1. Introduction
Heavy metals pose great hazards when they enter water bodies, with electroplating, metallurgy, mining, chemical industry, and processing being the main sources [
1]. The direct discharge of industrial wastewater containing heavy metals not only causes significant harm to human health but also damages the ecological environment [
2].
Currently, the common methods for treating heavy metals include electrocoagulation, electroflotation, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, membrane filtration, photocatalysis, nanotechnology, and adsorption. Based on the comparison of technical costs and economic benefits, the ranking is as follows: adsorption > ion exchange > electroflotation > membrane filtration > electrocoagulation > chemical precipitation > photocatalysis > nanotechnology. Among them, adsorption has advantages such as wide applicability and simple preparation method, and it has great application prospects.
High-temperature pyrolysis and low-temperature hydrothermal carbonization are commonly used methods for preparing activated carbon with high adsorption performance[
3]. The hydrothermal carbonization process is simple to operate, and the reaction materials do not require drying treatment. The hydrothermal carbon produced is widely used for adsorption and removal of pollutants[
4]. The hydrothermal carbonization process involves the dehydration and decarboxylation of functional groups, resulting in an increased carbon content and density, as well as enhanced adsorption performance[
5]. At the same time, hydrothermal carbon displays high adsorption characteristics for lead and arsenic [
6].
Bananas, as the fifth largest crop and the second largest fruit in the world, account for about 16% of the total fruit production. With the rapid growth of China's industrialization process, banana cultivation is becoming increasingly industrialized, and its production has increased rapidly, exceeding 12.1 million tons in 2022. Banana peels, as byproducts of banana processing in the food, beverage, and chemical industries, account for 30-40% of the total weight of bananas [
7] and are typical biomass waste. The main problems faced by banana peels are low recovery efficiency and long-term environmental pollution from landfilling. Studies have shown that the preparation of high-value hydrothermal carbon from banana peels using hydrothermal method [
8] exhibits good adsorption performance for lead and arsenic [
9]. To further improve the adsorption performance of hydrothermal carbon, modification is an effective method to modify the surface activity and affinity. However, few studies have been conducted on the surface modification of banana peel hydrothermal carbon, improving functional groups, and promoting surface affinity [
10].
Based on this, the effect of different concentrations of KOH solution, pH value, solid-liquid ratio, and adsorption time on the removal performance of lead ions in solution by hydrothermal carbon modified with KOH solution at 240°C was studied. The surface morphology of the modified hydrothermal carbon was analyzed by XRD and SEM to investigate the adsorption mechanism[
11]. This study aims to provide basic data and theoretical basis for the industrial application of KOH solution modified hydrothermal carbon in removing lead ions from solution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
Banana peel, purchased from Taiyuan City market.
2.2. Reagents
Potassium hydroxide (KOH), thymol blue (C31H32N2O13S), glacial acetic acid (CH3COOH), sodium acetate (CH3COONa), all reagents mentioned are analytical grade and sourced from Shanghai McClain Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. Hydrochloric acid is analytical grade and sourced from China Pharmaceutical Group Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. 1000 mL lead standard solution is sourced from Shanghai McClain Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.
2.3. Experimental methods
2.3.1. Preparation of Banana Peel Hydrothermal Char
Wash the banana peel purchased from the market with tap water, dry it in a 105°C drying oven until a constant weight is achieved, then crush it and pass it through an 80-mesh sieve. Place it in a reaction vessel and perform hydrothermal carbonization under N2. Increase the temperature from room temperature to 240°C at a rate of 10°C/min, and incubate for 120 min. Naturally cool to room temperature, place the hydrothermal product in a drying oven until a constant weight is achieved, grind it again, pass it through a 70-mesh sieve to obtain banana peel hydrothermal char.
2.3.2. Preparation of KOH-Modified Hydrothermal Char
Mix the prepared hydrothermal char (8±0.01 g) with different concentrations of KOH solution (0.05 mol/L, 0.1 mol/L, 0.5 mol/L, 1.0 mol/L). After immersing in a thermostatic water bath shaker at 45°C and 200 rpm for 6 h, pour the solid-liquid mixture into a vacuum filtration device, rinse it repeatedly with anhydrous ethanol and deionized water, collect the solid phase material, place it in a constant temperature drying oven at 105°C for 12 h, grind it and pass it through a 70-mesh sieve, and store it in a sealed bag for later use.
2.3.3. Adsorption experiment
Add ultrapure water to the lead stock solution to prepare lead ion stock solutions of 50 mg/L, 100 mg/L, 400 mg/L, etc. Take a certain amount of hydrothermal char and add it to the lead solution according to a certain solid-liquid ratio, then close the container and perform adsorption experiment in a thermostatic water bath shaker. After shaking, let it settle, take 10 ml of the supernatant in a centrifuge tube, and after centrifugation, measure its absorbance using spectrophotometry. Calculate the adsorption capacity and removal efficiency of the hydrothermal char based on the standard curve of the lead solution using formulas (1) and (2). This experiment was conducted in triplicates, and the results are the average of the three experiments.
In the formula, qe is the adsorption amount in mg/g; η is the removal rate in %; C0, Ce, t represent the initial concentration, adsorbed concentration, and time, respectively, in mg/L; V is the volume of the solution in L; m is the mass of the modified hydrothermal carbon in g.
2.3.4. Characterization methods for banana peel hydrothermal carbon
The pH of the solution was measured using a PHSJ-3F pH meter (accuracy: 0.1, Shanghai Yidian Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.).The concentration of lead in the solution was determined using a P4 UV-visible spectrophotometer (Shanghai Meipuda Instrument Co., Ltd.).The surface morphology of the hydrothermal carbon before and after modification was observed using a TESCAN MIRA LMS scanning electron microscope (Teske (China) Co., Ltd.) with an acceleration voltage of 10 kV and gold spray treatment. The physical properties of the hydrothermal carbon surface before and after modification were analyzed using a Panalytical Empyrean X-ray diffractometer (China Malvern Instruments Co., Ltd.).
3. Results and analysis
3.1. Surface structure and performance analysis of hydrothermal carbon before and after modification
3.1.1. SEM analysis
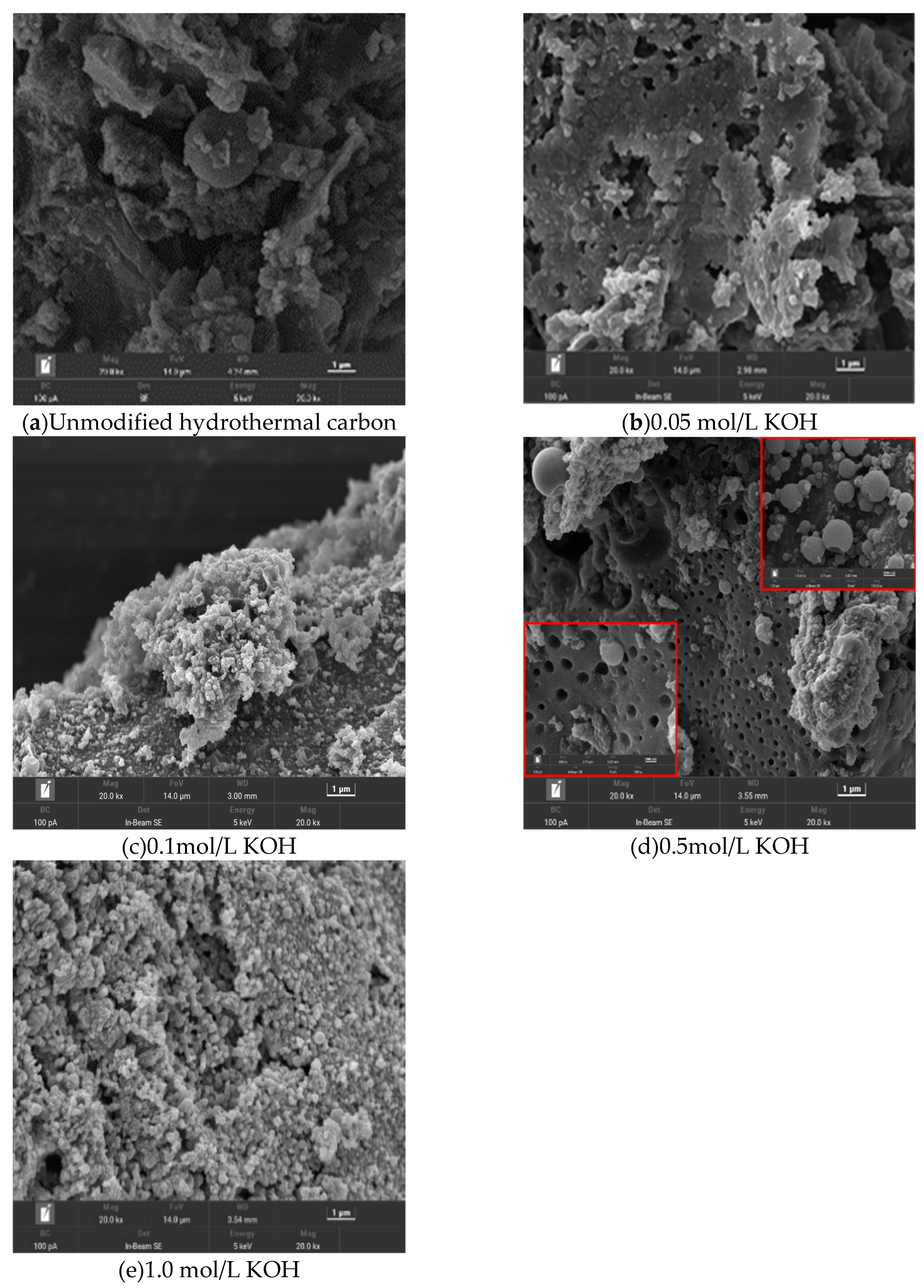
Figure 1 shows SEM images of hydrothermal carbon before and after modification with KOH solution. In image (a), the unmodified hydrothermal carbon has a smooth surface and fewer carbon microspheres. In image (b), the surface of hydrothermal carbon is relatively smooth with fewer and unevenly sized pores, which is because the low concentration of KOH did not cause significant changes in the surface structure[
12]. In image (c) of
Figure 4, as the concentration of the modification solution increases, the surface of the hydrothermal carbon begins to become rough, and there is a tendency to form microspheres. In image (d), with increasing concentration, the surface of the hydrothermal carbon forms many microsphere carbon particles and a large number of uniformly arranged pore structures. This is because cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and other components in the carbon material are cracked into small carbon chain molecules under the action of KOH, and then re-aggregated to form microspheres [
13]. The carbon pores are formed by the reaction in equation (3). In image (e), the surface of the hydrothermal carbon is very rough, and the pores are blocked by the generated carbon particles, which is not conducive to the smooth progress of physical adsorption[
14].
3.1.2. FT-IR analysis
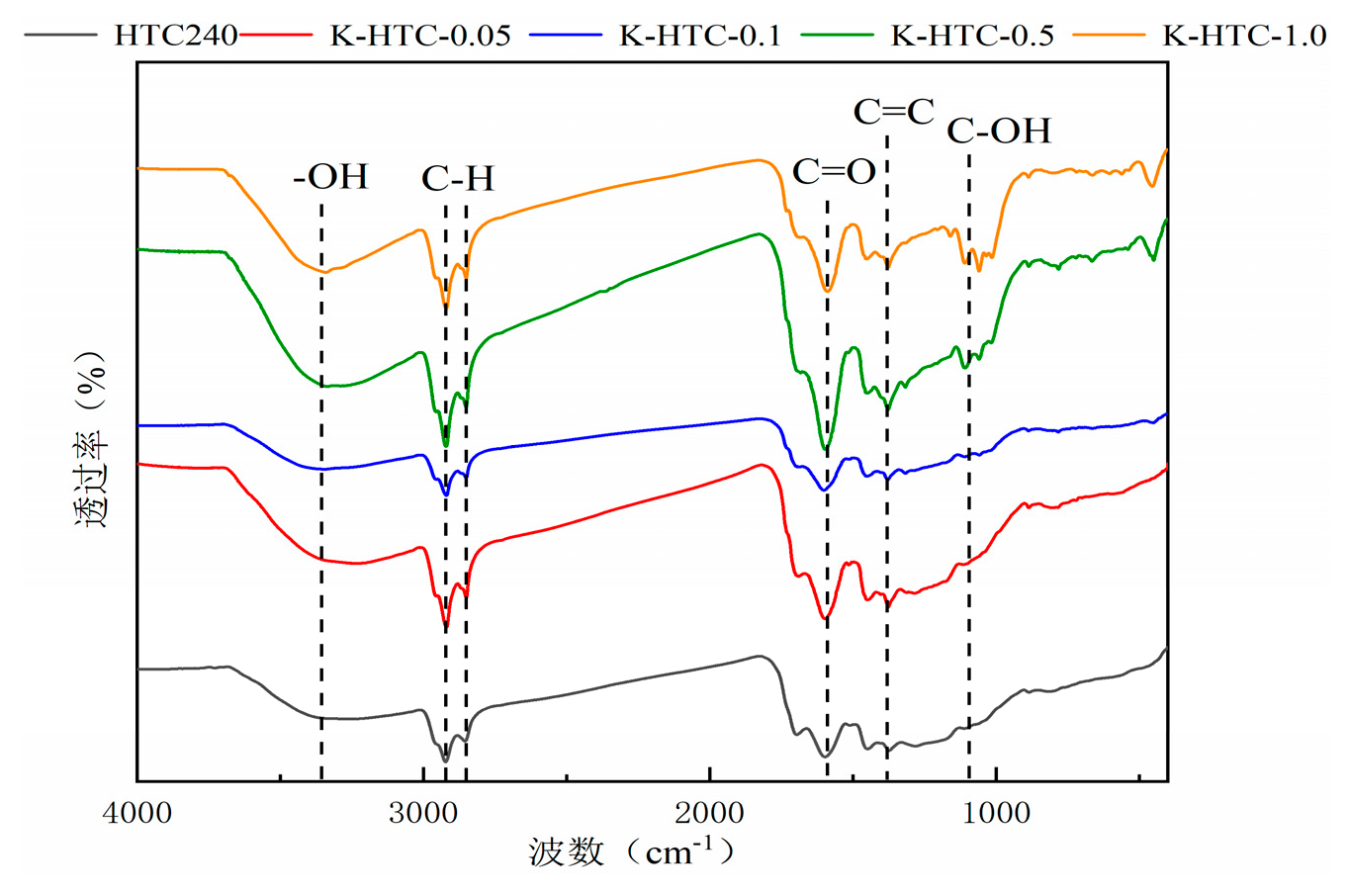
The FT-IR spectra of hydrothermal carbon before and after modification are shown in
Figure 2. From the figure, it can be seen that the types of functional groups in hydrothermal carbon are basically the same under different conditions, but there are some differences in the content. The infrared spectrum shows obvious absorption peaks at 3223 cm
-1, 2918 cm
-1, 2850 cm
-1, 1600 cm
-1, 1511 cm
-1, 1449 cm
-1, 1375 cm
-1, 1328 cm
-1, and 1059 cm
-1. The absorption peak at 3223 cm
-1 is attributed to the stretching vibration of -OH; the absorption peaks at 2918 cm
-1 and 2850 cm
-1 are attributed to the stretching vibration peaks of methyl and methylene C-H[
15]; the absorption peak at 1600 cm
-1 is attributed to the stretching vibration of carbonyl groups (aldehydes, ketones); the absorption peaks at 1511 cm
-1 and 1449 cm
-1 are mainly caused by stretching vibration of C=C, indicating the formation of hydrothermal carbon with aromatic structure. The absorption peak at 1317 cm
-1 is attributed to out-of-plane bending vibration of C-H; the absorption peak at 1107 cm
-1 is attributed to the stretching vibration of C-OH[
16].
According to
Figure 2, with the increase in concentration, the peak of alcohol-OH stretching vibration after modification at 0.5 mol/L is the widest among the four conditions. This indicates that the highest hydroxyl content is produced at this concentration[
17]. The stretching vibrations of C=C, C=O, and OH first increase and then stabilize, reaching the maximum stretching vibration at 0.5 mol/L KOH. The stretching vibration peaks of C-O/C-O-C gradually increase, indicating that a chemical reaction occurs with potassium hydroxide, leading to a higher degree of aromatization. Aromatic carbons are more stable under both biological and non-biological oxidation conditions. Due to the aromatic structure on the surface of hydrothermal carbon, cation-π adsorption is also considered a possible mechanism for the adsorption of heavy metals by biochar [
18].
3.1.3. XRD analysis
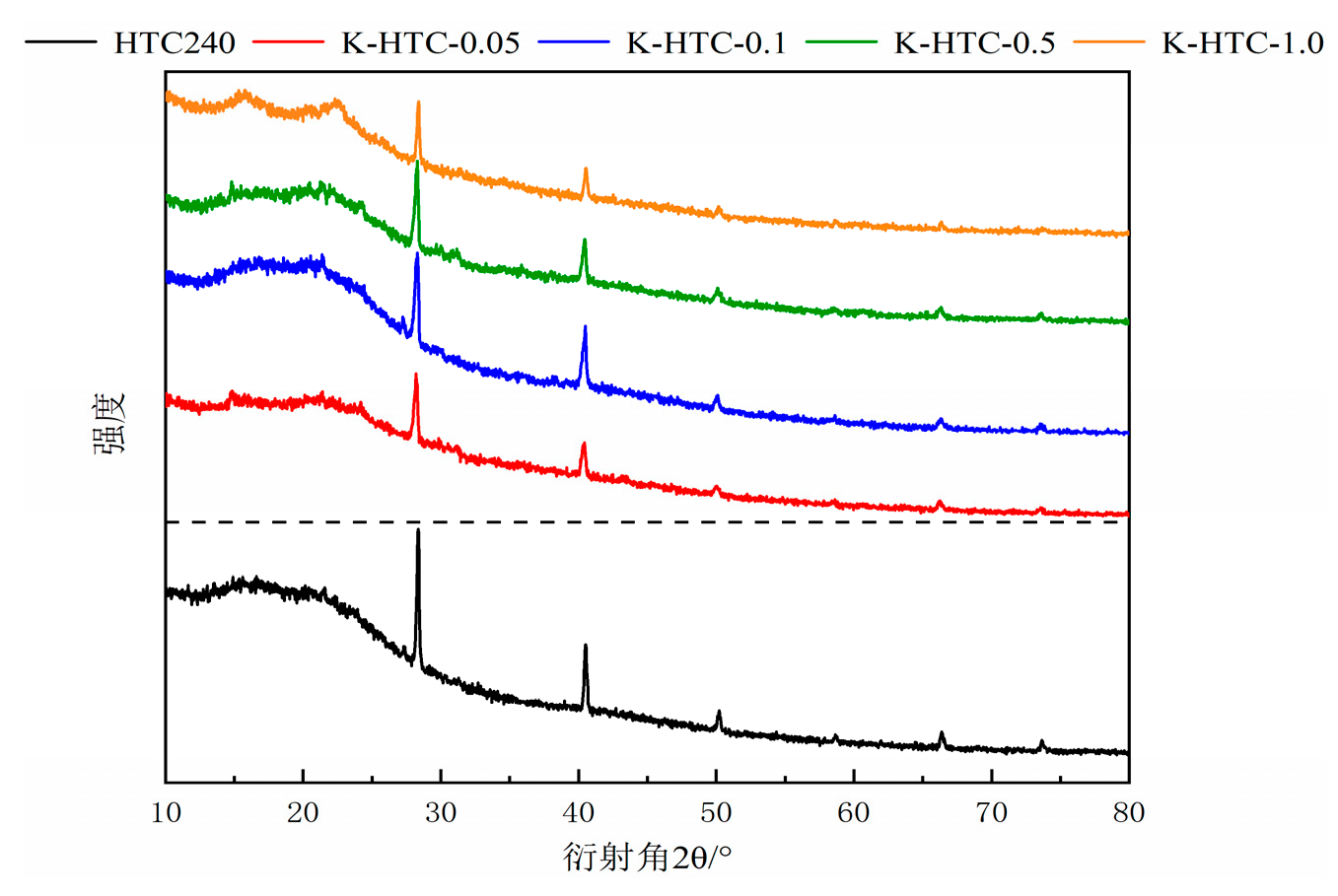
XRD characterization was performed on the hydrothermal carbons before and after modification, and the results are shown in
Figure 3. The characteristic diffraction peaks of potassium chloride were observed at approximately 23.1° and 42.8°. In the diffraction angle range of 10° to 30°, a broad peak was observed. With the increase in the concentration of the modifying agent, the peak area initially increased and then decreased [
19]. This indicates that the carbonization degree was highest at 0.1 mol/L, followed by 1.0 mol/L, 0.5 mol/L, and 0.05 mol/L. An increase in the concentration of the modifying agent improved the carbonization degree of the hydrothermal carbon, suggesting that the obtained material was mainly amorphous carbon and suitable as an adsorbent material [
20].
3.2. Analysis of Lead Ion Adsorption Performance of Hydrothermal Carbon
3.2.1. Influence of KOH Concentration on Adsorption Performance of Hydrothermal Carbon
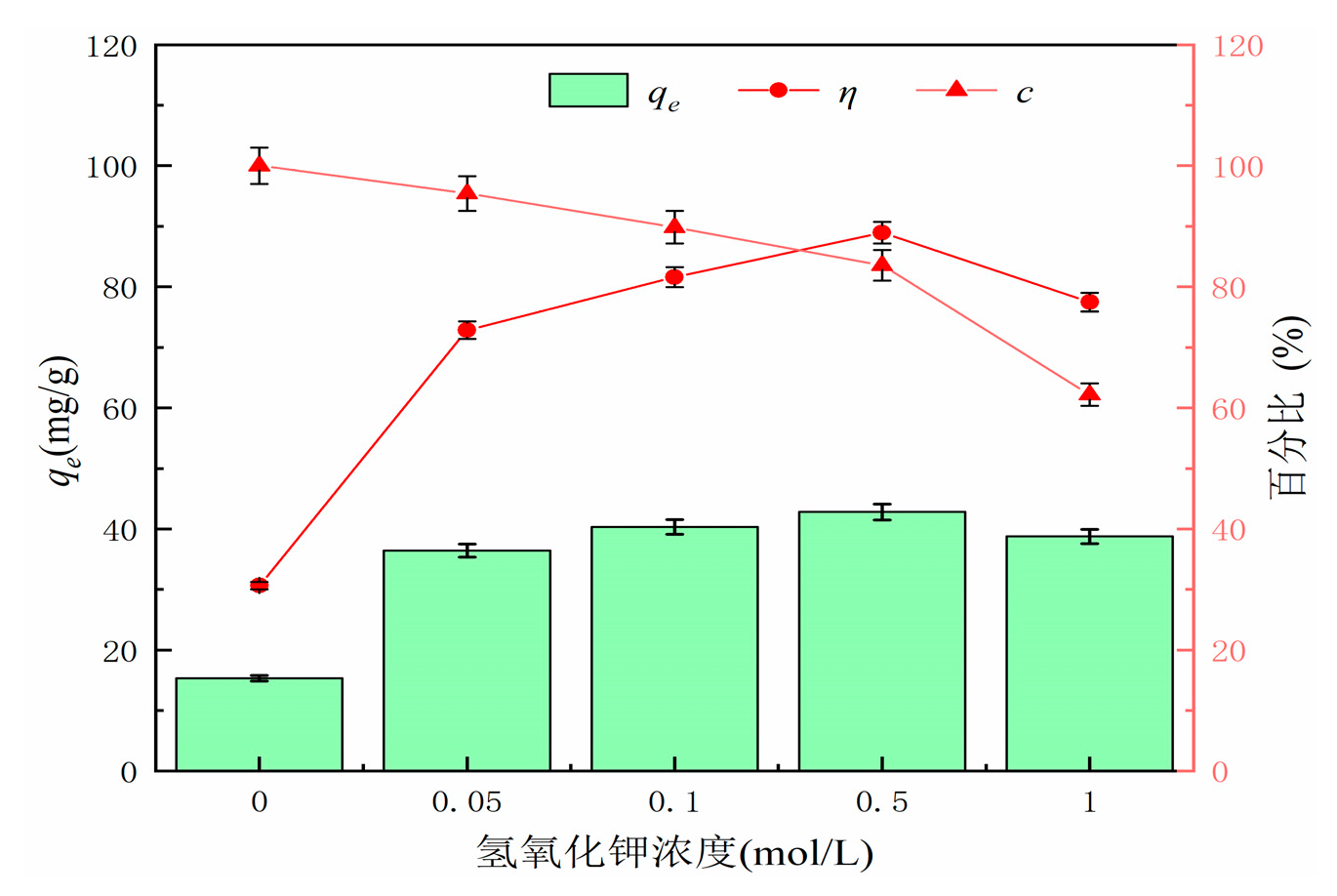
Different concentrations of KOH solution were used to modify the hydrothermal carbon derived from banana peel. Experimental conditions: pH = 7, adsorption time of 120 min, temperature of 25°C, solid-liquid ratio of 1 g/L, and initial concentration of 50 mg/L. The adsorption capacity and removal efficiency were calculated using formulas (1) and (2).
Figure 4 shows the effect of KOH concentration on the adsorption performance and yield of hydrothermal carbon. From the graph, it can be observed that the adsorption capacity and removal rate of KOH-modified hydrothermal carbon initially increase and then decrease. The maximum adsorption capacity is achieved when modified with a concentration of 0.5 mol/L KOH solution, with an adsorption capacity of 42.78 mg/g, which is 3.2 times higher than that of unmodified hydrothermal carbon (15.32 mg/g). The yield of modified hydrothermal carbon decreases with the increase of KOH concentration [
21]. This is because the strong alkali KOH continues to hydrolyze cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin in banana peels as the KOH concentration increases, resulting in a rapid decrease in carbon yield. KOH can also corrode the surface of hydrothermal carbon, opening up the blocked pores by tar deposition, and the chemical reaction in equation (3) leads to the destruction of the carbonaceous surface structure by KOH and the formation of new pore structures on the surface. This is further confirmed by the SEM analysis in
Figure 1(d). Considering that the modified hydrothermal carbon exhibits a higher adsorption capacity for lead ions with 0.5 mol/L KOH solution, subsequent adsorption experiments will be conducted based on this standard concentration [
22].
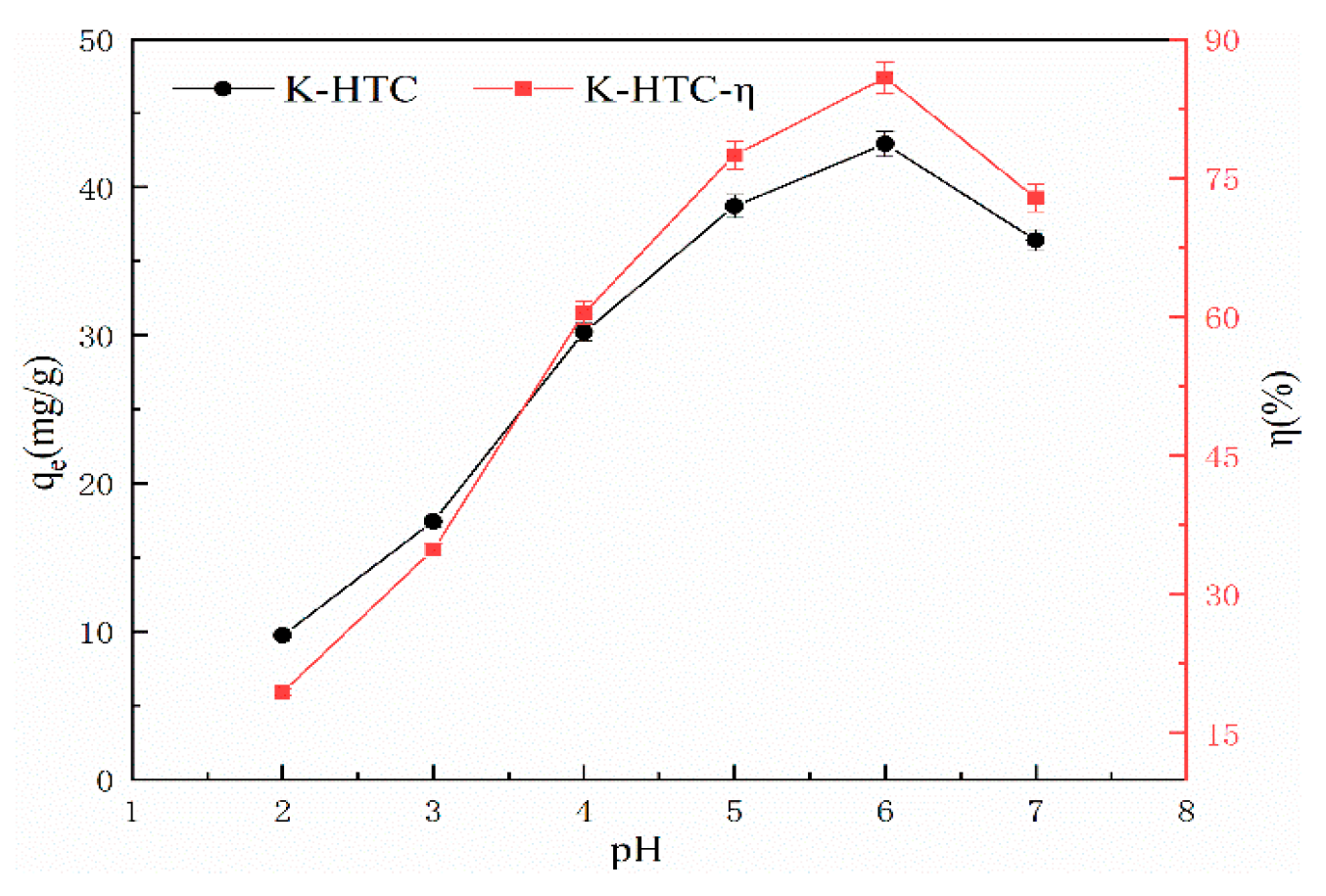
3.2.2. Effect of pH on the adsorption performance of lead ions
The experimental conditions include a pH range of 2 to 7, adsorption time of 120 minutes, temperature of 25℃, solid-liquid ratio of 1 g/L, and an initial concentration of 50 mg/L of KOH solution [
23].
Figure 5 shows the adsorption results of KOH-modified hydrothermal carbon with a concentration of 0.5 mol/L under different pH conditions.
Figure 4.
Effect of potassium hydroxide concentration on adsorption performance and yield of hydrothermal carbon before and after modification.
Figure 4.
Effect of potassium hydroxide concentration on adsorption performance and yield of hydrothermal carbon before and after modification.
From
Figure 5, it can be seen that the modified hydrothermal carbon exhibits an upward trend followed by a downward trend as the pH value increases. When the solution pH is 2, the adsorption capacity is 9.72 mg/g, and the removal rate is 19.44%; when the pH value increases from 3 to 6, the removal rate increases significantly. At pH 6, the adsorption capacity reaches a peak at 42.92 mg/g with a removal rate of 86.84%; when the pH is 7, the adsorption capacity of the modified hydrothermal carbon decreases. This is because when the H
+ concentration in the solution is too high, there is a competitive relationship between [Pb(H
2O)
6]
2+, Pb
2+, and H
+ [
24]. The higher the H
+ concentration, the weaker the competition of Pb(II), which cannot bind to the active sites on the modified hydrothermal carbon, thus hindering smooth adsorption [
25]. Combined with
Figure 2, it can be seen that the surface of the hydrothermal carbon contains a large number of oxygen-containing functional groups. A high concentration of H
+ can cause deprotonation of the oxygen-containing functional groups, which is favorable for binding with positively charged Pb
2+, and therefore increases the adsorption capacity.
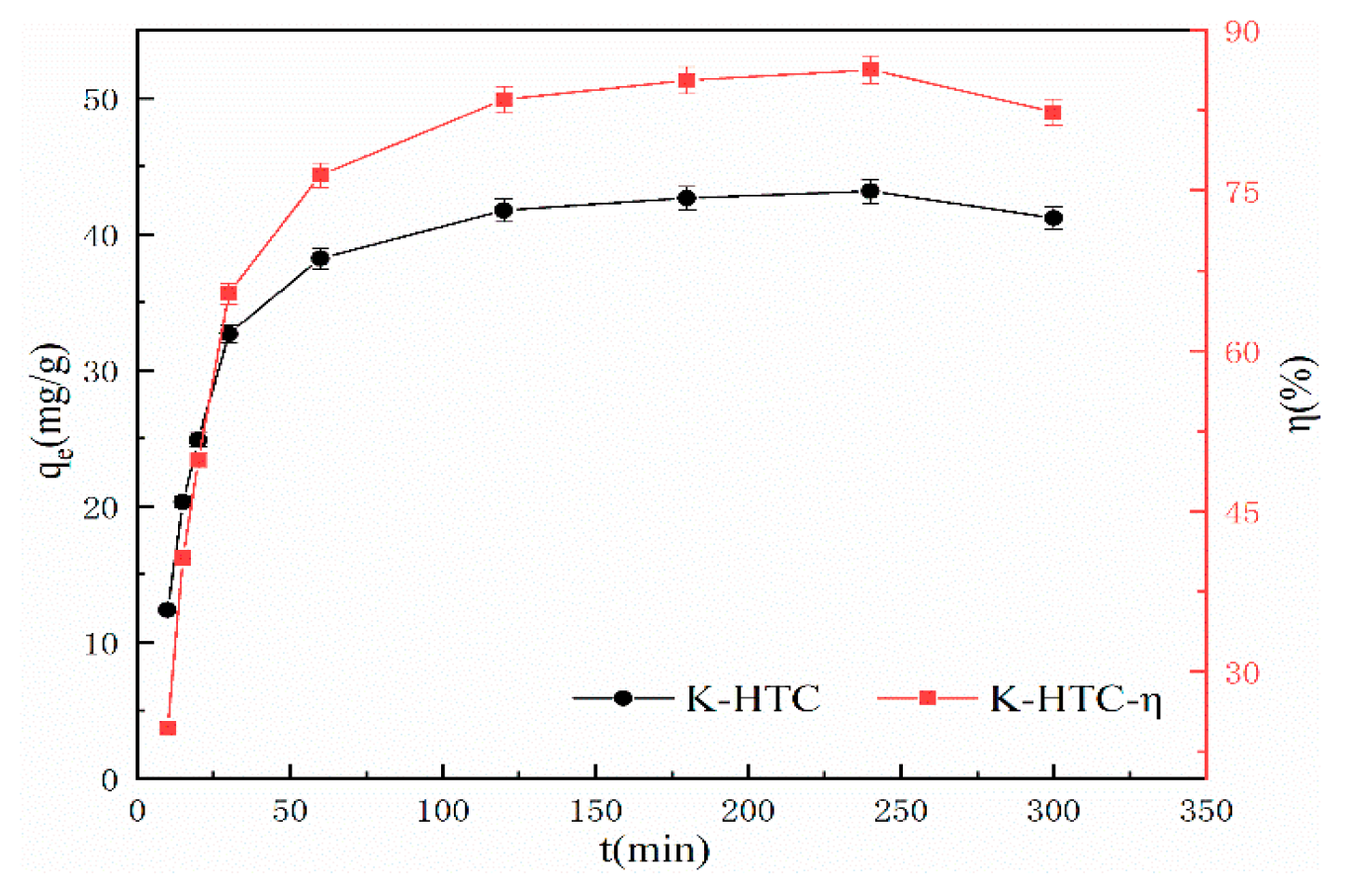
3.2.3. Analysis of Adsorption Performance and Kinetics of Hydrothermal Carbon Regarding Adsorption Time
To analyze the variation of water-thermal char adsorption process over time and provide evidence for the adsorption mechanism, the quasi-first-order kinetics, quasi-second-order kinetics, and Elovich three models are fitted. The model formulas are shown in equations (4) to (6). The experimental conditions are pH=7, adsorption time ranging from 0 to 6 hours, temperature of 25°C, solid-liquid ratio of 1 g/L, and initial concentration of 50 mg/L. The effect of modified water-thermal char adsorption time on Pb(II) adsorption is shown in
Figure 6.
According to
Figure 6, it can be seen that before 120 minutes, the modified hydrothermal carbon exhibits a linear increase in adsorption capacity for Pb(Ⅱ). With the increase in adsorption time, the adsorption rate of the modified hydrothermal carbon gradually decreases [
26]. After 240 minutes, the increase in adsorption rate slows down, and the removal efficiency tends to stabilize at 88.62%, reaching saturation. The results indicate that the adsorption process of the modified hydrothermal carbon mainly occurs within the first 120 minutes, with the adsorption rate greater than the desorption rate, allowing for a rapid adsorption process. After 240 minutes, the decrease in Pb(Ⅱ) concentration and the reduction in adsorption sites greatly reduce the probability of collision between them, which is unfavorable for adsorption [
27].
According to
Table 1, it can be seen that the correlation coefficient R
2 after fitting the pseudo second-order kinetics is 0.98, which is significantly higher than the fitting effect of the other two models. The calculated adsorption capacity (45.48 mg/g) of the pseudo second-order kinetics model for modified hydrothermal carbon is close to the actual adsorption capacity (44.61 mg/g), with a relative error of 1.9%. According to the modeling principles of the pseudo second-order kinetics model, it indicates that the adsorption process is complex, with different situations such as external liquid film diffusion, surface adsorption, and intra-particle diffusion [
28]. This is because the pseudo second-order kinetics equation can well describe the adsorption process of modified hydrothermal carbon and produce similar results as the isotherm simulation, indicating a chemical-physical adsorption process [
29].
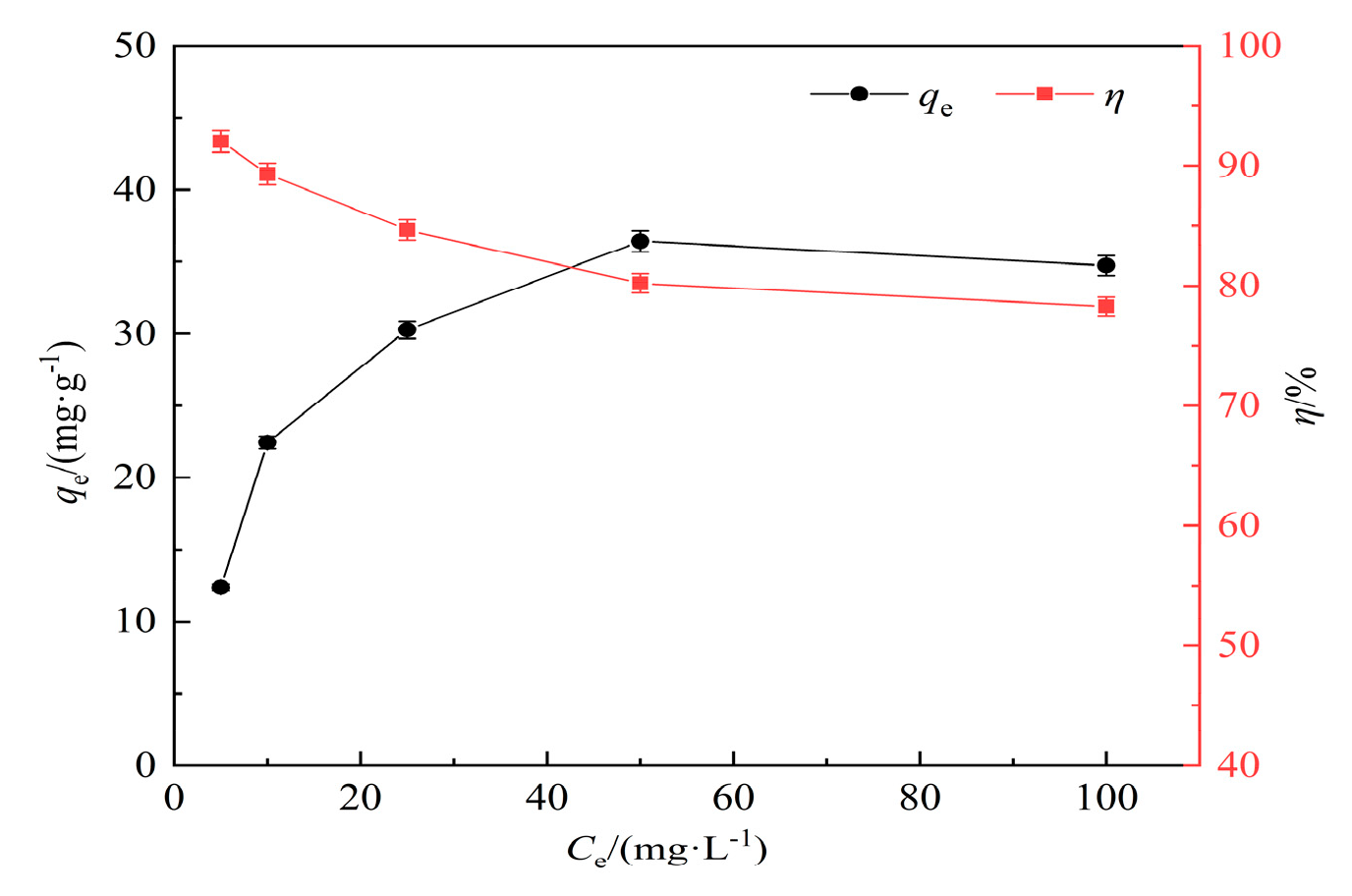
3.2.4. Removal rate and isothermal adsorption analysis of hydrothermal carbon for lead solution at different concentrations
In this experiment, lead (Pb(II)) solutions with concentrations of 5 mg/L, 10 mg/L, 25 mg/L, 50 mg/L, and 100 mg/L were selected. Experimental conditions: pH=7, adsorption time of 120 min, temperature of 25°C, solid-liquid ratio of 1 g/L, and a concentration of 0.5 mol/L for modified KOH. The effect of adsorption time on Pb(II) adsorption by modified hydrothermal carbon is shown in
Figure 6.
As shown in
Figure 7, with the increase of initial KOH concentration, the adsorption capacity of modified hydrothermal carbon for Pb(Ⅱ) shows a linear increase trend[
30]. When the initial concentration of lead solution is 5 mg/L, the removal rate can reach 92.05%. With the increase of initial concentration, the removal rate decreases significantly to 78.26% at 100 mg/L. This is because at lower initial concentrations, the affinity of the adsorbent for the adsorbate is high, and the content of Pb(Ⅱ) is low, which is conducive to the adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ)[
31]. With the increase of initial concentration, the concentration of Pb(Ⅱ) increases, and the driving force of concentration makes the adsorption sites move towards the interior of the pores, resulting in an increase in the adsorption capacity [
32].
3.2.5. Modified hydrothermal carbon isothermal adsorption analysis
To analyze the variation law of adsorption of hydrothermal carbon with time and provide basis for the adsorption mechanism, two kinetic models were used for fitting [
33]. The experimental conditions were pH=7, adsorption time of 0~6 hours, temperature of 25°C, solid-liquid ratio of 1 g/L, and initial concentration of 50 mg/L.
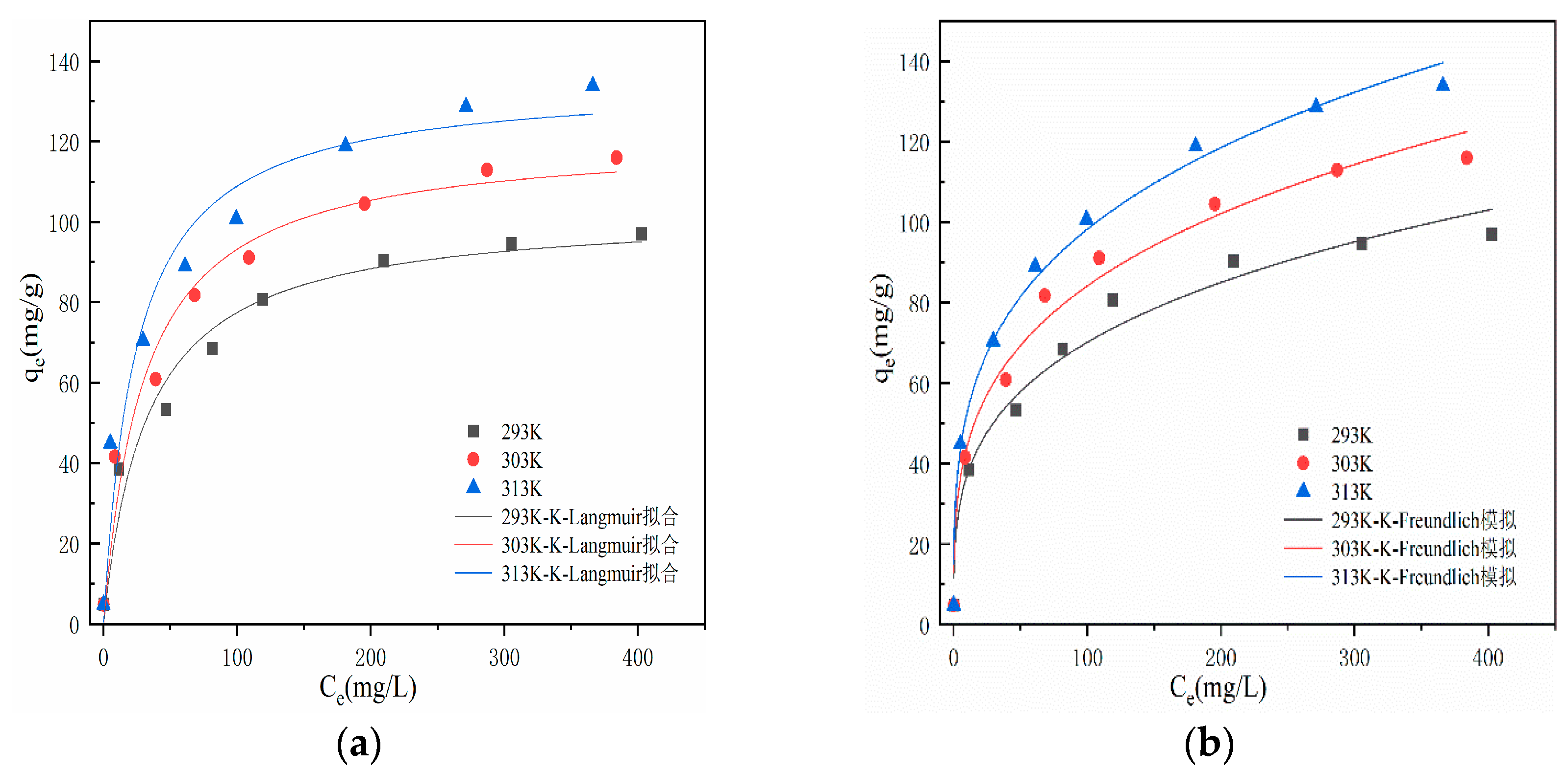
From
Figure 8, it can be seen that at a reaction temperature of 293K, the adsorption capacity of modified hydrothermal carbon for Pb(Ⅱ) increases from 4.85 mg/g to 119.31 mg/g within the range of adsorption equilibrium mass concentration of 5-200 mg/L. The adsorption capacity increases rapidly, exhibiting typical characteristics of chemical adsorption[
34]. With the increase of initial concentration, the adsorption capacity increases slowly, and the active sites on the surface of hydrothermal carbon transition from unsaturated state to saturated state, eventually reaching adsorption equilibrium. The adsorption capacity also varies at different temperatures, with the adsorption capacity of hydrothermal carbon gradually increasing as the temperature rises [
35]. The analysis suggests that the increase in temperature facilitates Brownian motion of molecules, increases the effective collision between Pb(Ⅱ) and surface active functional groups, and promotes molecules to enter deeper pore structures, thereby enhancing the adsorption capacity. This indicates that higher temperature is beneficial for smooth adsorption, and the adsorption process is endothermic [
36].
Table 2 shows the thermodynamic coefficients for adsorption. According to
Table 2, fitting of the Langmuir and Freundlich models to the adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ) on modified hydrothermal carbon at temperatures of 293K, 303K, and 313K yield correlation coefficients (R
2) of 0.96, 0.96, and 0.95, respectively, for the Langmuir model. The correlation coefficients are all greater than or equal to 0.95, and the values of KL are all less than 1, indicating that the adsorption is easy and the process is irreversible chemical adsorption [
37]. For the Freundlich model, the corresponding R2 values at 293K, 303K, and 313K are 0.97, 0.98, and 0.98, respectively. The correlation coefficients are all greater than 0.95 and higher than those of the Langmuir model. This suggests that the "active sites" on the modified hydrothermal carbon surface are randomly distributed, indicating differences in adsorption capacity and the characteristics of physical adsorption in multilayer form [
38]. When the value of 1/n in the Freundlich model is less than 1, it is considered that chemical adsorption occurs during the adsorption process. The analysis suggests that in the adsorption process of modified hydrothermal carbon, Pb(Ⅱ) first binds to the active sites on the surface, undergoes chemical adsorption, and as the reaction progresses, the number of active sites decreases and the driving force for chemical adsorption weakens [
39]. SEM analysis in
Figure 1 reveals that the modified hydrothermal carbon has a strong porous structure, and under the driving force of physical adsorption, Pb(Ⅱ) continuously fills the pores [
14] and undergoes internal diffusion, adsorbing onto new active sites on the modified hydrothermal carbon, resulting in multilayer physical adsorption [
40].
4. Conclusion
The physicochemical properties of phosphoric acid modified banana peel were studied by means of SEM, FT-IR and XRD. The effects of pH value, adsorption time, solid-liquid ratio and initial concentration of potassium hydroxide on the adsorption properties of modified hydrothermal carbon were studied. The adsorption mechanism of modified hydrothermal carbon on PB (II) was studied by adsorption thermodynamics and kinetic simulation. The following conclusions were reached:
- (1)
The modified hydrothermal carbon contains large carbonaceous particles and developed pore structures. After hydrothermal treatment, the material mainly consists of amorphous carbon with abundant oxygen-containing functional groups, providing active sites for adsorption.
- (2)
Adsorption experiments on hydrothermal carbon modified with different concentrations of KOH showed that the maximum adsorption capacity was achieved at 0.5 mol/L KOH modification. Factors such as pH, temperature, oscillation time, initial concentration, and the modified hydrothermal carbon showed a positive correlation with the adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ), while the solid-liquid ratio exhibited an initially increasing and then decreasing trend.
- (3)
The Freundlich model in the adsorption thermodynamics model is more suitable for the adsorption process of modified hydrothermal carbon on Pb(Ⅱ), with correlation coefficients (R^2) of 0.97, 0.98, and 0.98 at 293K, 303K, and 313K, respectively, indicating a multilayer adsorption process. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model in the adsorption kinetics model better represents the adsorption process of modified hydrothermal carbon on Pb(Ⅱ), indicating chemical-physical adsorption.
References
- Ding Lin, Wang Pengxiang, Liu Hao, et al. Research progress on the adsorption and removal of lead ions in wastewater using functionalized metal-organic framework materials [J]. Materials Guide, 2022, 36(20): 40-50.
- Zhu Junbo, Zhao Jianbing, Zhou Shiping, et al. Performance and adsorption mechanism of peanut shell biochar for removing lead and cadmium ions from water [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Science), 2022, 42(5): 78-86.
- JAGADEESH N, SUNDARAM B. Adsorption of Pollutants from Wastewater by Biochar: A Review[J/OL]. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 2023, 9: 100226. [CrossRef]
- Research on the reaction mechanism and product formation mechanism of cow dung hot water treatment. Central China Agricultural University., 2019. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CDFD&dbname=CDFDLAST2020&filename=1019065795.nh&v=.
- PAULINE A L, JOSEPH K. Hydrothermal carbonization of oily sludge for solid fuel recovery – investigation of chemical characteristics and combustion behaviour[J/OL]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 157: 105235. [CrossRef]
- SHAHROKHI-SHAHRAKI R, BENALLY C, EL-DIN M G, et al.. High efficiency removal of heavy metals using tire-derived activated carbon vs commercial activated carbon: Insights into the adsorption mechanisms[J/OL]. Chemosphere, 2021, 264: 128455. [CrossRef]
- JIANG F, CAO D, HU S, et al.. High-pressure carbon dioxide-hydrothermal enhance yield and methylene blue adsorption performance of banana pseudo-stem activated carbon[J/OL]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 354: 127137. [CrossRef]
- NIZAMUDDIN S, SIDDIQUI M T H, BALOCH H A, et al.. Upgradation of chemical, fuel, thermal, and structural properties of rice husk through microwave-assisted hydrothermal carbonization[J/OL]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(18): 17529-17539. [CrossRef]
- WU C, HUANG L, XUE S G, et al. Arsenic sorption by red mud-modified biochar produced from rice straw[J/OL]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(22): 18168-18178. [CrossRef]
- JOHNSON V E, LIAO Q, JALLAWIDE B W, et al.. Simultaneous removal of As(V) and Pb(II) using highly-efficient modified dehydrated biochar made from banana peel via hydrothermal synthesis[J/OL]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 663: 131115. [CrossRef]
- Qiu B, Tao X, Wang H, et al. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 155: 105081. [CrossRef]
- CUI Y, ZHAO B, XIE F, et al. Study on the preparation and feasibility of a novel adding-type biological slow-release carbon source[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 316: 115236. [CrossRef]
- ZANG J, TIAN P, YANG G, et al.. A facile preparation of pomegranate-like porous carbon by carbonization and activation of phenolic resin prepared via hydrothermal synthesis in KOH solution for high performance supercapacitor electrodes[J/OL]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2019, 30(12): 2900-2907. [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Plata F , Ruiz-Rosas R , E Morallón, et al. Activated Carbons Prepared through H3PO4-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonisation from Biomass Wastes: Porous Texture and Electrochemical Performance[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Bashir S, Zhu J, Fu Q, et al. Comparing the adsorption mechanism of Cd by rice straw pristine and KOH-modified biochar[J]. Environmental science and pollution research, 2018, 25: 11875-11883. [CrossRef]
- Xu J, Zhang Y, Li B, et al. Improved adsorption properties of tetracycline on KOH/KMnO4 modified biochar derived from wheat straw[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 296: 133981. [CrossRef]
- An Q, Jiang Y Q, Nan H Y, et al. Unraveling sorption of nickel from aqueous solution by KMnO4 and KOH-modified peanut shell biochar: Implicit mechanism[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 214: 846-854. [CrossRef]
- MARTINS A C, PEZOTI O, CAZETTA A L, et al.. Removal of tetracycline by NaOH-activated carbon produced from macadamia nut shells: Kinetic and equilibrium studies[J/OL]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 260: 291-299. [CrossRef]
- Tan G, Sun W, Xu Y, et al. Sorption of mercury (II) and atrazine by biochar, modified biochars and biochar based activated carbon in aqueous solution[J]. Bioresource technology, 2016, 211: 727-735. [CrossRef]
- LUO X, FU C, SHEN S, et al.. Free–templated synthesis of N–doped PtCu porous hollow nanospheres for efficient ethanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions[J/OL]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 330: 122602. [CrossRef]
- Lü F, Lu X, Li S, et al. Dozens-fold improvement of biochar redox properties by KOH activation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132203. [CrossRef]
- Sun K, Tang J, Gong Y, et al. Characterization of potassium hydroxide (KOH) modified hydrochars from different feedstocks for enhanced removal of heavy metals from water[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22: 16640-16651. [CrossRef]
- Komnitsas K A, Zaharaki D. Morphology of modified biochar and its potential for phenol removal from aqueous solutions[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2016, 4: 26. [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Xu Z, Xu L, et al. Modified biochar: synthesis and mechanism for removal of environmental heavy metals[J]. Carbon Research, 2022, 1(1): 8. [CrossRef]
- 30.JieYu, Xing Wang, Quanfagn Lu, et al. Study on the adsorption mechanism of chitosan-polyacrylic acid hydrogel on Pb2+ [J/OL]. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 53(4): 61-67. [CrossRef]
- Wongrod S, Simon S, Guibaud G, et al. Lead sorption by biochar produced from digestates: Consequences of chemical modification and washing[J]. Journal of environmental management, 2018, 219: 277-284. [CrossRef]
- Herath A, Layne C A, Perez F, et al. KOH-activated high surface area Douglas Fir biochar for adsorbing aqueous Cr (VI), Pb (II) and Cd (II)[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 269: 128409. [CrossRef]
- Liu H, Zhu J, Li Q, et al. Adsorption performance of methylene blue by KOH/FeCl3 modified biochar/alginate composite beads derived from agricultural waste[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(6): 2507. [CrossRef]
- Yakout S M, Daifullah A E H M, El-Reefy S A. Pore structure characterization of chemically modified biochar derived from rice straw[J]. Environmental Engineering & Management Journal (EEMJ), 2015, 14(2).
- Cheng N, Wang B, Wu P, et al. Adsorption of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by modified biochar: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 273: 116448. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Bolan N S, Tsang D C W, et al. Green immobilization of toxic metals using alkaline enhanced rice husk biochar: Effects of pyrolysis temperature and KOH concentration[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 720: 137584. [CrossRef]
- Williams N E, Oba O A, Aydinlik N P. Modification, Production, and Methods of KOH-Activated Carbon[J]. ChemBioEng Reviews, 2022, 9(2): 164-189.
- Sun K, Tang J, Gong Y, et al. Characterization of potassium hydroxide (KOH) modified hydrochars from different feedstocks for enhanced removal of heavy metals from water[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22: 16640-16651. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Wang L, Zhao H, et al. Utilization of KOH-modified fly ash for elimination from aqueous solutions of potentially toxic metal ions[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 223: 115396. [CrossRef]
- Khushk S, Zhang L, Pirzada A M, et al. Cr (VI) heavy metal adsorption from aqueous solution by KOH treated hydrochar derived from agricultural wastes[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing, 2019, 2119(1). [CrossRef]
- Argun M E, Dursun S. Removal of heavy metal ions using chemically modified adsorbents[J]. J. Int. Environ. Appl. Sci, 2006, 1(1-2): 27-40.
- Hossain N, Nizamuddin S, Shah K. Thermal-chemical modified rice husk-based porous adsorbents for Cu (II), Pb (II), Zn (II), Mn (II) and Fe (III) adsorption[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2022, 46: 102620. [CrossRef]
- Kharrazi S M, Mirghaffari N, Dastgerdi M M, et al. A novel post-modification of powdered activated carbon prepared from lignocellulosic waste through thermal tension treatment to enhance the porosity and heavy metals adsorption[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 366: 358-368. [CrossRef]
- Ogunlalu O, Oyekunle I P, Iwuozor K O, et al. Trends in the mitigation of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using unmodified and chemically-modified agricultural waste adsorbents[J]. Current Research in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2021, 4: 100188. [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Xu Z, Xu L, et al. Modified biochar: synthesis and mechanism for removal of environmental heavy metals[J]. Carbon Research, 2022, 1(1): 8. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).