Submitted:
02 November 2023
Posted:
02 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. NPLs Interaction with Freshwater Phytoplankton Species
2.1. Advances in Uptake Availability of NPLs to Phytoplankton
2.2. Advances in Toxico-Availability of NPLs to Phytoplankton
| Species | Type of NPLs | Size of NPLs | Concentration | Duration | Observed effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Alexandrium tamarense (marine dinoflagellate) |
PS (plain) | 100 nm 1 µm |
0, 0.1, 1, 5, 10, 50, 100 mg L-1 | 4 days | Inhibition of growth, photosynthetic production and extracellular carbonic anhydrase activities stronger in MPLs than in NPLs. Intracellular paralytic shellfish toxins production stimulated by NPLs and decreased by MPLs. | [56] |
|
Anabaena sp. (freshwater cyanobacteria) C. reinhardtii (freshwater green algae) |
PHB (polyhydroxybutyrate, mechanically broken-down) | 200 nm | 0, 50 mg L-1 | 3 days | Decrease in growth, increase in ROS production and membrane damage, secondary NPLs may be more toxic than primary. Biodegradable plastics show the same toxic effects to organisms as non-biodegradable. | [57] |
|
Chlorella sp. (freshwater green algae) |
PS (plain) PS-NH2 PS-COOH |
200 nm | 0, 1 mg L-1 | 3 days | EPS aged NPLs significantly lowered the oxidative stress and cytotoxic impact, eco-corona may change the way NPLs interact with the organisms. | [58] |
|
Chlorella vulgaris (freshwater green algae) |
PS (plain) PS-COOH |
20, 50, 500 nm |
0, 250 mg L-1 | 28 days | Smaller NPLs have a higher impact - decrease in algal viability and pigments; increase in ROS, lactate dehydrogenase activity and starch grains content; shrinkage in cell wall. Bigger PS could aggregate and sediment making them non-bioavailable. | [49] |
|
Chlorella pyrenoidosa (freshwater green algae) |
PS (plain) | 100 nm 1 µm |
0, 10, 50, 100 mg L-1 |
30 days | Hetero- and homoaggregation observed, EPS production increased, during the first phase growth rate and photosynthesis decreased, while in the second phase growth and photosynthesis recovered. | [47] |
| PS (plain) | 80 nm | 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 mg L-1 | 4 days | Strong inhibition of growth, photosynthetic pigments and efficiency after 24–48 h, after 96 h inhibition lowered. Heteroaggregation, ROS production, gene expression changes, membrane and DNA damage observed. | [48] | |
|
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (freshwater green algae) |
PS (plane) | 300–600 nm | 0, 5, 25, 50, 100 mg L-1 |
10 days | A decrease in growth, photosinthetic activity and EPS follows an increase in concentration, observed higher soluble proteins and membrane damage. | [54] |
| PS (fluorescent) | 51 nm | 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 mg L-1 | 2 days | Adsorped to the surface of algae, passing into the outer layer when the cell is dividing. | [40] | |
|
Cocconeis placentula var lineata (freshwater diatom) |
P(Sco-MMA) (poly(styrene-co-methyl methacrylate) ) | 100 - 2800 nm |
0, 0.0001, 0.001, 0.1,10 mg L-1 |
28 days | Significant increase in teratogenic effects in the lowest concentration (deformed valve outline, changes in characteristics of longitudinal and central area, and mixed type). | [59] |
|
Dunaliella tertiolecta (marine green algae) |
PS-COOH (fluorescent) | 40 nm | 0, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50 mg L-1 | 3 days | Aggregation, adsorbed on the surface of algae, potential trophic transfer. | [36] |
| PS-NH2 | 50 nm | Aggregation, inhibition of algal growth. | ||||
|
Euglena gracilis (freshwater euglena) |
PS (fluorescent) | 100 nm, 5 µm |
1 mg L-1 (NPLs or MPLs) +/- 0.5 mg L-1 (Cd2+) |
4 days | MPLs alone inhibits the growth while mixture with Cd2+ increases it. NPLs shows lower toxicity than MPLs while in mixture with Cd2+ acts synergistically and exceed toxic effects. | [51] |
|
Microcystis aeruginosa (freshwater cyanobacteria) |
PS (plain) | 60 nm | 0, 25, 50, 100 mg L-1 |
30 days | Growth inhibited at the beginning while aggregation rates were high. After 10 days growth increases, while aggregation decreases, connection between growth rate and aggregation. Negative effect on photosynthetic activity, SOD and MDA affected in the beginning, then mitigated. Production of microcystin increased with the concentration increase. | [60] |
|
Phaeodactylum tricornutum (marine diatom) |
PS (plain and fluorescent) | 50, 100 nm | 0, 0.1, 1, 5, 10, 20, 50 mg L-1 | 3 days | Hetero- and homoaggregation observed, during the first 24 hours changes in oxidative stress, photosynthesis, membrane integrity and DNA damage, while after 48 h these responses were mitigated. Growth, Chlat levels and fluorescence and protein content negatively influenced after 72 h. | [39] |
| PS-COOH | 60 nm | 0, 1, 5, 50, 100 mg L-1 |
3 days | EPS reduces aggregation and ROS production, toxicity of NPLs not observed with or without EPS. | [61] | |
|
Platymonas helgolandica0 (marine green algae) |
PS (plain) | 70 nm | 0, 0.02, 0.2, 2 mg L-1 |
6 days | Observed morphological changes, inhibition of growth during the first 4 days, increase in growth (after 5 days) and membrane permeability, disturbance in mitochondrial and chloroplast functions. | [45] |
|
Rhodomonas baltica (marine red algae) |
PMMA PMMA-COOH |
50 nm | 0, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 mg L-1 |
3 days | PMMA aggregated, impacted cell viability and size, pigments, membrane integrity, ROS formation, lipid peroxidation, DNA content and photosynthetic capacity, while PMMA-COOH influenced viability, metabolic activity, photosynthetic performance and algal growth changes. PMMA physico-chemical charactaristics important in response to interaction with cells. | [62] |
|
Scenedesmus subspicatus (freshwater green algae) |
PE (plain) PE (from Atlantic Gyre, mechanically broken-down) |
<450 nm | 0, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 mg L-1 |
2 days | PE from the Atlantic gyre negatively influencing algal growth more than plain PE, may be due to presence of other contaminants like metals. | [63] |
|
Scenedesmus quadricauda (freshwater green algae) |
PS (plane) | 100 nm | 0, 10, 25, 50, 100, 200 mg L-1 | 14 days | Increase in growth, antioxidant enzyme activity, pigments, soluble proteins and soluble polysaccharides. Observed strong defensive and recovery response to stress. | [46] |
|
Synechococcus elongatus (freshwater cyanobacteria) |
PS-NH2 | 50 nm | 2 – 9 mg L-1 | 2 days | PS-NH2 negatively impacted growth rate, PS-SO3H had no effect. PS-NH2 induced oxidative stress and membrane permeability which lead to damage. | [52] |
| PS-SO3H | 52.03 nm | |||||
|
Tetraselmis chuii, Nannochloropsis gaditana, Isochrysis galbana, Thalassiosira weissflogii (marine algae) |
PMMA | 40 nm | 0 - 304.1 mg L-1 | 3 days | Growth rates inhibited at higher concentrations with T. weissflogii being the most affected. Big aggregates observed which could explain higher tolerance to PMMA. | [16] |
2.3. Phytoplankton Feedback on NPLs Uptake and Toxico-Availability
3. NPLs Interactions with Freshwater Zooplankton Species
3.1. Advances in Uptake Availability via Direct Exposure
3.2. Advances in Uptake Availability via Trophic Transfer
3.3. Advances in "Toxico-Availability” Research
| Species | Type of NP | Size of NP | Concentration | Duration | Path of NPLs entrance | Observed effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Artemia franciscana (marine) |
PS-COOH (fluorescent) | 40 nm | 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2.5, 5 mg L-1 |
14 days | waterborne | Aggregation, accumulation and excretion noticed, potential trophic transfer. | [36] |
| PS-NH2 | 190 nm | 0, 1 mg L-1 0 - 200 mg L-1 |
14 days 2 days |
waterborne and foodborne - D. salina | Found in the gut, higher levels by direct uptake than through trophic transfer, observed damage to the digestive tract, no difference in mortality and immobilization in short-term exposure. | [99] | |
| PS (amine) PS (sulfate) |
100 nm | 0, 1, 10, 100 mg L-1 |
2 days | waterborne, different levels of temperature, salinity and humic acid and bentonite |
Amine NPLs produced additional toxic effects at high salinity, while at low temperatures HA and bentonite reduced toxicity. Multi-stressor experiment showed that toxicity depends on the physico-chemical characteristics of the water. | [105] | |
|
Brachionus koreanus (freshwater) |
PS (plain) | 50 nm | 10 mg L-1 | 1 day | pre-exposed to NPLs, waterborne to POPs | Pre-exposure to NPLs leads to oxidative damage of membranes and disruption of multixenobiotic resistance (MXR) functions, NPLs subsequently enhanced the toxicity of persistent organic pollutants (POPs). | [106] |
| PS (plain and fluorescent) |
50 nm | 0, 1, 10 mg L-1 | ~1,5 days | maternal transfer to unexposed neonats | Maturation time and reproduction negatively impacted at higher concentration. Bioaccumulated maternally transfered NPLs in offspring. Parent exposures induces an increase in ROS production in offspring. | [94] | |
|
Brachionus plicatilis (freshwater) |
PMMA | 40 nm | 4.7, 9.4, 18.9, 37.5, 75.0 mg L-1 |
2 days | waterborne | Mortality increased after exposure, especially in higher concentrations. | [16] |
|
Daphnia galeata × longispina (freshwater) |
PS (fluorescent) | 100 nm | 0, 5, 20 mg L-1 | 29 days | waterborne with/without inoculated spores of parasite Metschnikowia bicuspidata | Increased number of infected hosts in the presence of NPLs, lifespan and reproduction ability are reduced. Parasite reproduction is three times lower in high NPLs concentration. NPLs have a hormetic effect on the host, increasing its fitness. | [107] |
|
Daphnia longispina (freshwater) |
PS (fluorescent) | 50 nm, 100 nm |
0, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 2, 10, 20, 100 mg L-1 |
4 days | waterborne | Smaller NPLs may be more toxic due to higher bioavailability and particle toxicity. | [101] |
|
Daphnia magna (freshwater) |
PS (plain) | 50 nm | 0.05, 0.5 mg L-1 |
21 days | waterborne | Increase in energy reserves, no changes in oxidative stress and swimming activity. | [108] |
| HDPE - (mechanically broken-down) | 90 - 200 nm | High / low mix of fractions | 98 / 134 days | waterborne and in mixture with smaller fractions | HDPE nanoplastic not toxic but the fraction of leached additives and short chain HDPE cause toxicity. | [109] | |
| PS (fluorescent) | 51 nm | 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 mg L-1 | 3 days | foodborne - C. reinhardtii | Presence in the gut and damage to the intestinal walls, trophic transfer detected. | [40] | |
| PS (plain) | 100 nm | 1 mg L-1 | 2 days | waterborne | Plain PS had the highest acute toxicity and ROS production, activated MAPKs but didn't influence AChE changes, while PS-COOH, PS-n-NH2 and PS-p-NH2 activated antioxidant system and lowered ROS production. | [78] | |
| PS-p-NH2 | 50-100 nm | ||||||
| PS-COOH | 300 nm | ||||||
| PS-n-NH2 | 110 nm | ||||||
| PS-NH2 | 53 nm | 0, 0.0032, 0.032. 0.32 mg L-1 |
64.3 ± 32.5 days | waterborne | Highest concentration increased mortality, long term exposure to low concentrations leads to a decrease in survival, offspring and delay in first brood. | [77] | |
| PS-COOH | 26nm, 62 nm |
||||||
| Eu-PS NPD (NPLs debrise) Fe-PS NPD | 640 nm | 0, 1, 7 mg L-1 | 21 days | foodborne - Pseudokirchinella subcapitata | Fe-PS-NPD impacted reproduction time, increased mortality and decreased the number of neonats. Eu-PS-NPD lowered number of neonats per brood. Smaller NPD (Fe-PS-NPD) have a higher impact on the reproduction than the larger NPD (Eu-PS-NPD). | [41] | |
| PS-COOH (fluorescent) | 20 nm, 200 nm | 0, 0.1, 50 mg L-1 |
21 days | waterborne | Molting and time to first brood prolonged, changes in the body length, neonat production in 200 nm may be higher because of hormesis. | [100] | |
| PS (fluorescent) | 80 nm | 0, 5 mg L-1 | 28 days | foodborne - Chlorella pyrenoidosa | Trophic transfer observed, higher accumulation through direct exposure than foodborne. Histopathological damages in the intestinal. | [98] | |
| Amidine PS | 20, 40, 60, and 100 nm | 0.5 to 30 mg L-1 (0.5 to 100 mg L-1 for 100nm NPLs) | 2 days | waterborne | Exposure in lake water. The effect depended on the primary size of PS, with 20 and 40-nm-size PS NPLs inducing a stronger effect. | [75] | |
|
Daphnia pulex (freshwater) |
PS (fluorescent) | 75 nm | 0, 0.1, 0.5, 1 and 2 mg L-1 |
21 days | waterborne | Growth inhibition, reproduction time longer while number of neonats reduced, heat shot proteins (HSP70 and HSP90) increased in the higher concentrations. | [87] |
| PS (plain) | 75 nm | 0, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 2 mg L-1 |
21 days | waterborne | Increase in concentration of NPLs stimulates increase in ROS production which leads to increase in antioxidative gene expression and enzyme activity, possible negative effects on cell survival and proliferation via MAPK pathways. | [102] | |
| PS (plain) | 71.18 ± 6.03 nm | 0, 1 mg L-1 | 4 days | waterborne | 208 differentially expressed genes analysed - changes in the expression for oxidative stress, immune defense and glycometabolism pathways. | [103] | |
|
Daphnia magna ,larvae Thamnocephalus platyurus, and rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus (freshwater) |
Amidine PS | 226.0 ± 8.6 nm |
0 to 400 mg L−1 | 1 day and 2 days | waterborne | The toxicity decreased in the order D. magna (48 h -immobilization) > B. calyciflorus (24 h - lethality) > T. platyurus (24 h - lethality). Amidine PS were more toxic than carboxyl PS. Alginate and humic acid formed eco-corona on amidine PS nanospheres and reduced toxicity to zooplankton. | [74] |
| Carboxyl PS | 220.1 ± 9.1 nm |
0 to 400 mgL-1 |
3.4. Effect of Zooplankton on NPLs Biouptake and Toxico Availability
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the environment and human health: Current consensus and future trends. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chao, J.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.C.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Research progress of nanoplastics in freshwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and nanoplastics in aquatic environments: Aggregation, deposition, and enhanced contaminant transport. Environmental Science & Technology 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkola, A.; Krause, S.; Lynch, I.; Sambrook Smith, G.H.; Nel, H. Nano and microplastic interactions with freshwater biota – current knowledge, challenges and future solutions. Environment International 2021, 152, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaylarde, C.C.; Baptista Neto, J.A.; da Fonseca, E.M. Nanoplastics in aquatic systems - are they more hazardous than microplastics? Environmental Pollution 2021, 272, 115950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atugoda, T.; Piyumali, H.; Wijesekara, H.; Sonne, C.; Lam, S.S.; Mahatantila, K.; Vithanage, M. Nanoplastic occurrence, transformation and toxicity: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2023, 21, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; El Hadri, H.; Nguyen, B.; Grassl, B.; Rowenczyk, L.; Tufenkji, N.; Feng, S.; Wiesner, M. Nanoplastics are neither microplastics nor engineered nanoparticles. Nature Nanotechnology 2021, 16, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.; An, Y.J. Effects of micro- and nanoplastics on aquatic ecosystems: Current research trends and perspectives. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2017, 124, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, X.; Zou, H.; Guo, R.-B.; Fu, S.-F. Effects of size and surface charge on the sedimentation of nanoplastics in freshwater. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission, E. Chemicals strategy for sustainability. Commission, E., Ed. 2022.
- Gigault, J.; Halle, A.t.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.-Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.-L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current opinion: What is a nanoplastic? Environmental Pollution 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.; Carson, H.; Thiel, M.; Moore, C.; Borerro, J.; Galgani, F.; Ryan, P.; Reisser, J. Plastic pollution in the world’s oceans: More than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besseling, E.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Foekema, E.M.; Koelmans, A.A. Quantifying ecological risks of aquatic micro- and nanoplastic. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 2019, 49, 32–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Emergence of nanoplastics in the aquatic environment and possible impacts on aquatic organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Nowack, B. A meta-analysis of ecotoxicological hazard data for nanoplastics in marine and freshwater systems. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 2020, 39, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venâncio, C.; Ferreira, I.; Martins, M.A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Lopes, I.; Oliveira, M. The effects of nanoplastics on marine plankton: A case study with polymethylmethacrylate. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2019, 184, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, K.M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Sinclair, T.M.; Hayashi, T.I.; Naito, W. Illustrating a species sensitivity distribution for nano- and microplastic particles using bayesian hierarchical modeling. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 2022, 41, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, B.E.; Sharpe, E.E.; Brander, S.M.; Landis, W.G.; Harper, S.L. Critical gaps in nanoplastics research and their connection to risk assessment. Frontiers in Toxicology 2023, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolahpur Monikh, F.; Vijver, M.G.; Kortet, R.; Lynch, I.; Peijnenburg, W. Emerging investigator series: Perspectives on toxicokinetics of nanoscale plastic debris in organisms. Environmental Science: Nano 2022. [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Aldridge, D.C. Microplastics in freshwater systems: A review of the emerging threats, identification of knowledge gaps and prioritisation of research needs. Water Research 2015, 75, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a vector for chemicals in the aquatic environment: Critical review and model-supported reinterpretation of empirical studies. Environmental Science & Technology 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogel, T.; Bjoroy, O.; Toto, B.; Bienfait, A.M.; Sanden, M. Micro- and nanoplastic toxicity on aquatic life: Determining factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, J.; Ji, R.; Pan, K.; Miao, A.-J. Microplastics in aquatic environments: Occurrence, accumulation, and biological effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Tao, J.; Cheng, M.; Deng, R.; Chen, S.; Yin, L.; Li, R. Microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment: Macroscopic transport and effects on creatures. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 407, 124399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.R.; Lian, F.; Xiao, Z.G.; Gu, S.G.; Cao, X.S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, B.S. Potential toxicity of nanoplastics to fish and aquatic invertebrates: Current understanding, mechanistic interpretation, and meta-analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2022, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Hu, D.; Wen, X.; Ren, X. Recent advances in toxicological research of nanoplastics in the environment: A review. Environmental Pollution 2019, 252, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.L.; Fu, S.F.; Zou, H.; Su, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.F. Effects of nanoplastics on microalgae and their trophic transfer along the food chain: Recent advances and perspectives. Environmental Science-Processes & Impacts 2021, 23, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larue, C.; Sarret, G.; Castillo-Michel, H.; del Real, A.E.P. A critical review on the impacts of nanoplastics and microplastics on aquatic and terrestrial photosynthetic organisms. Small 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-K.; Lin, C.; Nguyen, H.-L.; Le, V.-G.; Haddout, S.; Um, M.-J.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D. Ecotoxicity of micro- and nanoplastics on aquatic algae: Facts, challenges, and future opportunities. Journal of Environmental Management 2023, 346, 118982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Li, R.X.; Li, F.; Guo, X.W.; Xu, L.J.; Gan, L.; Yan, M.T.; Wang, J. Toxicity of nanoplastics to aquatic organisms: Genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, individual level and beyond individual level. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agathokleous, E.; Iavicoli, I.; Barcelo, D.; Calabrese, E.J. Micro/nanoplastics effects on organisms: A review focusing on 'dose'. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, M.; Duffus, J.H.; Templeton, D.M. Explanatory dictionary of key terms in toxicology: Part ii (iupac recommendations 2010). Pure and Applied Chemistry 2010, 82, 679–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaveykova, V.I.; Li, M.; Worms, I.A.; Liu, W. When environmental chemistry meets ecotoxicology: Bioavailability of inorganic nanoparticles to phytoplankton. CHIMIA 2020, 74, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijver, M.G.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M. Emerging investigator series: The dynamics of particle size distributions need to be accounted for in bioavailability modelling of nanoparticles. Environmental Science: Nano 2018, 5, 2473–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpowicz, M.; Zieliński, P.; Grabowska, M.; Ejsmont-Karabin, J.; Kozłowska, J.; Feniova, I. Effect of eutrophication and humification on nutrient cycles and transfer efficiency of matter in freshwater food webs. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 2521–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergami, E.; Pugnalini, S.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Manfra, L.; Faleri, C.; Savorelli, F.; Dawson, K.A.; Corsi, I. Long-term toxicity of surface-charged polystyrene nanoplastics to marine planktonic species dunaliella tertiolecta and artemia franciscana. Aquatic Toxicology 2017, 189, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, C.; Toullec, J.; Lambert, C.; Le Goïc, N.; Seoane, M.; Moriceau, B.; Huvet, A.; Berchel, M.; Vincent, D.; Courcot, L. , et al. Do transparent exopolymeric particles (tep) affect the toxicity of nanoplastics on chaetoceros neogracile? Environmental Pollution 2019, 250, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, T.M.; Hartmann, N.B.; Kleijn, J.M.; Garnæs, J.; van de Meent, D.; Jan Hendriks, A.; Baun, A. The toxicity of plastic nanoparticles to green algae as influenced by surface modification, medium hardness and cellular adsorption. Aquatic Toxicology 2017, 183, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendra, M.; Staffieri, E.; Yeste, M.P.; Moreno-Garrido, I.; Gatica, J.M.; Corsi, I.; Blasco, J. Are the primary characteristics of polystyrene nanoplastics responsible for toxicity and ad/absorption in the marine diatom phaeodactylum tricornutum? Environmental Pollution 2019, 249, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.W.; An, Y.J. Trophic transfer and individual impact of nano-sized polystyrene in a four-species freshwater food chain. Scientific Reports 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monikh, F.A.; Chupani, L.; Vijver, M.G.; Peijnenburg, W. Parental and trophic transfer of nanoscale plastic debris in an assembled aquatic food chain as a function of particle size. Environmental Pollution 2021, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Tang, B.Z.; Wang, W.X. Cell cycle control of nanoplastics internalization in phytoplankton. Acs Nano 2021, 15, 12237–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tao, S.; Liu, S.; Hu, T.; Zheng, K.; Shen, M.; Meng, G. Research advances on impacts micro/nanoplastics and their carried pollutants on algae in aquatic ecosystems: A review. Aquat Toxicol 2023, 264, 106725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsi, I.; Bellingeri, A.; Eliso, M.C.; Grassi, G.; Liberatori, G.; Murano, C.; Sturba, L.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Bergami, E. Eco-interactions of engineered nanomaterials in the marine environment: Towards an eco-design framework. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, J. Polystyrene nanoplastics cause growth inhibition, morphological damage and physiological disturbance in the marine microalga platymonas helgolandica. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2020, 158, 111403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.-r.; Wang, B.-l.; Nan, F.-r.; Lv, J.-p.; Liu, X.-d.; Liu, Q.; Feng, J.; Xie, S.-l. Effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on the physiological and biochemical characteristics of microalga scenedesmus quadricauda. Environmental Pollution 2023, 319, 120987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Ai, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, P.; Kang, L.; Li, W.; Gu, W.; He, Q.; Li, H. Phytoplankton response to polystyrene microplastics: Perspective from an entire growth period. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Gao, P.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhang, W. Mechanism of the inhibition and detoxification effects of the interaction between nanoplastics and microalgae chlorella pyrenoidosa. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazeem, L.J.; Yesilay, G.; Bououdina, M.; Perna, S.; Cetin, D.; Suludere, Z.; Barras, A.; Boukherroub, R. Investigation of the toxic effects of different polystyrene micro-and nanoplastics on microalgae chlorella vulgaris by analysis of cell viability, pigment content, oxidative stress and ultrastructural changes. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2020, 156, 111278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, P.; Li, M. Adverse physiological and molecular level effects of polystyrene microplastics on freshwater microalgae. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, M. Exposure of microalgae euglena gracilis to polystyrene microbeads and cadmium: Perspective from the physiological and transcriptional responses. Aquatic Toxicology 2020, 228, 105650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.-J.; Li, J.-W.; Xu, E.G.; Sun, X.-D.; Zhu, F.-P.; Ding, Z.; Tian, H.; Dong, S.-S.; Xia, P.-F.; Yuan, X.-Z. Short-term exposure to positively charged polystyrene nanoparticles causes oxidative stress and membrane destruction in cyanobacteria. Environmental Science: Nano 2019, 6, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoane, M.; González-Fernández, C.; Soudant, P.; Huvet, A.; Esperanza, M.; Cid, Á.; Paul-Pont, I. Polystyrene microbeads modulate the energy metabolism of the marine diatom chaetoceros neogracile. Environmental Pollution 2019, 251, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Yin, Z.; Hu, T.; Hu, D.; Liu, C.; Zhu, L. Influence of polystyrene microplastics on the growth, photosynthetic efficiency and aggregation of freshwater microalgae chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo-Belda, M.; Pérez-Olivares, A.V.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; Martin-Betancor, K.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Mitrano, D.M.; Rosal, R.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Tracking nanoplastics in freshwater microcosms and their impacts to aquatic organisms. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 445, 130625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, X.X.; Zhang, B.H.; Li, L.Y.; Zhao, Y.R.; Lv, M.C.; Li, J.; Kan, C.X.; Zhao, Y. The effects of two sized polystyrene nanoplastics on the growth, physiological functions, and toxin production of alexandrium tamarense. Chemosphere 2022, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pleiter, M.; Tamayo-Belda, M.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; Amariei, G.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Secondary nanoplastics released from a biodegradable microplastic severely impact freshwater environments. Environmental Science: Nano 2019, 6, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, L.; Omer, S.; Jetly, N.; Jenifer, M.A.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Suraishkumar, G.K.; Mukherjee, A. Eco-corona formation lessens the toxic effects of polystyrene nanoplastics towards marine microalgae chlorella sp. Environmental Research 2020, 188, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarini, G.; Secco, S.; Taurozzi, D.; Venditti, I.; Battocchio, C.; Marcheggiani, S.; Mancini, L.; Fratoddi, I.; Scalici, M.; Puccinelli, C. Teratogenic effects of environmental concentration of plastic particles on freshwater organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, Z. Polystyrene nanoplastics affect growth and microcystin production of microcystis aeruginosa. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 13394–13403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G.; Gabellieri, E.; Cioni, P.; Paccagnini, E.; Faleri, C.; Lupetti, P.; Corsi, I.; Morelli, E. Interplay between extracellular polymeric substances (eps) from a marine diatom and model nanoplastic through eco-corona formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, T.; Almeida, A.C.; Georgantzopoulou, A. Characterization of cell responses in rhodomonas baltica exposed to pmma nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudrimont, M.; Arini, A.; Guégan, C.; Venel, Z.; Gigault, J.; Pedrono, B.; Prunier, J.; Maurice, L.; Ter Halle, A.; Feurtet-Mazel, A. Ecotoxicity of polyethylene nanoplastics from the north atlantic oceanic gyre on freshwater and marine organisms (microalgae and filter-feeding bivalves). Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2020, 27, 3746–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Belda, M.; Vargas-Guerrero, J.J.; Martín-Betancor, K.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; González-Pleiter, M.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Understanding nanoplastic toxicity and their interaction with engineered cationic nanopolymers in microalgae by physiological and proteomic approaches. Environmental Science: Nano 2021, 8, 2277–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Belda, M.; Pulido-Reyes, G.; González-Pleiter, M.; Martín-Betancor, K.; Leganés, F.; Rosal, R.; Fernández-Piñas, F. Identification and toxicity towards aquatic primary producers of the smallest fractions released from hydrolytic degradation of polycaprolactone microplastics. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiu, R.-F.; Vazquez, C.I.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Chiu, M.-H.; Chen, C.-S.; Ni, C.-W.; Gong, G.-C.; Quigg, A.; Santschi, P.H.; Chin, W.-C. Nano- and microplastics trigger secretion of protein-rich extracellular polymeric substances from phytoplankton. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Wick, P.; Nowack, B. Placing nanoplastics in the context of global plastic pollution. Nature Nanotechnology 2021, 16, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Interaction of nanoplastics with extracellular polymeric substances (eps) in the aquatic environment: A special reference to eco-corona formation and associated impacts. Water Research 2021, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Worms, I.A.M.; Jakšić, Ž.; Slaveykova, V.I. Aquatic organisms modulate the bioreactivity of engineered nanoparticles: Focus on biomolecular corona. Frontiers in Toxicology 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, W.; Kang, F.; Lu, J. Nature and value of freely dissolved eps ecosystem services: Insight into molecular coupling mechanisms for regulating metal toxicity. Environmental Science & Technology 2018, 52, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, K.J.; Joz-Roland, A.; Buffle, J. Different roles of pedogenic fulvic acids and aquagenic biopolymers on colloid aggregation and stability in freshwaters. Limnology and Oceanography 1997, 42, 1714–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, S.; Li, C.H.; Lu, X.D.; Chen, S.S.; Yin, B.; Zhang, C.H.; Ge, Y. Microalgal extracellular polymeric substances and their interactions with metal(loid)s: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 2019, 49, 1769–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-S.; Anaya, J.M.; Zhang, S.; Spurgin, J.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Xu, C.; Miao, A.-J.; Chen, E.Y.; Schwehr, K.A.; Jiang, Y. Effects of engineered nanoparticles on the assembly of exopolymeric substances from phytoplankton. PLoS One 2011, 6, e21865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, J.; Stoll, S.; Slaveykova, V.I. Influence of nanoplastic surface charge on eco-corona formation, aggregation and toxicity to freshwater zooplankton. Environmental Pollution 2019, 252, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochelon, A.; Stoll, S.; Slaveykova, V.I. Polystyrene nanoplastic behavior and toxicity on crustacean daphnia magna: Media composition, size, and surface charge effects. Environments 2021, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadare, O.O.; Wan, B.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, L.-H. Eco-corona vs protein corona: Effects of humic substances on corona formation and nanoplastic particle toxicity in daphnia magna. Environmental Science & Technology 2020, 54, 8001–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelpsiene, E.; Torstensson, O.; Ekvall, M.T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Cedervall, T. Long-term exposure to nanoplastics reduces life-time in daphnia magna. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Jiang, R.; Hu, S.; Xiao, X.; Wu, J.; Wei, S.; Xiong, Y.; Ouyang, G. Investigating the toxicities of different functionalized polystyrene nanoplastics on daphnia magna. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2019, 180, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Karbalaei, S.; Maselli, V.; Walker, T.R. Micro(nano)plastics sources, fate, and effects: What we know after ten years of research. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances 2022, 6, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchere, O.; Audroin, T.; Hetier, J.; Metais, I.; Chatel, A. The need to investigate continuums of plastic particle diversity, brackish environments and trophic transfer to assess the risk of micro and nanoplastics on aquatic organisms. Environmental Pollution 2021, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröter, L.; Ventura, N. Nanoplastic toxicity: Insights and challenges from experimental model systems. Small 2022, 18, 2201680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemec Kokalj, A.; Heinlaan, M.; Novak, S.; Drobne, D.; Kühnel, D. Defining quality criteria for nanoplastic hazard evaluation: The case of polystyrene nanoplastics and aquatic invertebrate daphnia spp. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seda, J.; Petrusek, A. Daphnia as a model organism in limnology and aquatic biology: Introductory remarks. Journal of Limnology 2011, 70, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, J.; Ritschar, S.; Laforsch, C.; Mair, M.M. The complexity of micro- and nanoplastic research in the genus daphnia – a systematic review of study variability and a meta-analysis of immobilization rates. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 458, 131839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Nowack, B. Meta-analysis of bioaccumulation data for nondissolvable engineered nanomaterials in freshwater aquatic organisms. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 2022, 41, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, S.; Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B. Ingestion of micro- and nanoplastics in daphnia magna – quantification of body burdens and assessment of feeding rates and reproduction. Environmental Pollution 2017, 228, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, P.; Cai, M.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Polystyrene nanoplastic exposure induces immobilization, reproduction, and stress defense in the freshwater cladoceran daphnia pulex. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicentini, D.S.; Nogueira, D.J.; Melegari, S.P.; Arl, M.; Köerich, J.S.; Cruz, L.; Justino, N.M.; Oscar, B.V.; Puerari, R.C.; da Silva, M.L.N. , et al. Toxicological evaluation and quantification of ingested metal-core nanoplastic by daphnia magna through fluorescence and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometric methods. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 2019, 38, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Wang, W.X. Accumulation kinetics and gut microenvironment responses to environmentally relevant doses of micro/nanoplastics by zooplankton daphnia magna. Environmental Science & Technology 2023, 57, 5611–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Wang, W.X. Selective ingestion and response by daphnia magna to environmental challenges of microplastics. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfra, L.; Rotini, A.; Bergami, E.; Grassi, G.; Faleri, C.; Corsi, I. Comparative ecotoxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles in natural seawater and reconstituted seawater using the rotifer brachionus plicatilis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2017, 145, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Gao, R.-Y.; Wang, Z.-J.; Shao, Q.-Q.; Hu, Y.-W.; Jia, H.-B.; Liu, X.-J.; Dong, F.-Q.; Fu, L.-M.; Zhang, J.-P. Daphnia magna uptake and excretion of luminescence-labelled polystyrene nanoparticle as visualized by high sensitivity real-time optical imaging. Chemosphere 2023, 326, 138341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Guilhermino, L. Transgenerational effects and recovery of microplastics exposure in model populations of the freshwater cladoceran daphnia magna straus. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631-632, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, I.-C.; Shim, K.-Y.; Kim, K.; Jeong, C.-B. Maternal exposure to nanoplastic induces transgenerational toxicity in the offspring of rotifer brachionus koreanus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology 2023, 269, 109635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, S.; Baranov, V.; Nel, H.A.; Drummond, J.D.; Kukkola, A.; Hoellein, T.; Sambrook Smith, G.H.; Lewandowski, J.; Bonet, B.; Packman, A.I. , et al. Gathering at the top? Environmental controls of microplastic uptake and biomagnification in freshwater food webs. Environmental Pollution 2021, 268, 115750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Chen, H.; Shen, M.; Tao, J.; Chen, S.; Yin, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Xiao, R.; Li, R. Recent advances on the transport of microplastics/nanoplastics in abiotic and biotic compartments. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2022, 438, 129515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venancio, C.; Ciubotariu, A.; Lopes, I.; Martins, M.A.; Oliveira, M. Is the toxicity of nanosized polymethylmethacrylate particles dependent on the exposure route and food items? Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Gao, D.; Kong, C.; Junaid, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, G.; Wang, J. Trophic transfer of nanoplastics and di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in a freshwater food chain (chlorella pyrenoidosa-daphnia magna-micropterus salmoides) induced disturbance of lipid metabolism in fish. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 459, 132294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, L.; Cui, R.; Il Kwak, J.; An, Y.-J. Trophic transfer of nanoplastics through a microalgae–crustacean–small yellow croaker food chain: Inhibition of digestive enzyme activity in fish. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2022, 440, 129715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuda, O.; Dumont, E.R.; Matthews, S.; Xu, E.G.; Berk, D.; Tufenkji, N. Sub-lethal effects of nanoplastics upon chronic exposure to daphnia magna. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances 2022, 7, 100136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Machado, A.A.; Ghadernezhad, N.; Wolinska, J. Potential for high toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics to the european daphnia longispina. Environmental Sciences Europe 2023, 35, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Huang, Y.H.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wu, D.L.; Yu, P.; Li, Y.M.; Cai, M.Q.; Zhao, Y.L. Polystyrene nanoplastic induces ros production and affects the mapk-hif-1/nfκb-mediated antioxidant system in daphnia pulex. Aquatic Toxicology 2020, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Pérez, E.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Polystyrene nanoplastic induces oxidative stress, immune defense, and glycometabolism change in daphnia pulex: Application of transcriptome profiling in risk assessment of nanoplastics. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 402, 123778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, M.; Yu, P.; Chen, M.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y. Age-dependent survival, stress defense, and ampk in daphnia pulex after short-term exposure to a polystyrene nanoplastic. Aquatic Toxicology 2018, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lins, T.F.; O'Brien, A.M.; Kose, T.; Rochman, C.M.; Sinton, D. Toxicity of nanoplastics to zooplankton is influenced by temperature, salinity, and natural particulate matter. Environmental Science-Nano 2022, 9, 2678–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.B.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Seo, J.S.; Wang, M.; Lee, J.S. Nanoplastic ingestion enhances toxicity of persistent organic pollutants (pops) in the monogonont rotifer brachionus koreanus via multixenobiotic resistance (mxr) disruption. Environ Sci Technol 2018, 52, 11411–11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrianos, S.; Manzi, F.; Agha, R.; Azoubib, N.; Schampera, C.; Wolinska, J. Nanoplastics modulate the outcome of a zooplankton-microparasite interaction. Freshwater Biology 2023, 68, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, B.; Sugni, M.; Casati, L.; Parolini, M. Molecular, biochemical and behavioral responses of daphnia magna under long-term exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics. Environment International 2022, 164, 107264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekvall, M.T.; Gimskog, I.; Hua, J.; Kelpsiene, E.; Lundqvist, M.; Cedervall, T. Size fractionation of high-density polyethylene breakdown nanoplastics reveals different toxic response in daphnia magna. Scientific Reports 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, M.; Wu, D.; Yu, P.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Effects of nanoplastics at predicted environmental concentration on daphnia pulex after exposure through multiple generations. Environmental Pollution 2020, 256, 113506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinlaan, M.; Viljalo, K.; Richter, J.; Ingwersen, A.; Vija, H.; Mitrano, D.M. Multi-generation exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics showed no major adverse effects in daphnia magna. Environmental Pollution 2023, 323, 121213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, F.; Constantinou, J.; Lynch, I. Nanomaterials in the environment acquire an “eco-corona” impacting their toxicity to daphnia magna—a call for updating toxicity testing policies. PROTEOMICS 2020, 20, 1800412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, F.; Lynch, I. Secreted protein eco-corona mediates uptake and impacts of polystyrene nanoparticles on daphnia magna. Journal of Proteomics 2016, 137, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdolahpur Monikh, F.; Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B.; Kortet, R.; Akkanen, J.; Lee, J.-S.; Shi, H.; Lahive, E.; Uurasjärvi, E.; Tufenkji, N. , et al. Exposure protocol for ecotoxicity testing of microplastics and nanoplastics. Nature Protocols 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlaan, M.; Kasemets, K.; Aruoja, V.; Blinova, I.; Bondarenko, O.; Lukjanova, A.; Khosrovyan, A.; Kurvet, I.; Pullerits, M.; Sihtmäe, M. , et al. Hazard evaluation of polystyrene nanoplastic with nine bioassays did not show particle-specific acute toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 136073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Gao, C.; Liu, R. Combined toxicity of micro/nanoplastics loaded with environmental pollutants to organisms and cells: Role, effects, and mechanism. Environment International 2023, 171, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Q.; Hao, Z.; Yu, S.; Liu, J. Analytical methods and environmental processes of nanoplastics. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2020, 94, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadri, H.; Gigault, J.; Maxit, B.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Nanoplastic from mechanically degraded primary and secondary microplastics for environmental assessments. NanoImpact 2020, 17, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, A.I.; Patsiou, D.; Summers, S.; Everaert, G.; Henry, T.B.; Gutierrez, T. Challenges and recommendations in experimentation and risk assessment of nanoplastics in aquatic organisms. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry 2023, 167, 117262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Beltzung, A.; Frehland, S.; Schmiedgruber, M.; Cingolani, A.; Schmidt, F. Synthesis of metal-doped nanoplastics and their utility to investigate fate and behaviour in complex environmental systems. Nature Nanotechnology 2019, 14, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, W.Y.; Ying Tang, D.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Kay Lup, A.N.; Chew, K.W. Nature’s fight against plastic pollution: Algae for plastic biodegradation and bioplastics production. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology 2020, 4, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, L.; Hao, L.; Shi, Y.; Lyu, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Current advances, challenges and strategies for enhancing the biodegradation of plastic waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaveykova, V. Phytoplankton controls on the transformations of metal-containing nanoparticles in aquatic environmen. In Environmental nanoparzicles: Sources, occurrence, analysis and fate, Jimenez Lamana, J., Szpunar J.,, Ed. Royal Society of Chemistry,: 2022; Vol. in press. [CrossRef]
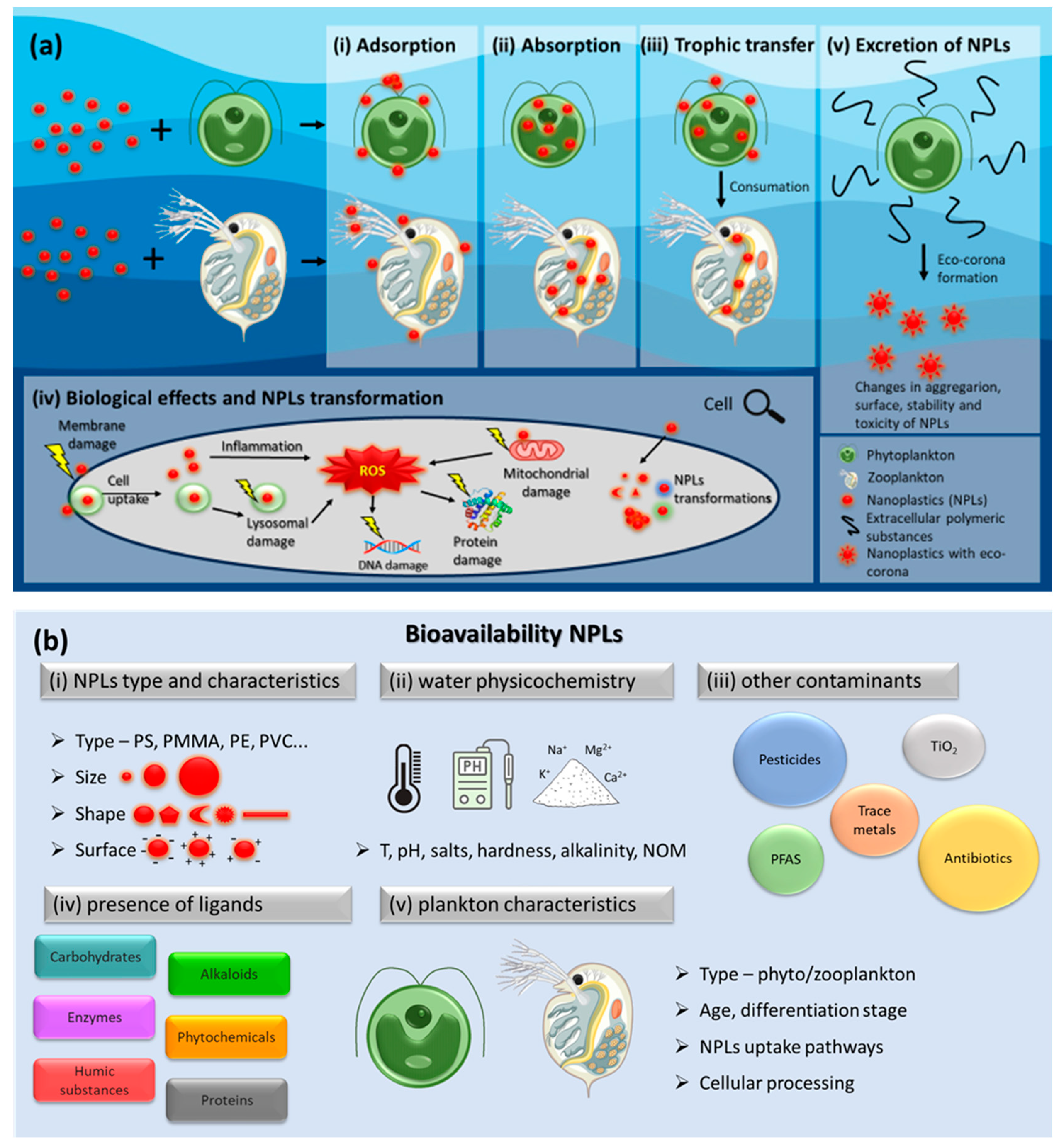
According to the European Commission, plastic particles would be defined as nanomaterials if 50% or more of the plastic particles “in an unbound state or as an aggregate or as an agglomerate and where, for 50 % or more of the particles in the number size distribution, one or more external dimensions is in the size range 1 nm-100 nm. In specific cases and where warranted by concerns for the environment, health, safety or competitiveness the number size distribution threshold of 50 % may be replaced by a threshold between 1 and 50 %” [10]. However, most frequently the term NPLs is used for materials within the size range 1–1000 nm [11]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





