Submitted:
01 November 2023
Posted:
01 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
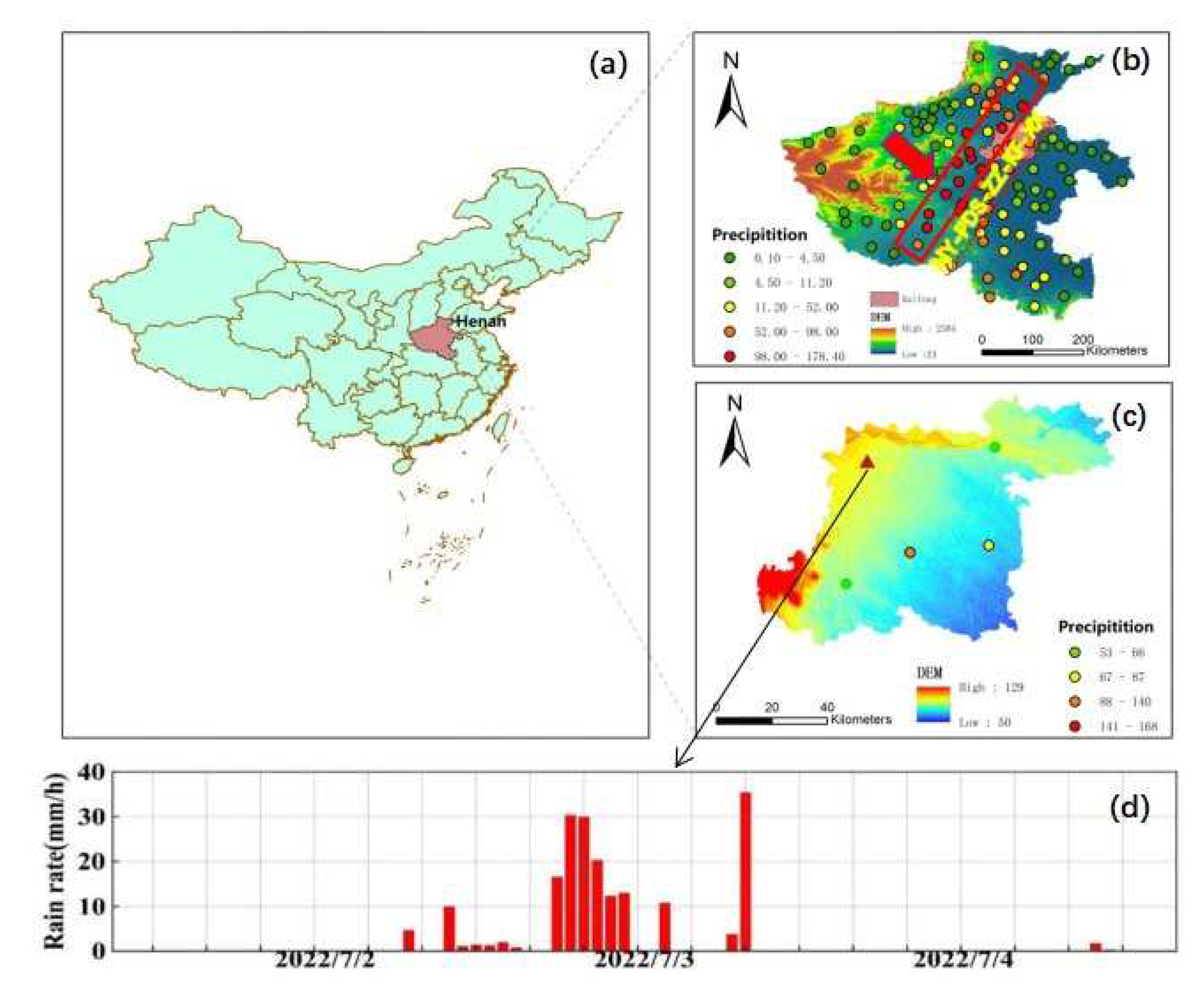
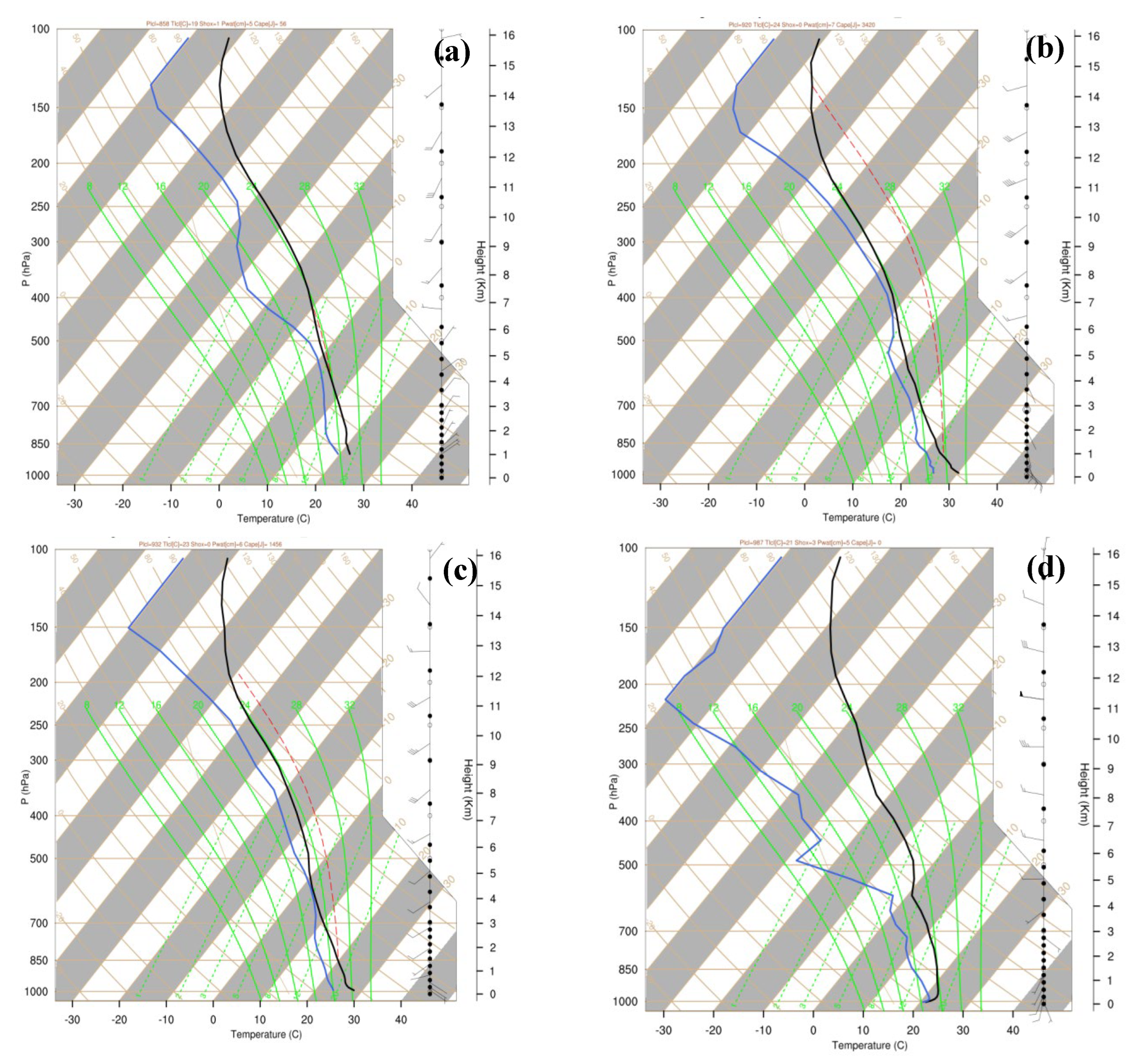
2.1. The Heavy Rainfall Case
2.2. The Model
2.2. AGRI Radiance and MWR Data
2.3. Quality Control
2.4. Model Configureurations and Experiment Design
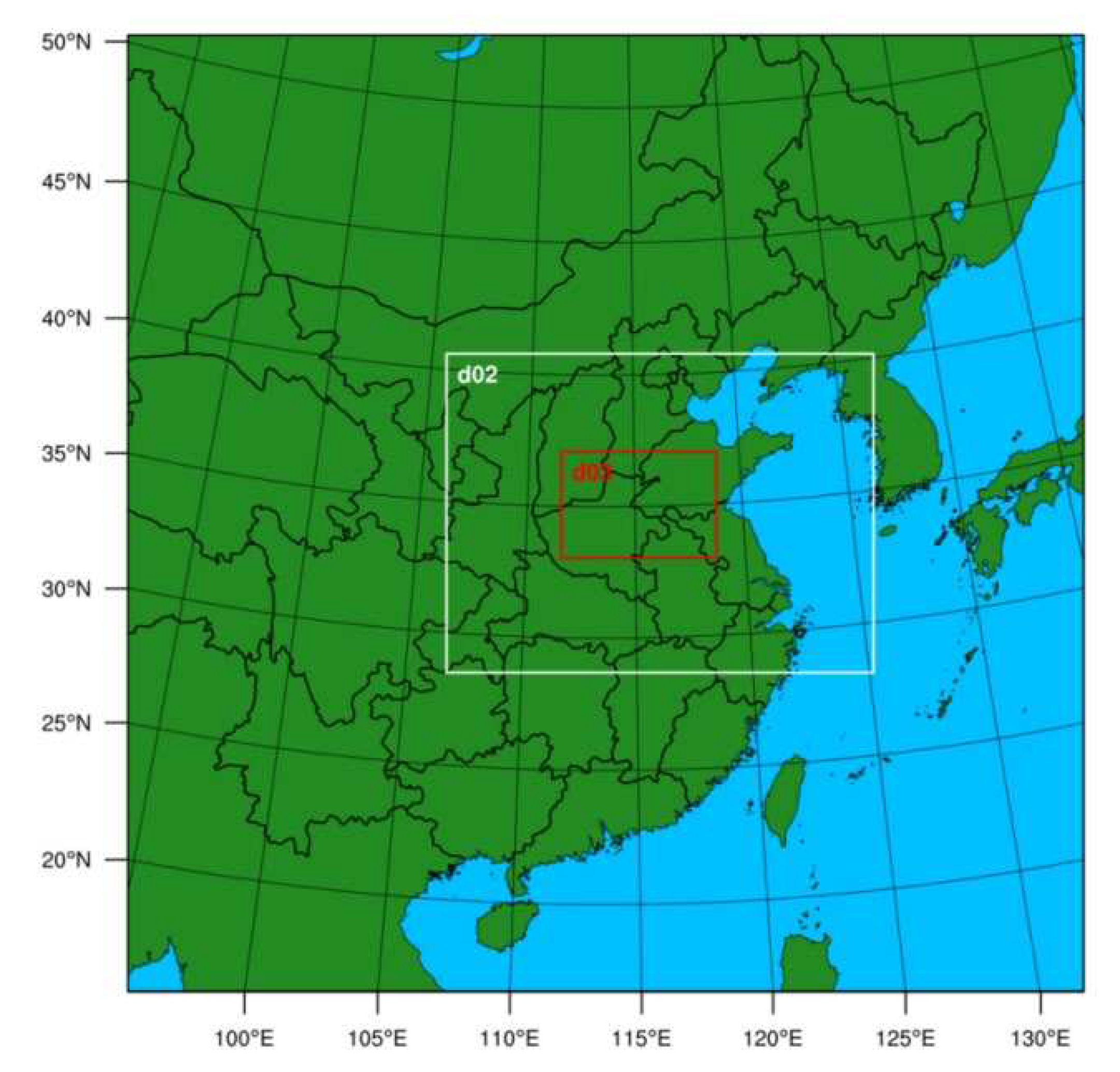
3. Results
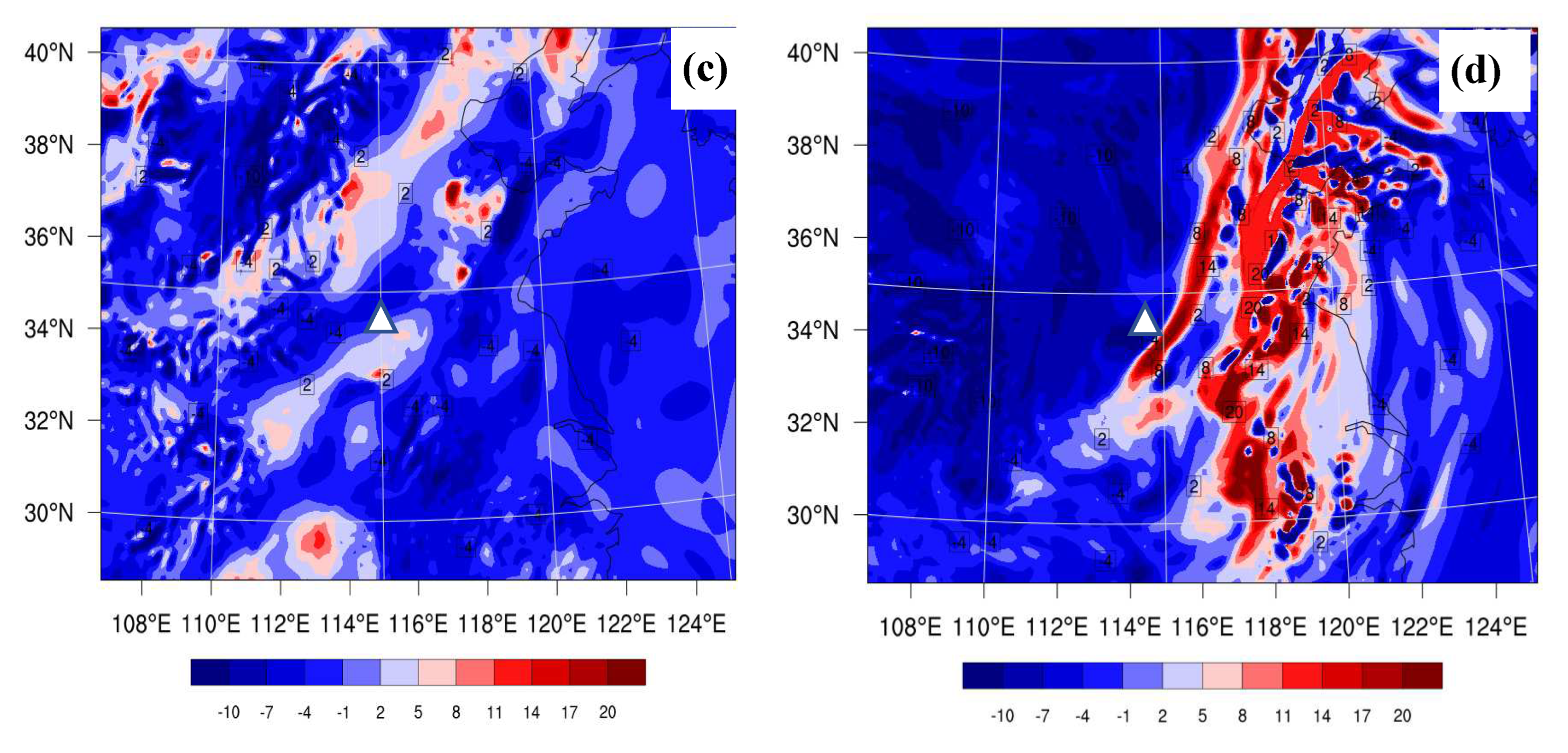
3.1. The Impact of Data Assimilation on Humidity Condition
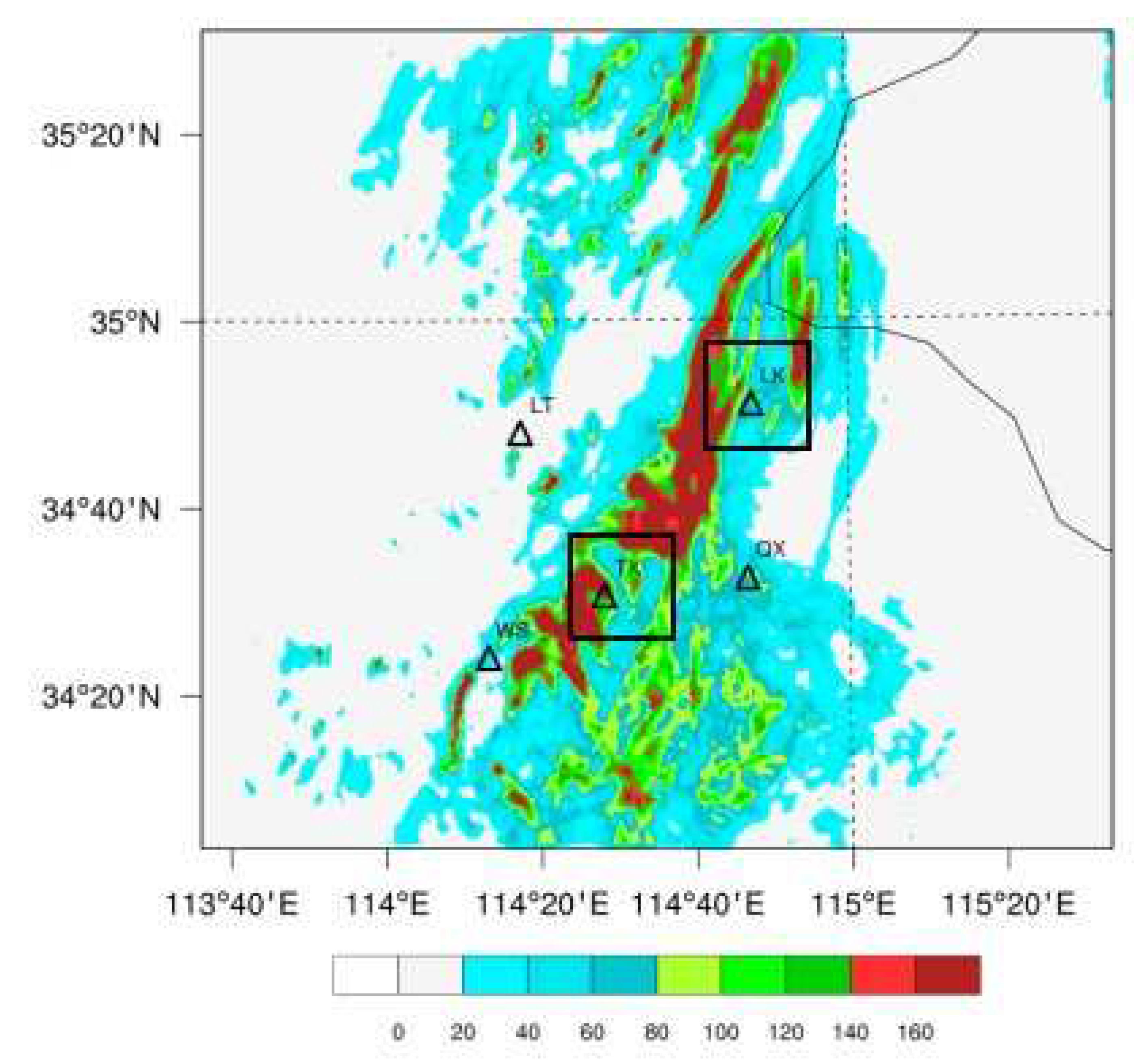
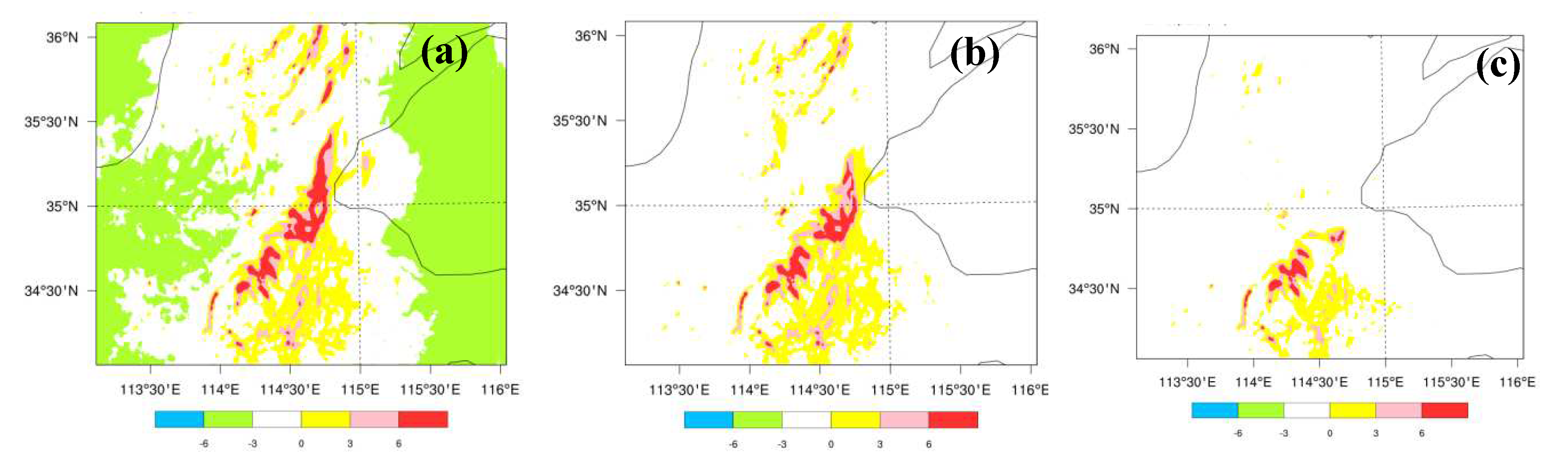
3.2. The Effects of Data Assimilation on 24-h Accumulated Rainfall Forecast
4. Discussion
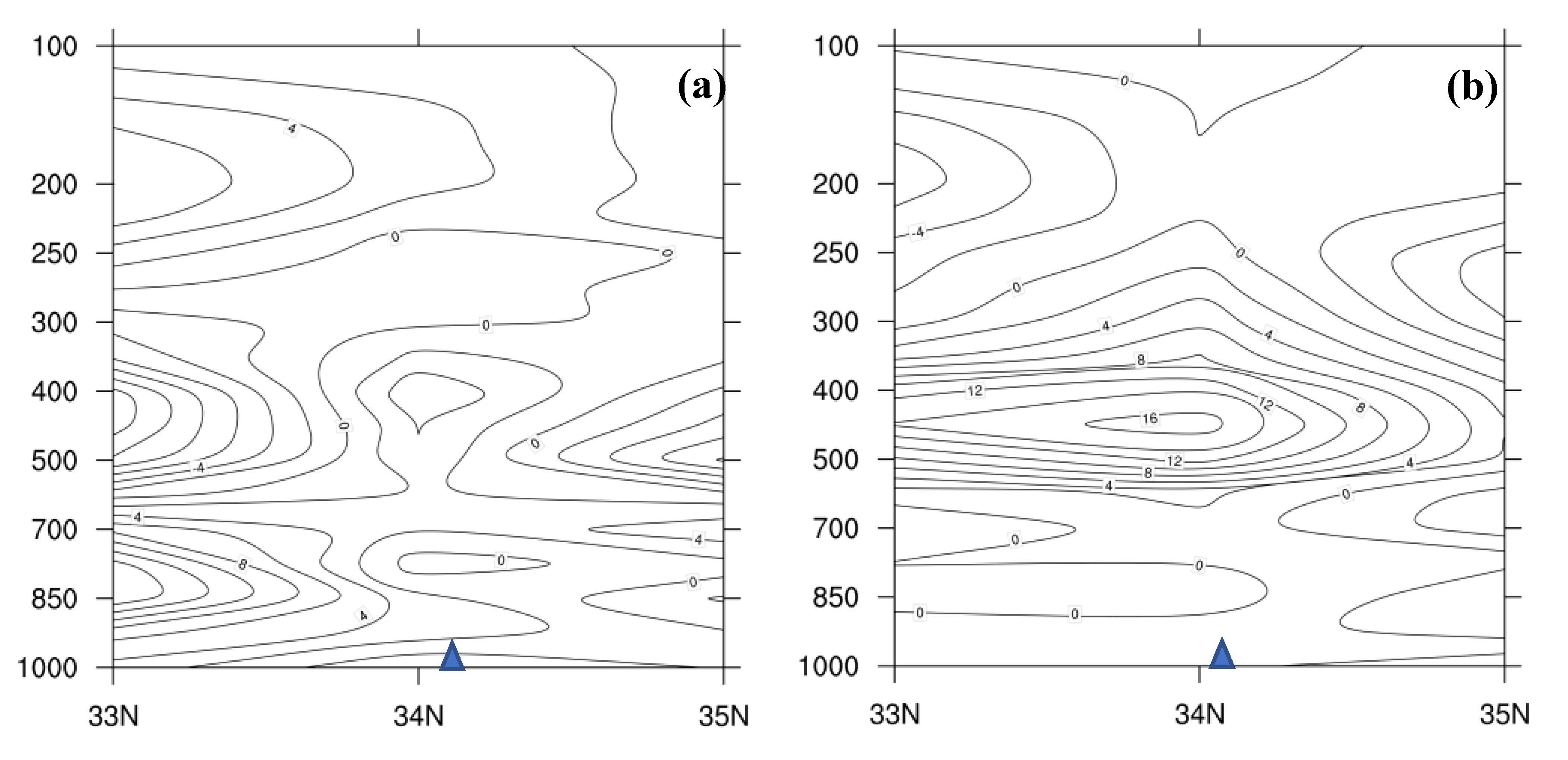
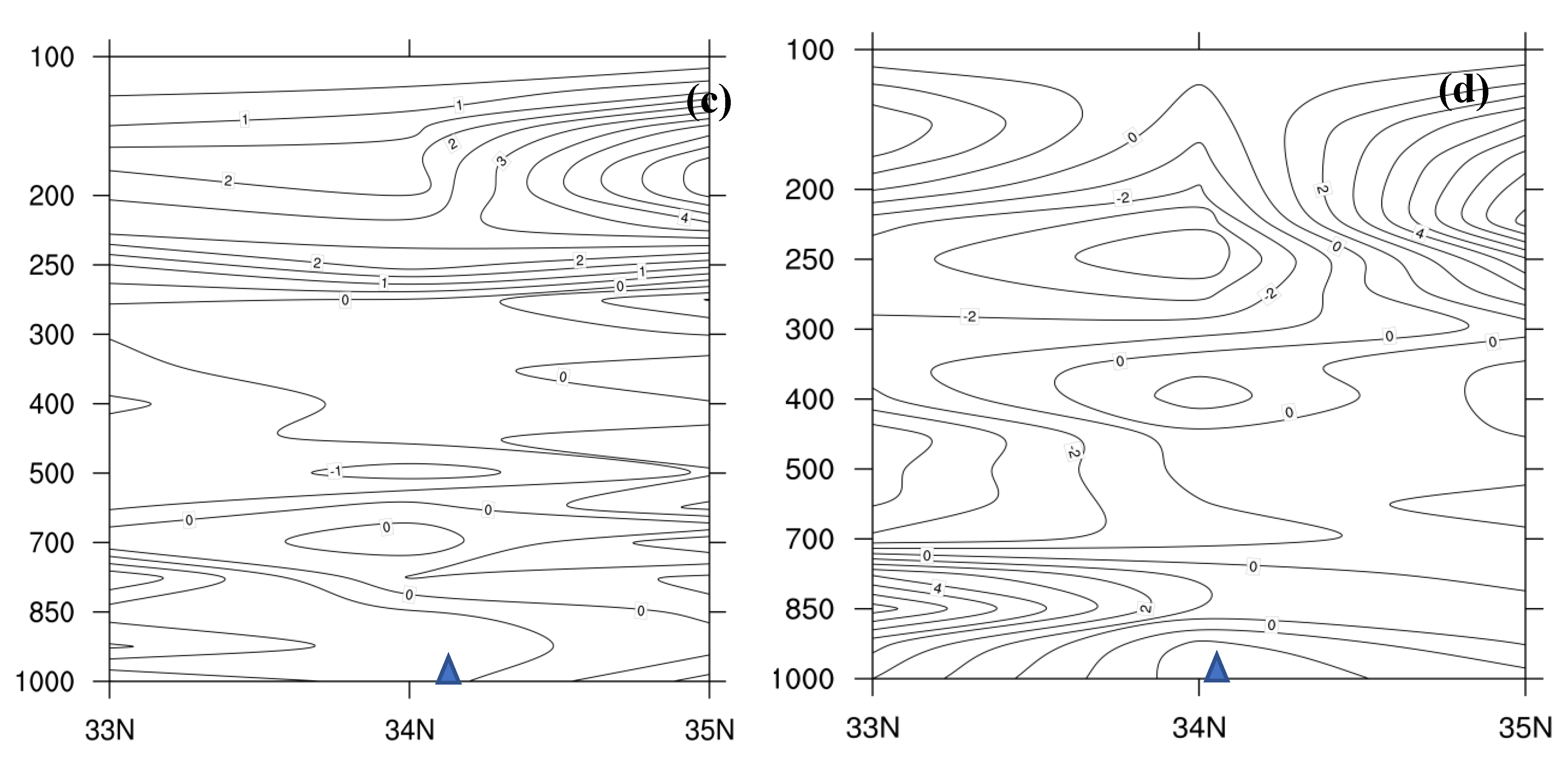
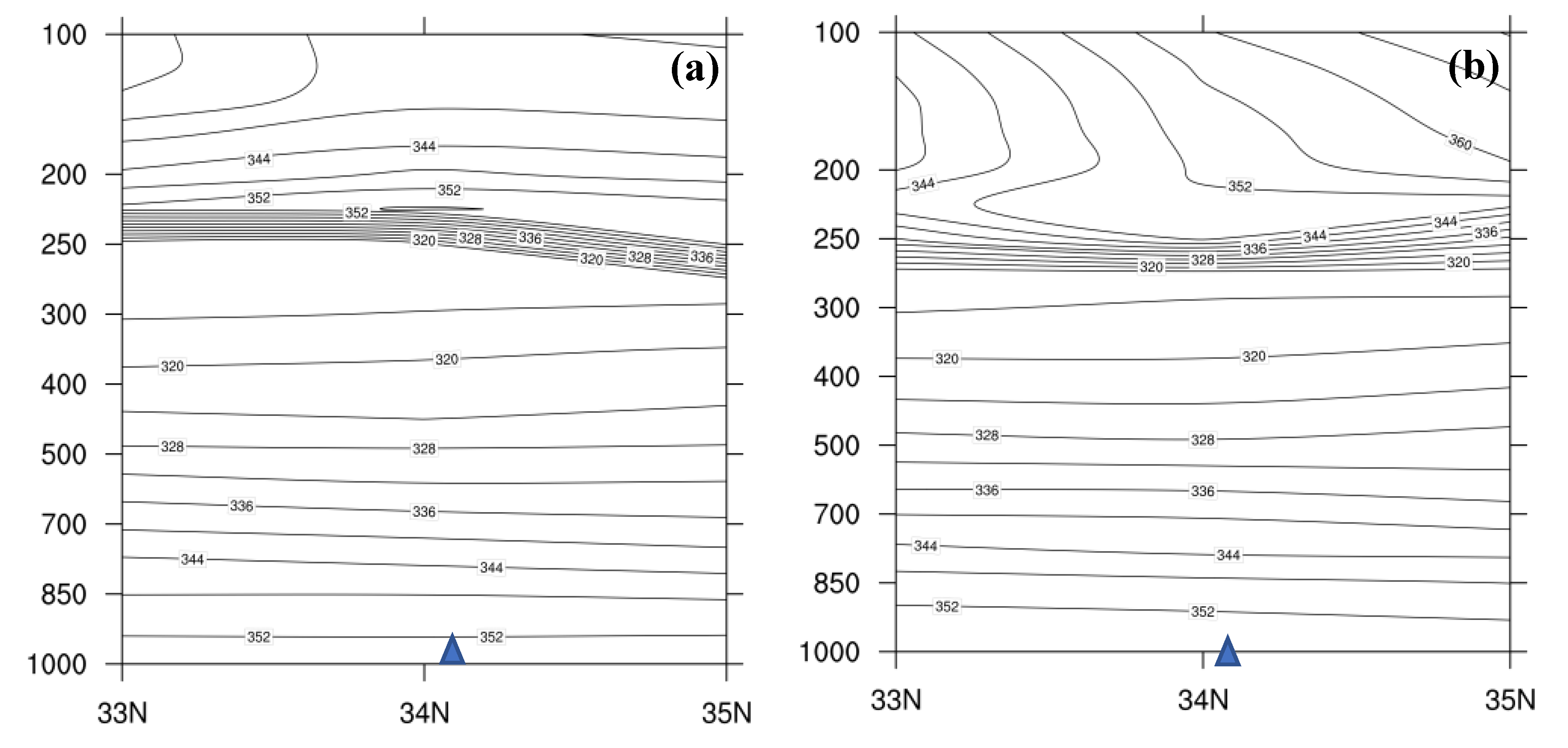
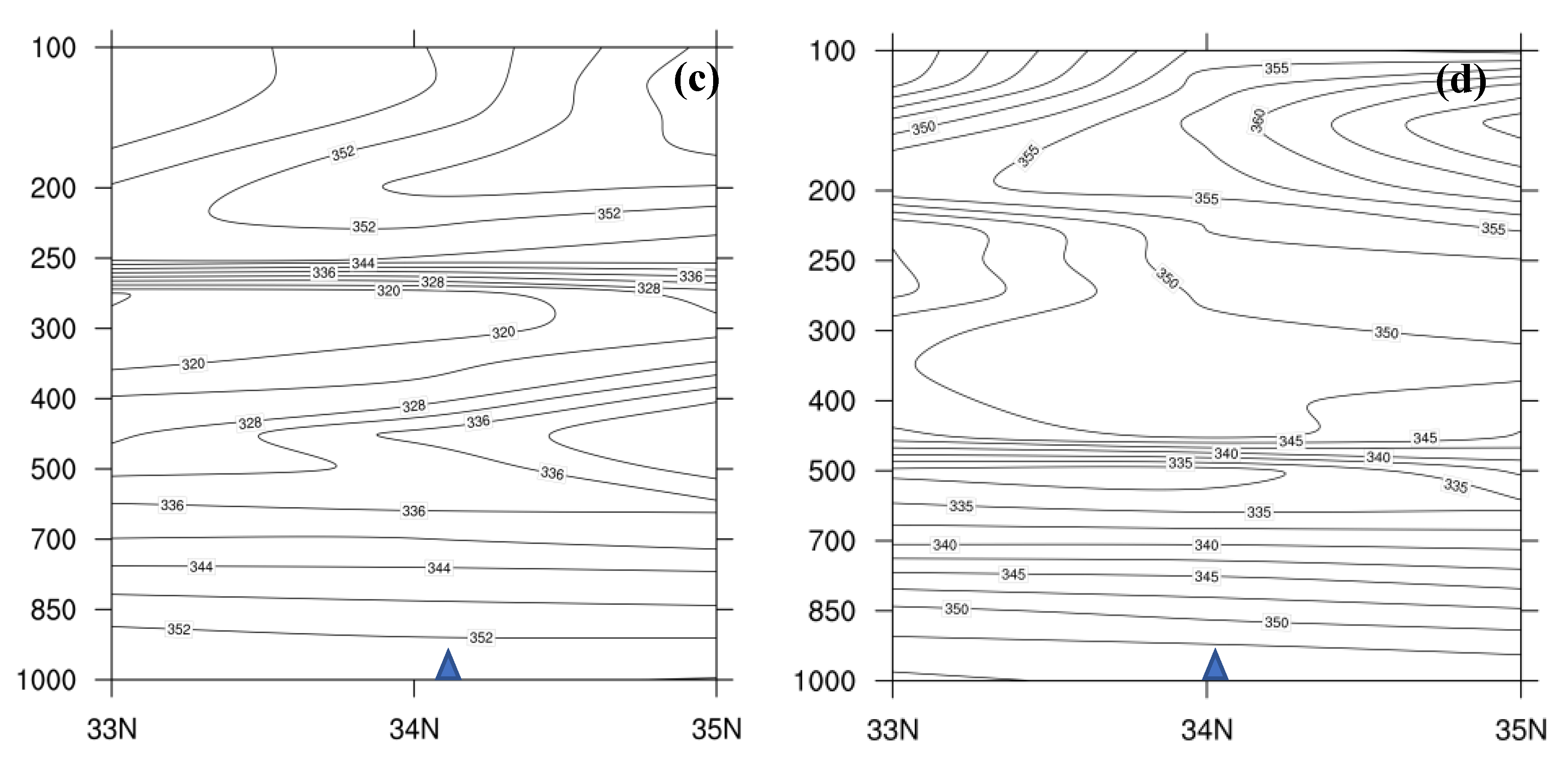
4.1. Height and Wind Fields Analysis
4.2. Water Vapor Condition Analysis
4.3. Dynamic Condition Analysis
4.4. Terrain Condition Analysis
4.4.1. Experiment Scheme
- ▪
- The first set of experiment reducd the elevation of the Taihang Mountains (34.57°N-40.72°N, 110.27°E-114.55°E) by 50% to smooth the west-to-east elevation gradient. This experiment was labeled as “Test1”.
- ▪
- The second set of experiment reducd the elevation of the Taihang Mountains by 75%, this experiment was labeled as “Test2”.
- ▪
- The third set of experiment directly lowered the elevation of the Taihang Mountains by 100%, shifting the transition zone between the plateau and plain to the border area between Shaanxi and Shanxi provinces. This experiment was denoted as “Test3”.
- ▪
- The fourth set of experiment raised the elevation of the Taihang Mountains by 50% relative to the baseline, referred to as “Test4”.
- ▪
- The fifth set of experiment increasd the elevation of the Taihang Mountains by 75%, labeled as “Test5”.
- ▪
- Lastly, the sixth set of experiment focused on elevating the Taihang Mountains by 100%, designated as “Test6”.
4.4.2. Terrain and Precipitation Analysis
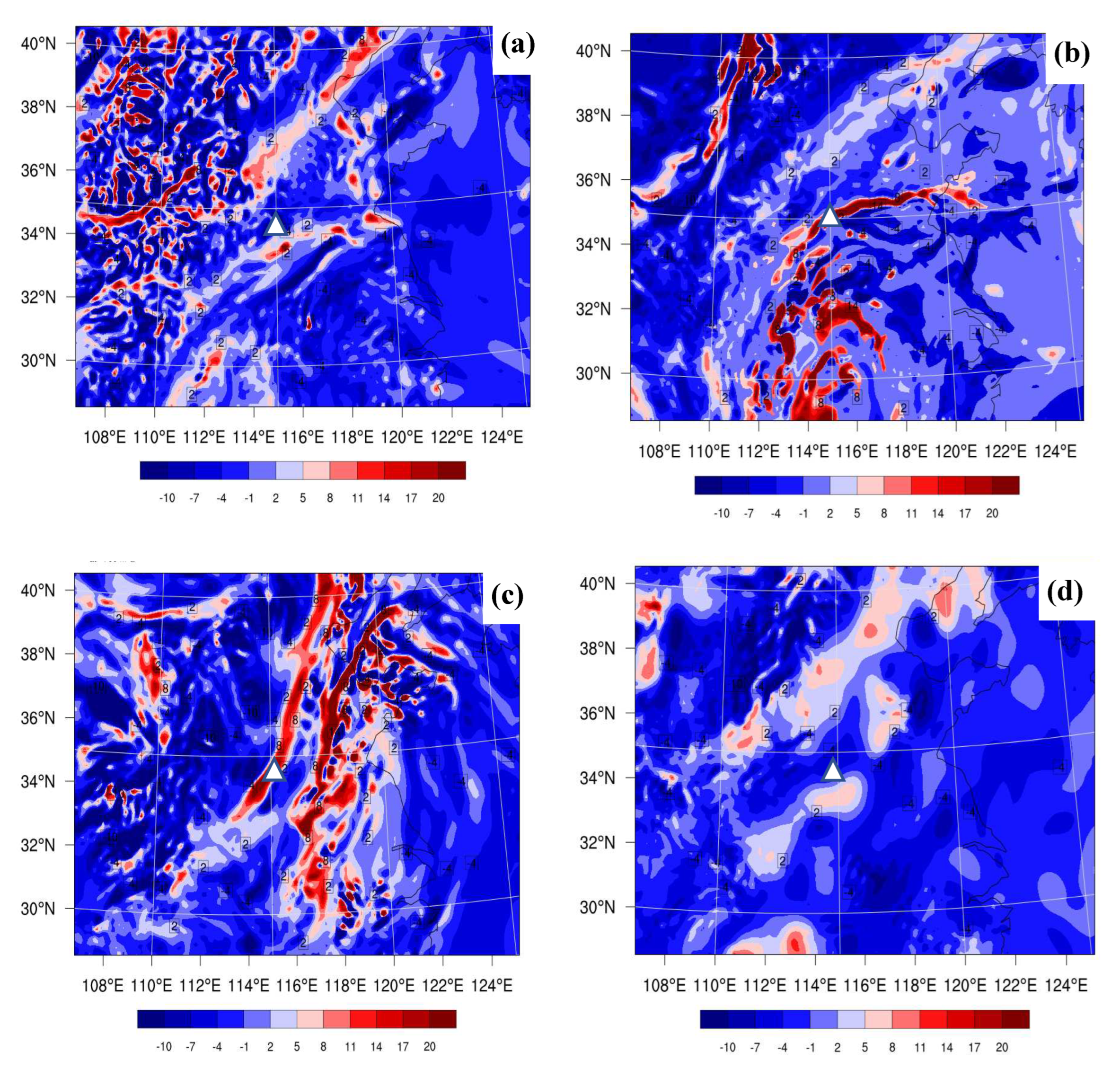
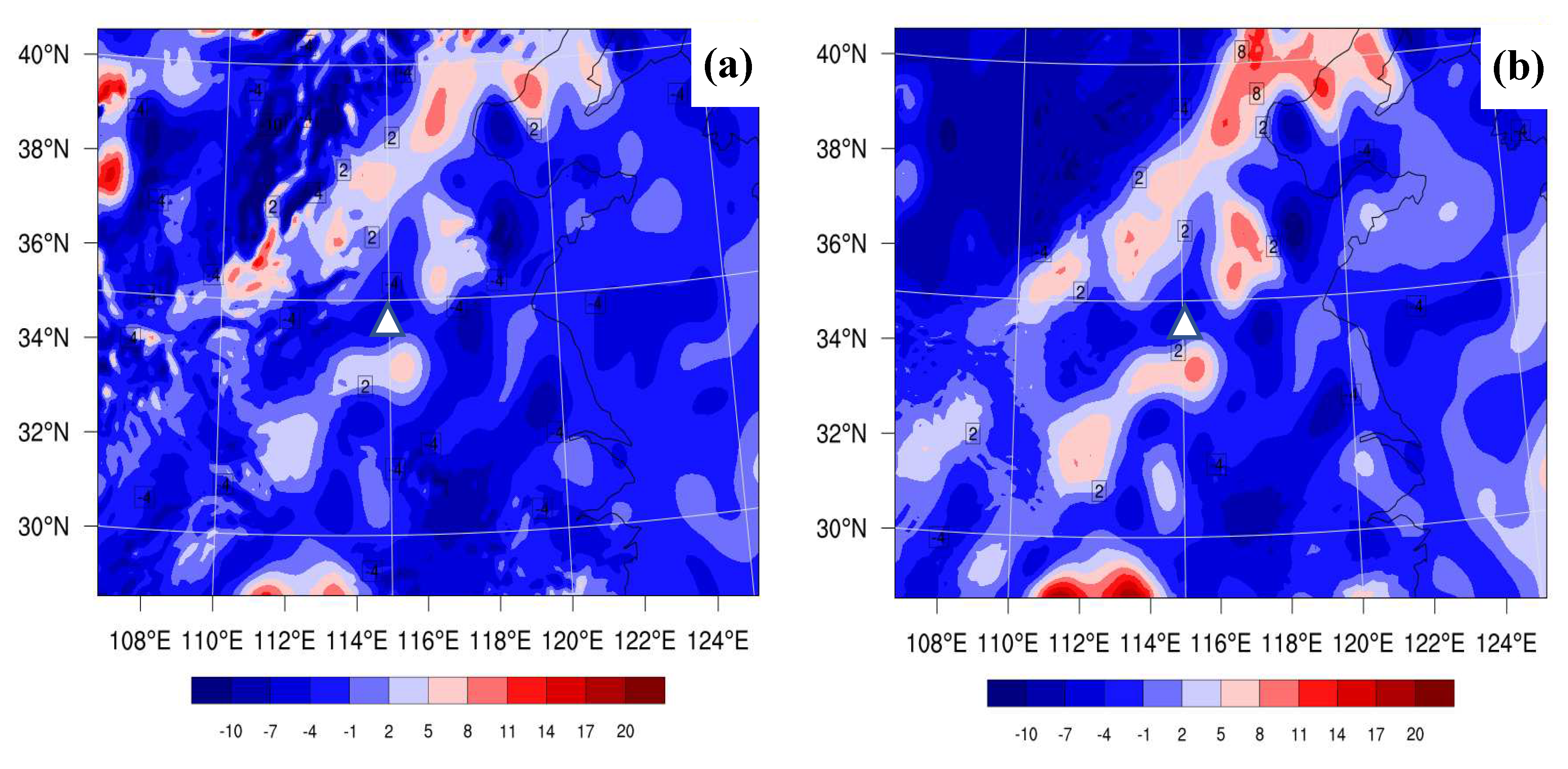
4.4.3. Terrain and Jet Stream Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P.; Alcamo, J.; Thomas, H.; Frank, K. Estimating the impact of global change on flood and drought risks in Europe: a continental, integrated analysis. Climatic Change 2006, 75, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.M.; Wang, C.C.; Li, W. A Review on Study of Change in Precipitation Extremes. Climate Change Research 2007, 3, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.Y. Heavy Rain in China; Science Press, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Suppiah, R.; Hennessy, K.J. Trends in total rainfall, heavy rain events and number of dry days in Australia, 1910–1990. Int. J.Climatol. 1998, 18, 1141–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Zhang, J.Y. Meteorological Disaster Series-Heavy Rain and Flood. Beijing: China Meteorological Press. 2009.
- Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L.; Vitolo, R.; Stephenson, D.B.; Krajewski, W.F. On the frequency of heavy rainfall for the Midwest of the United States. Journal of Hydrology 2011, 400, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarini, G.; Smith, J.A.; Vecchi, G.A. Changing frequency of heavy rainfall over the central United States. Journal of Climate 2013, 26, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yang, G.M. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics of Rainstorm in China During 1981-2010. Meteorology 2014, 40, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H. The major advances and development process of the theory of heavy rainfalls in China. Torrential Rain and Disasters 2019, 38, 395–406. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Liu, Z.; Yin, R.; Zhou, S.; Zong, L.; Ning, G.; Xu, X.; Guo, Y.; et al. Role of water vapor modulation from multiple pathways in the occurrence of a record-breaking heavy rainfall event in China in 2021. Earth and Space Science 2022, 9, e2022EA002357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.T.; Zhao, S.X.; Zhou, X.P.; Sun, S.Q.; Tao, S.Y. Progress of Research on sub-synoptic scale and mesoscale Torrential Rain systems. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 2003, 27, 618–627. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, M. Statistical analysis of continuous rainstorm in China in the past 50 years and its large-scale circulation background. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 2007, 31, 779–792. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, R.; Du, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Dai, K.; Shen, X.S.; et al. Science and prediction of heavy rainfall over China: Research progress since the reform and opening-up of the People’s Republic of China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica 2020, 78, 419–450. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.C.; Bi, B.G.; Jin, R.H.; Xu, Z.F.; Xue, F. The development and application of the modern weather forecast in China for the recent ten years. Acta Meteorologica Sinica 2014, 72, 1069–1078. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, D.H.; Sun, H.L.; Sun, S.; Liu, Y.J. The strategy of Chinese meteorological Service and development: 2005-2020. Advances in Earth Science 2005, 20, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Shu, A.; Li, H.; Xu, D.; Min, J. Assimilation of Himawari-8 imager radiance data with the WRF-3DVAR system for the prediction of Typhoon Soudelor. Natural Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 1569–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Shu, A.; Li, H.; Shen, F.; Min, J.; Su, H. Effects of assimilating clearsky FY-3D MWHS2 radiance on the numerical simulation of tropical storm ampil. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Min, J. Assimilating AMSU-A radiance data with the WRF hybrid En3DVAR system for track predictions of typhoon megi (2010). Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 2015, 32, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Min, J.; Shen, F.; Ban, J.; Chen, P. Assimilation of MWHS radiance data from the FY-3B satellite with the WRF Hybrid-3DVAR system for the forecasting of binary typhoons. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2016, 8, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutty, G.; Muraleedharan, R.; Kesarkar, A.P. Impact of representing model error in a hybrid ensemble-variational data assimilation system for track forecast of tropical cyclones over the Bay of Bengal. Pure and Applied Geophysics 2018, 175, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, P.M.M.; Vendrasco, E.P.; Saraiva, I.; Trindade, M.; de Oliveira, M.B.L.; Saraiva, J.; Trindade, M.; Betânia, M.; Oliveira, L.; Saraiva, J.; et al. Impact of radar data assimilation on the simulation of a heavy rainfall event over manaus in the Central Amazon. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2022, 179, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Pan, X.; You, W.; Zhu, X.; Zang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Jin, S. Impact of CALIPSO profile data assimilation on 3-D aerosol improvement in a size-resolved aerosol model. Atmospheric Research 2021, 264, 105877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, W.; Cao, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B. Assimilation of all-sky radiance from the FY-3 MWHS-2 with the Yinhe 4D-Var system. J. Meteor. Res. 2022, 36, 750–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.C.; You, W.; Zang, Z.L.; Pan, X.B.; Hu, Y.W.; Liang, Y.F. A threedimensional variational data assimilation system for aerosol optical properties based on WRF-chem v4.0: Design, development, and application of assimilating himawari-8 aerosol observations. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 1821–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Min, J.Z.; Liu, Z.Q. The impact of AMSR2 radiance data assimilation on the analysis and forecast of typhoon son-tinh. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 2017, 41, 372–384. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, S.; Min, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T. Added value of assimilating Himawari-8 AHI water vapor radiances on analyses and forecasts for “7.19” severe storm over north China. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres 2018, 123, 3374–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Shu, A.; Li, H.; Shen, F.; Min, J.; Su, H. Effects of assimilating clearsky FY-3D MWHS2 radiance on the numerical simulation of tropical storm ampil. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H. FY-4 meteorological satellite and its application prospect. Aerosp. Shanghai 2016, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, Fengyun-4. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2017, 98, 1637–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, R.; Shen, F. Impacts of FY-4A AGRI radiance data assimilation on the forecast of the super typhoon “in-fa” (2021). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Xu, D.; Li, H.; Min, J.; Liu, R. Assimilation of GPM microwave imager radiance data with the WRF hybrid 3DEnVar system for the prediction of typhoon chan-hom (2015). Atmospheric Research 2021, 251, 105422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Sawada, Y.; Kunii, M. Comparison of assimilating all-sky and clear-sky infrared radiances from Himawari-8 in a mesoscale system. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2019, 145, 745–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Kotsuki, S.; Lien, G.Y.; Maejima, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Miyoshi, T. Assimilation of himawari-8 all-sky radiances every 10 minutes: Impact on precipitation and flood risk prediction. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres 2018, 123, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Lien, G.; Nishizawa, S.; Yoshida, R.; Adachi, S.A.; Terasaki, K.; Okamoto, K.; Tomita, H.; Bessho, K. Assimilating all-sky himawari-8 satellite infrared radiances: A case of typhoon soudelor(2015). Monthly Weather Review 2018, 146, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamide, M.; Zhang, F. Assimilation of all-sky infrared radiances from himawari-8 and impacts of moisture and hydrometer initialization on convectionpermitting tropical cyclone prediction. Monthly Weather Review 2018, 146, 3241–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, D.; Westwater, E.R.; Gasiewski, A.J.; Klein, M.; Leuski, V.Y.; Liljegren, J.C. Ground-based millimeter-and submillimeter-wave observations of low vapor and liquid water contents. IEEE Trans. Geoscience Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löhnert, U.; Maier, O. Operational profiling of temperature using ground-based microwave radiometry at Payerne: Prospects and challenges. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Fan, S.; Li, B.; Mao, J.; Lin, D. Assimilation of ground-based microwave radiometer on heavy rainfall forecast in beijing. Atmosphere 2021, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, Y.; Kunii, M.; Saito, K. Mesoscale data assimilation of Myanmar Cyclone Nargis. Part II: Assimilation of GPS-derived precipitable water vapor. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan. 2011, 89, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.W.; Min, J.Z.; Xu, D.M. Analysis of FY-4A AGRI radiance data bias characteristics and a correction experiment. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 2020, 44, 679–694. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.S. Scientific issues and perspective of assimilation of meteorolo gical satellite data. Acta Meteorologica Sinica 2009, 67, 903–911. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Li, S.X.; Zhang, Y.X. The Diagnosis and Analysis of a Regional Rainstorm Process in Kaifeng. Henan Science 2012, 30, 1142–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.H.; Lv, Z.Y. Analysis of the Causes of a Local Heavy Rainfall in Kaifeng of Henan Province in 2016. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences 2017, 45, 186–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C.H.; Li, S.X. Analysis on Extremity of the “7·19” Severe Rainstorm Process in Kaifeng. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences 2021, 44, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, R.; Matricardi, M.; Brunel, P. An improved fast radiative transfer model for assimilation of satellite radiance observations. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 1999, 125, 1407–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.; Hocking, J.; Turner, E.; Rayer, P.; Rundle, D.; Brunel, P.; Vidot, J.; Roquet, P.; Matricardi, M.; Geer, A.; et al. An update on the RTTOV fast radiative transfer model (currently at version 12). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 2717–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Min, J.Z.; Liu, Z.Q. The impact of AMSR2 radiance data assimilation on the analysis and forecast of typhoon son-tinh. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 2017, 41, 372–384. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Lu, F.; Fang, X.; Zhou, Y.Q. Application and development of FY-4 meteorological satellite. Aerospace Shanghai 2017, 34, 8–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ware, R.; Carpenter, R.; Güldner, J.; Liljegren, J.; Nehrkorn, T.; Solheim, F.; Vandenberghe, F. A Multichannel Radiometric Profiler of Temperature, Humidity, and Cloud Liquid. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 8079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caumont, O.; Cimini, D.; Löhnert, U.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Bleisch, R.; Buffa, F.; Ferrario, M.E.; Haefele, A.; Huet, T.; Madonna, F.; et al. Assimilation of Humidity and Temperature Observations Retrieved from Ground-Based Microwave Radiometers into a Convective-Scale NWP Model. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 2692–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, H.; Li, J. Influence of Assimilating Ground-Based Microwave Radiometer Data into the WRF Model on Precipitation. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2020, 13, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temimi, M.; Fonseca, R.M.; Nelli, N.R.; Valappil, V.K.; Weston, M.J.; Thota, M.S.; Wehbe, Y.; Yousef, L. On the Analysis of Ground-Based Microwave Radiometer Data during Fog Conditions. Atmos. Res. 2020, 231, 104652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Fan, S.; Li, B.; Mao, J.; Lin, D. Assimilation of ground-based microwave radiometer on heavy rainfall forecast in beijing. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Fan, S.; Mao, J.; Li, B.; Guo, C.; Zhang, S. Impact of Assimilating Ground-Based Microwave Radiometer Data on the Precipitation Bifurcation Forecast: A Case Study in Beijing. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ai, W.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhao, X. Correction of sea surface wind speed based on SAR rainfall grade classification using convolutional neural network. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2022, 16, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P. Bias and data assimilation. Q. J. R. Meteorological Soc. A J. Atmos. Sci. Appl. meteorology Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 131, 3323–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zeng, Z. A quality control procedure for GPS radio occultation data. Journal of Geop. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.K.; Zou, X.; Li, G.; Ma, X.L. Quality control of surface station temperature data with non-Gaussian observation-minus-background distributions. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres 2010, 115, D16312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.Z.; Sheng, T.L.; Chen, H.S.; Sun, L.P. Numerical experiment on quality control and variational assimilation of satellite image retrieval. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science 2000, 11, 410–418. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Ai, W.; Hu, S.; Du, X.; Chen, N. Sea surface wind direction retrieval based on convolution neural network and wavelet analysis. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2022, 05, 3868–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M. Developing the science product algorithm testbed for Chinese next-generation geostationary meteorological satellites: Fengyun-4 series. Journal of Meteo-rological Research 2017, 31, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Min, M.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.P.; Li, B.; Tang, S. Intercomparisons of cloud mask products among Fengyun-4A, Himawari-8, and MODIS. IEEE Trans. Geosci.Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 8827–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auligné, T.; McNally, A.P.; Dee, D.P. Adaptive bias correction for satellite data in a numerical weather prediction system. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2007, 133, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q.; Ma, L.; Jiang, S.; Lei, L.; Lyu, W.; Wang, Z. Analysis of convective instability data derived from a ground-based microwave radiometer before triggering operations for artificial lightning. Atmospheric research 2020, 243, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, R.; García-Ortega, E.; López, L.; Marcos, J.L. A method to improve the accuracy of continuous measuring of vertical profiles of temperature and water vapor density by means of a ground-based microwave radiometer. Atmospheric Research 2013, 122, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Tan, J.G. Quality control of temperature and humidity profile retrievals from ground-based microwave radiometer. J. Appl. Meteorological Sci. 2017, 28, 209–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain-Fritsch convective parameterization: An update. Journal of Applied Meteorology 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Dudhia, J.; Ray, P.; Miao, S.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Treinish, L. Understanding the sensitivity of WRF hindcast of Beijing extreme rainfall of 21 July 2012 to microphysics and model initial time. Atmospheric Research 2022, 271, 106085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Tang, J.P.A. Mesoscale analysis and diagnose of an extreme bursting torrential rain. Meteorological Science 2009, 29, 797–803. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.M. Research on a Case of Heavy Rain in Xinjiang from South Asia High Abnormity. Meteorology 2003, 29, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Feng, S.; Chen, J. Physical Mechanisms of Summer Precipitation Variations in the Tarim Basin in Northwestern China. Journal of Climate 2015, 28, 3579–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
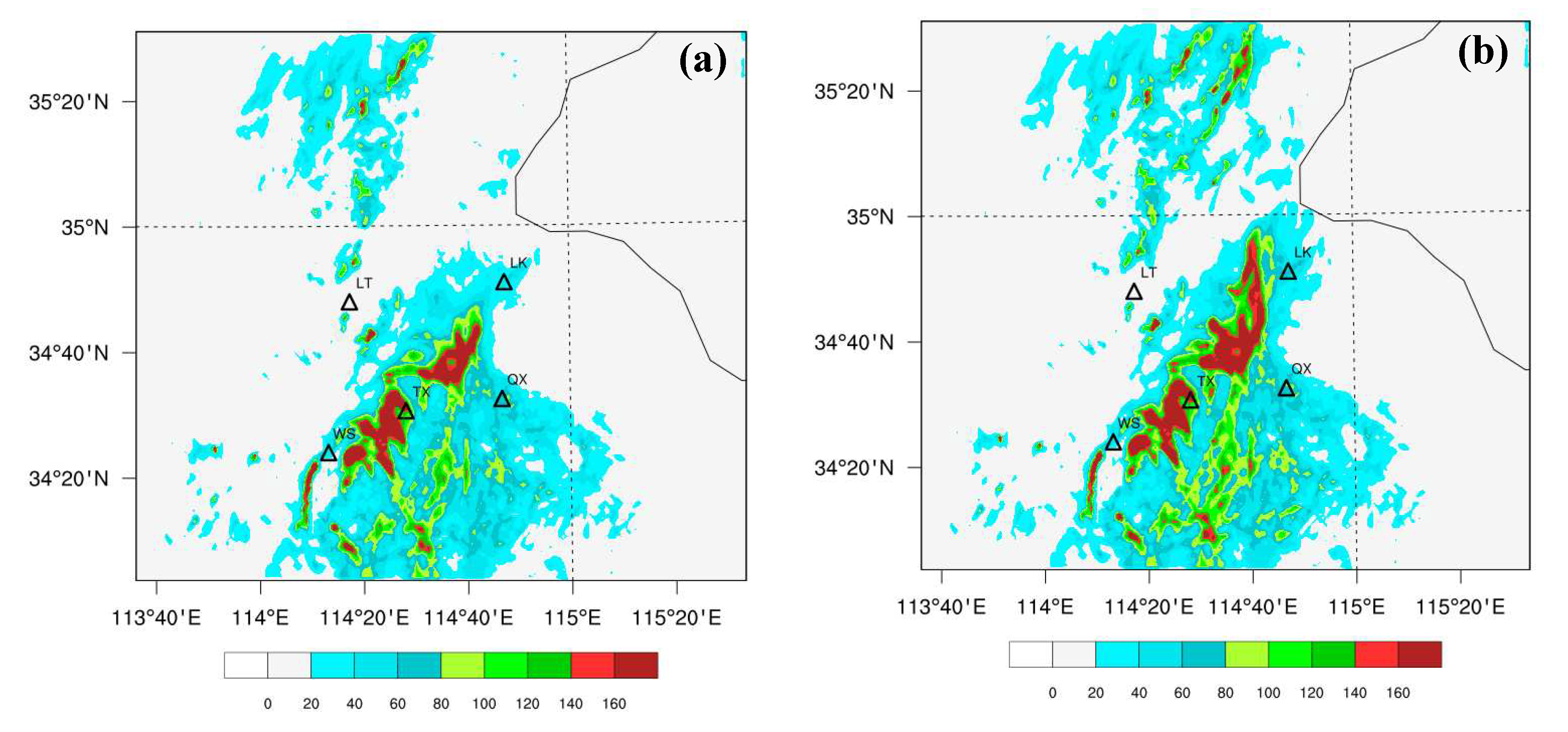
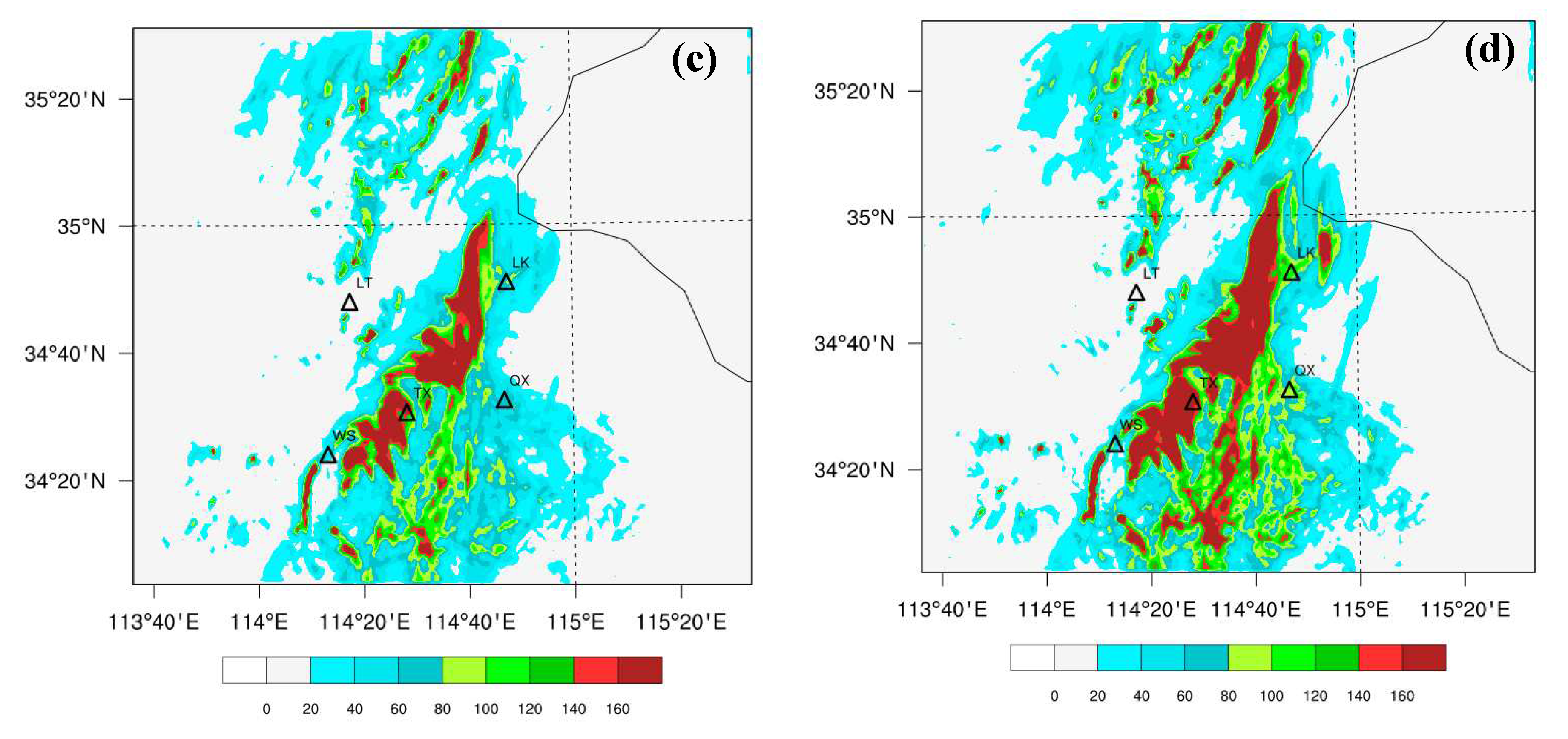
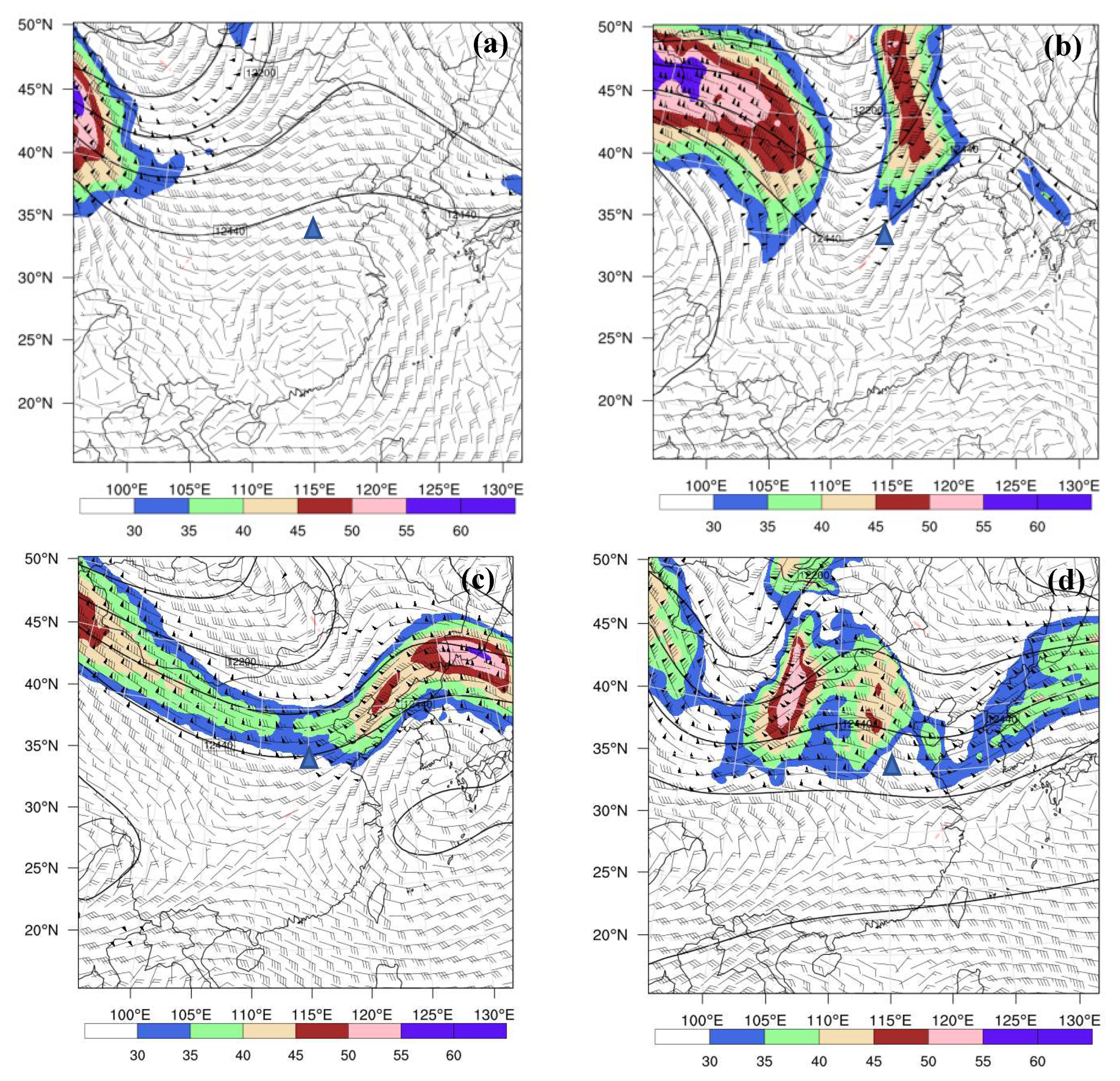
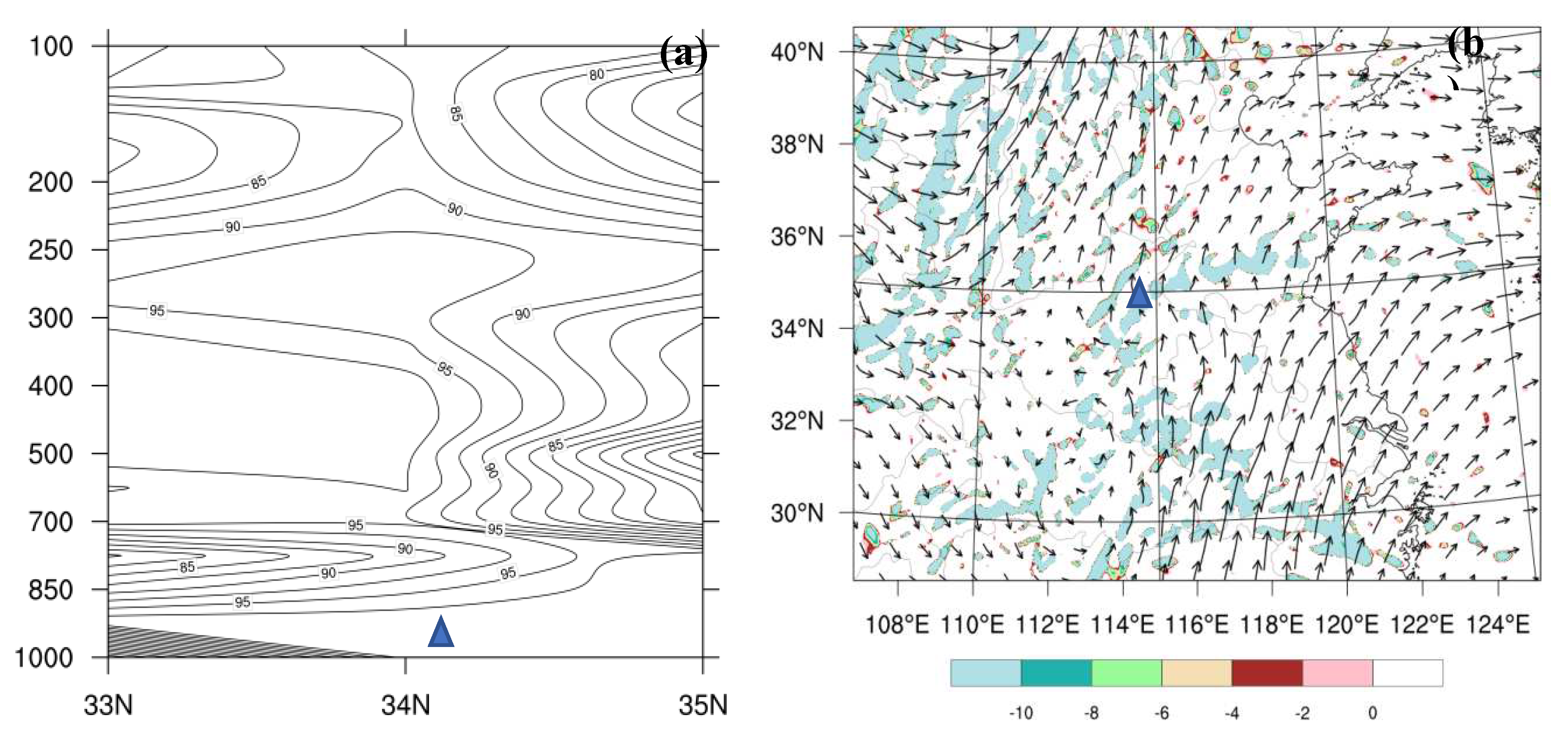
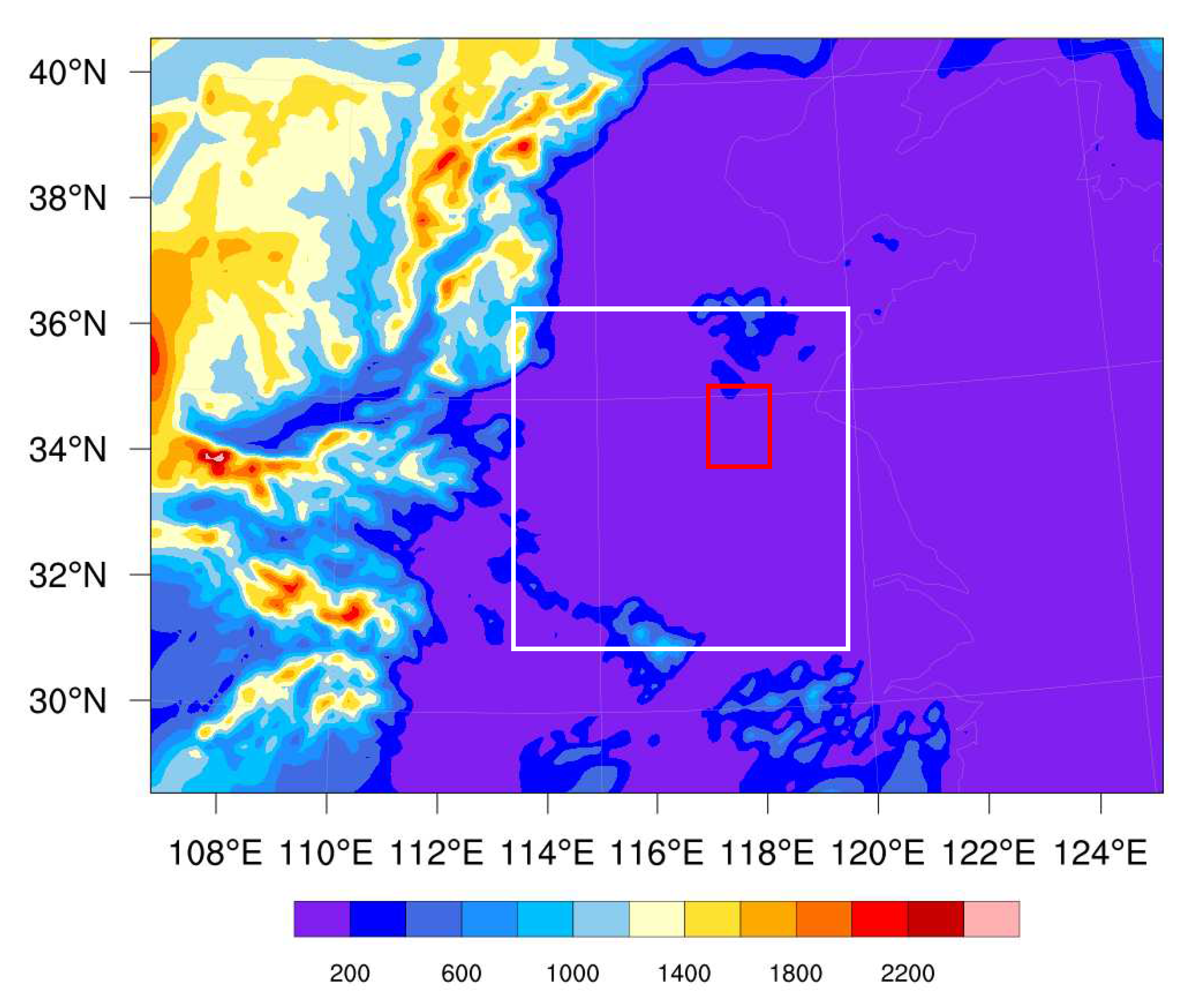
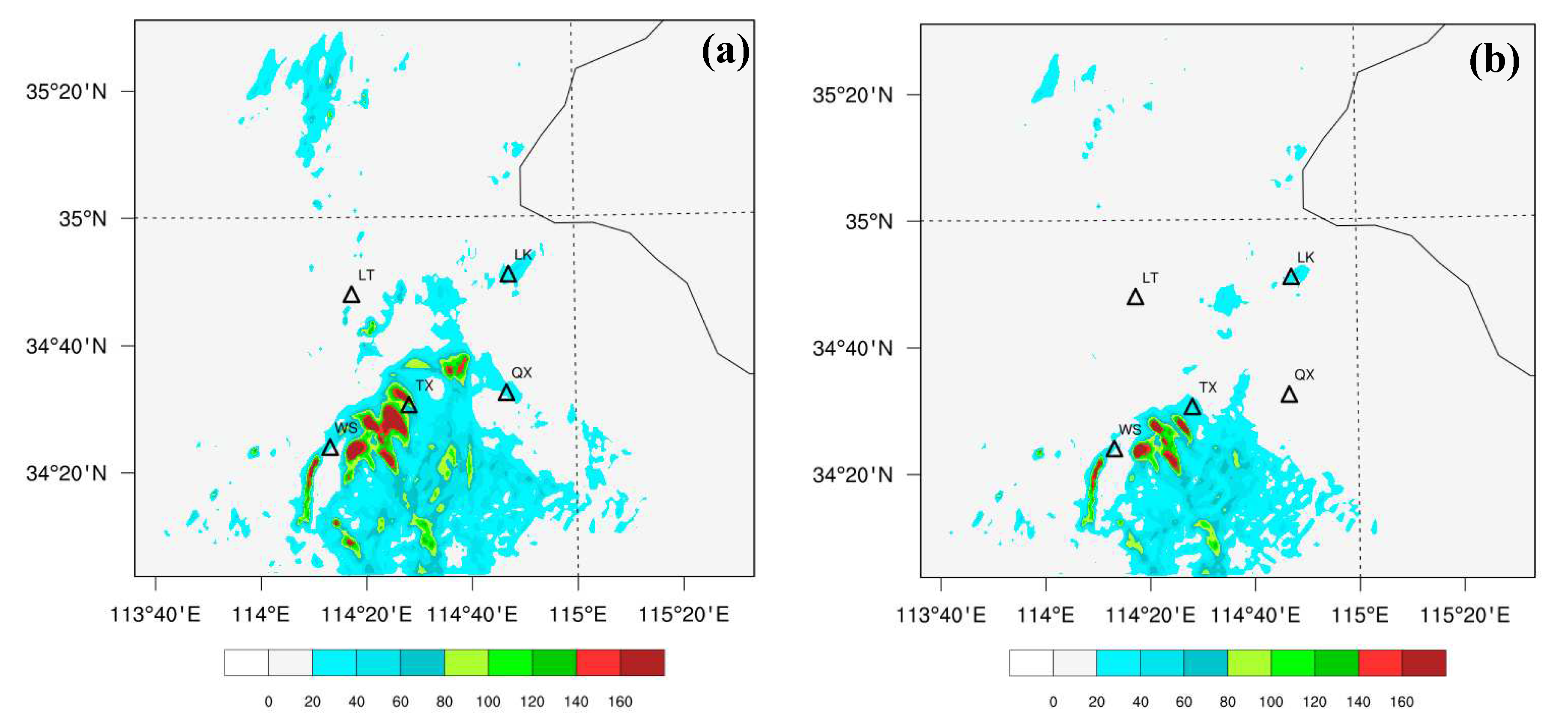
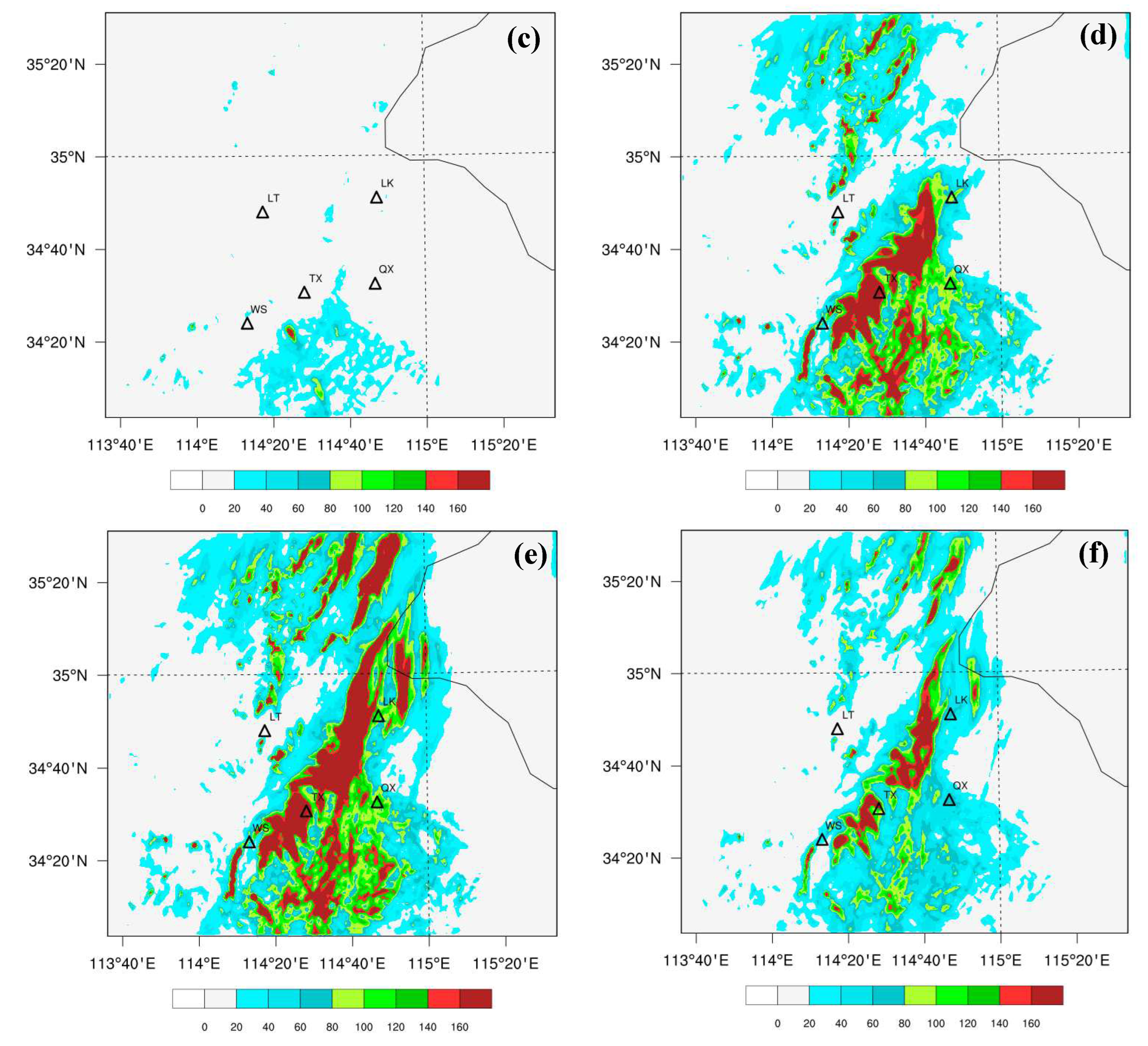
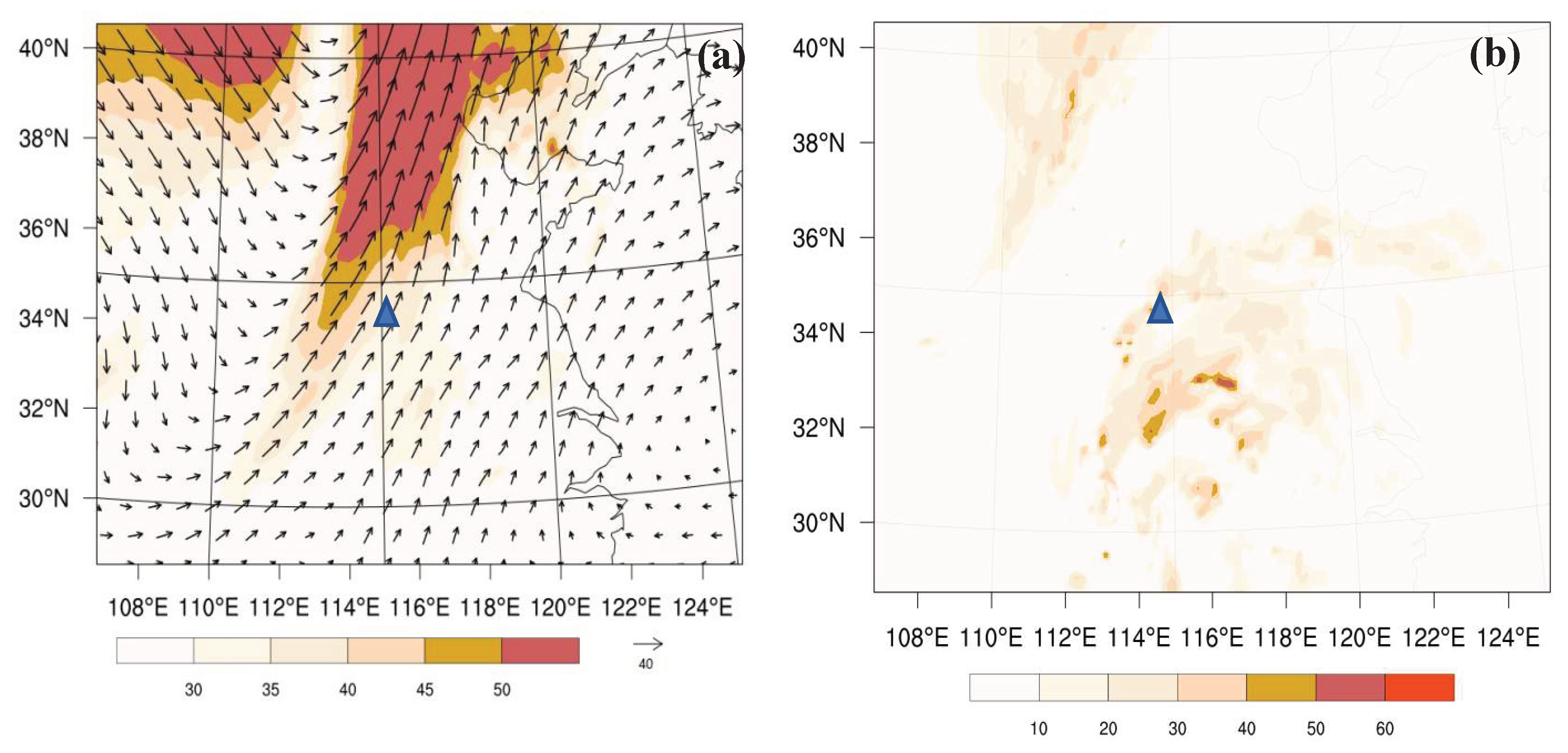
| Scheme | Assimilated Data | Assimilation Interval |
|---|---|---|
| CTRL | No | |
| Test1 | temperature and humidity profiles from seven MWRs | 1-h |
| Test2 | FY-4A AGRI radiance channels 9–14 | 1-h |
| Test3 | both FY-4A AGRI and MWR data | 1-h |
| Scheme | Changes in Terrain Height/% | Latitude/N | Longitude/E |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 0 | 34.57°N-40.72° | 110.27°E-114.55° |
| Test1 | -50 | 34.57°N-40.72° | 110.27°E-114.55° |
| Test2 | -75 | 34.57°N-40.72° | 110.27°E-114.55° |
| Test3 | -100 | 34.57°N-40.72° | 110.27°E-114.55° |
| Test4 | +50 | 34.57°N-40.72° | 110.27°E-114.55° |
| Test5 | +75 | 34.57°N-40.72° | 110.27°E-114.55° |
| Test6 | +100 | 34.57°N-40.72° | 110.27°E-114.55° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





