1. Introduction
Listeria monocytogenes (LM), a gram-positive bacillus widespread in the environment, is a pathogen responsible for human listeriosis, a serious food-borne zoonotic disease especially relevant to the elderly, immunosuppressed individuals, pregnant women and newborns [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Transmission generally occurs through the consumption of ready-to-eat (RTE) foods such as soft cheese, vegetables, fruit, meat, and salads [
5,
6,
7].
The clinical manifestations of bacterial infections can take the form of non-invasive or invasive infections depending on the bacterial load, degree of virulence among strains, and the host's immune system [
8]. The non-invasive form usually occurs in immunocompetent subjects causing typical symptoms of febrile gastroenteritis (with high bacterial load 10
9 CFU/ml), while in immunosuppressed subjects such as the elderly, pregnant women and newborns, LM may cause meningitis, meningo-encephalitis, sepsis, and fetal infections [
8]. Despite its relatively low incidence (1931 cases were reported in Europe in 2020), listeriosis is a serious health issue because it is associated with a high hospitalization (97.3%) and case-fatality (12.8%) rate [
9]. Furthermore, Italy, with 155 notified cases in 2020, has been classified by ECDC as the fourth European country with the highest incidence rate of listeriosis [
9]. Moreover, in 2020 the phenomenon is likely underestimated due lately not only to the slowdown of laboratory investigations because of SARS-COV-2 but also because the cases reported only concern hospitalized patients; mandatory notification doesn’t include non-invasive cases of listeriosis which resolve spontaneously.
Thus, listeriosis is subjected to constant epidemiological control through the collection of clinical strains and their phenotypic and molecular characterization [
10].
Currently, 13 serotypes of LM have been identified, but only four (1/2a, 1/2b, 1/2c, and 4b) are responsible for most confirmed clinical cases in Europe and worldwide [
10,
11,
12].
Serotype 4b appears to be the most virulent since it is responsible for most of the epidemics in humans, despite serotype 1/2a is the most frequently isolated one from food [
10,
11,
12].
For typing, the gold standard techniques are considered
Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) and
Multi-Virulence-Locus Sequence Typing (MvLST) based on the sequencing of seven housekeeping genes and six virulence genes, respectively, to improve the discriminatory power between strains [
13,
14,
15,
16].
Unfortunately, in Sicily the listeriosis is underestimated because under notificated, furthermore, the characterization of human clinical isolates is not determined.
This work aimed to evaluate the molecular characters and phenotypic resistances to antibiotics predicted by the EUCAST 2023 guidelines of clinical strains from cases of listeriosis. We also considered clinical and anamnestic information of patients in accordance with privacy policies. The strains, collected from cases of listeriosis of Palermo’s hospital during December 2018 to June 2020 at
the Department of Health Promotion, Mother and Child Care, Internal Medicine and Medical Specialties (PROMISE) of the University of Palermo, Italy, as local reference laboratory, were sent with survey form to Italian National Institute of Health (ISS) for genomic sequencing. Locally strains were characterized to determine serogroup, sequence typing (ST), virulence type (VT) in addition antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed [
13,
14,
15,
16].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection of patients
The 23 strains of LM species were isolated from biological samples of patients with invasive listeriosis, hospitalized in different hospitals in Palermo from December 2018 to June 2020, with sepsis and in some cases also other complications.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of Listeriosis patients, risk factors (cancer, solid organ transplantation, inflammatory diseases, age >65 years and pregnancy), date of collection of strains, and type of biological sample (blood culture, CSF, ascitic fluid, nasal swab) were obtained from the ISS listeriosis notification questionnaire associated with each clinical strain. Data were collected anonymously in accordance with patients' privacy. (Data available in
Supplementary Table S1).
2.3. PCR Serogroup
All the 23 LM strains were serogrouped by amplifying five target genes (prs, lmo0737, lmo1118, ORF2110, and ORF2819) using primer and amplification conditions previously described [
13]. This technique can discriminate 13 different serotypes previously grouped in 5 serogroups: IIa (1/2a, 3a), IIb (1/2b, 3b, 7), IIc (1/2c, 3c), IVb (4ab, 4b, 4d, 4e), and finally IVa (4a, 4c) [
13].
2.4. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST)
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) was performed according to the protocol described by Moura et al., 2016. PCR product of single PCR of seven housekeeping genes (
abcZ,
blgA,
cat,
dapE,
dat,
ldh,
lhkA), were sequenced using Genetic Analyser (Applied Biosystems, United States) [
17,
18,
19].
The sequence type (ST) and Clonal Complex (CC) of each LM clinical strain were assigned by inserting the sequences into the Institute Pasteur MLST database. Moreover, a phylogenetic tree was built using MEGAX software [
20], based on the concatenated DNA sequences (3288 bp) of the seven housekeeping genes.
The evolutionary history was deduced using the UPGMA method while the evolutionary distances were calculated using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method [
20]
.
2.5. Multi-Virulence-Locus Sequence Typing (MVLST)
Multi-Virulence-Locus Sequence Typing (MVLST) analyses were carried out using primers and PCR protocols reported in Zhang et al. (2004) [
15], to identify the Virulence type (VT) and Epidemic Clones (EC) of 23 LM strains. Six virulence genes (clpP, dal, inlB, inlC, lisR, prfA) were amplified and then sequenced. The sequences obtained were concatenated following the order provided in the MvLST database [
21] and, then, compared with multiple alignments to reference sequences. The phylogenetic tree was determined by analyzing the concatamers of each 23 LM strain using the Neighbor-Joining method that include MegaX software [
20].
2.6. Antibiotic Susceptibility of L. monocytogenes Isolates
Several antimicrobial agents exhibit in vitro activity against
L. monocytogenes [
22].
The primary therapy for invasive
listeriosis consists of supportive therapy along with
penicillin or ampicillin in combination with gentamicin Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole can be used to treat for patients who are allergic to pencillin or pregnant women [
23].
This was performed using the Kirby-Bauer method (Disc diffusion Technique). The sensitivity discs were specifically designed and contained appropriate concentrations of different Gram positive antibiotics which include: Ampicillin (10μg/disc), Erythromycin (15μg/disc), Meropenem (10μg/disc), Penicillin G (10μg/disc) and Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (25µg/disc). Pure isolates were closely streaked onto the surface of Nutrient agar plates. The plates were then incubated at 37°C for 18-24 hours. Following incubation, they were observed for zones of inhibition surrounding each disc. Interpretive breakpoints were determined according to guidelines established by European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) [
24].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of Listeriosis patients
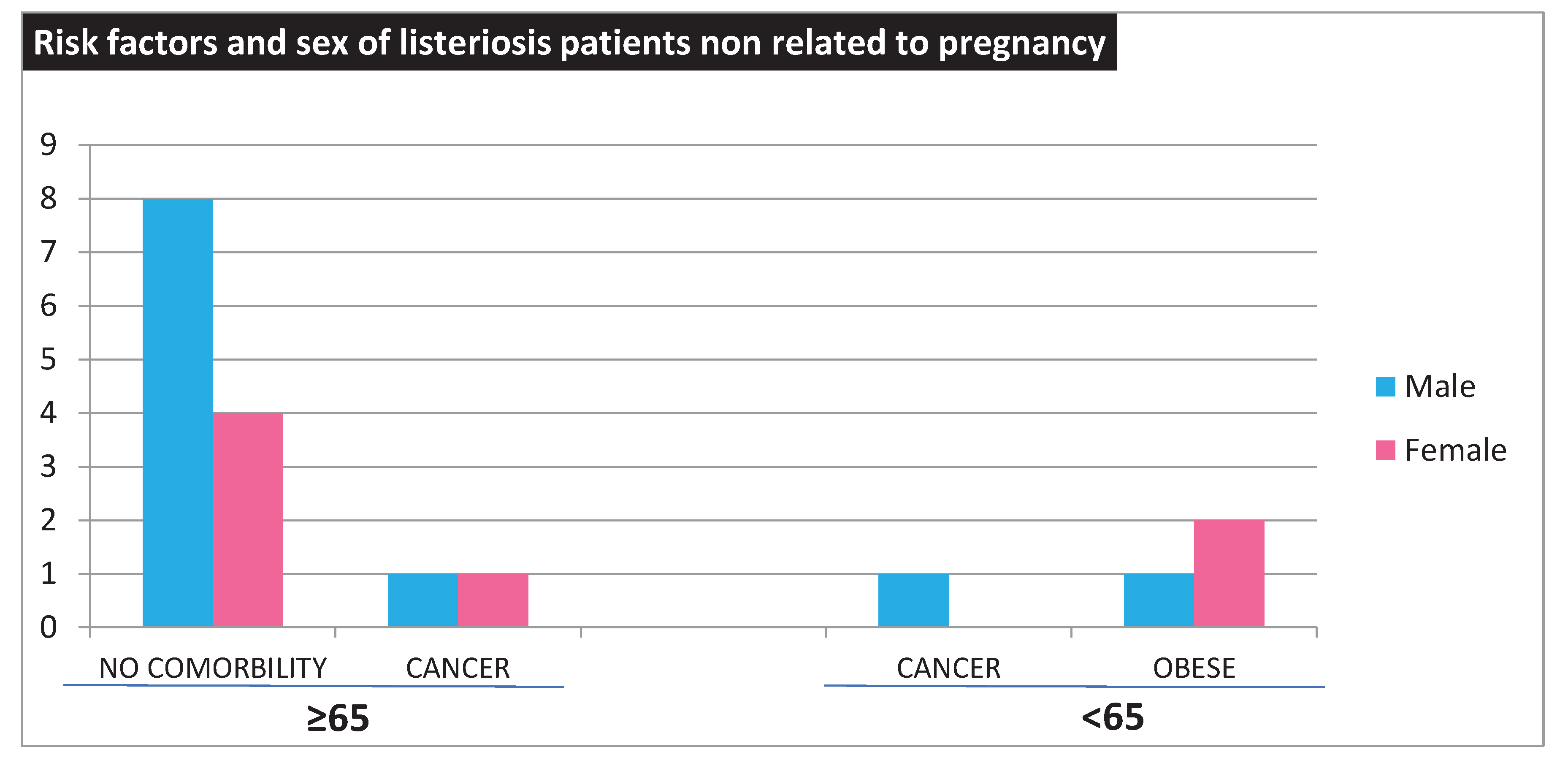
LM strains were isolated from 23 hospitalized patients between 2018 and 2020 in Palermo, Italy, including thirteen males and ten females. The demographic and clinical data of our patients show a greater prevalence in males (n=13, 56%) than in females (n= 10, 44%), consistent with the literature report indicating a higher susceptibility among males. There were eighteen cases of listeriosis (78%) not associated with pregnancy. However, there were 14 patients over the age of 65, two of whom also had cancer. Four patients were younger than 65 years of age, among which three were obese and one had cancer (
Figure 1).
Furthermore, five cases of pregnancy-associated listeriosis (3 newborns and two mother) leading to premature births due to intrauterine infections, are included in the study.
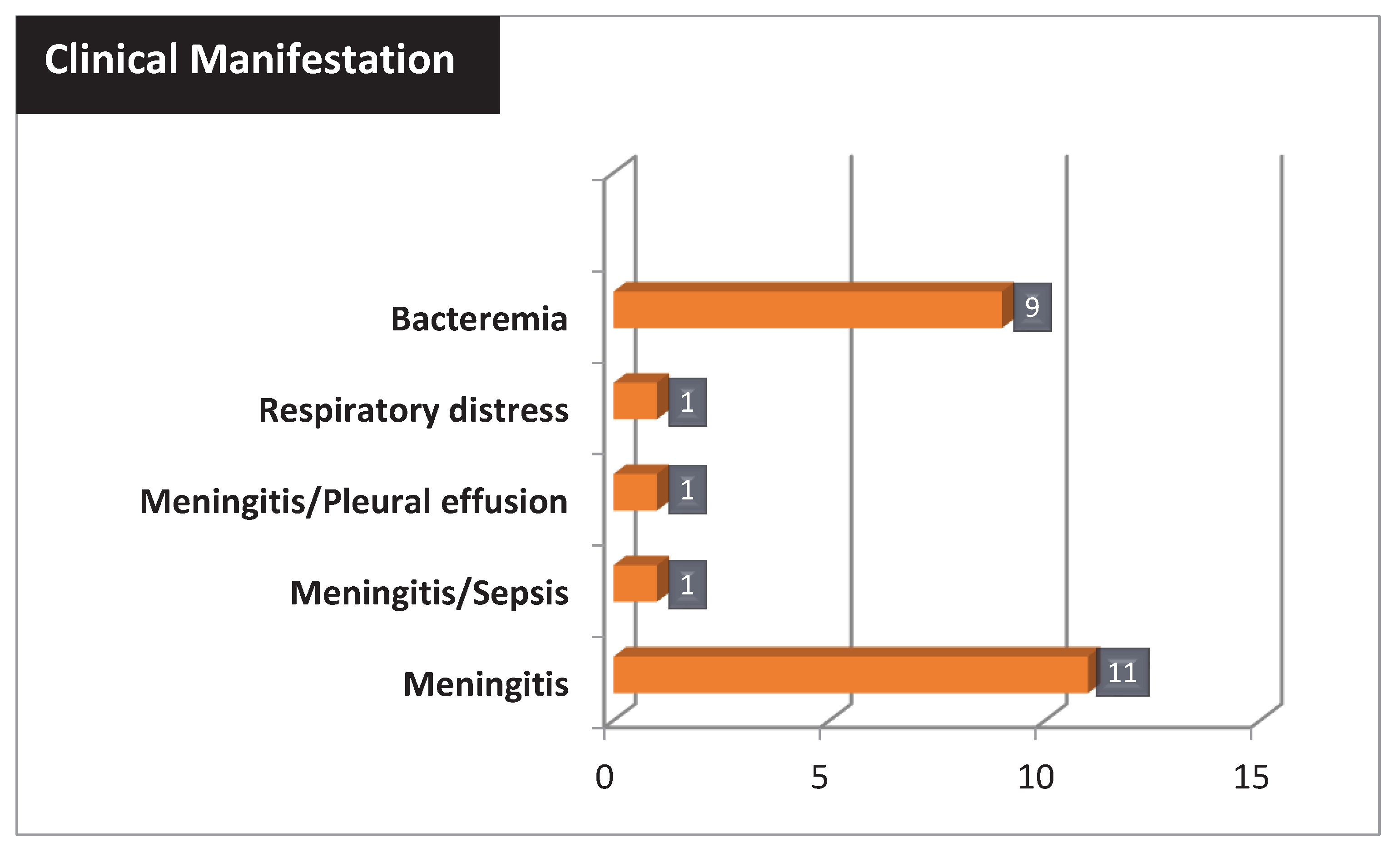
The most common clinical manifestation of listeriosis was meningitis present in 14 patients (60,86%), two of whom were associated with sepsis and pleural effusion. Instead, 9/23 patients (39,13%) showed only bacteremia (
Figure 2).
In addition, a total of four deaths were associated with listeriosis, including patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy (cancer and ulcerative colitis), a 49 year-old woman with meningitis, and a preterm newborn with meningitis.
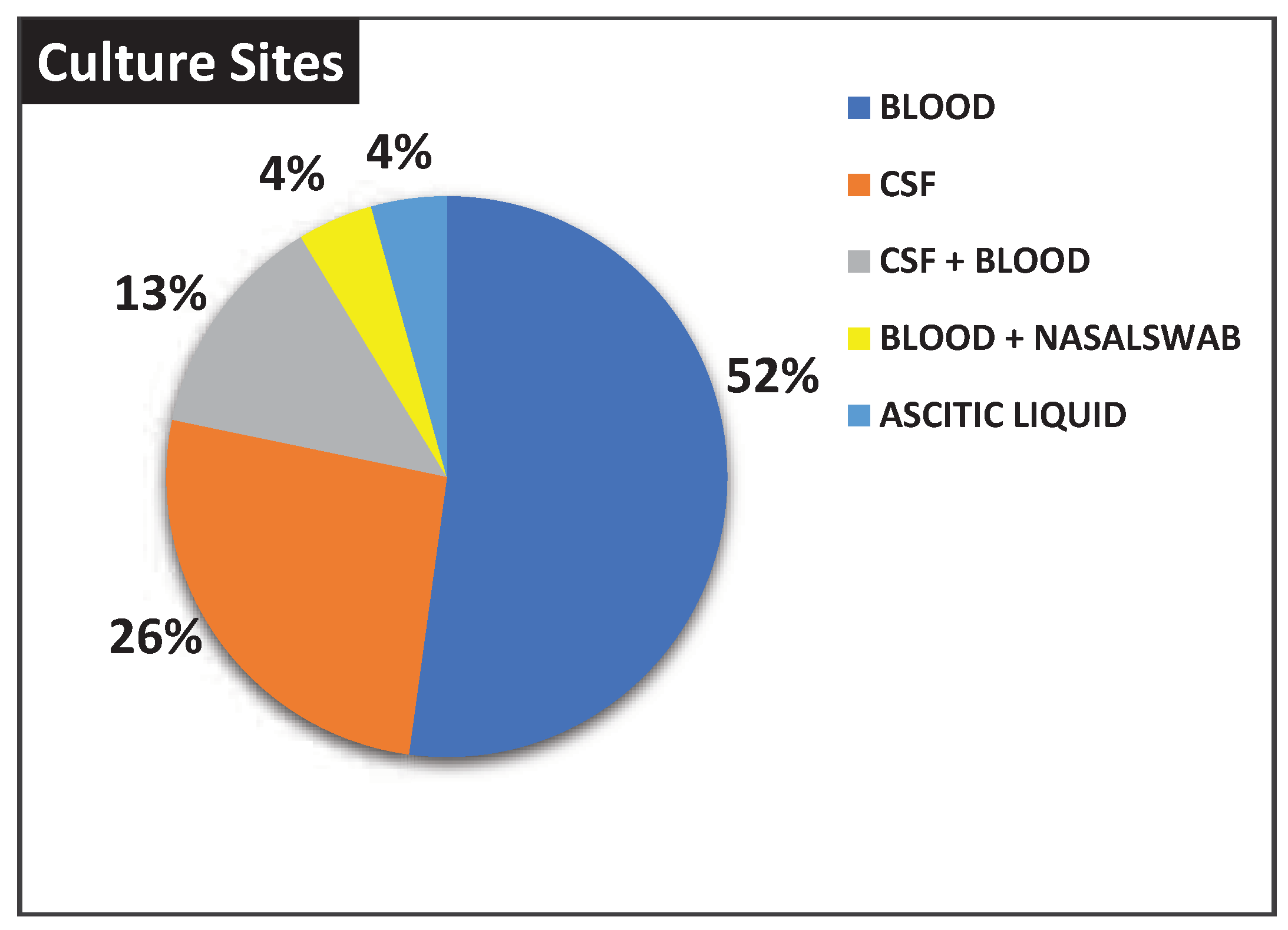
Moreover, twelve (52%) and six (26%) patients were positive respectively in blood and CSF culture, while there were three cases (13%) positive in blood + CSF culture. In addition, two other cases were associated with isolation from ascitic fluid (4%) and nasal swabs + blood (4%), respectively (
Figure 3).
3.2. Serogroup
The results showed the presence of only two different serogroups IIa and IVb. Specifically, the prevalent serogroup was IVb associated with 95,6% of the isolates examined (n=22), and only one strain belonged to IIa (4,4%).
These results agree with the epidemiological information of clinical strains circulating in the European population provided by ECDC for 2019, according to which strains with serotype 4b appear to be prevalent among human isolates compared to strains of serotype 1/2a [
9].
While serogroup IVb clinical strains were isolated in newborns, pregnant women, the elderly, and cancer patients (subjects at risk for listeriosis) with meningitis; serogroup IIa clinical strains were isolated in a patient with ulcerative colitis with sepsis caused by bacteremia, but without central nervous system involvement.
3.3. MLST and MvLST Analysis
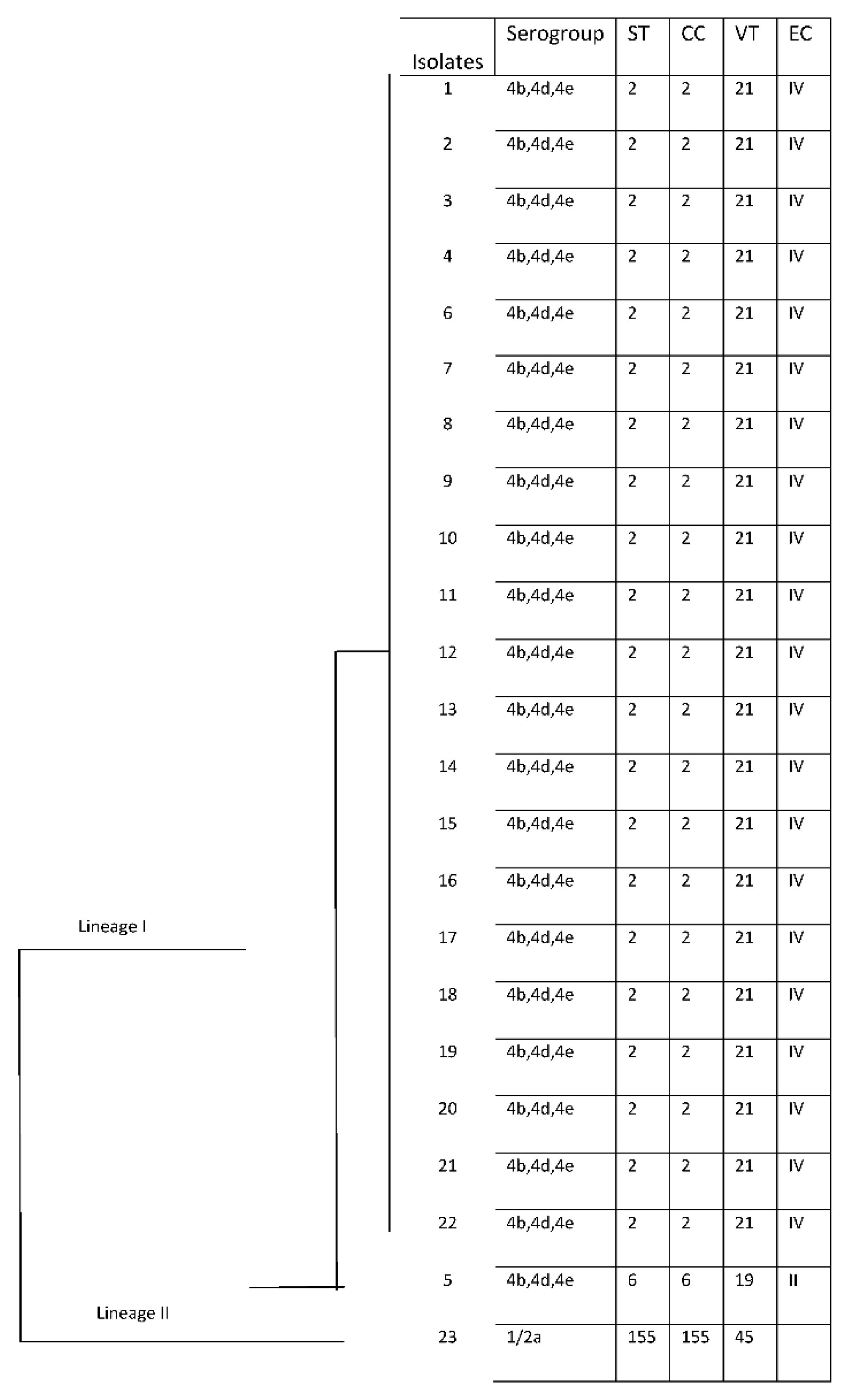
Three different STs and VT were obtained among all strains, which were included in three clonal complexes (CCs) and two Epidemic Clones (EC).
Among 3 STs, ST 2 (CC2)/VT 21 (ECIV) was predominant in 21 isolates (91%), followed by ST6 (CC6)/VT19 (ECII) and ST155(CC155)/VT45 were shown in one strain (4%), respectively (
Table 1). In particular, predominantly ST2 was isolated from blood samples (52%, 11/21) but also from CSF (14,28%, 3/21), ascetic liquid (4,76%, 1/21) and nasal swab (4,76%, 1/21) sample; the only ST6 was isolated from CSF, while ST155 from blood.
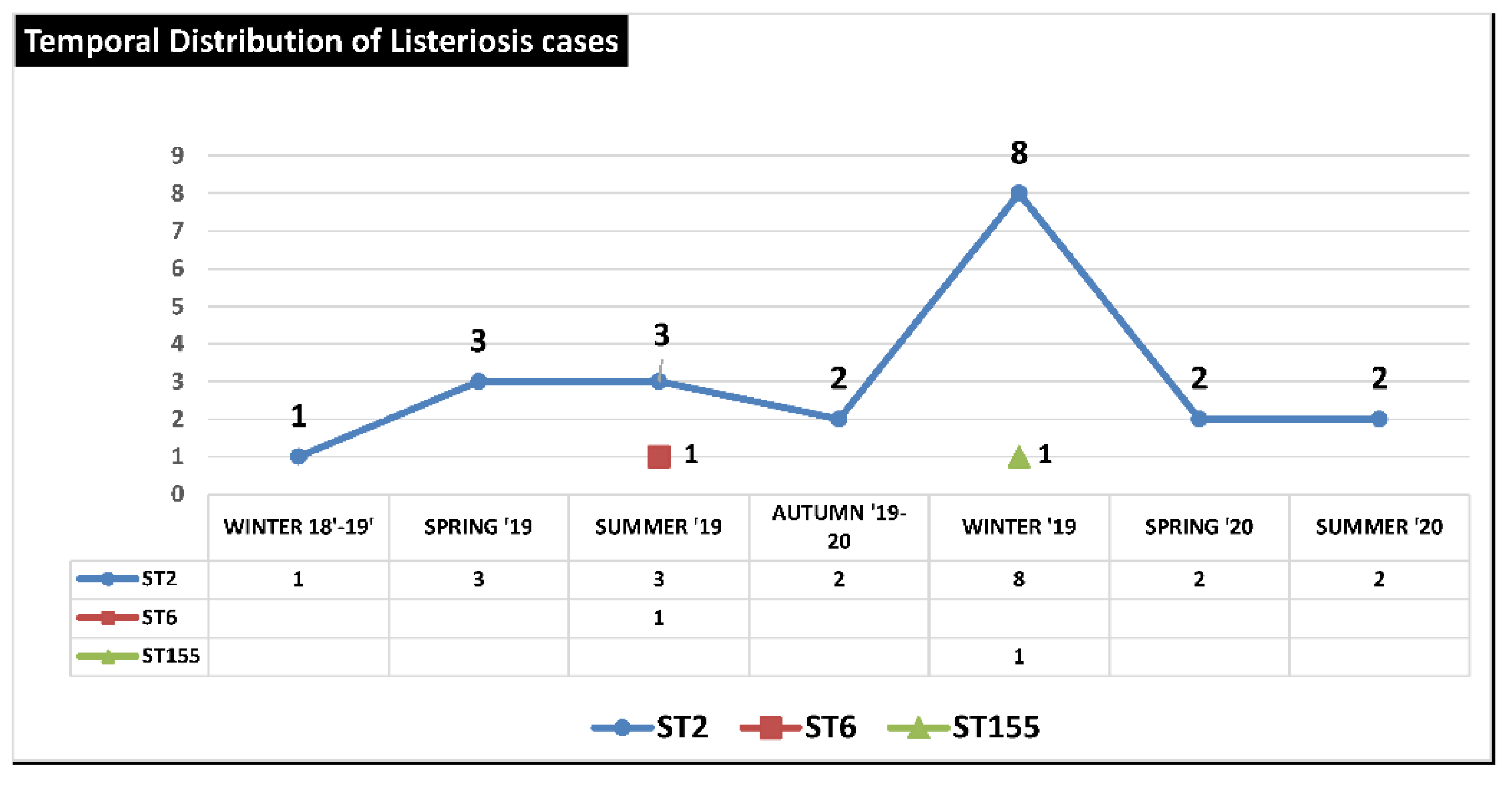
The temporal distribution and frequency of STs from December 2018 to July 2020 showed a clear predominance of strains with ST 2 probably originating from a single epidemic outbreak, while ST6 and ST155 appeared in only two isolated cases (
Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Temporal Distribution of Listeriosis cases from Winter 2018-2019 to Summer 2020 in Province of Palermo (Italy).
Figure 4.
Temporal Distribution of Listeriosis cases from Winter 2018-2019 to Summer 2020 in Province of Palermo (Italy).
All the results concerning the molecular characterization of the clinical isolates are summarized in
Figure 5.
3.4. Multilocus sequence typing (MLST)
A maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic tree was built based on the seven concatenated housekeeping gene sequences of 23 strains with Mega X software to analyze the phylogenetic relationship of different STs.
The results obtained according to the epidemiological studies published in Radoshevich et al. [
25], in which CC 6, CC 2, and CC 155 represent, respectively, the 2
nd, 4
th, and 8
th Clonal Complex most represented among clinical LM isolates.
Sequence Type 2 (N=21, 91%) is the prevalent ST in the epidemic population circulating in Palermo in the period between December 2018 and July 2020.
Moreover, ST2 is associated with the largest epidemic outbreak in Italy recorded in 1997 [
26], which led to the hospitalization of 292 people (20% of patients) (children and primary school staff), caused by eating contaminated tuna and corn salad.
Sequence Type 6 (n=1; 4%) is considered hypervirulent ST in LM species and shows a wide and intercontinental diffusion.
In particular, numerous outbreaks caused by ST6 have been reported in literature: in Switzerland in 2016 [
27], in South Africa in 2017-2018 [
28], in five EU states (Austria, Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and the United Kingdom) during 2015-2018 probably linked to the consumption of frozen vegetables (probably corn), which caused 32 cases of human listeriosis and 6 deaths [
29].
The most recent outbreak associated with ST6 of
L. monocytogenes was recorded in Switzerland related to the consumption of contaminated cheese in the period 2018-2020 which caused a total of 34 cases of listeriosis and 10 deaths [
30]. Sequence Type 155 (n=1; 4%) includes only one strain of LM with serogroup IIa among our 23 LM clinical isolates. In Italy, 22 isolates with ST155 were reported in Lombardy in the period from 2008 to 2014, with a peak of 10 cases in 2011 [
31].
Moreover, recent studies published in literature, show that ST 155 has a specific mutation in the
prfA gene which determines the synthesis of a longer version of the master transcriptional activator of the virulence gene and consequently a lower expression of
inlA, inlB, and
prfA and no expression of
hly and
actA, causing a reduction in the virulence potential of these strains and inability to cause meningitis [
32].
3.5. Multi-Virulence-Locus Sequence Typing (MvLST)
Virulence Type 21 (n=21; 91%), according to the MvLST database for LM species , has been associated with many epidemic outbreaks around the world, including in the UK (1989), USA (1979), France (2000), Germany (1953), New Zealand (1989), Denmark (1962), Canada (1950), and Italy (2012, contaminated food sources identified as ricotta-based products) [
33].
Virulence Type 19 (n=1; 4%) has been identified in Finland (1987, animals), Mexico (1999, environment), France (1993 and 2003, pregnant women) and the USA (1996, 1997, 2002, 2004, 2005 both from human, animal and food clinical cases) [
34].
Virulence Type 45 (n=1; 4%) has been isolated from human subjects in China (1991) and Canada (2002), while from food sources in the USA (1999), New Zealand (1999), and China (2002) [
35]. Moreover, VT 45 was prevalent in the LM strains isolated in Brazil during the period 1979-2015 and present in all food categories examined [
36].
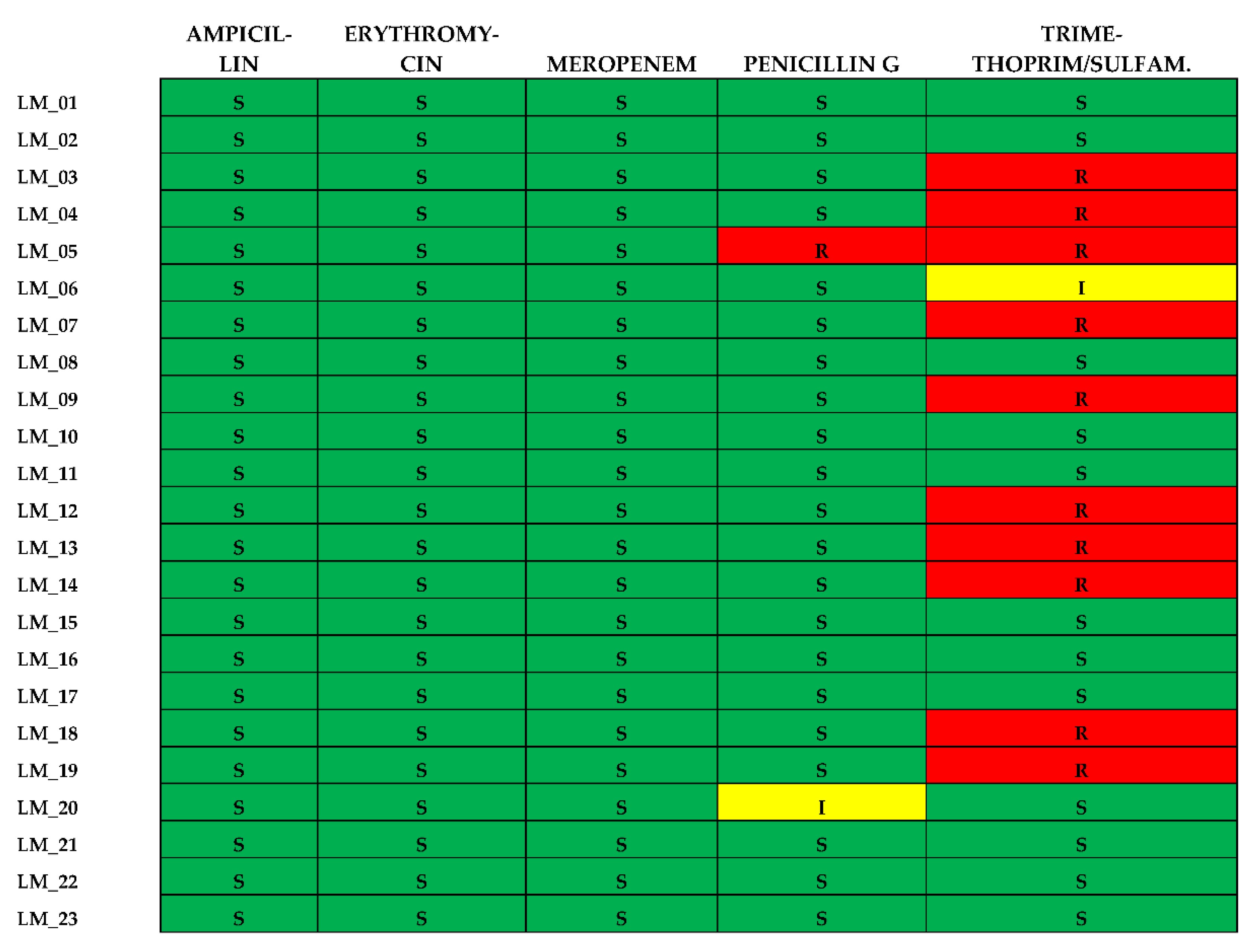
3.6. Antibiotic Susceptibility of L. monocytogenes Isolates
All 23 isolates were found to be susceptible to Ampicillin, Erythromycin and Meropenem. Resistance to the other two antibiotics was as follows: Penicillin G (n=1; 4,3%) and Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (n=10; 43,4%). No isolate was defined as multidrugresistant (MDR). All the results concerning the antibiotic susceptibility of the clinical isolates are summarized in
Figure 6.
4. Conclusions
In summary, in this study analysis of the prevalence and characteristics of clinical LM isolates in Palermo during 2018-2020, were performed.
The results of this study highlighted a higher prevalence of cases of listeriosis in males and patients aged over 65, coinciding with the trend data published by the ECDC for the year 2020 [
9].
Furthermore, serogroup 4b, 4d, 4e were dominant in our study (95%), linked to cases of sepsis and/or meningitis, while, only one strain belonging to serogroup IIa (4%) was associated with ulcerative proctocolitis without the involvement of the SNC, suggesting less virulence in the brain but more damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
Our results agree with ISS (the Italian National Institute of Health) laboratory surveillance reports [
34] on listeriosis in Italy for the year 2020, which showed that serogroups predominantly were 4b, 4d, 4e (43%) as compared to 1/2a, 3a (31%).
A prevalence of ST2/VT21 in the epidemic population from December 2018 to July 2020 in Palermo (Italy) indicated that many cases are likely related to epidemics that cannot be identified without advanced molecular typing methods, which are crucial for identifying listeriosis outbreaks in which geographical and temporal spread is extensive.
Moreover, our study revealed the presence of a hypervirulent strain ST6/VT19, associated with several epidemic outbreaks particularly in Europe in 2015-2020 [
37].
Indeed, due to the worldwide commercialization of food products, hypervirulent strains spread rapidly over large geographic areas causing multi-country outbreaks.
In accordance with the literature data [
38,
39], our results showed 43,4% of isolates resistant to treatment with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, it would be appropriate to evaluate alternative empirical therapies in case of penicillin allergies, to increase the probability of patient survival.
To ensure the public health and achieve food safety, integrated health surveillance systems at an international level are essential to carry out large-scale epidemiological studies to rapidly identify and eliminate contaminated food products based on a comparison of clinical and food strain typing results.
It is also important to monitor the spread of virulence genes between different LM strains, not only for the differentiation between low virulence and hypervirulent ST but also to identify new therapeutic targets.
In conclusion, molecular surveillance in hospital and school canteens is particularly important where there is a high number of subjects susceptible to listeriosis, including immunosuppressed patients, pregnant women, and children.
Our data support the possibility of a circulating clone associated with food contaminations.
Additional studies are underway to evaluate the origin of spreading the clone, resistance to various chemical-physical stresses, and degree of biofilm formation that could facilitate their presence in the industry and contaminate food products.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1 Information of the 23 Listeriosis patients; Table S2 MLST, MvLST and serovar of 23 LM isolates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G. and M.P.; methodology M.R.T., E.G.,; formal analysis, A.G, T.F., M.R.T, F.D, O.D.; investigation, I.A., E.G., C.M. and M.R.T.; writing—original draft preparation M.R.T., I.A., C.M. and T.F.; writing—review and editing, A.G., T.F., , I.A., F.D, E.G., F.D., M.P. and O.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All data used in the study were anonymized, according to the requirements set by Italian Data Protection Code (leg. Decree 196/2003) and by the general authorizations issued by the Data Protection Authority. Approval by the Ethics Committee was obtained by Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Policlinico “P. Giaccone” of Palermo (protocols n°07/2019).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Swaminathan, B.; Gerner-Smidt, P. The epidemiology of human listeriosis. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, F.B.; van Overbeek, L.S.; Baars, J.J.; Koomen, J.; Abee, T.; Besten, H.M.D. Genomic characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolated during mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) production and processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 360, 109438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.K.; Murray, R.; Flockhart, L.; Pintar, K.; Pollari, F.; Fazil, A.; Nesbitt, A.; Marshall, B. Estimates of the Burden of Foodborne Illness in Canada for 30 Specified Pathogens and Unspecified Agents, Circa 2006. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ma, X. Genomic Characterization of Clinical Listeria monocytogenes Isolates in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 751003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, E.J.; Jackson, K.A.; Johnson, S.D.; Graves, L.M.; Silk, B.J.; Mahon, B.E. Listeriosis Outbreaks and Associated Food Vehicles, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravkova, M.; Verbikova, V.; Michna, V.; Babak, V.; Cahlikova, H.; Karpiskova, R.; Kralik, P. Detection and Quantification of Listeria monocytogenes in Ready-to-eat Vegetables, Frozen Vegetables and Sprouts Examined by Culture Methods and Real-time PCR. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 5, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.iss.it/alimentazionenutrizionesicurezzaalimenti/asset_publisher/I5M6X036FZD6/content/id/5254206.
- W F Schlech 3rd 1, “Foodborne listeriosis”. 2000. [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/surveillance-atlas-infectious-diseases.
- Hedberg, C. Listeria in Europe: the need for a European surveillance network is growing. Eurosurveillance 2006, 11, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- J. McLaughlin, R.T. Mitchell, W.J. Smerdonc, K. Jewelld “Listeria monocytogenes, and listeriosis: a review of hazard characterization for use in microbiological risk assessment of foods” (2003).
- Renato, H. Orsi, Henk, C. den Bakker, Martin Wiedmann. “Listeria monocytogenes lineages: genomics, evolution, ecology and phenotypic characteristics” (2011).
- Michel Doumith, Carmen Buchrieser, Philippe Glaser, Christine Jacquet, and Paul Martin (2004) “Differentiation of the Major Listeria monocytogenes Serovars by Multiplex PCR”.
- Salcedo, C.; Arreaza, L.; Alcalá, B.; de la Fuente, L.; Vázquez, J.A.; Kazor, C.E.; Mitchell, P.M.; Lee, A.M.; Stokes, L.N.; Loesche, W.J.; et al. Development of a Multilocus Sequence Typing Method for Analysis of Listeria monocytogenes Clones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jayarao, B.M.; Knabel, S.J. Multi-Virulence-Locus Sequence Typing ofListeria monocytogenes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhan, L.; Mei, L. Prevalence, Genotypic Characteristics and Antibiotic Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes From Retail Foods in Bulk in Zhejiang Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Guo, W. Analysis of Multilocus Sequence Typing and Virulence Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes Isolates from Chinese Retail Ready-to-Eat Food. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moura, A.; Criscuolo, A.; Pouseele, H.; Maury, M.M.; Leclercq, A.; Tarr, C. Whole genome-based population biology and epidemiological surveillance of Listeria monocytogenes. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://bigsdb.pasteur.fr/listeria/listeria.html.
- Available online: https://www.megasoftware.net.
- Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/mvlstdatabase/home.
- Marco, F., Almela, M., Nolla-Salas, J., Coll, P., Gasser, I., Ferrer, M.D., & de Simon, M. In vitro activities of 22 antimicrobial agents against Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated in Barcelona, Spain. Diagnostic microbiology and infectious disease 2000, 38, 259–261. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/listeria/risk-groups/pregnant-women.html. [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.W. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single diffusion method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radoshevich, L.; Cossart, P. Listeria monocytogenes: towards a complete picture of its physiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 2018, 16, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aureli, P.; Fiorucci, G.C.; Caroli, D.; Marchiaro, G.; Novara, O.; Leone, L.; Salmaso, S. An Outbreak of Febrile Gastroenteritis Associated with Corn Contaminated byListeria monocytogenes. New Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1236–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althaus, D.; Jermini, M.; Giannini, P.; Martinetti, G.; Reinholz, D.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; et al. Local outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 4b sequence type 6 due to contaminated meat pâté. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2017, 14, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.M.; Tau, N.P.; Smouse, S.L.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Ramalwa, N.R.; et al. Outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes in South Africa, 2017–2018: laboratory activities and experiences associated with whole-genome sequencing analysis of isolates. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2019, 16, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/epidemiological-update-multi-country-outbreak-listeria-monocytogenes-pcr-serogroup-ivb.
- Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Bloemberg, G.V.; Müller, A.; et al. Listeriosis Caused by Persistence of Listeria monocytogenes Serotype 4b Sequence Type 6 in Cheese Production Environment. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2021, 27, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato Ettore, “Epidemiologia della listeriosi invasiva in Regione Lombardia: identificazione dei genotipi emergenti”. Università degli Studi di Milano, Scienze biomediche, cliniche e sperimentali. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Eva Wagner, Andreas Zaiser, Rebekka Leitner, Narciso M. Quijada, Nadja Pracser, Ariane Pietzka, Werner Ruppitsch, Stephan Schmitz-Esser, Martin Wagner & Kathrin Rychli. “Virulence characterization and comparative genomics of Listeria monocytogenes sequence type 155 strains”. 2020.
- Available online: https://www.sites.google.com/site/mvlstdatabase/isolates-information-sorted-by-vts/isolates-belonging-to-vt21.
- Available online: https://www.sites.google.com/site/mvlstdatabase/isolates-information-sorted-by-vts/isolates-belonging-to-vt19.
- Available online: https://www.sites.google.com/site/mvlstdatabase/isolates-information-sorted-by-vts/isolates-belonging-to-vt45.
- Silva, D.; Vallim, D.C.; Rosas, C.d.O.; Mello, V.; Brandão, M.L.L.; Filippis, I. Genetic diversity of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 1/2a strains collected in Brazil by Multi-Virulence-Locus Sequence Typing. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 72, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althaus, D.; Jermini, M.; Giannini, P.; Martinetti, G.; Reinholz, D.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Lehner, A.; Stephan, R. Local outbreak of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 4b sequence type 6 due to contaminated meat pâté. Foodborne pathogens and disease 2017, 14, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsak, D.; Krawczyk-Balska, A. Identification of the molecular mechanism of trimethoprim resistance in Listeria monocytogenes. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease 2017, 14, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.; Nam, H.M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Tamilselvam, B.; Murinda, S.E.; Oliver, S.P. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in Listeria monocytogenes isolated from dairy farms. Foodbourne Pathogens & Disease 2005, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).