1. Introduction
Platelets are key players in hemostasis and thrombus formation [
1,
2], but recently they were also linked to tumor progression and inflammation [
3,
4]. Besides routine platelet counts, the in vivo imaging of radiolabeled platelets also holds valuable diagnostic potential which was recognized several decades ago. Thrombus formation, intravascular clotting, and different entities of peripheric circulation problems have been imaged in the clinic using radiolabeled platelets. First radiolabeling studies on platelets date back to the 1950s [
5], and platelet scintigraphy or single photon emission tomography (SPECT) in clinical practice with
111In-Oxine (
111In-8-hydroxyquinoline) and
99mTc-HMPAO (hexamethylpropylene amine oxime) became widespread in the 1980s [
6,
7,
8]. These lipophilic complexes are not specific to platelets, therefore a laborious purification procedure is required before imaging [
9]. To overcome this bottleneck, the focus has turned to platelet-specific labels such as receptor-specific radiolabeled peptides, and monoclonal antibodies, since the 1990s [
10,
11]. However, these have not yet fully made their way to the clinics in routine nuclear medical practice. Despite the long history of platelet radiolabeling,
111In-Oxine still serves as the gold standard among the numerous compounds developed over the years [
12], but Indium-111 is an expensive and not always readily available isotope. During the slow washout from the oxine complex, free
111In-ions redistribute to bind transferrin and the imaging results would show bone marrow uptake, making platelet or free indium ion uptake indistinguishable. As recent tumour-related clinical research has shown, there are still unanswered questions regarding the in vivo biodistribution and trafficking of platelets. Therefore, the study of novel platelet-specific radiopharmaceuticals for easy access in pre-clinical models and not just for thrombosis diagnostics is a current topic.
In this paper, with this background, we report a novel method for a lipid-specific radiolabeling of platelets with
99mTc using duramycin, which is a phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) -binding natural, polycyclic peptide antibiotic [
13,
14]. Duramycin conjugated with HYNIC (hydrazinonicotinamide), a bifunctional complexing agent for
99mTc, has been previously proposed as a novel radiopharmaceutical for apoptosis imaging [
15,
16,
17]. Here we show that
99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin can be used for the stable radiolabeling of platelets, without significant alteration of platelet activity, and demonstrate the applicability of the thus labeled platelets for in vivo small animal SPECT/CT imaging investigations. As platelet membranes do contain PE, the mechanism of radiolabeling is a simple membrane anchoring of the complexated
99mTc-ion to the platelet membrane by duramycin binding to PE.
The reported use of a simplified platelet radiolabel, should prove useful in studying tumor, CNS and immunological research questions. We therefore aimed at performing and reporting this PE-duramycin based isotope labeling of platelets in our experiments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Platelet Purification
Washed human platelet concentrate was purchased from the Hungarian National Blood and Transfusion Service (Budapest, Hungary) and was used within 24 hours after arrival. 9 mL platelet concentrate was mixed with 1 mL ACD-A solution in a plastic tube (Greiner VACUETTE
® ACD-A, Greiner Bio-One Ltd., Hungary) and 10 μL prostaglandin E1 solution (100 μg/mL in EtOH, Avanti Polar Lipids, USA) was added. First, platelets were centrifuged at 800 x g for 15 min a room temperature (Nüve NF800R, RA200 swing-out rotor) and the supernatant was discarded. The pellet was gently resuspended in 1 mL HEPES-buffered Tyrode's Solution (THB, 119 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 25 mM, HEPES pH 7.4, 2 mM CaCl
2, 2 mM MgCl
2 6 g/l Glucose, pH 7.4), and 0.5 mL of the washed platelet concentrate was further purified with size exclusion chromatography (SEC) using a 3.5 mL gravity column filled with Sepharose CL-2B gel (GE Healthcare, Sweden) equilibrated with THB solution. 0.5 mL fractions were collected, and absorbance at 405 nm was measured with a BioTek Synergy 2 plate reader using 96-well plates [
18]. Purified platelets corresponding to the void volume of the column (from 1 mL to 2 mL elution volumes) were combined and used for radiolabeling.
2.2 Platelet Counting with Microfluidic Resistive Pulse Sensing
Concentration and size characterization of purified platelets was performed with microfluidic resistive pulse sensing (MRPS) using an nCS1 instrument (Spectradyne LLC, USA) [
19]. Samples were diluted 100-fold in THB solution containing bovine serum albumin (BSA, Merck Life Science Ltd, Hungary) at 1 mg/mL. MRPS measurements were performed using factory-calibrated TS-10k cartridges with a measurement range from 1 500 nm to 10 000 nm.
2.3 Platelet-Activation Test
SEC purified platelets were diluted 10-fold in THB solution, and duramycin (Merck Life Science Ltd, Budapest, Hungary) was added to reach a final concentration of 0.35 μg/mL. Activation with thrombin at 1 U/mL final concentration was used as positive control. Mixing was performed in a 96-well plate, and quickly placed in a BioTek Synergy 2 plate reader and absorbance was measured at 405 nm at different time points for one hour [
18].
2.4 Transmission Electron Microscopy
Untreated platelets as a negative control, platelets treated with duramycin at 0.35 μg/mL concentration and activated with A23187 Ca-ionophore (at 10 μM final concentration, Merck Life Science) as positive control were investigated by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Samples were centrifuged and fixed by a fixative solution (containing 3.2% formaldehyde, 0.32% glutaraldehyde, 1% saccharose, 40 mM CaCl2, and 0.1 M sodium-cacodylate) at 4°C overnight. For post-fixation, we applied 1% osmium tetroxide for 1 hour. Next, the platelet pellets were dehydrated by graded ethanol series, then embedded in Spurr low viscosity epoxy resin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, EM0300) according to the recommendation of the manufacturer. Ultrathin sections were made by a Reichert U3 ultramicrotome and were collected on Formvar-coated copper grids. Uranyl acetate and Reynold's lead citrate were used to counterstain.
The samples were examined by MORGAGNI 268D transmission electron microscope (FEI, Eindhoven, Netherlands), equipped with Quemesa 11 MegaPixel bottom-mounted CCD camera (EMSIS, Münster, Germany).
2.5 Radiolabeling with 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin
HYNIC-Duramycin kit was purchased from Molecular Targeting Technologies (West Chester, PA, USA). Radiolabeling was done following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, 0.5 ml of freshly eluted 99mTc-pertechnetate (1 to 3 GBq eluted from an Ultra-Technekow FM 2.15-43.00 GBq technetium generator (Curium, Netherlands)) solution was applied to the glass vial of the kit. The vial was incubated at 80 °C for 20 minutes to complete the labeling. Next, 0.25 mL of CL-2B purified platelets in THB was mixed with 0.25 mL 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin (0.4 to 1 GBq) and incubated for 30 minutes at 30 °C with 200 RPM shaking in a neoMix cool thermomixer (Neolab, Heidelberg, Germany). Radiolabeled platelets were separated from free 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin by SEC using the same protocol as described in the previous section. The fractions corresponding to the void volume of the column (from 1 mL to 2 mL elution volumes) were pooled and used for testing the stability of the radiolabeling or for in vivo SPECT/CT investigations.
The radiolabeling stability test was performed by mixing 0.25 mL of 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin labeled platelets with 2.25 mL human plasma (supernatant of platelet concentrate after the 800 x g centrifugation and filtered with a 0.45 μm syringe filter (VWR International, Debrecen, Hungary)). 100 μL aliquots were placed in LoBind Eppendorf tubes and incubated at 37 °C with 200 RPM shaking in a neoMix cool thermomixer (Neolab, Heidelberg, Germany). At each time point, two separation procedures were performed in parallel to separate platelets from the free 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin: The samples were filtered with either 0.45μm (5000 x g, 3 min) or 100 kDa MWCO (12 300 x g, 10 min) centrifuge filters and the activities of the flow through and retentates were measured in a dose calibrator (ISOMED2010, Nuvia, Rueil Malmaison, France).
2.6 In Vivo SPECT/CT Imaging
Five healthy 6-week-old NMRI Nu/Nu mice (body weight between 22 g and 26 g) bred in the Animal House of Semmelweis University were used for the biodistribution studies. Animals were allowed free access to food and water and were kept under humidity, temperature, and light-controlled conditions. All procedures were conducted in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines and the guidelines set by the European Communities Council Directive (86/609 EEC) and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the IEM and Semmelweis University (PE/EA/599-5/2021). A volume of 100 μl to 200 μl radiolabeled platelets in THB with an activity of 24.5 ± 1.6 MBq (Mean ± SD) was administered intravenously into the lateral tail vein. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane for the whole duration of imaging. SPECT/CT acquisitions were carried out using a nanoScan SPECT/CT (Mediso, Budapest, Hungary) and started 3.5 hours post-injection. SPECT and CT acquisitions were reconstructed using Nucline (Mediso, Budapest, Hungary). Volumes of interest (VOI) were manually delineated around selected organs (lungs, liver, and spleen). VOI uptake data are reported in % organ activity / injected dose and in standardized uptake value (SUV), which is defined as the ratio of the tissue radioactivity concentration and the injected activity divided by the body weight.
3. Results and Discussion
Since the aim of our study was to test a novel radiolabeling procedure for platelets, we chose a separation protocol based on size exclusion chromatography (or gel filtration other words) which ensures the highest platelet purity [
20,
21,
22]. It was also reported previously, that gel filtration causes less ultrastructural changes in platelets than washing by centrifugation [
23]. In this study, the mesoporous Sepharose CL-2B cross-linked agarose gel was used to purify platelets, which ensures the removal of proteins and other biological nanoparticles smaller than 40 000 MDa (for globular proteins). In practice, this means that this stationary phase can remove even low-density lipoprotein particles (LDL), if present.
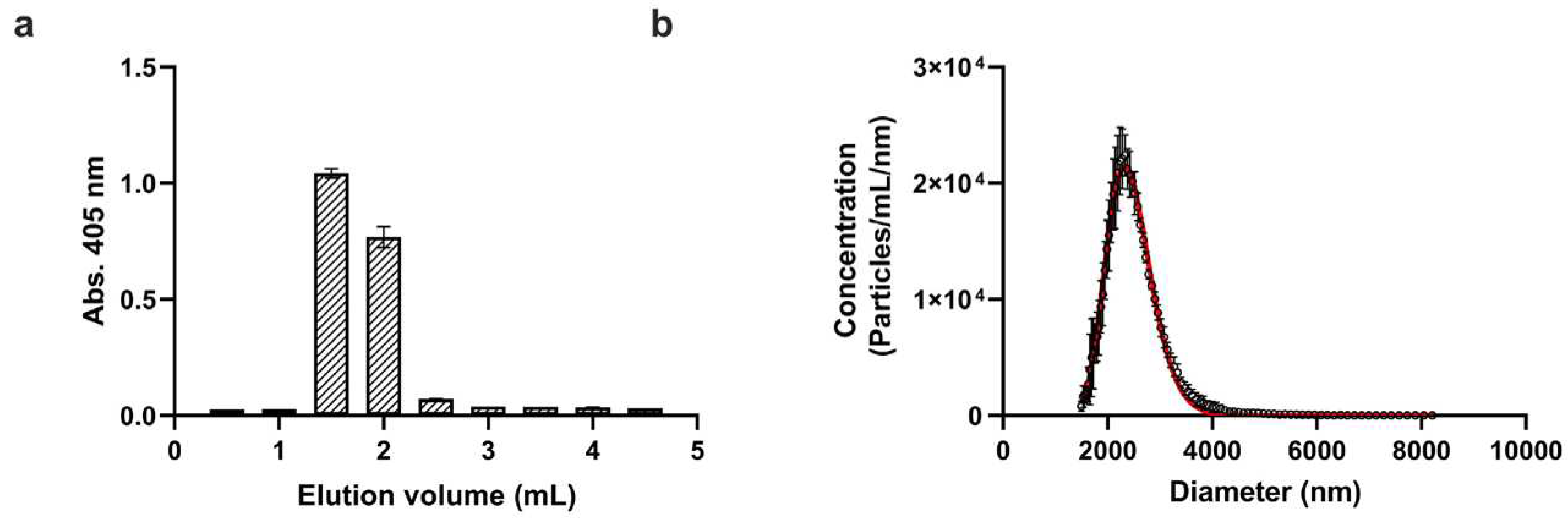
Figure 1a shows the elution profile of the washed platelets based on absorbance measurements at 405 nm. Since the total volume of the used gravity column was 3.5 mL, the excluded or void volume falls slightly above 1 mL. Accordingly, purified platelet fractions were detected between 1 mL and 2 mL elution volumes, which were pooled and used in further steps.
Next, the size and concentration of purified platelets were determined with a novel microfluidic resistive pulse sensing instrument, which operates based on the Coulter principle [
19]. The obtained size distribution is shown in
Figure 1b. Since platelets are biconvex discoid (lens-shaped) structures, the ‘diameter’ value indicated by MRPS cannot be directly translated to the physical dimensions of platelets. On the other hand, the mean value of 2.405 m, obtained from the fitting of a lognormal function to the measured distribution, agrees well with the known size of platelets, which is 2 to 3 m in greatest diameter [
24]. The measured platelet concentration was 2.27⋅10
9 mL
-1, which corresponds to approximately 20% of the initial platelet count in the concentrate. This yield can be explained mostly by loss due to non-specific adsorption during gel filtration which was quantified in more detail during the radiochemical purification.
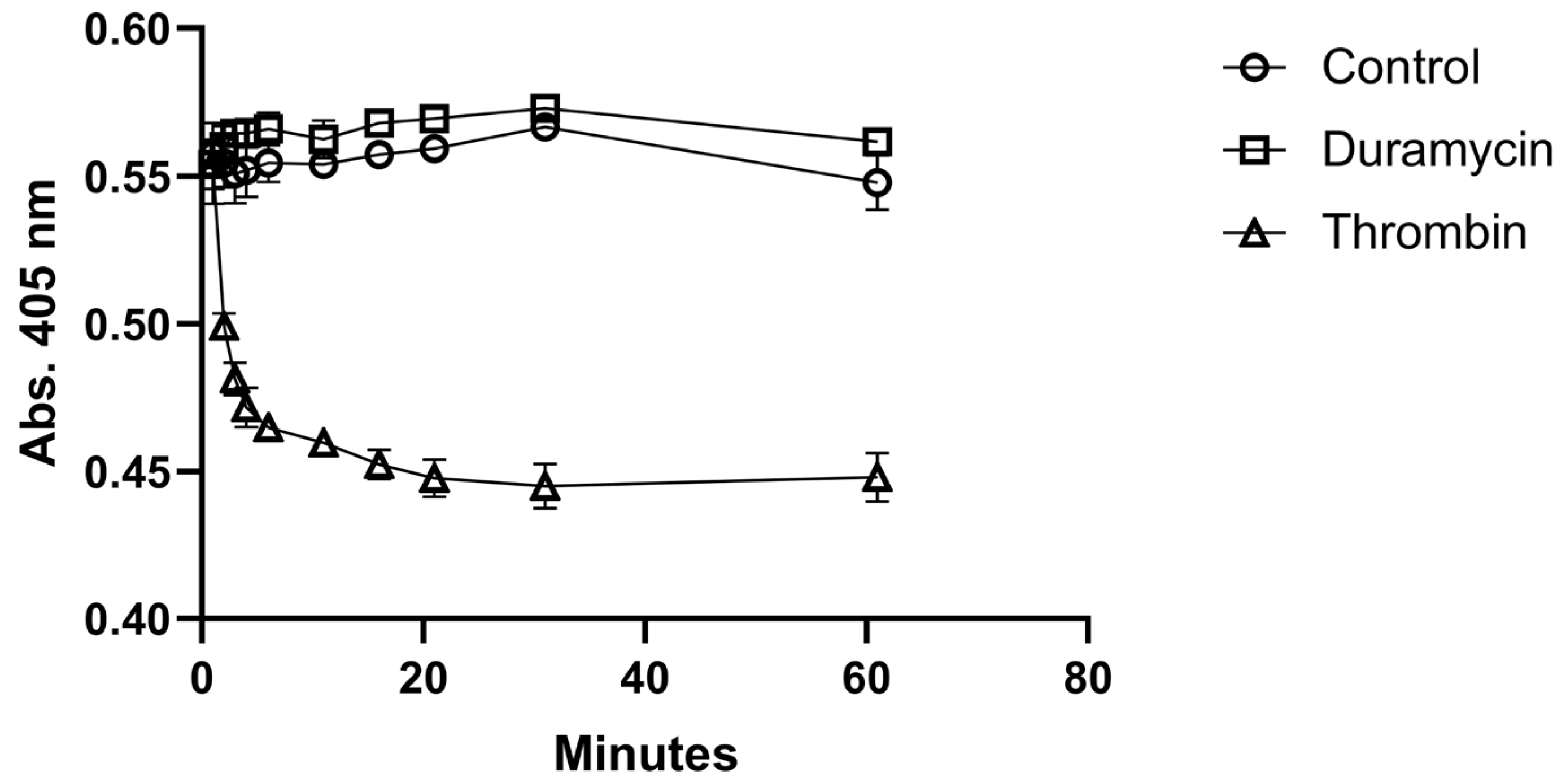
Before radiolabeling, the possible activation of platelets by duramycin was tested. The activation test was performed in a 96-well plate by measuring the absorbance as the function of time at 405 nm.
Figure 2. shows the time evaluation of absorbance of the duramycin-treated, the control, and the thrombin-treated samples. While a quick activation can be observed for the sample activated by thrombin, the addition of duramycin does not result in significant activation when compared to the control sample. Platelet activation was also assessed by TEM.
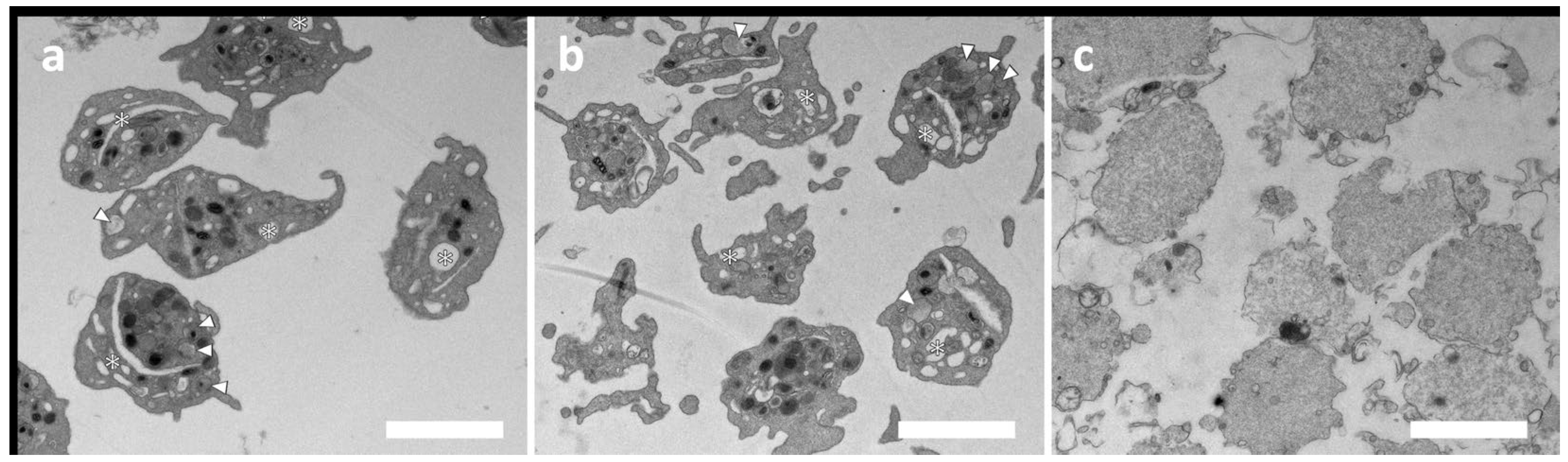
Figure 3 shows the TEM images of untreated (a), duramycin-treated (b), and activated platelets (with A23187 ionophore in this case). While the duramycin-treated sample (b) shows a typical morphology of resting platelets (a), the ionophore-treated sample contains degranulated platelets due to activation. In summary, both the 96-well plate aggregometry and the TEM investigations indicate that duramycin does not activate the platelets significantly.
Radiolabeling of purified platelets was performed by simply mixing with
99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin and incubating for 30 minutes at 30 °C with shaking. Purification was performed with the same gel filtration procedure that was used for the isolation of platelets.
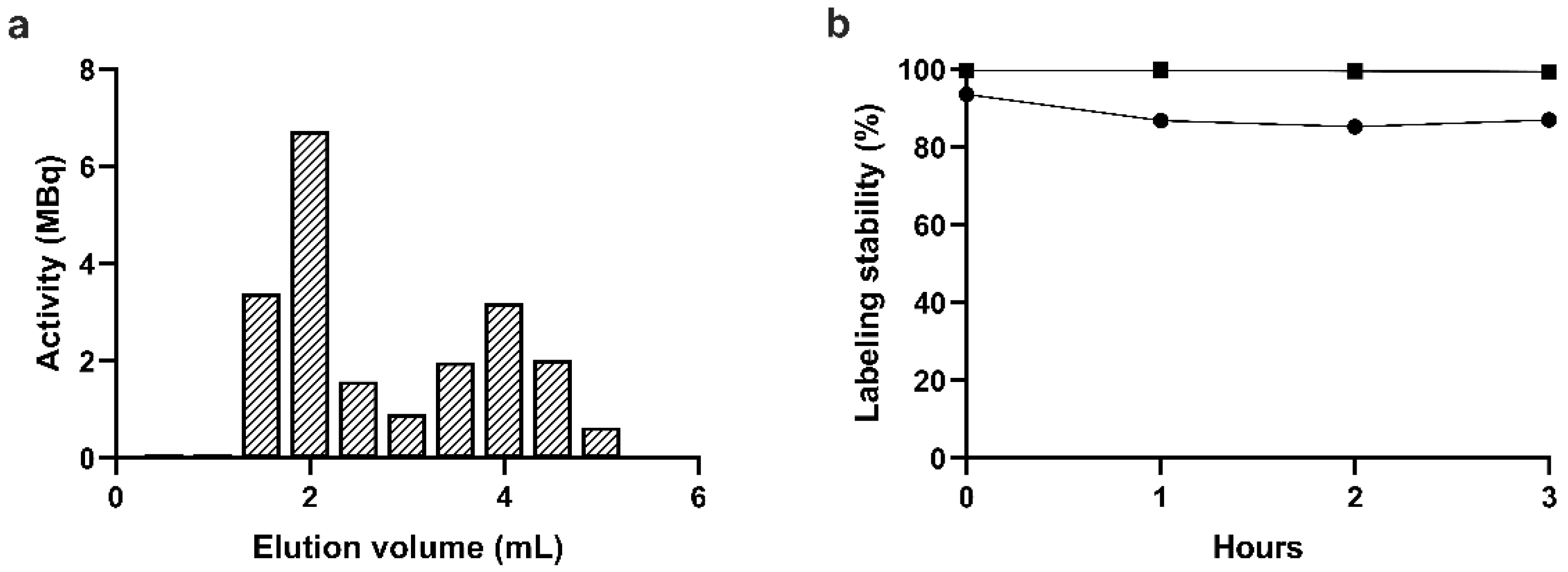
Figure 4a shows the elution profile of the reaction mixture as determined by measuring the radioactivity of each 0.5 mL fraction in a dose calibrator. Based on the elution profile, the labeling efficiency defined as the activity of the platelet fractions divided by the total activity of the eluate was 57%. On the other hand, the remaining activity on the column was approx. 2/3 of the total activity of the sample loaded on the column, which is in line with the low yield of the gel filtration-based purification procedure observed with MRPS. Taking into account the remaining activity of the column, the overall radiolabeling yield was 19%. Nevertheless, the fractions corresponding to the elution volume from 1 mL to 2 mL contain radiolabeled platelets with purity above 97%, the specific activity of which is sufficient for small animal SPECT imaging (100 MBq/mL to 300 MBq/mL).
Plasma stability of the radiolabeling was assessed by 10-fold dilution of the labeled platelets in 0.8 μm filtered plasma and the mixture was incubated at 37 °C with shaking for up to 3 hours. At each time point, platelets were separated from the supernatant by filtration using either a 100 kDa MWCO filter or a 0.45 μm pore-size filter. Labeling stability percentages defined as the ratio of the activity of the platelet fraction and the filtrate are shown in
Figure 4b. While >99% plasma stability was observed when determined by the 100 kDa MWCO filter, it dropped to 87% when determined by the 0.45 μm pore-size filter. This observation indicates that
99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin is not released as a single molecule from the surface of platelets, but as attached to membrane fragments or to extracellular vesicles released from platelets during incubation.
The specific activity of the
99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin labeled platelets in terms of labeled PE lipids per total number of PE lipids in one platelet can be estimated based on the platelet concentration, the activity concentration, the total phospholipid content, and the ratio of externally accessible PE lipids in platelets. The total phospholipid content of platelets was reported to be 3.5 mg/10
10 platelets, and 25% of that consists of PE [
25]. Calculating with an average molecular weight of 750 g/mol, the molar content of PE in platelets is 4.67·10
-16 mol/platelet or 7·10
7 PE molecules/platelet. However, the externally accessible amount of PE in platelets is only 6.9% of the total PE lipids as measured by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonate, which yields 4.8·10
6 labelable PE/platelet [
26]. This can be compared to the number of
99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin molecules per platelet that can be calculated from the specific activity of the purified sample. In a typical experiment, we had 100 MBq to 300 MBq activity in 1 mL with an estimated platelet concentration of 2·10
8 mL
-1. Using the A = N·λ formula, where A is the activity of the sample in Bq, N is the number of decaying atoms, and λ is the decay constant defined as λ= ln 2 / t
1/2, where t
1/2 is the half-life of
99mTc (6 hours), the number concentration of
99mTc in the labeled platelet sample was approx. 3.1·10
12 mL
-1 to 9.3·10
12 mL
-1. This yields 0.54 - 1.6 ·10
4 99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin molecules per platelet, which means that approximately 0.3% to 1% of PE molecules on the surface of the platelets are labeled.
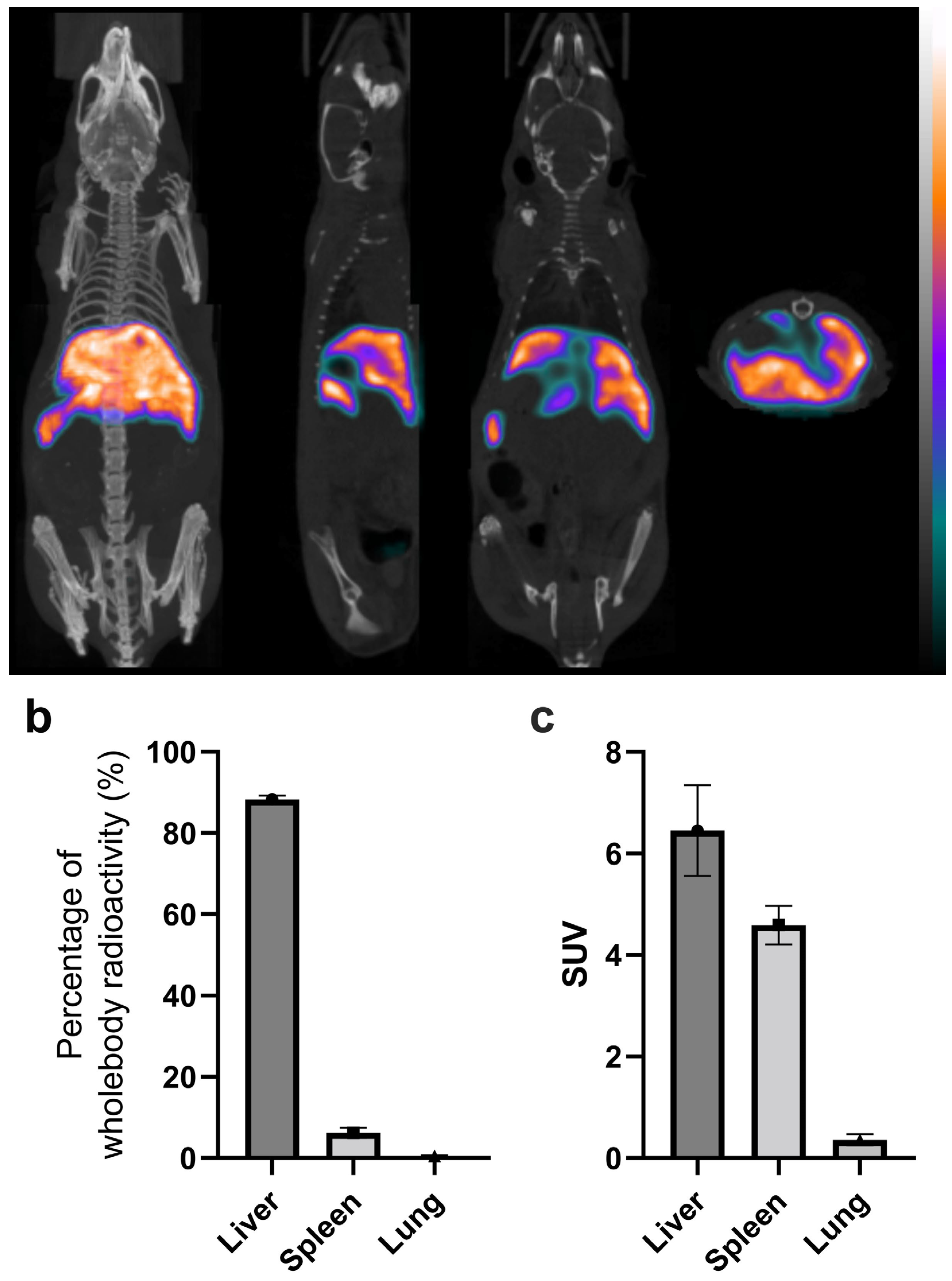
In vivo imaging results of labeled platelets 3.5 hours p.i. are shown in
Figure 5. Tissue distributions in the liver, spleen, and lungs in the percentage of whole-body radioactivity and in SUV are shown in
Figure 5b and c, respectively. High liver uptake is apparent from the unsegmented images, which already shows the in vivo stability of the radiolabeling as free
99mTc-HYNIC-Duramycin has low tissue uptake and fast clearance from the circulation through the renal-urinary system [
15].
However, the use of radiolabeled platelets for imaging of thrombosis was introduced in the 1970’s [
27], and studies reporting the biodistribution of in vitro labeled platelets in small animals are scarce [
28]. The distribution of
111In-Tropolone and
111In-Oxine labeled platelets in rabbits was reported by Dewanjee et al., who also observed significant liver uptake. Still, the activity in the blood was the highest after 24 h p.i. for both compounds according to this study [
29]. Due to the technical difficulties associated with the in vitro radiolabeling of autologous platelets in a clinical setting, the research focus in the field turned to radiolabeled compounds that specifically bind to platelets in vivo. Among these compounds, a radiolabeled monoclonal antibody to platelets [
11,
30], and bitistatin, an α
IIbβ
3 (glycoproteins IIb/IIIa) receptor-specific peptide should be mentioned [
10]. Significant activity in the kidneys is reported in these studies, probably due to the in vivo labeling strategy, which results in the free radiolabeled compound in the circulation which is quickly secreted by the renal-urinary system. Recently, Lee et al. reported the PET/CT imaging of platelets labeled with a novel radioiodinated gold nanoprobe in tumor-bearing mice [
31]. However, the distribution of the nanoprobe labeled platelets in healthy animals is not reported in this study, Lee et al. also found the highest uptake of the labeled platelets in the liver followed by accumulation in the blood and in the lungs with low activity in the kidneys.
This technetium-based platelet-selective labeling process might be realized in a more uniform and protocol-based way than In-oxime radiolabeling. However, the most important advantage of our method for further clinical use is that patient, and staff dosimetry is significantly lower in any 99mTc-based radiopharmaceutical than for 111In-oxime. The same dosimetry consideration applies to the half-life of 99mTc as compared to 111In. Therefore, this type of kit-based approach, coupled to also standardizable SEC separation as opposed to centrifugation-based hemolysis-prone cell / PLT whole-blood separations can be eventually more readily trained and applied in clinical practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M., Z.V. and K.M.; methodology, Z.V.; software, K.Sz. I.H.; validation, K.Sz.; formal analysis, D.M., K.Sz., B.J., Z.V. and I.H.; investigation, K.M., D.M. and Z.V.; resources, D.M.; data curation, K.Sz., R.B., D.Sz. and I.H.; writing—original draft preparation, D.M., Z.V., P.P. and I.H.; writing—review and editing, D.M., Z.V. and B.G.; visualization, R.B.; supervision, R.B., Zs.B.; project administration, D.M.; funding acquisition, D.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.