Submitted:
30 October 2023
Posted:
31 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Derivation of the Higgs Potential from Catastrophe Theory
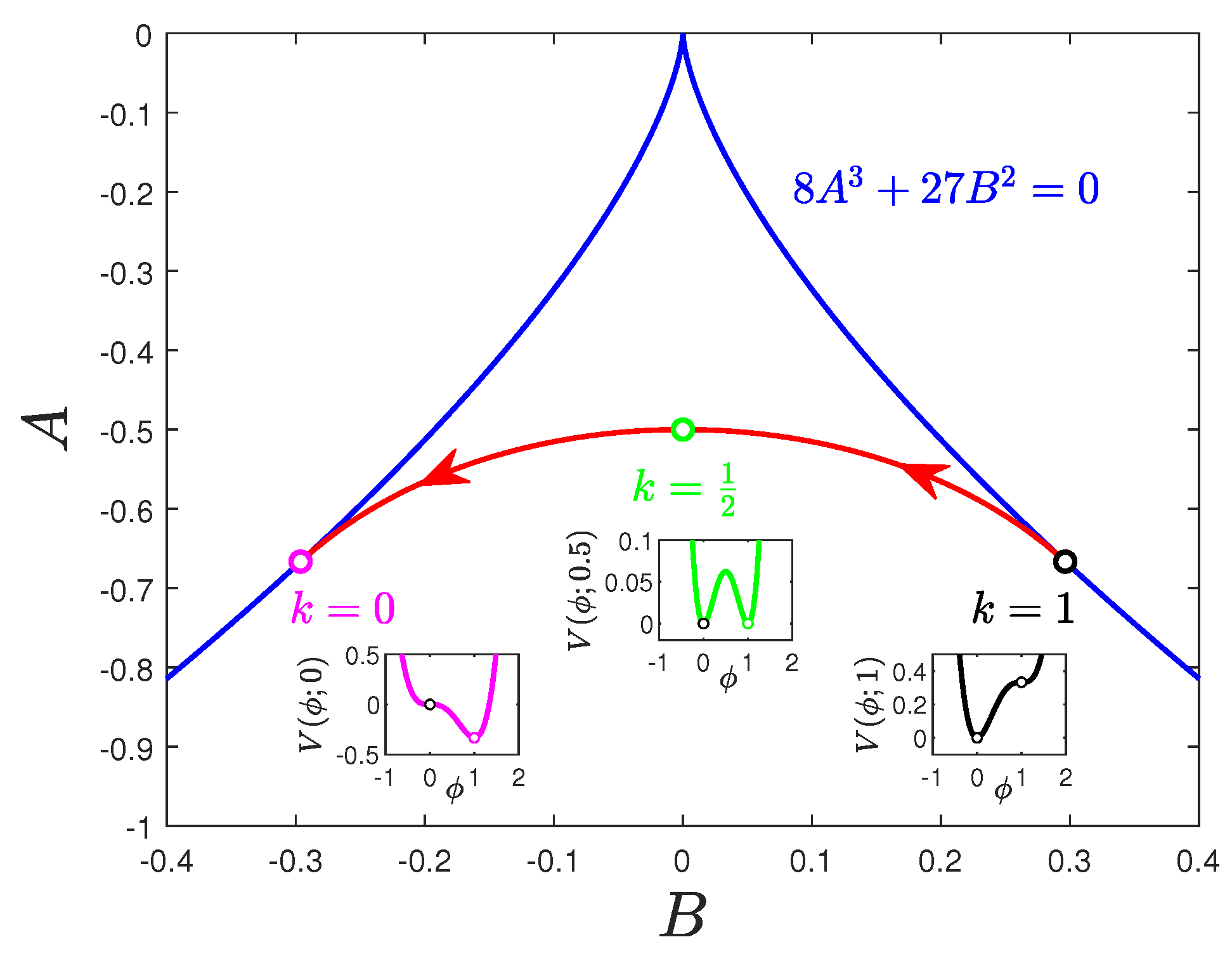
2.1. Method 1: Relying on Catastrophe Theory and Stable Isolated States
2.2. Method 2: Implementing a Shortcut
2.2.1. Utilizing a Familiarity Heuristic
2.2.2. Looking Back to Landau’s Theory of Phase Transitions
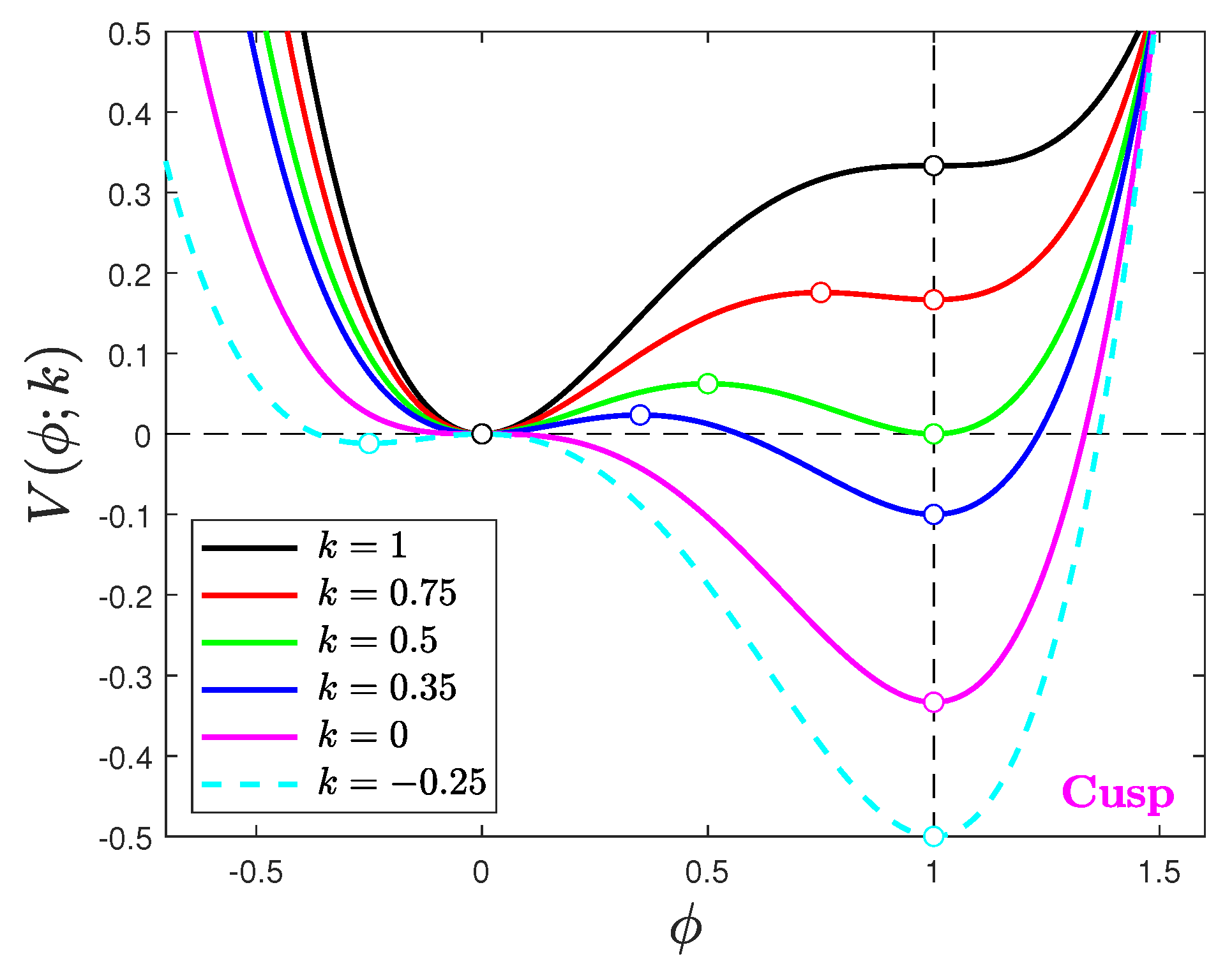
3. Discussion of Phase Transitions
3.1. The Higgs Phase Transition
3.2. The Maxwell Convention and Chemical Reactions
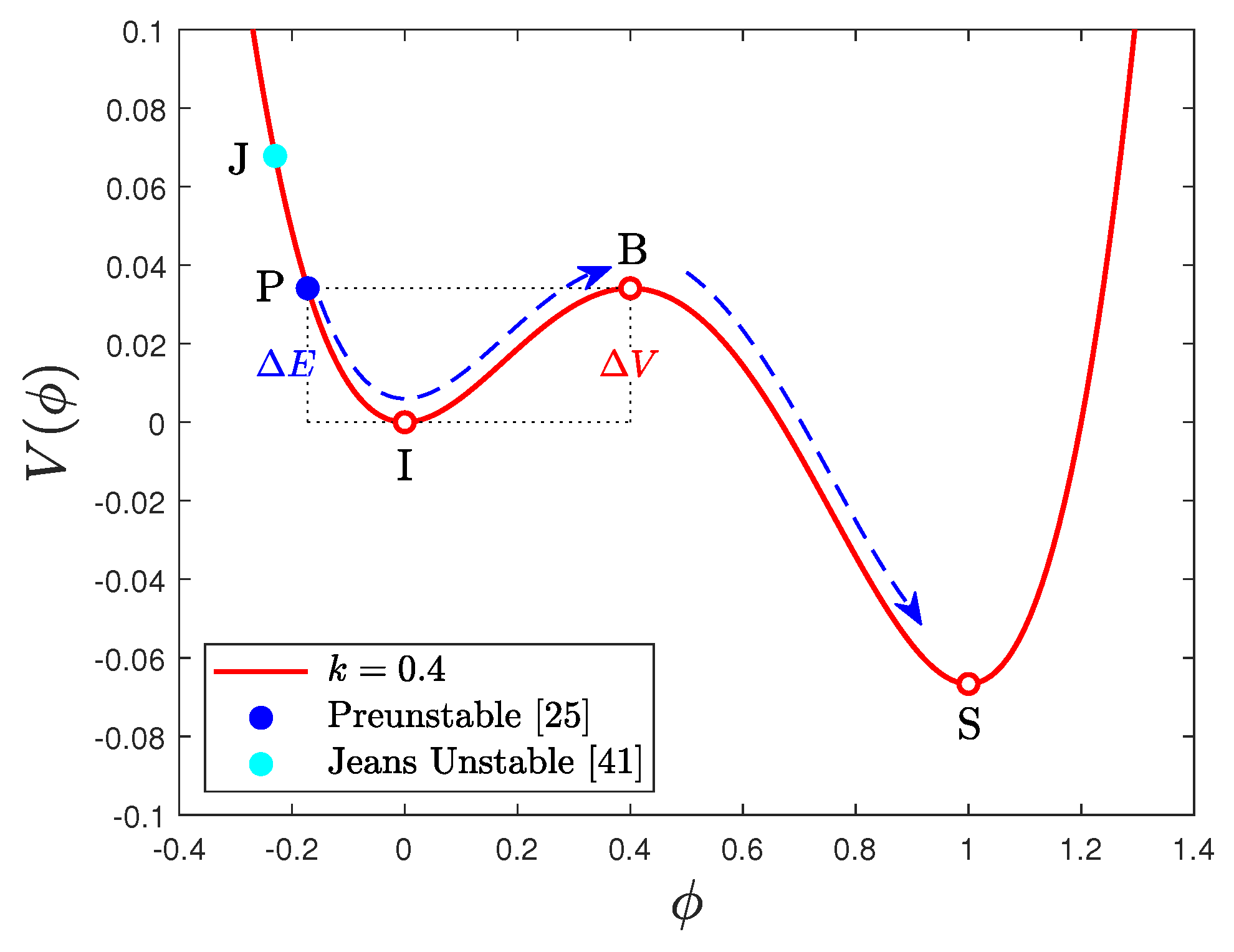
3.3. Overcoming the Energy Barrier
3.4. Star-Forming Phase Transitions
3.5. Peculiar -Transitions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
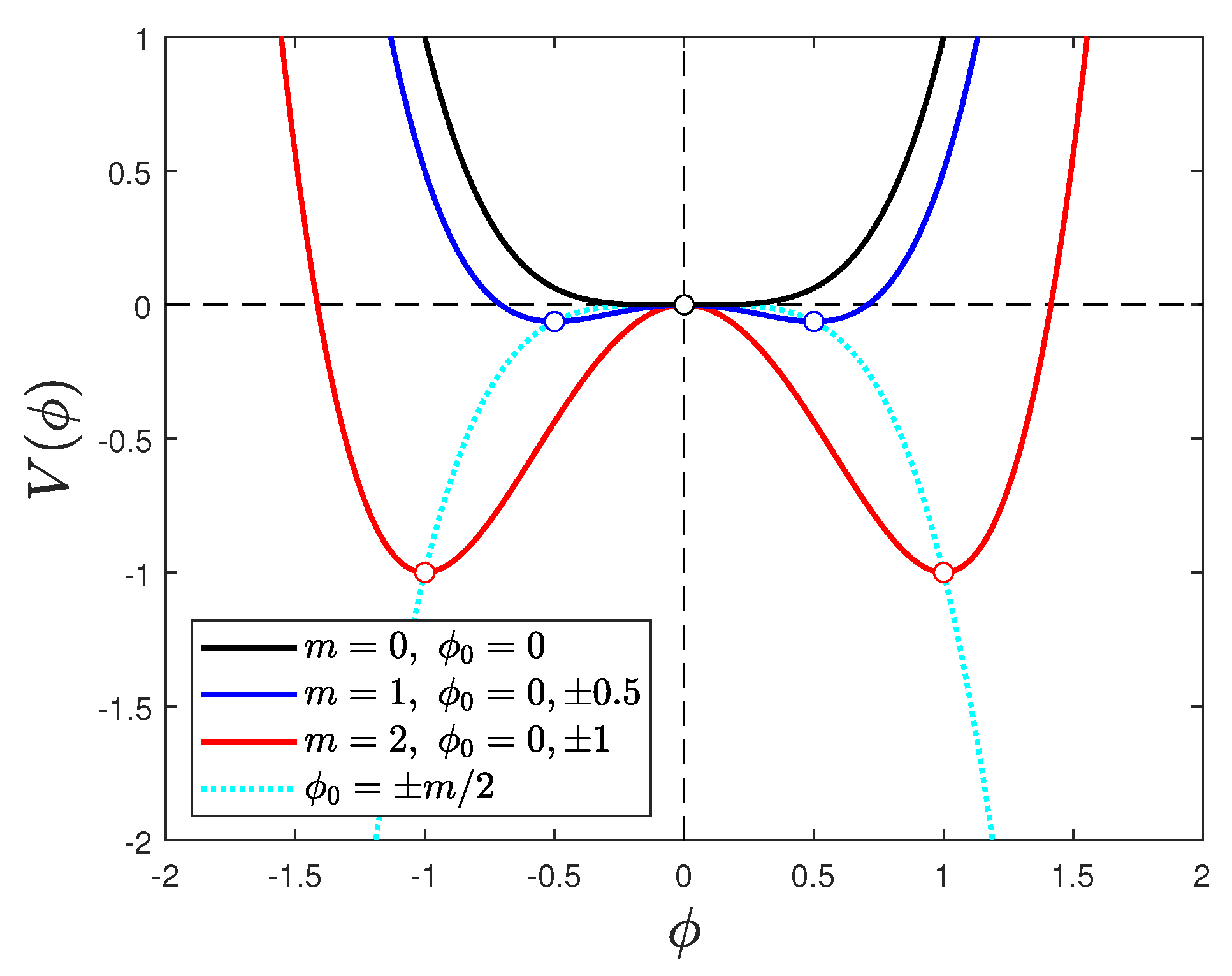
Appendix A. The Potentials of Higher-Order Catastrophes
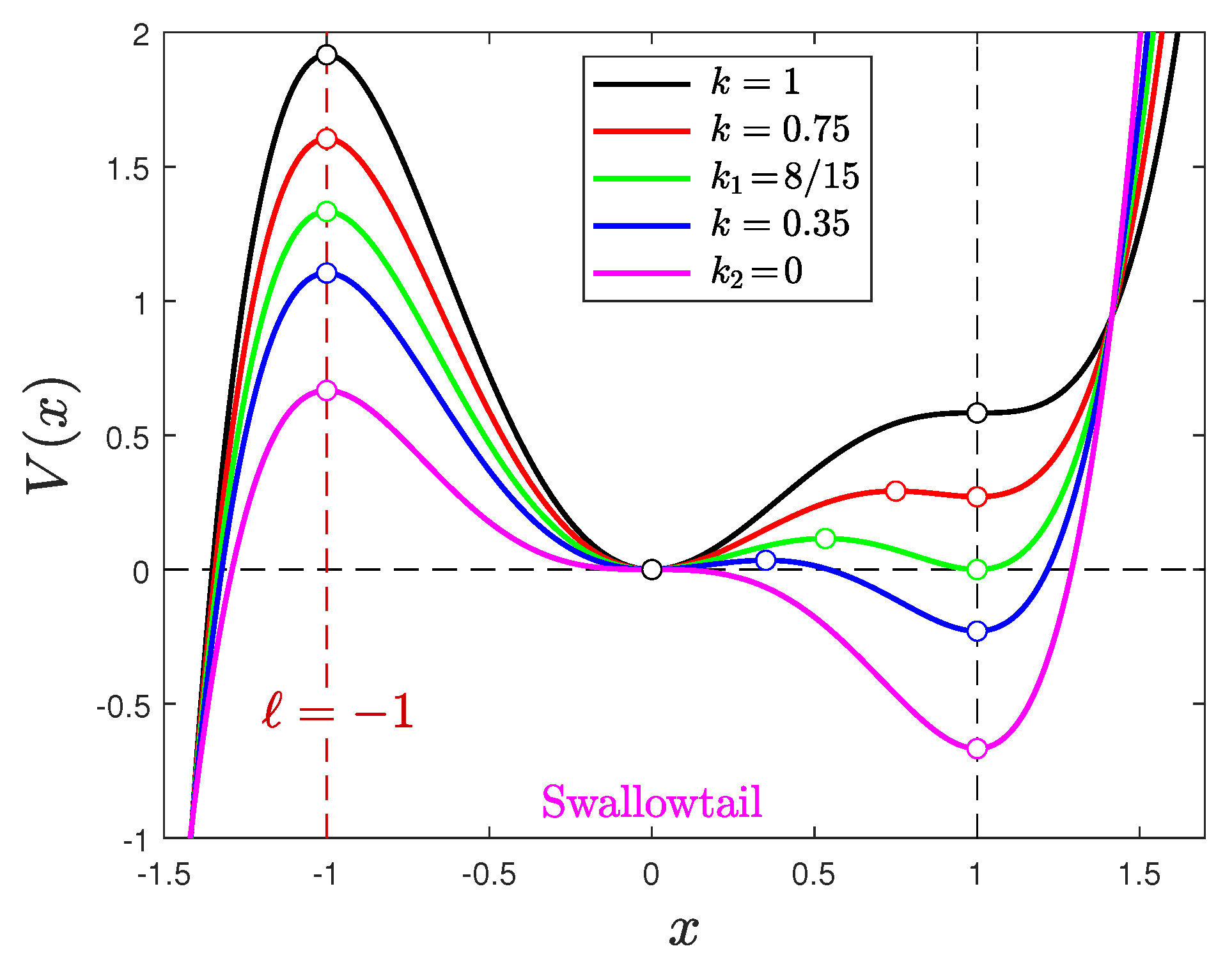
Appendix A.1. Swallowtail Potentials
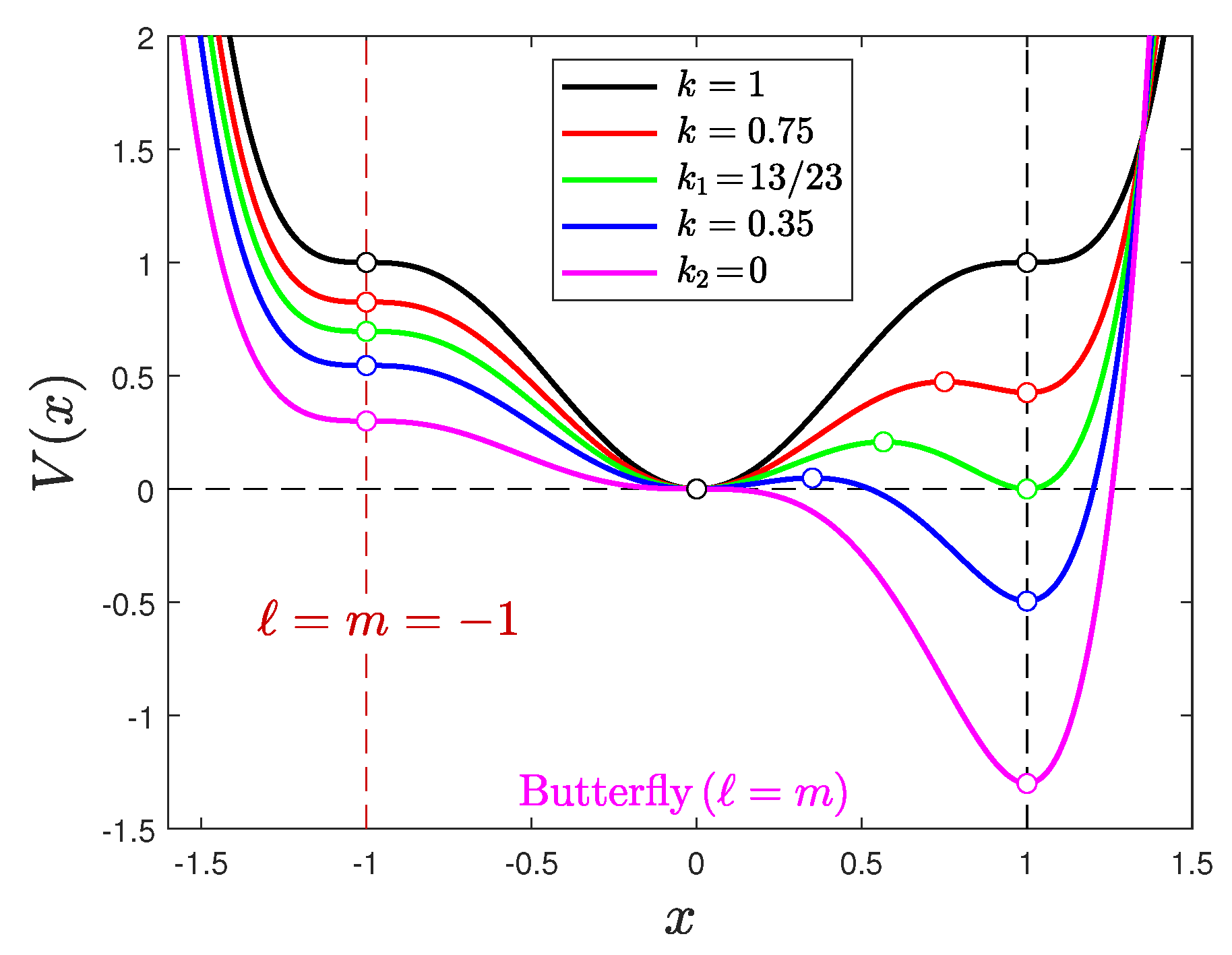
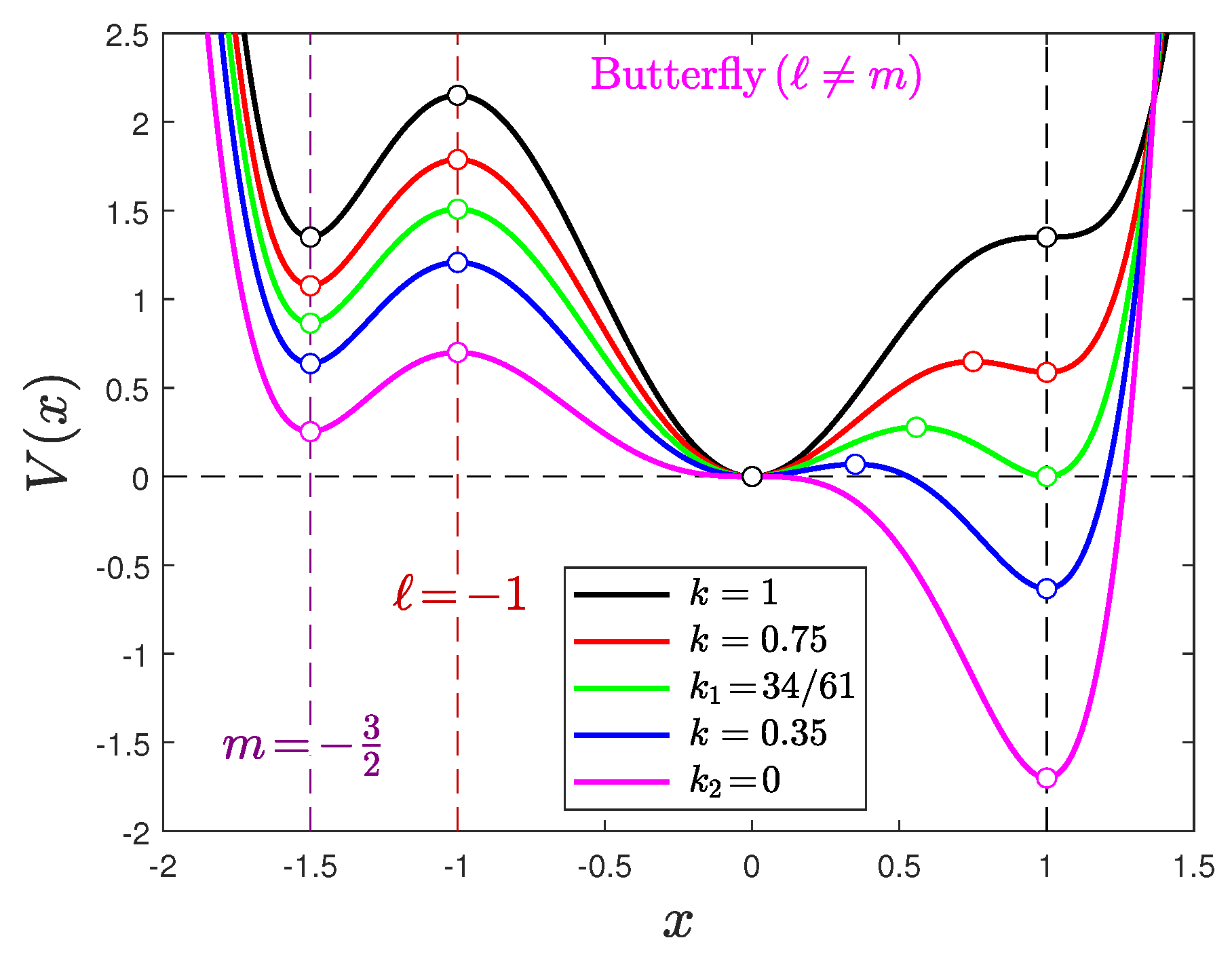
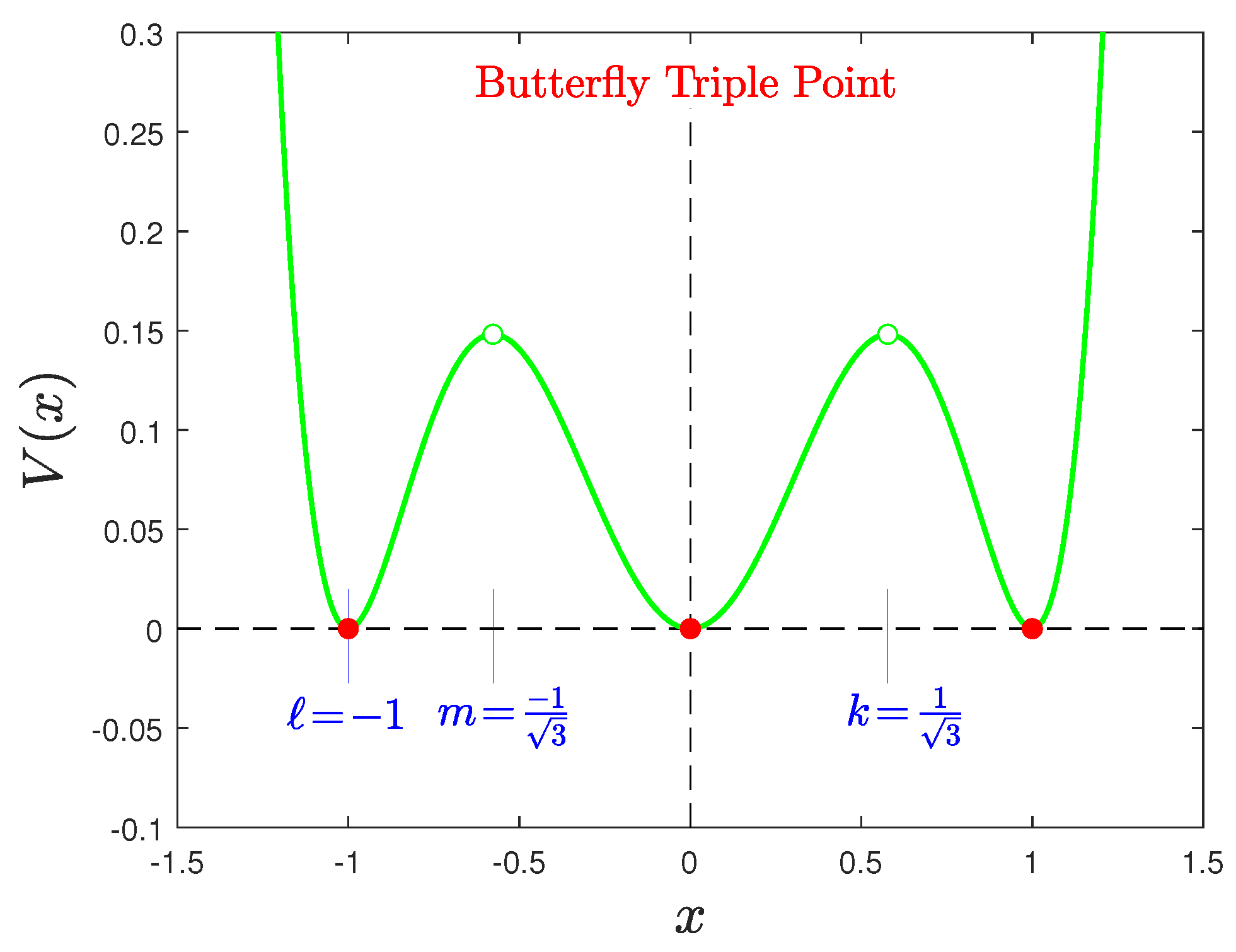
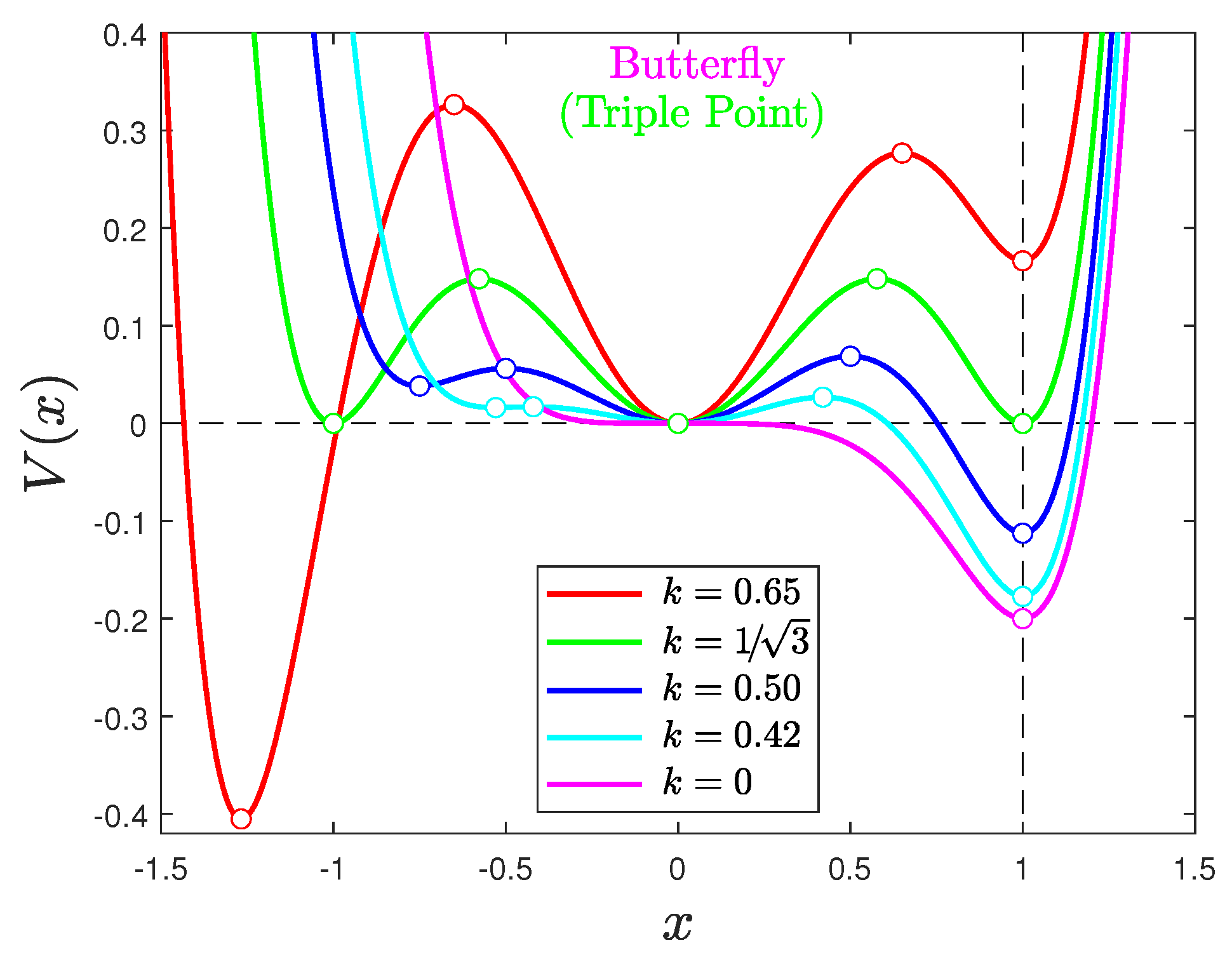
Appendix A.2. Butterfly and Triple-Point Potentials
References
- Landau, L. D.; Lifshitz, E. G. Statistical physics, 3rd ed., Vol. 5, Part 1, Pergamon Press, New York, 1980.
- Tohline, J. E.; Bodenheimer, P. H.; Christodoulou, D. M. The crucial role of cooling in the making of molecular clouds and stars. Astrophys. J., 1987, 322, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D. M.; Tohline, J. E. Phase transition time scales for cooling and isothermal media. Astrophys. J., 1990, 363, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, R. Structural stability and morphogenesis, Benjamin Press, Reading, 1975.
- Poston, T.; Stewart, I. Catastrophe theory and its applications, Dover, New York, 1988.
- Gilmore, R. Catastrophe theory for scientists and engineers, Dover, New York, 1981.
- Drazin, P. G.; Reid, W. H. Hydrodynamic stability, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1981.
- Christodoulou, D. M.; Kazanas, D.; Shlosman, I.; Tohline, J. E. Phase-transition theory of instabilities. IV. Astrophys. J., 1995, 446, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. The quantum theory of fields, Vol. II, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1995.
- Peskin, M. E.; Schroeder, D. V. An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1995.
- Perkins, D. H. Introduction to high energy physics, 4th ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000.
- Bali, G. S. QCD forces and heavy quark bound states. Phys. Rep., 2001, 343, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D. Introduction to elementary particles, 2nd ed., Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008.
- Goldstone, J. Field theories with “Superconductor” solutions. Nuovo Cim., 1961, 19, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Gravitation and cosmology, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1972.
- D’Onofrio, M.; Rummukainen, K.; Tranberg, A. Sphaleron rate in the minimal Standard Model. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2014, 113, 141602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Rummukainen, K. Standard Model cross-over on the lattice. Phys. Rev. D, 2016, 93, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, F. A solution to the electroweak horizon problem in the Rh=ct universe. Eur. Phys. J. C, 2018, 78, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melia, F. The electroweak horizon problem. Phys. Dark Universe, 2022, 37, 101057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, J. M. There is no electroweak horizon problem. Phys. Dark Universe, 2022, 37, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aad, G.; Abajyan, T.; Abbott, B.; Abdallah, J.; Abdel Khalek, S.; Abdelalim, A.A.; Abdinov, O.; Aben, R.; Abi, B.; Abolins, M.; et al. (ATLAS Collaboration) Observation of a new particle in the search for the Standard Model Higgs boson with the ATLAS detector at the LHC. Phys. Lett. B, 2012, 716, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrchyan, S.; Khachatryan, V.; Sirunyan, A. M.; Tumasyan, A.; Adam, W.; Aguilo, E.; Bergauer, T.; Dragicevic, M.; Erö, J.; Fabjan, C.; et al. (CMS Collaboration) Observation of a new boson at a mass of 125 GeV with the CMS experiment at the LHC. Phys. Lett. B, 2012, 716, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyla, P. A.; Barnett, R. M.; Beringer, J.; Dahl, O.; Dwyer, D.A.; Groom, D.E.; Lin, C.-J.; Lugovsky, K.S.; Pianori, E.; Robinson, D.J.; et al. (Particle Data Group) Review of particle physics, Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys., 2020, 2020(8), 083C01.
- Workman, R.L.; Burkert, V.D.; Crede, V.; Klempt, E.; Thoma, U.; Tiator, L.; Agashe, K.; Aielli, G.; Allanach, B.C.; Amsler, C.; et al. (Particle Data Group) Review of particle physics. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2022, 2022(8), 083C01. [Google Scholar]
- Whitworth, A. Global gravitational stability for one-dimensional polytropes. Mon. Not. Roy. Astr. Soc., 1981, 195, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D. M.; Kazanas, D.; Shlosman, I.; Tohline, J. E. Phase-transition theory of instabilities. I. Astrophys. J., 1995, 446, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohline, J. E. Star formation: Phase transition, not Jeans instability. Astrophys. J., 1985, 292, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohline, J. E.; Christodoulou, D. M. Star formation via the phase transition of an adiabatic gas. Astrophys. J., 1988, 325, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D. M.; Kazanas, D.; Shlosman, I.; Tohline, J. E. Phase-transition theory of instabilities. II. Astrophys. J., 1995, 446, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwikert, S. R.; Curran, T. Familiarity and recollection in heuristic decision making. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen., 2014, 143, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K. Statistical mechanics, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1963.
- Pippard, A. B. Elements of classical thermodynamics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1966.
- Stanley, H. E. Introduction to phase transitions and critical phenomena, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1971.
- Gilmore, R. Catastrophe time scales and conventions. Phys. Rev. A, 1979, 20, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerk-Maxwell, J. On the dynamical evidence of the molecular constitution of bodies. J. Chem. Soc., 1875, 28, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espenson, J. H. Chemical kinetics and reaction mechanisms, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, 1995.
- Steinfeld, J. I.; Francisco, J. S.; Hase, W. L. Chemical kinetics and dynamics, 2nd ed., Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, N.J., 1999.
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J. Physical chemistry, 8th ed., Freeman, New York, 2006.
- Berg, J. M.; Tymoczko, J. L.; Gatto, Jr., G. J.; Stryer, L. Biochemistry, 9th ed., Freeman & Co., New York, 2019.
- Wade, L. G.; Simek, J. W. Organic chemistry, 10th ed., Pearson, Upper Saddle River, N.J., 2023.
- Jeans, J. H. The stability of a spherical nebula. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A, 1902, 199, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bertin, G.; Radicati, L.A. The bifurcation from the Maclaurin to the Jacobi sequence as a second-order phase transition. Astrophys. J., 1976, 206, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S. Oscillation and collapse of interstellar clouds. Astrophys. J., 1976, 208, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J. H., Jr. The influence of initial velocity fields upon star formation. Astrophys. J., 1979, 233, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J. H., Jr.; Fleck, R. C. Star formation: The influence of velocity fields and turbulence. Astrophys. J., 1982, 256, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D. M.; Kazanas, D. E. Varying-G gravity. Mon. Not. Roy. Astr. Soc., 2023, 519, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. Crystal statistics. I. A two-dimensional model with an order-disorder transition. Phys. Rev., 1944, 65, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Dangelmayr, G.; Eikemeier, H. Phase diagrams and catastrophes, In Structural stability in physics, ed. Güttinger, W. & Eikemeier, H., Springer, Berlin, pp. 186-198, 1979.
- Madsen, A.; Als-Nielsen, J.; Hallmann, J.; Roth, T.; Lu, W. Critical behavior of the order-disorder phase transition in β-brass investigated by x-ray scattering. Phys. Rev. B, 2016, 94, 014111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar. S. Ellipsoidal figures of equilibrium, Yale University Press, New Haven, CT, 1969.
- Bardeen, J.M. A reexamination of the post-Newtonian Maclaurin spheroids. Astrophys. J., 1971, 167, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachisu, I.; Eriguchi, Y. Bifurcations and phase transitions of self-gravitating and uniformly rotating fluid. Mon. Not. Roy. Astr. Soc., 1983, 204, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachisu, I.; Eriguchi, Y. Bifurcation points on the Maclaurin sequence. PASJ, 1984, 36, 497. [Google Scholar]
- Eriguchi, Y.; Hachisu, I. Maclaurin hamburger sequence. Astron. Astrophys., 1985, 148, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Hachisu, I. A versatile method for obtaining structures of rapidly rotating stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 1986, 61, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachisu, I.; Tohline, J.E.; Eriguchi, Y. Fragmentation of rapidly rotating gas clouds. I. A universal criterion for fragmentation. Astrophys. J., 1987, 323, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Qian, Y.; Lan, Y.; Cui, W. Swallowtail-type diffraction catastrophe beams. Optics Express, 2021, 29, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannotti, A.; Diebel, F.; Denz, C. Dynamics of the optical swallowtail catastrophe. Optica, 2017, 4, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugis, I.; Hassen Kareem, M. Application of swallowtail catastrophe theory to transient stability assessment of multi-machine power system. J. Theor. Appl. Infor. Tech., 2013, 55, 390. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | In contrast, Landau [1] was not thinking about isospin or null quantities when he formulated his theory. To him, symmetries were visible in the arrangement of atoms in a crystal or in the (mis)alignment of magnetic moments in magnetic materials |
| 2 | In all fairness to Landau [1], Thom’s catastrophe theory [4] did not exist in Landau’s time, so he did not know that his Taylor expansion of the potential was not formally correct near the degenerate critical point. In fact, he was apparently lucky to get the rest of the perturbation () right when he correctly eliminated the cubic term (), albeit based on an inconclusive argument (that, for , the curve of phase transitions degenerates to a single point in the plane, where P is pressure); the counterargument is that functions and may have the same zeroes [5] and/or that . |
| 3 | |
| 4 | The point or is where the evolutionary path crosses the B-axis in the control parameter plane (see Figure 3 below). |
| 5 | Recall that catastrophe theory is applicable only to gradient systems [6], so it does not account for time, and qualitative conventions have been invented to describe actual time evolution before and after a phase transition (or “catastrophe”). |
| 6 | So, not all butterfly phase-transition paths are covered in the present investigation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




