1. Introduction
Hyperuricemia, a prevalent condition, can arise from elevated urate synthesis or impaired renal or intestinal excretion [
1]. Gout, the clinical manifestation of hyperuricemia, is precipitated by urate deposition [
2]. Additionally, gout and hyperuricemia have been linked to various diseases, including chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome [
3]. An effective approach to managing hyperuricemia involves inhibiting excessive uric acid (UA) production and preventing its buildup in the bloodstream, thereby maintaining a desirable level of serum uric acid (SUA). The elimination of urate primarily occurs through glomerular filtration in the kidney. The ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter ABCG2 has been recognized as a significant urate transporter [
4,
5], exhibiting high expression in both intestinal and renal epithelial cells [
6,
7]. ABCG2 plays a critical role in the regulation of renal urate overload and extra-renal urate underexcretion, making it a potentially valuable target for pharmacological intervention in the management of hyperuricemia or gout [
8,
9].
Cortex Fraxini has been utilized in China for the treatment of hyperuricemia [
10]. However, the specific active compounds within Cortex Fraxini and their relationship with ABCG2 remain unknown. Since the active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) are those that can be absorbed into the bloodstream following oral administration, it is imperative to identify the specific components of medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini that can regulate ABCG2. Hence, it is imperative to identify the "effective form" of components in Cortex Fraxini that can efficiently, rapidly, and accurately activate ABCG2.
In order to expedite the process of drug discovery, various protein-ligand interaction-based methods have been devised. Among these, the integration of bioaffinity ultrafiltration and LC-MS (BA-UF-MS) has been employed to swiftly screen affinity ligands from intricate mixtures [
11]. This approach proves to be time-efficient, cost-effective, and eliminates the need for intricate chemical compound isolation procedures.
This study presents an integrated approach utilizing BA-UF-MS for the screening of potential ABCG2 activators from medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini. Initially, BA-UF-MS enables the swift separation and identification of the hit compound that binds to ABCG2. Subsequently, the activity of the identified hit compound is confirmed through in
vitro and in
vivo assays. Furthermore, the molecular docking and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assay were employed to confirm the affinity between the hit compound and ABCG2. As a result, a potent ABCG2 activator was successfully identified from the medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini. This study represents the first attempt to utilize this integrated method for screening ABCG2 activators from Cortex Fraxini. The overall research framework is depicted in
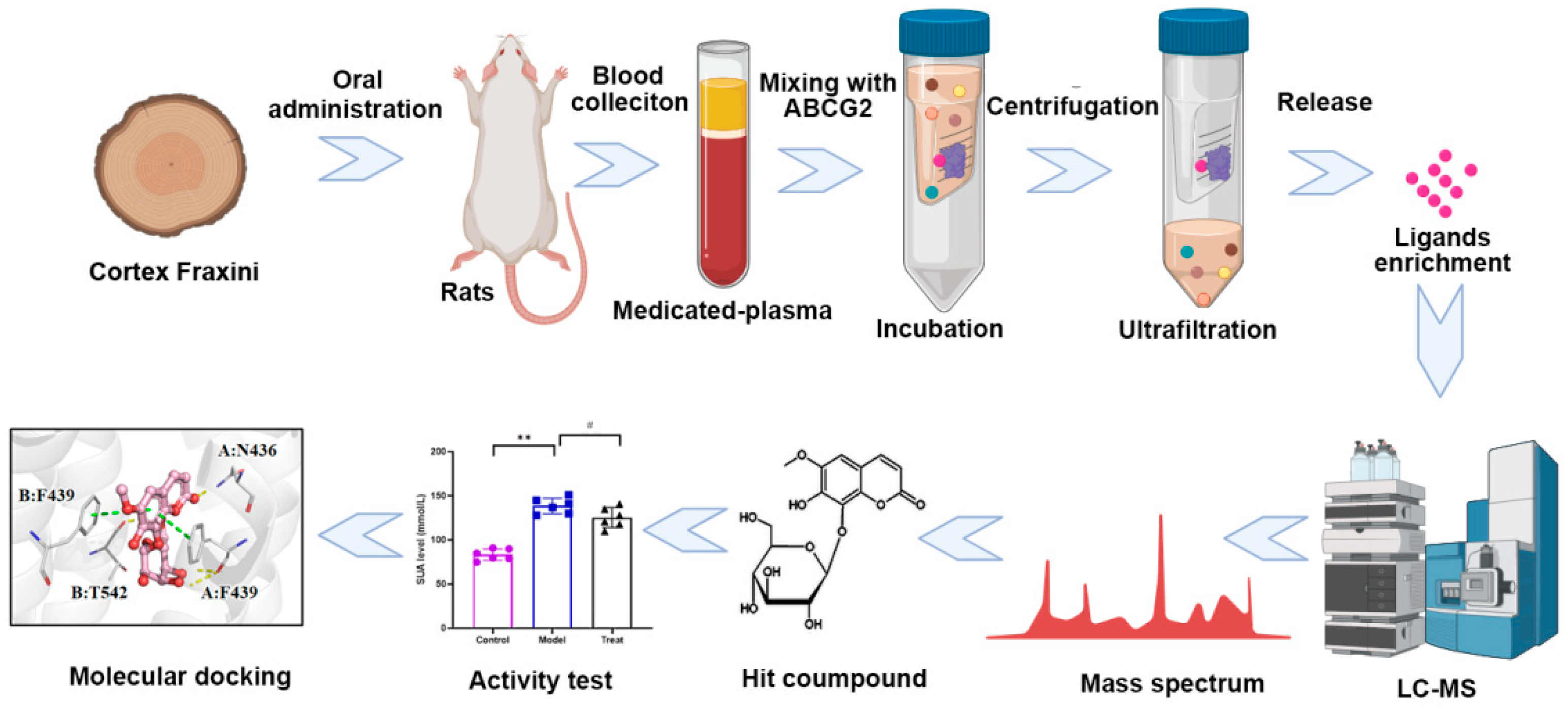
Figure 1 (Created with BioRender.com). It is anticipated that the implementation of this strategy will expedite the process of natural-product based drug discovery.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and reagents
Chemical compounds of fumitremorgin C and fraxin were produced from MedChemExpress (Shanghai, China). Cortex Fraxini (Lot: 220509) was purchased from the GuoDa drugstore (Shanghai, China). HPLC-grade reagents were obtained from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, USA). All other chemicals were bought from standard commercial sources. Recombinant ABCG2 was purchased from Feiyue Biotechnology Co., LTD (Wuhan, China), and centrifugal ultrafiltration filters with a cut-off membrane were provided by Merck millipore Co. LTD (Billerica, USA). 14C-uric acid was purchased from American Radiolabeled Chemicals (St. Louis, USA). Membrane vesicles obtained from ABCG2-overexpressing cells were purchased from SOLVO Biotechnology Biotechnology (Budapest, Hungary).
2.2. Preparation of the Cortex Fraxini extract
The powdered Cortex Fraxini (1.0 kg) was subjected to ultrasonic extraction using 10 L of 75% ethanol and a power of 500 W for a duration of 1 hour. The resulting extracting solution was then centrifuged at a speed of 4,000 rpm for a duration of 3 minutes. Subsequently, the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure at a temperature of 50°C. The remaining solution was then subjected to lyophilization in order to obtain a freeze-dried powder of Cortex Fraxini extract.
2.3. Preparation of medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini
A total of six male Sprague Dawley rats weighing 200 g were procured from the Experimental Animal Center of Xuzhou Medical University in Xuzhou, China. All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines and regulations set forth by the Medical Ethic Committee of Xuzhou Medical University (NO. L20210226100). The prepared Cortex Fraxini extract, suspended in 0.5% CMC-Na, was administered to rats via intragastric gavage at a dose of 1.7 g/kg body weight [
12]. Blood samples were collected via retro-orbital bleeding at specific time intervals (0.5, 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h). Approximately 0.5 mL of blood was collected at each time point and immediately centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The resulting plasma samples from six rats were combined and stored at -80℃ until further analysis.
2.4. Screen of potential ABCG2 ligands with BA-UF-MS
The method employed for analysis involved three steps: loading, washing, and releasing [
13]. The ABCG2 solution (5 μg/mL) was prepared using phosphate buffer solution (PBS, 100 mM, pH 7.4). Subsequently, 100 μL of medicated-plasma and 100 μL of ABCG2 solution were combined in an EP tube and incubated at 37℃ for 30 minutes. Following incubation, the formed ABCG2-ligand complexes were filtered through a 10 kDa ultrafiltration (UF) membrane. The target-ligand complexes were retained by centrifugation at 13 000 rpm for 10 minutes, while unbound compounds in the UF tube were eliminated through six rounds of washing with 200 μL of PBS and subsequent centrifugation. Unbound compounds successfully traversed the UF membrane, whereas ligands bound to the ABCG2 protein did not. Consequently, the ABCG2-ligand complexes were isolated and acquired. Subsequently, the attached ligands were liberated by subjecting them to ultrasonication and centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 10 minutes, repeated three times. The filtrates from each sample were consolidated for subsequent BA-UF-MS analysis.
To address the issue of nonspecific binding in the ligand screening process, the ABCG2 protein was subjected to denaturation by boiling it in water for a duration of one hour. A control group was established by co-incubating the denatured protein with medicated-plasma, followed by conducting the subsequent screening procedure in a similar manner. Subsequently, liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS, Orbitrap Exploris 120, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) was employed to analyze and identify compounds that specifically target ABCG2 within the medicated-plasma. The LC-HRMS conditions utilized in this analysis are provided in the
supporting information. By comparing the peak areas of LC-HRMS chromatograms obtained from the experimental and control samples (representing inactive ABCG2), potential ABCG2 ligands were identified and screened within the medicated-plasma.
2.5. Optimization of experimental parameters
In order to attain the most favorable screening outcomes, various factors that have the potential to influence the results were examined. These factors encompassed the concentration of ABCG2 (ranging from 1 to 20 mg/ml), the duration of incubation (ranging from 5 to 60 minutes), the temperature of incubation (25, 37, and 42℃), and the size of ultrafiltration filters (ranging from 10 to 100 kDa). Fumitremorgin C (a known ligand of ABCG2) was selected as representative compounds to optimize the screening conditions. The adsorption ratio (mg/g) of fumitremorgin C was used to evaluate optimization procedure, which was calculated as ma/m0, where ma (mg) represented the mass of adsorptive and subsequently eluted fumitremorgin C, and m0 (mg) represented the mass of added fumitremorgin C for incubation.
2.6. Study of 14C-UA uptake by membrane vesicles
The evaluation of the
14C-UA uptake of Cortex Fraxini extract or hit compounds was conducted using membrane vesicles obtained from ABCG2-overexpressing cells [
14]. In 96-well plates, membrane vesicles,
14C-UA, and a hit compound solution were combined and incubated with PBS buffer for a duration of 30 minutes at a temperature of 37°C. The uptake reactions of
14C-UA were initiated by the addition of MgATP, and the membrane vesicles were subsequently washed three times with ice-cold DPBS (Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline) in order to terminate the reaction after a period of 5 minutes. Following filtration through glass fiber filters, the filters were washed three times with ice-cold DPBS. The quantity of substrate present within the filtered vesicles was determined by measuring intracellular radioactivity using a liquid scintillation counter (PerkinElmer, USA) subsequent to the addition of scintillant. Each treatment was measured in triplicate.
2.7. Study of SUA-lowing effect of the hit compound in hyperuricemic rats
The hit compound was assessed in a rat model of acute hyperuricemia induced by hypoxanthine and potassium cyanate [
15]. Six SD rats were allocated to each of the following groups: control, hyperuricemic model, and treatment. The hyperuricemic model group rats were administered xanthine intragastrically and potassium oxonate subcutaneously. The treatment group rats were orally administered 10 mg/kg of the hit compound (dissolved in 0.5% CMC-Na) 3 hours prior to xanthine and potassium oxonate administration. Blood samples were collected via retro-orbital bleeding after 6 hours of hyperuricemia induction. The levels of SUA were assessed using the UA ELISA kit (Bioroyee Co., LTD, Beijing, China).
2.8. Molecular docking
Molecular docking was conducted to simulate the process of molecular recognition and determine the binding energies between the hit compound and ABCG2 (PDB ID: 6VXI) using PyMOL v1.3 software.
2.9. Surface plasmon resonance analysis
The local surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) experiment was performed using an OpenSPR (NicoyaLifesciences, Waterloo, Canada) for the analysis of SPR [
16]. The COOH sensor chip was utilized for capture-coupling to immobilize ABCG2 protein (50 μg/mL), and the interaction between ABCG2 and the hit compound was observed at 37 °C. The running buffer utilized in this study was PBS buffer containing 5% DMSO. Solutions of varying concentrations of the hit compound were sequentially flowed through the chips at a rate of 20 μL/min. Simultaneously, running buffer correction was conducted.
2.10. Statistical analysis
All experimental data were analyzed using SPSS software (19.0) and recorded as mean ± standard deviation for three replicates. Statistical significance was determined at a threshold of P<0.05.
3. Results
3.1. ABCG2 activated assay of the Cortex Fraxini extract
The activity of the Cortex Fraxini extract on ABCG2 was assessed, revealing a significant effect with an EC50 value of 35.26 mg/mL as determined by 14C uptake. The ABCG2 activity of the Cortex Fraxini extract had been observed, but the specific bioactive constituents responsible for affecting ABCG2 in medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini have not been previously identified. Therefore, BA-UF-MS was employed to identify the active constituents that target ABCG2.
3.2. Optimization conditions for ligand screen
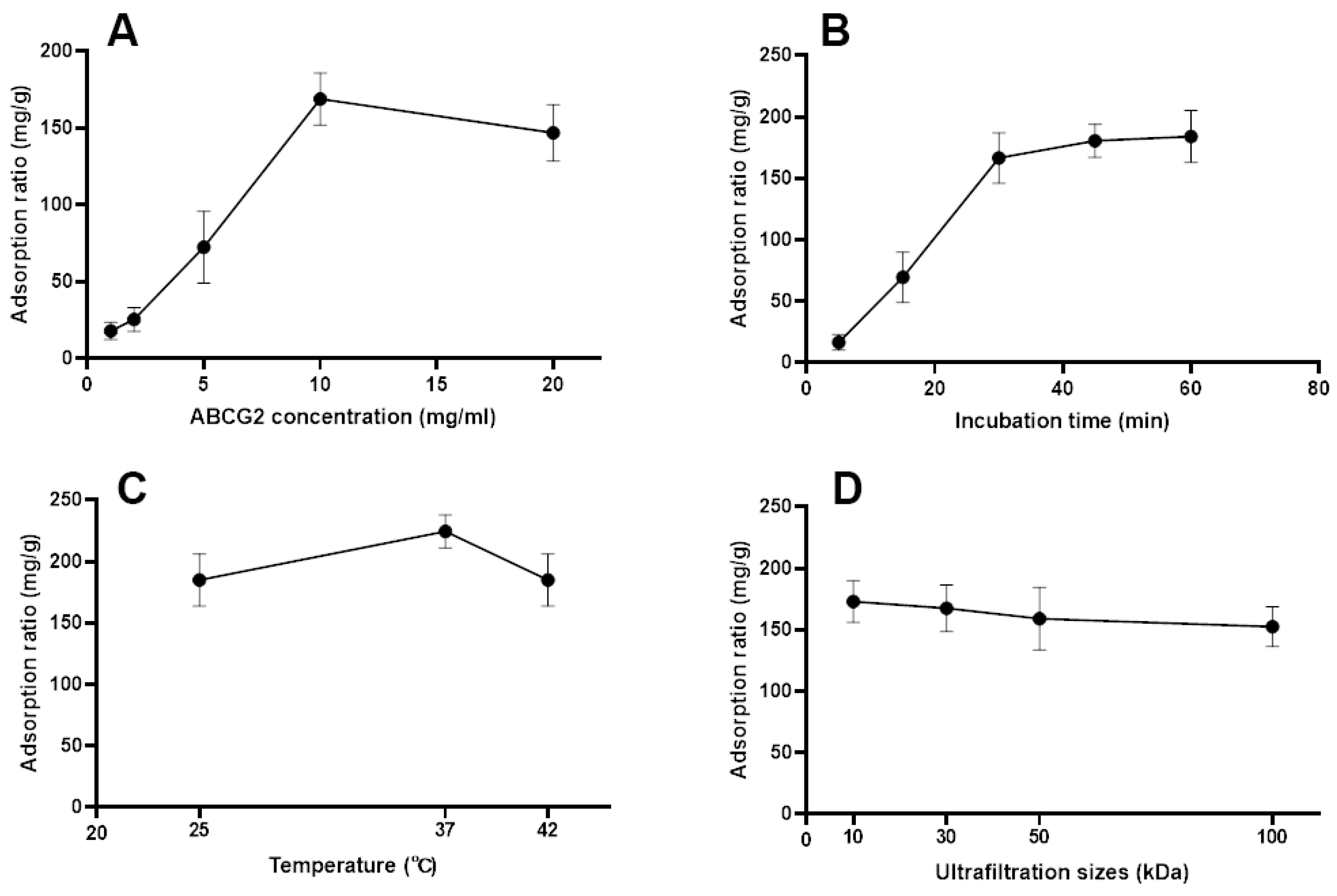
Upon incubation of the medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini with ABCG2, protein-ligand complexes were formed. In order to achieve optimal screening performance with BA-UF-MS, it is necessary to investigate certain important parameters. The protein concentration of ABCG2 directly impacts the screening results. The results depicted in
Figure 2A demonstrate that the binding quantity of fumitremorgin C exhibited an upward trend with increasing concentrations of ABCG2 up to 10 mg/ml, beyond which higher concentrations of ABCG2 had a detrimental impact. Furthermore, the duration of incubation influenced the binding quantity of ligands to target proteins.
Figure 2B illustrates a substantial increase in the binding quantity of fumitremorgin C to ABCG2 from 5 minutes to 30 minutes, with no discernible changes observed when the incubation time reached 60 minutes, indicating the saturation of ABCG2 binding at the 30-minute mark. Excessive incubation duration may result in a decline in protein activity, consequently leading to a diminished degree of binding [
17]. The activity of ABCG2 is influenced by temperature. As depicted in
Figure 2C, an incubation temperature of 37℃ exhibited the highest level of binding for fumitremorgin C. The size of the ultrafiltration tube played a significant role, thus necessitating an investigation of ultrafiltration sizes of 10, 30, 50 and 100 kDa.
Figure 2D demonstrates that the 10 kDa ultrafiltration tube yielded the greatest amount of ligand binding. In conclusion, the optimal screening conditions were determined to be as follows: ABCG2 concentration of 10 mg/ml, incubation time of 30 minutes, incubation temperature of 37°C, and 10 kDa of ultrafiltration size.
3.3. Screen for ABCG2 ligands using BA-UF-MS
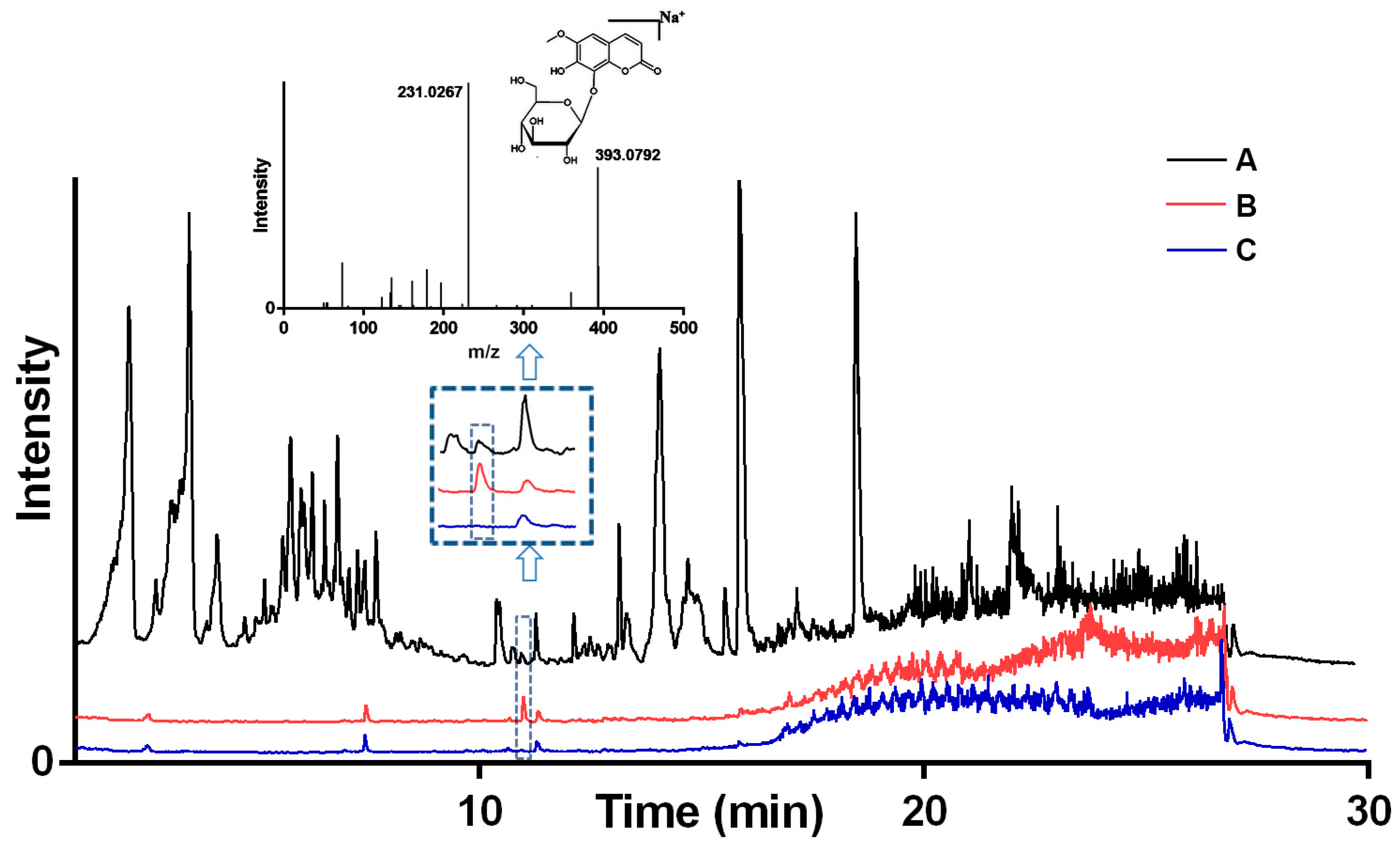
The experiment involves incubating ABCG2 with the medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini, where ligands with high affinity interact with the ABCG2 protein. Other components do not exhibit any specific interaction with ABCG2, and thorough washing steps are employed to eliminate low affinity ligands. During the releasing phase, an organic solvent was employed to liberate binding ligands. Subsequently, the bound compounds were extracted using an organic solution and subjected to analysis via LC-MS. Utilizing the optimized conditions, medicated-plasma was screened using BA-UF-MS, and the resulting chromatograms of medicated-plasma, eluent solution from ABCG2, and a deactivated control sample solution were presented in
Figure 3. By evaluating the peak area, a distinctive peak was observed in the chromatogram of the eluent solution, with a higher peak area compared to that of the control group, indicating favorable specificity. Based on the strategy principle, it was observed that this particular constituent possessed the ability to bind to ABCG2, thereby qualifying it as a potential ligand for ABCG2. The identification of potential active components was accomplished through the utilization of MS fragments and a self-constructed database comprising approximately 4,500 compounds derived from natural herbs. Consequently, the compound fraxin was determined to be the hit compound.
3.4. Activity test of the hit compound in vitro and in vivo
It is important to note that the binding of a compound to a protein does not necessarily imply its role as an inhibitor or activator, as the compound may exhibit non-specific binding to non-functional sites of the protein [
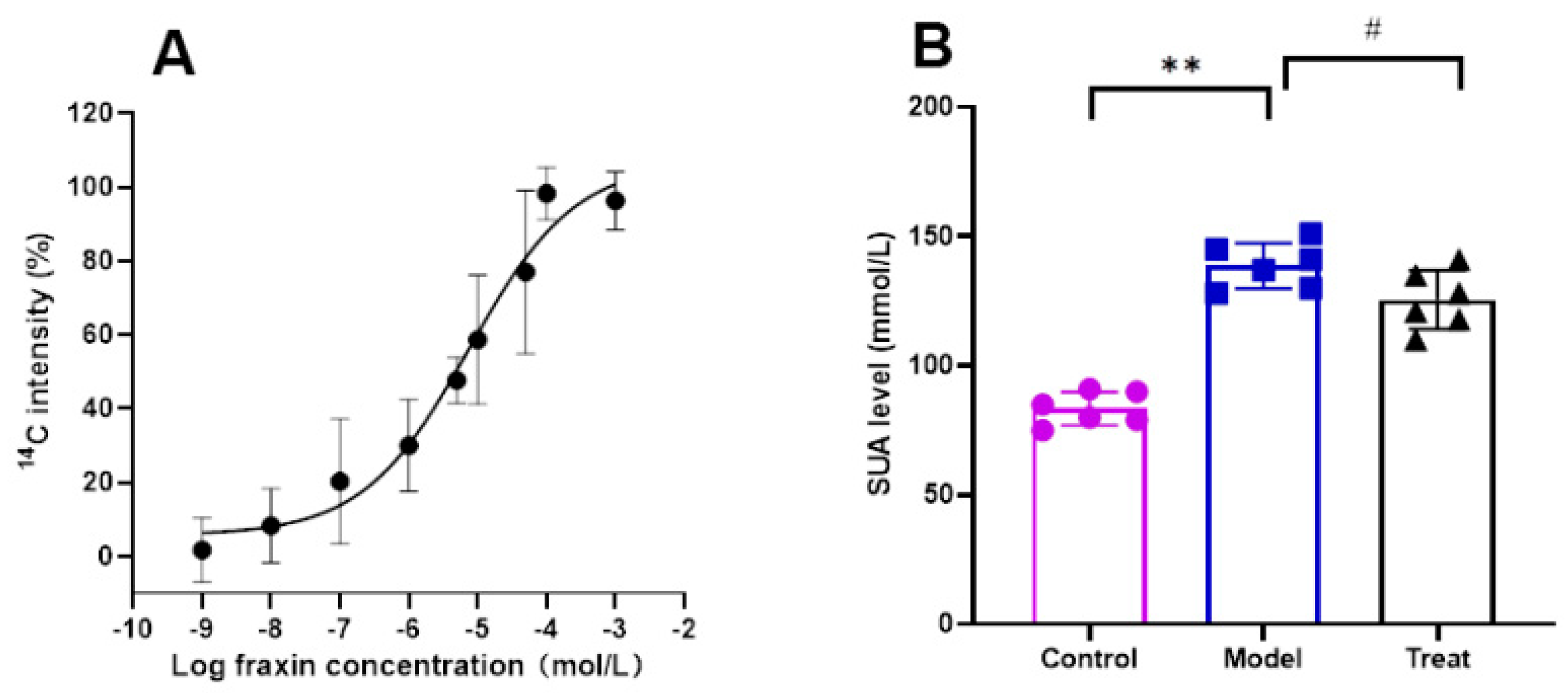
18]. The binding of a compound to a protein does not necessarily indicate whether it functions as an inhibitor or activator, as the compound may bind non-specifically to non-functional sites on the protein. Additional pharmacological investigation is required to determine the activating effect of the hit compound on ABCG2. The activity of fraxin was confirmed to activate ABCG2 in a concentration-dependent manner, as evidenced by the promotion of ABCG2 -mediated uptake of
14C -UA with an EC
50 of 7.55 μM, as depicted in
Figure 4A. To further validate its efficacy, fraxin was subsequently assessed for its ability to reduce SUA levels in rats. The findings of the study demonstrated that intragastrically administered fraxin led to a significant reduction in the level of SUA in rats (
P<0.05), as depicted in
Figure 4B. These results were consistent with the outcomes of the target screening.
3.5. Affinity verification between fraxin and ABCG2
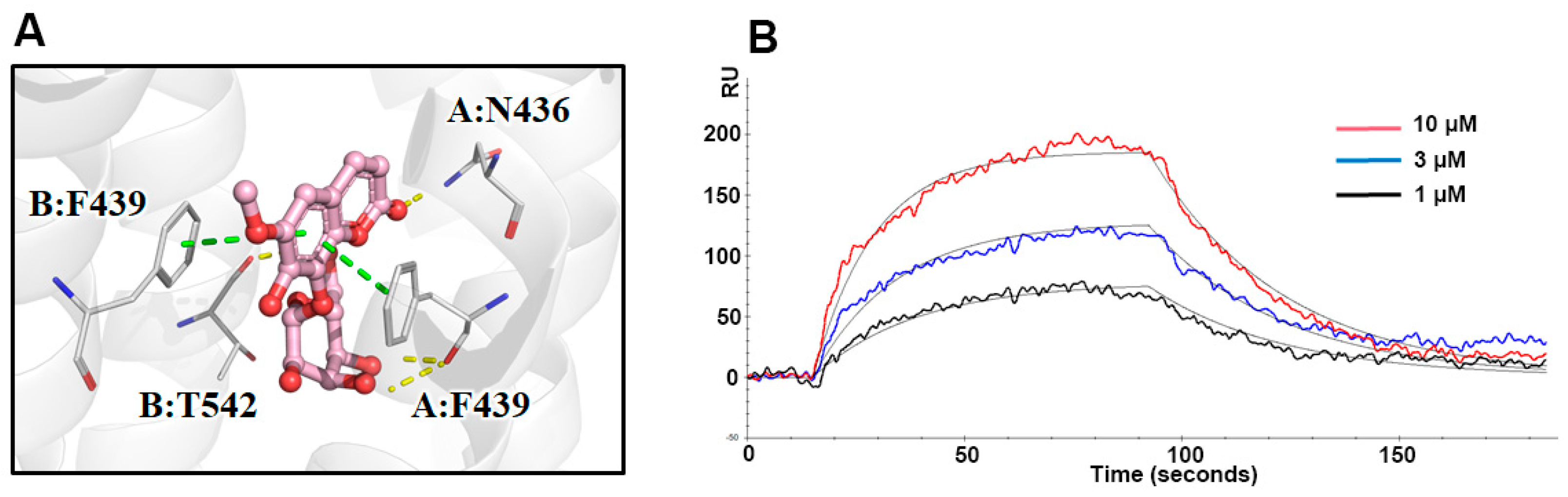
Molecular docking analysis was employed to investigate the binding sites and interaction between the hit compound and ABCG2. Fraxin exhibited a strong affinity towards the active pocket of ABCG2, as illustrated in
Figure 5A, forming hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking with F439, F349, N436, and T542. The binding energy of fraxin with ABCG2 was calculated to be -13.145 kcal/mol. The docking results strongly suggested that fraxin has the potential to act as a ligand for ABCG2. To further validate the binding activity of ABCG2, the K
D value of fraxin was determined using SPR assay. The obtained result indicated that the K
D value for fraxin was calculated as 141.2 μM (
Figure 5B).
4. Discussion
ABCG2 is a crucial urate transporter highly expressed in the epithelial cells of the intestine and kidney. This transporter plays a pivotal role in both renal urate overload and extra-renal urate underexcretion. Limited attention is currently devoted to UA-lowering drugs that target sites beyond the kidney. Additionally, numerous components found in TCMs exhibit low bioavailability when orally administered, resulting in limited absorption into the bloodstream and reaching the intended target organs. Conversely, certain components directly impact target sites within the intestine, such as by modulating the gut microbiota to reduce UA levels[
19]. Given these considerations, we have selected ABCG2 as the protein target.
Commonly employed drugs for the treatment of hyperuricemia include benzbromarone, allopurinol, and febuxostat. Nevertheless, prolonged administration of these drugs is associated with various adverse effects, such as hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity [
20]. Consequently, the identification of novel hyperuricemic drugs with reduced toxicity and fewer side effects has become a prominent research area in recent years. TCMs have been widely recognized as a valuable resource for identifying hit compounds in the field of drug discovery [
21]. The diverse chemical structures present in these compounds offer a vast pool from which potential leads for drug development and optimization can be selected and refined. Considerable attention has been directed towards exploring the bioactive compounds derived from TCMs, as they hold promise as a novel and safer source for anti-hyperuricemia drug leads.
It is important to note that the pharmacological effects of TCMs primarily rely on the absorption of their components into the bloodstream. However, the oral administration of TCMs results in a significantly low transfer of these components into the blood. Moreover, the presence of numerous dietary and endogenous substances further complicates the identification and separation of the absorbed ingredients from TCMs. Given the intricate nature of the chemical constituents found in natural medicines and the minuscule concentration of their bioactive components within living organisms, the identification of potential target ligands from constituents absorbed into the bloodstream poses a formidable challenge [
17]. Traditional approaches to isolating target protein ligands involve separation techniques and bioassay-guided fractionation. However, these conventional methods for screening bioactive compounds from complex systems are both time-consuming and labor-intensive [
22]. Consequently, a targeted protein-oriented screening method would serve as an efficient strategy for the identification of active compounds from such intricate systems [
23]. The utilization of target screens offers numerous benefits, primarily due to their enhanced speed and convenience in directly capturing target compounds, thereby eliminating the necessity for repetitive separation protocols of non-target analytes [
24,
25]. Consequently, the implementation of the BA-UF-MS strategy is anticipated to expedite the process of natural-product based drug discovery.
Cortex Fraxini has been utilized in the management of hyperuricemia and gout, thus presenting a promising opportunity to identify potential therapeutic components from Cortex Fraxini that target hyperuricemia. The assessment of a compound's binding ability to a specific protein is essential in evaluating the biological effects of TCMs [
26]. Notably, Cortex Fraxini extract demonstrated significant activity in
14C-UA uptake experiments, indicating the presence of potential ABCG2 activators within Cortex Fraxini. Employing the BA-UF-MS strategy, fraxin was screened and confirmed to exhibit activity both in
vitro and in
vivo, thereby suggesting its potential as an anti-hyperuricemia agent [
27].
To explore the interaction between the hit compound and ABCG2, we employed molecular docking and SPR assay. Molecular docking, a virtual method influenced by force field, temperature, and pH, provides a theoretical understanding of the receptor-ligand interaction [
28]. To complement this, we conducted real experiments and determined the binding affinity between fraxin and ABCG2 to be 141.2 μM using SPR assay. These findings substantiate the mechanistic perspective and validate the accuracy and reliability of the BA-UF-MS strategy.
5. Conclusions
In the current investigation, fraxin was identified from medicated-plasma of Cortex Fraxini using a rapid and efficient BA-UF-MS strategy. The bioactivity of fraxin was assessed through in vitro and in vivo experiments, including determination of the EC50 value, evaluation of its SUA lowering effect, analysis of molecular docking scores, and determination of the affinity constant KD. The findings unequivocally established that fraxin possesses promising bioactivity in reducing UA levels, making it a potential candidate for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. In summary, the findings of this study indicate that medicated-plasma derived from TCM holds promise as a valuable resource for identifying potential hit compounds. Furthermore, the BA-UF-MS approach proves to be an effective strategy for the discovery of active ingredients from biological samples.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Xiuxiu Huang; methodology, Wenqing Dong; validation, Xiao Luo; formal analysis, Lu Xu; investigation, Lu Xu; resources, Lu Xu; data curation, Lu Xu; writing—original draft preparation, Yinan Wang.; writing—review and editing, Yinan Wang.; visualization, Yinan Wang; supervision, Yinan Wang; project administration, Yinan Wang; funding acquisition, Yinan Wang. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
Please add: This research was partial funded by the project of scientific and technological development of traditional Chinese medicine in Jiangsu province, grant number MS2021106. The APC was covered by Yinan Wan”.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Johnson, R.J.; Bakris, G.L.; Borghi, C.; Chonchol, M.B.; Chertow, G.M. Hyperuricemia, Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Report of a Scientific Workshop Organized by the National Kidney Foundation. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 2018, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardin, T.; Richette, P. Definition of hyperuricemia and gouty conditions. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2014, 26, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaspa, M.A.; Andres-Hernando, A.; Kuwabara, M. Uric acid and hypertension. Hypertension Research 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, K.M.; Dixon, E.E.; Lewis, R.M.; Allan, J.; Gamble, G.D.; Phipps-Green, A.J.; Halperin Kuhns, V.L.; Horne, A.M.; Stamp, L.K.; Merriman, T.R.; Dalbeth, N.; Woodward, O.M. The ABCG2 Q141K hyperuricemia and gout associated variant illuminates the physiology of human urate excretion. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, O.M.; Kottgen, A.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Guggino, W.B.; Kottgen, M. Identification of a urate transporter, ABCG2, with a common functional polymorphism causing gout. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 10338–10342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiburkova, B.; Pavelcova, K.; Pavlikova, M.; Jesina, P.; Pavelka, K. The impact of dysfunctional variants of ABCG2 on hyperuricemia and gout in pediatric-onset patients. Arthritis Res Ther 2019, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huls, M.; Brown, C.D.; Windass, A.S.; Sayer, R.; van den Heuvel, J.J.; Heemskerk, S.; Russel, F.G.; Masereeuw, R. The breast cancer resistance protein transporter ABCG2 is expressed in the human kidney proximal tubule apical membrane. Kidney Int 2008, 73, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lin, H.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, L.; Gao, L.; Li, L. Mangiferin promotes intestinal elimination of uric acid by modulating intestinal transporters. Eur J Pharmacol 2020, 888, 173490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.H.; Chang, Y.P.; Li, T.; Han, F.; Li, C.J.; Li, X.Y.; Xue, M.; Cheng, Y.; Meng, Z.Y.; Han, Z.; Sun, B.; Chen, L.M. Empagliflozin Attenuates Hyperuricemia by Upregulation of ABCG2 via AMPK/AKT/CREB Signaling Pathway in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Int J Biol Sci 2020, 16, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Xin, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, C. (1)H NMR and MS based metabolomics study of the therapeutic effect of Cortex Fraxini on hyperuricemic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2016, 185, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.P.; Chen, J.; Hong, J.Y.; Hao, H.; Qi, L.W.; Lu, J.; Fu, Y.; Wu, B.; Yang, H.; Li, P. A strategy for screening of high-quality enzyme inhibitors from herbal medicines based on ultrafiltration LC-MS and in silico molecular docking. Chem Commun (Camb) 2015, 51, 1494–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Ou, Y.; Zeng, B.; Lou, X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, C. Metabolic profile of esculin in rats by ultra high performance liquid chromatography combined with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2016, 1020, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Guo, L.; Sheng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Jiang, Z.; Tian, H. Rapid identification and isolation of neuraminidase inhibitors from mockstrawberry (Duchesnea indica Andr.) based on ligand fishing combined with HR-ESI-Q-TOF-MS. Acta Pharm Sin B 2020, 10, 1846–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Ashizawa, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Saito, R.; Motoki, K.; Sakai, M.; Chikamatsu, N.; Hagihara, C.; Hashiba, M.; Iwanaga, T. Pharmacological Evaluation of Dotinurad, a Selective Urate Reabsorption Inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2019, 371, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Meng, Q.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ai, W.; Zhao, Z.; Kang, D.; Dong, Y.; Liang, R.; Wu, T.; Pang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P. Novel Human Urate Transporter 1 Inhibitors as Hypouricemic Drug Candidates with Favorable Druggability. J Med Chem 2020, 63, 10829–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Che, D.; Wei, D.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Fu, J.; Zhou, N.; He, H. Phenothiazine antipsychotics exhibit dual properties in pseudo-allergic reactions: Activating MRGPRX2 and inhibiting the H(1) receptor. Mol Immunol 2019, 111, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, B.; Cao, J.; Zheng, H.; Ye, L.H. Ligand fishing based on bioaffinity ultrafiltration for screening xanthine oxidase inhibitors from citrus plants. J Sep Sci 2021, 44, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Kong, J.; Yao, C.H.; Liu, X.F.; Liu, J.H. Rapid identification of urokinase plasminogen activator inhibitors from Traditional Chinese Medicines based on ultrafiltration, LC-MS and in silico docking. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2019, 164, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wen, J.; Guan, B.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Wei, M.; Qiu, H. Folic acid and zinc improve hyperuricemia by altering the gut microbiota of rats with high-purine diet-induced hyperuricemia. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 907952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Saag, K.G.; Becker, M.A.; Borer, J.S.; Gorelick, P.B.; Whelton, A.; Hunt, B.; Castillo, M.; Gunawardhana, L.; Investigators, C. Cardiovascular Safety of Febuxostat or Allopurinol in Patients with Gout. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Tian, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Guan, Y.; Tong, S.; Yan, J. Screening and characterization of aldose reductase inhibitors from Traditional Chinese medicine based on ultrafiltration-liquid chromatography mass spectrometry and in silico molecular docking. J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 264, 113282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudencio, S.P.; Pereira, F. Dereplication: racing to speed up the natural products discovery process. Nat Prod Rep 2015, 32, 779–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesla, L.; Moaddel, R. Comparison of analytical techniques for the identification of bioactive compounds from natural products. Nat Prod Rep 2016, 33, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, X.; Tian, X.; Wu, G. Pharmaceutical applications of affinity-ultrafiltration mass spectrometry: Recent advances and future prospects. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2016, 131, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, B.X.; Guo, M. Current advances in screening for bioactive components from medicinal plants by affinity ultrafiltration mass spectrometry. Phytochem Anal 2018, 29, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.A.; Ishikawa, N.; Tanaka, M.; Uemura, K.; Sugimitsu, N.; Suganami, A.; Tamura, Y.; Koyano, T.; Kowithayakorn, T.; Ishibashi, M. Hes1 inhibitor isolated by target protein oriented natural products isolation (TPO-NAPI) of differentiation activators of neural stem cells. Chem Sci 2016, 7, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.C.; Kong, L.D. Protective effects of cortex fraxini coumarines against oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and renal dysfunction in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2011, 666, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Niu, H.; Nie, A.; Bian, M. Bioactivity-guided separation of potential alpha-glycosidase inhibitor from clerodendranthus spicatus based on HSCCC coupled with molecular docking. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).