Submitted:
30 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
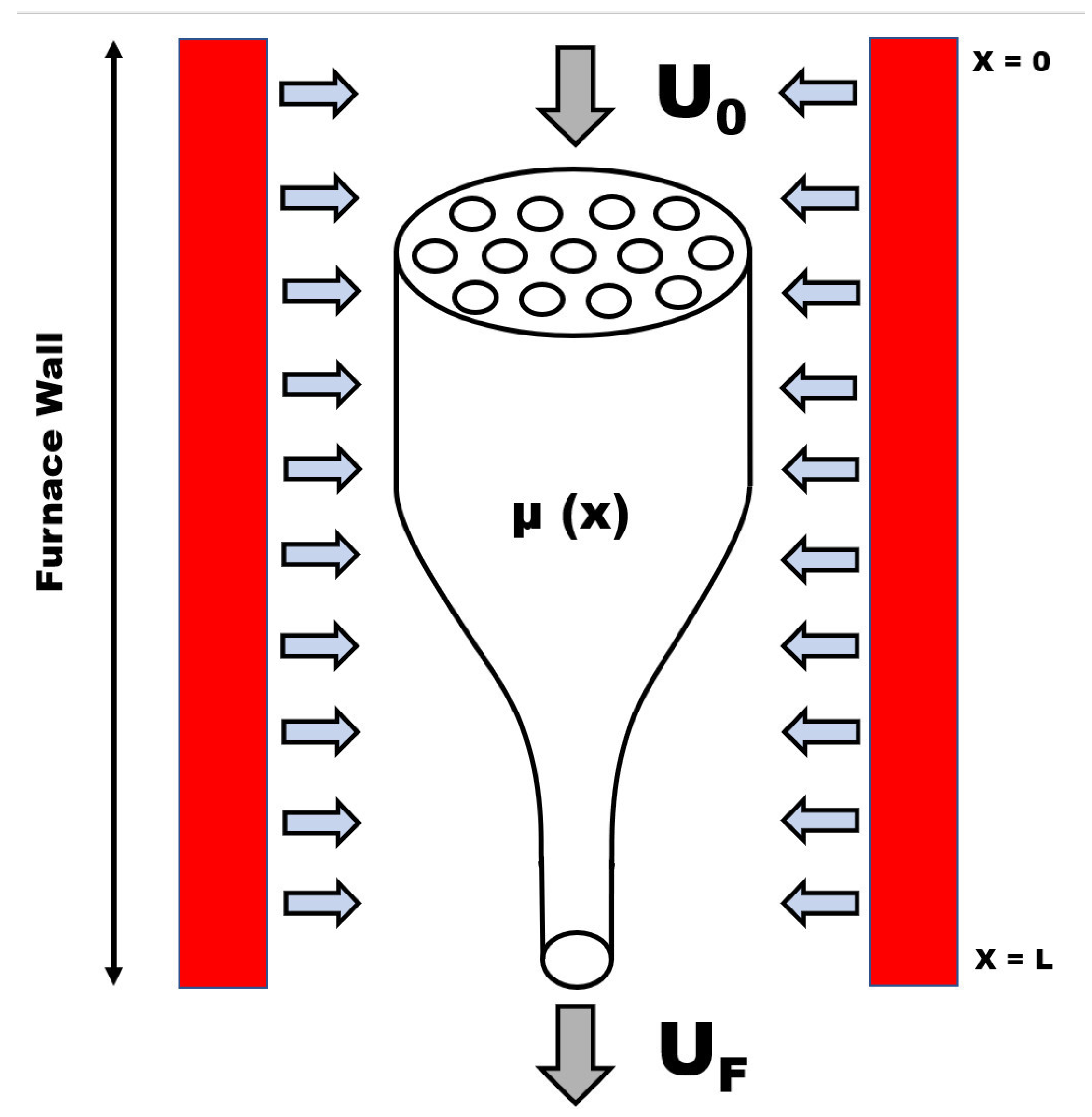
2. Model Description
2.1. Three-dimensional model
2.2. Non-Dimensionalization
2.3. Final Asymptotic Equations
2.3.1. Leading-order model for the transverse flow
2.3.2. The case of a circular tube
2.3.3. The cross-plane problem and the complex variable formulation
2.3.4. The Generalised Elliptical Pore Model (GEPM)
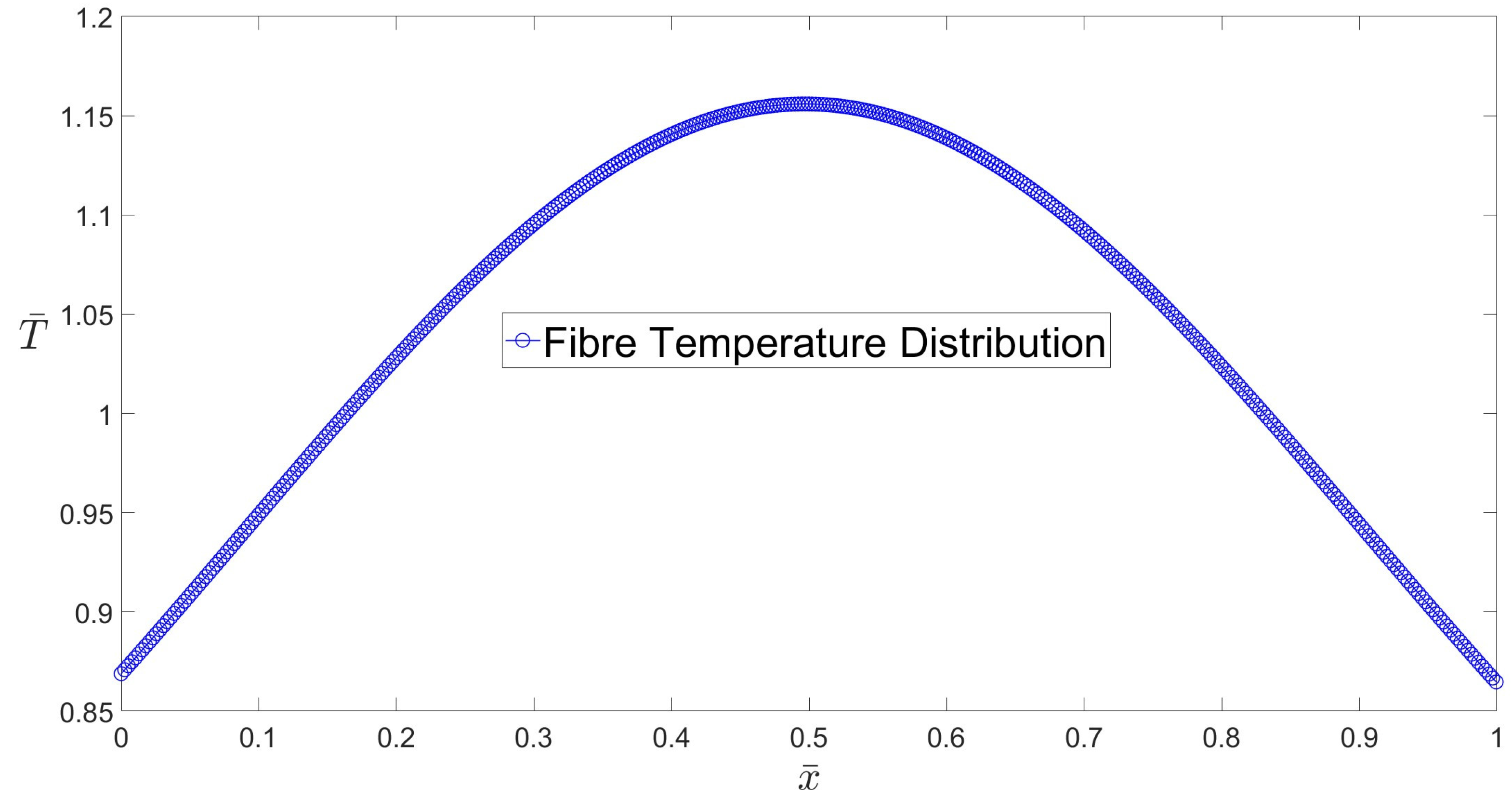
2.3.5. Fibre temperature profile and glass viscosity
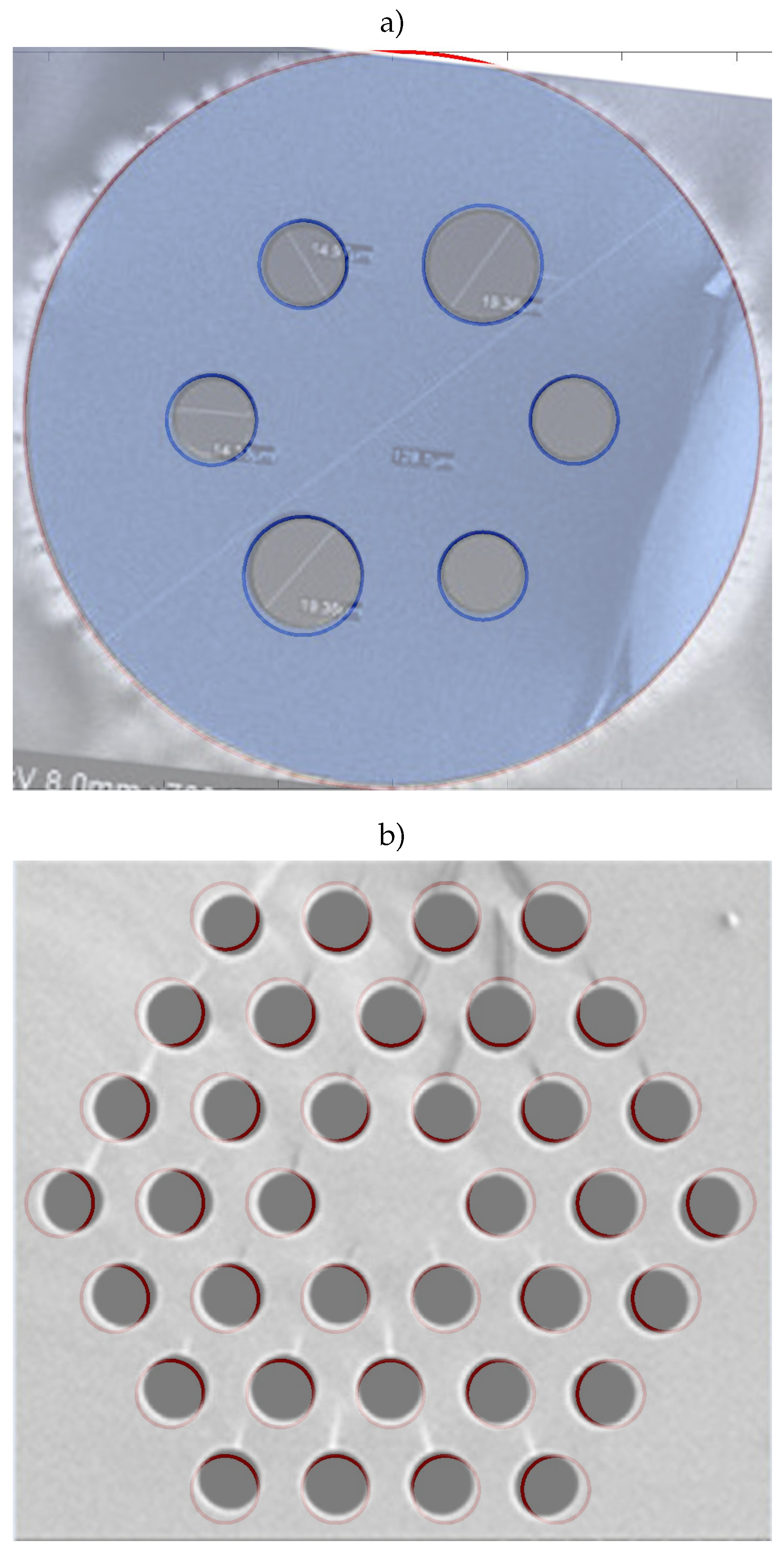
3. Results
3.1. Solution methodology
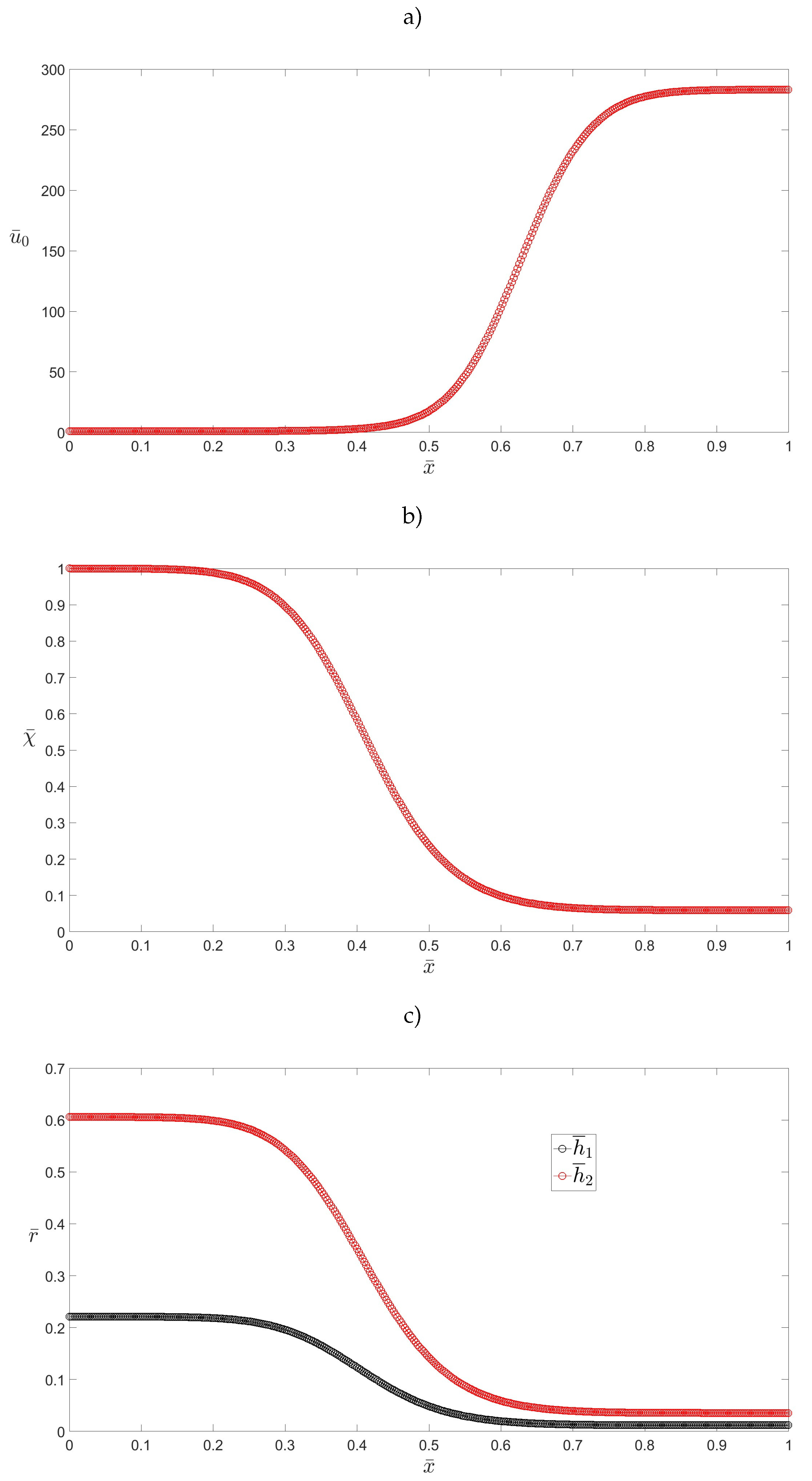
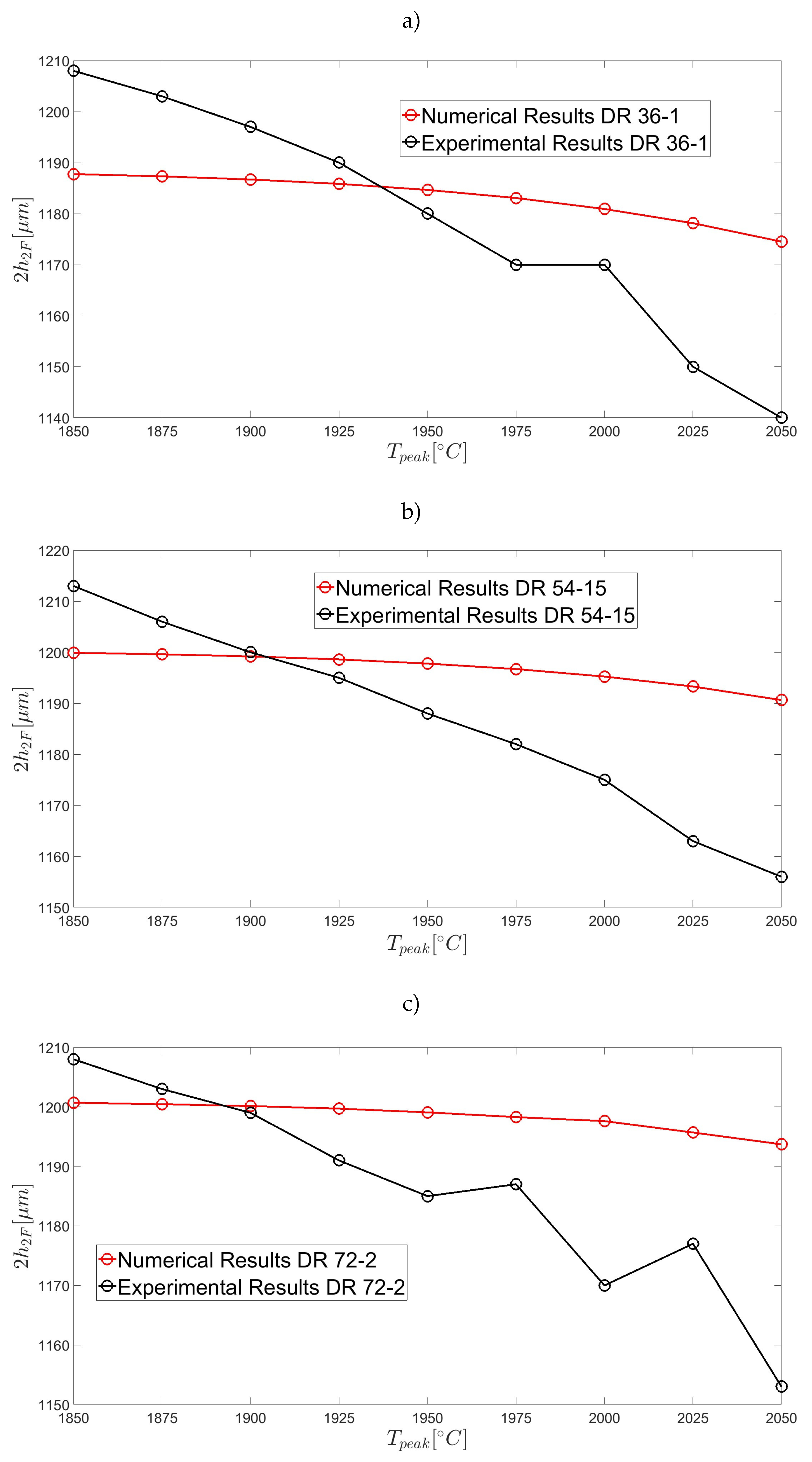
3.2. Annular Capillaries: Slow Drawing Ratios (SDRs)
3.3. Annular Capillaries: High Drawing Ratios (HDRs)
3.4. Holey Fibres (HFs)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCFs | Photonic Crystal Fibres |
| MOFs | Microstructured Optical Fibres |
| TIR | Total Internal reflection |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| GEPM | Generalized Elliptical Pore Model |
| DR | Drawing Ratio |
| SDRs | Slow Drawing Ratios |
| HDRs | High Drawing Ratios |
| HFs | Holey Fibres |
| SEM | Scanning Elecron Microscope |
References
- Russell, P.S. Photonic-Crystal Fibers. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2006, 24, 4729–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.C. Photonic crystal fibres. Nature 2003, 424, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczynski, R. Photonic Crystal Fibers. Acta Physica Polonica A 2004, 106, 141–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monro, T.M.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H. PROGRESS IN MICROSTRUCTURED OPTICAL FIBERS. Annual Review of Materials Research 2006, 36, 467–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, W.; Percival, R.; Bouwmans, G.; Knight, J.; Russell, P. High power air-clad photonic crystal fibre laser. Optics express 2003, 11, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, G.; Knight, J.; Bouwmans, G.; Russell, P.; Williams, D.; Roberts, P.; Mangan, B. Hollow core photonic crystal fibers for beam delivery. Optics express 2004, 12, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Teodoro, F.; Brooks, C.D. 1.1 MW peak-power, 7 W average-power, high-spectral-brightness, diffraction-limited pulses from a photonic crystal fiber amplifier. Optics letters 2005, 30, 2694–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dainese, P.; St. Russell, P.J.; Joly, N.; Knight, J.C.; Wiederhecker, G.S.; Fragnito, H.L.; Laude, V.; Khelif, A. Stimulated Brillouin scattering from multi-GHz-guided acoustic phonons in nanostructured photonic crystal fibres. Nature Physics 2006, 2, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikov, S.V.; Zhu, Y.; Taylor, J.R.; Gapontsev, V.P. Supercontinuum self-Q-switched ytterbium fiber laser. Optics letters 1997, 22, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyachionjeka, K.; Tarus, H.; Langat, K. Design of a photonic crystal fiber for optical communications application. Scientific African 2020, 9, e00511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabid, F.; Knight, J.C.; Antonopoulos, G.; Russell, P.S.J. Stimulated Raman scattering in hydrogen-filled hollow-core photonic crystal fiber. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2002, 298, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monro, T.M.; Belardi, W.; Furusawa, K.; Baggett, J.C.; Broderick, N.G.R.; Richardson, D.J. Sensing with microstructured optical fibres. Measurement Science and Technology 2001, 12, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.A.F.; Pospori, A.; Demirci, G.; Çetinkaya, O.; Gawdzik, B.; Antunes, P.; Bang, O.; Mergo, P.; André, P.; Webb, D.J. Fast Bragg Grating Inscription in PMMA Polymer Optical Fibres: Impact of Thermal Pre-Treatment of Preforms. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matovich, M.A.; Pearson, J.R.A. Spinning a Molten Threadline. Steady-State Isothermal Viscous Flows. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals 1969, 8, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, U.C.; Runk, R.B. Physical behavior of the neck–down region during furnace drawing of silica fibers. Journal of Applied Physics 1978, 49, 4417–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicksman, L.R. The Dynamics of a Heated Free Jet of Variable Viscosity Liquid at Low Reynolds Numbers. Journal of Basic Engineering 1968, 90, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.R. A model for unsteady analysis of preform drawing. AIChE Journal 1989, 35, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Gospodinov, P.; Roussinov, V.I. Stability loss and sensitivity in hollow fiber drawing. Physics of Fluids 1994, 6, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitt, A.D.; Furusawa, K.; Monro, T.M.; Please, C.P.; Richardson, D.J. The mathematical modelling of capillary drawing for holey fibre manufacture. Journal of Engineering Mathematics 2002, 43, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, G.; Epple, P.; Scharrer, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Rauh, C.; Delgado, A. Influence of Surface Tension and Inner Pressure on the Process of Fibre Drawing. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2010, 28, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, G.; Epple, P.; Scharrer, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Rauh, C.; Delgado, A. Asymptotic Analysis of Flow Processes at Drawing of Single Optical Microfibres. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyce, C.J.; Fitt, A.D.; Monro, T.M. The mathematical modelling of rotating capillary tubes for holey-fibre manufacture. Journal of Engineering Mathematics 2008, 60, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyce, C.J.; Fitt, A.D.; Monro, T.M. Mathematical Modeling as an Accurate Predictive Tool in Capillary and Microstructured Fiber Manufacture: The Effects of Preform Rotation. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2008, 26, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroni, M.; Breward, C.J.W.; Cummings, L.J.; Griffiths, I.M. Asymptotic solutions of glass temperature profiles during steady optical fibre drawing. Journal of Engineering Mathematics 2013, 80, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, G.; Lee, S.; Gatternig, B.; Delgado, A. An Asymptotic Energy Equation for Modelling Thermo Fluid Dynamics in the Optical Fibre Drawing Process. Energies 2022, 15, 7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewynne, J.N.; Ockendon, J.R.; Wilmott, P. A systematic derivation of the leading-order equations for extensional flows in slender geometries. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 1992, 244, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewynne, J.N.; HOWELL, P.D.; Wilmott, P. SLENDER VISCOUS FIBRES WITH INERTIA AND GRAVITY. The Quarterly Journal of Mechanics and Applied Mathematics 1994, 47, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, I.M.; Howell, P.D. The surface-tension-driven evolution of a two-dimensional annular viscous tube. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2007, 593, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, I.M.; Howell, P.D. Mathematical modelling of non-axisymmetric capillary tube drawing. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2008, 605, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, L.J.; Howell, P.D. On the evolution of non-axisymmetric viscous fibres with surface tension, inertia and gravity. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 1999, 389, 361–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, Y.M.; Buchak, P.; Crowdy, D.G.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H. Drawing of micro-structured fibres: circular and non-circular tubes. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2014, 755, 176–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Stokes, Y.M.; Buchak, P.; Crowdy, D.G.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H. Microstructured optical fibre drawing with active channel pressurisation. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2015, 783, 137–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, Y.M.; Wylie, J.J.; Chen, M.J. Coupled fluid and energy flow in fabrication of microstructured optical fibres. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2019, 874, 548–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchak, P.; Crowdy, D.G.; Stokes, Y.M.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H. Elliptical pore regularisation of the inverse problem for microstructured optical fibre fabrication. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2015, 778, 5–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowdy, D.G. Compressible bubbles in Stokes flow. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2003, 476, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchak, P.; Crowdy, D.G. Surface-tension-driven Stokes flow: A numerical method based on conformal geometry. Journal of Computational Physics 2016, 317, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.C.; Tanner, R.I.; Barton, G.W.; Lwin, R.; Large, M.; Poladian, L. Fabrication of microstructured optical fibers-part I: problem formulation and numerical modeling of transient draw process. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2005, 23, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.C.; Large, M.; Barton, G.W.; Tanner, R.I.; Poladian, L.; Lwin, R. Role of material properties and drawing conditions in the fabrication of microstructured optical fibers. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2006, 24, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.C.; Tanner, R.I.; Barton, G.W.; Lwin, R.; Large, M.; Poladian, L. Fabrication of microstructured optical fibers-part II: numerical modeling of steady-state draw process. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2005, 23, 2255–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzi, G.; Epple, P.; Scharrer, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Rauh, C.; Delgado, A. Numerical Solution and Experimental Validation of the Drawing Process of Six-Hole Optical Fibers Including the Effects of Inner Pressure and Surface Tension. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2012, 30, 1306–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Stokes, Y.M.; Buchak, P.; Crowdy, D.G.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H. Asymptotic Modelling of a Six-Hole MOF. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2016, 34, 5651–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichting, H.; Gersten, K. Boundary-Layer Theory; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, W.E.; Deville, M.O. Slow Viscous Flow; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosz, M.H.; Ahmed, G.; Lapshina, N.; Keding, R.; Babic, F.; Joly, N.Y.; St. Russell, P.J. Reducing losses in solid-core photonic crystal fibers using chlorine dehydration. Optical Materials Express 2016, 6, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
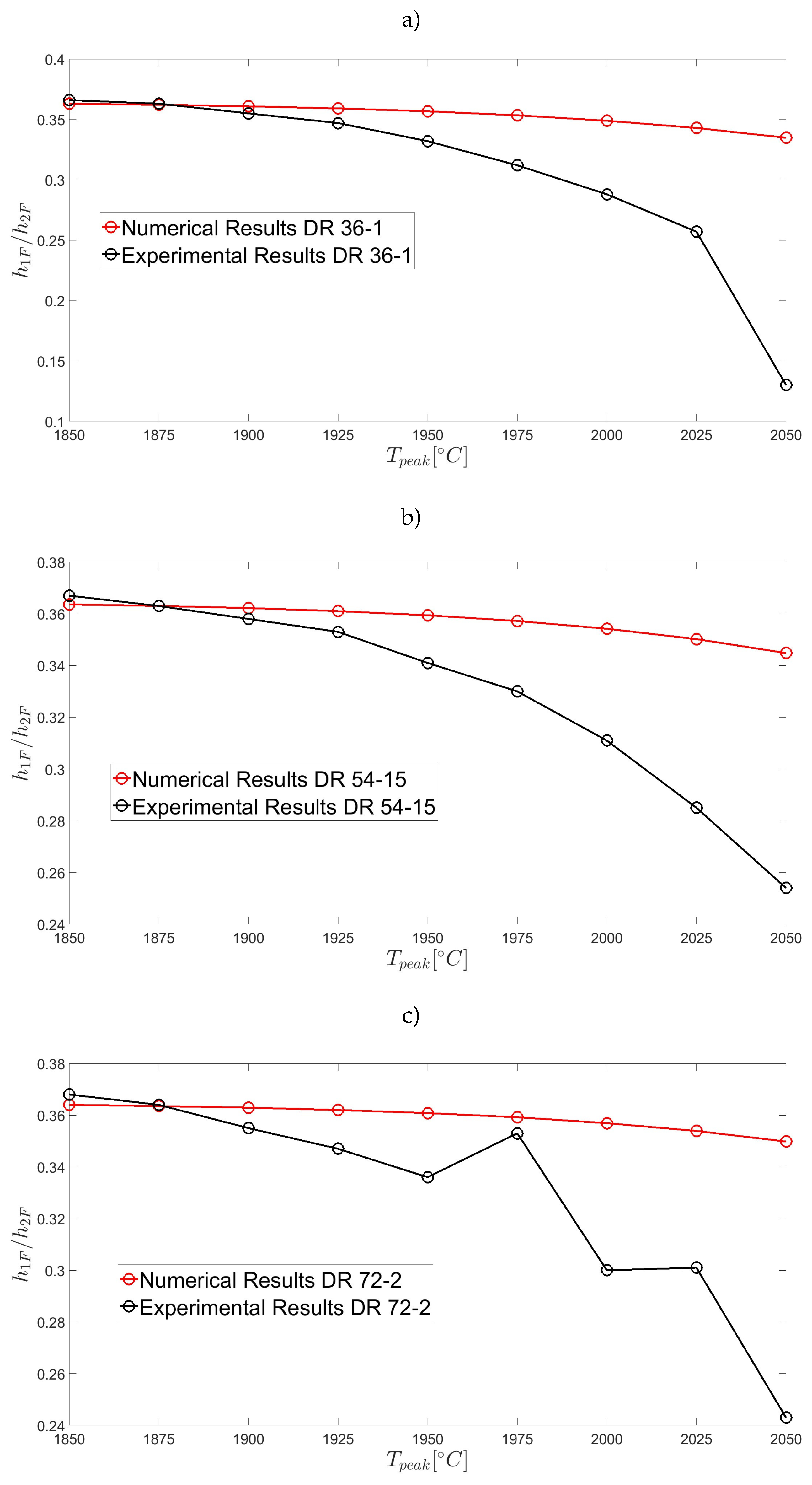
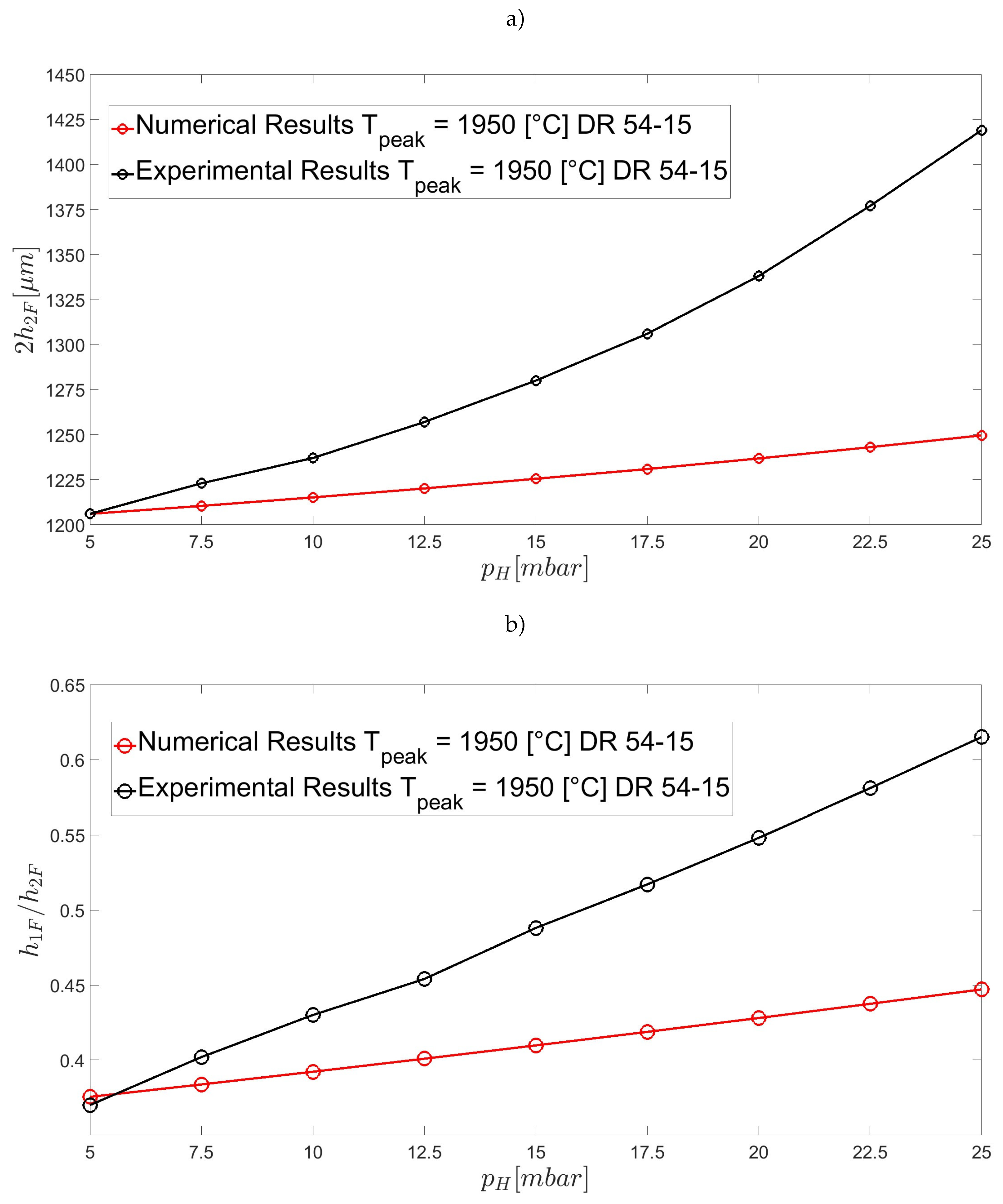
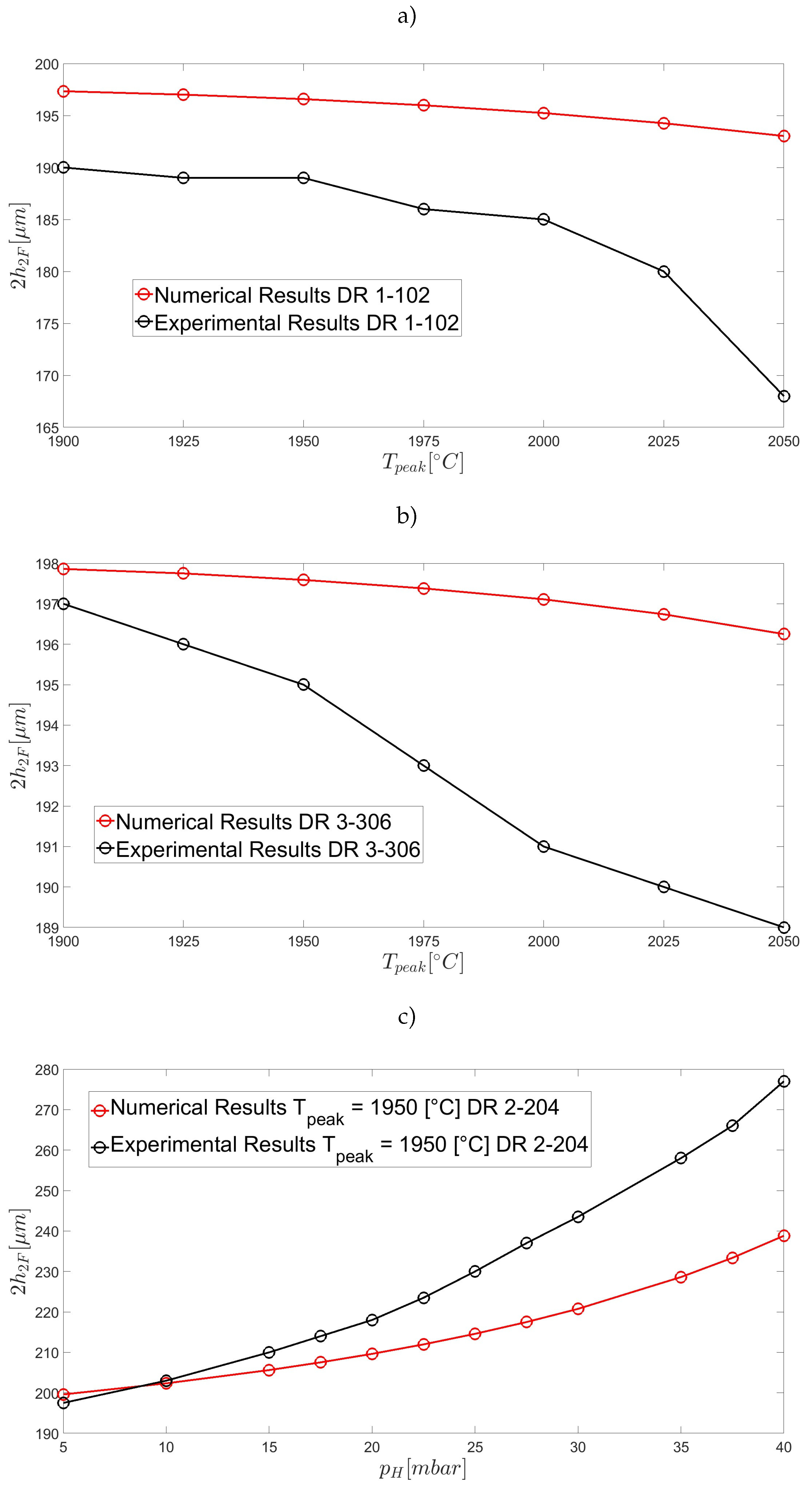
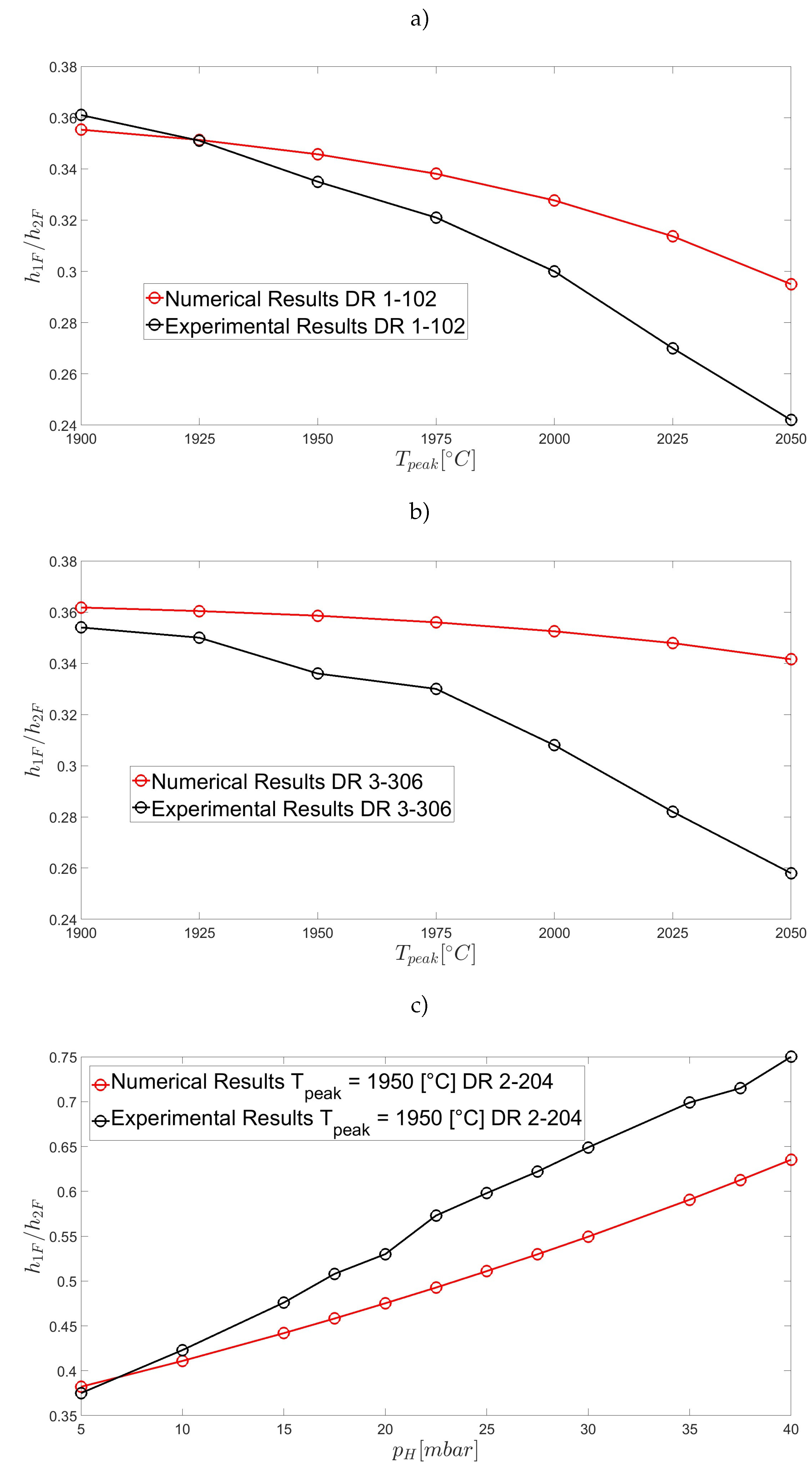
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot zone length | L | 0.12 | m |
| Density | 2200 | kg m | |
| Surface tension | 0.25 | N m | |
| Initial external radius | 1 × 10 | m | |
| Initial internal radius | 3.65 × 10 | m | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 36-1 | ||
| Feed speed | 6 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 1.67 × 10 | m s | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 54-15 | ||
| Feed speed | 9 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 2.5 × 10 | m s | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 72-2 | ||
| Feed speed | 1.2 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 3.33 × 10 | m s | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 1-102 | ||
| Feed speed | 1.67 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 1.7 × 10 | m s | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 2-204 | ||
| Feed speed | 3.33 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 0.34 × 10 | m s | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 3-306 | ||
| Feed speed | 5.00 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 0.51 × 10 | m s | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 20-187 | ||
| Feed speed | 3.33 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 0.312 × 10 | m s | |
| Drawing ratio | DR 10-42 | ||
| Feed speed | 1.67 × 10 | m s | |
| Draw speed | 0.7 × 10 | m s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





