Submitted:
30 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. General aim of this study:
1.2. Main hypotheses:
1.2.1. Health indicators:
1.2.2. Healthy life style:
2. Materials and Methods
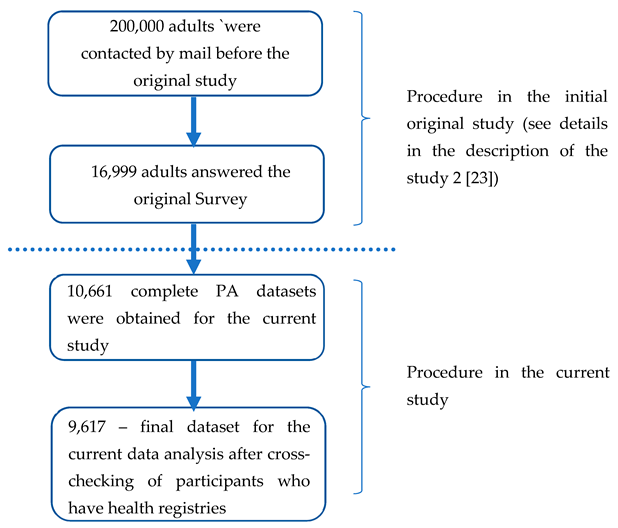
2.1. Participants and original data collections
2.2. Study design and variables
2.3. Data analysis
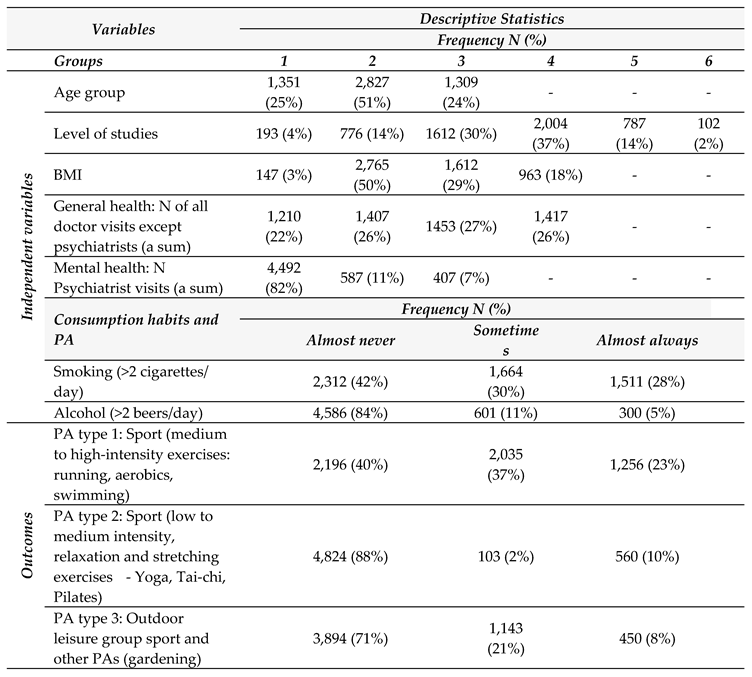
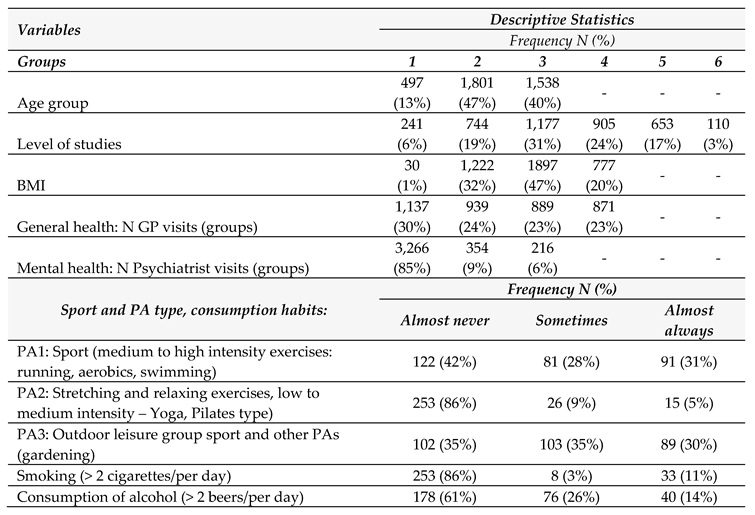
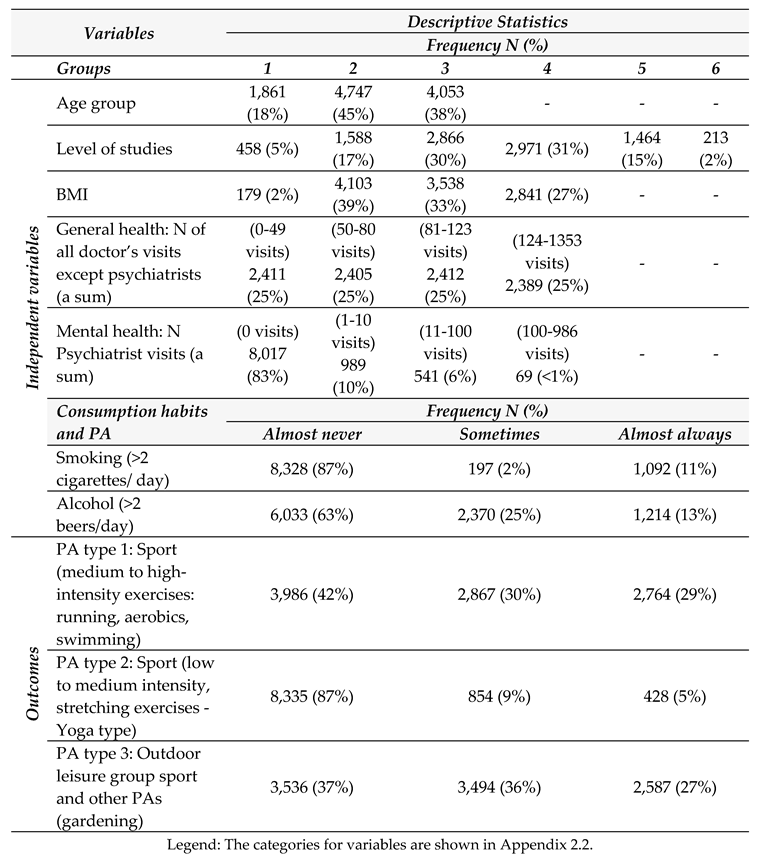
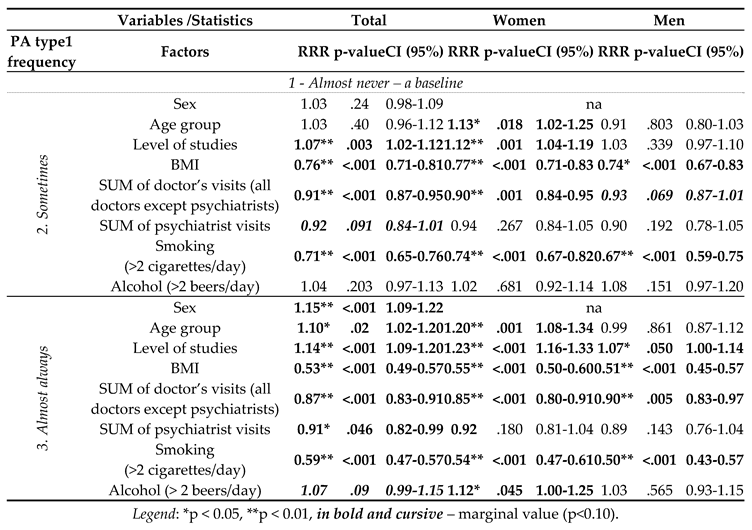
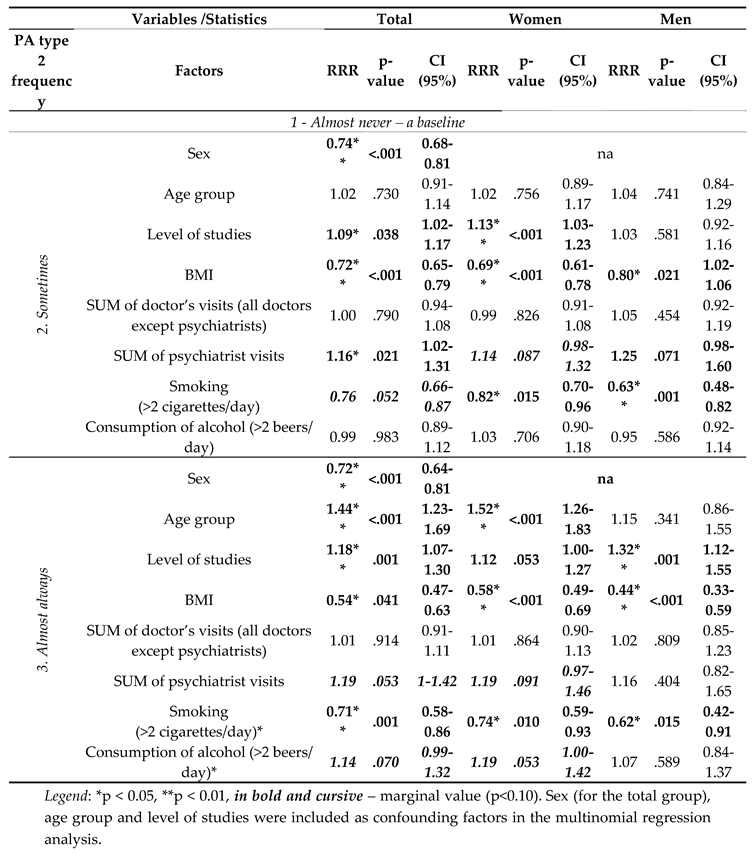
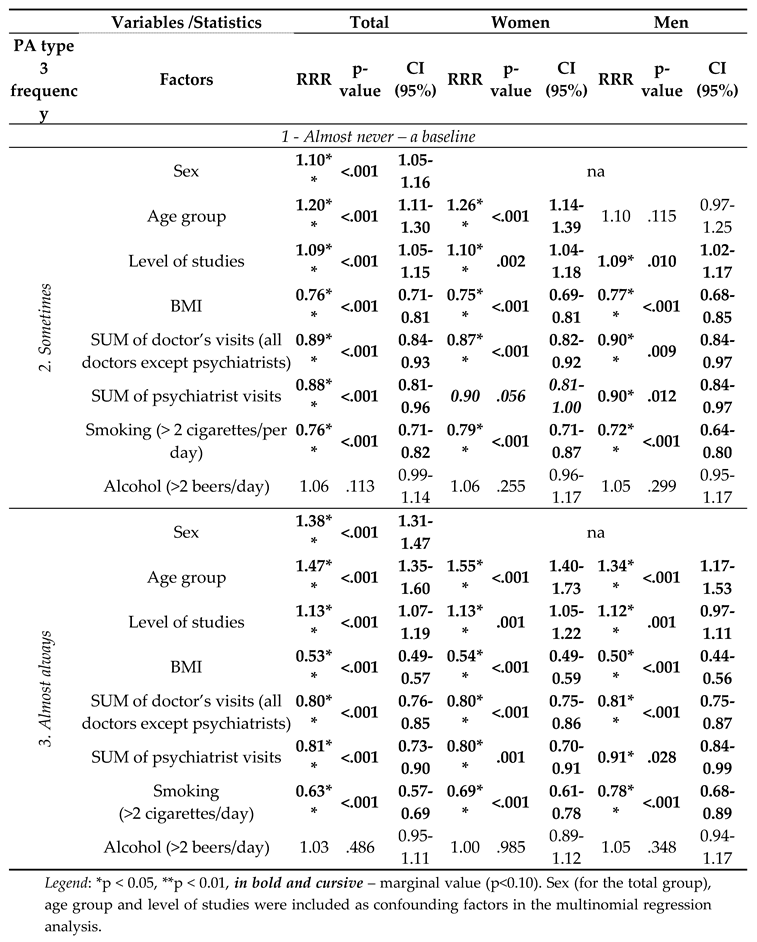
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. General Discussion
4.2. Study Limitations
4.3. Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest

 |
 |
References
- Moylan, S.; Eyre, H.A.; Maes, M.; Baune, B.T.; Jacka, F.N.; Berk, M. Exercising the Worry Away: How Inflammation, Oxidative and Nitrogen Stress Mediates the Beneficial Effect of Physical Activity on Anxiety Disorder Symptoms and Behaviours. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerterp, K.R. Control of Energy Expenditure in Humans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, B.E.; Watson, K.B.; Ridley, K.; Pfeiffer, K.A.; Herrmann, S.D.; Crouter, S.E.; McMurray, R.G.; Butte, N.F.; Bassett, D.R.; Trost, S.G.; et al. Utility of the Youth Compendium of Physical Activities. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2018, 89, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henchoz, Y.; Dupuis, M.; Deline, S.; Studer, J.; Baggio, S.; N’Goran, A.A.; Daeppen, J.-B.; Gmel, G. Associations of Physical Activity and Sport and Exercise with At-Risk Substance Use in Young Men: A Longitudinal Study. Prev. Med. 2014, 64, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katano, H.; Ohno, M.; Yamada, K. Protection by Physical Activity Against Deleterious Effect of Smoking on Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Young Japanese. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Södergren, M.; Wang, W.C.; Salmon, J.; Ball, K.; Crawford, D.; McNaughton, S.A. Predicting Healthy Lifestyle Patterns among Retirement Age Older Adults in the WELL Study: A Latent Class Analysis of Sex Differences. Maturitas 2014, 77, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnafick, F.-E.; Thøgersen-Ntoumani, C. The Effect of the Physical Environment and Levels of Activity on Affective States. J. Environ. Psychol. 2014, 38, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conger, S.A.; Bassett, D.R. A Compendium of Energy Costs of Physical Activities for Individuals Who Use Manual Wheelchairs. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 2011, 28, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (2021). Physical Activity Fact Sheet (No. WHO/HEP/HPR/RUN/2021.2). World Health Organization.
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Asare, M. Physical Activity and Mental Health in Children and Adolescents: A Review of Reviews. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzum, H.; Stickel, A.; Corona, M.; Zeller, M.; Melrose, R.J.; Wilkins, S.S. Potential Benefits of Physical Activity in MCI and Dementia. Behav. Neurol. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morres, I.D.; Hatzigeorgiadis, A.; Stathi, A.; Comoutos, N.; Arpin-Cribbie, C.; Krommidas, C.; Theodorakis, Y. Aerobic Exercise for Adult Patients with Major Depressive Disorder in Mental Health Services: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Depress. Anxiety 2019, 36, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.; O’ Sullivan, R.; Caserotti, P.; Tully, M.A. Consequences of Physical Inactivity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Reviews and Meta-analyses. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-C.; Chao, C.-L.; Huang, M.-N. Psychological Effects of Physical Activity: A Quasi-Experiment in an Indigenous Community. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2014, 26, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Pereira, J.; Silverio, J.; Carvalho, S.; Ribeiro, J.C.; Fonte, D.; Ramos, J. Moderate Exercise Improves Depression Parameters in Treatment-Resistant Patients with Major Depressive Disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2011, 45, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, J.; Videbech, P.; Thomsen, C.; Gluud, C.; Nordentoft, M. DEMO-II Trial. Aerobic Exercise versus Stretching Exercise in Patients with Major Depression—A Randomised Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinas, P.C.; Koutedakis, Y.; Flouris, A.D. Effects of Exercise and Physical Activity on Depression. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 180, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Marín, J.; Asún, S.; Estrada-Marcén, N.; Romero, R.; Asún, R. Efectividad de un programa de estiramientos sobre los niveles de ansiedad de los trabajadores de una plataforma logística: un estudio controlado aleatorizado. Aten. Primaria 2013, 45, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, G.W.; Silverman, D.H.S.; Siddarth, P.; Ercoli, L.M.; Miller, K.J.; Lavretsky, H.; Wright, B.C.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Barrio, J.R.; Phelps, M.E. Effects of a 14-Day Healthy Longevity Lifestyle Program on Cognition and Brain Function. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 14, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Gray, T.; Truong, S.; Sahlberg, P.; Bentsen, P.; Passy, R.; Ho, S.; Ward, K.; Cowper, R. A Systematic Review Protocol to Identify the Key Benefits and Efficacy of Nature-Based Learning in Outdoor Educational Settings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczak, M.; Avalosse, H.; Vancorenland, S.; Verniest, R.; Callens, M.; Van Broeck, N.; Fantini-Hauwel, C.; Mierop, A. A Nationally Representative Study of Emotional Competence and Health. Emotion 2015, 15, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefken, K.; Junge, A.; Laemmle, L. How Does Sport Affect Mental Health? An Investigation into the Relationship of Leisure-Time Physical Activity with Depression and Anxiety. Hum. Mov. 2019, 20, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, S.A.; Eather, N.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Hillman, C.H.; Lubans, D.R. High-Intensity Interval Training for Cognitive and Mental Health in Adolescents. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, A.A.; Mavilidi, M.F.; Smith, J.J.; Hillman, C.H.; Eather, N.; Barker, D.; Lubans, D.R. Review of High-Intensity Interval Training for Cognitive and Mental Health in Youth. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martland, R.; Mondelli, V.; Gaughran, F.; Stubbs, B. Can High-Intensity Interval Training Improve Physical and Mental Health Outcomes? A Meta-Review of 33 Systematic Reviews across the Lifespan. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 430–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakoulis, A.; Fatouros, I.G. Psychological Adaptations to High-Intensity Interval Training in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Topical Review. Sports 2022, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluska, S.A.; Schwenk, T.L. Physical Activity and Mental Health. Sports Med 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindwall, M.; Ljung, T.; Hadžibajramović, E.; Jonsdottir, I.H. Self-Reported Physical Activity and Aerobic Fitness Are Differently Related to Mental Health. Ment. Health Phys. Act. 2012, 5, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisha, N.E.; Sussman, S. Relationship of High School and College Sports Participation with Alcohol, Tobacco, and Illicit Drug Use: A Review. Addict. Behav. 2010, 35, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanly, S.L.; Maniazhagu, D. Individual and Combined Interventions of Tai Chi, Pilates and Yogic Practices on Cardio Respiratory Endurance of b.Ed. Trainees. Int. J. Phys. Educ. Sports Manag. Yogic Sci. 2020, 10, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Gao, S. Effects of Mind-Body Exercises on Cognitive Impairment in People with Parkinson’s Disease: A Mini-Review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 931460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.J.; Remick, R.A.; Davis, J.C.; Vazirian, S.; Khan, K.M. Exercise as Medicine—the Use of Group Medical Visits to Promote Physical Activity and Treat Chronic Moderate Depression: A Preliminary 14-Week Pre–Post Study. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2015, 1, e000036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, W.; Wongwattanapong, T.; Laskin, J.J.; Ajjimaporn, A. Benefits of Thai Yoga on Physical Mobility and Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Overweight/Obese Older Women: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2021, 43, 101345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takiguchi, Y.; Matsui, M.; Kikutani, M.; Ebina, K. The Relationship between Leisure Activities and Mental Health: The Impact of Resilience and COVID-19. Appl. Psychol. Health Well-Being 2023, 15, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, G.; Jopp, D.; Gobet, F.; Ogawa, M.; Ishioka, Y.; Masui, Y.; Inagaki, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Yasumoto, S.; Ishizaki, T.; et al. The Impact of Leisure Activities on Older Adults’ Cognitive Function, Physical Function, and Mental Health. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0225006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondé, M.P.; Santana, V.S. Participation in Leisure Activities: Is It a Protective Factor for Women’s Mental Health? J. Leis. Res. 2000, 32, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müllersdorf, M.; Granström, F.; Sahlqvist, L.; Tillgren, P. Aspects of Health, Physical/Leisure Activities, Work and Socio-Demographics Associated with Pet Ownership in Sweden. Scand. J. Public Health 2010, 38, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.Y.; Powell, M.P.; Peel, C.; Zhu, S.; Allman, R. Leisure-Time Physical Activity and Health-Care Utilization in Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2006, 14, 392–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.L.; Harrison, E.L.; Reeder, B.A.; Sari, N.; Chad, K.E. Is Self-Reported Physical Activity Participation Associated with Lower Health Services Utilization among Older Adults? Cross-Sectional Evidence from the Canadian Community Health Survey. J. Aging Res. 2015, 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Rottenberg, Y.; Cohen, A.; Stessman, J. Physical Activity and Health Service Utilization Among Older People. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musich, S.; Wang, S.S.; Hawkins, K.; Greame, C. The Frequency and Health Benefits of Physical Activity for Older Adults. Popul. Health Manag. 2017, 20, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, S.; Levante, A.; García-Conesa, M.-T.; Lecciso, F.; Scoditti, E.; Carluccio, M.A.; Calabriso, N.; Damiano, F.; Santarpino, G.; Verri, T.; et al. Assessment of Subjective Well-Being in a Cohort of University Students and Staff Members: Association with Physical Activity and Outdoor Leisure Time during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashper, K.; King, J. The Outdoors as a Contested Leisure Terrain. Ann. Leis. Res. 2022, 25, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, E.K.; Williams, N.; Schwartz, F.; Bullard, C. Benefits of Campus Outdoor Recreation Programs: A Review of the Literature. J. Outdoor Recreat. Educ. Leadersh. 2017, 9, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandford, R.A.; Duncombe, R.; Armour, K.M. The Role of Physical Activity/Sport in Tackling Youth Disaffection and Anti-social Behaviour. Educ. Rev. 2008, 60, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henstock, M.; Barker, K.; Knijnik, J. 2, 6, Heave! Sail Training’s Influence on the Development of Self-Concept and Social Networks and Their Impact on Engagement with Learning and Education. A Pilot Study. J. Outdoor Environ. Educ. 2013, 17, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornienko, D.S.; Rudnova, N.A. Exploring the Associations between Happiness, Lifesatisfaction, Anxiety, and Emotional Regulation among Adults during the Early Stage of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Russia. Psychol. Russ. State Art 2023, 16, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosanova, V.I.; Bondarenko, I.N.; Fomina, T.G. Conscious Self-Regulation, Motivational Factors, and Personality Traits as Predictors of Students’ Academic Performance: A Linear Empirical Model. Psychol. Russ. State Art 2022, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlomov, K.D.; Bochaver, A.A.; Korneev, A.A. Well-Being and Coping with Stress Among Russian Adolescents in Different Educational Environments. Psychol. Russ. State Art 2021, 14, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.B.; Stevenson, K.T.; Larson, L.R.; Peterson, M.N.; Seekamp, E. Outdoor Activity Participation Improves Adolescents’ Mental Health and Well-Being during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmstad University, Center of Research on Welfare, Health and Sport, Halmstad, Sweden; Johnson, U. ; Ivarsson, A.; Halmstad University, Center of Research on Welfare, Health and Sport, Halmstad, Sweden; Parker, J.; Halmstad University, Center of Research on Welfare, Health and Sport, Halmstad, Sweden; Andersen, M.B.; Halmstad University, Center of Research on Welfare, Health and Sport, Halmstad, Sweden; Svetoft, I.; Halmstad University, School of Business, Engineering and Science, Halmstad, Sweden Connection in the Fresh Air: A Study on the Benefits of Participation in an Electronic Tracking Outdoor Gym Exercise Programme. Montenegrin J. Sports Sci. Med. 2019, 8, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deforche, B.; Lefevre, J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Hills, A.P.; Duquet, W.; Bouckaert, J. Physical Fitness and Physical Activity in Obese and Nonobese Flemish Youth. Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel Mart??Nez-Gonz??Lez, M.; Javier Varo, J.; Luis Santos, J.; De Irala, J.; Gibney, M.; Kearney, J.; Alfredo Mart??Nez, J. Prevalence of Physical Activity during Leisure Time in the European Union: Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Park, N.; Sun, J.K.; Smith, J.; Peterson, C. Life Satisfaction and Frequency of Doctor Visits. Psychosom. Med. 2014, 76, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Omar, K.; Rütten, A. Relation of Leisure Time, Occupational, Domestic, and Commuting Physical Activity to Health Indicators in Europe. Prev. Med. 2008, 47, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G.; Carnemolla, M.; Everett, C.J. Adherence to Healthy Lifestyle Habits in US Adults, 1988-2006. Am. J. Med. 2009, 122, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liutsko, L.; Mikolajczak, M.; Veraksa, A.; Leonov, S. OP VIII – 4 Type of Physical Activity, Diet, Bmi and Tobacco/Alcohol Consumption Relationship: Which of Them Affect More Our Health? In Proceedings of the Green, physical activity, mobility; BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, March 2018; p. A16.1-A16. [Google Scholar]
- Holstila, A.; Mänty, M.; Rahkonen, O.; Lahelma, E.; Lahti, J. Changes in Leisure-Time Physical Activity and Physical and Mental Health Functioning: A Follow-up Study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guddal, M.H.; Stensland, S.Ø.; Småstuen, M.C.; Johnsen, M.B.; Zwart, J.-A.; Storheim, K. Physical Activity and Sport Participation among Adolescents: Associations with Mental Health in Different Age Groups. Results from the Young-HUNT Study: A Cross-Sectional Survey. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, M.; Stull, T.; Claussen, M.C. Prevention and Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders through Physical Activity, Exercise, and Sport. Sports Psychiatry 2022, 1, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancassiani, F.; Machado, S.; Preti, A. Physical Activity, Exercise and Sport Programs as Effective Therapeutic Tools in Psychosocial Rehabilitation. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2018, 14, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspersen, C. J. , Pereira, M. A., & Curran, K. M. Changes in Physical Activity Patterns in the United States, by Sex and Cross-Sectional Age. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2000, 32, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Egli, T.; Bland, H.W.; Melton, B.F.; Czech, D.R. Influence of Age, Sex, and Race on College Students’ Exercise Motivation of Physical Activity. J. Am. Coll. Health 2011, 59, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-M. Physical Activity and Weight Gain Prevention. JAMA 2010, 303, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, L.C.; Matthews, K.A. Understanding the Association between Socioeconomic Status and Physical Health: Do Negative Emotions Play a Role? Psychol. Bull. 2003, 129, 10–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerovasili, V.; Agaku, I.T.; Vardavas, C.I.; Filippidis, F.T. Levels of Physical Activity among Adults 18–64 Years Old in 28 European Countries. Prev. Med. 2015, 81, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maertl, T.; De Bock, F.; Huebl, L.; Oberhauser, C.; Coenen, M.; Jung-Sievers, C. ; on behalf of the COSMO Study Team Physical Activity during COVID-19 in German Adults: Analyses in the COVID-19 Snapshot Monitoring Study (COSMO). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paavola, M.; Vartiainen, E.; Haukkala, A. Smoking, Alcohol Use, and Physical Activity: A 13-Year Longitudinal Study Ranging from Adolescence into Adulthood. J. Adolesc. Health 2004, 35, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza-Gardner, A.K.; Barry, A.E. Examining Physical Activity Levels and Alcohol Consumption: Are People Who Drink More Active? Am. J. Health Promot. 2012, 26, e95–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peele, S.; Brodsky, A. Exploring Psychological Benefits Associated with Moderate Alcohol Use: A Necessary Corrective to Assessments of Drinking Outcomes? Drug Alcohol Depend. 2000, 60, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge, T.; Clarke, P.; Dwan, R. The Relationship Between Physical Activity and Alcohol Use Among Adults in the United States: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Am. J. Health Promot. 2017, 31, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J. F. Age-Related Decline in Physical Activity: A Synthesis of Human and Animal Studies. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2000, 32, 1598–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Peral-Suárez, Á.; Cuadrado-Soto, E.; Perea, J.M.; Navia, B.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Ortega, R.M. Physical Activity Practice and Sports Preferences in a Group of Spanish Schoolchildren Depending on Sex and Parental Care: A Gender Perspective. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





