Submitted:
26 January 2024
Posted:
29 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
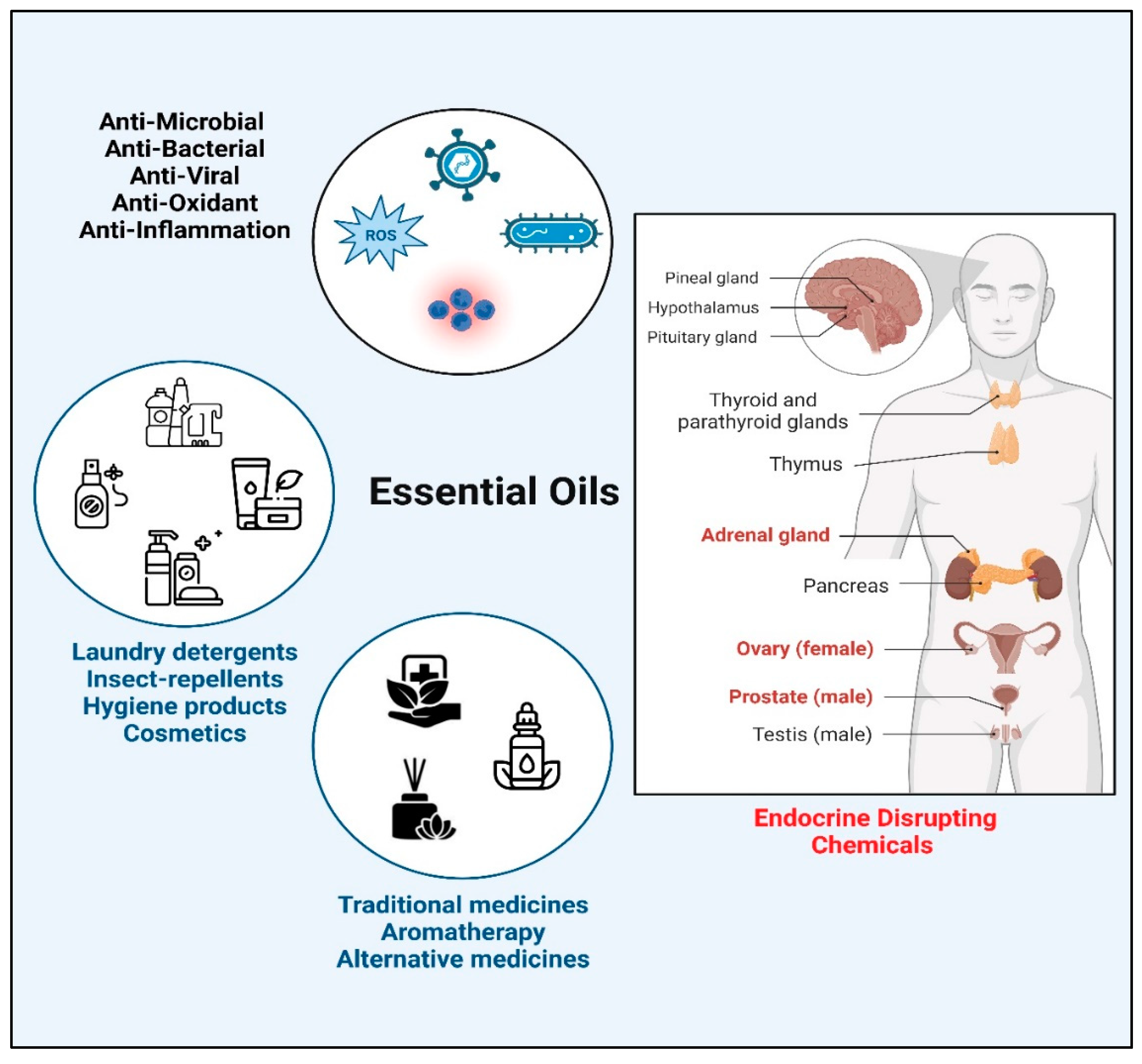
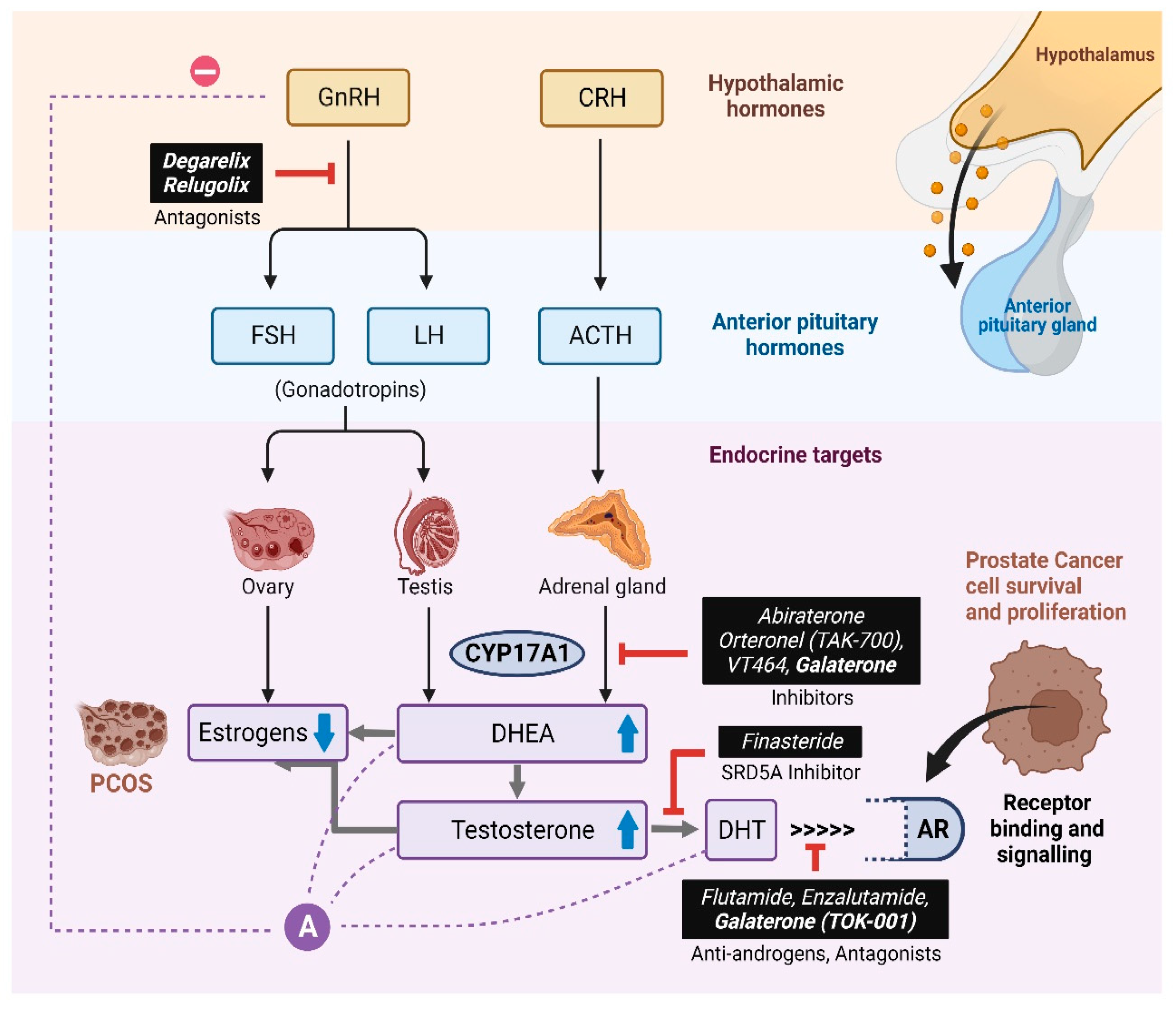
1. Introduction
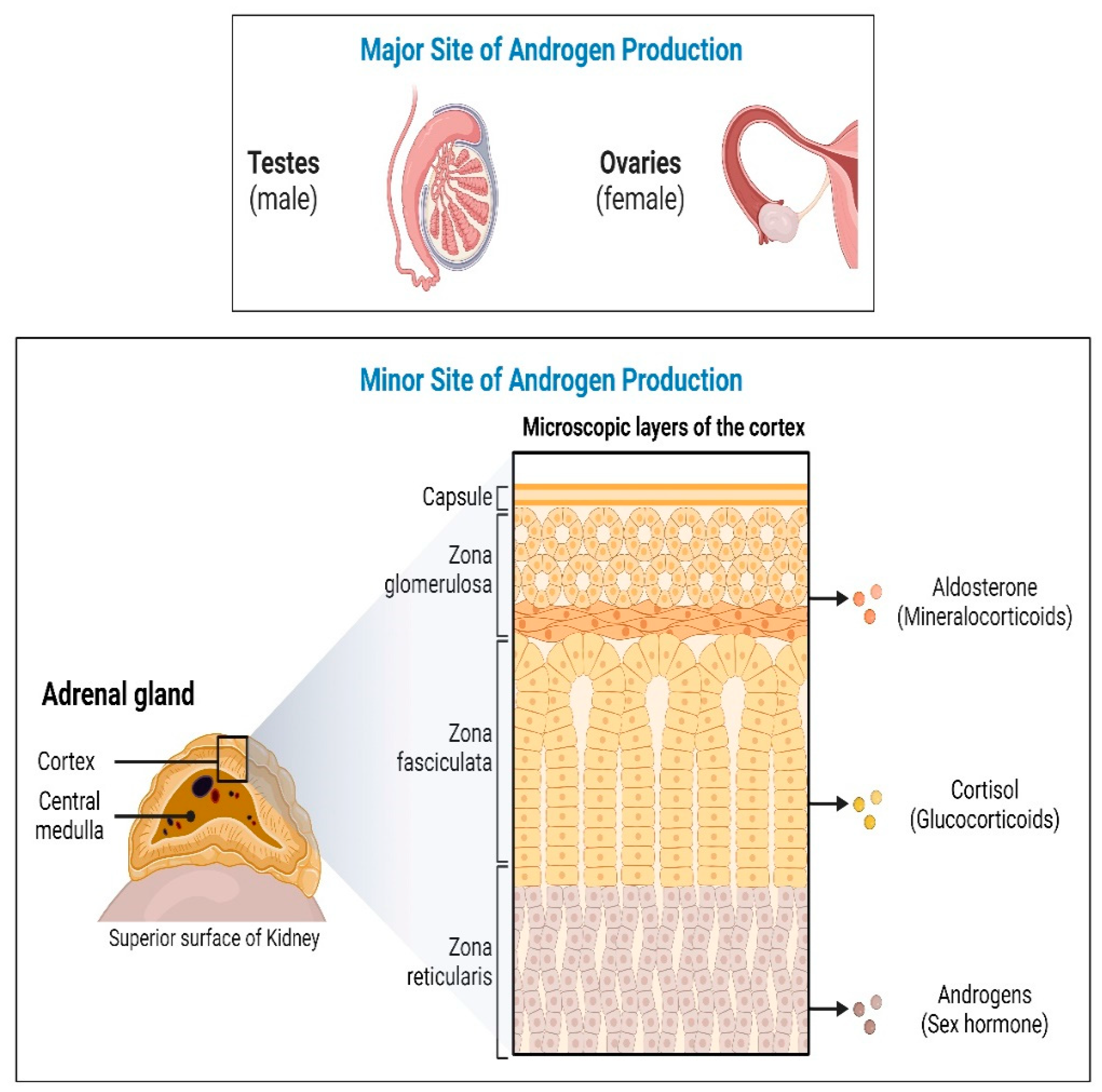
2. Materials and Methods
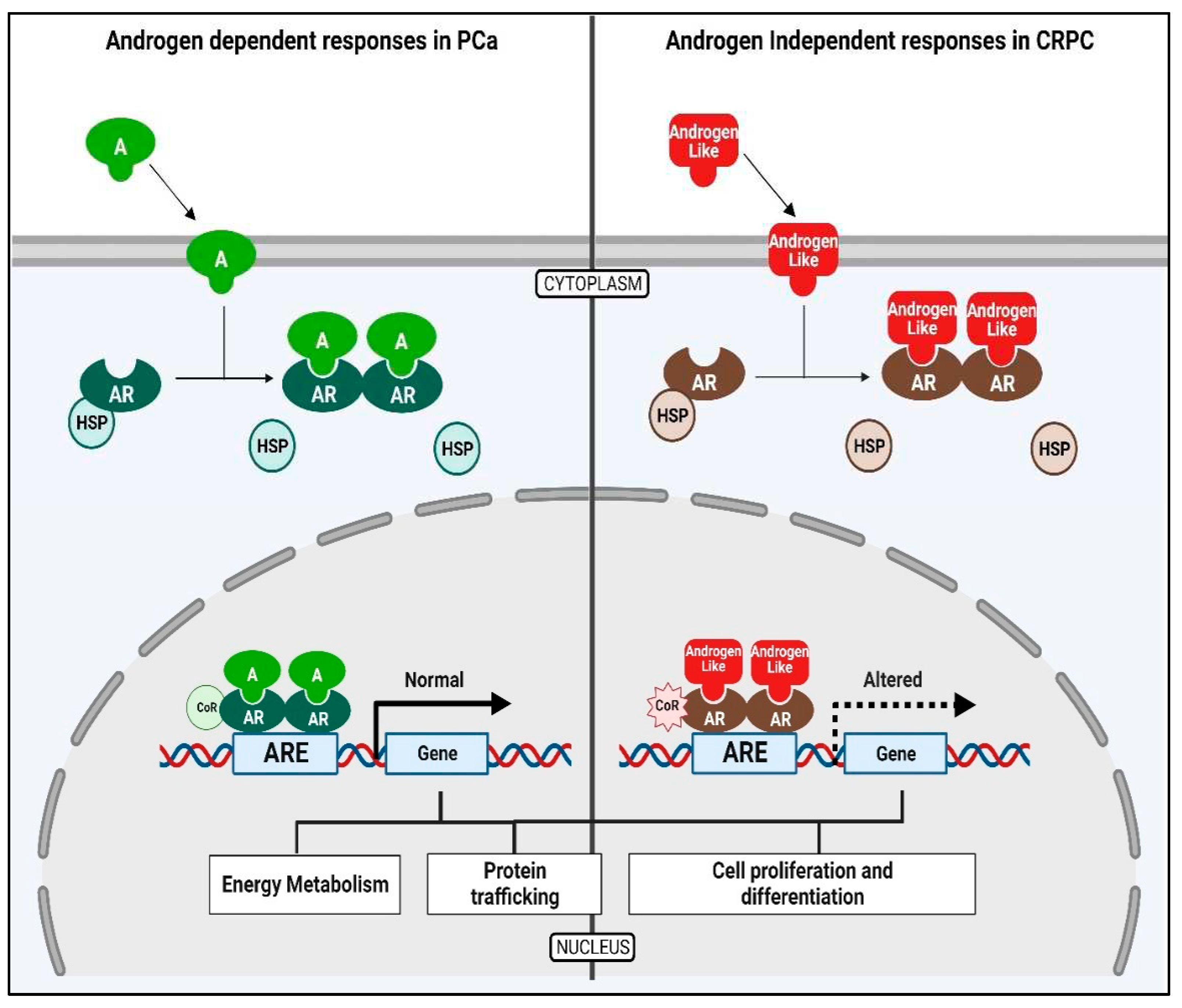
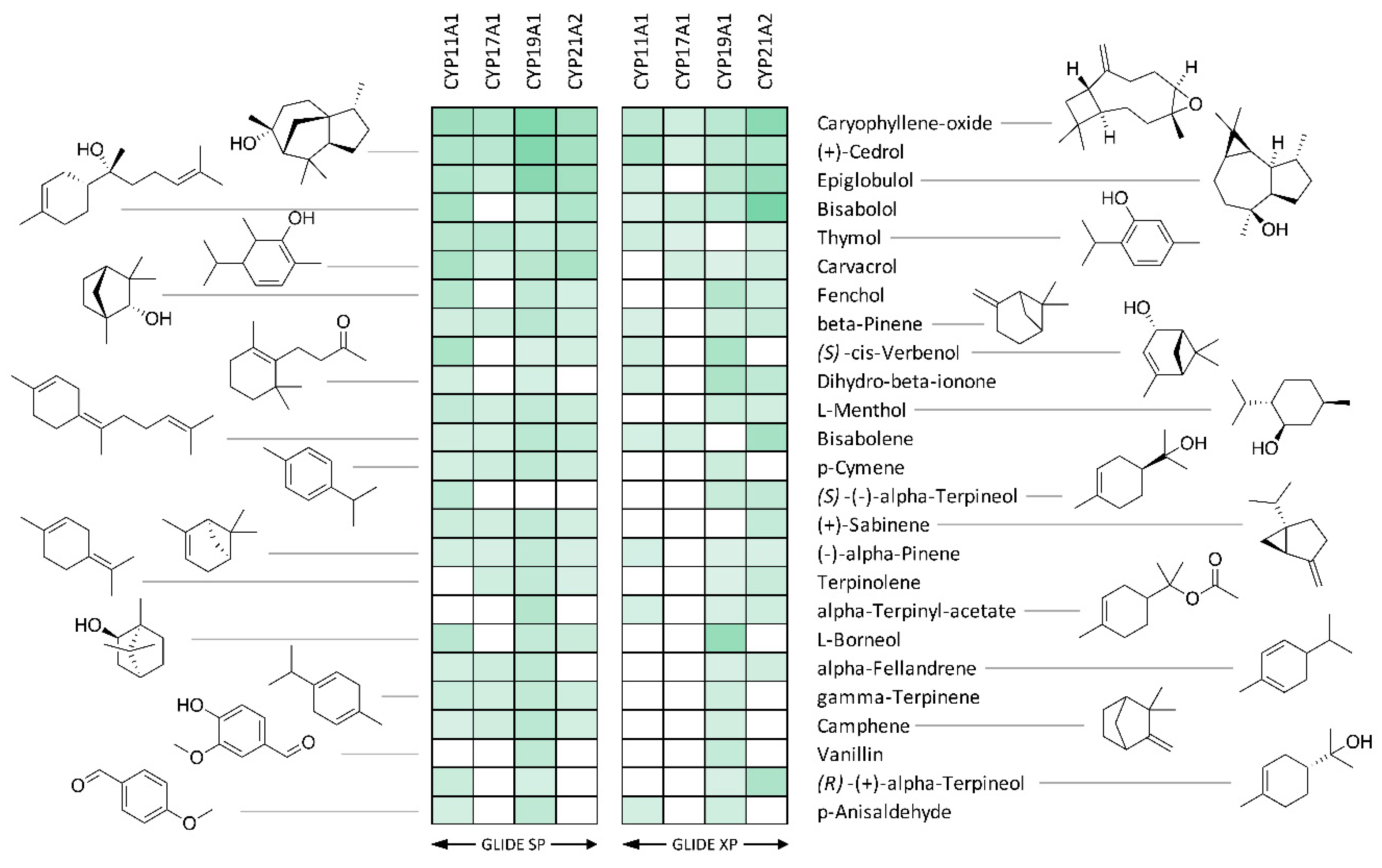
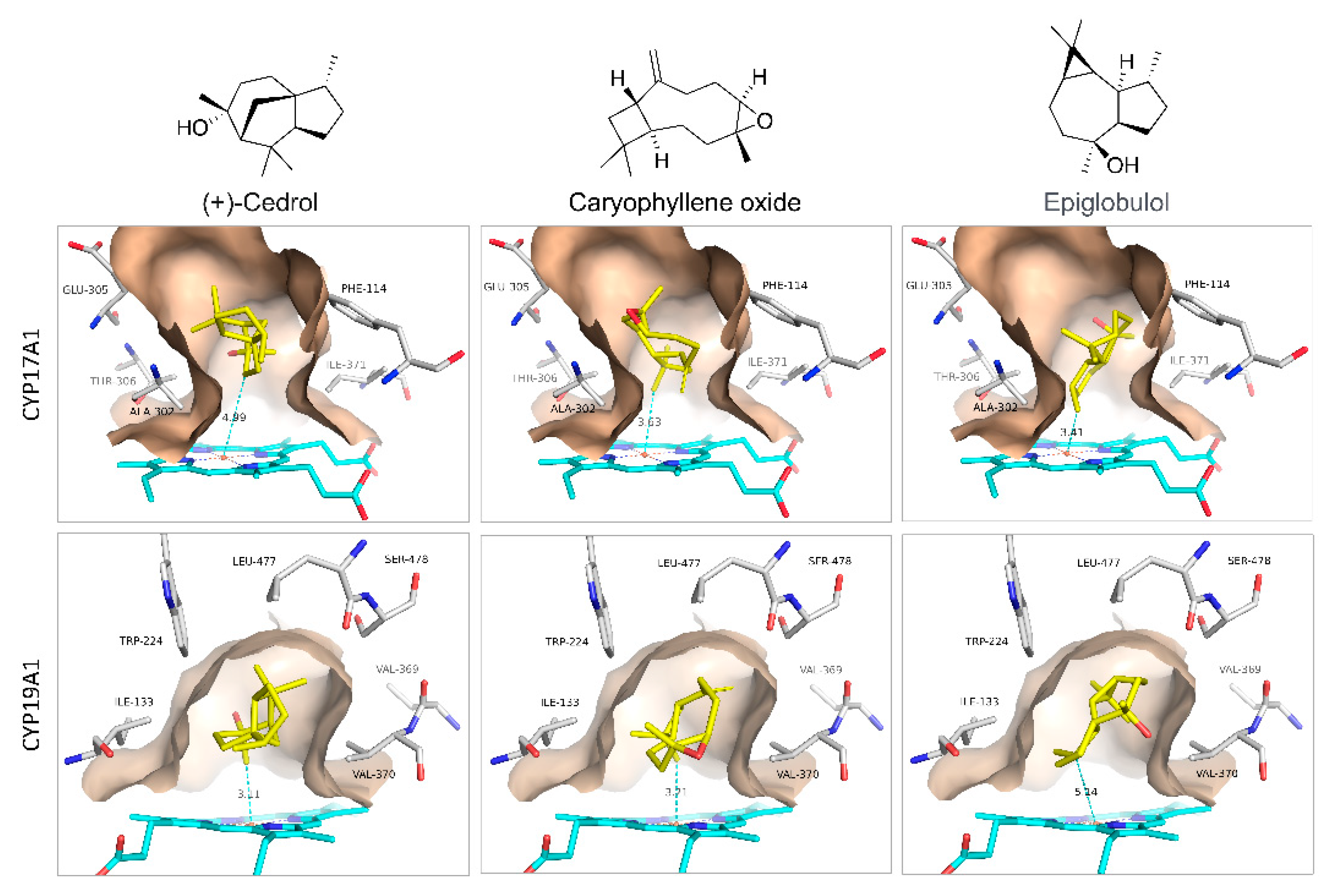
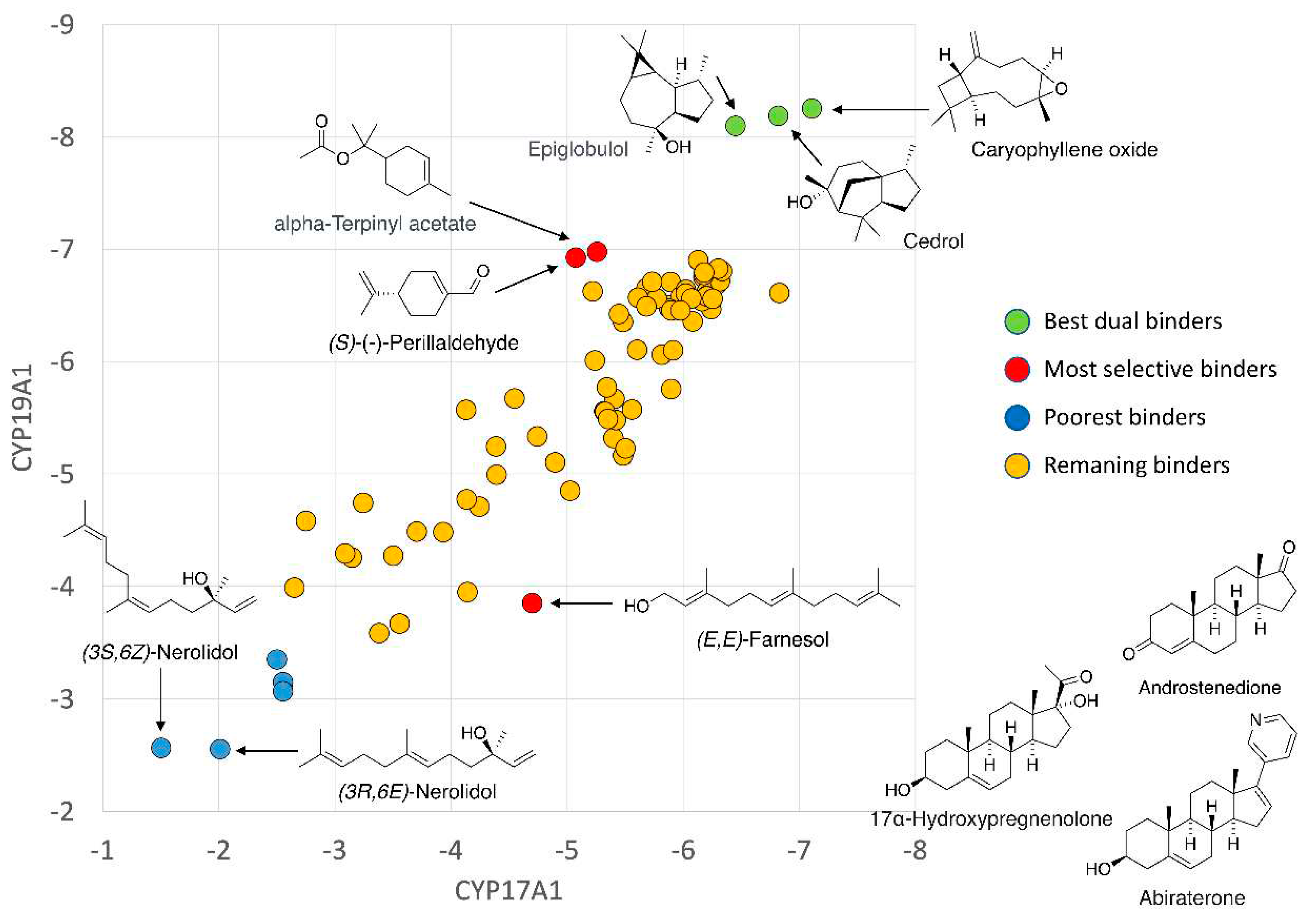
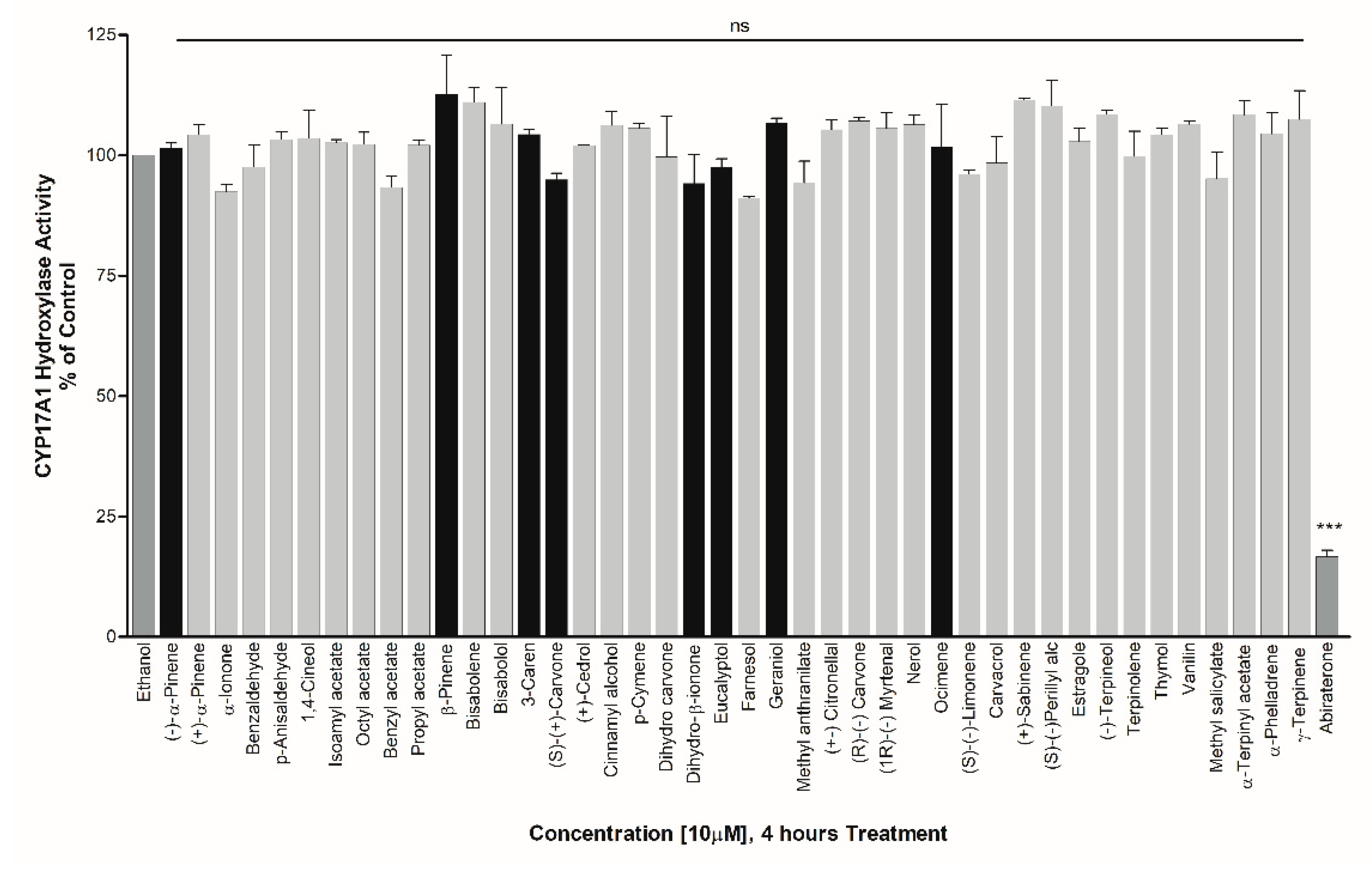
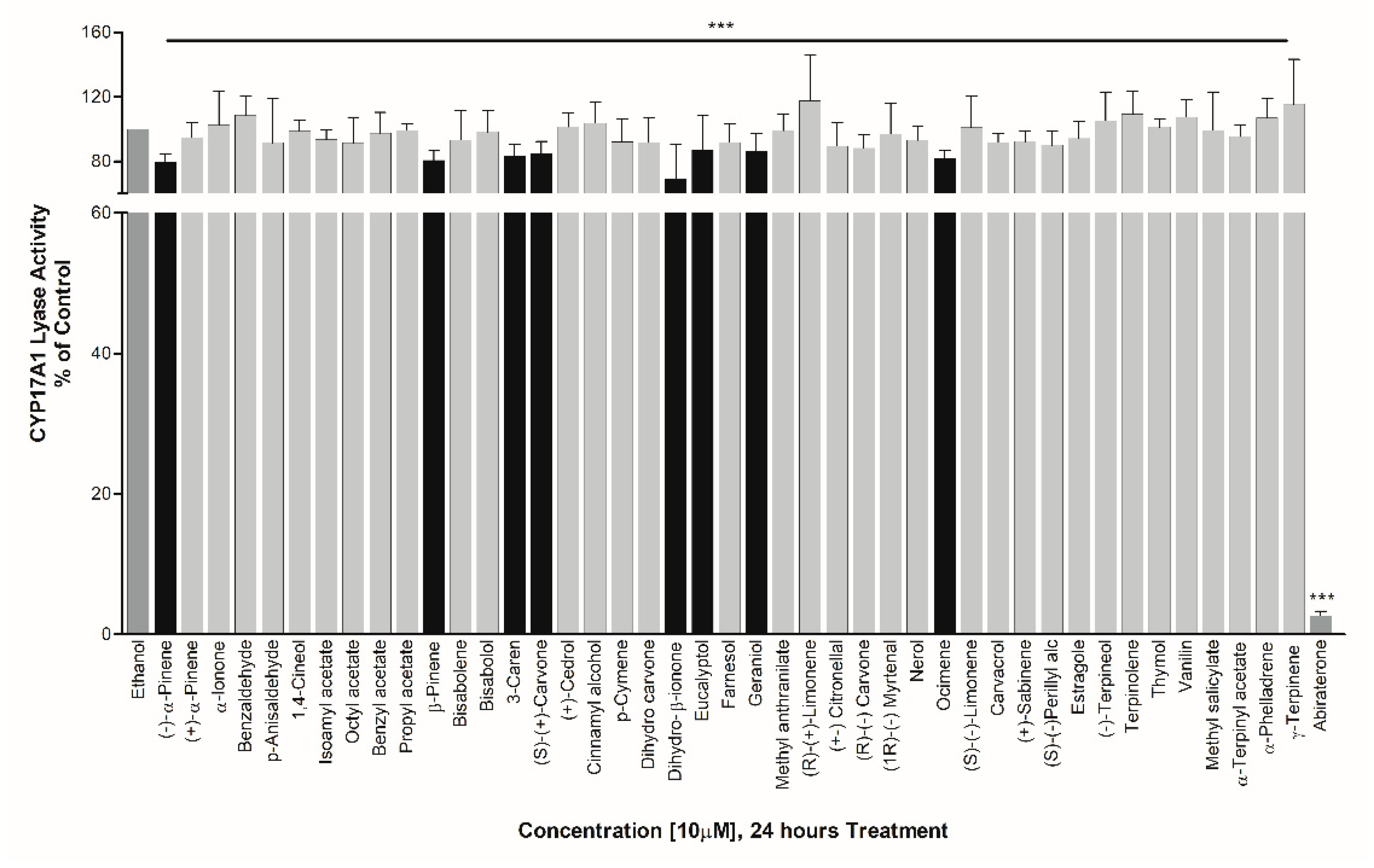
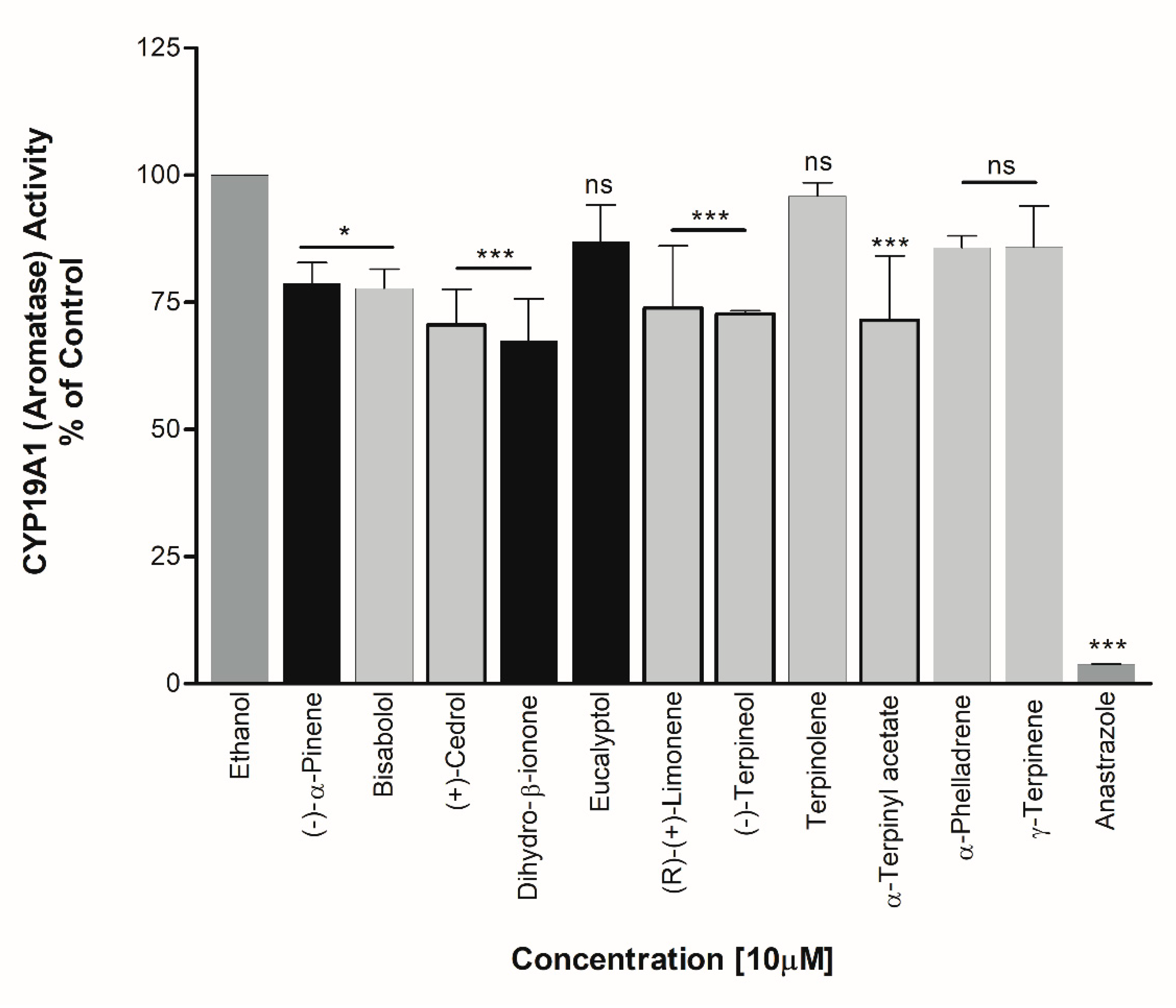
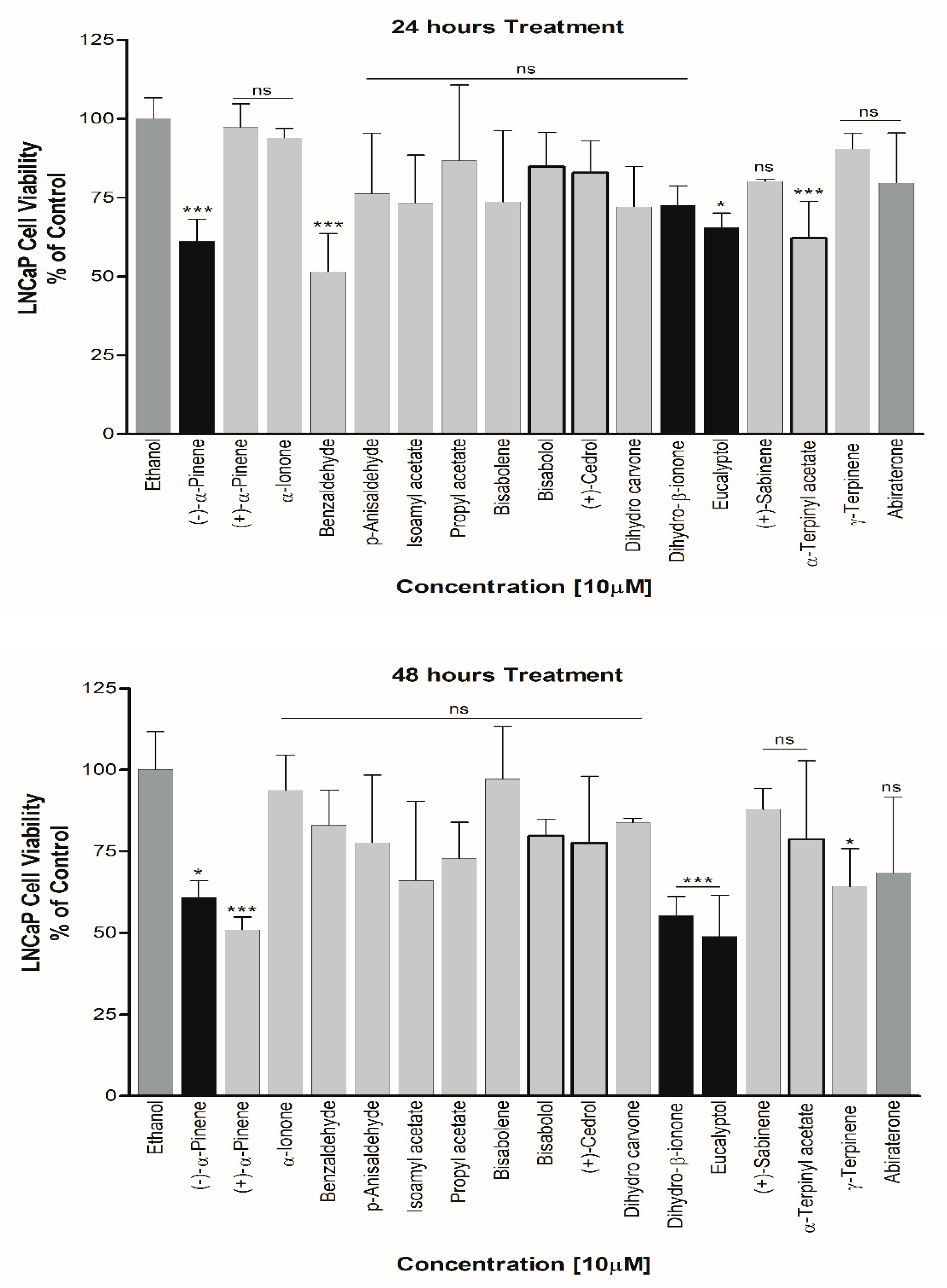
3. Results
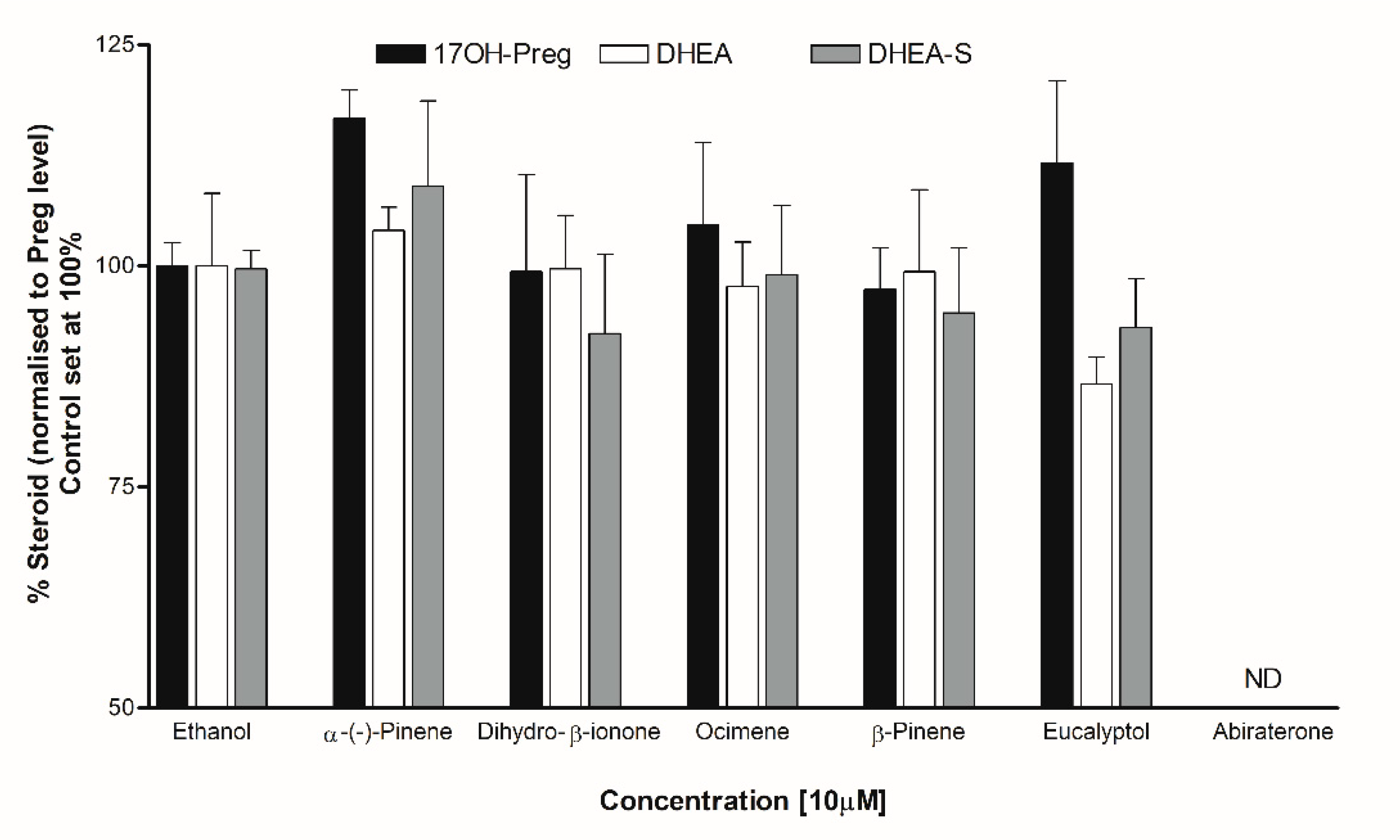
Steroid analysis by LC-MS/MS
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendonca, A.; Jackson-Davis, A.; Moutiq, R.; Thomas-Popo, E. Chapter 14 - Use of Natural Antimicrobials of Plant Origin to Improve the Microbiological Safety of Foods. In Food and Feed Safety Systems and Analysis; Ricke, S.C., Atungulu, G.G., Rainwater, C.E., Park, S.H., Eds.; Academic Press, 2018; pp. 249–272. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, C.; Maurel, O.M.; Musumeci, T.; Bonaccorso, A.; Drago, F.; Souto, E.M.B.; Pignatello, R.; Carbone, C. Essential Oils: Pharmaceutical Applications and Encapsulation Strategies into Lipid-Based Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential Oils, Part I: Introduction. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils – A review. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paco, N. Terpenes in Essential Oils: Bioactivity and Applications. In Terpenes and Terpenoids; Shagufta, P., Areej Mohammad, A.-T., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2020; p. Ch. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Sharmeen, J.B.; Mahomoodally, F.M.; Zengin, G.; Maggi, F. Essential Oils as Natural Sources of Fragrance Compounds for Cosmetics and Cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.C.; Schmidt, E. Essential Oils, Part III: Chemical Composition. Dermatitis 2016, 27, 161–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, J.T.; Shropshire, B.C.; Nagy, T.R.; Chambers, K.D.; Li, Y.; Korach, K.S. Essential Oils and Health. Yale J Biol Med 2020, 93, 291–305. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, B.; Al-Wabel, N.A.; Shams, S.; Ahamad, A.; Khan, S.A.; Anwar, F. Essential oils used in aromatherapy: A systemic review. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 2015, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—a review. International Journal of Food Microbiology 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.R.; Rana, A.; Jaitak, V. Essential Oils: An Impending Substitute of Synthetic Antimicrobial Agents to Overcome Antimicrobial Resistance. Current Drug Targets 2019, 20, 605–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Terekeci, H.; Sandal, S.; Kelestimur, F. Endocrine disrupting chemicals: exposure, effects on human health, mechanism of action, models for testing and strategies for prevention. Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders 2020, 21, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, D.V.; Lipson, N.; Korach, K.S.; Bloch, C.A. Prepubertal gynecomastia linked to lavender and tea tree oils. N Engl J Med 2007, 356, 479–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr Rev 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteson, K.J.; Picado-Leonard, J.; Chung, B.C.; Mohandas, T.K.; Miller, W.L. Assignment of the gene for adrenal P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase) to human chromosome 10. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1986, 63, 789–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.C.; Picado-Leonard, J.; Haniu, M.; Bienkowski, M.; Hall, P.F.; Shively, J.E.; Miller, W.L. Cytochrome P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): cloning of human adrenal and testis cDNAs indicates the same gene is expressed in both tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1987, 84, 407–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallan, P.S.; Nagy, L.D.; Lei, L.; Gonzalez, E.; Kramlinger, V.M.; Azumaya, C.M.; Wawrzak, Z.; Waterman, M.R.; Guengerich, F.P.; Egli, M. Structural and kinetic basis of steroid 17alpha,20-lyase activity in teleost fish cytochrome P450 17A1 and its absence in cytochrome P450 17A2. J Biol Chem 2015, 290, 3248–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, M.X.; Simpson, E.R.; Waterman, M.R. Expression of bovine 17 alpha-hydroxylase cytochrome P-450 cDNA in nonsteroidogenic (COS 1) cells. Science 1986, 234, 1258–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagibashi, K.; Hall, P.F. Role of electron transport in the regulation of the lyase activity of C21 side-chain cleavage P-450 from porcine adrenal and testicular microsomes. J Biol Chem 1986, 261, 8429–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.V.; Flück, C.E. NADPH P450 oxidoreductase: structure, function, and pathology of diseases. Pharmacol Ther 2013, 138, 229–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auchus, R.J.; Lee, T.C.; Miller, W.L. Cytochrome b5 augments the 17,20-lyase activity of human P450c17 without direct electron transfer. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, 3158–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.V.; Miller, W.L. Regulation of 17,20 lyase activity by cytochrome b5 and by serine phosphorylation of P450c17. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 13265–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Rodriguez, H.; Ohno, S.; Miller, W.L. Serine phosphorylation of human P450c17 increases 17,20-lyase activity: implications for adrenarche and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995, 92, 10619–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.V.; Mellon, S.H.; Miller, W.L. Protein phosphatase 2A and phosphoprotein SET regulate androgen production by P450c17. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 2837–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempna, P.; Hirsch, A.; Hofer, G.; Mullis, P.E.; Fluck, C.E. Impact of differential P450c17 phosphorylation by cAMP stimulation and by starvation conditions on enzyme activities and androgen production in NCI-H295R cells. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3686–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.H.; Tee, M.K.; Miller, W.L. Human cytochrome p450c17: single step purification and phosphorylation of serine 258 by protein kinase a. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1677–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.L.; Tee, M.K. The post-translational regulation of 17,20 lyase activity. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2015, 408, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, M.K.; Miller, W.L. Phosphorylation of human cytochrome P450c17 by p38alpha selectively increases 17,20 lyase activity and androgen biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 23903–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, G.S. Endocrine disruptors and prostate cancer risk. Endocr Relat Cancer 2008, 15, 649–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.H.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E.-l. Androgen receptor: structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-Q.; Zeng, X.-B.; Li, J.; Zhu, K.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Lu, H.-M.; Yin, D.-C.; Lin, S.-X. Comparison of the roles of estrogens and androgens in breast cancer and prostate cancer. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 2020, 121, 2756–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 2010, 31, 455–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J Chem Inf Model 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28, 235–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrunak, E.M.; DeVore, N.M.; Porubsky, P.R.; Scott, E.E. Structures of human steroidogenic cytochrome P450 17A1 with substrates. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 32952–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Griswold, J.; Erman, M.; Pangborn, W. X-ray structure of human aromatase reveals an androgen-specific active site. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2010, 118, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.; Di Nardo, G.; Griswold, J.; Egbuta, C.; Jiang, W.; Gilardi, G.; Ghosh, D. Structural basis for the functional roles of critical residues in human cytochrome p450 aromatase. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5821–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Griswold, J.; Erman, M.; Pangborn, W. Structural basis for androgen specificity and oestrogen synthesis in human aromatase. Nature 2009, 457, 219–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2013, 27, 221–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, J.C.; Cholleti, A.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Timlin, M.R.; Uchimaya, M. Epik: a software program for pK( a ) prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J Comput Aided Mol Des 2007, 21, 681–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVore, N.M.; Scott, E.E. Structures of cytochrome P450 17A1 with prostate cancer drugs abiraterone and TOK-001. Nature 2012, 482, 116–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.; Petrunak, E.M.; Estrada, D.F.; Scott, E.E. Structural insights into the function of steroidogenic cytochrome P450 17A1. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2017, 441, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Egbuta, C.; Lo, J. Testosterone complex and non-steroidal ligands of human aromatase. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2018, 181, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra Precision Glide: Docking and Scoring Incorporating a Model of Hydrophobic Enclosure for Protein−Ligand Complexes. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainey, W.E.; Saner, K.; Schimmer, B.P. Adrenocortical cell lines. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2004, 228, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdar, A.F.; Oie, H.K.; Shackleton, C.H.; Chen, T.R.; Triche, T.J.; Myers, C.E.; Chrousos, G.P.; Brennan, M.F.; Stein, C.A.; La Rocca, R.V. Establishment and characterization of a human adrenocortical carcinoma cell line that expresses multiple pathways of steroid biosynthesis. Cancer Res 1990, 50, 5488–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Gong, S.; Roy-Burman, P.; Lee, P.; Culig, Z. Current mouse and cell models in prostate cancer research. Endocr Relat Cancer 2013, 20, R155–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Cell Viability Assays. In Assay Guidance Manual, Markossian, S.; Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Arkin, M., Auld, D., Austin, C., Baell, J., Chung, T.D.Y., Coussens, N.P., Dahlin, J.L., Devanarayan, V., Foley, T.L., Glicksman, M., Gorshkov, K., Haas, J.V., Hall, M.D., Hoare, S., Inglese, J., Iversen, P.W., Kales, S.C., Lal-Nag, M., Li, Z., McGee, J., McManus, O., Riss, T., Saradjian, P., Sittampalam, G.S., Tarselli, M., Trask, O.J. Jr., Wang, Y., Weidner, J.R., Wildey, M.J., Wilson, K., Xia, M., Xu, X., Eds.; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda (MD), 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Sari, G.; Ozdal, T.; Capanoglu, E. Guidelines for cell viability assays. Food Frontiers 2020, 1, 332–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, G.A.; Barrie, S.E.; Jarman, M.; Rowlands, M.G. Novel Steroidal Inhibitors of Human Cytochrome P45017.alpha.-Hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase): Potential Agents for the Treatment of Prostatic Cancer. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 1995, 38, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhane, S.S.; Dick, B.; Hu, Q.; Hartmann, R.W.; Pandey, A.V. Specificity of anti-prostate cancer CYP17A1 inhibitors on androgen biosynthesis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2016, 477, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño, P.R.; Parween, S.; Pandey, A.V. Bioactivity of Curcumin on the Cytochrome P450 Enzymes of the Steroidogenic Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Staels, B.; Hum, D.W.; Miller, W.L. Regulation of steroidogenesis in NCI-H295 cells: a cellular model of the human fetal adrenal. Mol Endocrinol 1993, 7, 423–33. [Google Scholar]
- Potts, G.O.; Creange, J.E.; Harding, H.R.; Schane, H.P. Trilostane, an orally active inhibitor of steroid biosynthesis. Steroids 1978, 32, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.W.; Fishman, L.M. Biosynthesis and metabolism of steroid hormones by human adrenal carcinomas. Braz J Med Biol Res 2000, 33, 1235–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán, F.M.; VandeVoort, C.A.; Overstreet, J.W.; Lasley, B.L.; Conley, A.J. Molecular Target of Endocrine Disruption in Human Luteinizing Granulosa Cells by 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin: Inhibition of Estradiol Secretion Due to Decreased 17α-Hydroxylase/17,20-Lyase Cytochrome P450 Expression. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McManus, J.M.; Bohn, K.; Alyamani, M.; Chung, Y.M.; Klein, E.A.; Sharifi, N. Rapid and structure-specific cellular uptake of selected steroids. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0224081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrieu, T.; du Toit, T.; Vogt, B.; Mueller, M.D.; Groessl, M. Parallel targeted and non-targeted quantitative analysis of steroids in human serum and peritoneal fluid by liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 2022, 414, 7461–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siiteri, P.K.; Thompson, E.A. Studies of human placental aromatase. Journal of Steroid Biochemistry 1975, 6, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D.; Simpson, E.R. Assay of aromatase activity. Methods Enzymol 1991, 206, 477–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zehetner, P.; Höferl, M.; Buchbauer, G. Essential oil components and cytochrome P450 enzymes: a review. Flavour and Fragrance Journal 2019, 34, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Myslivečková, Z.; Szotáková, B.; Špičáková, A.; Lněničková, K.; Ambrož, M.; Kubíček, V.; Krasulová, K.; Anzenbacher, P.; Skálová, L. The inhibitory effects of β-caryophyllene, β-caryophyllene oxide and α-humulene on the activities of the main drug-metabolizing enzymes in rat and human liver in vitro. Chem-Biol Interact 2017, 278, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špičáková, A.; Bazgier, V.; Skálová, L.; Otyepka, M.; Anzenbacher, P. beta-caryophyllene oxide and trans-nerolidol affect enzyme activity of CYP3A4 - in vitro and in silico studies. Physiological research 2019, 68 (Suppl 1), S51–s58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-U.; Kwon, S.-S.; Kong, T.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S. Inhibitory Effects of Cedrol, β-Cedrene, and Thujopsene on Cytochrome P450 Enzyme Activities in Human Liver Microsomes. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A 2014, 77, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.N.; Patel, N.; Bershadskiy, A.; Sokoloff, A.; Singer, E.A. Androgen synthesis inhibitors in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Asian Journal of Andrology 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.D.; Ellison, S.J.; Baker, J.G.; Stagg, D.B.; Wardell, S.E.; Park, S.; Alley, H.M.; Baldi, R.M.; Yllanes, A.; Andreano, K.J.; Stice, J.P.; Lawrence, S.A.; Eisner, J.R.; Price, D.K.; Moore, W.R.; Figg, W.D.; McDonnell, D.P. Androgen receptor antagonism drives cytochrome P450 17A1 inhibitor efficacy in prostate cancer. J Clin Invest 2017, 127, 2326–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, I.M.; Abbott, D.H. The hunt for a selective 17,20 lyase inhibitor; learning lessons from nature. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2016, 163, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, T.M.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Pandey, A.V.; Grudzińska, A.; Sharma, K.; Yakubu, J.; Björkling, F. Non-steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors: Discovery and Assessment. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2023, 66, 6542–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Pas, R.; Hofland, L.J.; Hofland, J.; Taylor, A.E.; Arlt, W.; Steenbergen, J.; van Koetsveld, P.M.; de Herder, W.W.; de Jong, F.H.; Feelders, R.A. Fluconazole inhibits human adrenocortical steroidogenesis in vitro. J Endocrinol 2012, 215, 403–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.; Reid, A.H.M.; Yap, T.A.; Raynaud, F.; Dowsett, M.; Settatree, S.; Barrett, M.; Parker, C.; Martins, V.; Folkerd, E.; Clark, J.; Cooper, C.S.; Kaye, S.B.; Dearnaley, D.; Lee, G.; de Bono, J.S. Phase I Clinical Trial of a Selective Inhibitor of CYP17, Abiraterone Acetate, Confirms That Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Commonly Remains Hormone Driven. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008, 26, 4563–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, M.; Hara, T.; Hitaka, T.; Kaku, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Takahashi, J.; Asahi, S.; Miki, H.; Tasaka, A.; Kusaka, M. Orteronel (TAK-700), a novel non-steroidal 17,20-lyase inhibitor: Effects on steroid synthesis in human and monkey adrenal cells and serum steroid levels in cynomolgus monkeys. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012, 129, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njar, V.C.O.; Brodie, A.M.H. Discovery and Development of Galeterone (TOK-001 or VN/124-1) for the Treatment of All Stages of Prostate Cancer. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 58, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Hu, Q. CYP17 inhibitors—abiraterone, C17,20-lyase inhibitors and multi-targeting agents. Nature Reviews Urology 2014, 11, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, S.; Hansen, C.H.; Petrunak, E.M.; Scott, E.E.; Styrishave, B.; Jorgensen, F.S.; Olsen, L. Promising Tools in Prostate Cancer Research: Selective Non-Steroidal Cytochrome P450 17A1 Inhibitors. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 29468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.; Hansen, C.H.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Islin, J.; Styrishave, B.; Olsen, L.; Jorgensen, F.S. Structure-based optimisation of non-steroidal cytochrome P450 17A1 inhibitors. Chemical communications 2017, 53, 3118–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, T.M.; Rogova, O.; Andersen, K.L.; Yadav, R.; Brixius-Anderko, S.; Scott, E.E.; Olsen, L.; Jorgensen, F.S.; Bjorkling, F. Discovery of Novel Non-Steroidal Cytochrome P450 17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Int J Mol Sci, 2020; 21, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Wrobel, T.M.; Rogova, O.; Sharma, K.; Rojas Velazquez, M.N.; Pandey, A.V.; Jorgensen, F.S.; Arendrup, F.S.; Andersen, K.L.; Bjorkling, F. Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationships of Novel Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Biomolecules, 2022; 12, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Malikova, J.; Brixius-Anderko, S.; Udhane, S.S.; Parween, S.; Dick, B.; Bernhardt, R.; Pandey, A.V. CYP17A1 inhibitor abiraterone, an anti-prostate cancer drug, also inhibits the 21-hydroxylase activity of CYP21A2. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2017, 174, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, C.D.; Bart, A.G.; Yadav, R.; Scott, E.E.; Aubé, J. Effects of fluorine substitution on substrate conversion by cytochromes P450 17A1 and 21A2. 2021, 19, 7664–7669.
- Richards, J.; Lim, A.C.; Hay, C.W.; Taylor, A.E.; Wingate, A.; Nowakowska, K.; Pezaro, C.; Carreira, S.; Goodall, J.; Arlt, W.; McEwan, I.J.; de Bono, J.S.; Attard, G. Interactions of Abiraterone, Eplerenone, and Prednisolone with Wild-type and Mutant Androgen Receptor: A Rationale for Increasing Abiraterone Exposure or Combining with MDV3100. Cancer Research 2012, 72, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.B.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Vessella, R.; Hess, D.L.; Kalhorn, T.F.; Higano, C.S.; True, L.D.; Nelson, P.S. Maintenance of Intratumoral Androgens in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Mechanism for Castration-Resistant Tumor Growth. Cancer Research 2008, 68, 4447–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, M.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Auchus, R.J.; Storbeck, K.-H. The role of adrenal derived androgens in castration resistant prostate cancer. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2020, 197, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambury, R.M.; Rathkopf, D.E. Novel and next-generation androgen receptor–directed therapies for prostate cancer: Beyond abiraterone and enzalutamide. Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations 2016, 34, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hu, Q.; Hartmann, R.W. Recent Progress in Pharmaceutical Therapies for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2013, 14, 3958–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




