Submitted:
23 October 2023
Posted:
30 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Experimental methods
2.3.1. Preparation of banana peel hydrothermal charcoal
2.3.2. Preparation of phosphoric acid modified hydrothermal carbon
2.3.3. Adsorption experiment
2.3.4. Characterization of hydrothermal carbon in banana peel
3. Results
3.1. Surface structure and properties of hydrothermal carbon before and after modification
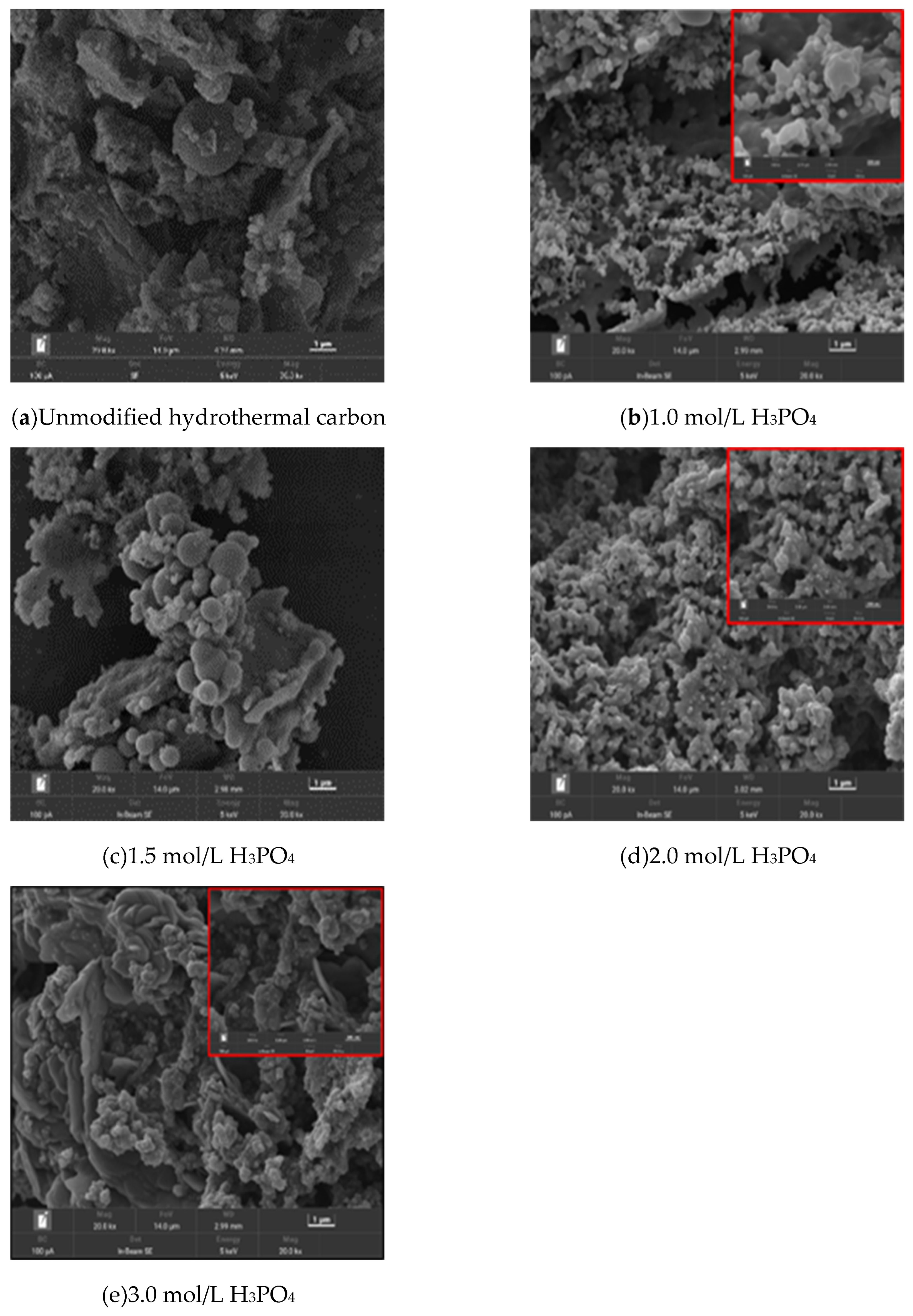
3.1.1. SEM analysis
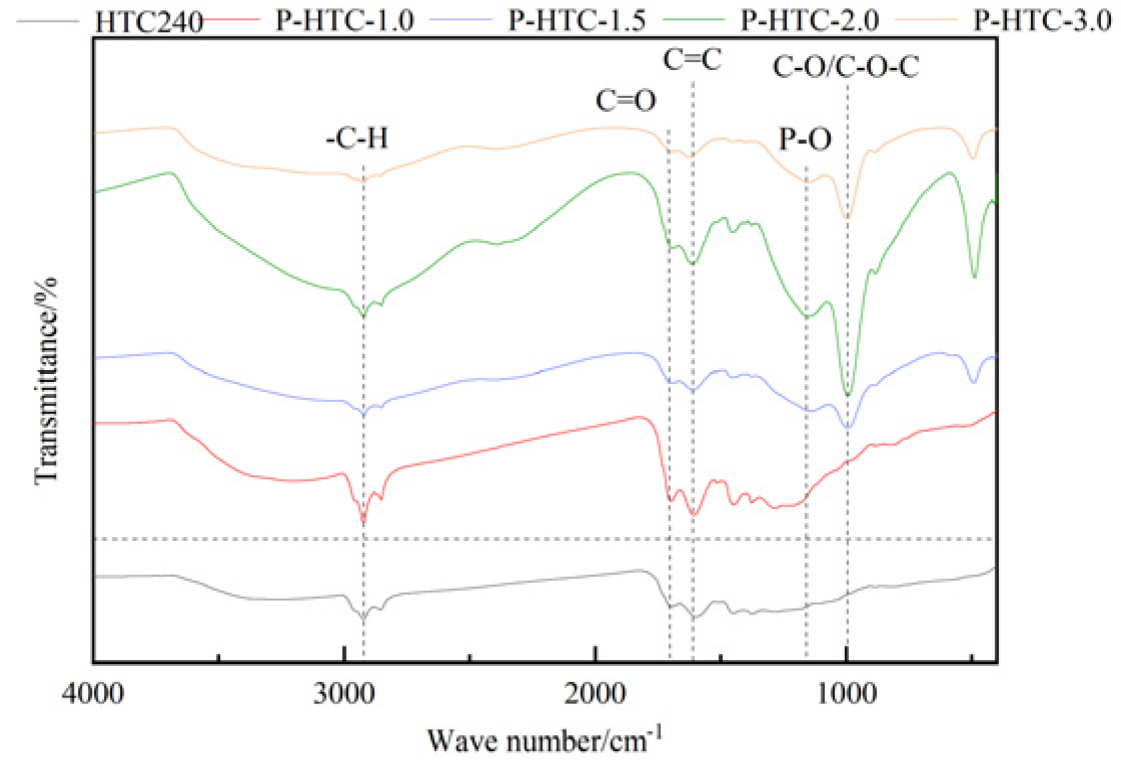
3.1.2. FT-IR analysis
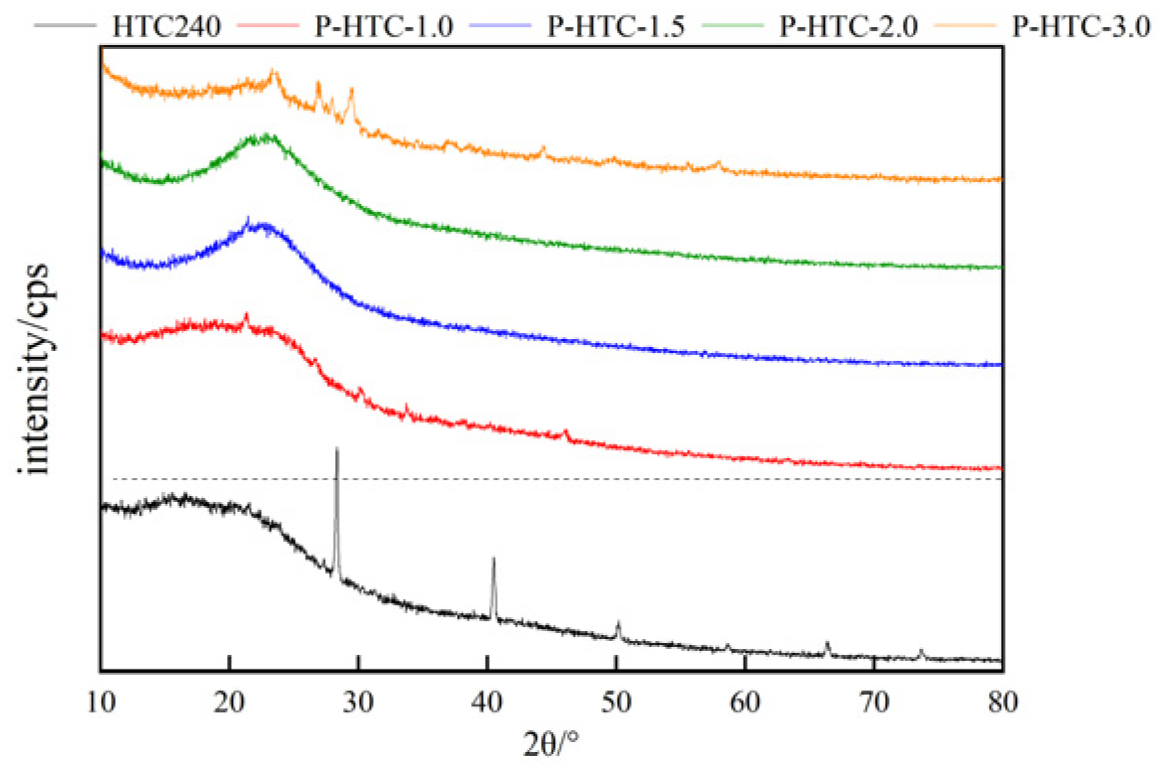
3.1.3. XRD analysis
3.2. Analysis of adsorption performance of lead ions by modified hydrothermal carbon
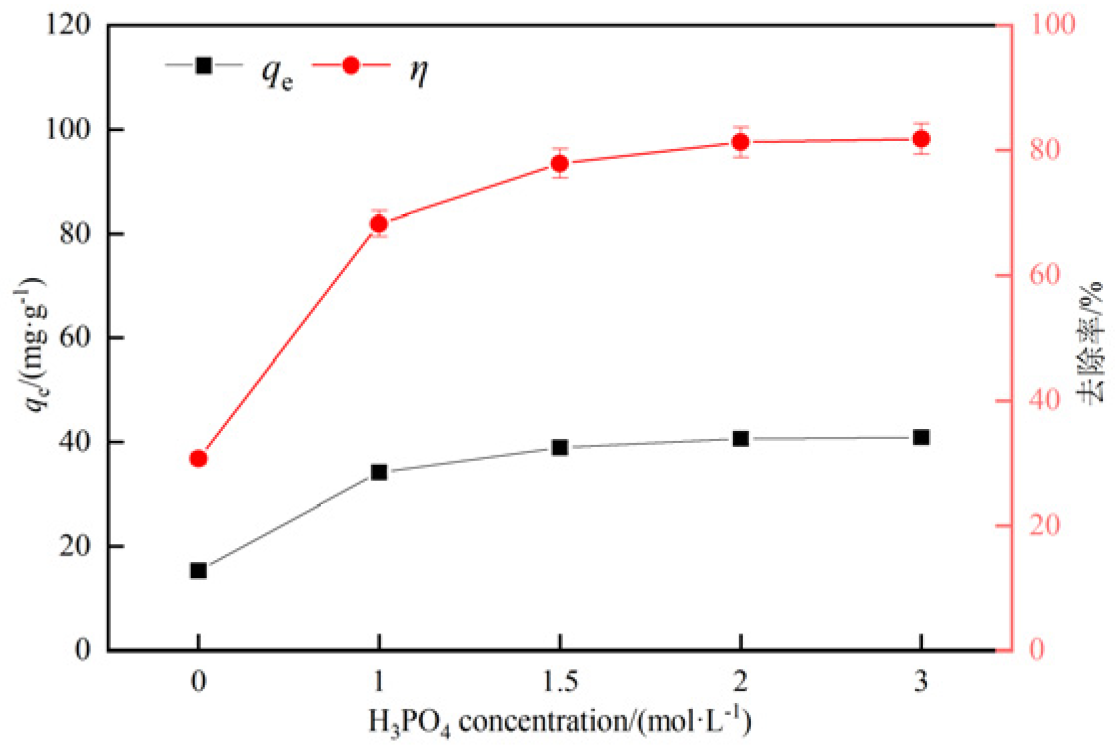
3.2.1. Influence of phosphoric acid concentration on adsorption effect of hydrothermal carbon
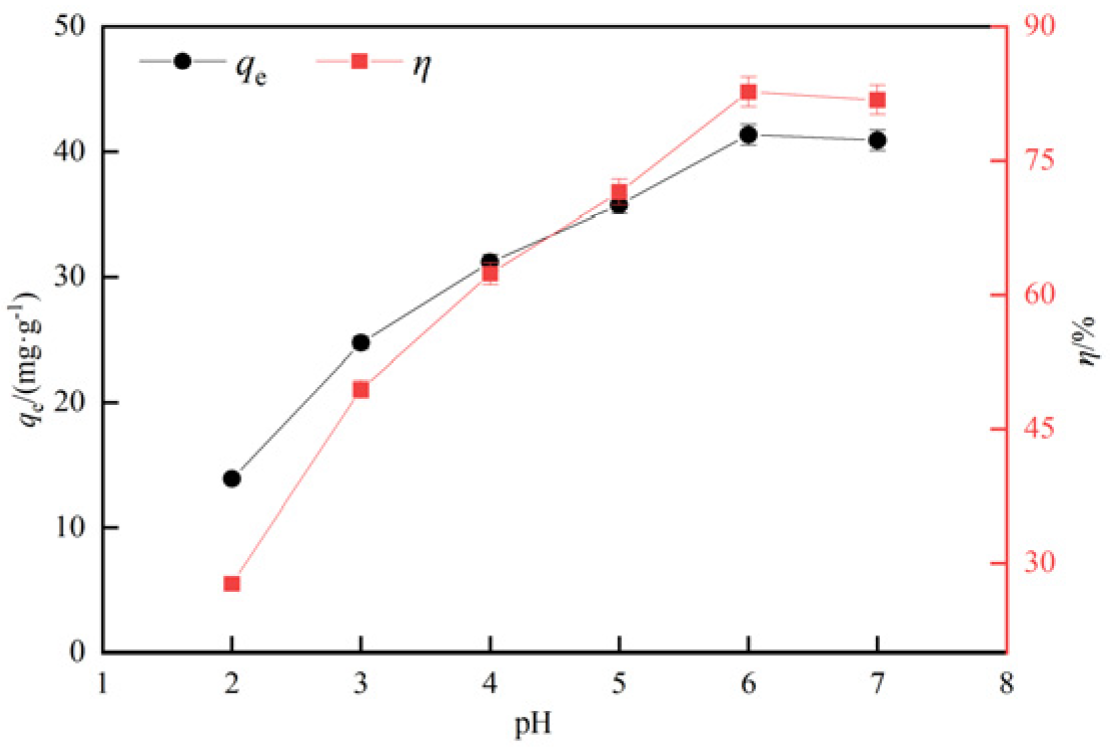
3.2.2. Influence of pH value on adsorption effect of lead ion
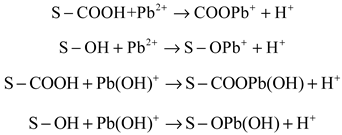
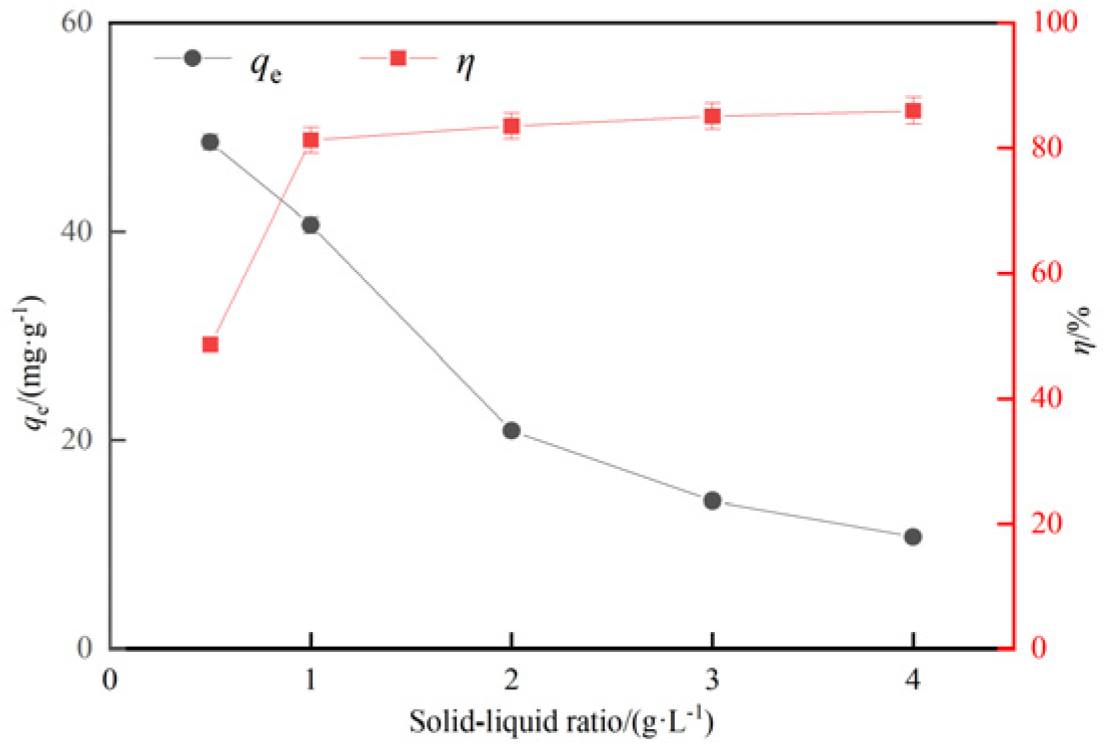
3.2.3. Influence of solid-liquid ratio on adsorption effect of hydrothermal carbon
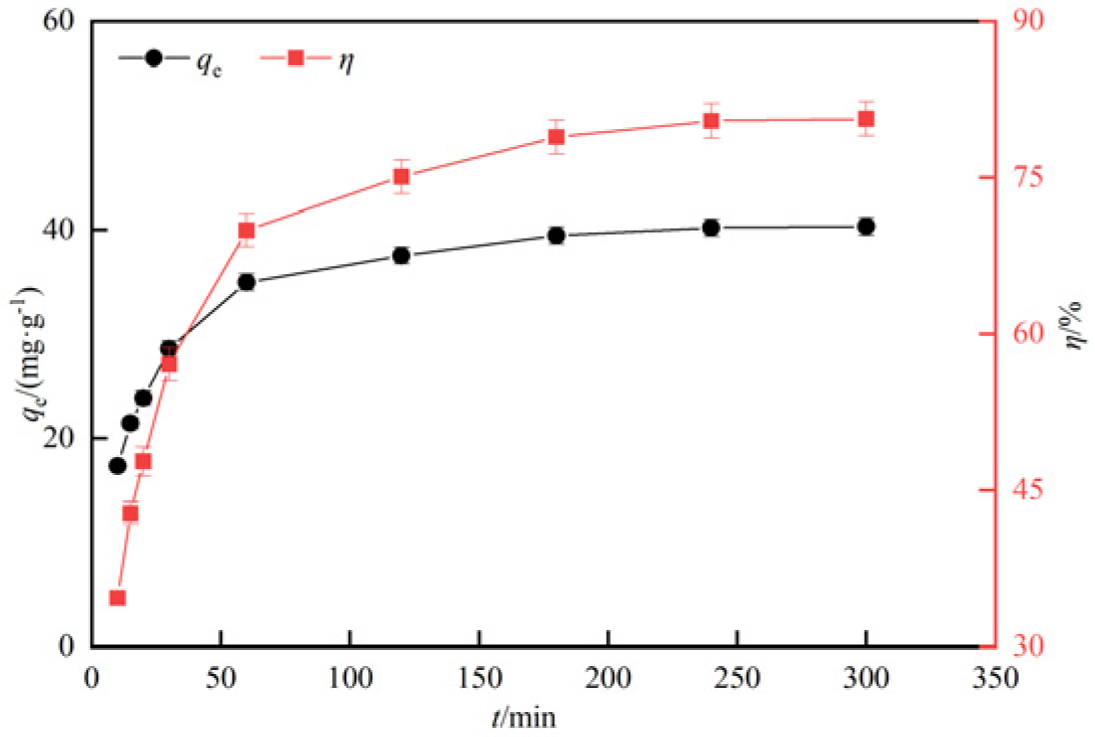
3.2.4. Analysis of adsorption performance and kinetics by adsorption time
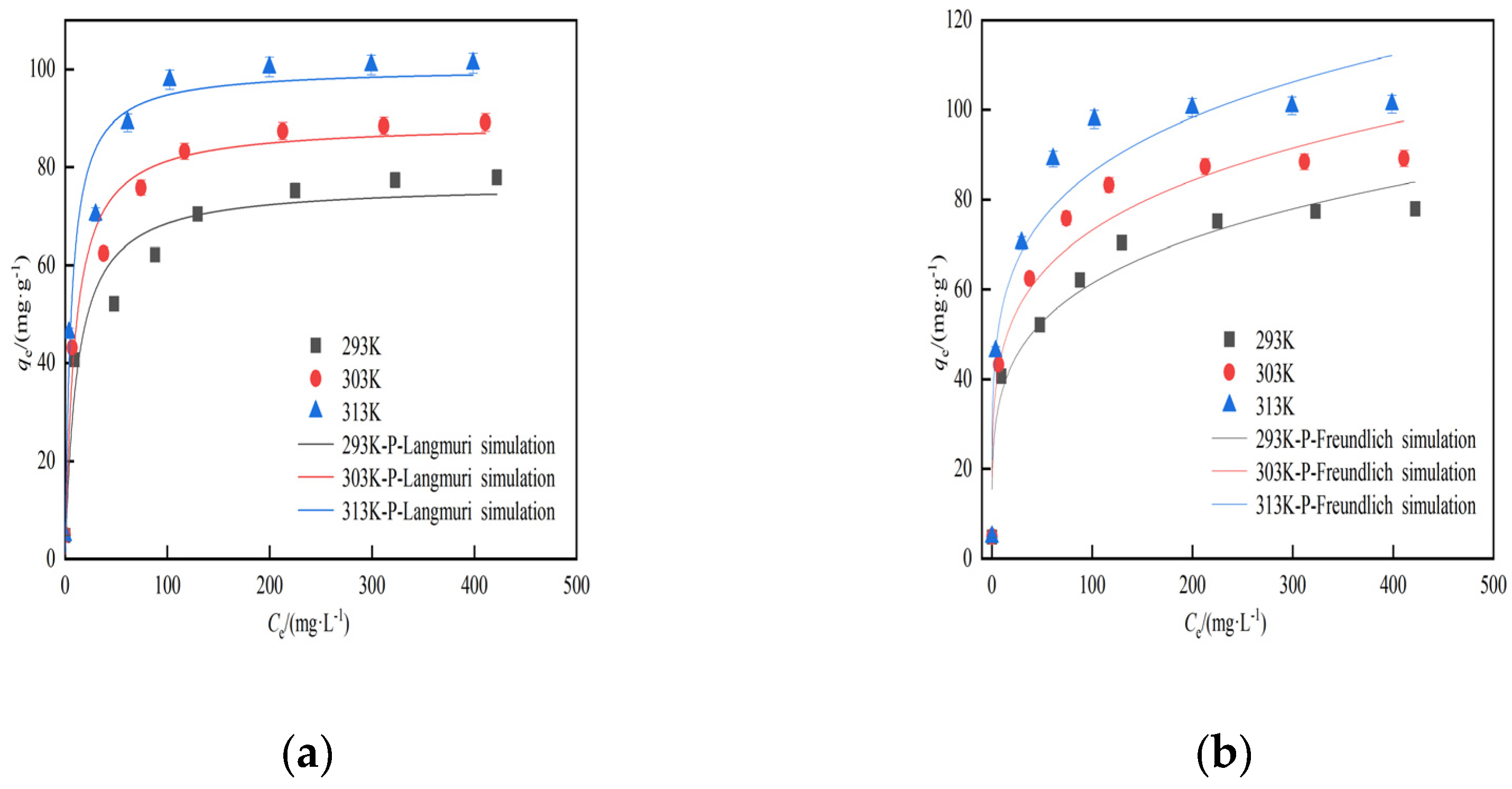
3.2.5. Modified hydrothermal carbon isothermal adsorption analysis
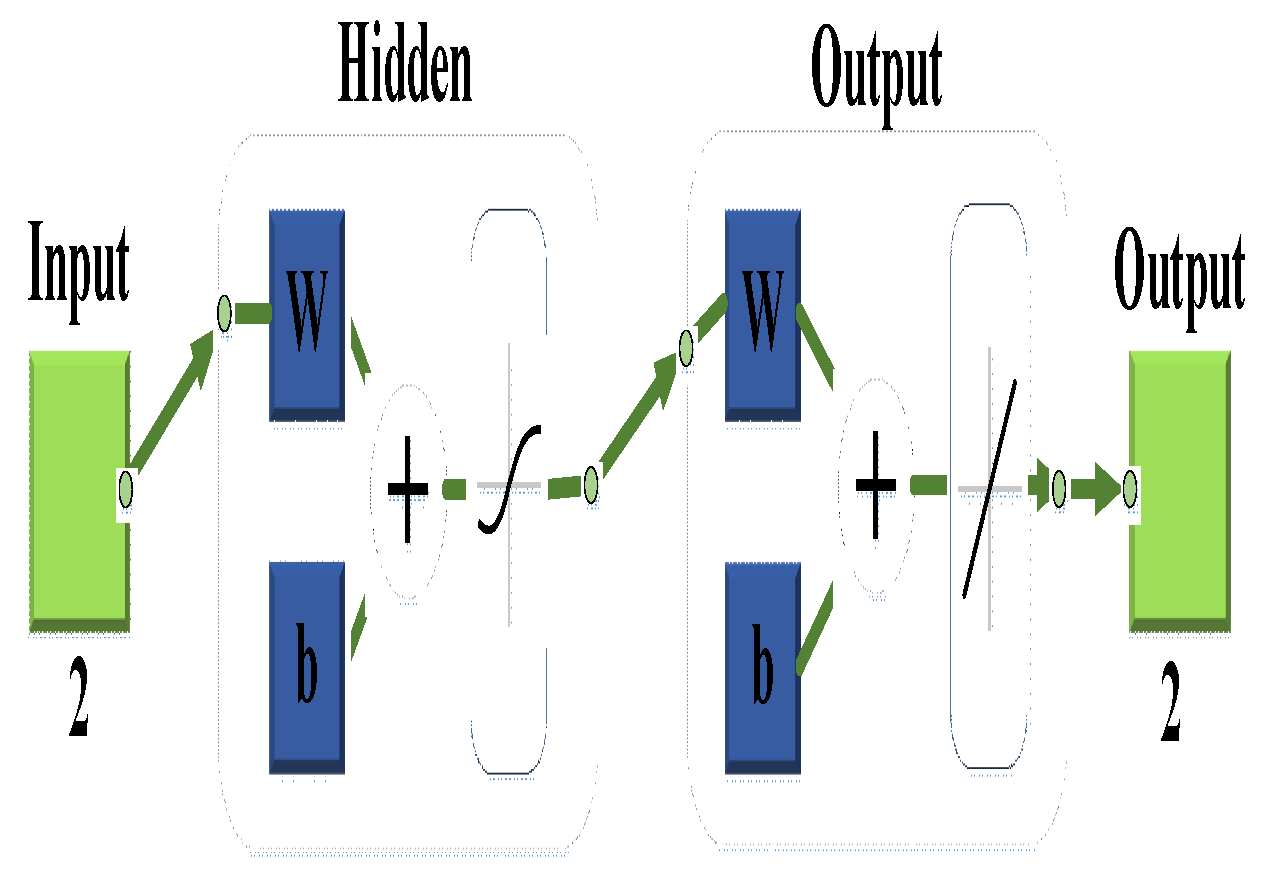
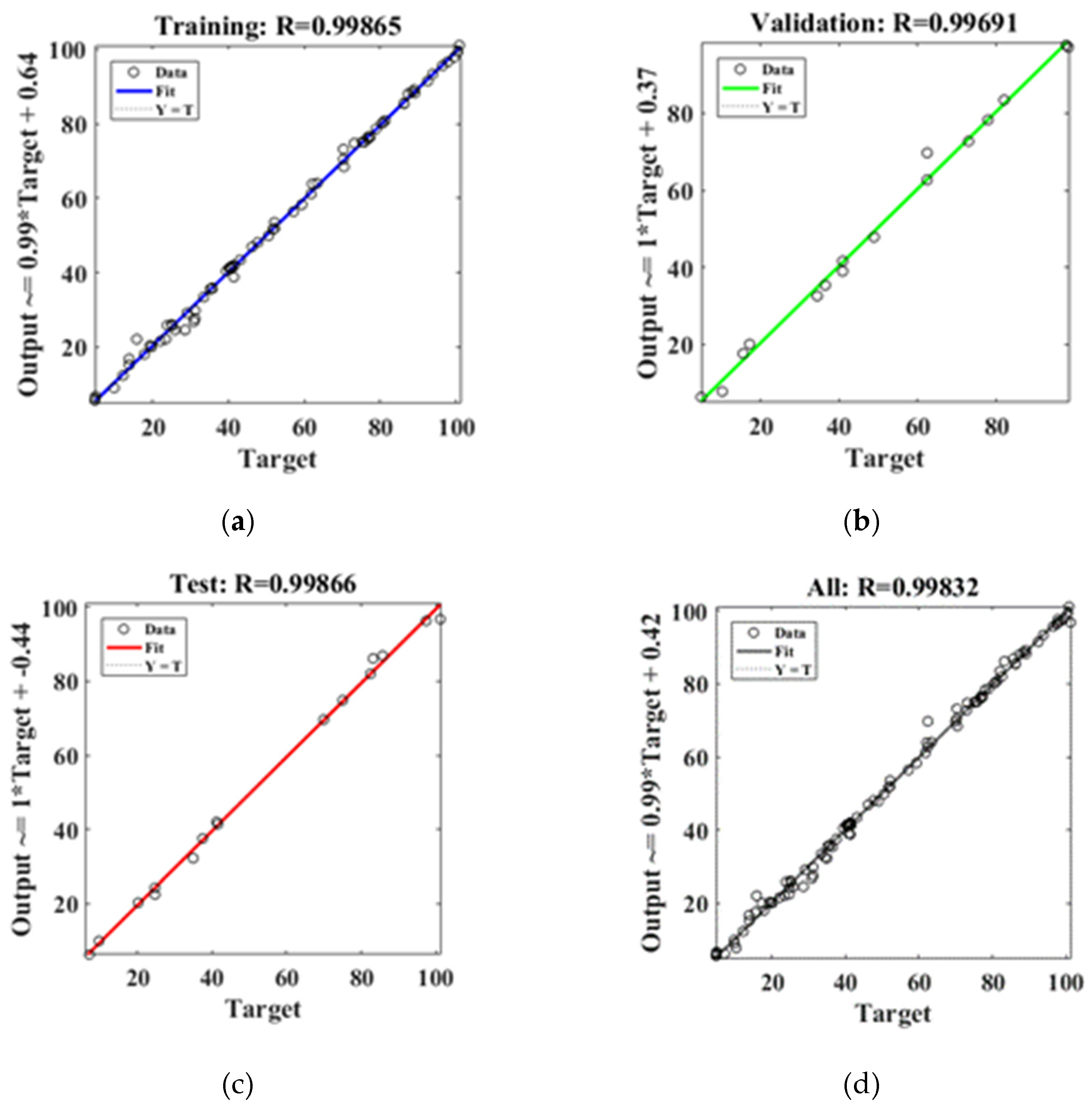
3.2.6. Artificial neural network model
3.2.7. Modified hydrothermal carbon isothermal adsorption analysis
4. Conclusion
- (1)
- There is a large carbon sphere particle in the modified hydrothermal carbon, the diameter of 2-3μm, hydrothermal material is mainly amorphous carbon shape, its surface has a large number of oxygen-containing functional groups, which is conducive to adsorption.
- (2)
- The adsorption experiments of hydrothermal carbon modified with different concentrations of phosphoric acid showed that pH value, temperature, oscillation time and initial concentration were positively correlated with the adsorption capacity of Pb(Ⅱ) by hydrothermal carbon modified with different concentrations of phosphoric acid, while the solid-liquid ratio was opposite to the adsorption capacity.
- (3)
- Langmuir model of isotherm model is more suitable to describe the thermodynamic process of Pb(Ⅱ) adsorption by modified hydrothermal carbon, indicating that the adsorption is mainly monolayer chemisorption. The quasi-second-order kinetic model can better describe the kinetic adsorption process of Pb(Ⅱ) by hydrothermal carbon, indicating that the chemical adsorption is the main process. Artificial neural network fitting correlation R=0.99.
- (4)
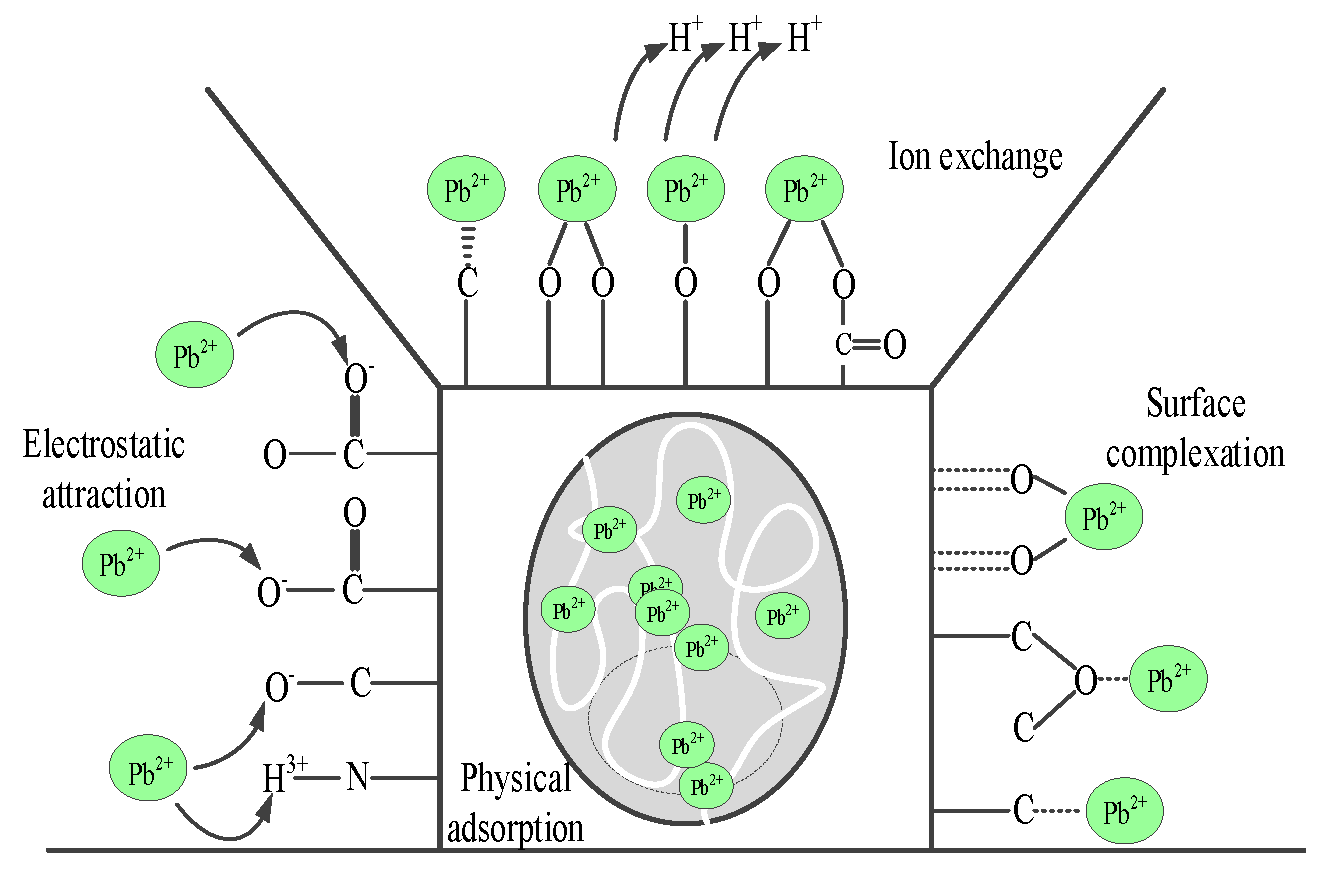
- Through model fitting and characterization analysis, the adsorption mechanism of Pb(Ⅱ) on hydrothermal carbon was studied, including physical adsorption, electrostatic attraction, ion exchange and surface complexation.
References
- DING L, WANG P, LIU H, et al. Research Progress in Functionalized Metal-Organic Frameworks Materials for Adsorptive Removal of Lead Ions from Wastewater [J]. Material Guide, 2022, 36(20): 40-50. [CrossRef]
- ZHU J B, ZHAO J B, ZHOU S P, et al. Study on Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of Peanut Shell Biochar for Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Water [J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University, 2022, 42(5): 78-86.
- Yao Jiakang,Wang Leiming,Zhang Guangwei,Tao Jinliang,Shi Xiaoping,Wei Feng. Plate structure optimization and performance study of a new continuous flow electrocoagulation reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2023,194. [CrossRef]
- Madrid Felipe M Galleguillos,ArancibiaBravo María P,Sepúlveda Felipe D,Lucay Freddy A,Soliz Alvaro,Cáceres Luis. Ultrafine Kaolinite Removal in Recycled Water from the Overflow of Thickener Using Electroflotation: A Novel Application of Saline Water Splitting in Mineral Processing.[J]. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland),2023,28(9). [CrossRef]
- Song Wenxin,Gao Zhimin,Tan Fengxun,Cheng Xiaoxiang,Yang Tao,Wu Daoji,Yang Jingxin,Liang Heng. Calcium sulfite oxidation activated by ferrous iron integrated with membrane filtration for removal of typical algal contaminants[J]. Chemosphere,2023,333. [CrossRef]
- Abdul Sattar Jatoi,Humair Ahmed Baloch,Shaukat Ali Mazari,N. M. Mubarak,Nizamuddin Sabzoi,Shaheen Aziz,Suhail Ahmed Soomro,Rashid Abro,Syed Feroz Shah. A review on extractive fermentation via ion exchange adsorption resins opportunities, challenges, and future prospects[J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery,2021(prepublish). [CrossRef]
- Gherbi Bachir,Laouini Salah Eddine,Meneceur Souhaila,Bouafia Abderrhmane,Hemmami Hadia,Tedjani Mohammed Laid,Thiripuranathar Gobika,Barhoum Ahmed,Menaa Farid. Effect of pH Value on the Bandgap Energy and Particles Size for Biosynthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles: Efficiency for Photocatalytic Adsorption of Methyl Orange[J]. Sustainability,2022,14(18).
- Wang Leshi,Hao Jiuxiao,Yu Xintian,Zhang Bingjie,Sui Jun,Wang Chuanxin. Method development for the identification, extraction and characterization of melanoidins in thermal hydrolyzed sludge.[J]. The Science of the total environment,2022.
- Chuan Chen,Guangmin Liu,Qing An,Lin Lin,Yong Shang,Chunli Wan. From wasted sludge to valuable biochar by low temperature hydrothermal carbonization treatment: Insight into the surface characteristics[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,263(C). [CrossRef]
- JAGADEESH N, SUNDARAM B. Adsorption of Pollutants from Wastewater by Biochar: A Review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 2023, 9: 100226. [CrossRef]
- Sun W, Bai L, Chi M, et al. Study on the Evolution Pattern of the Aromatics of Lignin during Hydrothermal Carbonization[J]. Energies, 2023, 16. [CrossRef]
- WU K. Study on reaction mechanism and product formation mechanism of water heat treatment of cow manure [D]. Huazhong Agricultural University, 2019.
- PAULINE A L, JOSEPH K. Hydrothermal carbonization of oily sludge for solid fuel recovery – investigation of chemical characteristics and combustion behaviour[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021. [CrossRef]
- SHAHROKHI-SHAHRAKI R, BENALLY C, EL-DIN M G, et al. High efficiency removal of heavy metals using tire-derived activated carbon vs. commercial activated carbon: Insights into the adsorption mechanisms[J]. 2020.128455. [CrossRef]
- Lohn Pereira Nathan Roberto,dos Anjos Felipe Eduardo,Faverzani Magnago Rachel. Lignocellulosic Residues of Banana Cultivation: A Review of the Cellulose Extraction Chemical Processes[J]. Revista Virtual de Química,2019,11(4).
- JIANG F, CAO D, HU S, et al. High-pressure carbon dioxide-hydrothermal enhance yield and methylene blue adsorption performance of banana pseudo-stem activated carbon[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 354: 127137. [CrossRef]
- NIZAMUDDIN S, SIDDIQUI M T H, BALOCH H A, et al. Upgradation of chemical, fuel, thermal, and structural properties of rice husk through microwave-assisted hydrothermal carbonization[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(18): 17529-17539.
- WU C, HUANG L, XUE S G, et al. Arsenic sorption by red mud-modified biochar produced from rice straw[J/OL]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2017, 24(22): 18168-18178.
- JOHNSON V E, LIAO Q, JALLAWIDE B W, et al. Simultaneous removal of As(V) and Pb(II) using highly-efficient modified dehydrated biochar made from banana peel via hydrothermal synthesis[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 663: 131115.
- Quesada-Plata F, Ruiz-Rosas R, E Morallón, et al. Activated Carbons Prepared through H3PO4-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonisation from Biomass Wastes: Porous Texture and Electrochemical Performance[J]. ChemPlusChem, 2016.
- CUI Y, ZHAO B, XIE F, et al. Study on the preparation and feasibility of a novel adding-type biological slow-release carbon source[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 316: 115236. [CrossRef]
- SUN K, TANG J, GONG Y, et al. Characterization of potassium hydroxide (KOH) modified hydrochars from different feedstocks for enhanced removal of heavy metals from water[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(21): 16640-16651. [CrossRef]
- Liu A, Liu S, Liu P, et al. Water sorption on coal: effects of oxygen-containing function groups and pore structure[J]. International Journal of Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 8(5):20. [CrossRef]
- Wu Q, Yu S, Hao N, et al. Characterization of products from hydrothermal carbonization of pine[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017:78. [CrossRef]
- WANG Y M. Hydrothermal preparation, adsorption properties and mechanism of corn cob carbon - based adsorbent [D]. Anhui Agricultural University, 2018.
- SHAKYA A, VITHANAGE M, AGARWAL T. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on biochar properties and Cr(VI) adsorption from water with groundnut shell biochars: Mechanistic approach[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 215: 114243.
- LUO X, FU C, SHEN S, et al. Free–templated synthesis of N–doped PtCu porous hollow nanospheres for efficient ethanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 330: 122602.
- TIBERG C, SJÖSTEDT C, PERSSON I, et al. Phosphate effects on copper(II) and lead(II) sorption to ferrihydrite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 120: 140-157.
- B Y Z A, D Y Y A C, D G L A C, et al. Adsorption mechanism of cadmium on microplastics and their desorption behavior in sediment and gut environments: The roles of water pH, lead ions, natural organic matter and phenanthrene[J]. Water Research, 2020, 184. [CrossRef]
- Nagireddi S, Uppaluri R, Golder A. Role of protonation and functional groups in Pd(II) recovery and reuse characteristics of commercial anion exchange resin-synthetic electroless plating solution systems[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2018, 22:227-238.
- DEBEVC S, WELDEKIDAN H, SNOWDON M R, et al. Valorization of almond shell biomass to biocarbon materials: Influence of pyrolysis temperature on their physicochemical properties and electrical conductivity[J]. Carbon Trends, 2022, 9: 100214. [CrossRef]
- IGHALO J O, RANGABHASHIYAM S, DULTA K, et al. Recent advances in hydrochar application for the adsorptive removal of wastewater pollutants[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2022, 184: 419-456.
- Fang D, Zhuang X, Huang L, et al. Developing the new kinetics model based on the adsorption process: From fitting to comparison and prediction[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 725:138490.
- Chen M, Wang X, Zhang H. Comparative research on selective adsorption of Pb(II) by biosorbents prepared by two kinds of modifying waste biomass: Highly-efficient performance, application and mechanism[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 288:112388. [CrossRef]
- Ting Wang, Liu W, Xiong L, et al. Influence of pH, ionic strength and humic acid on competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) onto titanate nanotubes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Rostami S, Toghraie D, Shabani B, et al. Measurement of the thermal conductivity of MWCNT-CuO/water hybrid nanofluid using artificial neural networks (ANNs)[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2021, 143(2):1097-1105.
- Věra Krková. Kolmogorov's theorem and multilayer neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 1992, 5( 3):501-506. [CrossRef]
- Abd A A, Naji S Z, Hashim A S, et al. Carbon dioxide removal through Physical Adsorption using Carbonaceous and non-Carbonaceous Adsorbents: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5):104142.
- Jawad A H, Abdulhameed A S, Mastuli M S. Acid-factionalized biomass material for methylene blue dye removal: a comprehensive adsorption and mechanism study[J].
- Peng H, Guo J. Removal of chromium from wastewater by membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption electrocoagulation, electrochemical reduction, electrodialysis, electrodeionization, photocatalysis and nanotechnology: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Swa B, Jhkb C, Msid E, et al. Biochar surface complexation and Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) adsorption in aqueous solutions depend on feedstock type - ScienceDirect[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 712. [CrossRef]

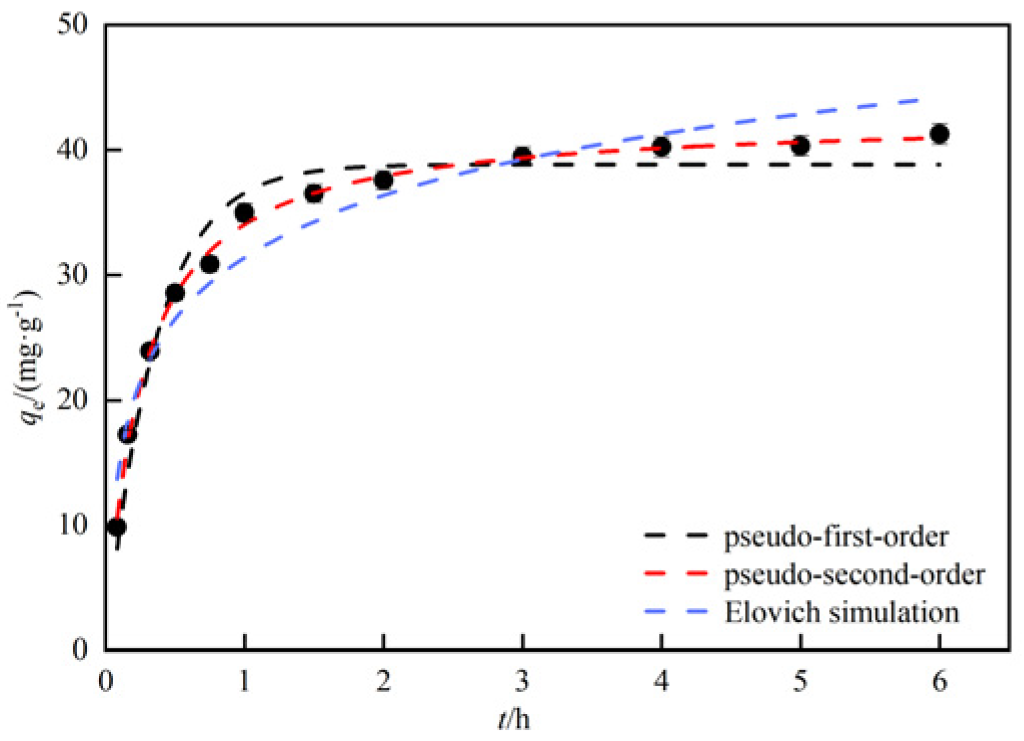
| Dynamic model | Parameters and correlation coefficients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pseudo-first-order | K1 | qe | h0 | R2 |
| 1/min | mg/g | mg/(min∙g) | ||
| 2.8241 | 38.84 | 109.53 | 0.95 | |
| pseudo-second-order | K2 | qe | h0 | R2 |
| g/(mg∙min) | mg/g | mg/(min∙g) | ||
| 0.0928 | 42.68 | 169.04 | 0.99 | |
| Elovich | α | β | - | R2 |
| 582.59 | 0.14 | - | 0.94 | |
| Isotherm model | Experimental conditions | Parameters and related parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | T/K | KL/L∙mg−1 | qm/mg∙g−1 | R2 |
| 293 | 0.0853 | 76.54 | 0.95 | |
| 303 | 0.1057 | 88.94 | 0.97 | |
| 313 | 0.1704 | 103.24 | 0.96 | |
| Freundlich | T/K | KF(mg/g(1/mg)1/n) | 1/n | R2 |
| 293 | 22.4625 | 0.22 | 0.94 | |
| 303 | 28.7186 | 0.20 | 0.92 | |
| 313 | 35.8388 | 0.19 | 0.90 | |
| Input value | Predicted value | Actual value | Error value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Temperature | Time | Solid-liquid ratio | Initial concentration | qF | ηc | qe | η | |∆q| | |∆η| |
| K | min | g/L | mg/L | mg/g | % | mg/g | % | % | % | |
| 2 | 293 | 120 | 1 | 50 | 13.1 | 13.2 | 13.8 | 27.6 | 5 | 4.3 |
| 7 | 313 | 120 | 1 | 50 | 44.4 | 87.8 | 46.2 | 92.4 | 3.8 | 4.9 |
| 7 | 293 | 300 | 1 | 50 | 40.9 | 80.2 | 40.3 | 80.7 | 1.5 | 0.6 |
| 7 | 293 | 120 | 2 | 50 | 15.23 | 60.4 | 15.8 | 63.4 | 3.6 | 4.8 |
| 7 | 293 | 120 | 1 | 150 | 74.1 | 24.8 | 75.2 | 25.1 | 1.5 | 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




