Submitted:
01 November 2023
Posted:
02 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and methods
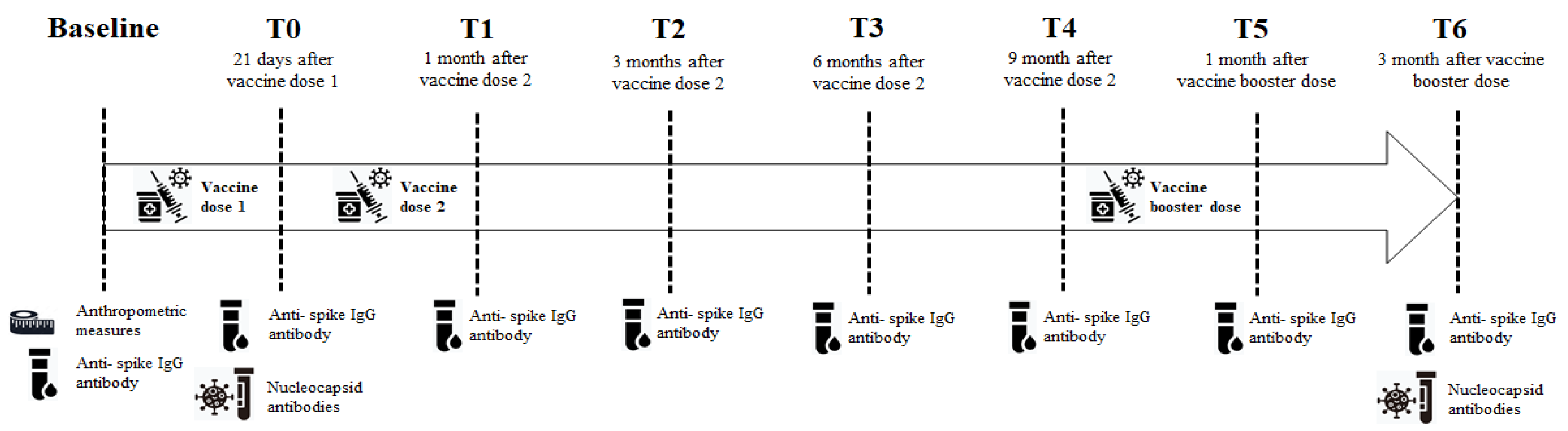
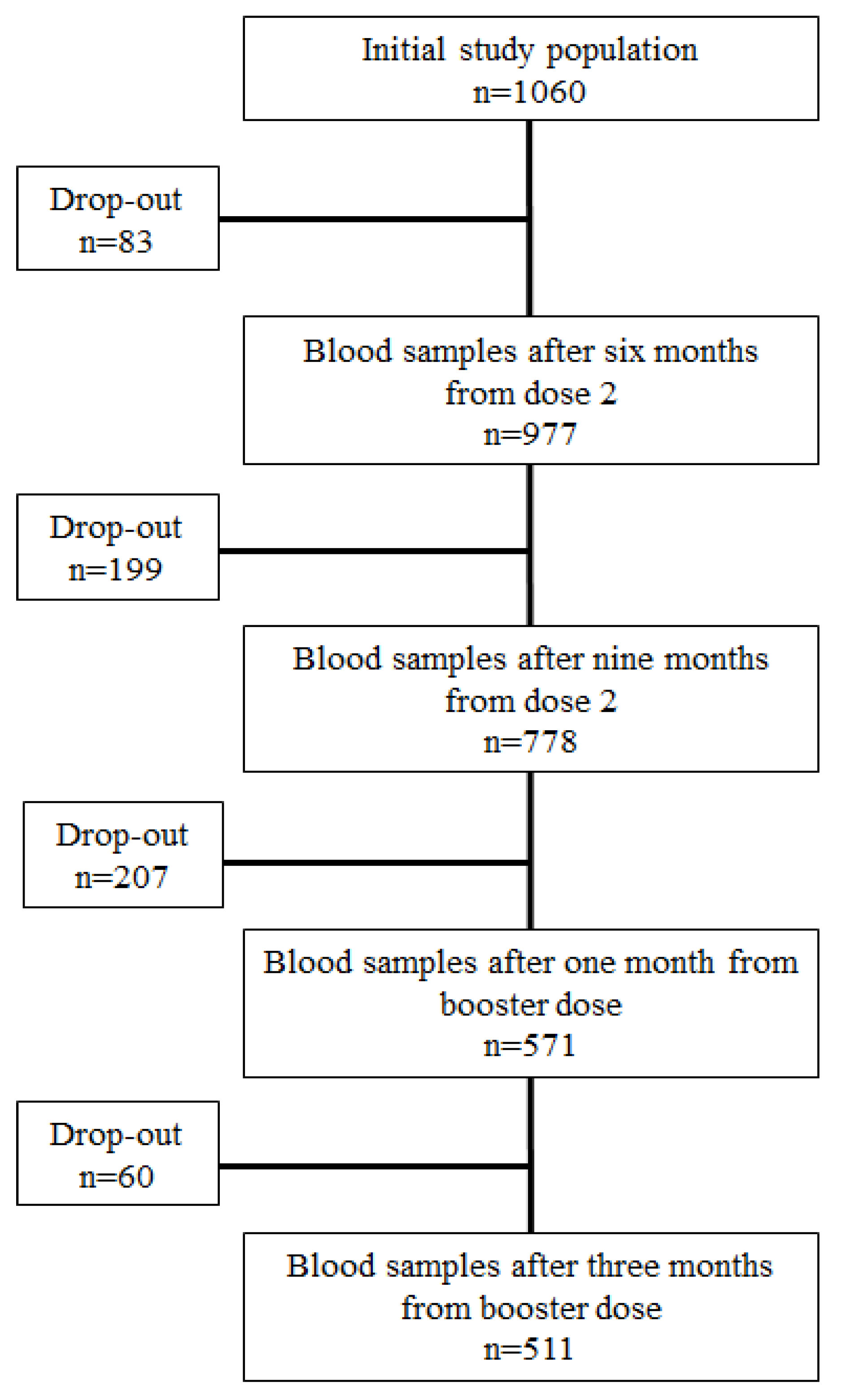
2.1. Study design and population
2.2. Serological testing
2.3. Anthropometric measures
2.4. Statistical analyses
3. Results
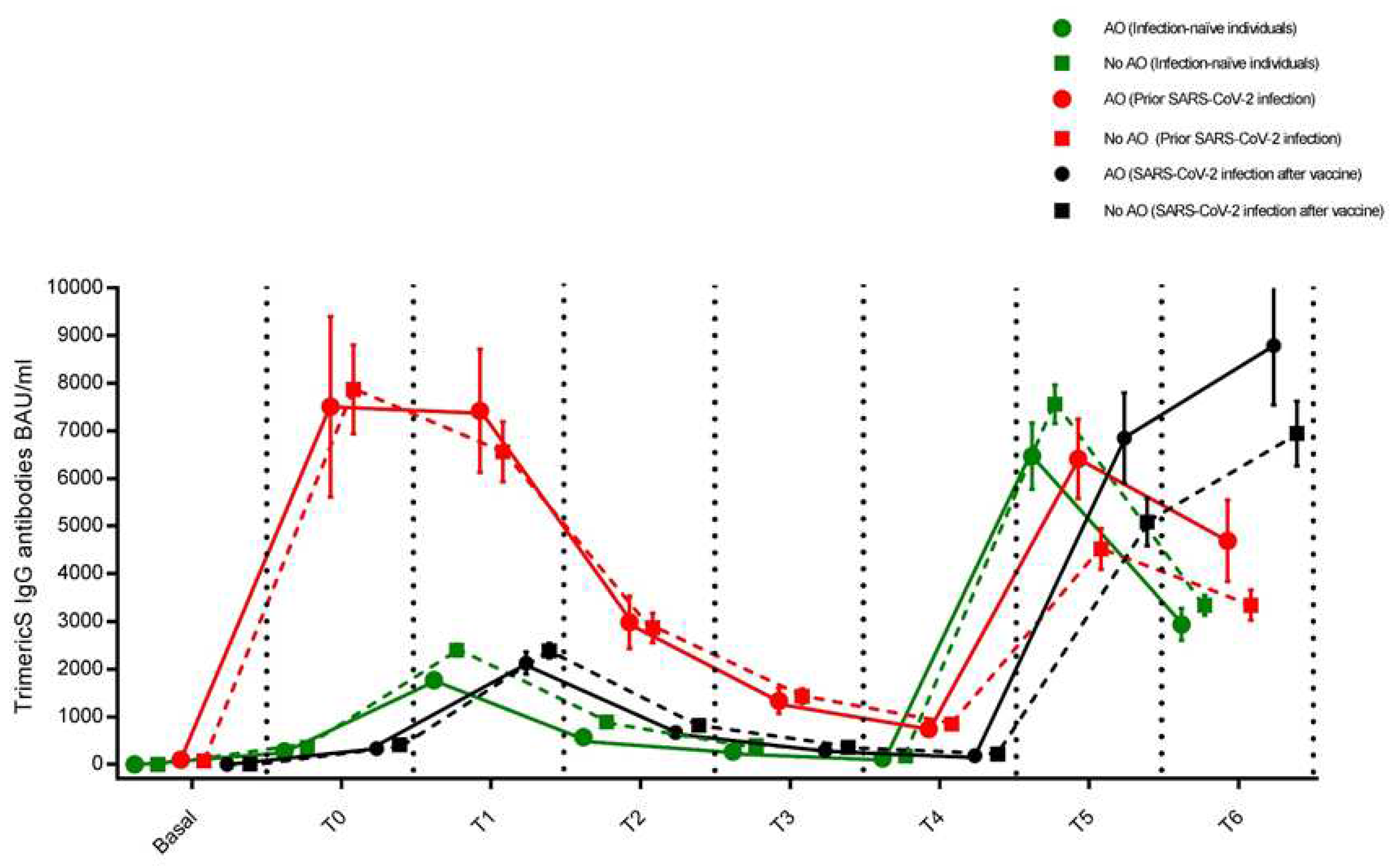
3.1. Individuals who had never been infected with SARS-CoV-2 (Infection-naïve individuals)
3.2. Individuals who had developed the infection before the vaccine cycle (Prior infected individuals)
3.3. Individuals who developed the infection during the vaccine cycle
3.4. Multivariable linear regression analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stefan N, Birkenfeld AL, Schulze MB. Global pandemics interconnected — obesity, impaired metabolic health and COVID-19. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2021;17:135–49.
- Busetto L, Bettini S, Fabris R et al. Obesity and COVID-19: An Italian Snapshot. Obesity 2020;28:1600–5.
- Földi M, Farkas N, Kiss S et al. Visceral Adiposity Elevates the Risk of Critical Condition in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obesity 2021;29:521–8.
- Sanoudou D, Hill MA, Belanger MJ et al. Editorial: Obesity, metabolic phenotypes and COVID-19. Metabolism 2022;128:155121.
- Butsch WS, Hajduk A, Cardel MI et al. COVID-19 vaccines are effective in people with obesity: A position statement from The Obesity Society. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2021;29:1575–9.
- Tubjaroen C, Prachuapthunyachart S, Potjalongsilp N et al. Immunogenicity of an mRNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine among Adolescents with Obesity or Liver Transplants. Vaccines (Basel) 2022;10:1867.
- Nasr M-JC, Geerling E, Pinto AK. Impact of Obesity on Vaccination to SARS-CoV-2. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022;13:898810.
- Piernas C, Patone M, Astbury NM et al. Associations of BMI with COVID-19 vaccine uptake, vaccine effectiveness, and risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes after vaccination in England: a population-based cohort study. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2022;10:571–80.
- Bates JT, Farmer AP, Bierdeman MA et al. IgG Antibody Response to the Pfizer BNT162b2 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Healthcare Workers with Healthy Weight, Overweight, and Obesity. Vaccines (Basel) 2022;10:512.
- Basilico S, Dubini C, Milani V et al. Could fat distribution have a greater influence than BMI on the antibody titre after SARS-CoV -2 vaccine? Obesity 2022;30:1321–2.
- Malavazos AE, Basilico S, Iacobellis G et al. Antibody responses to BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine: Infection-naïve individuals with abdominal obesity warrant attention. Obesity 2022;30:606–13.
- Watanabe M, Balena A, Tuccinardi D et al. Central obesity, smoking habit, and hypertension are associated with lower antibody titres in response to COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2022;38:e3465.
- Gaborit B, Fernandes S, Loubet P et al. Early humoral response to COVID-19 vaccination in patients living with obesity and diabetes in France. The COVPOP OBEDIAB study with results from the ANRS0001S COV-POPART cohort. Metabolism 2023;142:155412.
- Tartof SY, Slezak JM, Fischer H et al. Effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine up to 6 months in a large integrated health system in the USA: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2021;398:1407–16.
- Levin EG, Lustig Y, Cohen C et al. Waning Immune Humoral Response to BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine over 6 Months. N Engl J Med 2021;385:e84.
- Shrotri M, Navaratnam AMD, Nguyen V et al. Spike-antibody waning after second dose of BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1. Lancet 2021;398:385–7.
- Lustig Y, Gonen T, Meltzer L et al. Superior immunogenicity and effectiveness of the third compared to the second BNT162b2 vaccine dose. Nat Immunol 2022;23:940–6.
- Lombardi A, Consonni D, Oggioni M et al. SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibody titres after vaccination with BNT162b2 in naïve and previously infected individuals. J Infect Public Health 2021;14:1120–2.
- Manisty C, Otter AD, Treibel TA et al. Antibody response to first BNT162b2 dose in previously SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. Lancet 2021;397:1057–8.
- Krammer F, Srivastava K, Alshammary H et al. Antibody Responses in Seropositive Persons after a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2021;384:1372–4.
- Ebinger JE, Fert-Bober J, Printsev I et al. Antibody responses to the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in individuals previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nat Med 2021;27:981–4.
- Anichini G, Terrosi C, Gandolfo C et al. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response in Persons with Past Natural Infection. N Engl J Med 2021;385:90–2.
- Neeland IJ, Ross R, Després J-P et al. Visceral and ectopic fat, atherosclerosis, and cardiometabolic disease: a position statement. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology 2019;7:715–25.
- Pérez-Alós L, Armenteros JJA, Madsen JR et al. Modeling of waning immunity after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and influencing factors. Nat Commun 2022;13:1614.
- Abdollahi A, Afsharyzad Y, Vaezi A et al. Importance of the COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Dose in Protection and Immunity. Vaccines 2022;10:1708.
- Watanabe M, Balena A, Masi D et al. Rapid Weight Loss, Central Obesity Improvement and Blood Glucose Reduction Are Associated with a Stronger Adaptive Immune Response Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine. Vaccines 2022;10:79.
- Renna LV, Bertani F, Podio A et al. Impact of BNT162b2 Booster Dose on SARS-CoV-2 Anti-Trimeric Spike Antibody Dynamics in a Large Cohort of Italian Health Care Workers. Vaccines 2023;11:463.
- Golec M, Zembala-John J, Fronczek M et al. Relationship between anthropometric and body composition parameters and anti-SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG titers in females vaccinated against COVID-19 according to the heterologous vaccination course: A cohort study. Ito E (ed.). PLoS ONE 2023;18:e0287128.
- Glück V, Tydykov L, Mader A-L et al. Humoral immunity in dually vaccinated SARS-CoV-2-naïve individuals and in booster-vaccinated COVID-19-convalescent subjects. Infection 2022. [CrossRef]
- Herzberg J, Fischer B, Lindenkamp C et al. Persistence of Immune Response in Health Care Workers After Two Doses BNT162b2 in a Longitudinal Observational Study. Front Immunol 2022;13:839922.
- Grant RW, Dixit VD. Adipose tissue as an immunological organ. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2015;23:512–8.
- Fasshauer M, Blüher M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2015;36:461–70.
- Romacho T, Elsen M, Röhrborn D et al. Adipose tissue and its role in organ crosstalk. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2014;210:733–53.
- Fan X, Han J, Zhao E et al. The effects of obesity and metabolic abnormalities on severe COVID-19-related outcomes after vaccination: A population-based study. Cell Metabolism 2023;35:585-600.e5.
- Frasca D, Reidy L, Cray C et al. Influence of obesity on serum levels of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients. PLoS One 2021;16:e0245424.
- Kara Z, Akçin R, Demir AN et al. Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in People with Severe Obesity. OBES SURG 2022;32:2987–93.
- Ahn S-Y, Sohn S-H, Lee S-Y et al. The effect of lipopolysaccharide-induced obesity and its chronic inflammation on influenza virus-related pathology. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 2015;40:924–30.
- Ryan PM, Caplice NM. Is Adipose Tissue a Reservoir for Viral Spread, Immune Activation, and Cytokine Amplification in Coronavirus Disease 2019? Obesity 2020;28:1191–4.
- Simonnet A, Chetboun M, Poissy J et al. High Prevalence of Obesity in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) Requiring Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Obesity 2020;28:1195–9.
- Kalligeros M, Shehadeh F, Mylona EK et al. Association of Obesity with Disease Severity Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Obesity 2020;28:1200–4.
- Klang E, Kassim G, Soffer S et al. Severe Obesity as an Independent Risk Factor for COVID-19 Mortality in Hospitalized Patients Younger than 50. Obesity 2020;28:1595–9.
- Wajnberg A, Mansour M, Leven E et al. Humoral response and PCR positivity in patients with COVID-19 in the New York City region, USA: an observational study. The Lancet Microbe 2020;1:e283–9.
- Soffer S, Glicksberg BS, Zimlichman E et al. The association between obesity and peak antibody titer response in COVID-19 infection. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2021;29:1547–53.
- Wrigley Kelly NE, Kenny G, Cassidy FC et al. Individuals with obesity who survive SARS-CoV-2 infection have preserved antigen-specific T cell frequencies. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2022;30:1927–31.
- Muena NA, García-Salum T, Pardo-Roa C et al. Induction of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies by CoronaVac and BNT162b2 vaccines in naïve and previously infected individuals. eBioMedicine 2022;78:10397.
- Pilz S, Theiler-Schwetz V, Trummer C et al. SARS-CoV-2 reinfections: Overview of efficacy and duration of natural and hybrid immunity. Environ Res 2022;209:112911.
- Goldberg Y, Mandel M, Bar-On YM et al. Protection and Waning of Natural and Hybrid Immunity to SARS-CoV-2. N Engl J Med 2022;386:2201–12.
- Babouee Flury B, Güsewell S, Egger T et al. Risk and symptoms of COVID-19 in health professionals according to baseline immune status and booster vaccination during the Delta and Omicron waves in Switzerland-A multicentre cohort study. PLoS Med 2022;19:e1004125.
| Abdominal Obesity (n=149) | No Abdominal obesity (n=362) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n=511) |
No Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (n=76) | Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (n=34) |
SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccine (n=39) |
p-value | No Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (n=186) | Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (n=75) | SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccine (n=101) |
p-value | |
| Age, years | 44.03±11.88 | 52.02±10.64 | 47.26±9.18 | 48.26±8.28 | 0.0286 | 42.28±12.02 | 41.73±11.20 | 40.15±11.70 | 0.3386 |
| Race | |||||||||
| Caucasian | 492 (96.28) | 72 (94.74) | 31 (91.18) | 36 (92.31) | 181 (97.31) | 71 (94.67) | 101 (100.00) | ||
| Latin-American | 13 (2.54) | 3 (3.95) | 3 (8.82) | 3 (7.69) | 0.7117* | 2 (1.08) | 2 (2.67) | 0 (0.00) | 0.2074* |
| African | 2 (0.39) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 2 (1.08) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | ||
| Arabic | 4 (0.78) | 1 (1.32) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.54) | 2 (2.67) | 0 (0.00) | ||
| Gender | |||||||||
| Male | 166 (32.49) | 30 (39.47) | 8 (23.53) | 14 (35.90) | 0.2656 | 56 (30.11) | 28 (37.33) | 30 (29.70) | 0.4271 |
| Female | 345 (67.51) | 46 (60.53) | 26 (76.47) | 25 (64.10) | 130 (69.89) | 47 (62.67) | 71 (70.30) | ||
| Smoking status | |||||||||
| Smoker | 98 (19.18) | 11 (14.47) | 4 (11.76) | 10 (25.64) | 0.2128 | 36 (19.35) | 11 (16.67) | 26 (25.74) | 0.1794 |
| Non smoker | 413 (80.82) | 65 (85.53) | 30 (88.24) | 29 (74.36) | 150 (80.65) | 64 (85.33) | 75 (74.26) | ||
| Comorbidities | |||||||||
| Hypertension | 59 (11.55) | 25 (32.89) | 7 (20.59) | 6 (15.38) | 0.0944 | 12 (6.45) | 3 (4.00) | 6 (5.94) | 0.7435 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 4 (0.78) | 0 (0.00) | 2 (5.88) | 0 (0.00) | 0.0509* | 0 (0.00) | 1 (1.33) | 1 (0.99) | 0.2357* |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 17 (3.33) | 6 (7.89) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.56) | 0.2318* | 7 (3.76) | 1 (1.33) | 2 (1.98) | 0.5268* |
| Dyslipidemia | 32 (6.26) | 9 (11.84) | 4 (11.76) | 5 (12.82) | 1.000* | 7 (3.76) | 3 (4.00) | 4 (3.96) | 1.000* |
| Cancer | 3 (0.59) | 1 (1.32) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (2.56) | 1.000* | 1 (0.54) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 1.000* |
| Anthropometric measurements | |||||||||
| Weight, kg | 70.54±15.12 | 84.08±13.74 | 88.28±16.96 | 80.86±14.45 | 0.1026 | 64.38±11.15 | 65.40±12.29 | 65.53±10.23 | 0.6481 |
| Height, cm | 167.63±8.78 | 168.47±10.54 | 166.14±9.01 | 167.21±8.61 | 0.4903 | 166.91±8.39 | 168·21±8.65 | 168.56±8.10 | 0.2252 |
| Waist, cm | 85.78±13.51 | 100.69±8.76 | 103.26±11.23 | 99.79±9.47 | 0.2745 | 79.61±9.20 | 76.63±9.23 | 79.19±9.22 | 0.9254 |
| Waist male, cm | 94.63±11.85 | 107.25±5.64 | 112.88±9.79 | 107.93±6.56 | 0.1104 | 89.26±7.47 | 87.38±7.93 | 87.75±7.91 | 0.4994 |
| Waist female, cm | 81.52±12.13 | 96.41±7.74 | 100.31±10.05 | 95.24±7.64 | 0.0751 | 75.46±6.31 | 75.02±6.49 | 75.58±7.13 | 0.8975 |
| WHtR | 0.51±0.08 | 0.60±0.05 | 0.62±0.06 | 0.60±0.05 | 0.0589 | 0.48±0.05 | 0.47±0.05 | 0.47±0.05 | 0.5170 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.00±4.45 | 29.53±3.28 | 31.79±4.39 | 28.81±3.76 | 0.00019 | 23.02±2.91 | 22.96±2.87 | 23.02±2.89 | 0.9869 |
| BMI classes | |||||||||
| Underweight | 20 (3.91) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 12 (6.45) | 2 (2.67) | 6 (5.94) | ||
| Normal weight | 265 (51.86) | 7 (9.21) | 1 (2.94) | 7 (17.95) | 0.0951* | 129 (69.35) | 51 (68.00) | 70 (69.31) | 0.8376* |
| Overweight | 156 (30.53) | 34 (44.74) | 13 (38.24) | 20 (51.28) | 43 (23.12) | 22 (29.33) | 24 (23.76) | ||
| Obesity | 70 (13.70) | 35 (46.05) | 20(58.82) | 12 (30.77) | 2 (1.08) | 0 (0.00) | 1 (0.99) | ||
| Abdominal Obesity (n=149) | No abdominal obesity (n=362) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibodies levels | Total (n=511) |
No Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (n=76) |
SARS-CoV-2 infection before vaccine (n=34) |
SARS-CoV-2 infection after vaccine (n=39) |
p-value | No Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection (n=186) | SARS-CoV-2 infection before vaccine (n=75) | SARS-CoV-2 infectionaftervaccine(n=101) | p-value |
| Baseline | 9.67±1.40 n=90 |
4.81 n=11 |
98.93±74.44 n=6 |
4.81 n=8 |
<0.0001 *° |
5.59±0.58n=32 | 71.81±24.26n=13 | 6.11±1.19n=20 | <0.0001*° |
| 21 days after dose 1 |
680.84±49.58 | 274.16±36.40 | 7511.83±1895.77 | 333.58±61.94 | <0.0001 *° |
362.54±26.99 | 7872.56±931.04 | 410.72±32.39 | <0.0001*° |
| 1 month after dose 2 |
2837.32±110.30 | 1773.18±155.93 | 7420.51±1296.00 | 2130.24±231.39 | <0.0001 *° |
2399.17±123.48 | 6562.31±631.09 | 2386.67±156.08 | <0.0001*° |
| 3 months after dose 2 |
1035.22±43.80 | 575.90±53.28 | 2985.81±550.26 | 672.12±68.08 | <0.0001 *° |
892.48±44.54 | 2868.23±308.43 | 820.87±60.84 | <0.0001*° |
| 6 months after dose 2 |
463.96±21.32 | 267.78±14.63 | 1335.15±267.46 | 296.44±30.03 | <0.0001 *° |
391.60±22.71 | 1431.65±155.39 | 358.84±29.21 | <0.0001*° |
| 9 months after dose 2 |
243.18±11.93 | 126.78±14.62 | 746.25±131.40 | 183.41±32.79 | <0.0001 *° |
176.38±10.74 | 847.73±92.92 | 216.88±17.25 | <0.0001*° |
| 1 month after dose 3 |
6218.25±237.47 | 6470.55±695.82 | 6413.54±832.40 | 6850.16±947.21 | 0.8892 |
7561.64 ±406.80 | 4521.62±429.76 | 5084.36±500.43 | <0.0001#* |
| 3 month after dose 3 |
4175.81±181.19 | 2943.17±335.19 | 4692.80±854.60 | 8791.71±1246.30 | <0.0001 #° |
3346.92±208.06 | 3345.35±314.00 | 6944.18±682.39 | <0.0001#° |
| p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariable considering abdominal obesity | Multivariable considering BMI class | |
| Sex | 0.7120 | 0.5955 | 0.5656 |
| Age | 0.3000 | 0.4485 | 0.5412 |
| IgG-TrimetricS antibody level at booster dose | 0.0675 | 0.0855 | 0.0526 |
| Prior SARS-CoV-2-infection | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Abdominal obesity | 0.1053 | 0.1092 | - |
| Interaction with prior SARS-CoV-2-infection* Abdominal obesity | 0.0163 | - | |
| BMI classes | 0.0803 | - | 0.0821 |
| Interaction with prior SARS-CoV-2-infection* BMI classes | - | 0.4176 | |
| Smoking status | 0.0925 | 0.3785 | 0.2968 |
| Hypertension | 0.0062 | 0.0020 | 0.0063 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.5878 | ||
| Cardiovascular diseases | 0.7262 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 0.5087 | ||
| Cancer | 0.3900 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





