Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
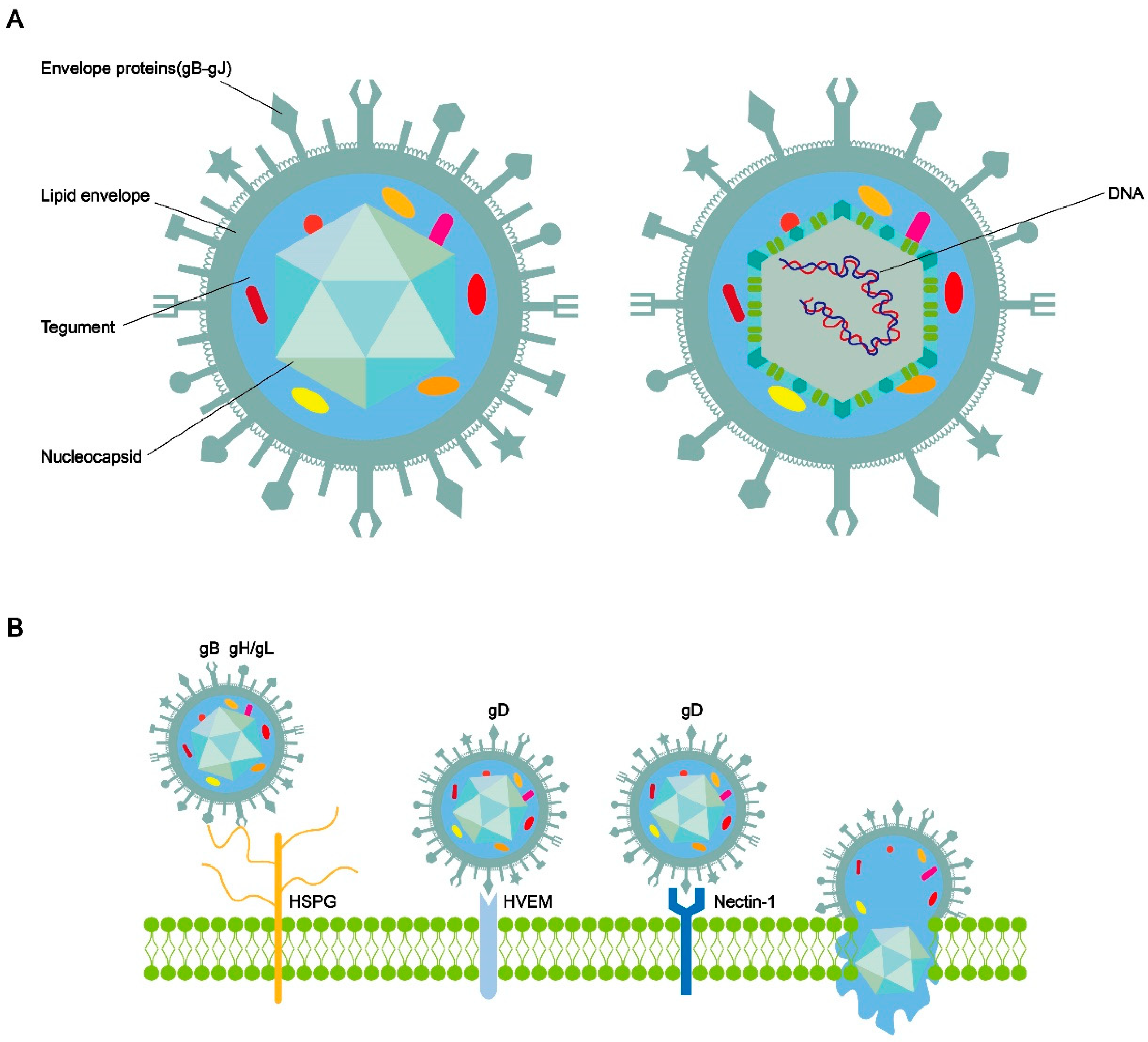
The structure of HSV-1 and the process of entry into cells
The association between HSV-1 infection and vestibular neuritis
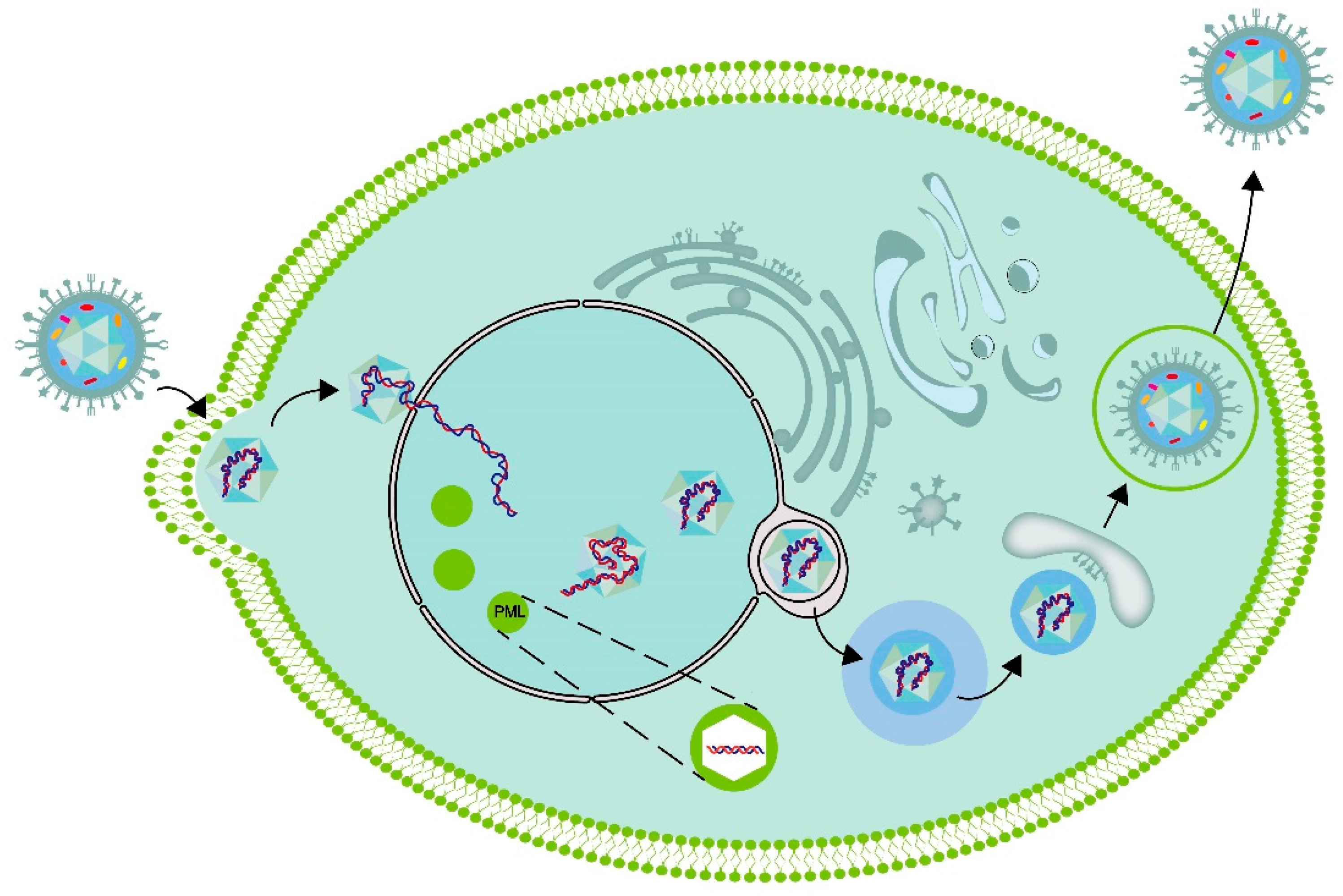
Transportation of HSV-1 in vestibular ganglion
The replication process of the virus within the cell
The latency and reactivation of HSV-1
Host cell processes caused by HSV-1 infection
Immune cell process caused by HSV-1 infection
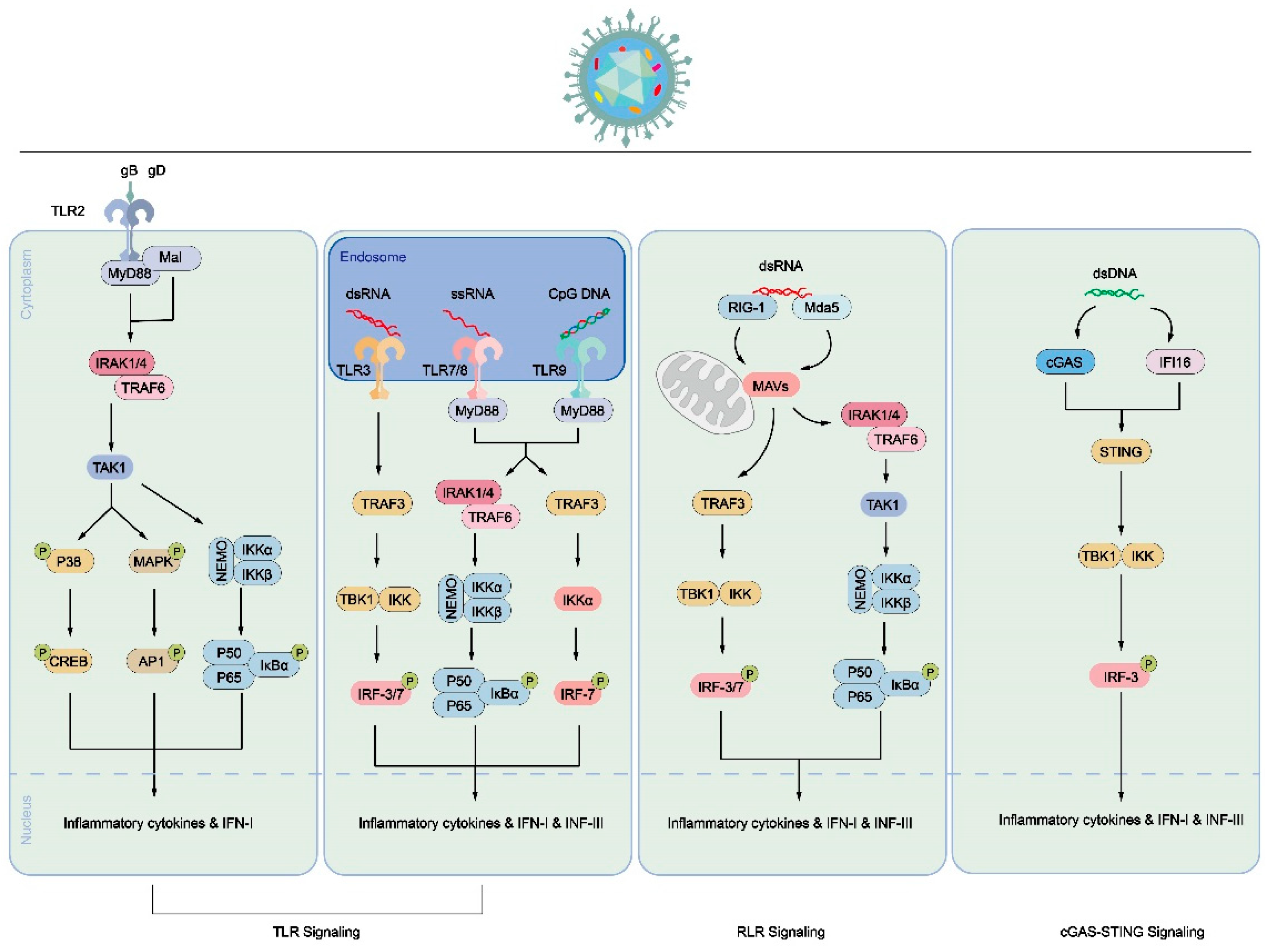
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Theil, D.; Arbusow, V.; Derfuss, T.; Strupp, M.; Pfeiffer, M.; Mascolo, A.; Brandt, T. Prevalence of HSV-1 LAT in human trigeminal, geniculate, and vestibular ganglia and its implication for cranial nerve syndromes. Brain Pathol 2001, 11, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbusow, V.; Schulz, P.; Strupp, M.; Dieterich, M.; von Reinhardstoettner, A.; Rauch, E.; Brandt, T. Distribution of herpes simplex virus type 1 in human geniculate and vestibular ganglia: implications for vestibular neuritis. Ann Neurol 1999, 46, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, Y.; Takasu, T.; Fukuda, S.; Inuyama, Y.; Sato, K.C.; Nagashima, K. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 in human vestibular ganglia. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 1993, 503, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, P.; Arbusow, V.; Strupp, M.; Dieterich, M.; Rauch, E.; Brandt, T. Highly variable distribution of HSV-1-specific DNA in human geniculate, vestibular and spiral ganglia. Neurosci Lett 1998, 252, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstein, K.M.; Seung, H.I. Vestibular neuronitis. Laryngoscope 1971, 81, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbusow, V.; Strupp, M.; Wasicky, R.; Horn, A.K.; Schulz, P.; Brandt, T. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 in human vestibular nuclei. Neurology 2000, 55, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S. [Detection of latent herpes simplex virus in human vestibular ganglia]. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi 1996, 71, 561–571. [Google Scholar]
- Esaki, S.; Goshima, F.; Kimura, H.; Ikeda, S.; Katsumi, S.; Kabaya, K.; Watanabe, N.; Hashiba, M.; Nishiyama, Y.; Murakami, S. Auditory and vestibular defects induced by experimental labyrinthitis following herpes simplex virus in mice. Acta Otolaryngol 2011, 131, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, Y. [An experimental herpes simplex virus infection in the vestibular nerve]. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 1994, 97, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünewald, K.; Desai, P.; Winkler, D.C.; Heymann, J.B.; Belnap, D.M.; Baumeister, W.; Steven, A.C. Three-dimensional structure of herpes simplex virus from cryo-electron tomography. Science 2003, 302, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Chen, D.H.; Jakana, J.; Rixon, F.J.; Chiu, W. Visualization of tegument-capsid interactions and DNA in intact herpes simplex virus type 1 virions. J Virol 1999, 73, 3210–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrag, J.D.; Prasad, B.V.; Rixon, F.J.; Chiu, W. Three-dimensional structure of the HSV1 nucleocapsid. Cell 1989, 56, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loret, S.; Guay, G.; Lippé, R. Comprehensive characterization of extracellular herpes simplex virus type 1 virions. J Virol 2008, 82, 8605–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallbracht, M.; Backovic, M.; Klupp, B.G.; Rey, F.A.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Common characteristics and unique features: A comparison of the fusion machinery of the alphaherpesviruses Pseudorabies virus and Herpes simplex virus. Adv Virus Res 2019, 104, 225–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möhl, B.S.; Chen, J.; Longnecker, R. Gammaherpesvirus entry and fusion: A tale how two human pathogenic viruses enter their host cells. Adv Virus Res 2019, 104, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, M.; Mori, Y. Entry of betaherpesviruses. Adv Virus Res 2019, 104, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasiu, D.; Whitbeck, J.C.; de Leon, M.P.; Lou, H.; Hannah, B.P.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Bimolecular complementation defines functional regions of Herpes simplex virus gB that are involved with gH/gL as a necessary step leading to cell fusion. J Virol 2010, 84, 3825–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J. Cascade of events governing cell-cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gD, gH/gL, and gB. J Virol 2010, 84, 12292–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, J.; Atanasiu, D.; Saw, W.T.; Gallagher, J.R.; Cox, R.G.; Whitbeck, J.C.; Brown, L.M.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H. The Fusion Loops of the Initial Prefusion Conformation of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Fusion Protein Point Toward the Membrane. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchele, W.; Brandt, T. Vestibular neuritis--a horizontal semicircular canal paresis? Adv Otorhinolaryngol 1988, 42, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbusow, V.; Dieterich, M.; Strupp, M.; Dreher, A.; Jäger, L.; Brandt, T. Herpes zoster neuritis involving superior and inferior parts of the vestibular nerve causes ocular tilt reaction. Neuro Ophthalmology 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Gyo, K.; Yanagihara, N. Herpetic vestibular neuritis: an experimental study. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 1995, 519, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, D.; Horn, A.K.; Derfuss, T.; Strupp, M.; Arbusow, V.; Brandt, T. Prevalence and distribution of HSV-1, VZV, and HHV-6 in human cranial nerve nuclei III, IV, VI, VII, and XII. J Med Virol 2004, 74, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, L.; Book, M.; Smetana, Z.; Alkin, M.; Soupayev, Z.; Mendelson, E. Herpes simplex virus type 1 in saliva of patients with vestibular neuronitis: a preliminary study. Neurologist 2011, 17, 330–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehm, P.C.; Camarena, V.; Nayak, S.; Gardner, J.B.; Wilson, A.; Mohr, I.; Chao, M.V. Cultured vestibular ganglion neurons demonstrate latent HSV1 reactivation. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 2268–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rujescu, D.; Herrling, M.; Hartmann, A.M.; Maul, S.; Giegling, I.; Konte, B.; Strupp, M. High-risk Allele for Herpes Labialis Severity at the IFNL3/4 Locus is Associated With Vestibular Neuritis. Front Neurol 2020, 11, 570638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philpot, S.J.; Archer, J.S. Herpes encephalitis preceded by ipsilateral vestibular neuronitis. J Clin Neurosci 2005, 12, 958–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.E.; Murray, J.W.; Wolkoff, A.W.; Wilson, D.W. Reconstitution of herpes simplex virus microtubule-dependent trafficking in vitro. J Virol 2006, 80, 4264–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharkwal, H.; Smith, C.G.; Wilson, D.W. Blocking ESCRT-mediated envelopment inhibits microtubule-dependent trafficking of alphaherpesviruses in vitro. J Virol 2014, 88, 14467–14478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodeik, B.; Ebersold, M.W.; Helenius, A. Microtubule-mediated transport of incoming herpes simplex virus 1 capsids to the nucleus. J Cell Biol 1997, 136, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saksena, M.M.; Wakisaka, H.; Tijono, B.; Boadle, R.A.; Rixon, F.; Takahashi, H.; Cunningham, A.L. Herpes simplex virus type 1 accumulation, envelopment, and exit in growth cones and varicosities in mid-distal regions of axons. J Virol 2006, 80, 3592–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Saksena, M.; Armati, P.; Boadle, R.A.; Holland, D.J.; Cunningham, A.L. Anterograde transport of herpes simplex virus type 1 in cultured, dissociated human and rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Virol 2000, 74, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, T.L.; Stokin, G.B.; Lillo, C.; Rodrigues, E.M.; Westerman, E.L.; Williams, D.S.; Goldstein, L.S. Axonal stress kinase activation and tau misbehavior induced by kinesin-1 transport defects. J Neurosci 2009, 29, 5758–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaether, C.; Skehel, P.; Dotti, C.G. Axonal membrane proteins are transported in distinct carriers: a two-color video microscopy study in cultured hippocampal neurons. Mol Biol Cell 2000, 11, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jung, P.; Brown, A. Axonal transport of neurofilaments: a single population of intermittently moving polymers. J Neurosci 2012, 32, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.A.; Das, U.; Tang, Y.; Roy, S. Mechanistic logic underlying the axonal transport of cytosolic proteins. Neuron 2011, 70, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinone, S.E.; Zaichick, S.V.; Smith, G.A. Resolving the assembly state of herpes simplex virus during axon transport by live-cell imaging. J Virol 2010, 84, 13019–13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.A.; Gross, S.P.; Enquist, L.W. Herpesviruses use bidirectional fast-axonal transport to spread in sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 3466–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Valencia, J.R.; Tsimtsirakis, E.; Evilevitch, A. Role of HSV-1 Capsid Vertex-Specific Component (CVSC) and Viral Terminal DNA in Capsid Docking at the Nuclear Pore. Viruses 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, M.P.; Chen, L.B.; Knipe, D.M. The intranuclear location of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein is determined by the status of viral DNA replication. Cell 1984, 36, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruyn Kops, A.; Knipe, D.M. Formation of DNA replication structures in herpes virus-infected cells requires a viral DNA binding protein. Cell 1988, 55, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charman, M.; Weitzman, M.D. Replication Compartments of DNA Viruses in the Nucleus: Location, Location, Location. Viruses 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feric, M.; Vaidya, N.; Harmon, T.S.; Mitrea, D.M.; Zhu, L.; Richardson, T.M.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Pappu, R.V.; Brangwynne, C.P. Coexisting Liquid Phases Underlie Nucleolar Subcompartments. Cell 2016, 165, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brangwynne, C.P.; Eckmann, C.R.; Courson, D.S.; Rybarska, A.; Hoege, C.; Gharakhani, J.; Jülicher, F.; Hyman, A.A. Germline P granules are liquid droplets that localize by controlled dissolution/condensation. Science 2009, 324, 1729–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzir, I.; Haimov, E.; Lampel, A. Tuning the Dynamics of Viral-Factories-Inspired Compartments Formed by Peptide-RNA Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation. Adv Mater 2022, 34, e2206371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, S.; Nag, N.; Shukla, H.; Padhi, A.K.; Tripathi, T. Comprehensive analysis of liquid-liquid phase separation propensities of HSV-1 proteins and their interaction with host factors. J Cell Biochem 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Lum, K.K.; Treen, N.; Núñez, C.T.; Yang, J.; Howard, T.R.; Levine, M.; Cristea, I.M. IFI16 phase separation via multi-phosphorylation drives innate immune signaling. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, 6819–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyffert, M.; Georgi, F.; Tobler, K.; Bourqui, L.; Anfossi, M.; Michaelsen, K.; Vogt, B.; Greber, U.F.; Fraefel, C. The HSV-1 Transcription Factor ICP4 Confers Liquid-Like Properties to Viral Replication Compartments. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenheuer, C.H.; Danko, C.G.; Baines, J.D. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Dramatically Alters Loading and Positioning of RNA Polymerase II on Host Genes Early in Infection. J Virol 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.A.; Hoey, T.; Thut, C.J.; Admon, A.; Tjian, R. Drosophila TAFII40 interacts with both a VP16 activation domain and the basal transcription factor TFIIB. Cell 1993, 75, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingles, C.J.; Shales, M.; Cress, W.D.; Triezenberg, S.J.; Greenblatt, J. Reduced binding of TFIID to transcriptionally compromised mutants of VP16. Nature 1991, 351, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, H.; Knipe, D.M. Proteomic analysis of the herpes simplex virus 1 virion protein 16 transactivator protein in infected cells. Proteomics 2015, 15, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babb, R.; Huang, C.C.; Aufiero, D.J.; Herr, W. DNA recognition by the herpes simplex virus transactivator VP16: a novel DNA-binding structure. Mol Cell Biol 2001, 21, 4700–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, J.P. Regulation of herpes simplex virus gene expression. Gene 2001, 271, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajcáni, J.; Andrea, V.; Ingeborg, R. Peculiarities of herpes simplex virus (HSV) transcription: an overview. Virus Genes 2004, 28, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.C.; Dybas, J.M.; Hughes, J.; Weitzman, M.D.; Boutell, C. The HSV-1 ubiquitin ligase ICP0: Modifying the cellular proteome to promote infection. Virus Res 2020, 285, 198015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, N.T.; Petroski, M.D.; Wagner, E.K. Functional modules important for activated expression of early genes of herpes simplex virus type 1 are clustered upstream of the TATA box. Virology 1998, 246, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrozza, M.J.; DeLuca, N.A. Interaction of the viral activator protein ICP4 with TFIID through TAF250. Mol Cell Biol 1996, 16, 3085–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Schaffer, P.A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 regulates expression of immediate-early, early, and late genes in productively infected cells. J Virol 1992, 66, 2904–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Silverstein, S. Herpes simplex viruses with mutations in the gene encoding ICP0 are defective in gene expression. J Virol 1992, 66, 2916–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.C.; Mohr, I. A cultured affair: HSV latency and reactivation in neurons. Trends Microbiol 2012, 20, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, K.; Derfuss, T. Control of HSV-1 latency in human trigeminal ganglia--current overview. J Neurovirol 2011, 17, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.L.; Sawtell, N.M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript gene regulates the establishment of latency. J Virol 1997, 71, 5432–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perng, G.C.; Slanina, S.M.; Yukht, A.; Ghiasi, H.; Nesburn, A.B.; Wechsler, S.L. The latency-associated transcript gene enhances establishment of herpes simplex virus type 1 latency in rabbits. J Virol 2000, 74, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.M.; Sedarati, F.; Javier, R.T.; Wagner, E.K.; Stevens, J.G. Herpes simplex virus latent phase transcription facilitates in vivo reactivation. Virology 1990, 174, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perng, G.C.; Dunkel, E.C.; Geary, P.A.; Slanina, S.M.; Ghiasi, H.; Kaiwar, R.; Nesburn, A.B.; Wechsler, S.L. The latency-associated transcript gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is required for efficient in vivo spontaneous reactivation of HSV-1 from latency. J Virol 1994, 68, 8045–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, G.C.; Jones, C.; Ciacci-Zanella, J.; Stone, M.; Henderson, G.; Yukht, A.; Slanina, S.M.; Hofman, F.M.; Ghiasi, H.; Nesburn, A.B.; et al. Virus-induced neuronal apoptosis blocked by the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript. Science 2000, 287, 1500–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.L.; Preston, C.M.; Sawtell, N.M. De novo synthesis of VP16 coordinates the exit from HSV latency in vivo. PLoS Pathog 2009, 5, e1000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Viejo-Borbolla, A. Pathogenesis and virulence of herpes simplex virus. Virulence 2021, 12, 2670–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafezi, W.; Lorentzen, E.U.; Eing, B.R.; Müller, M.; King, N.J.; Klupp, B.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Kühn, J.E. Entry of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) into the distal axons of trigeminal neurons favors the onset of nonproductive, silent infection. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1002679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawtell, N.M.; Triezenberg, S.J.; Thompson, R.L. VP16 serine 375 is a critical determinant of herpes simplex virus exit from latency in vivo. J Neurovirol 2011, 17, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knipe, D.M.; Cliffe, A. Chromatin control of herpes simplex virus lytic and latent infection. Nat Rev Microbiol 2008, 6, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rujescu, D.; Hartmann, A.M.; Giegling, I.; Konte, B.; Herrling, M.; Himmelein, S.; Strupp, M. Genome-Wide Association Study in Vestibular Neuritis: Involvement of the Host Factor for HSV-1 Replication. Front Neurol 2018, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Voytek, C.C.; Margolis, T.P. Immunohistochemical analysis of primary sensory neurons latently infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol 2000, 74, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, T.P.; Dawson, C.R.; LaVail, J.H. Herpes simplex viral infection of the mouse trigeminal ganglion. Immunohistochemical analysis of cell populations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992, 33, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertke, A.S.; Swanson, S.M.; Chen, J.; Imai, Y.; Kinchington, P.R.; Margolis, T.P. A5-positive primary sensory neurons are nonpermissive for productive infection with herpes simplex virus 1 in vitro. J Virol 2011, 85, 6669–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowerdew, S.E.; Wick, D.; Himmelein, S.; Horn, A.K.; Sinicina, I.; Strupp, M.; Brandt, T.; Theil, D.; Hüfner, K. Characterization of neuronal populations in the human trigeminal ganglion and their association with latent herpes simplex virus-1 infection. PLoS One 2013, 8, e83603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roizman, B. Polykaryocytosis induced by viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1962, 48, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avitabile, E.; Di Gaeta, S.; Torrisi, M.R.; Ward, P.L.; Roizman, B.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. Redistribution of microtubules and Golgi apparatus in herpes simplex virus-infected cells and their role in viral exocytosis. J Virol 1995, 69, 7472–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeg, U.; Dienes, H.P.; Müller, S.; Falke, D. Involvement of actin-containing microfilaments in HSV-induced cytopathology and the influence of inhibitors of glycosylation. Arch Virol 1986, 91, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampar, B.; Ellison, S.A. Chromosomal aberrations induced by an animal virus. Nature 1961, 192, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizman, B. The programming of herpes virus multiplication in doubly-infected and in puromycin-treated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1963, 49, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizman, B.; Roane, P.R., Jr. THE MULTIPLICATION OF HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. II. THE RELATION BETWEEN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND THE DUPLICATION OF VIRAL DNA IN INFECTED HEP-2 CELLS. Virology 1964, 22, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, M.; Blaho, J.A. The herpes simplex virus type 1 regulatory protein ICP27 is required for the prevention of apoptosis in infected human cells. J Virol 1999, 73, 2803–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, D.; Cantrell, D.A. Metabolism, migration and memory in cytotoxic T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2011, 11, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, F.; Sasseville, A.M.; Chabaud, S.; Massie, B.; Siegel, R.M.; Langelier, Y. The ribonucleotide reductase R1 subunits of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 protect cells against TNFα- and FasL-induced apoptosis by interacting with caspase-8. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, F.; Bertrand, L.; Pearson, A.; Grandvaux, N.; Langelier, Y. The ribonucleotide reductase R1 subunits of herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 protect cells against poly(I · C)-induced apoptosis. J Virol 2011, 85, 8689–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finnen, R.L.; Johnston, S.M.; Neron, C.E.; Banfield, B.W. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the HSV-2 serine/threonine kinase Us3. Virology 2011, 417, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartier, A.; Komai, T.; Masucci, M.G. The Us3 protein kinase of herpes simplex virus 1 blocks apoptosis and induces phosporylation of the Bcl-2 family member Bad. Exp Cell Res 2003, 291, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetti, L.; Roizman, B. Herpes simplex virus protein kinase US3 activates and functionally overlaps protein kinase A to block apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 9411–9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Du, M.; Jin, H.; Ma, Y.; He, B.; et al. ICP34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus facilitates the initiation of protein translation by bridging eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha (eIF2alpha) and protein phosphatase 1. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 24785–24792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orvedahl, A.; Alexander, D.; Tallóczy, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Burns, D.; Leib, D.A.; Levine, B. HSV-1 ICP34.5 confers neurovirulence by targeting the Beclin 1 autophagy protein. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 1, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, R.D.; Sourvinos, G.; Leiper, C.; Clements, J.B.; Orr, A. Formation of nuclear foci of the herpes simplex virus type 1 regulatory protein ICP4 at early times of infection: localization, dynamics, recruitment of ICP27, and evidence for the de novo induction of ND10-like complexes. J Virol 2004, 78, 1903–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, A.; Luker, G.D.; Barchet, W.; Leib, D.A.; Akira, S.; Colonna, M. Herpes simplex virus type 1 activates murine natural interferon-producing cells through toll-like receptor 9. Blood 2004, 103, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, T.; Hara, H.; Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, N.; Akira, S.; Saito, T. Cutting edge: TLR2 directly triggers Th1 effector functions. J Immunol 2007, 178, 6715–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, P.; Tovey, M.G.; Raschilas, F.; Brassart, L.; Meritet, J.F.; Porcher, R.; Lebon, P. Type I interferon subtypes produced by human peripheral mononuclear cells from one normal donor stimulated by viral and non-viral inducing factors. Eur Cytokine Netw 2007, 18, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leoni, V.; Gianni, T.; Salvioli, S.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gH/gL and gB bind Toll-like receptor 2, and soluble gH/gL is sufficient to activate NF-κB. J Virol 2012, 86, 6555–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Li, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Lu, Q.; Yan, J.; Mossman, K.L.; Lin, R.; Zheng, C. The herpes simplex virus 1-encoded envelope glycoprotein B activates NF-κB through the Toll-like receptor 2 and MyD88/TRAF6-dependent signaling pathway. PLoS One 2013, 8, e54586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Chan, M.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Reed, G.; Bronson, R.; Arnold, M.M.; Knipe, D.M.; Finberg, R.W. Herpes simplex virus 1 interaction with Toll-like receptor 2 contributes to lethal encephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Pergolizzi, S.; Cimino, F.; Lauriano, E.R.; Speciale, A.; D'Angelo, V.; Sicurella, M.; Argnani, R.; Manservigi, R.; Marconi, P. Role of Herpes Simplex Envelope Glycoprotein B and Toll-Like Receptor 2 in Ocular Inflammation: An ex vivo Organotypic Rabbit Corneal Model. Viruses 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, L.; Holt, A.C.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 2001, 413, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Ciancanelli, M.J.; Zhang, P.; Harschnitz, O.; Bondet, V.; Hasek, M.; Chen, J.; Mu, X.; Itan, Y.; Cobat, A.; et al. TLR3 controls constitutive IFN-β antiviral immunity in human fibroblasts and cortical neurons. J Clin Invest 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinert, L.S.; Harder, L.; Holm, C.K.; Iversen, M.B.; Horan, K.A.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Holm, T.H.; Mogensen, T.H.; Owens, T.; et al. TLR3 deficiency renders astrocytes permissive to herpes simplex virus infection and facilitates establishment of CNS infection in mice. J Clin Invest 2012, 122, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leib, D.A. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis: toll-free access to the brain. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 731–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, J.; Sato, A.; Akira, S.; Medzhitov, R.; Iwasaki, A. Toll-like receptor 9-mediated recognition of Herpes simplex virus-2 by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J Exp Med 2003, 198, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, K.; Svensson, A.; Hait, A.S.; Schlüter, K.; Tunbäck, P.; Nordström, I.; Padyukov, L.; Liljeqvist, J.; Mogensen, T.H.; Paludan, S.R. Cutting Edge: Genetic Association between IFI16 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Resistance to Genital Herpes Correlates with IFI16 Expression Levels and HSV-2-Induced IFN-β Expression. J Immunol 2017, 199, 2613–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzalli, M.H.; DeLuca, N.A.; Knipe, D.M. Nuclear IFI16 induction of IRF-3 signaling during herpesviral infection and degradation of IFI16 by the viral ICP0 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, E3008–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrady, C.D.; Zheng, M.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Liu, C.; Carr, D.J. Resistance to HSV-1 infection in the epithelium resides with the novel innate sensor, IFI-16. Mucosal Immunol 2012, 5, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Ansari, M.A.; Kumar, B.; Dutta, D.; Roy, A.; Chikoti, L.; Pisano, G.; Dutta, S.; Vahedi, S.; Veettil, M.V.; et al. Histone H2B-IFI16 Recognition of Nuclear Herpesviral Genome Induces Cytoplasmic Interferon-β Responses. PLoS Pathog 2016, 12, e1005967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verjans, G.M.; Hintzen, R.Q.; van Dun, J.M.; Poot, A.; Milikan, J.C.; Laman, J.D.; Langerak, A.W.; Kinchington, P.R.; Osterhaus, A.D. Selective retention of herpes simplex virus-specific T cells in latently infected human trigeminal ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 3496–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Velzen, M.; Jing, L.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Sette, A.; Koelle, D.M.; Verjans, G.M. Local CD4 and CD8 T-cell reactivity to HSV-1 antigens documents broad viral protein expression and immune competence in latently infected human trigeminal ganglia. PLoS Pathog 2013, 9, e1003547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Koelle, D.M.; Cao, J.; Vazquez, J.; Huang, M.L.; Hladik, F.; Wald, A.; Corey, L. Virus-specific CD8+ T cells accumulate near sensory nerve endings in genital skin during subclinical HSV-2 reactivation. J Exp Med 2007, 204, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Peng, T.; Johnston, C.; Phasouk, K.; Kask, A.S.; Klock, A.; Jin, L.; Diem, K.; Koelle, D.M.; Wald, A.; et al. Immune surveillance by CD8αα+ skin-resident T cells in human herpes virus infection. Nature 2013, 497, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Haas, J.; Chong, T.M.; Bruckner, J.J.; Dann, G.C.; Dong, L.; Marshak, J.O.; McClurkan, C.L.; Yamamoto, T.N.; Bailer, S.M.; et al. Cross-presentation and genome-wide screening reveal candidate T cells antigens for a herpes simplex virus type 1 vaccine. J Clin Invest 2012, 122, 654–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, N.J.; Magaret, A.; Laing, K.J.; Kask, A.S.; Wang, M.; Mark, K.E.; Schiffer, J.T.; Wald, A.; Koelle, D.M. Peripheral blood CD4 T-cell and plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) reactivity to herpes simplex virus 2 and pDC number do not correlate with the clinical or virologic severity of recurrent genital herpes. J Virol 2012, 86, 9952–9963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, K.J.; Magaret, A.S.; Mueller, D.E.; Zhao, L.; Johnston, C.; De Rosa, S.C.; Koelle, D.M.; Wald, A.; Corey, L. Diversity in CD8(+) T cell function and epitope breadth among persons with genital herpes. J Clin Immunol 2010, 30, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelle, D.M.; Corey, L.; Burke, R.L.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Cohen, G.H.; Pichyangkura, R.; Triezenberg, S.J. Antigenic specificities of human CD4+ T-cell clones recovered from recurrent genital herpes simplex virus type 2 lesions. J Virol 1994, 68, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valyi-Nagy, T.; Deshmane, S.L.; Raengsakulrach, B.; Nicosia, M.; Gesser, R.M.; Wysocka, M.; Dillner, A.; Fraser, N.W. Herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant strain in1814 establishes a unique, slowly progressing infection in SCID mice. J Virol 1992, 66, 7336–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakim, L.M.; Jones, C.M.; Gebhardt, T.; Preston, C.M.; Carbone, F.R. CD8(+) T-cell attenuation of cutaneous herpes simplex virus infection reduces the average viral copy number of the ensuing latent infection. Immunol Cell Biol 2008, 86, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Pesnicak, L.; Cohen, J.I.; Straus, S.E. Rates of reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus from mouse trigeminal ganglia ex vivo correlate directly with viral load and inversely with number of infiltrating CD8+ T cells. J Virol 2007, 81, 8157–8164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derfuss, T.; Segerer, S.; Herberger, S.; Sinicina, I.; Hüfner, K.; Ebelt, K.; Knaus, H.G.; Steiner, I.; Meinl, E.; Dornmair, K.; et al. Presence of HSV-1 immediate early genes and clonally expanded T-cells with a memory effector phenotype in human trigeminal ganglia. Brain Pathol 2007, 17, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, K.D.; Nash, T.C.; Sawyer, S.; Krahl, T.; Patstone, G.; Reed, J.C.; Krajewski, S.; Dalton, D.; Buchmeier, M.J.; Sarvetnick, N. Interferon-gamma protects against herpes simplex virus type 1-mediated neuronal death. Virology 1997, 238, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knickelbein, J.E.; Khanna, K.M.; Yee, M.B.; Baty, C.J.; Kinchington, P.R.; Hendricks, R.L. Noncytotoxic lytic granule-mediated CD8+ T cell inhibition of HSV-1 reactivation from neuronal latency. Science 2008, 322, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, G.M.; Lepisto, A.J.; Freeman, M.L.; Sheridan, B.S.; Cherpes, T.L.; Hendricks, R.L. Early CD4(+) T cell help prevents partial CD8(+) T cell exhaustion and promotes maintenance of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 latency. J Immunol 2010, 184, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Khanna, K.M.; Chen, X.; Fink, D.J.; Hendricks, R.L. CD8(+) T cells can block herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) reactivation from latency in sensory neurons. J Exp Med 2000, 191, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Velzen, M.; Laman, J.D.; Kleinjan, A.; Poot, A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Verjans, G.M. Neuron-interacting satellite glial cells in human trigeminal ganglia have an APC phenotype. J Immunol 2009, 183, 2456–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeil, P.A.; Leib, D.A. Herpes simplex virus γ34.5 interferes with autophagosome maturation and antigen presentation in dendritic cells. mBio 2012, 3, e00267–00212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubinski, J.M.; Jiang, M.; Hook, L.; Chang, Y.; Sarver, C.; Mastellos, D.; Lambris, J.D.; Cohen, G.H.; Eisenberg, R.J.; Friedman, H.M. Herpes simplex virus type 1 evades the effects of antibody and complement in vivo. J Virol 2002, 76, 9232–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Viruses associated with VN | Family of viruses |
|---|---|
| Herpes simplex virus | Alphaherpesvirinae |
| Varicella-zoster virus | |
| Human Cytomegalovirus | Betaherpesvirinae |
| Epstein-Barr virus | Gammaherpesvirinae |
| Influenza virus A | Non-herpesvirus family |
| Influenza virus B | |
| Adenoviruses | |
| Rubella virus | |
| Parainfluenza virus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





