Submitted:
31 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Generation of anti-DNA antibodies
3. Penetration of anti-DNA antibodies into live cells (Figure 1)
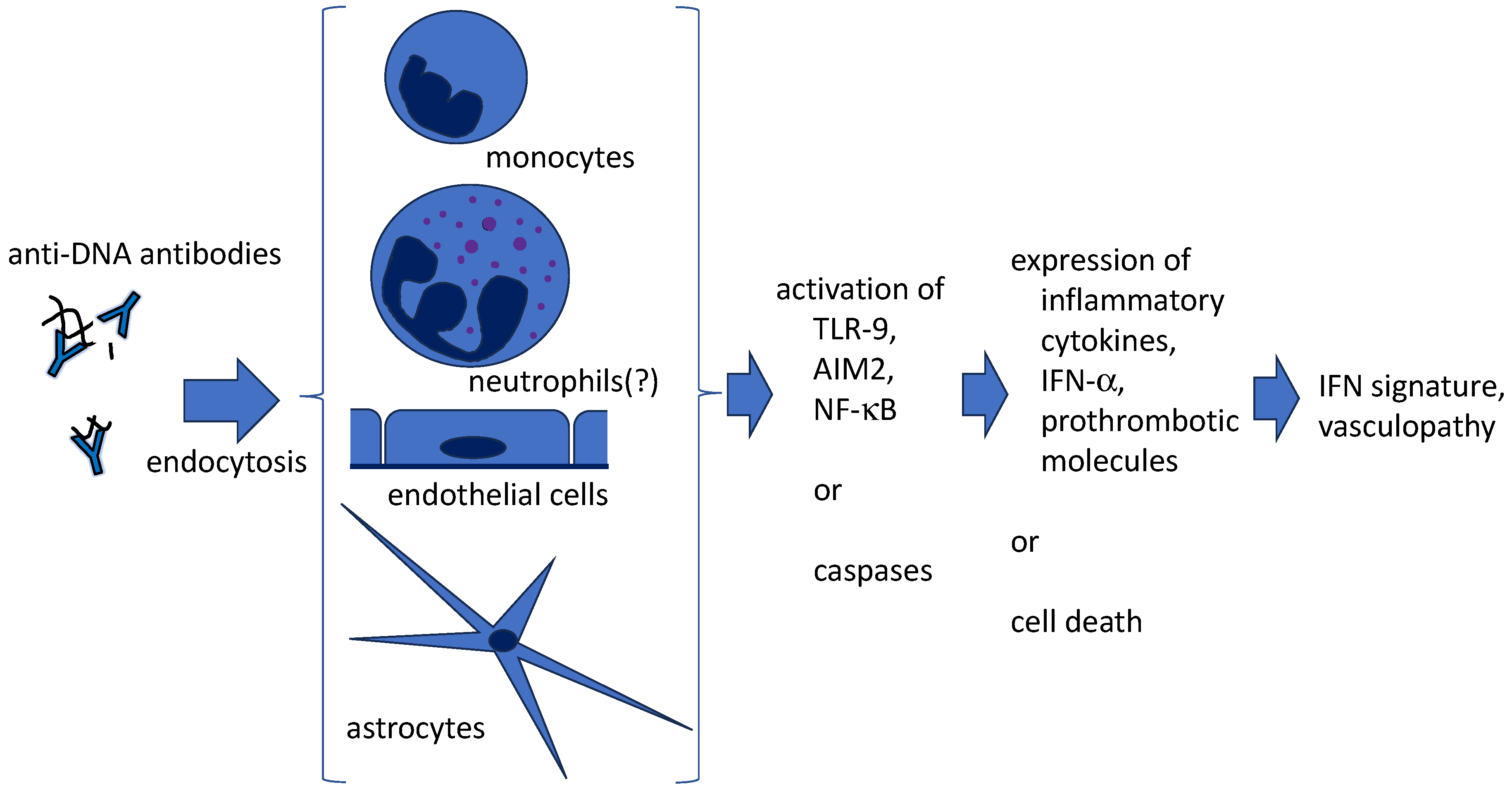
4. Anti-DNA antibodies and NETs
4.1. What are NETs?
4.2. NETs in autoimmune diseasses
4.2.1. SLE
4.2.2. APS
4.2.3. AAV
4.3. Quantification of NETs
4.4. Anti-NET antibodies
4.5. Amplification of SLE disease activity by anti-DNA antibodies and NETs (Figure 2)
4.5.1. Aggravation of IFN signature
4.5.2. Protection of NETs from nuclease resistance by anti-DNA antibodies
4.5.3. Thrombogenic properties
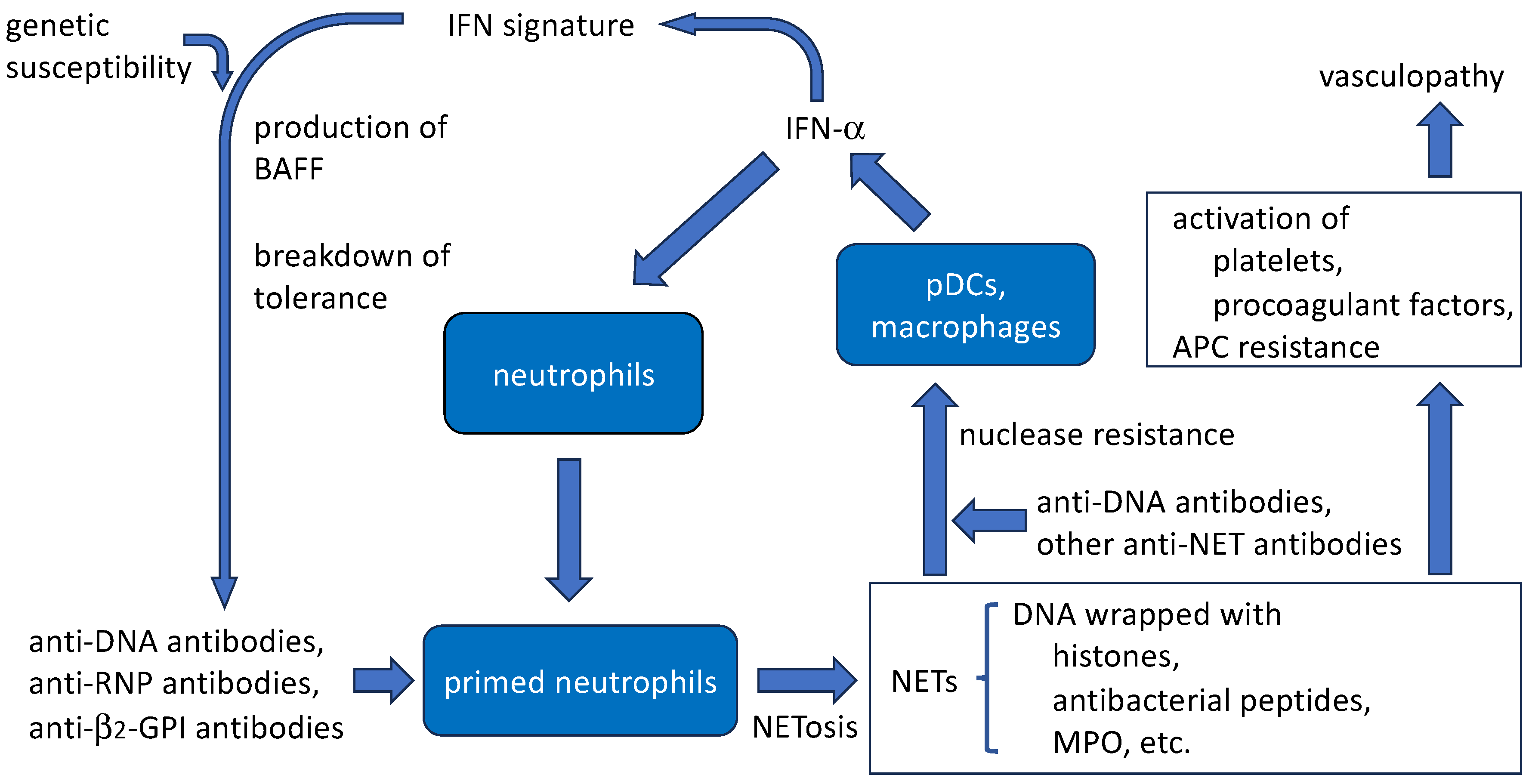
4.5.4. Induction of NET release by anti-DNA antibodies
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z, Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Hughes G. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameer MA, Chaudhry H, Mushtaq J, Khan OS, Babar M, Hashim T, Zeb S, Tariq MA, Patlolla SR, Ali J, et al. An overview of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) pathogenesis, classification, and management. Cureus 2022, 14, e30330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisetsky DS, Lipsky PE. New insights into the role of antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsokos GC, Lo MS, Reis PC, Sullivan KE. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, Brinks R, Mosca M, Ramsey-Goldman R, Smolen JS, Wofsy D, Boumpas DT, Kamen DL, et al. 2019 European League Against Rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji H, Ohmura K, Jin H, Naito R, Arase N, Kohyama M, Suenaga T, Sakakibara S, Kochi Y, Okada Y, et al. Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies recognize DNA presented on HLA class II molecules of systemic lupus erythematosus risk alleles. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson C, Chida AS, Adlowitz D, Silver L, Fox E, Jenks SA, Palmer E, Wang Y, Heimburg-Molinaro J, Li QZ, et al. Molecular basis of 9G4 B cell autoreactivity in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4926–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Bañuelos E, Yu Y, Li J, Cashman KS, Paz M, Trejo-Zambrano MI, Bugrovsky R, Wang Y, Chida AS, Sherman-Baust CA, et al. Affinity maturation generates pathogenic antibodies with dual reactivity to DNase1L3 and dsDNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety LP, Park YH, Jang YJ. Autoantigen spermatid nuclear transition protein I enhances pro-inflammatory cytokine production stimulated by anti-DNA autoantibodies in macrophages. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2022, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden H, Klopf J, Ibrahim N, Knöbl V, Sotir A, Mekis R, Nowikovsky K, Eilenberg W, Neumayer C, Brostjan C. Quantitation of oxidized nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in plasma samples of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 206, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke MS, Mistry N, Wood C, Herbert KE, Lunec J. Immunogenicity of DNA damaged by reactive oxygen species –– implications for anti-DNA antibodies in lupus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon-Segovia D, Ruiz-Arguelles A, Fishbein E. Antibody to nuclear ribonucleoprotein penetrates live human mononuclear cells through Fc receptors. Nature 1978, 271, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Segovia D, Llorente L, Fishbein E, Díaz-Jouanen E. Abnormalities in the content of nucleic acids of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to DNA antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1982, 23, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlahakos D, Foster MH, Ucci AA, Barrett KJ, Datta SK, Madaio MP. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies penetrate cells, bind to nuclei, and induce glomerular proliferation and proteinuria in vivo. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1992, 2, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannikou M, Bellou S, Eliades P, Hatzioannou A, Mantzaris MD, Carayanniotis G, Avrameas S, Lymberi P. DNA-histone complexes as ligands amplify cell penetration and nuclear targeting of anti-DNA antibodies via energy-independent mechanisms. Immunology 2015, 147, 73–81. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park H, Kim M, Seo Y, Ham Y, Cho MY, Kwon MH. Cytosolic internalization of anti-DNA antibodies by human monocytes induces production of pro-inflammatory cytokines independently of the tripartite motif-containing 21 (TRIM21)-mediated pathway. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang JY, Jeong JG, Jun HR, Lee SC, Kim JS, Kim YS, Kwon MH. A nucleic acid-hydrolyzing antibody penetrates into cells via caveolae-mediated endocytosis, localizes in the cytosol and exhibits cytotoxicity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im SR, Im SW, Chung HY, Pravinsagar P, Jang YJ. Cell- and nuclear-penetrating anti-dsDNA autoantibodies have multiple arginines in CDR3 of VH and increase cellular level of pERK and Bcl-2 in mesangial cells. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton KA, Tømmerås B, Marion TN, Rekvig OP. Pure anti-dsDNA mAbs need chromatin structures to promote glomerular mesangial deposits in BALB/c mice. Autoimmunity 2010, 43, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito M, Makino Y, Inoue K, Watanabe Y, Hoshi O, Kubota T. Anti-DNA antibodies cross-reactive with b2-glycoprotein I induce monocyte tissue factor through the TLR9 pathway. Immunol. Med. 2021, 44, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbetter EA, Rifkin IR, Hohlbaum AM, Beaudette BC, Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A. Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and Toll-like receptors. Nature 2002, 416, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillatreau S, Manfroi B, Dörner T. Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells during systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue K, Ishizawa M, Kubota T. Monoclonal anti-dsDNA antibody 2C10 escorts DNA to intracellular DNA sensors in normal mononuclear cells and stimulates secretion of multiple cytokines implicated in lupus pathogenesis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virachith S, Saito M, Watanabe Y, Inoue K, Hoshi O, Kubota T. Anti-b2-glycoprotein I antibody with DNA binding activity enters living monocytes via cell surface DNA and induces tissue factor expression. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 195, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz N, Stock AD, Putterman C. Neuropsychiatric lupus: new mechanistic insights and future treatment directions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manca, E. Autoantibodies in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE): Can they be used as biomarkers for the differential diagnosis of this disease? Clin. Rev. Allerg. Immunol. 2022, 63, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamou M, Grodzki AC, van Oostrum M, Wollscheid B, Lein PJ. Fc gamma receptors are expressed in the developing rat brain and activate downstream signaling molecules upon cross-linking with immune complex. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue K, Hoshi O, Kubota T. Internalization of anti-DNA antibodies by rat brain cells: a possible pathogenetic mechanism of neuropsychiatric lupus. Med. Res. Arch. 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Koob, AO. Astrocytes imagined. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon RE, Nemeth JF, Singh S, Lingham RB, Grewal IS. Harnessing SLE autoantibodies for intracellular delivery of biologic therapeutics. Trends. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattray Z, Deng G, Zhang S, Shirali A, May CK, Chen X, Cuffari BJ, Liu J, Zou P, Rattray NJW, et al. ENT2 facilitates brain endothelial cell penetration and blood-brain barrier transport by a tumor-targeting anti-DNA autoantibody. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145875. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei H, Araki A, Watanabe H, Ichinose A, Sendo F. Rapid killing of human neutrophils by the potent activator phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) accompanied by changes different from typical apoptosis or necrosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1996, 59, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, Weinrauch Y, Zychlinsky A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs TA, Abed U, Goosmann C, Hurwitz R, Schulze I, Wahn V, Weinrauch Y, Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A. Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 231–241. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Köckritz-Blickwede M, Goldmann O, Thulin P, Heinemann K, Norrby-Teglund A, Rohde M, Medina E. Phagocytosis-independent antimicrobial activity of mast cells by means of extracellular trap formation. Blood 2008, 111, 3070–3080. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi S, Gold JA, Andina N, Lee JJ, Kelly AM, Kozlowski E, Schmid I, Straumann A, Reichenbach J, Gleich GJ, et al. Catapult-like release of mitochondrial DNA by eosinophils contributes to antibacterial defense. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 949–953. [CrossRef]
- Middleton EA, He XY, Denorme F, Campbell RA, Ng D, Salvatore SP, Mostyka M, Baxter-Stolzfus A, Borczuk AC, Loda M, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immmunothrombosis in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Blood 2020, 136, 1169–1179. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandpur R, Carmona-Rivera C, Vivekanandan-Giri A, Gizinski A, Yalavarthi S, Knight JS, Friday S, Li S, Patel RM, Subramanian V, et al. NETs are a source of citrullinated autoantigens and stimulate inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 178ra40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lande R, Ganguly D, Facchinetti V, Frasca L, Conrad C, Gregorio J, Meller S, Chamilos G, Sebasigari R, Riccieri V, et al. Neutrophils activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells by releasing self-DNA–peptide complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra19. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romo GS, Caielli S, Vega B, Connolly J, Allantaz F, Xu Z, Punaro M, Baisch J, Guiducci C, Coffman RL, et al. Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 73ra20. [Google Scholar]
- van Avondt K, Fritsch-Stork R, Derksen RHWM, Meyaard L. Ligation of signal inhibitory receptor on leukocytes-1 suppresses the release of neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bont CM, Boelens WC, Pruijn GJM. NETosis, complement, and coagulation: a triangular relationship. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 19–27. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foret T, Dufrost V, du Mont LS, Costa P, Lakomy C, Lagrange J, Lacolley P, Regnault V, Zuily S, Wahl D. A new pro-thrombotic mechanism of neutrophil extracellular traps in antiphospholipid syndrome: impact on activated protein C resistance. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2993–2998. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ünlü O, Zuily S, Erkan D. The clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 3, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalavarthi S, Gould TJ, Rao AN, Mazza LF, Morris AE, Núñez-Álvarez C, Hernández-Ramírez D, Bockenstedt PL, Liaw PC, Cabral AR, et al. Release on neutrophil extracellular traps by neutrophils stimulated with antiphospholipid antibodies. A newly identified mechanism of thrombosis in the antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2990–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng H, Yalavarthi S, Kanthi Y, Mazza LF, Elfline MA, Luke CE, Pinsky DJ, Henke PK, Knight JS. In vivo role of neutrophil extracellular traps in antiphospholipid antibody-mediated venous thrombosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden M, van den Hoogen LL, Westerlaken GHA, Fritsch-Stork RDE, van Roon JAG, Radstake TRDJ, Meyaard L. Neutrophil extracellular trap release is associated with antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and anti-phospholipid syndrome. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorch SK, Kubes P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam LS, Kraaij T, Kamerling SWA, Bakker JA, Scherer UH, Rabelink TJ, van Kooten C, Teng YKO. Intrinsically distinct role of neutrophil extracellular trap formation in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis compared to systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden H, Ibrahim N, Klopf J, Zagrapan B, Mauracher LM, Hell L, Hofbauer TM, Ondracek AS, Schoergenhofer C, Jilma B, et al. ELISA detection of MPO-DNA complexes in human plasma is error-prone and yields limited information on neutrophil extracellular traps formed in vivo. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta B, Battaglia J, Barnes BJ. Detection of neutrophil extracellular traps in patient plasma: method development and validation in systemic lupus erythematosus and healthy donors that carry IRF5 genetic risk. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 951254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends EJ, van Dam LS, Kraaij T, Kamerling SWA, Rabelink TJ, van Kooten C, Teng YKO. A high-throughput assay to assess and quantify neutrophil extracellular trap fprmation. J.Vis.Exp. 2019, 143, e59150. [CrossRef]
- Jeremic I, Djuric O, Nikolic M, Vlajnic M, Nikolic A, Radojkovic D, Bonaci-Nikolic B. Neutrophil extracellular traps-associated markers are elevated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattanda F, Nakazawa D, Watanabe-Kusunoki K, Kusunoki Y, Shida H, Masuda S, Nishio S, Tomaru U, Atsumi T, Ishizu A. The presence of anti-neutrophil extracellular trap antibody in patients with microscopic polyangiitis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo Y, Yalavarthi S, Gockman K, Madison JA, Gudjonsson JE, Kahlenberg JM, McCune WJ, Bockenstedt PL, Karp DR, Knight JS. Anti-neutrophil extracellular trap antibodies and impaired neutrophil extracellular trap degradation in antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo Y, Navaz S, Tsodikov A, Kmetova K, Kluge L, Ambati A, Hoy CK, Yalavarthi S, de Andrade D, Tektonidou MG, et al. Anti-neutrophil extracellular trap antibodies in antiphospholipid antibody-positive patients: results from the Antiphospholipid Syndrome Alliance for Clinical Trials and InternatiOnal Networking clinical database and repository. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan M, Wang Z, Bao H, Di C, Xia C, Zhang X, Liu Y. Antibodies against neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) potentiate clinical performance of anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 249, 109297. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiochos B, Trejo-Zambrano D, Fenaroli P, Rosenberg A, Baer A, Garg A, Sohn J, Li J, Petri M, Goldman DW, et al. The DNA sensors AIM2 and IFI16 are SLE autoantigens that bind neutrophil extracellular traps. eLife 2022, 11, e72103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel F, Andreeva L, Knackstedt LS, Streeck R, Frese CK, Goosmann C, Hopfner KP, Zychlinsky A. The cytosolic DNA sensor cGAS recognizes neutrophil extracellular traps. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eaax7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou H, Wojciak-Stothard B, Ruseva MM, Cook HT, Kelleher P, Pickering MC, Mongkolsapaya J, Screaton GR, Xu X. Autoantibody-dependent amplification of inflammation in SLE. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patiño-Trives AM, Pérez-Sánchez C, Pérez-Sánchez L, Luque-Tévar M, Ábalos-Aguilera MC, Alcaide-Ruggiero L, Arias-de la Rosa I, Román-Rodríguez C, Seguí P, Espinosa M, et al. Anti-dsDNA antibodies increase the cardiovascular risk in systemic lupus erythematosus promoting a distinctive immune and vascular activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2417–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




