1. Introduction
Solar radiation is the source of energy for all movements. As far as the land surface process is concerned, the surface energy balance guarantees the coordination of interactions between land and atmosphere strongly. Energy and material exchanges between land and atmosphere, especially heat and moisture exchanges, have important influences on climate change, which is the core of land surface process studies. Given different climatic backgrounds and underlying surfaces, there are considerable differences in energy exchange processes between the land and atmosphere (Hu et al., 1994; Li et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2003; Bao et al., 2004; Ling et al., 2022). The surface energy can change the structure of the boundary layer, as well as its changing rules, and by changing the energy and material exchange between the land and atmosphere, the surface energy, especially the latent heat flux, affects regional and global climates (Trenberth et al., 2001; Mahrt et al., 2005; Steven et al., 2007; Zhu et al., 2007). In addition, climate change is sensitive to changes of the latent heat flux, which affects the changes of the latent heat flux in turn (Jacobs and De Bruin, 1992; Sun et al., 2021).
Mainly affected by aerodynamic resistance and surface resistance, the degree of coupling between surface vegetation and the surrounding atmosphere can indicate the exchange capacity of matter and energy between land and atmosphere (Penman et al., 1951; Bange, 1953; Mcnaughton et al., 1983; Jarvis et al., 1986). Considered to be an important parameter for water-heat balance near the ground, latent heat flux is mainly affected by the interactions between environmental and surface factors, and the heat (radiation and temperature) and water (soil moisture and atmospheric water vapour pressure deficit) factors are key to controlling latent heat flux between the land and atmosphere (Jarvis et al., 1986; Kellner, 2001; Wever et al., 2002; Al-Shibli et al., 2021). To study the spatial and temporal changes of the latent heat flux during the background of global climate change, researching the degree of coupling between the land and atmosphere and analysing the influence of the environmental factors (mainly considering solar radiation and water vapour pressure deficit) on the latent heat flux are very important. Known as the kidneys of the earth, the alpine wetlands are the main ecological barrier of the Tibetan plateau and one of the most important water conservation areas in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, which are combinations of water, soil and vegetation and are also the area of the most fragile ecological environment, being sensitive to climate change (Li et al., 2009; Li et al., 2012; Tan et al., 2014; Lin et al., 2021). The latent heat flux in the wetlands is larger during the vegetation growing season, is larger at noon, and smaller in the mornings and evenings, the monthly average latent heat flux is higher than those in the nearby alpine meadows (Yu et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2015). Therefore, the study of latent heat flux in alpine wetlands is particularly important. In summary, researching the degree of coupling between the land and atmosphere and exploring the influence of solar radiation and water vapour pressure deficit on the latent heat flux in alpine wetlands of the Yellow River source area play important roles in understanding the hydrological processes of the Yellow River source area, climate change and the regional ecological environment.
At present, the latent heat flux and their environmental control mechanism have being heavily researched. Current research shows that both WRF mode and MODIS satellite data can better describe the latent heat flux of the underlying meadows and the model simulation results are greatly affected by soil moisture and vegetation coverage (Wu et al., 2013; Ye et al., 2014). On a variety of different underlying surfaces such as forest, Phragmites communis, maize field and semi-arid meadow underlying surfaces, the main environmental impact factors of latent heat flux are the net radiation, and other environmental impact factors, like water vapour pressure deficit, the soil temperature and moisture, the relative humidity and the difference between the ground temperature and air temperature can be relatively ignored (Wang et al., 2005; Yu et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2008; Ding et al., 2014). Furthermore, the influence degree of the net radiation on the latent heat flux recedes with an increasing time scale and the influence degree of the water vapour pressure deficit and soil water content increases (Li, 2015). These studies, which focused on the forest, grassland and farmland ecosystems, lack research on the alpine wetlands, relatively. In addition, research on the effects of these environmental factors on the latent heat flux is still qualitative for the most part and lacks quantitative evaluations and calculations.
Therefore, this study, taking the alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region of the Tibetan Plateau as an example and using eddy-related systems field observation data, analyzed the coupling degree between alpine wetlands and atmosphere and quantitatively calculated the impact of environmental factors (solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit) on the latent heat flux. Then, the WRF model was used to simulate the water and heat exchange process between land and atmosphere on alpine wetlands, and the sensitivity experiment on the environmental factors affecting the latent heat flux was carried out. In this way, we can verify the results of the observations, and further explore the physical mechanism of environmental factors influencing the latent heat flux. This has the potential to provide reference information for exploring the influences of environmental factors on the latent heat flux over the alpine wetlands of the Yellow River source region and the research on climate change in the Yellow River source region and even the world in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The Yellow River source region is located in the northeastern part of the Tibetan Plateau and is characterised by many landscape types, such as basins, meadows, valleys, valleys, glaciers, lakes and permafrost. In this study, we use observations from the Maduo Observatory of Climate and Environment of the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resource, CAS (Lat: 96.38°, Lon: 35.03°, altitude above the sea: 4313.0 m, seen in
Figure 1, located in the southwest of the Yellow River source region. The observatory is under the care of people all the year round, and professional personnel maintain the observatory twice a year in late May and late September. The studied region experiences cold air and a lack of oxygen, with long periods of sunshine and strong ultraviolet rays. Here, the cold season occupies seven to eight months and the warm season occupies four to five months. In addition, this place has a dry climate and experiences small annual temperature contrast but large daily temperature contrast. The annual averaged temperature is -3.3℃, while the annual averaged precipitation amount is 380-470 mm. This region has a typical plateau high cold climate, with a uniform surface of alpine meadows or seasonal wetlands, both of which are flat and open terrains (Chen et al., 2016).
2.2. Eddy Flux and Radiation Data Processing
The flux data used in this study are obtained from observations of the open vorticity correlation flux observing system. This system consists of a CR5000 data acquisition device, a CSAT3 ultrasonic anemometer (Campbell), Li-7500 CO2/H2O analyser (Li-Cor Company) and a 1 G PC card. The system calculates the online flux using the vorticity correlation principle and stores the time series of the average CO2 flux, latent heat flux and sensible heat flux for 30 min, automatically adjusting the in-line flux with changes in the revised air density. The radiation observation system instrument is NR01 four component/net radiation sensors produced by Netherlands Hukse flux company. This instrument has independent sunlight (short wavelength range, 305~2800 nm) and far-infrared (long wavelength range, 4500~50000 nm) radiation measurements, which can be used to measure near the ground four independent components of radiation balance. The observation times have a range within Beijing time of 00:00-23:30, recording every 0.5 hour, and the record is the average of the value measured ten minutes before and after the time (e.g., the record at 2:00 is the average of the actual measurements from 1:50 to 2:10). To measure the temperature of the air and the surface, a Pt100 temperature sensor was installed in the ground radiation intensity meter. The data used in this study are from June 1 to August 31, 2014, and include the sun shortwave radiation, the ground shortwave upward radiation, the ground longwave upward radiation, atmospheric longwave downward radiation, sensible heat flux, latent heat flux and conventional meteorological elements, to calculate and compare with simulation results.
Due to weather-related factors, terrain conditions and the physical limitations of the instrument, quality control of the observed data is needed in order to carry out physical process analysis. This is done based on the universal standard of rejecting flux data (Guo et al., 2004; Li et al., 2007; He et al., 2014), the specific methods used in this study are as follows:
1) Due to precipitation, the latent heat flux at noon is negative, and the radiation data are not stable, thus, only data from clear days are used.
2) When turbulence is weak, the uncertainty of the flux data is large. The friction wind speed (u*) is the measure of the turbulence intensity. All flux data where u*> 0.1 m·s-1 is selected.
3) As turbulence is weak at night, the sensor probe is easily covered by dew condensation or frost, and the night-time latent heat flux is small. Therefore, the data can only be used when the downward shortwave radiation must be greater than zero.
3. Method
3.1. Calculation of Control
According to the Penman-Monteith equation (Monteith, 1973), the latent heat flux density (
λE) depends on the available energy (
FA), the water vapour pressure deficit (
D), the aerodynamic resistance (
ra), the surface resistance (
rc), the thermodynamic psychrometric constant (
γ), the density of the air (
ρ) and the rate of change of the saturated vapour pressure with temperature (Δ),
Previous studies have shown that the available energy (FA) is proportional to the solar radiation (Rs), as is βRs (Wang et al., 2005). Through linear fitting, the energy closure of the alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region is 68.0%. β is proved to be 0.554. Surface resistance (rc) can be composed of response functions of minimum surface resistance, solar radiation, water vapor pressure deficit, atmospheric temperature and soil water capacity (Monteith, 1973; Stewart, 1988). The response functions of solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit can be defined as hyperbolic function and inverse proportional function, respectively (Ciencial et al., 1997; Wang et al., 2005).
In order to quantify the effect of environmental factors on the latent heat flux, we introduced control (Jacobs and de Bruin, 1992), so the relative control (
) exercised by an environmental controlling factor (x) over the latent heat flux (
λE) is defined as,
The superscripts R in the above equation denotes the relative control. Mainly considering the influence of external atmospheric environmental factors (solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit) on the latent heat flux, assuming
Rs,
D,
ra,
γ and Δ are independent variables mutually, we bring Eq.1 into Eq.2, which obtained the expression of the relative control exercised by solar radiation and water vapor pressure difecit over the latent heat flux, respectively,
and
f1(
Rs) and
f2(
D)represent the response functions of solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit, respectively. The parameter
m is
3.2. Coupling between Alpine Wetlands and Atmosphere
The starting point of calculating the coupled water vapour flux between the alpine wetlands and atmosphere is the Penman-Monteith equation. Let the aerodynamic resistance (
ra) tend to infinity or zero, then, the latent heat flux (
λE) can be expressed in the following two formulas,
and
When ra → ∞, the extremum of λE is called the equilibrium lent heat flux (λEeq), when ra → 0, the extremum of λE is called the imposed latent heat flux (λEimp).
Introducing the decoupling coefficient (Ω) as the evaluation index of the coupling of the water vapour flux between alpine wetlands and atmosphere, the decoupling coefficient can be expressed as
The coupling factor (ω) represents the degree of coupling between the solar radiation (or water vapour pressure deficit) and the latent heat flux density.
When
,
. This reflects the relative importances of aerodynamic resistance and surface resistance. Combining Eq.6 - Eq.8 and substituting the results into Eq.1 yields
The real latent heat flux is decided by λEeq, λEimp and Ω. The values of Ω range between 0 and 1. When deciding the value of λE, Ω reflects the relative importance of λEeq and λEimp (Steduto et al., 1998). When Ω = 0, the two systems are completely coupled, and the latent heat flux is mainly affected by the water vapour pressure deficit and the surface resistance. When Ω = 1, the two systems are completely unable to couple, and the latent heat flux is mainly influenced by solar radiation (or available energy).
4. Model Scheme Design
4.1. Introduction of WRF Model
WRF (Weather Research and Forecasting Model) is a new generation of mesoscale numerical model, which is fully compressible and non-static equilibrium model. It is jointly developed by organizations such as NCEP/NCAR. The first edition of it was released in October 2000. This study uses the WRF 3.8.1 version released in August 2016. The model uses Arakawa C-grid staggering in the horizontal direction and terrain-following coordinates in the vertical direction, and has higher resolution in the horizontal and vertical directions, Time-split integration using a 2nd- or 3nd-order Runge-Kutta scheme, Four map projections are supported for real-data simulation: Lambert conformal, polar stereographic, Mercator, and latitude-longitude allowing rotated pole. WRF provides a number of available physical parameterization options, which have detailed descriptions of the radiation process and the land surface dynamic process, etc., and can accurately simulate the complex interactions between different physical processes and can be used for simulation of atmospheric processes at various spatial and temporal scales (Li et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2013; Xin et al., 2013; Wang et al., 2013; Wen et al., 2015). It can be used not only for the simulation of real weather, but also as a theoretical basis for the research of basic physical processes by exploring the module groups it contains. It’s main advantage is that it can couple the atmosphere to the land surface, and explore the physical mechanism of environmental factors affecting the latent heat flux.
4.2. Modification of the Noah LSM
Developed on the basis of the OSU (Oregon State University) model, Noah LSM is a refined regional land surface scheme, and suitable for weather and climate applications (EK et al., 2003). Its framework is as follows: The potential evaporation of the land surface is calculated by the Penman formula during the day, which is similar to the formula proposed by Mahrt and Ek (1984). The multi-layer soil model (Mahrt and Pan, 1984), the original vegetation model (Pan and Mahrt, 1987) and suitably complex vegetation resistance (Chen et al., 1997) are also used in this scheme. The land surface scheme has a vegetation layer and the temperature and humidity of each soil layer, the water storage capacity of the vegetation canopy and the amount of snow on the land surface as prediction constants. The scheme has four layers of soil, the soil thickness from the surface layer to the bottom layer is 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, and 1.0 m, respectively, and the soil thickness is 2 m in total. Due to the limited research data in Tibetan Plateau, there are many problems in the application of the above land surface scheme to the special underlying surface of the plateau. Referring to Chen et al. (2017, 2018) correcting the soil hydrothermal parameterization scheme in Tibetan Plateau region through soil test data, our study uses it in Noah LSM to improve the simulation effect of soil water and heat parameters in Tibetan Plateau region.
The temperature of the land surface in the Noah LSM uses a simple and linear land surface energy balance formula proposed by Mahrt and Ek (1984). The ground and vegetation are seen as an integral part of the land surface. The heat flux of the ground is calculated by the common soil temperature diffusion formula
Among it, the volumetric heat capacity C (J·m
-3·K
-1) and the thermal conductivity λ (W·m
-1·K
-1) are functions of soil volumetric water content Θ. In the soil composition, the part of solid does not change much, and the value of the soil heat capacity mainly depends on the proportion of water and air, which is
In the above formula, Cwater = 4.2×106 J·m-3·K-1, Csoil = 1.26×106 J·m-3·K-1, Cair = 1004 J·m-3·K-1. Θsat is saturated soil volumetric water content, numerically equaling to soil porosity, and determined by soil type (Cosby et al., 1984). Since the soil is a porous, finely-divided medium, its heat exchange involves three mechanisms which are radiation, convection and conduction. When the diameter of pore is less than 5 ×10-4 m, consider only the last item (Xu et al., 2010). As the source of energy for all movements, solar radiation is reflected by the surface, and the absorbed net radiation drives the entire surface hydrothermal process, including the ground-to-air transport of sensible heat flux, latent heat flux, etc. It can be seen from Eq.11 that the correction of the parameterization scheme of thermal conductivity will affect the surface temperature and the simulation of the sensible heat flux and latent heat flux further.
This study focuses on the summer simulation, which mainly considers the water-heat exchange of the surface in the non-freezing state, ignoring the influence of the solid ice. The actual thermal conductivity (λ) of the soil containing a certain amount of water is calculated from the thermal conductivity in the saturated state (λ
sat) and the dry state (λ
dry), Kersten number (K
e) being its weight coefficient. Its expression is
Because of the heat conductivity (λ
sat) in the saturated state being determined by the soil type, in order to modify the parameterization scheme of soil thermal conductivity, we modify the rest item of the expression. According to the research of Chen et al. (2017, 2018), the calculation schemes of dry soil density (ρ
dry), dry soil thermal conductivity (λ
dry)) and Kersten number (K
e) are corrected as
S is the soil saturation, which is the ratio of the actual water content (Θ) to the saturated water content (Θsat) of the soil.
4.3. WRF Simulation Scheme
This study uses two-grid nesting. The simulation period is from 0:00 on May 31, 2014 (Beijing time, the same below) to 23:00 on August 31, 2014 and total 93 days, and the simulation results are output every 60 minutes. The underlying surface data uses the USGS-based land use and vegetation type data with a resolution of 1km. The NCEP/NCAR 1°×1° reanalysis data recorded 4 times every day are used for pretreatment as the initial field and boundary conditions of the WRF. The vertical direction of the model is divided into 27 layers, and the top pressure of the model is 50hpa. The parameterization schemes of physical process adopted include: Rapid Radiative Transfer Model (RRTM) Longwave, MM5 (Dudhia) Shortwave, WRF Single-Moment 3-Class (WSM3) scheme, Similarity theory (MM5), Yonsei University (YSU) PBL, and no cumulus parameterization scheme for both grids. The land surface parameterization scheme used by the model is respectively the original and modified Noah LSM scheme. The grid parameter settings of the simulation area are shown in
Table 1.
In order to analyze the process of water-heat exchange between land and atmosphere in alpine wetlands and to explore the environmental factors affecting the process of water-heat exchange, we design 3 sets of experiments, which are Ocase, Rscase, and Dcase. In the experiments, the environmental factors affecting the latent heat flux mainly include the solar radiation and the water vapor pressure deficit. In order to test the simulation performance of the model, the simulation of the surface energy budget is mainly concerned.
Ocase is an experiment with each environmental factor keeping the current state, truly simulating the characteristics of water-heat exchange between land and atmosphere and radiation budget in alpine wetlands, to test the ability of model simulating them. The original and modified Noah LSM scheme are respectively used for the experiment, verifying the adaptability of the modified land surface scheme in alpine wetlands and improve the simulation ability of model in alpine wetlands.
Rscase is an experiment increasing solar radiation by 30% on the basis of the original without changing water vapor pressure deficit, to simulate the effect of solar radiation on latent heat flux. The modified Noah LSM scheme is used for the experiment.
Dcase is an experiment increasing water vapor pressure deficit by 30% on the basis of the original without changing solar radiation, to simulate the effect of water vapor pressure deficit on latent heat flux. The modified Noah LSM scheme is used for the experiment.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Relative Control Exercised by Environmental Factors over Latent Heat Flux
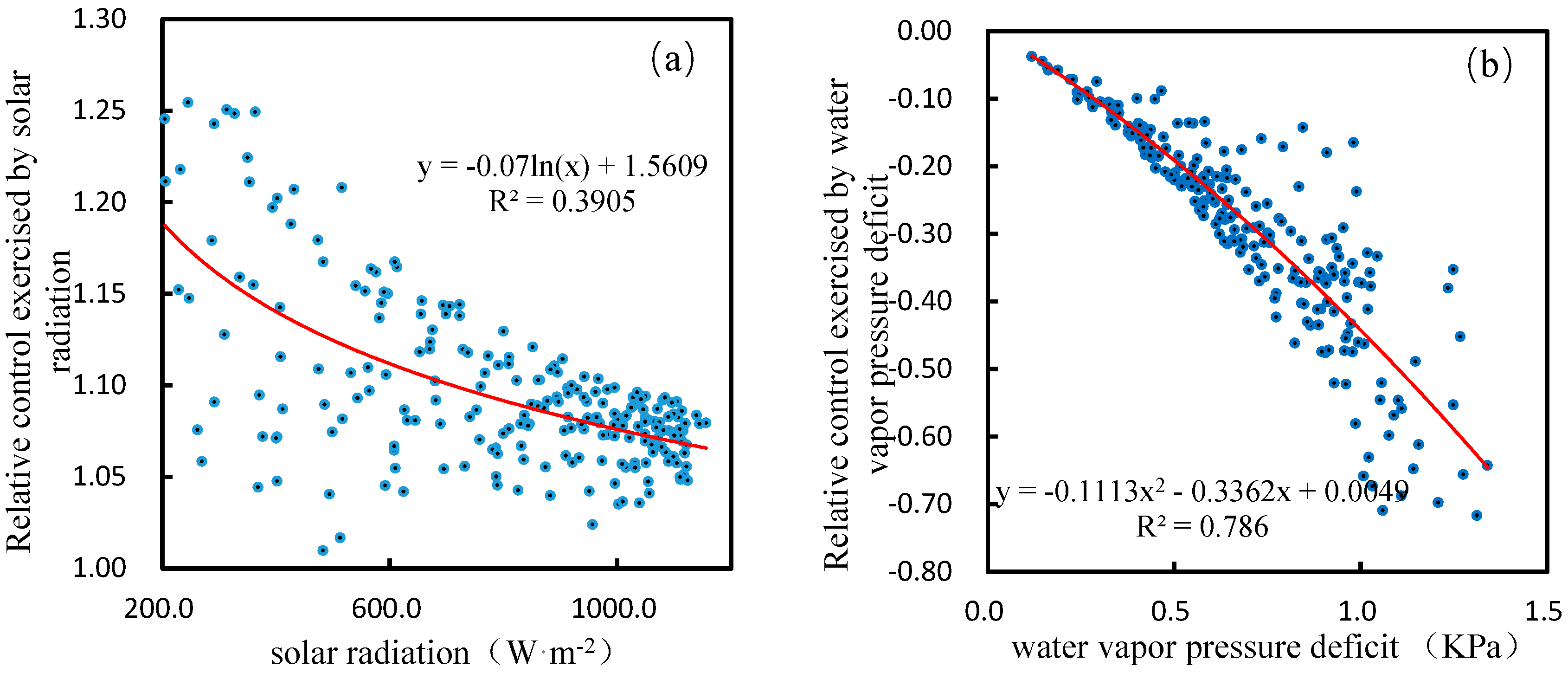
Using the observation data, through the above calculation of the control, the range of relative control exercised by solar radiation over latent heat flux is 1.01 to 1.25, with an average of 1.10, and the variation is affected by the same degree of solar radiation and resistance ratio. As shown in
Figure 2a, as solar radiation increases, the relative control exercised by solar radiation over latent heat flux gradually decreases. Since the values are all greater than 1, it indicates that the small increase of solar radiation can cause a large increase in latent heat flux. As shown in
Figure 2b the absolute value of the relative control exercised by water vapor pressure deficit over latent heat flux increases with the increase of the vapor pressure deficit. And its value is less than 0, indicating that the water vapor pressure deficit always plays a role in reducing the surface latent heat flux in the alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region, and with the increase of water vapor pressure deficit, this effect is also more intense.
As shown in
Figure 3, solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit play an opposite role in affecting latent heat flux in alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region. Solar radiation always plays a role in increasing the latent heat flux, and the water vapor pressure deficit always plays a role in reducing the latent heat flux, but the opposite effect of solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit on the latent heat flux is not corresponding. In general, with the increase of the relative control exercised by the solar radiation over the latent heat flux, the absolute value of relative control exercised by water vapor pressure decreases. During the vegetation growthing season in alpine wetlands, the relative control exercised by solar radiation over latent heat flux is always greater than the relative control exercised by water vapor pressure deficit. This conclusion is in line with the Ω theory. During the vegetation growthing season, the average value of Ω is 0.38 in alpine wetlands, with the coupling between the wetland and the atmosphere being poor, and the latent heat flux is mainly affected by solar radiation. The actual situation is consistent with it. The latent heat flux is mainly affected by solar radiation in alpine wetlands surface with sufficient water supply and low aerodynamic resistance. Ω can be used to quantify the effect of surface resistance on latent heat flux, but does not quantify the effects of solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit on latent heat flux. The equations for the relative control exercised by solar radiation and water vapour pressure deficit over the latent heat flux show that the relationship between the relative control exercised by solar radiation (or the water vapour pressure deficit) and Ω is non-linear and depends not only on the Ω factor but also on other factors, such as the solar radiation, the water vapour pressure deficit and their response functions.
Simulation results
5.2. Adaptability of Model in Alpine Wetlands Surface
Above, through the observation data, the degree of influence of environmental factors (solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit) on latent heat flux has been calculated. Next, the numerical model is used to verify the results of observation data, and further explore the physical mechanism of environmental factors affecting latent heat flux. First of all, we must test the adaptability of the model in the alpine wetlands surface. In the Ocase experiment, the two groups of simulation results (WRF: original Noah scheme, WRF+: modified Noah scheme) were selected for comparing with observation data in the grid point where the Maduo Observatory is located from June 1, 2014 to August 31, 2014.
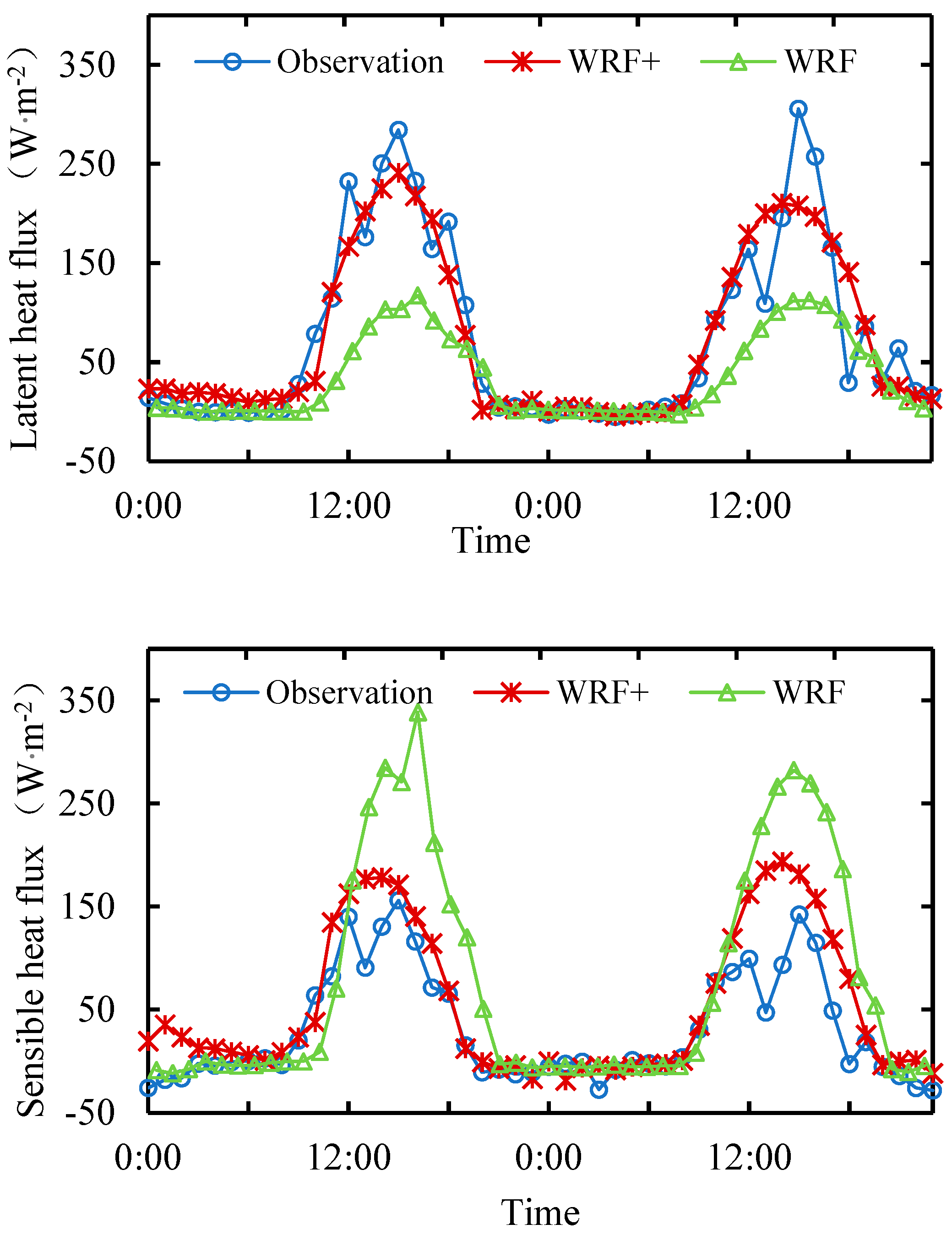
Figure 5 shows the diurnal comparison between the simulation results and observation data of energy flux and radiation budget for two consecutive days (0:00 on August 17, 2014 - 23:00 on August 18, 2014). It can be seen that both schemes of the model can simulate the diurnal variation of energy flux and net radiation. The difference between the simulation results and the observed data is mainly reflected in the variation of daytime flux. The original Noah scheme overestimates the sensible heat flux, but underestimates the latent heat flux. Compared with WRF, WRF+ effectively increases the latent heat flux and decreases the sensible heat flux during the day, narrowing the difference between the simulated value and the observed value. Due to the influence of precipitation, soil moisture and other complex water-atmosphere processes, the observed latent heat flux oscillates significantly. In general, the simulated results of WRF+ do not show this characteristic well. The oscillation amplitude of the simulated value of latent heat flux is much smaller than the observed value, and the oscillation amplitude of the simulated value of sensible heat flux is much larger than the observed value. Because RMSD (root-mean-square deviation) is very sensitive to small deviations, RMSD of flux are generally large. WRF+ effectively increases the oscillation amplitude of latent heat flux and reduces the oscillation amplitude of sensible heat flux. By using WRF+ instead of WRF, the RMSD of latent heat flux is decreased from 58.06 to 49.94, and the RMSD of sensible heat flux is decreased from 79.41 to 62.20. The model has a good effect on the simulation of net radiation, and WRF+ has little effect on the simulation of net radiation.
And there are also instrument errors and other errors in observation data, such as causing negative latent heat flux. In order to eliminate this error based on latent heat flux, average diurnal processing is carried out, as shown in
Figure 5 The average diurnal variation peak of the simulated latent heat flux by WRF is 115.54 W·m
-2, while that of the observed data reach up to 184.58 W·m
-2, which WRF+ increases to 168.72 W·m
-2. From the above, we can see that the latent heat flux of WRF+ simulation has significantly increased, which is close to the observed value. It can be seen from the figure, WRF+ mainly improves the simulation effect during the day and slightly effects on it at night.
Figure 4.
Two consecutive days of diurnal comparison between simulation results and observation data of sensible heat flux, latent heat flux and net radiation in alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region from August 17 to 18, 2014.
Figure 4.
Two consecutive days of diurnal comparison between simulation results and observation data of sensible heat flux, latent heat flux and net radiation in alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region from August 17 to 18, 2014.
Figure 5.
Comparison of the average diurnal variation between simulation results and observation data of latent heat flux in alpine wetlands over the source region of the Yellow River in summer 2014.
Figure 5.
Comparison of the average diurnal variation between simulation results and observation data of latent heat flux in alpine wetlands over the source region of the Yellow River in summer 2014.
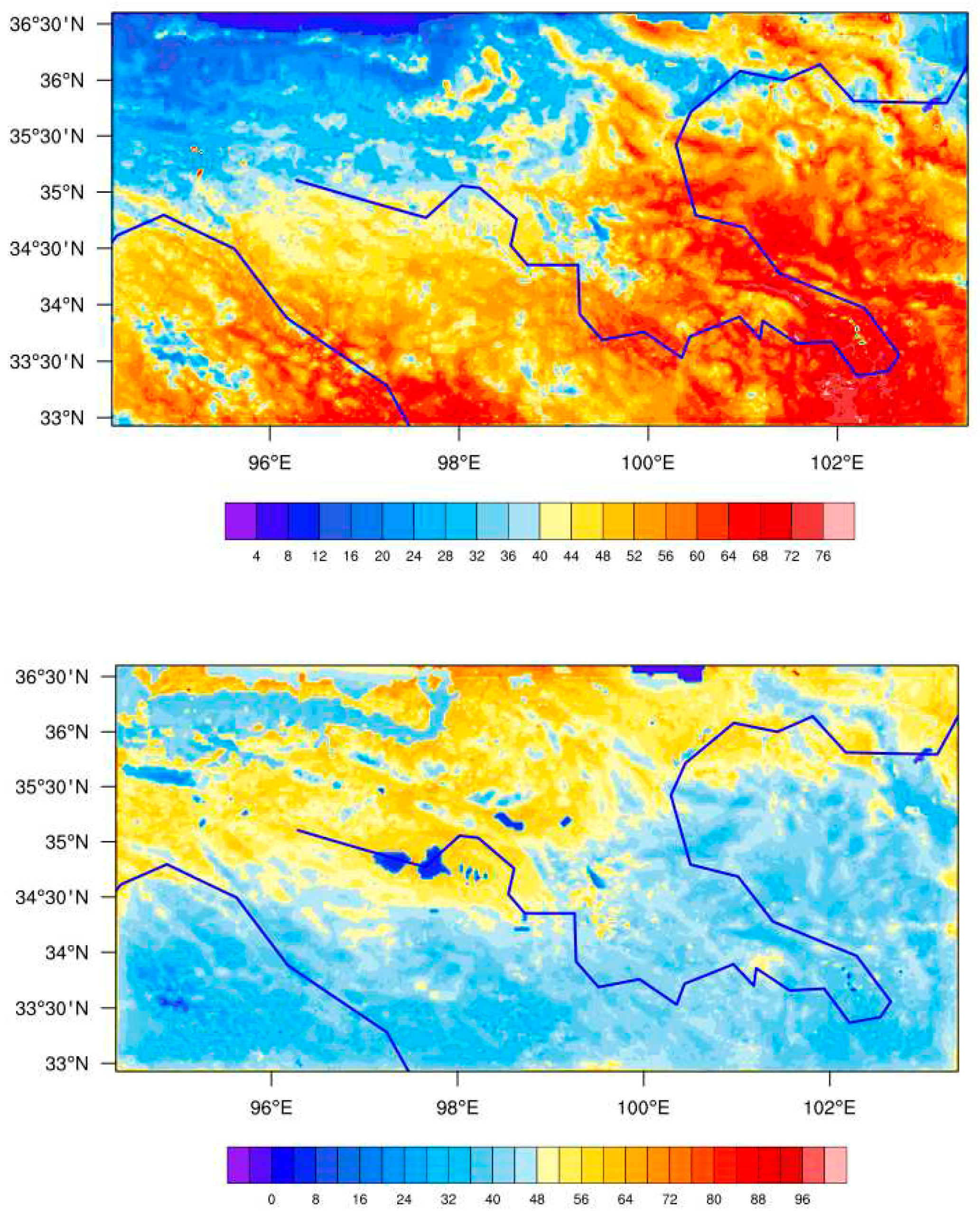
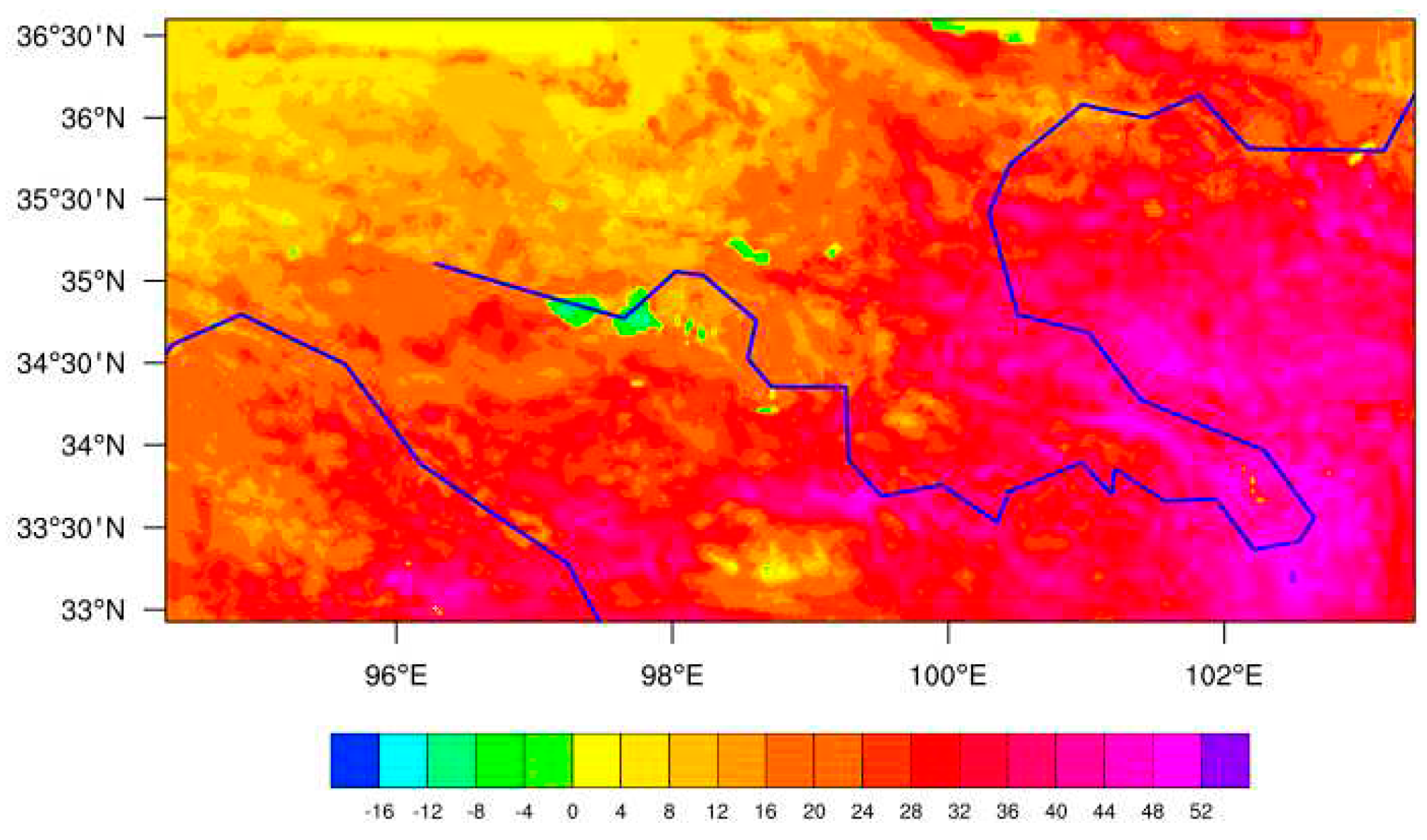
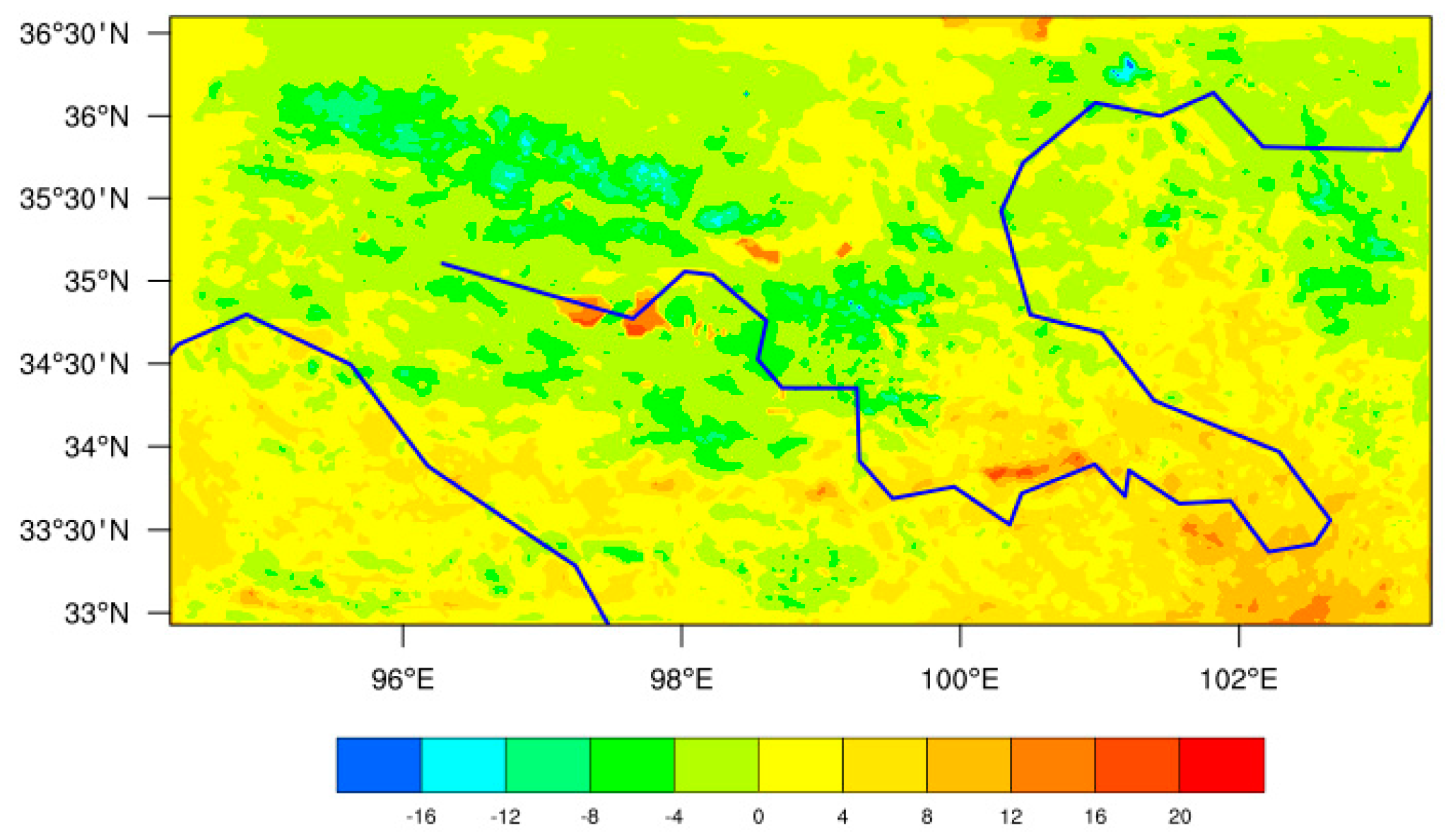
Figure 6 shows the regional distribution of energy flux in alpine wetlands over the source region of the Yellow River. It can be found that the high-value regions of latent heat flux are mainly distributed on both sides of the river, and the alpine wetland in the source area of the Yellow River is the main source of latent heat flux on the Tibetan plateau. The regional distribution of sensible heat flux tends to be high in the north and low in the south. Zaling lake and Eling lake are the low value regions of sensible heat flux, and the sensible heat flux is obviously lower than that in the surrounding areas. In general, the regional distribution of latent heat flux and sensible heat flux in alpine wetlands over the source region of the Yellow River present an opposite trend.
Due to the limitation of resolution, the simulated values are the average state of the grid region where the observation points are located, which is still different from the actual value. WRF+ can better simulate the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of energy flux in alpine wetlands over the source region of the Yellow River. Next, we will study the influence of environmental factors on the latent heat flux, mainly considering the expression of the model on the latent heat flux. Therefore, it is feasible to use WRF+ to simulate the latent heat flux under the change of environmental factors, due to the simulated value of latent heat flux being very close to the observed value.
5.3. WRF+ Simulating the Influence of Environmental Factors on Latent Heat Flux
Rscase and Dcase compared with Ocase, using modified Noah scheme, we explore the effect of increasing solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit on latent heat flux respectively.
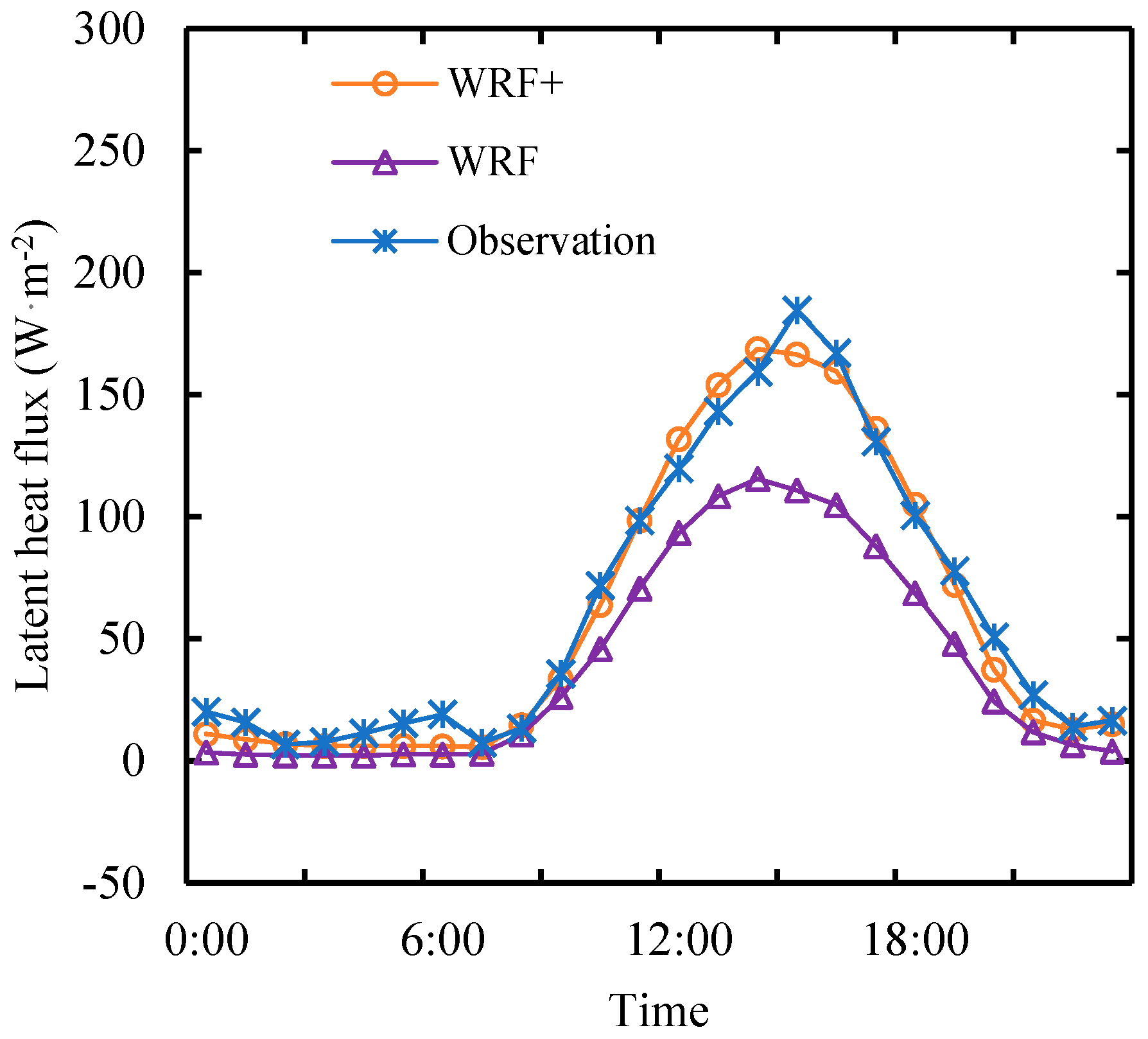
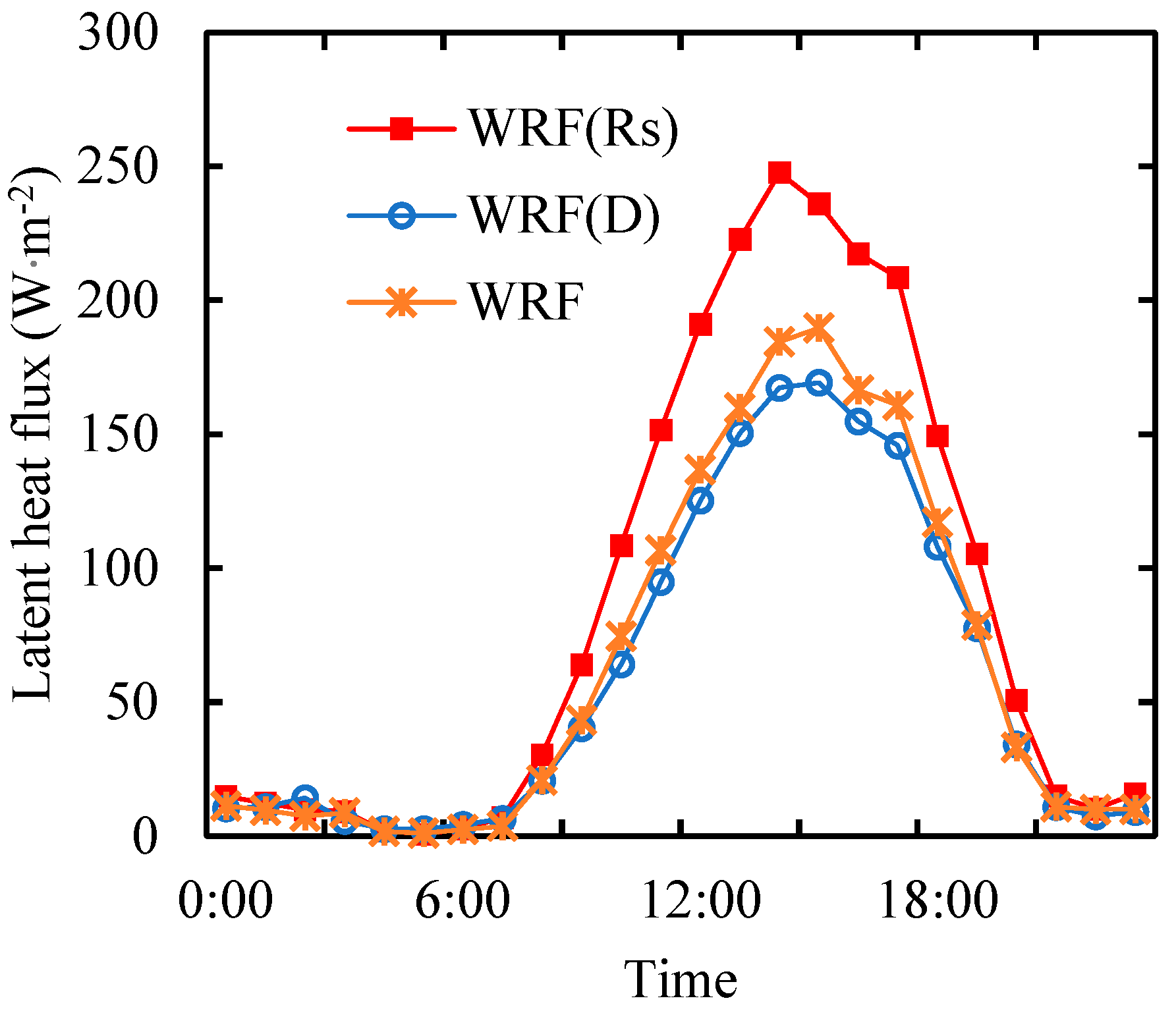
Figure 7 shows the average diurnal variation of latent heat flux in the three groups of experiments. It can be seen that when solar radiation increases by 30%, the latent heat flux also increases, and the diurnal peak value of latent heat flux increases from 189.64 W·m
-2 to 247.6 W·m
-2. It can also be seen that when water vapor pressure deficit increases by 30%, the latent heat flux decreases, and the daily peak value of latent heat flux decreases to 169.19 W·m
-2. According to the analysis of WRF+ simulation results, the relative control exercised by solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit over latent heat flux on clear day in alpine wetlands is 1.23 and -0.28, respectively. The former is slightly larger than that calculated previously (1.10), and the absolute value of the latter is slightly smaller than that calculated previously (-0.29). With the change of environmental factors, the average daily amount of latent heat flux increases from 5.57 MJ·m
-2 to 7.50 MJ·m
-2 and decreases to 5.17 MJ·m
-2, respectively. The change of solar radiation to the average daily amount of latent heat flux is 4.83 times as many as the change of water vapor pressure deficit to the average daily amount of latent heat flux. It can be seen from the simulation results that solar radiation plays a role in increasing latent heat flux, while water vapor pressure deficit always plays a role in reducing latent heat flux, and solar radiation has a greater influence on latent heat flux. The results are consistent with Ω theory and calculation. In addition, solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit only change the latent heat flux during the day, and has little influence on the change of the latent heat flux at night. Moreover, environmental factors have great influence on the latent heat flux at noon and small influence in the morning and evening.
Figure 8 shows the regional distribution characteristics of the difference of latent heat flux based on 3 cases in alpine wetlands underlying surface. It can be seen that the difference of latent heat flux based on Rscase subtracting Ocase is always greater than 0 in alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region, indicating that solar radiation always plays a role in increasing latent heat flux, which is consistent with the previous calculation results. Moreover, the difference of latent heat flux based on Rscase subtracting Ocase shows an increasing trend from northwest to southeast, which indicates that the coupling degree decreases gradually from northwest to southeast. The difference of latent heat flux based on Dcase subtracting Ocase is always less than 0 in alpine wetlands over the Yellow River source region, indicating that water vapor pressure deficit always plays a role in decreasing latent heat flux, which is also consistent with the previous calculation results. The maximum value is located in the northwest of the source area of the Yellow River. But the water vapor pressure deficit plays a role in increasing the latent heat flux along the northwest to southeast, gradually. As the results calculated before, the effect of solar radiation and water vapor pressure deficit on latent heat flux are not corresponding, which can be confirmed from this figure. It shows that in the region where the difference of latent heat flux between Rscase and Ocase appears the maximum, the difference of latent heat flux between Dcase and Ocase latent heat flux is not the maximum value.
Above, through physical process analysis based on observation data and model calculation, we find that solar radiation is the main environmental factor that affects latent heat flux, and water vapor pressure deficit has a small impact on latent heat flux on the underlying surface of alpine wetland in the source region of the Yellow River. The influence of solar radiation on latent heat flux is about 5 times as many as the influence of water vapor pressure deficit. In addition, solar radiation always increases the latent heat flux on the underlying surface of the alpine wetland in the source area of the Yellow River, while the vapor pressure deficit is just the opposite. However, the contrary effect on the latent heat flux is not corresponding.
6. Conclusions
In this study, based on the field observation data and WRF model, the environmental factors affecting latent heat flux of alpine wetlands underlying surface were discussed, and the degree of influence was quantitatively evaluated for the first time. The land surface parameterization scheme of alpine wetlands underlying surface based on previous research on them was transplanted into the Land-Atmosphere Coupling WRF model to simulate the water-heat exchange process between alpine wetlands underlying surface and atmosphere, which can effectively improve the adaptability of WRF model to the special underlying surface of alpine wetlands in the source region of Yellow River. It was found that for the alpine wetlands underlying surface, solar radiation was still the main environmental factor affecting latent heat flux, and the influence degree is 5 times that of water vapor pressure deficit. The coupling degree between the alpine wetlands and the atmosphere is poor, and the actual situation is also the same. The results can provide a new research approach for the study of the parameterization of latent heat flux and evaporation under the context of global climate change.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W. and X.Y.; methodology, Y.X. and J.C.; simulation, Y.X.; data analysis, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Project supported by Open Research Fund Program of Plateau Atmosphere and Environment Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province; Incubation Project of Yibin University (2019QD21).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The research was provided under Project supported by Open Research Fund Program of Plateau Atmosphere and Environment Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province and Incubation Project of Yibin University (2019QD21).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Al-Shibli, F. M.; Ottom, M. A.; Saoub, H.; Al-weshah, R. Comparative analysis of potential evapotranspiration calculation methods with ERA-reanalysis climate models’ projections in Western Asia, Jordan. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 2021, 19, 4849–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bange, G. G. J. On the quantitative explanation of stomatal transpiration. Acta Botanica Neerlandica 1953, 2, 255–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zuo, H. C.; Lv, S. H. The effect of improved land surface process parameters in arid area on climatic simulation in GCM. Plateau Meteorology 2004, 23, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Betts, A. K.; Chen, F.; Mitchell, K. E.; Janjić, Z. I. Assessment of land surface and boundary layer models in two operational versions of the NCEP Eta Model using FIFE data. Monthly Weather Review 1997, 125, 2896–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. L.; Wen, J.; Tian, H.; Zhang, T. T.; Yang, X. Y.; Jia, D.Y.; Lai, X. A Study of Soil Thermal and Hydraulic Properties and Parameterizations for CLM in the SRYR. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2018, 123, 8487-8499. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. L.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. T.; Jia, D.Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. L. Characteristics of water and heat exchanges and their crucial influencing factors on the alpine wetland during the warm season in the source region of the Yellow River. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese) 2017, 41, 302-312. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. L.; Wen, J.; Tian, H. Up-Scaling Research for Soil Moisture inYellow River Source Region. Plateau Meteorology 2016, 35, 1212–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Cienciala, E.; Kucera, J.; Lindroth, A. Canopy transpiration from a boreal forest in sweden during a dry year. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 1997, 86, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosby, B. J.; Hornberger, G. M.; Clapp, R. B.; Ginn, T. R. A statistical exploration of the relationships of soil moisture characteristics to the physical properties of soils. Water Resources Research 1984, 20, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R. S.; Kang, S. Z.; Zhang, Y. Q.; Tong,L.; Li, S. E. Characteristics of water vapor and heat fluxes and the controlling factors over a maize field in the arid inland region. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 2014, 45, 312-319.
- EK, M. B.; Mitchell, K. E.; Lin, Y.; Rogers, E.; Grunmann, P.; Koren, V.; Gayno, G.; Tarpley, J. D. Implementation of Noah land surface model advances in the National Centers for Environmental Prediction operational mesoscale Eta Model. Journal of Geophysical Research 2003, 108, 8851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. X.; Mei, X. R.; Lu, Z. G.; Zhao, Q. S. Field evapotranspiration measurement based on eddy covariance technology. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 2004, 8, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. Q. Research advance about the energy budget and transportation of water vapour in the HEIFE area. Advances in Earth Science 1994, 9, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- He, J. J. Characteristic of latent heat flux in typical steppe. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 2014, 30, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, C. M. J.; De Bruin, H. A. R. The Sensitivity of Regional Transpiration to Land Surface Characteristics: Significance of Feedback. Journal of Climate 1992, 5, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P. G.; McNaughton, K. G. Stomatal Control of Transpiration: Scaling Up from Leaf to Region. Advances in Ecological Research 1986, 15, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, E. Surface Energy Fluxes and Control of Evapotranspiration from a Swedish Spahgnum Mire. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2001, 110, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. G.; Lu, S. H.; Ao, Y. H.; Wen, X. Numerical Simulation of Impact of Ecological Environment Change on Lake Effect in the Source Region of the Yellow River. Plateau Meteorology 2012, 31, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. N.; Shi, S. B.; Cao, G. M.; Yang, Y. G.; Shen, Z. X. The observational studies on characteristics of microclimate in haibei alpine meadow regions of Qi-Lian mountain. Plateau Meteorology 2000, 19, 512–519. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. J. Environmental controls on water and heat exchanges over rainfed maize cropland in northeast China. Climatic and Environmental Research 2015, 20, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. X.; Chang, G. G.; Xiao, J. S; Zhou, B. R.; Fu, Y. Relationship between wetlands changes and climate change in the Yellow River source region. Journal of Natural Resources 2009, 24, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. M.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. X.; Shi, X. H.; Shen, H. Y.; Wang, Z. Y. Change in extreme climatic events over the sources of the three rivers in the prometaphase 21st century. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology 2012, 34, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. J.; Xu, Z. Z.; Wang, Y. L.; ZHOU, L.; Zhou, G. S. Latent and sensible heat fluxes and energy balance in a maize agroecosystem. Journal of Plant Ecology 2007, 31, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z. Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang Z., Y. Assessment of ecological importance of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on ecosystem service flows. Journal of Mountain Science 2021, 18, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Shi, Z. T.; Gu, S. X.; Peng, H. Y.; Feng, G. J.; Huo, H. Energy balance and evapotranspiration characteristics of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) plantations in Xishuangbanna, Southwest of China. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 2022, 20, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; EK, M. B. The influence of atmosphere stability on potential evaporation. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology 1984, 23, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; Pan, H. L. A two-layer model of soil hydrology. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 1984, 29, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D. Boundary-Layer adjustment over small scale changes of surface heat flux. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 2005, 116, 313-330. [CrossRef]
- Monteith, J. L. Principles of Environmental Physics. London: Edward Arnold 1973.
- Mackay, D. S.; Ahl, D. E.; Ewers, B. E.; Samanta, S.; Gower, S. T.; Burrows, S. N. Physiological Tradeoffs in the Parameterization of a Model of Canopy Transpiration. Advances in Water Resources 2003, 26, 79–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcnaughton, K. G.; Jarvis, P. G. Predicting effects of vegetation changes on transpiration and evaporation. New York: Academic Press 1983.
- Steven, P. O.; Foken, T.; Vogt, R.; Kohsiek, W.; DeBruin, H. A. R.; Bernhofer, C.; Christen, A.; Gorsel, E. V.; Grantz, D.; Feigenwinter, C.; Lehner, I.; Liebethal, C.; Liu, H. P.; Mauder, M.; Pitacco, A.; Ribeiro, L.; Weidinger, T. The energy balance experiment EBEX-2000. Part I:Overview and energy balance. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 2007, 123, 1-28. [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.L.; Mahrt, L. Interaction between soil hydrology and boundary-layer development. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 1987, 38, 185-202. [CrossRef]
- Penman, H. L.; Schofield, R. K. Some physical aspects of assimilation and transpiration: Carbon dioxide fixation and photosynthesis. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol. 1951, 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, J. B. Modelling Surface Conductance of Pine Forest. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 1988, 43(1), 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T. C. Maize canopies under two-soil water regimes Ⅲ. Variation in coupling with the atmosphere and the role of leaf area index. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 1988, 89, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Q.; Li H., Y.; Wang, X. J.; Shamsuddin, S. Water resources response and prediction under climate change in Tao'er River Basin, Northeast China. Journal of Mountain Science 2021, 18, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P. Discuss the importance of wetland protection and reverting cultivated land to wetland. Resources Economization & Environmental Protection 2014, 3, 142-143.
- Trenberth, K. E.; Caron, J. M.; Stepaniak, D. P. The atmospheric energy budget and implications for surface fluxes and ocean heat transports. Climate Dynamics 2001, 17, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X. H.; Dong, W. J.; Liao, X. H. Numerical simulations of radiation budget and energy balance using WRF model in summer over semi-arid northeastern China. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica 2015, 36, 2196–2203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. H.; Sun, C. Design and preliminary test of the regional climate model(WRFC)based on coupling WRF3.2 and CLM4.0. Plateau Meteorology 2013, 32, 1626–1637. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T. J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X. J.; Zhao, S. Q.; Wang, J. Numerical simulation of summer boundary layer structure over undulating topography of loess plateau simulated by WRF model. Plateau Meteorology 2013, 32, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Wever, L. A.; Flanagan, L. B.; Carlson, P. J. Seasonal and interannual variation in evapotranspiration, energy balance, and surface conductance in a northern temperate grassland. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2002, 112, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. G.; Kellomaki, S. Role of solar radiation and water vapour pressure deficit in controlling latent heat flux density in a cots pine forest. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 2005, 115, 131-149.
- Wang, X. X.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. H.; Zhu, Q. J.; Hu, Y. M. Correlation analysis of water and heat fluxes with environmental variables over lawn in semi-arid area. Journal Of Basic Science and Engineering 2008, 16, 770–777. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. M.; Ma, W. Q.; Ma, Y. M. Observation and simulation analyses on characteristics of land surface heat flux in northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in summer. Plateau Meteorology 2013, 32, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X. Z.; Wang, J. C.; Zhang, L. X. Physics of Frozen Soil. Beijing: Science Press 2001.
- Xin, Y.; Wang, C. H.; Shen, Y. F.; Chen, H. W. Forecast examination of surface global horizontal irradiance over middle of xinjiang using WRF model. Plateau Meteorology 2015, 32, 1368–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Peng, L. C.; Liao, Q.; Li, Z. M. Estimation of latent heat flux over semiarid areas for clear sky days using modis data. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis 2014, 50, 835–842. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W. Y.; Zhou, G. S.; Chi, D. C.; He, Q. J.; Zhou, L. Evapotranspiration of phragmitescommunis community in Panjin wetland and its controlling factors. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2008, 28, 4594–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C. M.; Lettenmaier, D. P. Long-term climate and derived surface hydrology and energy flux data for Mexico: 1925-2004. Journal of Climate 2007, 20, 1936–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, X. Y. The influence of synoptic conditions on the averaged surface heat and radiation budget energy over desert or gobi. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 2003, 27, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. H.; Zhou, B. R.; Xiao, H. B. Comparison of soil moisture and heat features between alpine meadow and alpine wetland. Journal of Arid Meteorology 2015, 33, 783–789. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).