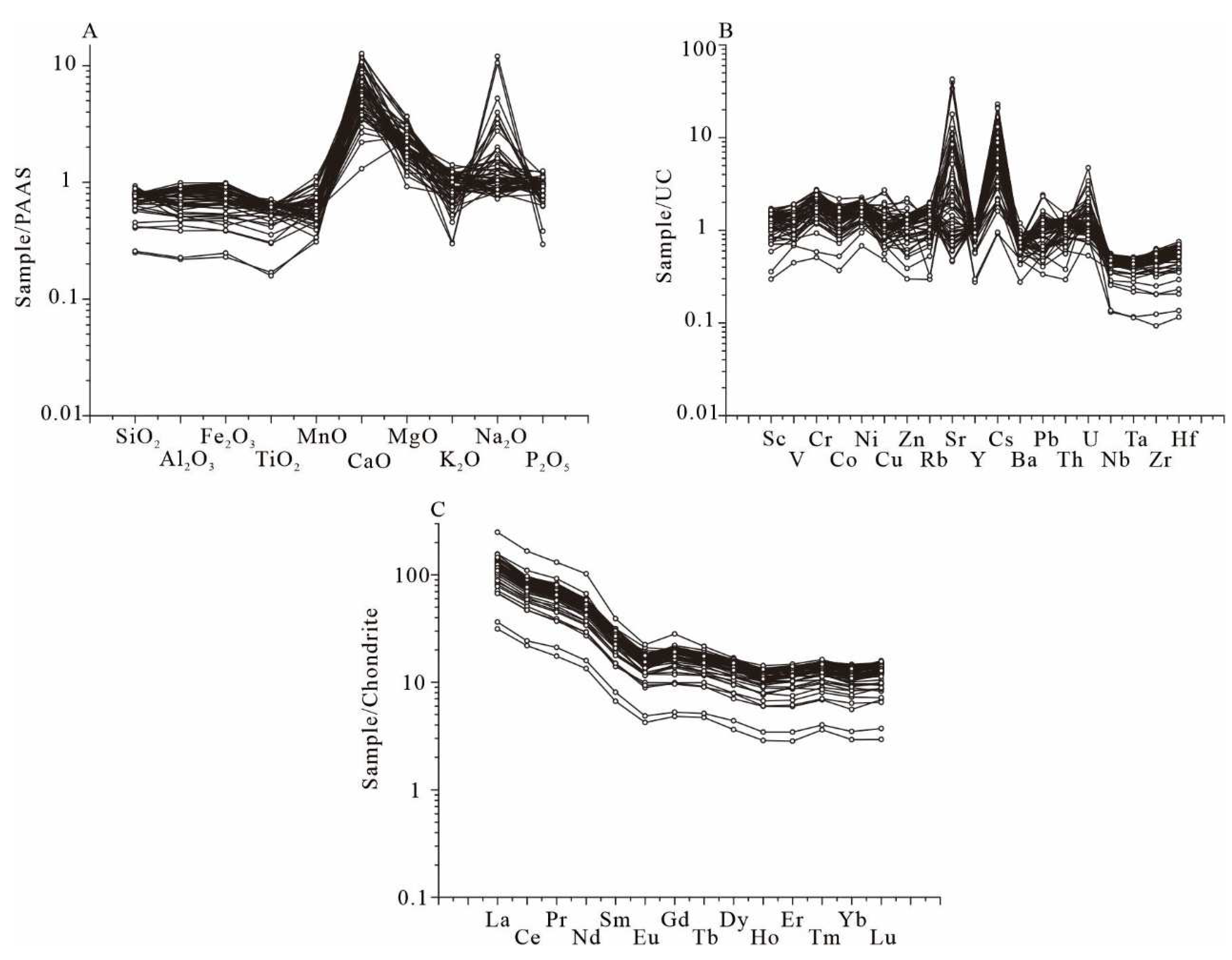
4.2. Trace and Rare Elements Geochemistry
5. Discussion
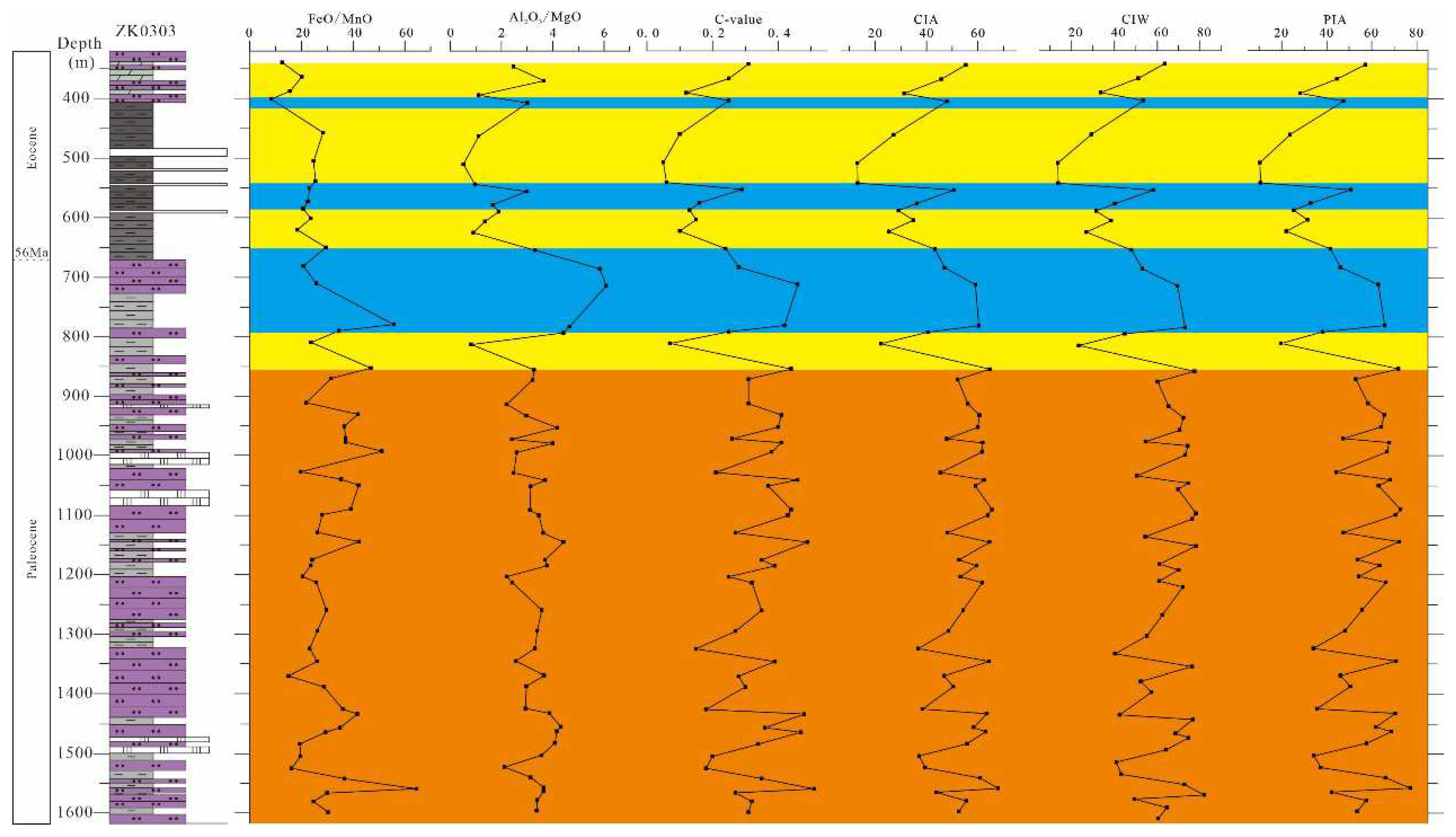
5.1. Palaeoclimate and Palaeoweathering
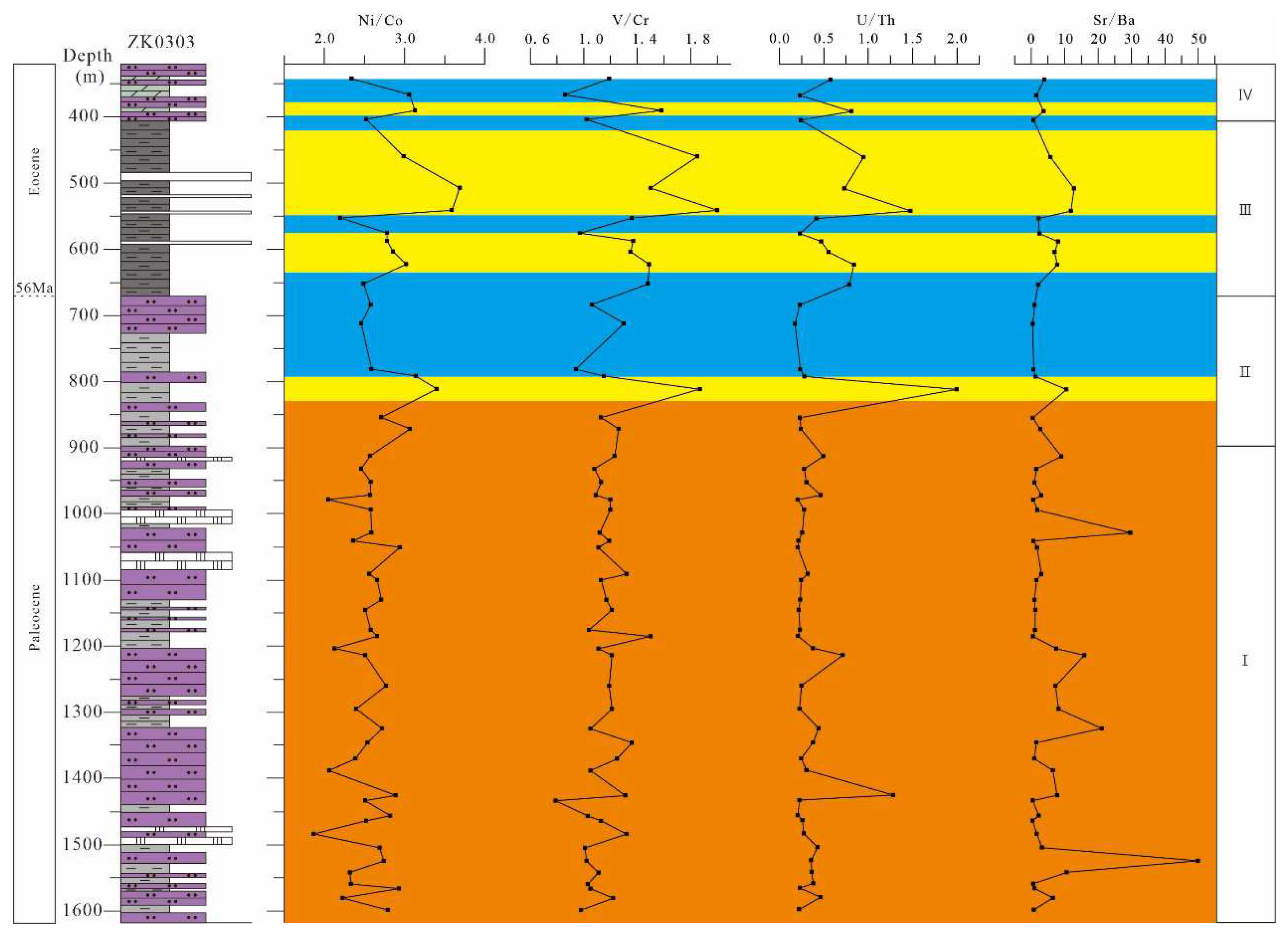
5.2. Redox Conditions
5.3. Palaeosalinty
- Playa-lake (stage Ⅰ):
- Brackish lake (stage Ⅱ):
- Saline lake (stage Ⅲ):
- Brackish playa-lake (stage Ⅳ):
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abels, H.A.; Lauretano, V.; Yperen, A.V.; Hopman, T.; Zachos, J.C.; Lourens, L.J.; Gingerich, P.D.; Bowen, G.J. Carbon isotope excursions in paleosol carbonate marking five early Eocene hyperthermals in the Bighorn Basin, Wyoming. Clim. Past 2015, 11, 1857–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, M.R.; Crook, K.A. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 1986, 92, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boynton, W.V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In Developments in Geochemistry; Henderson, P., Ed.; Elsevier, 1984; pp. 63–114. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.; Hu, K.; Bian, L.Z; Wang, L.G.; Zhang, Y. Trace and rare earth elements geochemistry of Jurassic mudstones in the northern Qaidam basin, northwest China. Chem. Erde-Geochem. 2012, 72, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, X. Late Paleoproterozoic sedimentary and mafic rocks in the Hekou area, SW China: Implication for the reconstruction of the Yangtze Block in Columbia. Precambrian Res. 2013, 231, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Ding, Z.L.; Tang, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.L. Early Eocene carbon isotope excursions: Evidence from the terrestrial coal seam in the Fushun Basin, Northeast China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3559–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.W. Discussion on the regional structural features of Jianghan Basin since the indosinian movement. J. Geomech. 1996, 04, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.G.; Zhang, C.C.; Huang, N.; Teng, L.; Li, C.H.; Shao, W.; Zeng, M. Geological significance of rare earth elements in marine shale of the upper Permian Dalong Formation in the lower Yangtze region, south China. Minerals 2023, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedo, C.M.; Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosoils, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 1995, 23, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.G.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.B.; Feng, X.L.; Wang, D.; Song, C.Y.; Zeng, S.Q. Elemental geochemistry of the early Jurassic black shales in the Qiangtang Basin, eastern Tethys: constraints for palaeoenvironment conditions. Geol. J. 2016, 51, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilder, S.A.; Keller, G.R.; Luo, M.; Goodell, P.C. Timing and spatial distribution of rifting in China. Tectonophysics 1991, 197, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.T.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Z.S.; Peng, S.Z.; Xiao, G.Q.; Ge, J.Y.; Hao, Q.Z.; Qiao, Y.S.; Liang, M.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Yin, Q.Z.; Wei, J.J. A major reorganization of Asian climate by the early Miocene. Clim. Past 2008, 4, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, L. The CIW index: a new chemical index of weathering. Sediment. Geol. 1988, 55, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Tada, R.; Jiang, X.; Suganuma, Y.; Imsamut, S.; Charusiri, P.; Ichinnorov, N.; Khand, Y. Drastic shrinking of the Hadley circulation during the mid-Cretaceous Supergreenhouse. Clim. Past 2012, 8, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzel, A.; März, C.; Vogt, C.; Brumsack, H.J. Geochemical environment of Cenomanian-Turonian black shale deposition at Wunstorf (northern Germany). Cretaceous Res. 2011, 32, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Raza, A.; Min, K.; Kohn, B.P.; Reiners, P.W.; Ketcham, R.A.; Wang, J.; Gleadow, A.J.W. Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic thermotectonic evolution along a transect from the north China craton through the Qinling orogen into the Yangtze craton, central China. Tectonics 2006, 25, TC6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.L.; Liu, Z.J.; Bechtel, A.; Strobl, S.A.I.; Sun, P.C. Tectonic and climate control of oil shale deposition in the Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation (Songliao Basin, NE China). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 102, 1717–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johanson, C.M.; Fu, Q. Hadley cell widening: model simulations versus observation. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, M.J. The system controlling the composition of clastic sediments. Geol. Soc. Amer. Spec. Pap. 1993, 284, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.; Manning, D.A.C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem. Geol. 1994, 111, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.N.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Yang, S.G.; Xu, H.M.; Yu, X.C.; Hu, H.B. A research on early Eocene homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions in halite and its paleoclimatic significance in Jiangling depression. Miner. Deposits (Beijing, China) 2016, 35, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.N.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Yang, S.G.; Xu, H.M.; Hu, H.B.; Yu, X.C.; Liu, J.L. Paleotemperatures of Early Eocene in the Jiangling depression: Evidence from fluid inclusions in thenardite. Acta Geol. Sin. 2015, 89, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Lu, S.; Xue, H.; Zhang, P.; Wu, S. The formation environment and developmental models of argillaceous dolomite in the Xingouzui Formation, the Jianghan Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 67, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhu, P.M.; Kusky, T.M.; Gu, Y.; Peng, S.B.; Yuan, Y.F.; Fu, J.M. Has the Yangtze craton lost its root? A comparison between the North China and Yangtze cratons. Tectonophysics 2015, 655, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L. Characteristics and formation of potash deposits in continental rift basins: a review. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 515–527. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Yu, X.C.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, L.C.; Xu, H.M.; Li, J.; Wang, C.L. A tentative discussion on regional metallogenic background and mineralization mechanism of subterranean brines rich in potassium and lithium in south China block. Miner. Deposits (Beijing, China) 2016, 35, 1119–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.L.; Zhao, Y.J.; Fang, X.M.; Lv, F.L.; Wang, L.C.; Yan, M.D.; Zhang, H.; Ding, T. Plate tectonic control on the distribution and formation of the marine potash deposits. Acta Geol. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 2015, 89, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Cui, X.J.; Liu, F.T. Cenozoic rifting and volcanism in eastern China: a mantle dynamic link to the Indo-Asian collision? Tectonophysics 2004, 393, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Vecchi, G.A.; Reichler, T. Expansion of Hadley cell under global warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L06805. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, S.M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 1989, 21, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.; McDaniel, D.K.; Hanson, G.N. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics. Spec. Pap. - Geol. Soc. Am. 1993, 284, 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- McLennan, S.M.; Hemming, S.R.; Taylor, S.R.; Eriksson, K.A. Early Proterozoic crustal evolution: geochemical and Nd-Pb isotopic evidence from metasedimentary rocks, southwestern North America. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1153–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.T.; Liu, Z.J.; Bruch, A.A.; Liu, R.; Hu, F. Palaeoclimatic evolution during Eocene and its influence on oil shale mineralisation, Fushun Basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 45, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Van der Weijden, C.H.; Woittiez, J.R.W. Chemical processes affecting the mobility of major, minor and trace elements during weathering of granitic rocks. Chem. Geol. 1988, 68, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Young, G.M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic-rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Bera, M.K.; Ghosh, R.; Bera, S.; Filley, T.; Pande, K.; Rathore, S.S.; Rai, J.; Sarkar, A. Do the large carbon isotopic excursions in terrestrial organic matter across Paleocene-Eocene boundary in India indicate intensification of tropical precipitation? Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2013, 387, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.B.; Donelick, R.A.; O’Sullivan, P.B.; Jonckheere, R.; Yang, Z.; She, Z.B.; Miu, X.L.; Ge, X. Provenance and hinterland exhumation from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb and fission-track double dating of Cretaceous sediments in the Jianghan Basin, Yangtze block, central China. Sediment. Geol. 2012, 281, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.J.; Liu, C.L.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, L.C.; Liu, B.K.; Zhang, L.B. Paleocene mineral assemblage characteristics of Jianghan depression and their significance for potash formation. Miner. Deposits (Beijing, China) 2014, 33, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.S.; Faure, M.; Wang, B.; Zhou, X.M.; Song, B. Late Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic geological features of South China: Response to the Indosinian collision events in Southeast Asia. C. R. Geosci. 2008, 340, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.J.; Wang, P.X. How old is the Asian monsoon system? Palaeobotanical records from China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2005, 222, 181–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. J. Geol. 1985, 94, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, X.H.; Fang, X.M.; Kaufman, A.J.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Zan, J.B.; Yang, Y.B.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, H.M.; Schulte, R.F.; Piatak, N.M. Sedimentological and mineralogical records from drill core SKD1 in the Jianghan Basin, Central China, and their implications for late Cretaceous-early Eocene climate change. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 182, 103936.1–10393614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.H.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Yan, K.; Luo, Z. Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum lacustrine sediments in deep drill core SKD1 in the Jianghan Basin: a record of enhanced precipitation in central China. Glob. Planet. Change 2021, 205, 103620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribovillard, N.; Algeo, T.J.; Lyons, T.; Riboulleau, A. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chem. Geol. 2006, 232, 12–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanas, H.A.; Assal, E.M. Provenance, tectonic setting and source area-paleoweathering of sandstones of the Bahariya Formation in the Bahariya Oasis, Egypt: An implication to paleoclimate and paleogeography of the southern Neo-Tethys region during Early Cenomanian. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 413, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, X.C.; Yan, K. Palynology and stratigraphy of the thick evaporate-bearing Shashi Formation in Jiangling Depression, Jianghan Basin of South China, and its paleoclimate change. China Geol. 2020, 2, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, L.C.; Zhang, L.B. Carbon and oxygen isotopes characteristics of Paleocene saline lake facies carbonates in Jiangling depression and their environmental significance. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2013, 34, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Yan, K.; Yu, X.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, D.H.; Shen, L.J; Li, R.Q.; You, C. 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Volcanic Rocks in the Jiangling Basin, China. Minerals 2022, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Yu, X.C.; Li, R.Q.; Yan, K.; You, C. Origin of lithium-potassium brines in the Jianghan Basin, South China: constraints by water-rock reactions of Mesozoic-Cenozoic igneous rocks. Minerals 2021, 11, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worash, G. Geochemistry provenance and tectonic setting of the Adigrat sandstone northern Ethiopia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2002, 35, 185–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.L.; Mei, L.F.; Liu, Y.S.; Luo, J.; Min, C.Z.; Lu, S.L.; Li, M.H.; Guo, L.B. Multiple provenance of rift sediments in the composite basin-mountain system: constraints from detrital Zircon U-Pb geochronology and heavy minerals of the early Eocene Jianghan Basin, Central China. Sediment. Geol. 2017, 349, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.L.; Wu, F.L.; Fang, X.M. A transient south subtropical forest ecosystem in central China driven by rapid global warming during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum. Gondwana Res. 2022, 101, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, C.L.; Mischke, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, X.C. Reconstruction of early Paleogene landscapes and climate in the Jianghan Basin, central China: Evidence from evaporates and palynology. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2022, 601, 111095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.Q.; Chen, K.Q.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Zhan, H.J. Constituent evolution and exploration potential in Jianghan depression. Nat. Gas Ind. 2003, 23, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.H.; Li, Z.X.; Li, W.X.; Su, L.; Yang, J.H. Detrital provenance evolution of the Ediacaran-Silurian Nanhua foreland basin, South China. Gondwana Res. 2015, 28, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.C.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Li, H.N. Sedimentary characteristics and palaeoclimatic significance of glauberite in Paleocene lacustrine deposits of the Jiangling depression, central China. Geosci. J. 2018, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.C.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, C.L.; Xu, H.M. Provenance of rift sediments in a composite basin-mountain system: constraints from petrography, whole-rock geochemistry, and detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Paleocene Shashi Formation, southwestern Jianghan Basin, central China. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2018, 107, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Q.; Shu, L.S.; Deng, P.; Wang, B.; Zu, F.P. The sedimentary features of the Jurassic-Tertiary terrestrial strata in southeast China. J. Stratigr. 2003, 27, 224–263. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.F.; Sun, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Li, Y.F.; Ma, H.L.; Lu, C.; Yang, C.; Guo, G.W. Geochemical characteristics of the Jurassic Yan’an and Zhiluo Formations in the northern margin of Ordos Basin and their paleoenvironmental implications. Acta Geol. Sin. 2016, 90, 3454–3472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, H.J.; Liao, J.D.; Liu, C.M. Distribution characteristics and applications of trace elements in Junggar Basin. Nat. Gas Explor. Dev. 2007, 30, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
| No. | Depth | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | MnO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | P2O5 | FeO | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | wt% | |
| ZK1 | 339 | 43.84 | 14.49 | 5.47 | 0.61 | 0.12 | 7.67 | 5.87 | 3.37 | 1.19 | 0.16 | 1.54 | 16.9 |
| ZK2 | 363 | 58.40 | 10.13 | 3.79 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 8.10 | 2.77 | 2.36 | 1.93 | 0.12 | 1.45 | 11.4 |
| ZK3 | 387 | 27.91 | 8.73 | 3.21 | 0.34 | 0.11 | 15.98 | 7.87 | 1.91 | 1.70 | 0.12 | 1.68 | 11.5 |
| ZK4 | 400.5 | 52.83 | 11.96 | 4.28 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 8.45 | 3.97 | 2.55 | 2.31 | 0.11 | 0.90 | 12.3 |
| ZK5 | 457 | 25.56 | 8.04 | 2.76 | 0.30 | 0.05 | 15.98 | 7.30 | 1.97 | 3.91 | 0.12 | 1.45 | 20.1 |
| ZK6 | 504.5 | 15.65 | 4.14 | 1.65 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 11.85 | 8.09 | 1.12 | 14.44 | 0.06 | 0.84 | 16.7 |
| ZK7 | 538.5 | 16.13 | 4.27 | 1.79 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 14.32 | 4.44 | 1.10 | 12.62 | 0.05 | 0.94 | 14.3 |
| ZK8 | 550 | 43.88 | 13.52 | 5.17 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 6.34 | 4.53 | 3.42 | 3.82 | 0.13 | 1.78 | 16.6 |
| ZK9 | 573 | 37.08 | 9.65 | 3.61 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 10.50 | 5.81 | 2.62 | 4.20 | 0.10 | 1.35 | 18.0 |
| ZK10 | 585 | 28.37 | 8.89 | 3.37 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 13.38 | 4.72 | 2.29 | 6.30 | 0.11 | 1.20 | 15.2 |
| ZK11 | 601 | 35.55 | 9.57 | 3.79 | 0.41 | 0.08 | 13.38 | 7.06 | 2.52 | 2.39 | 0.13 | 1.94 | 22.1 |
| ZK12 | 620.5 | 26.33 | 7.25 | 2.80 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 15.29 | 8.03 | 1.68 | 4.75 | 0.10 | 1.29 | 22.5 |
| ZK13 | 650 | 40.97 | 12.08 | 4.74 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 10.42 | 3.65 | 2.74 | 3.30 | 0.19 | 2.24 | 16.2 |
| ZK14 | 681.5 | 55.94 | 11.79 | 4.34 | 0.61 | 0.08 | 8.76 | 2.02 | 2.87 | 1.99 | 0.10 | 1.60 | 11.0 |
| ZK15 | 710 | 51.70 | 16.26 | 6.49 | 0.66 | 0.06 | 5.28 | 2.67 | 4.12 | 2.25 | 0.11 | 1.44 | 9.9 |
| ZK16 | 779.5 | 49.33 | 16.76 | 6.30 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 4.87 | 3.60 | 4.83 | 1.82 | 0.15 | 2.51 | 11.1 |
| ZK17 | 790 | 50.12 | 11.01 | 4.77 | 0.64 | 0.06 | 11.91 | 2.49 | 2.63 | 2.01 | 0.12 | 1.90 | 13.8 |
| ZK18 | 809.9 | 22.91 | 6.29 | 2.18 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 19.37 | 7.74 | 1.23 | 1.61 | 0.10 | 1.90 | 10.7 |
| ZK19 | 853 | 49.94 | 16.84 | 6.57 | 0.68 | 0.06 | 3.85 | 5.14 | 4.33 | 1.69 | 0.19 | 2.72 | 17.1 |
| ZK20 | 870 | 43.87 | 14.42 | 5.55 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 8.57 | 4.49 | 3.68 | 1.44 | 0.14 | 1.61 | 10.6 |
| ZK21 | 911.5 | 41.73 | 15.22 | 6.06 | 0.52 | 0.09 | 7.28 | 6.93 | 3.87 | 1.46 | 0.20 | 1.90 | 10.8 |
| ZK22 | 930.5 | 45.32 | 16.36 | 6.86 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 5.55 | 5.51 | 4.40 | 1.29 | 0.17 | 2.22 | 9.6 |
| ZK23 | 951 | 48.27 | 16.64 | 6.23 | 0.63 | 0.06 | 5.57 | 3.98 | 4.14 | 1.92 | 0.16 | 2.01 | 14.7 |
| ZK24 | 970.5 | 40.03 | 13.35 | 5.30 | 0.50 | 0.06 | 10.50 | 5.55 | 3.38 | 1.09 | 0.14 | 2.26 | 13.3 |
| ZK25 | 977.5 | 47.69 | 17.13 | 6.27 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 5.21 | 4.29 | 4.60 | 1.25 | 0.16 | 1.93 | 11.9 |
| ZK26 | 993 | 45.97 | 15.97 | 6.25 | 0.56 | 0.04 | 5.13 | 6.15 | 4.12 | 1.32 | 0.17 | 2.20 | 12.7 |
| ZK27 | 1027.5 | 51.74 | 10.46 | 3.87 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 9.25 | 4.22 | 2.33 | 1.44 | 0.13 | 1.56 | 12.8 |
| ZK28 | 1040 | 48.54 | 16.68 | 6.83 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 5.17 | 4.50 | 4.32 | 1.08 | 0.15 | 2.02 | 14.9 |
| ZK29 | 1050 | 45.90 | 15.57 | 6.03 | 0.56 | 0.05 | 6.31 | 4.97 | 4.05 | 0.97 | 0.16 | 2.02 | 12.0 |
| ZK30 | 1090 | 47.59 | 17.58 | 6.82 | 0.62 | 0.06 | 4.43 | 5.65 | 4.34 | 1.09 | 0.18 | 2.19 | 12.0 |
| ZK31 | 1099.5 | 48.27 | 17.07 | 6.44 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 4.78 | 4.94 | 4.36 | 1.08 | 0.17 | 1.91 | 11.2 |
| ZK32 | 1129.5 | 51.33 | 12.46 | 4.66 | 0.63 | 0.06 | 9.67 | 3.43 | 3.00 | 1.21 | 0.12 | 1.52 | 13.0 |
| ZK33 | 1145 | 48.35 | 17.61 | 6.95 | 0.64 | 0.05 | 4.51 | 3.98 | 4.74 | 0.99 | 0.16 | 2.28 | 11.5 |
| ZK34 | 1175 | 47.81 | 14.60 | 6.07 | 0.65 | 0.07 | 8.79 | 3.95 | 3.76 | 1.04 | 0.15 | 1.74 | 12.6 |
| ZK35 | 1185 | 48.63 | 16.42 | 6.21 | 0.63 | 0.07 | 6.40 | 4.35 | 4.20 | 1.10 | 0.15 | 1.70 | 11.3 |
| ZK36 | 1203.5 | 42.85 | 14.59 | 4.87 | 0.56 | 0.10 | 8.87 | 6.60 | 3.43 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 2.04 | 16.5 |
| ZK37 | 1213.5 | 46.39 | 16.34 | 5.71 | 0.66 | 0.09 | 5.77 | 6.76 | 3.80 | 1.21 | 0.18 | 2.26 | 13.1 |
| ZK38 | 1260 | 50.10 | 14.15 | 5.75 | 0.66 | 0.06 | 7.89 | 3.96 | 3.39 | 1.18 | 0.16 | 1.84 | 12.2 |
| ZK39 | 1295 | 40.04 | 13.50 | 4.96 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 10.47 | 3.98 | 3.31 | 0.90 | 0.13 | 1.57 | 11.1 |
| ZK40 | 1325 | 39.47 | 9.79 | 3.08 | 0.52 | 0.06 | 13.90 | 2.96 | 2.28 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 1.44 | 11.3 |
| ZK41 | 1346.5 | 48.45 | 16.38 | 6.19 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 4.57 | 6.40 | 3.94 | 1.05 | 0.16 | 2.11 | 11.8 |
| ZK42 | 1370.5 | 52.52 | 11.72 | 4.64 | 0.63 | 0.11 | 9.54 | 3.20 | 2.55 | 1.64 | 0.14 | 1.59 | 12.9 |
| ZK43 | 1388.5 | 47.69 | 13.29 | 5.39 | 0.65 | 0.07 | 9.42 | 4.48 | 3.17 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 1.98 | 13.5 |
| ZK44 | 1426.5 | 36.28 | 12.75 | 4.57 | 0.46 | 0.07 | 16.50 | 4.34 | 3.16 | 1.27 | 0.15 | 2.45 | 17.9 |
| ZK45 | 1434.5 | 49.47 | 16.79 | 7.01 | 0.66 | 0.05 | 4.84 | 4.34 | 4.53 | 0.86 | 0.17 | 2.25 | 10.7 |
| ZK46 | 1457.5 | 50.46 | 15.80 | 5.60 | 0.71 | 0.05 | 6.79 | 3.66 | 4.04 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 1.89 | 11.7 |
| ZK47 | 1465 | 51.78 | 16.31 | 6.58 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 4.91 | 3.92 | 4.05 | 1.17 | 0.15 | 1.94 | 10.3 |
| ZK48 | 1485 | 54.15 | 13.76 | 5.00 | 0.63 | 0.09 | 6.85 | 3.37 | 3.23 | 1.31 | 0.14 | 1.72 | 10.9 |
| ZK49 | 1505.5 | 38.27 | 11.79 | 4.63 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 16.44 | 3.31 | 2.86 | 1.00 | 0.11 | 2.08 | 14.2 |
| ZK50 | 1525.5 | 51.27 | 9.04 | 3.54 | 0.57 | 0.11 | 11.15 | 4.27 | 1.94 | 1.17 | 0.12 | 1.78 | 14.5 |
| ZK51 | 1543 | 46.84 | 16.56 | 5.87 | 0.61 | 0.07 | 5.86 | 5.28 | 4.41 | 0.94 | 0.18 | 2.60 | 12.0 |
| ZK52 | 1560.5 | 49.50 | 17.71 | 7.05 | 0.65 | 0.05 | 3.44 | 4.86 | 4.54 | 0.96 | 0.15 | 3.49 | 9.1 |
| ZK53 | 1567 | 50.03 | 11.60 | 4.91 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 11.30 | 3.19 | 2.88 | 1.09 | 0.14 | 1.74 | 13.9 |
| ZK54 | 1581.5 | 47.64 | 14.62 | 5.24 | 0.60 | 0.08 | 7.49 | 4.31 | 3.70 | 1.04 | 0.15 | 2.00 | 13.1 |
| ZK55 | 1599.5 | 55.45 | 12.25 | 4.70 | 0.61 | 0.06 | 7.22 | 3.64 | 3.01 | 1.25 | 0.14 | 1.88 | 11.6 |
| No. | Depth | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Rb | Sr | Y | Cs | Ba | Pb | Th | U | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | |
| ZK1 | 339 | 14.3 | 90.7 | 75.9 | 15.7 | 36.8 | 36.0 | 83.7 | 18.8 | 141.0 | 1440.0 | 21.1 | 15.3 | 363.0 | 22.2 | 9.3 | 5.4 | 12.2 | 0.9 | 88.3 | 2.6 | 93.5 |
| ZK2 | 363 | 9.4 | 47.0 | 54.8 | 8.0 | 24.4 | 49.7 | 51.6 | 12.6 | 93.0 | 498.0 | 18.3 | 8.0 | 344.0 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 1.5 | 9.3 | 0.7 | 75.7 | 2.2 | 62.4 |
| ZK3 | 387 | 8.6 | 70.5 | 44.6 | 9.0 | 28.1 | 23.0 | 65.9 | 11.1 | 78.6 | 1033.0 | 13.8 | 7.0 | 276.0 | 17.4 | 6.9 | 5.6 | 7.1 | 0.5 | 51.7 | 1.7 | 75.8 |
| ZK4 | 400.5 | 11.3 | 67.4 | 66.3 | 12.6 | 31.8 | 17.5 | 65.3 | 15.3 | 105.0 | 256.0 | 23.0 | 7.6 | 412.0 | 14.0 | 10.2 | 2.5 | 12.1 | 1.0 | 103.0 | 3.5 | 94.1 |
| ZK5 | 457 | 7.9 | 75.6 | 40.8 | 8.6 | 25.8 | 24.5 | 36.3 | 10.4 | 73.5 | 1353.0 | 12.4 | 8.1 | 236.0 | 10.6 | 7.4 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 0.5 | 38.8 | 1.2 | 74.9 |
| ZK6 | 504.5 | 3.3 | 26.7 | 17.8 | 3.7 | 13.6 | 12.0 | 21.2 | 4.2 | 33.0 | 3393.0 | 6.1 | 3.4 | 265.0 | 5.0 | 3.1 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 0.3 | 23.6 | 0.8 | 86.6 |
| ZK7 | 538.5 | 3.9 | 40.9 | 20.4 | 5.2 | 18.8 | 39.0 | 122.0 | 5.3 | 36.0 | 1803.0 | 6.5 | 3.5 | 152.0 | 8.2 | 4.0 | 6.0 | 3.4 | 0.3 | 17.7 | 0.7 | 63.6 |
| ZK8 | 550 | 13.9 | 87.8 | 64.5 | 13.8 | 30.3 | 43.1 | 61.6 | 18.1 | 117.0 | 834.0 | 21.7 | 10.5 | 390.0 | 18.4 | 14.2 | 5.9 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 59.6 | 2.2 | 180.0 |
| ZK9 | 573 | 9.2 | 47.2 | 48.8 | 9.2 | 25.6 | 16.8 | 43.6 | 12.3 | 94.2 | 948.0 | 16.8 | 7.2 | 383.0 | 9.2 | 8.9 | 2.1 | 9.2 | 0.7 | 64.7 | 2.3 | 157.0 |
| ZK10 | 585 | 8.6 | 58.8 | 42.9 | 8.8 | 24.6 | 22.5 | 38.9 | 11.1 | 81.0 | 3345.0 | 13.2 | 7.3 | 416.0 | 12.6 | 7.0 | 3.3 | 7.2 | 0.6 | 47.5 | 1.7 | 150.0 |
| ZK11 | 601 | 9.5 | 70.8 | 52.3 | 10.3 | 29.5 | 32.5 | 40.5 | 13.1 | 105.0 | 3798.0 | 17.3 | 12.0 | 542.0 | 9.6 | 8.1 | 4.5 | 8.6 | 0.7 | 66.5 | 2.1 | 159.0 |
| ZK12 | 620.5 | 6.5 | 48.5 | 32.5 | 7.2 | 21.8 | 17.4 | 27.5 | 8.4 | 58.6 | 3414.0 | 12.5 | 6.0 | 437.0 | 13.5 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 6.4 | 0.5 | 38.8 | 1.3 | 90.2 |
| ZK13 | 650 | 12.6 | 92.3 | 62.4 | 13.3 | 33.1 | 34.7 | 56.2 | 16.4 | 112.0 | 609.0 | 19.4 | 11.1 | 298.0 | 21.8 | 12.1 | 9.5 | 11.2 | 0.9 | 64.6 | 2.0 | 130.0 |
| ZK14 | 681.5 | 10.8 | 61.2 | 57.5 | 10.1 | 26.1 | 29.6 | 78.3 | 14.2 | 111.0 | 446.0 | 21.4 | 7.8 | 466.0 | 9.6 | 9.2 | 2.1 | 12.1 | 0.9 | 91.7 | 3.1 | 122.0 |
| ZK15 | 710 | 15.1 | 96.7 | 74.5 | 14.5 | 35.7 | 13.9 | 77.8 | 21.0 | 147.0 | 209.0 | 24.1 | 12.5 | 480.0 | 14.2 | 13.4 | 2.4 | 13.0 | 1.0 | 113.0 | 4.0 | 194.0 |
| ZK16 | 779.5 | 16.4 | 90.5 | 96.1 | 16.3 | 42.2 | 25.8 | 85.2 | 22.5 | 195.0 | 280.0 | 24.1 | 32.0 | 411.0 | 14.2 | 14.6 | 3.4 | 11.9 | 1.1 | 97.1 | 3.5 | 163.0 |
| ZK17 | 790 | 10.4 | 69.1 | 60.0 | 9.4 | 29.6 | 21.7 | 60.6 | 13.4 | 113.0 | 339.0 | 22.2 | 17.8 | 270.0 | 9.4 | 11.6 | 3.3 | 12.7 | 1.1 | 87.3 | 3.2 | 93.3 |
| ZK18 | 809.9 | 5.6 | 58.7 | 31.4 | 7.1 | 24.1 | 20.3 | 38.9 | 7.3 | 55.0 | 3208.0 | 9.1 | 10.4 | 303.0 | 28.3 | 6.6 | 13.1 | 5.3 | 0.4 | 35.6 | 1.4 | 51.4 |
| ZK19 | 853 | 15.2 | 89.0 | 78.7 | 13.0 | 35.2 | 29.1 | 88.6 | 20.8 | 163.0 | 165.0 | 24.9 | 19.9 | 414.0 | 7.5 | 14.0 | 3.2 | 13.3 | 1.1 | 98.5 | 3.8 | 200.0 |
| ZK20 | 870 | 13.1 | 82.8 | 65.9 | 10.2 | 31.3 | 19.8 | 68.3 | 17.8 | 138.0 | 1012.0 | 20.1 | 18.1 | 379.0 | 6.8 | 10.8 | 2.6 | 10.5 | 0.9 | 81.5 | 3.0 | 149.0 |
| ZK21 | 911.5 | 15.9 | 96.8 | 78.9 | 14.9 | 38.3 | 46.2 | 107.0 | 21.3 | 173.0 | 3874.0 | 21.9 | 30.3 | 431.0 | 13.3 | 11.2 | 5.5 | 12.1 | 0.8 | 92.8 | 3.0 | 182.0 |
| ZK22 | 930.5 | 17.0 | 90.4 | 83.6 | 16.9 | 41.5 | 62.7 | 89.5 | 21.8 | 186.0 | 692.0 | 24.3 | 24.7 | 472.0 | 17.1 | 14.0 | 3.9 | 12.6 | 1.0 | 94.4 | 3.3 | 207.0 |
| ZK23 | 951 | 16.5 | 88.9 | 78.6 | 15.8 | 40.8 | 40.1 | 78.2 | 21.4 | 175.0 | 415.0 | 24.7 | 22.4 | 431.0 | 36.2 | 10.9 | 3.3 | 11.8 | 1.0 | 103.0 | 3.6 | 179.0 |
| ZK24 | 970.5 | 13.4 | 79.4 | 72.6 | 15.0 | 38.6 | 29.9 | 78.2 | 17.2 | 168.0 | 1040.0 | 19.2 | 65.5 | 355.0 | 20.3 | 12.4 | 5.8 | 10.8 | 0.9 | 83.4 | 2.9 | 130.0 |
| ZK25 | 977.5 | 17.8 | 114.0 | 94.8 | 21.9 | 45.0 | 31.0 | 96.0 | 22.6 | 203.0 | 303.0 | 23.9 | 30.8 | 499.0 | 17.0 | 14.7 | 3.0 | 14.0 | 1.0 | 96.7 | 3.5 | 198.0 |
| ZK26 | 993 | 16.1 | 102.0 | 84.7 | 16.7 | 43.1 | 28.8 | 92.7 | 19.4 | 205.0 | 666.0 | 22.0 | 52.1 | 362.0 | 9.8 | 11.6 | 3.2 | 11.1 | 1.0 | 88.7 | 2.8 | 176.0 |
| ZK27 | 1027.5 | 9.0 | 55.2 | 49.5 | 10.1 | 26.2 | 17.8 | 58.7 | 11.1 | 104.0 | 11837.0 | 19.2 | 31.1 | 399.0 | 9.1 | 8.7 | 2.3 | 10.8 | 0.8 | 84.7 | 2.6 | 84.7 |
| ZK28 | 1040 | 16.7 | 103.0 | 86.7 | 18.2 | 42.9 | 26.4 | 98.9 | 21.6 | 204.0 | 272.0 | 25.8 | 39.5 | 361.0 | 14.3 | 13.1 | 2.8 | 13.1 | 1.0 | 100.0 | 3.5 | 137.0 |
| ZK29 | 1050 | 16.5 | 95.2 | 85.6 | 13.8 | 40.6 | 20.3 | 97.7 | 21.2 | 204.0 | 639.0 | 22.8 | 50.2 | 370.0 | 8.9 | 12.4 | 2.6 | 11.2 | 0.9 | 82.8 | 3.1 | 138.0 |
| ZK30 | 1090 | 16.9 | 114.0 | 86.3 | 15.4 | 39.5 | 34.5 | 107.0 | 21.6 | 198.0 | 1247.0 | 23.6 | 50.8 | 410.0 | 15.3 | 13.7 | 4.4 | 12.6 | 1.0 | 96.6 | 3.7 | 154.0 |
| ZK31 | 1099.5 | 17.3 | 102.0 | 90.1 | 15.7 | 41.7 | 36.2 | 111.0 | 21.8 | 200.0 | 673.0 | 26.0 | 40.0 | 427.0 | 17.6 | 14.3 | 3.5 | 12.8 | 1.0 | 99.7 | 3.8 | 144.0 |
| ZK32 | 1129.5 | 11.8 | 73.7 | 63.2 | 12.1 | 32.8 | 20.4 | 76.0 | 14.9 | 129.0 | 289.0 | 21.4 | 25.8 | 311.0 | 11.8 | 11.8 | 2.8 | 12.3 | 1.0 | 83.9 | 3.0 | 99.9 |
| ZK33 | 1145 | 17.9 | 114.0 | 93.9 | 16.6 | 41.7 | 30.6 | 105.0 | 23.1 | 219.0 | 502.0 | 25.8 | 45.9 | 439.0 | 14.9 | 15.3 | 3.3 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 101.0 | 3.7 | 160.0 |
| ZK34 | 1175 | 14.4 | 74.7 | 72.1 | 15.1 | 39.0 | 26.1 | 90.4 | 18.6 | 167.0 | 380.0 | 24.7 | 34.1 | 356.0 | 18.3 | 12.8 | 3.0 | 12.7 | 1.0 | 92.7 | 3.4 | 156.0 |
| ZK35 | 1185 | 17.2 | 102.0 | 68.0 | 14.1 | 37.5 | 25.0 | 102.0 | 22.0 | 194.0 | 212.0 | 25.7 | 39.6 | 411.0 | 14.5 | 14.1 | 2.9 | 13.3 | 1.1 | 110.0 | 3.8 | 140.0 |
| ZK36 | 1203.5 | 14.1 | 77.9 | 70.0 | 18.8 | 40.1 | 38.7 | 86.6 | 17.6 | 166.0 | 3076.0 | 22.2 | 58.6 | 406.0 | 20.7 | 11.8 | 4.5 | 10.9 | 0.9 | 88.6 | 3.3 | 45.0 |
| ZK37 | 1213.5 | 15.0 | 85.2 | 70.6 | 14.6 | 36.6 | 29.5 | 89.9 | 18.2 | 167.0 | 6262.0 | 23.0 | 53.6 | 393.0 | 13.1 | 12.1 | 8.6 | 12.3 | 1.0 | 92.5 | 3.5 | 146.0 |
| ZK38 | 1260 | 13.4 | 80.2 | 67.4 | 12.0 | 33.2 | 22.5 | 84.3 | 17.1 | 147.0 | 3030.0 | 23.0 | 34.6 | 414.0 | 16.2 | 12.7 | 3.2 | 12.4 | 1.1 | 89.4 | 3.4 | 125.0 |
| ZK39 | 1295 | 13.2 | 75.3 | 62.3 | 15.1 | 36.3 | 24.5 | 80.9 | 16.9 | 155.0 | 3024.0 | 20.3 | 54.5 | 370.0 | 24.1 | 11.7 | 2.6 | 10.0 | 0.9 | 86.2 | 3.2 | 149.0 |
| ZK40 | 1325 | 8.3 | 48.7 | 46.2 | 9.5 | 25.8 | 16.5 | 51.5 | 10.4 | 95.9 | 13868.0 | 14.9 | 25.1 | 656.0 | 9.1 | 8.5 | 3.8 | 9.3 | 0.8 | 72.1 | 2.5 | 105.0 |
| ZK41 | 1346.5 | 16.3 | 74.0 | 54.3 | 13.6 | 34.6 | 25.9 | 93.3 | 20.1 | 189.0 | 708.0 | 24.5 | 50.5 | 450.0 | 9.3 | 12.5 | 4.7 | 12.0 | 1.0 | 102.0 | 3.9 | 138.0 |
| ZK42 | 1370.5 | 11.7 | 69.5 | 55.8 | 12.2 | 29.2 | 20.8 | 75.9 | 14.4 | 114.0 | 323.0 | 25.8 | 22.3 | 357.0 | 16.3 | 11.5 | 2.8 | 13.1 | 1.1 | 102.0 | 4.0 | 103.0 |
| ZK43 | 1388.5 | 13.0 | 68.8 | 65.6 | 19.0 | 39.1 | 28.1 | 83.1 | 15.6 | 144.0 | 2288.0 | 23.6 | 39.9 | 356.0 | 20.1 | 12.3 | 3.7 | 12.3 | 1.0 | 94.2 | 3.4 | 122.0 |
| ZK44 | 1426.5 | 12.2 | 79.2 | 60.5 | 12.5 | 36.1 | 47.5 | 142.0 | 15.3 | 153.0 | 2804.0 | 18.8 | 84.6 | 363.0 | 13.8 | 10.3 | 13.2 | 8.8 | 0.7 | 70.4 | 2.5 | 96.9 |
| ZK45 | 1434.5 | 17.4 | 61.6 | 77.9 | 16.4 | 41.1 | 25.8 | 101.0 | 21.2 | 216.0 | 161.0 | 26.0 | 61.9 | 389.0 | 14.5 | 15.0 | 3.4 | 13.4 | 1.1 | 99.5 | 3.6 | 147.0 |
| ZK46 | 1457.5 | 15.9 | 60.4 | 58.7 | 13.1 | 36.9 | 21.1 | 89.0 | 19.1 | 202.0 | 816.0 | 26.0 | 61.8 | 366.0 | 10.0 | 14.5 | 3.0 | 13.8 | 1.1 | 111.0 | 4.1 | 113.0 |
| ZK47 | 1465 | 16.2 | 72.9 | 64.5 | 13.8 | 34.8 | 25.6 | 89.4 | 20.4 | 178.0 | 165.0 | 27.9 | 42.2 | 456.0 | 13.3 | 13.0 | 3.4 | 13.3 | 1.1 | 116.0 | 4.4 | 116.0 |
| ZK48 | 1485 | 13.2 | 87.5 | 66.5 | 18.2 | 34.1 | 67.9 | 85.2 | 17.1 | 140.0 | 647.0 | 26.1 | 31.9 | 403.0 | 17.7 | 11.9 | 3.3 | 13.0 | 1.0 | 108.0 | 3.8 | 99.4 |
| ZK49 | 1505.5 | 12.0 | 58.9 | 58.5 | 16.5 | 44.4 | 25.8 | 66.7 | 14.4 | 144.0 | 857.0 | 19.1 | 56.1 | 268.0 | 43.5 | 10.7 | 4.6 | 9.7 | 0.8 | 75.6 | 2.9 | 83.2 |
| ZK50 | 1525.5 | 7.8 | 42.8 | 42.0 | 8.0 | 21.8 | 28.3 | 58.6 | 9.1 | 84.1 | 14887.0 | 18.4 | 27.5 | 298.0 | 7.0 | 8.1 | 2.9 | 10.6 | 0.8 | 77.9 | 3.0 | 72.8 |
| ZK51 | 1543 | 16.5 | 71.8 | 64.6 | 16.4 | 38.0 | 27.5 | 97.9 | 19.7 | 225.0 | 4382.0 | 24.6 | 78.5 | 411.0 | 19.2 | 14.6 | 5.3 | 12.7 | 1.0 | 96.3 | 3.7 | 115.0 |
| ZK52 | 1560.5 | 18.2 | 86.8 | 84.1 | 17.6 | 41.0 | 38.2 | 105.0 | 22.5 | 218.0 | 242.0 | 26.0 | 76.3 | 406.0 | 34.9 | 16.0 | 6.1 | 13.1 | 1.1 | 106.0 | 4.1 | 141.0 |
| ZK53 | 1567 | 11.1 | 61.2 | 58.3 | 11.4 | 33.4 | 40.6 | 156.0 | 12.8 | 132.0 | 287.0 | 23.8 | 27.6 | 306.0 | 15.3 | 11.7 | 2.7 | 12.7 | 1.0 | 94.6 | 3.4 | 92.4 |
| ZK54 | 1581.5 | 14.4 | 74.3 | 60.7 | 15.9 | 35.4 | 29.8 | 92.6 | 16.3 | 165.0 | 2949.0 | 21.3 | 48.4 | 454.0 | 17.6 | 12.2 | 5.7 | 11.5 | 0.9 | 90.4 | 3.4 | 108.0 |
| ZK55 | 1599.5 | 12.3 | 53.6 | 54.9 | 11.3 | 31.5 | 28.6 | 68.4 | 14.6 | 140.0 | 264.0 | 20.7 | 32.6 | 319.0 | 8.2 | 11.0 | 2.5 | 11.8 | 1.0 | 89.5 | 3.0 | 80.4 |
| No. | Depth | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | ppm | |
| ZK1 | 339 | 33.8 | 61.9 | 7.1 | 27.1 | 4.9 | 1.0 | 4.4 | 0.7 | 4.2 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 0.3 |
| ZK2 | 363 | 25.6 | 49.6 | 5.8 | 22.1 | 3.7 | 0.8 | 3.7 | 0.6 | 3.2 | 0.5 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 0.3 |
| ZK3 | 387 | 23.1 | 44.4 | 5.3 | 18.3 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 3.0 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 1.4 | 0.2 |
| ZK4 | 400.5 | 33.9 | 60.1 | 7.7 | 28.5 | 5.0 | 1.2 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 4.3 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 2.2 | 0.4 |
| ZK5 | 457 | 20.4 | 37.5 | 4.5 | 16.3 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| ZK6 | 504.5 | 9.4 | 17.5 | 2.1 | 8.0 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 |
| ZK7 | 538.5 | 10.9 | 19.4 | 2.5 | 9.5 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| ZK8 | 550 | 39.5 | 68.1 | 8.3 | 31.8 | 5.2 | 1.2 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| ZK9 | 573 | 24.4 | 46.1 | 5.6 | 21.0 | 3.7 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 3.3 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 0.3 |
| ZK10 | 585 | 21.4 | 40.7 | 4.7 | 17.5 | 2.8 | 0.7 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| ZK11 | 601 | 23.4 | 44.5 | 5.4 | 20.3 | 3.6 | 0.8 | 3.1 | 0.6 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 0.3 |
| ZK12 | 620.5 | 20.1 | 37.6 | 4.4 | 17.6 | 3.0 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| ZK13 | 650 | 33.8 | 59.2 | 7.2 | 27.1 | 4.5 | 1.1 | 4.0 | 0.7 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 2.1 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 0.3 |
| ZK14 | 681.5 | 31.0 | 57.3 | 7.2 | 27.9 | 4.5 | 1.0 | 4.2 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 0.4 |
| ZK15 | 710 | 35.0 | 65.0 | 7.9 | 32.4 | 5.4 | 1.3 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0.5 | 3.1 | 0.5 |
| ZK16 | 779.5 | 42.0 | 73.6 | 8.9 | 33.5 | 5.2 | 1.4 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 0.5 |
| ZK17 | 790 | 33.3 | 59.5 | 7.5 | 29.9 | 5.0 | 1.2 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 0.4 |
| ZK18 | 809.9 | 15.0 | 26.9 | 3.5 | 14.0 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 2.0 | 0.4 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| ZK19 | 853 | 39.4 | 70.2 | 8.7 | 35.2 | 6.3 | 1.5 | 5.2 | 0.9 | 5.3 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 0.5 |
| ZK20 | 870 | 33.3 | 61.6 | 7.6 | 29.3 | 4.8 | 1.0 | 4.6 | 0.8 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| ZK21 | 911.5 | 46.9 | 88.0 | 11.1 | 40.0 | 5.2 | 1.1 | 5.2 | 0.8 | 4.1 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 2.2 | 0.4 |
| ZK22 | 930.5 | 40.2 | 63.4 | 8.3 | 32.6 | 5.4 | 1.2 | 5.1 | 0.8 | 4.7 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.4 |
| ZK23 | 951 | 35.6 | 64.1 | 8.1 | 31.0 | 5.1 | 1.0 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 4.6 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 0.5 |
| ZK24 | 970.5 | 39.5 | 71.1 | 8.5 | 33.1 | 4.8 | 1.0 | 4.6 | 0.7 | 3.9 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 0.3 |
| ZK25 | 977.5 | 74.7 | 133.0 | 15.7 | 61.4 | 7.8 | 1.6 | 7.3 | 1.1 | 5.4 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 0.4 |
| ZK26 | 993 | 37.6 | 62.9 | 8.0 | 31.6 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 4.4 | 0.8 | 4.0 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| ZK27 | 1027.5 | 28.1 | 50.9 | 6.4 | 25.6 | 4.3 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 0.6 | 3.7 | 0.7 | 2.1 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 0.3 |
| ZK28 | 1040 | 42.3 | 71.7 | 8.9 | 34.3 | 5.4 | 1.1 | 5.2 | 0.9 | 4.9 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 2.9 | 0.4 |
| ZK29 | 1050 | 39.4 | 67.9 | 7.7 | 31.2 | 4.9 | 1.0 | 4.4 | 0.8 | 4.2 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| ZK30 | 1090 | 39.4 | 68.9 | 8.3 | 33.0 | 5.5 | 1.2 | 4.9 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| ZK31 | 1099.5 | 41.7 | 72.4 | 8.9 | 35.0 | 6.0 | 1.3 | 5.4 | 0.9 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 2.9 | 0.5 | 2.9 | 0.4 |
| ZK32 | 1129.5 | 33.6 | 58.4 | 7.3 | 29.1 | 5.1 | 1.1 | 4.3 | 0.8 | 4.1 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| ZK33 | 1145 | 46.5 | 76.7 | 9.6 | 36.2 | 6.2 | 1.3 | 5.6 | 0.9 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 0.4 | 2.9 | 0.5 |
| ZK34 | 1175 | 38.1 | 68.4 | 8.4 | 33.1 | 6.0 | 1.2 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 5.0 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 0.4 |
| ZK35 | 1185 | 41.6 | 73.4 | 9.1 | 35.7 | 6.3 | 1.3 | 5.4 | 0.9 | 5.3 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.4 |
| ZK36 | 1203.5 | 34.3 | 60.6 | 7.5 | 28.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 4.6 | 0.8 | 4.6 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| ZK37 | 1213.5 | 36.8 | 62.1 | 8.0 | 29.8 | 5.4 | 1.1 | 4.7 | 0.8 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| ZK38 | 1260 | 37.8 | 65.6 | 8.6 | 31.8 | 5.6 | 1.2 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 4.7 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| ZK39 | 1295 | 31.5 | 58.9 | 7.2 | 26.3 | 4.6 | 1.0 | 4.2 | 0.7 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 0.4 | 2.3 | 0.4 |
| ZK40 | 1325 | 29.8 | 53.9 | 6.9 | 24.1 | 4.3 | 0.8 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 3.0 | 0.6 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 0.3 |
| ZK41 | 1346.5 | 35.9 | 66.0 | 8.4 | 29.0 | 5.6 | 1.2 | 4.9 | 0.8 | 4.6 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.4 |
| ZK42 | 1370.5 | 41.3 | 76.2 | 10.0 | 35.6 | 6.0 | 1.2 | 5.7 | 1.0 | 5.2 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 0.4 |
| ZK43 | 1388.5 | 36.0 | 64.5 | 8.6 | 30.6 | 5.3 | 1.2 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 4.7 | 0.8 | 2.8 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| ZK44 | 1426.5 | 31.3 | 56.2 | 7.0 | 25.3 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 3.7 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 0.3 |
| ZK45 | 1434.5 | 43.1 | 74.2 | 9.6 | 34.1 | 6.0 | 1.2 | 5.3 | 0.9 | 5.0 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| ZK46 | 1457.5 | 41.8 | 73.5 | 9.5 | 33.3 | 6.0 | 1.2 | 5.3 | 0.9 | 4.9 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 0.4 |
| ZK47 | 1465 | 38.4 | 67.2 | 8.9 | 32.1 | 6.1 | 1.3 | 5.4 | 1.0 | 5.2 | 1.0 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 2.8 | 0.5 |
| ZK48 | 1485 | 35.4 | 62.5 | 7.9 | 29.5 | 5.7 | 1.1 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 4.9 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 0.4 |
| ZK49 | 1505.5 | 29.9 | 58.3 | 6.9 | 25.8 | 4.6 | 0.8 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 0.3 |
| ZK50 | 1525.5 | 26.5 | 47.0 | 6.2 | 22.2 | 4.1 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 1.9 | 0.3 |
| ZK51 | 1543 | 41.7 | 70.5 | 8.8 | 31.8 | 5.9 | 1.3 | 5.0 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 0.4 |
| ZK52 | 1560.5 | 42.4 | 72.7 | 9.3 | 35.1 | 6.0 | 1.1 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 4.9 | 0.9 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 2.8 | 0.5 |
| ZK53 | 1567 | 34.8 | 63.3 | 7.9 | 29.5 | 5.6 | 1.2 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 4.8 | 0.8 | 2.6 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 0.4 |
| ZK54 | 1581.5 | 43.6 | 77.6 | 9.7 | 35.0 | 5.6 | 1.1 | 5.0 | 0.8 | 4.4 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 0.4 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| ZK55 | 1599.5 | 32.9 | 61.3 | 7.8 | 28.5 | 5.4 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 4.1 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 0.3 |
| No. | FeO/MnO | Al2O3/MgO | C-value | CIA | CIW | PIA | U/Th | Ni/Co | V/Cr | Sr/Ba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK1 | 12.52 | 2.47 | 0.31 | 55.33 | 63.50 | 57.17 | 0.58 | 2.34 | 1.19 | 3.97 |
| ZK2 | 20.14 | 3.66 | 0.25 | 45.77 | 51.23 | 44.62 | 0.23 | 3.06 | 0.86 | 1.45 |
| ZK3 | 15.56 | 1.11 | 0.12 | 31.28 | 33.57 | 28.31 | 0.81 | 3.13 | 1.58 | 3.74 |
| ZK4 | 8.26 | 3.01 | 0.25 | 48.03 | 53.51 | 47.53 | 0.24 | 2.52 | 1.02 | 0.62 |
| ZK5 | 28.43 | 1.10 | 0.10 | 27.26 | 29.21 | 23.75 | 0.95 | 2.99 | 1.85 | 5.73 |
| ZK6 | 24.71 | 0.51 | 0.05 | 13.21 | 13.70 | 10.38 | 0.73 | 3.69 | 1.50 | 12.80 |
| ZK7 | 25.41 | 0.96 | 0.06 | 13.28 | 13.75 | 10.58 | 1.48 | 3.59 | 2.00 | 11.86 |
| ZK8 | 23.12 | 2.98 | 0.29 | 50.67 | 58.12 | 50.90 | 0.42 | 2.20 | 1.36 | 2.14 |
| ZK9 | 22.50 | 1.66 | 0.16 | 36.23 | 40.18 | 32.86 | 0.23 | 2.78 | 0.97 | 2.48 |
| ZK10 | 20.69 | 1.88 | 0.13 | 29.14 | 31.51 | 25.46 | 0.47 | 2.78 | 1.37 | 8.04 |
| ZK11 | 23.66 | 1.36 | 0.15 | 34.91 | 38.44 | 31.51 | 0.56 | 2.86 | 1.35 | 7.01 |
| ZK12 | 18.43 | 0.90 | 0.10 | 25.32 | 26.90 | 22.04 | 0.84 | 3.02 | 1.49 | 7.81 |
| ZK13 | 29.47 | 3.31 | 0.24 | 43.26 | 47.97 | 41.62 | 0.79 | 2.49 | 1.48 | 2.04 |
| ZK14 | 20.78 | 5.84 | 0.28 | 47.02 | 53.10 | 46.14 | 0.23 | 2.58 | 1.06 | 0.96 |
| ZK15 | 25.71 | 6.09 | 0.46 | 59.06 | 69.46 | 62.93 | 0.18 | 2.46 | 1.30 | 0.44 |
| ZK16 | 55.78 | 4.66 | 0.42 | 60.32 | 73.01 | 65.82 | 0.23 | 2.59 | 0.94 | 0.68 |
| ZK17 | 34.55 | 4.42 | 0.25 | 40.54 | 44.89 | 38.27 | 0.28 | 3.14 | 1.15 | 1.26 |
| ZK18 | 23.75 | 0.81 | 0.07 | 22.34 | 23.36 | 19.69 | 1.99 | 3.4 | 1.87 | 10.59 |
| ZK19 | 46.90 | 3.28 | 0.44 | 64.61 | 77.49 | 71.88 | 0.23 | 2.71 | 1.13 | 0.40 |
| ZK20 | 31.57 | 3.21 | 0.31 | 52.16 | 60.18 | 52.95 | 0.24 | 3.07 | 1.26 | 2.67 |
| ZK21 | 21.84 | 2.20 | 0.31 | 56.03 | 65.34 | 58.44 | 0.49 | 2.57 | 1.23 | 8.99 |
| ZK22 | 41.89 | 2.97 | 0.41 | 60.54 | 72.32 | 65.63 | 0.28 | 2.46 | 1.08 | 1.47 |
| ZK23 | 36.55 | 4.18 | 0.40 | 59.99 | 70.51 | 64.23 | 0.31 | 2.58 | 1.13 | 0.96 |
| ZK24 | 37.05 | 2.41 | 0.26 | 47.92 | 54.53 | 47.25 | 0.47 | 2.57 | 1.09 | 2.93 |
| ZK25 | 37.12 | 3.99 | 0.41 | 61.90 | 74.24 | 67.83 | 0.21 | 2.05 | 1.20 | 0.61 |
| ZK26 | 51.16 | 2.60 | 0.38 | 61.51 | 73.11 | 66.86 | 0.28 | 2.58 | 1.20 | 1.84 |
| ZK27 | 19.75 | 2.48 | 0.21 | 45.41 | 50.52 | 44.24 | 0.26 | 2.59 | 1.12 | 29.67 |
| ZK28 | 35.44 | 3.71 | 0.46 | 62.38 | 74.40 | 68.29 | 0.21 | 2.36 | 1.19 | 0.75 |
| ZK29 | 42.08 | 3.13 | 0.37 | 59.04 | 69.75 | 63.04 | 0.21 | 2.94 | 1.11 | 1.73 |
| ZK30 | 39.11 | 3.11 | 0.44 | 65.46 | 78.08 | 72.84 | 0.32 | 2.56 | 1.32 | 3.04 |
| ZK31 | 28.09 | 3.46 | 0.43 | 63.87 | 76.32 | 70.59 | 0.25 | 2.66 | 1.13 | 1.58 |
| ZK32 | 26.21 | 3.63 | 0.27 | 48.06 | 54.35 | 47.47 | 0.23 | 2.71 | 1.17 | 0.93 |
| ZK33 | 42.22 | 4.42 | 0.49 | 64.50 | 78.05 | 72.22 | 0.22 | 2.51 | 1.21 | 1.14 |
| ZK34 | 24.17 | 3.70 | 0.35 | 52.70 | 60.98 | 53.71 | 0.23 | 2.58 | 1.04 | 1.07 |
| ZK35 | 23.61 | 3.77 | 0.39 | 59.44 | 70.10 | 63.57 | 0.21 | 2.66 | 1.50 | 0.52 |
| ZK36 | 20.40 | 2.21 | 0.25 | 53.24 | 60.86 | 54.32 | 0.38 | 2.13 | 1.11 | 7.58 |
| ZK37 | 25.68 | 2.42 | 0.32 | 61.63 | 71.94 | 66.30 | 0.71 | 2.51 | 1.21 | 15.93 |
| ZK38 | 29.68 | 3.57 | 0.35 | 54.25 | 62.35 | 55.74 | 0.25 | 2.77 | 1.19 | 7.32 |
| ZK39 | 26.17 | 3.39 | 0.27 | 48.62 | 55.21 | 48.19 | 0.23 | 2.4 | 1.21 | 8.17 |
| ZK40 | 23.23 | 3.31 | 0.15 | 36.79 | 40.23 | 34.05 | 0.44 | 2.72 | 1.05 | 21.14 |
| ZK41 | 26.05 | 2.56 | 0.39 | 64.44 | 76.26 | 70.92 | 0.38 | 2.54 | 1.36 | 1.57 |
| ZK42 | 15.00 | 3.66 | 0.28 | 46.88 | 52.21 | 46.08 | 0.24 | 2.39 | 1.25 | 0.90 |
| ZK43 | 28.70 | 2.97 | 0.30 | 50.45 | 57.35 | 50.59 | 0.30 | 2.06 | 1.05 | 6.43 |
| ZK44 | 36.03 | 2.94 | 0.18 | 38.44 | 42.49 | 35.72 | 1.28 | 2.89 | 1.31 | 7.72 |
| ZK45 | 41.67 | 3.87 | 0.48 | 63.48 | 76.60 | 70.50 | 0.23 | 2.51 | 0.79 | 0.41 |
| ZK46 | 35.00 | 4.32 | 0.36 | 58.35 | 68.58 | 61.90 | 0.21 | 2.82 | 1.03 | 2.23 |
| ZK47 | 29.39 | 4.16 | 0.47 | 62.91 | 74.55 | 68.77 | 0.26 | 2.52 | 1.13 | 0.36 |
| ZK48 | 19.33 | 4.08 | 0.34 | 55.78 | 64.18 | 57.83 | 0.27 | 1.87 | 1.32 | 1.61 |
| ZK49 | 19.62 | 3.56 | 0.20 | 37.16 | 40.84 | 34.33 | 0.43 | 2.69 | 1.01 | 3.20 |
| ZK50 | 16.18 | 2.12 | 0.18 | 39.49 | 43.15 | 37.35 | 0.36 | 2.74 | 1.02 | 49.96 |
| ZK51 | 36.62 | 3.14 | 0.35 | 60.92 | 72.72 | 66.17 | 0.36 | 2.32 | 1.11 | 10.66 |
| ZK52 | 64.63 | 3.64 | 0.51 | 67.75 | 81.99 | 77.20 | 0.38 | 2.33 | 1.03 | 0.60 |
| ZK53 | 30.00 | 3.64 | 0.27 | 43.93 | 49.31 | 42.24 | 0.23 | 2.93 | 1.05 | 0.94 |
| ZK54 | 24.69 | 3.39 | 0.32 | 55.47 | 64.53 | 57.61 | 0.46 | 2.23 | 1.22 | 6.50 |
| ZK55 | 30.32 | 3.37 | 0.31 | 52.63 | 60.44 | 53.55 | 0.22 | 2.79 | 0.98 | 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





