Submitted:
27 October 2023
Posted:
30 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Secondary metabolites from Eurotium
2.1. Anthraquinones
2.2. Benzaldehyde derivatives
2.3. Indole diketopiperazine alkaloids
2.4. Other compounds
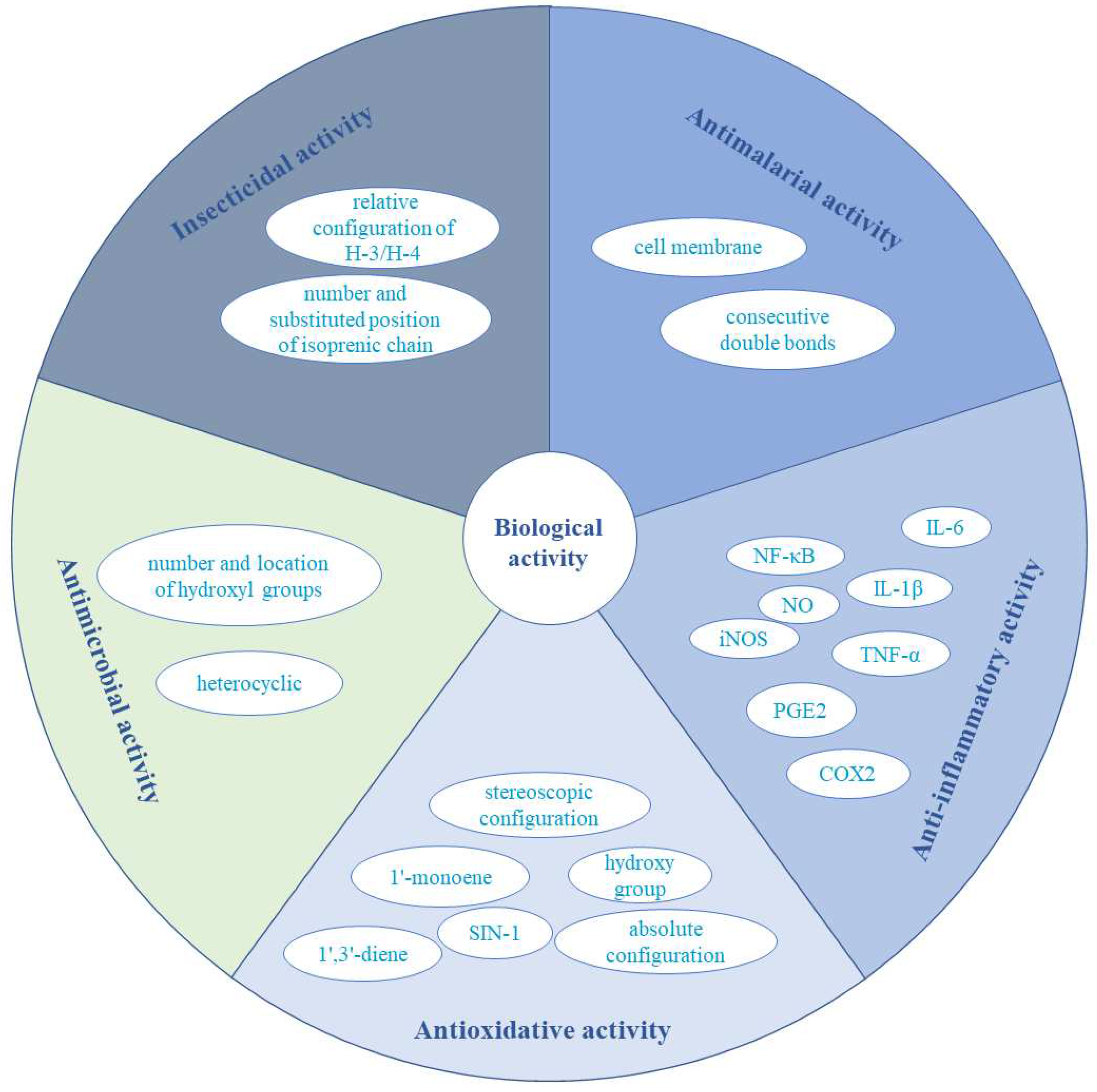
3. Bioactivities of secondary metabolites from Eurotium
3.1. Antioxidative activity
3.2. Antimicrobial activity
3.3. Cytotoxicity and antitumour activities
3.4. Insecticidal activity
3.5. Antimalarial activity
3.6. Anti-inflammatory activity
3.7. Other activities
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.; Wang, B.G. Chemical Diversity and Biological Function of Indolediketopiperazines from Marine-Derived Fungi. Marine Life Science & Technology 2020, 2, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubka, V.; Kolarik, M.; Kubatova, A.; Peterson, S.W. Taxonomic Revision of Eurotium and Transfer of Species to Aspergillus. Mycologia 2013, 105, 912–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podojil, M.; Sedmera, P.; Vokoun, J.; Betina, V.; Barathova, H.; Durackova, Z.; Horakova, K.; Nemec, P. Eurotium (AspergiUus) repens Metabolites and Their Biological Activity. Folia Microbiol 1978, 23, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Gao, L. Research Progress on the Secondary Products of Eurotium. Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2017, 30, 542–547. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.Q. Research Progress of Secondary Metabolites From Genus Eurotium and Their Biological Activities. Science and Technology of Food Industry 2013, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, R.A.; Mouchacca, J. Additional notes on species of Aspergillus, Eurotium and Emericella from Egyptian desert soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek International Journal of General and Molecular Microbiology 1975, 41, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kis-Papo, T.; Oren, A.; Wasser, S.P.; Nevo, E. Survival of Filamentous Fungi in Hypersaline Dead Sea Water. Microbial Ecology 2003, 45, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Weining, S.; Nevo, E. A MAPK Gene from Dead Sea Fungus Confers Stress Tolerance to Lithium Salt and Freezing-Thawing: Prospects for Saline Agriculture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005, 102, 18992–18997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbaguidi-Haore, H.; Roussel, S.; Reboux, G.; Dalphin, J.C.; Piarroux, R. Multilevel Analysis of the Impact of Environmental Factors and Agricultural Practices on the Concentration in Hay of Microorganisms Responsible for Farmer’s Lung Disease. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2009, 16, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Cao, F.; Guo, X.J.; Zhang, Y.R.; Kang, Z.J.; Zhu, H.J. Antibacterial Indole Alkaloids and Anthraquinones from a Sewage-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. Chemistry of Natural Compounds 2018, 54, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Ito, C.; Itoigawa, M.; Osawa, T. Antioxidants Produced by Eurotium herbariorum of Filamentous Fungi Used for the Manufacture of Karebushi, Dried Bonito (Katsuobushi). Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 2009, 73, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.B.; Kim, D.H.; Samson, R.A. Aspergillus Associated with Meju, a Fermented Soybean Starting Material for Traditional Soy Sauce and Soybean Paste in Korea. Mycobiology 2015, 43, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Liu, J.X.; Kang, D.D.; Huang, Y.M.; Kong, W.P.; Xiang, Y.X.; Zhu, X.C.; Duan, Y.W.; Huang, Y. Isolation and Characterization of Benzaldehyde Derivatives with Anti-inflammatory Activities from Eurotium cristatum, the Dominant Fungi Species in Fuzhuan Brick Tea. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 6630–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Mai, Z.M.; Wei, X.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Tian, X.P.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, F.Z.; et al. Euroticins A and B, Two Pairs of Highly Constructed Salicylaldehyde Derivative Enantiomers from a Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 85, 12754–12759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Ito, C.; Kimura, T.; Suzuki, A.; Nishida, Y.; Itoigawa, M. Isolation of Aromatic Compounds Produced by Eurotium herbariorum NU-2 from Karebushi, a Katsuobushi, and Their DPPH-Radical Scavenging Activities. Food Science and Technology Research 2014, 20, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.B.; Gao, Y.Q.; Han, R.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, Y.J.; Han, W.B.; Li, W.L.; Gao, J.M. Alkylated Salicylaldehydes and Prenylated Indole Alkaloids from the Endolichenic Fungus Aspergillus chevalieri and Their Bioactivities. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 2021, 69, 6524–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.M.; Liang, X.A.; Kong, Y.; Jia, B. Structural Diversity and Biological Activities of Indole Diketopiperazine Alkaloids from Fungi. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 2016, 64, 6659–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Radwan, M.M.; Leon, F.; Wang, X.; Jacob, M.R.; Tekwani, B.L.; Khan, S.I.; Lupien, S.; Hill, R.A.; Dugan, F.M.; et al. Antimicrobial and Antiprotozoal Activities of Secondary Metabolites from the Fungus Eurotium repens. Medicinal Chemistry Research 2012, 21, 3080–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May Zin, W.W.; Buttachon, S.; Dethoup, T.; Pereira, J.A.; Gales, L.; Inacio, A.; Costa, P.M.; Lee, M.; Sekeroglu, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; et al. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of the Metabolites Isolated from the Culture of the Mangrove-Derived Endophytic Fungus Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006. Phytochemistry 2017, 141, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, K.L.; Xu, Y.; She, Z.G.; Wang, C.Y. Dihydroisocoumarin Derivatives with Antifouling Activities from a Gorgonian-Derived Eurotium sp. Fungus. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 9132–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anke, H.; Kolthoum, I.; Zahner, H.; Laatsch, H. The Anthraquinones of the Aspergillus glaucus Group. I. Occurrence, Isolation, Identification and Antimicrobial Activity. Archives of Microbiology 1980, 126, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Dong-Li; Li, Xiao-Ming; Bin-Gui, W. Natural anthraquinone derivatives from a marine mangrove plant -derived endophytic fungus Eurotium rubrum: structural elucidation and DPPH radical scavenging activity. Microbiol Biotechnol 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gessler, N.N.; Egorova, A.S.; Belozerskaya, T.A. Fungal Anthraquinones. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology 2013, 49, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, M.; Evidente, A. Fungal Bioactive Anthraquinones and Analogues. Toxins 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Jia, A.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, M.H.; Ding, G.; Sun, L.Y.; Li, L.; Dai, M.X. Anthraquinones from the Saline-Alkali Plant Endophytic Fungus Eurotium rubrum. The Journal of Antibiotics 2017, 70, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, G.W.; McDorman, D.J.; Maroney, M.J. Iron Chelating Capability of Physcion, a Yellow Pigment from Aspergillus ruber. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 1980, 28, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, C.; Kogler, H.; Toti, L. Eurotinones, and Derivatives Thereof, Processes for Preparing Them, and Their Use. 2004.
- Gomes, N.M.; Dethoup, T.; Singburaudom, N.; Gales, L.; Silva, A.M.S.; Kijjoa, A. Eurocristatine, a New Diketopiperazine Dimer from the Marine Sponge-Associated Fungus Eurotium cristatum. Phytochemistry Letters 2012, 5, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.L.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. Natural Anthraquinone Derivatives from a Marine Mangrove Plant-Derived Endophytic Fungus Eurotium rubrum: Structural Elucidation and DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2009, 19, 675–680. [Google Scholar]
- Du, F.Y.; Li, X.M.; Song, J.Y.; Li, C.S.; Wang, B.G. Anthraquinone Derivatives and an Orsellinic Acid Ester from the Marine Alga-Derived Endophytic Fungus Eurotium cristatum EN-220. Helvetica Chimica Acta 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.J.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Wang, B.G. Alkaloid and Anthraquinone Derivatives Produced by the Marine-Derived Endophytic Fungus Eurotium rubrum. Helvetica Chimica Acta 2012, 95, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanokmedhakul, K.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Suwannatrai, R.; Soytong, K.; Prabpai, S.; Kongsaeree, P. Bioactive Meroterpenoids and Akaloids from the Fungus Eurotium chevalieri. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 5461–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kang, M.C.; Li, Y.; Kim, E.A.; Kang, S.M.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Questinol Isolated from Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium amstelodami in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2014, 24, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhao, Q.; Hao, J.D.; Wang, C.Y. Two Benzaldehyde Derivatives and Their Artefacts from a Gorgonian-Derived Eurotium sp. Fungus. Natural Product Research 2017, 31, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Cui, X.; Lee, D.S.; Ko, W.; Sohn, J.H.; Yim, J.H.; An, R.B.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. Inhibitory Effects of Benzaldehyde Derivatives from the Marine Fungus Eurotium sp. SF-5989 on Inflammatory Mediators Via the Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2014, 15, 23749–23765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.L.; Li, X.M.; Li, T.G.; Dang, H.Y.; Proksch, P.; WANG, B.G. Benzaldehyde Derivatives from Eurotium rubrum, an Endophytic Fungus Derived from the Mangrove Plant Hibiscus tiliaceus. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2008, 56, 1282–1285. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Jia, C.; Deng, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, B.; Yan, S.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Anti-inflammatory Prenylbenzaldehyde Derivatives Isolated from Eurotium cristatum. Phytochemistry 2019, 158, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.L. Secondary Metabolities and Their Bioactivities of a Hibiscus tiliaceus-Derived Endophytic Fungus Eurotium rubrum and a Mangrove Plant Rhizophora stylosa griff. 2008.
- Gao, J.; Leon, F.; Radwan, M.M.; Dale, O.R.; Husni, A.S.; Manly, S.P.; Lupien, S.; Wang, X.; Hill, R.A.; Dugan, F.M.; et al. Benzyl Derivatives with in Vitro Binding Affinity for Human Opioid and Cannabinoid Receptors from the Fungus Eurotium repens. Journal of Natural Products 2011, 74, 1636–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.P.; Ouyang, J.; Wu, X.L.; Zhou, F.; Lu, D.M.; Zhao, C.J.; Liu, C.F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, N.X.; et al. Dark tea extracts: Chemical constituents and modulatory effect on gastrointestinal function. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2020, 130, 110514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.Z.; Li, N.; Zhou, F.; Ouyang, J.; Lu, D.M.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, J.B.; et al. Microbial bioconversion of the chemical components in dark tea. Food Chemistry 2020, 312, 126043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Li, Y.L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.B.; Huang, J.A.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhu, M.Z. Polyphenols from Fu Brick Tea Reduce Obesity via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Gut Microbiota-Related Intestinal Oxidative Stress and Barrier Function. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2021, 69, 14530–14543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, J.X.; Chen, R.Y.; Xiao, L.K.; Wu, X.; Hu, L.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhu, M.Z.; Liu, Z.H.; et al. Comparison of the Fungal Community, Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Activity, and Taste Characteristics of Fu Brick Tea in Different Regions of China. Frontiers in Nutrition 2022, 9, 900138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Ma, Y.M.; Chen, D.; Chen, P.; Hu, Y. Studies on Structure and Biological Activity of Indole Diketopiperazine Alkaloids. Progress in Chemistry 2018, 30, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Du, F.Y.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Shang, Z.; Wang, B.G. Cristatumins A-D, New Indole Alkaloids from the Marine-Derived Endophytic Fungus Eurotium cristatum EN-220. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2012, 22, 4650–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.N.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Tang, T.; Zheng, S.J.; Wang, W.M.; Tang, J.T. A New Prenylated Indole Diketopiperazine Alkaloid from Eurotium cristatum. Molecules 2014, 19, 17839–17847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesonder, R.F.; Lamber, R.; Wicklow, D.T.; Biehl, M.L. Eurotium spp. and Echinulin in Feed Refused by Swine. ApPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY 1988, 54, 830–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetanina, O.F.; Kalinovskii, A.I.; Khudyakova, Y.V.; Slinkina, N.N.; Pivkin, M.V.; Kuznetsova, T.A. Metabolites from the Marine Fungus Eurotium repens. Chemistry of Natural Compounds 2007, 43, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, K.; Aoki, T.; Shibata, Y.; Kamisuki, S.; Sugawara, F.; Kuramochi, K.; Nakazaki, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Kuroiwa, K.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Structure-Activity Relationships of Neoechinulin A Analogues with Cytoprotection Against Peroxynitrite-induced PC12 Cell Death. The Journal of Antibiotics 2007, 60, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slack, G.J.; Puniani, E.; Frisvad, J.C.; Samson, R.A.; Miller, J.D. Secondary Metabolites from Eurotium Species, Aspergillus calidoustus and A. insuetus Common in Canadian Homes with a Review of Their Chemistry and Biological Activities. Mycological Research 2009, 113, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.L.; Li, X.M.; Proksch, P.; Wang, B.G. 7-O-Methylvariecolortide A, a New Spirocyclic Diketopiperazine Alkaloid from a Marine Mangrove Derived Endophytic Fungus, Eurotium rubrum. Natural Product Communications 2010, 5, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. PTP1B Inhibitory Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Fungal Strains Penicillium spp. and Eurotium sp. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2013, 23, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, K.L.; Wang, Y.; Fu, P.; Liu, P.P.; Wang, C.; Zhu, W.M. A Cytotoxic Pyrrolidinoindoline Diketopiperazine Dimer from the Algal Fungus Eurotium herbariorum HT-2. Chinese Chemical Letters 2013, 24, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.H.; Du, F.Y.; Li, X.M.; Pedpradab, P.; Xu, G.M.; Wang, B.G. Rubrumazines A-C, Indolediketopiperazines of the Isoechinulin Class from Eurotium rubrum MA-150, a Fungus Obtained from Marine Mangrove-Derived Rhizospheric Soil. Journal of Natural Products 2015, 78, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F.Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.M.; Zhu, L.W.; Wang, B.G. Indolediketopiperazine Alkaloids from Eurotium cristatum EN-220, an Endophytic Fungus Isolated from the Marine Alga Sargassum thunbergii. Marine Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.M.; Wang, J.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Fu, T.D.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, X.N.; Tian, X.P.; Xiao, Z.H.; Zhang, W.M.; et al. Variecolortins A-C, Three Pairs of Spirocyclic Diketopiperazine Enantiomers from the Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Organic Letters 2018, 20, 4593–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.M.; Wang, J.F.; Shi, X.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Zeng, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Tian, X.P.; Xiao, Z.H.; et al. Eurotiumins A–E, Five New Alkaloids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Marine Drugs 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsebai, M.F.; Schoeder, C.T.; Muller, C.E. Fintiamin: A Diketopiperazine from the Marine Sponge-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. Archiv der Pharmazie 2021, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.F.; Yi, Y.W.; Deng, J. Steroids from an Endophytic Eurotium rubrum Strain. Chemistry of Natural Compounds 2017, 53, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Wei, X.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zeng, Q.; Tian, X.P.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, S. Euroticins C–E, Three Pairs of Polycyclic Salicylaldehyde Derivative Enantiomers from a Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Organic Chemistry Frontiers 2021, 8, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Wei, X.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, S. Salicylaldehyde Derivatives from a Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. The Journal of Antibiotics 2020, 74, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.M.; Wei, X.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, J.F.; Shi, X.F.; Tian, X.P.; Zhang, W.M.; Wang, F.Z.; Zhang, S. Structurally Diverse Polycyclic Salicylaldehyde Derivative Enantiomers from a Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Marine Drugs 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, I.; El-Maraghy, S.; Zohri, A.N. Mycotoxin Producing Potential of Some Isolates of Aspergillus favus and Eurotium Groups From Meat Products. Microbiological Research 1994, 149, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Séguin, V.; Gente, S.; Heutte, N.; Vérité, P.; Kientz-Bouchart, V.; Sage, L.; Goux, D.; Garon, D. First Report of Mycophenolic Acid Production by Eurotium repens Isolated from Agricultural and Indoor Environments. World Mycotoxin Journal 2014, 7, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Huang, Z.; Shi, X.F.; Chen, X.C.; Tian, X.P.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhang, S. Analysis of Secondary Metabolites Produced by Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 Isolated from the South China Sea Sediment. Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs 2013, 32, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovio, E.; Garzoli, L.; Poli, A.; Luganini, A.; Villa, P.; Musumeci, R.; McCormack, G.P.; Cocuzza, C.E.; Gribaudo, G.; Mehiri, M.; et al. Marine Fungi from the Sponge Grantia Compressa: Biodiversity, Chemodiversity, and Biotechnological Potential. Marine Drugs 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.M.; Xia, G.P.; Chen, S.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, H.X.; She, Z.G. Eurothiocin A and B, Sulfur-Containing Benzofurans from a Soft Coral-Derived Fungus Eurotium rubrum SH-823. Marine Drugs 2014, 12, 3669–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.M.; Wang, J.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Fu, T.D.; Chen, Y.C.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, Z.H.; Huang, X.N.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhang, S.; et al. Three Pairs of New Spirocyclic Alkaloid Enantiomers From the Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Frontiers in Chemistry 2019, 7, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.M.; Wang, J.F.; Wei, X.Y.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Xiang, Y.; Tian, X.P.; Zhang, S.; Long, L.J.; Wang, F.Z. (+)- and (−)-Eurotone A: A Pair of Enantiomeric Polyketide Dimers from a Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Tetrahedron Letters 2019, 60, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.J.; Jing, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, N.S.; Cao, Y.G. Eurotium cristatum Produced β-hydroxy Acid Metabolite of Monacolin K and Improved Bioactive Compound Contents as well as Functional Properties in Fermented Wheat Bran. LWT-Food Science and Technology 2022, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Hamasaki, T. Metabolites of Eurotium Species, Their Antioxidative Synergism with Tocopherol. 1985.
- Li, D.L.; Li, X.M.; Li, T.G.; Dang, H.Y.; Wang, B.G. Dioxopiperazine Alkaloids Produced by the Marine Mangrove Derived Endophytic Fungus Eurotium rubrum. Helvetica Chimica Acta 2008, 91, 1888–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamunuarachchi, N.I.; Khan, F.; Kim, Y.M. Antimicrobial Properties of Actively Purified Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Different Marine Organisms. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 2021, 22, 920–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, L.; Sleiman, A.; Abdel-Massih, R.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols and Alkaloids in Middle Eastern Plants. Frontiers in Microbiology 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zheng, C.; Guo, L.; Li, W.; Sun, P.; Qin, L. Recent Developments and Future Prospects of Antimicrobial Metabolites Produced by Endophytes. Mycological Research 2010, 165, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, K.L.; Wang, C.Y. Antifouling Indole Alkaloids of a Marine-Derived Fungus Eurotium sp. Chemistry of Natural Compounds 2018, 54, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Cui, X.; Lee, D.S.; Sohn, J.H.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Neoechinulin A from the Marine Fungus Eurotium sp. SF-5989 Through the Suppression of NF-kb and p38 MAPK Pathways in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages. Molecules 2013, 18, 13245–13259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Kang, M.C.; Li, Y.; Kim, E.A.; Kang, S.M.; Jeon, Y.J. Asperflavin, an Anti-Inflammatory Compound Produced by a Marine-Derived Fungus, Eurotium amstelodami. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hui, J.F.; Yang, J.; Deng, J.J.; Fan, D.D. Eurocristatine, a Plant Alkaloid from Eurotium cristatum, Alleviates Insulin Resistance in db/db Diabetic Mice Via Activation of PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. European Journal of Pharmacology 2020, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.D.; Bao, Y.R.; Huang, Y.F.; Hu, D.; Li, X.X.; Guo, L.D.; Li, J.; Yao, X.S.; Gao, H. Three Pairs of Variecolortide Enantiomers from Eurotium sp. with Caspase-3 Inhibitory Activity. Fitoterapia 2014, 92, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
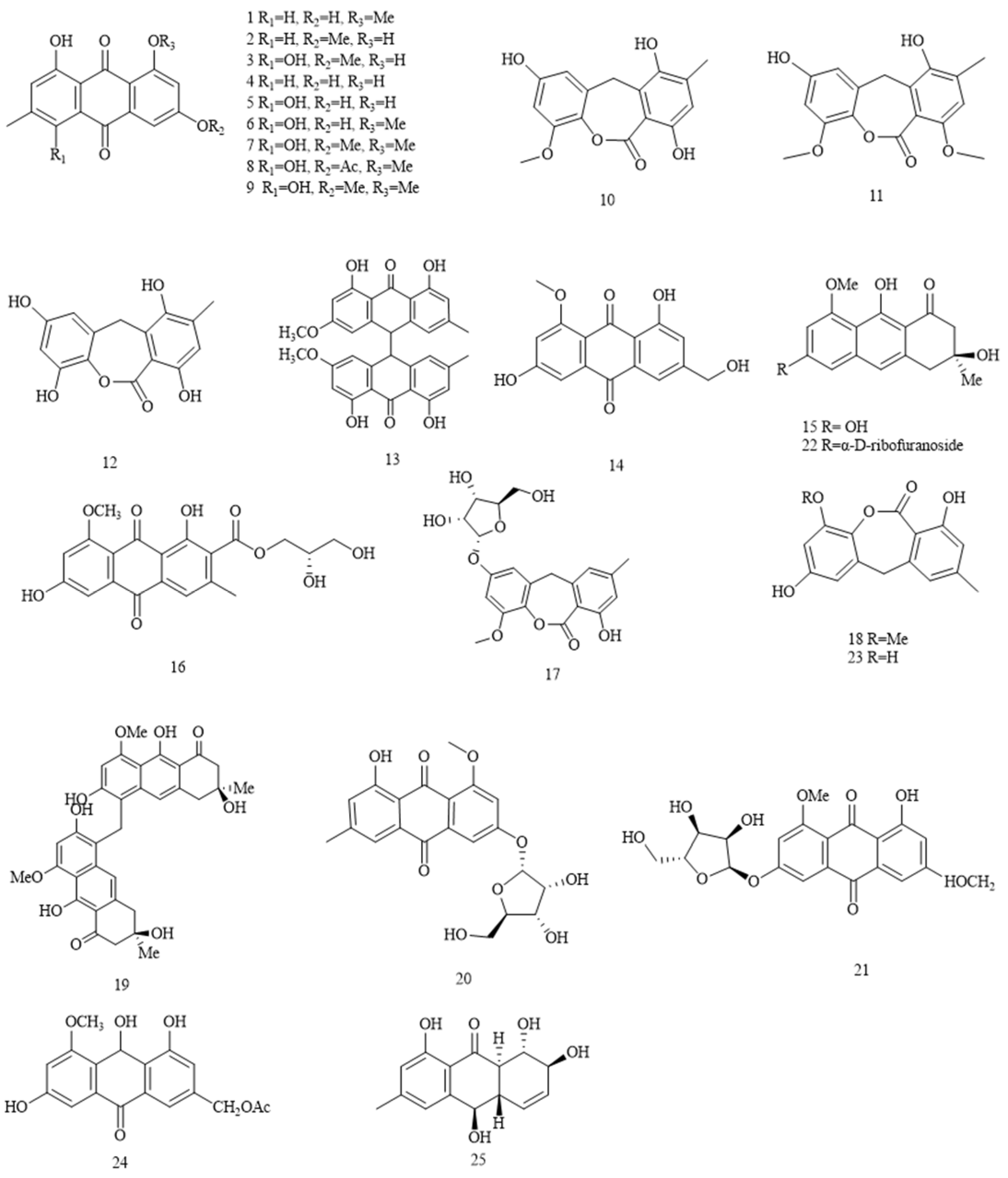
| NO. | Compound class and name | Bioactivity | Source | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthraquinones | |||||
| 1 | questin | antimicrobial activity antioxidative activity |
Eurotium sp. M30 XS-2012 E. herbariorum NU-2 E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 Eurotium E. rubrum |
[10] [15] [19] [21] [29] |
|
| 2 | physcion |
cytotoxic activity antiviral activity |
E. herbariorum NU-2 E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 E. repens E. chevalieri MUT 2316 |
[15] [19] [48] [66] |
|
| 3 | erythroglaucin | antimicrobial activity |
Eurotium E. cristatum KUFC 7356 |
[21] [28] |
|
| 4 | emodin | antimicrobial activity cytotoxic activity |
E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 Eurotium E. rubrum E. cristatum KUFC 7356 E. rubrum |
[19] [21] [25] [28] [31] |
|
| 5 | catenarin |
E. herbariorum NU-2 Eurotium E. rubrum E. cristatum KUFC 735 |
[15] [21] [25] [28] |
||
| 6 | rubrocristin |
Eurotium E. rubrum |
[21] [25] |
||
| 7 | rubrocristin-8-methylether | Eurotium | [21] | ||
| 8 | rubrocristin-6-acetate | Eurotium | [21] | ||
| 9 | querstin-6-methylether | Eurotium | [21] | ||
| 10 | 2-O-methyleurotinone |
antioxidative activity |
E. echinulatum E. rubrum |
[27] [29] |
|
| 11 | 2,12-dimethyleurotinone | E. echinulatum | [27] | ||
| 12 | eurotinone | E. echinulatum | [27] | ||
| 13 | physcion-10,10’-bianthrone | E.herbariorum NU-2 | [15] | ||
| 14 | questinol |
anti-inflammatory activity |
Eurotium sp. M30 XS-2012 E.herbariorum NU-2 E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 E. amstelodami |
[10] [15] [19] [33] |
|
| 15 | asperflavin |
antioxidative activity cytotoxic activity antimicrobial activity anti-inflammatory activity |
Eurotium sp. M30 XS-2012 E.herbariorum NU-2 E. rubrum E. cristatum EN-220 E. repens E. chevalieri MUT 2316 E. amstelodami |
[10] [15] [29] [30] [48] [66] [78] |
|
| 16 | variecolorquinone A |
Eurotium sp. M30 XS-2012 E. cristatum EN-220 |
[28] [30] |
||
| 17 | 2-O-methyl-4-O-(α-D-ribofuranosyl)-9-dehydroxyeurotinone | antioxidative activity | E. rubrum | [29] | |
| 18 | 2-O-methyl-9-dehydroxyeurotinone | antioxidative activity | E. rubrum | [29] | |
| 19 | eurorubrin | antioxidative activity antimicrobial activity insecticidal activity |
E. rubrum E. cristatum EN-220 |
[29] [30] |
|
| 20 | 3-O-(α-D-ribofuranosyl)-questin | antioxidative activity |
E. rubrum E. cristatum EN-220 |
[29] [30] |
|
| 21 | 3-O-(α-D-ribofuranosyl)-questinol | antimicrobial activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [30] | |
| 22 | asperflavin ribofuranoside | E. cristatum EN-220 | [30] | ||
| 23 | 9-dehydroxyeurotinone | cytotoxic activity antimicrobial activity |
E. rubrum | [31] | |
| 24 | acetylquestinol | E.chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 25 | rubrumol | cytotoxic activity | E. rubrum | [25] | |
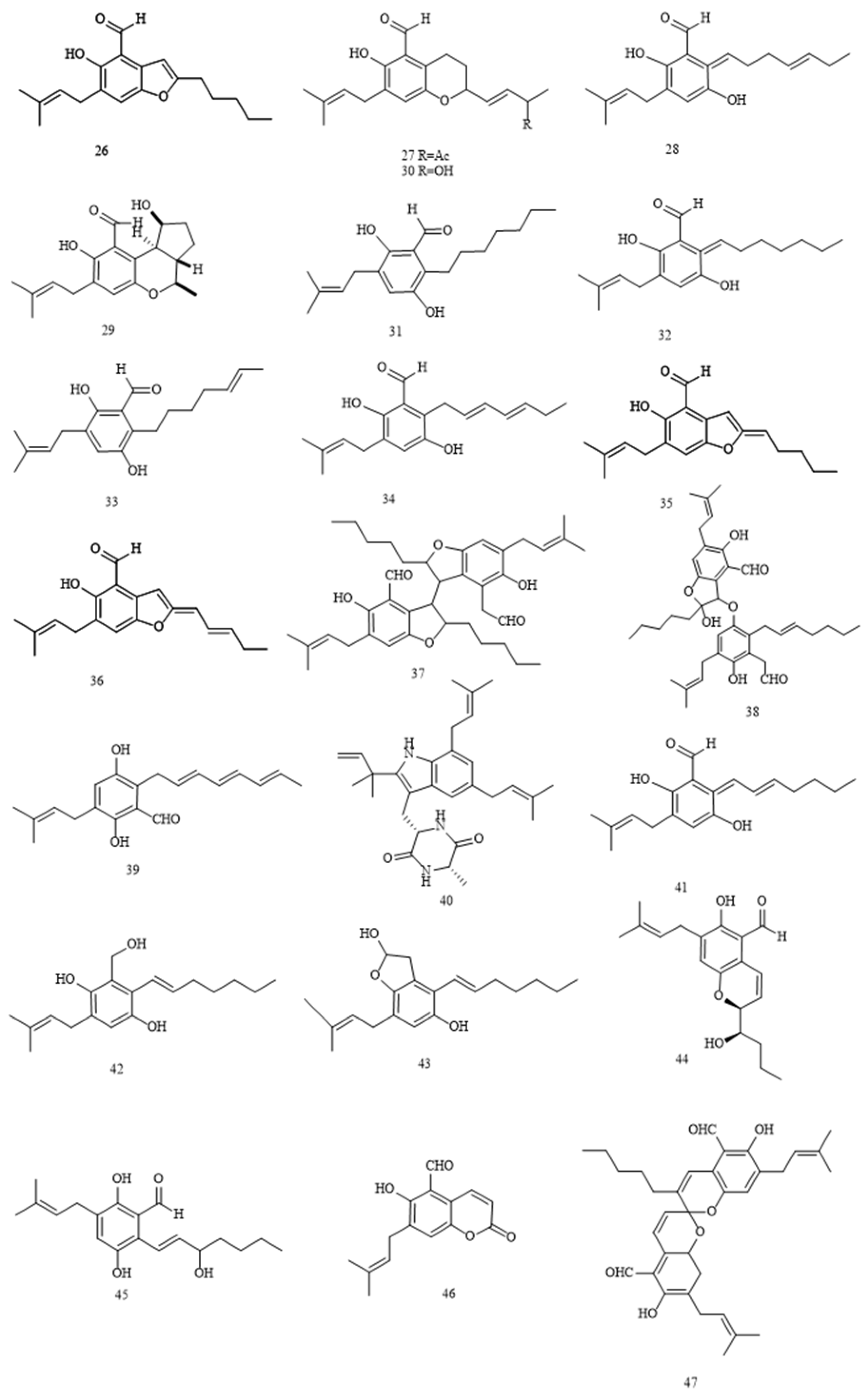
| Benzaldehyde derivatives | |||||
| 26 | 2-(2’,3-epoxy-1’-heptenyl)-6-hydroxy-5-(3’’-methyl-2’’-butenyl)-benzaldehyde | E. rubrum | [36] | ||
| 27 | (E)-6-hydroxy-7-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-2-(3-oxobut-1-enyl)-chroman-5-carbaldehyd | E. rubrum | [36] | ||
| 28 | 2-(1’,5’-heptadienyl)-3,6-dihydroxy-5-(3’’-methyl-2’’-butenyl)-benzaldehyde | E. rubrum | [36] | ||
| 29 | eurotirumin |
cytotoxic activity |
E. rubrum Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 |
[36] [62] |
|
| 30 | chaetopyranin | E. rubrum | [36] | ||
| 31 | flavoglaucin | antioxidative activity antimicrobial activity antimalarial activity anti-inflammatory activity cytotoxic activity |
Eurotium E. cristatum E. repens Eurotium sp. SF-5989 E. rubrum E. cristatum E. repens |
[11] [13] [18] [35] [36] [37] [39] |
|
| 32 | aspergin | E. rubrum | [36] | ||
| 33 | isotetrahydroauroglaucin | anti-inflammatory activity | Eurotium sp. SF-5989 E. rubrum | [35] [36] |
|
| 34 | isodihydroauroglaucin | antioxidative activity |
Eurotium E. cristatum E. rubrum E. repens |
[11] [13] [36] [39] |
|
| 35 | 2-(2’,3-epoxy-1’,3’-heptadienyl)-6-hydroxy-5-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-benzaldehyde |
antimicrobial activity antimalarial activity |
E. cristatum E. repens E. rubrum E. repens |
[13] [18] [36] [39] |
|
| 36 | 2-(2’,3-epoxy-1’,3’,5’-heptatrienyl)-6-hydroxy-5-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)-benzaldehyde |
E. rubrum E. cristatum |
[36] [13] |
||
| 37 | eurotirubrin A | E. rubrum | [38] | ||
| 38 | eurotirubrin B | E. rubrum | [38] | ||
| 39 | auroglaucin | antioxidative activity antimicrobial activity antimalarial activity |
Eurotium E. repens |
[11] [18] |
|
| 40 | tetrahydroauroglaucin | antioxidative activity antimicrobial activity antimalarial activity cytotoxic activity |
Eurotium E. cristatum E. repen s E. repens E. repens |
[11] [13] [18] [39] [48] |
|
| 41 | dihydroauroglaucin | antioxidative activity antimicrobial activity antiviral activity |
Eurotium E. cristatum E. repens E. repens E. chevalieri MUT 2316 |
[11] [13] [18] [39] [66] |
|
| 42 | (E)-2-(hept-1-enyl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-5-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-benzene-1,4-diol | antimicrobial activity antimalarial activity |
E. repens E. repens |
[18] [39] |
|
| 43 | (E)-4-(hept-1-enyl)-7-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-2,5-diol | E. repens | [39] | ||
| 44 | (3’S*,4’R*)-6-(3’,5-epoxy-4’-hydroxy-1’-heptenyl)-2-hydroxy-3-(3’’-methyl-2’’-butenyl)-benzaldehyde | Eurotium | [34] | ||
| 45 | 3’-OH-tetrahydroauroglaucin | Eurotium | [34] | ||
| 46 | cristaldehyde A | anti-inflammatory activity | E. cristatum | [37] | |
| 47 | cristaldehyde B | E. cristatum | [37] | ||
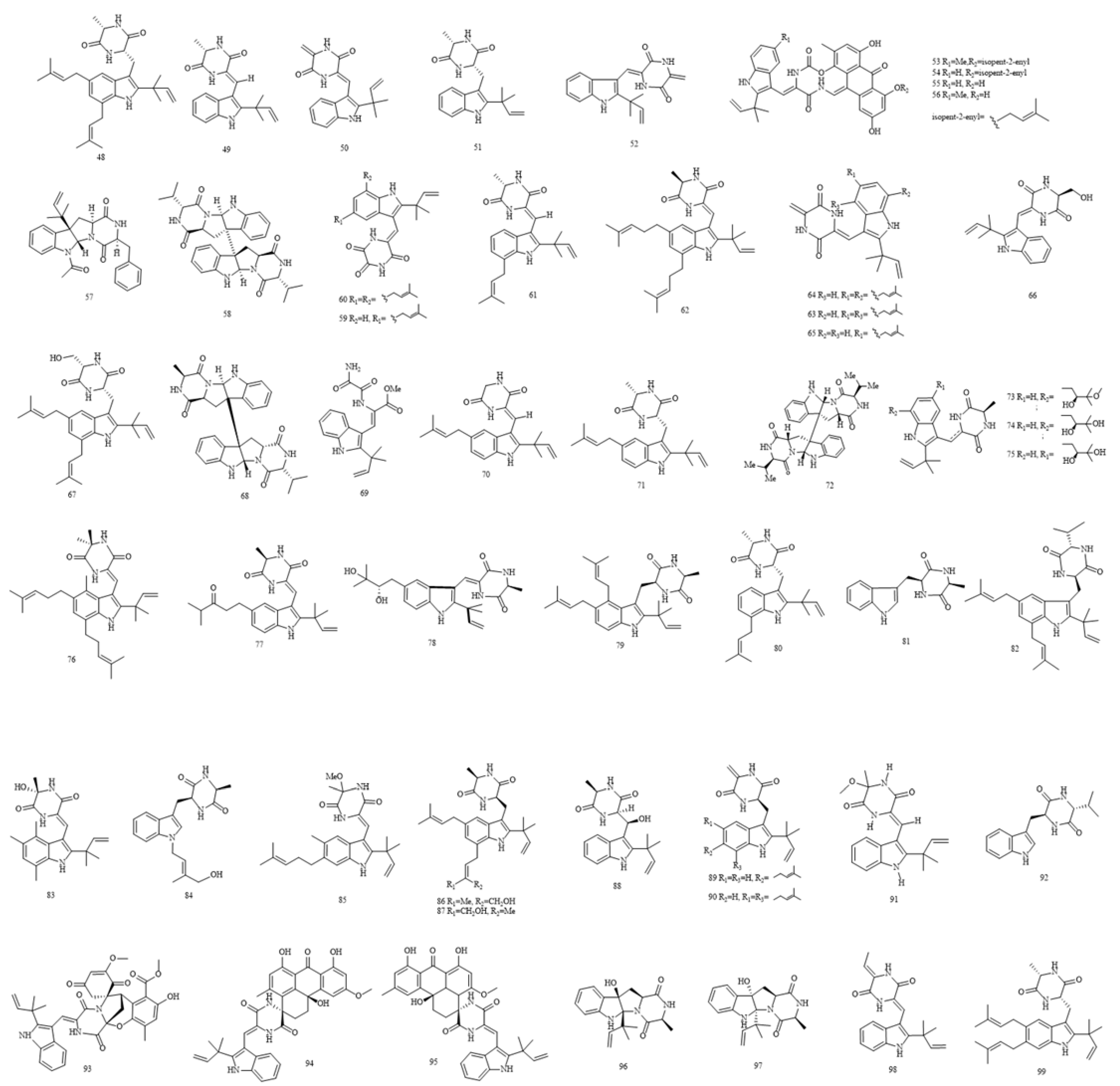
| Indole diketopiperazine alkaloids | |||||
| 48 | echinulin |
antimicrobial activity antioxidative activity insecticidal activity |
E. cristatum E. cristatum EN-220 E. cristatum E. repens E. repens E. amstelodami E. rubrum E. herbariorum E. cristatum EN-220 Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 Eurotium |
[28] [45] [46] [47] [48] [50] [55] [57] [76] |
|
| 49 | neoechinulin A | antimicrobial activity antioxidative activity insecticidal activity anti-inflammatory activity |
Eurotium sp. M30 XS-2012 E. cristatum E. cristatum EN-220 E. cristatum E. rubrum Hiji 025 E. amstelodami E. rubrum. E. herbariorum E. rubrum MA-150 Eurotium Eurotium sp. SF-5989 |
[10] [28] [45] [46] [49] [50] [54] [76] [77] |
|
| 50 | neoechinulin B | antioxidative activity |
E. herbariorum NU-2 E. amstelodami E. rubrum. E. herbariorum E. cristatum EN-220 Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 |
[15] [50] [55] [57] |
|
| 51 | preechinulin |
E. cristatum EN-220 E. amstelodami E. rubrum E. herbariorum |
[45] [50] |
||
| 52 | neoechinulin E |
insecticidal activity antioxidative activity |
E. cristatum E. amstelodami E. herbariorum E. rubrum MA-150 E. rubrum |
[28] [50] [54] [72] |
|
| 53 | 7-O-methylvariecolortide A |
caspase-3 inhibitory activity |
E. rubrum Eurotium |
[51] [80] |
|
| 54 | variecolortide A | E. rubrum | [51] | ||
| 55 | variecolortide B |
caspase-3 inhibitory activity |
E. rubrum E. rubrum MA-150 Eurotium |
[51] [54] [80] |
|
| 56 | variecolortide C |
caspase-3 inhibitory activity |
E. rubrum E. rubrum MA-150 Eurotium |
[51] [54] [80] |
|
| 57 | fructigenine A | Eurotium sp. SF-5130 | [52] | ||
| 58 | eurocristatine | E. cristatum | [28] | ||
| 59 | variecolorin J |
E. cristatum E. rubrum |
[28] [31] |
||
| 60 | 12-demethyl-12-oxo-eurotechinulin B | cytotoxic activity | E. rubrum | [31] | |
| 61 | variecolorin G | cytotoxic activity insecticidal activity antioxidative activity |
E. rubrum E. cristatum EN-220 E. rubrum MA-150 Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 |
[31] [45] [54] [57] |
|
| 62 | eurotechinulin B | E. rubrum | [31] | ||
| 63 | cryptoechinuline G | E. rubrum | [31] | ||
| 64 | alkaloid E-7 | cytotoxic activity insecticidal activity |
E. rubrum E. cristatum EN-220 |
[31] [55] |
|
| 65 | isoechinulin B | antioxidative activity | E. herbariorum NU-2 E. rubrum 31 | [15] [31] |
|
| 66 | cristatumin A | antimicrobial activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [45] | |
| 67 | cristatumin B | insecticidal activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [45] | |
| 68 | cristatumin C | E. cristatum EN-220 | [45] | ||
| 69 | cristatumin D | antimicrobial activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [45] | |
| 70 | isoechinulin A | antioxidative activity insecticidal activity |
E. herbariorum NU-2 E. cristatum EN-220 E. rubrum MA-150 Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 |
[15] [45] [54] [57] |
|
| 71 | tardioxopiperazine A | antimicrobial activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [45] | |
| 72 | cristatumin E | antimicrobial activity cytotoxic activity |
E. herbariorum HT-2 | [53] | |
| 73 | rubrumazine A | E. rubrum MA-150 | [54] | ||
| 74 | rubrumazine B | insecticidal activity |
E. rubrum MA-150 E. cristatum EN-220 |
[54] [55] |
|
| 75 | rubrumazine C | E. rubrum MA-150 | [54] | ||
| 76 | dehydroechinulin |
insecticidal activity antioxidative activity |
E. cristatum E. rubrum MA-150 E. cristatum EN-220 Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 |
[46] [54] [55] [57] |
|
| 77 | variecolorin E | E. rubrum MA-150 | [54] | ||
| 78 | dihydroxyisoechinulin A | antimicrobial activity |
Eurotium sp. M30 XS-2012 E. rubrum MA-150 |
[10] [54] |
|
| 79 | variecolorin L | E. rubrum MA-150 | [54] | ||
| 80 | tardioxopiperazine B | E. rubrum MA-150 | [54] | ||
| 81 | L-alanyl-L-tryptophan anhydride | antimicrobial activity |
Eurotium sp. M30 XS-2012 E. rubrum MA-150 |
[10] [54] |
|
| 82 | cristatumin F | E. cristatum | [46] | ||
| 83 | variecolorin O | antioxidative activity |
E. herbariorum NU-2 E. cristatum Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 |
[15] [46] [57] |
|
| 84 | N-(4’-hydroxyprenyl)-cyclo(alanyltryptophyl) | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | ||
| 85 | isovariecolorin I | insecticidal activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | |
| 86 | 30-hydroxyechinulin | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | ||
| 87 | 29-hydroxyechinulin | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | ||
| 88 | rubrumline M | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | ||
| 89 | neoechinulin C | insecticidal activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | |
| 90 | didehydroechinulin | insecticidal activity | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | |
| 91 | variecolorin H | E. cristatum EN-220 | [55] | ||
| 92 | (11R,14S)-3-(1H-indol-3ylmethyl)6-isopropyl-2,5-piperazinedione | E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 93 | variecolortin A | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [56] | |
| 94 | variecolortin B | cytotoxic activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [56] | |
| 95 | variecolortin C | cytotoxic activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [56] | |
| 96 | eurotiumin A | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [57] | |
| 97 | eurotiumin B | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [57] | |
| 98 | eurotiumin C | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [57] | |
| 99 | fintiamin | Eurotium | [58] | ||
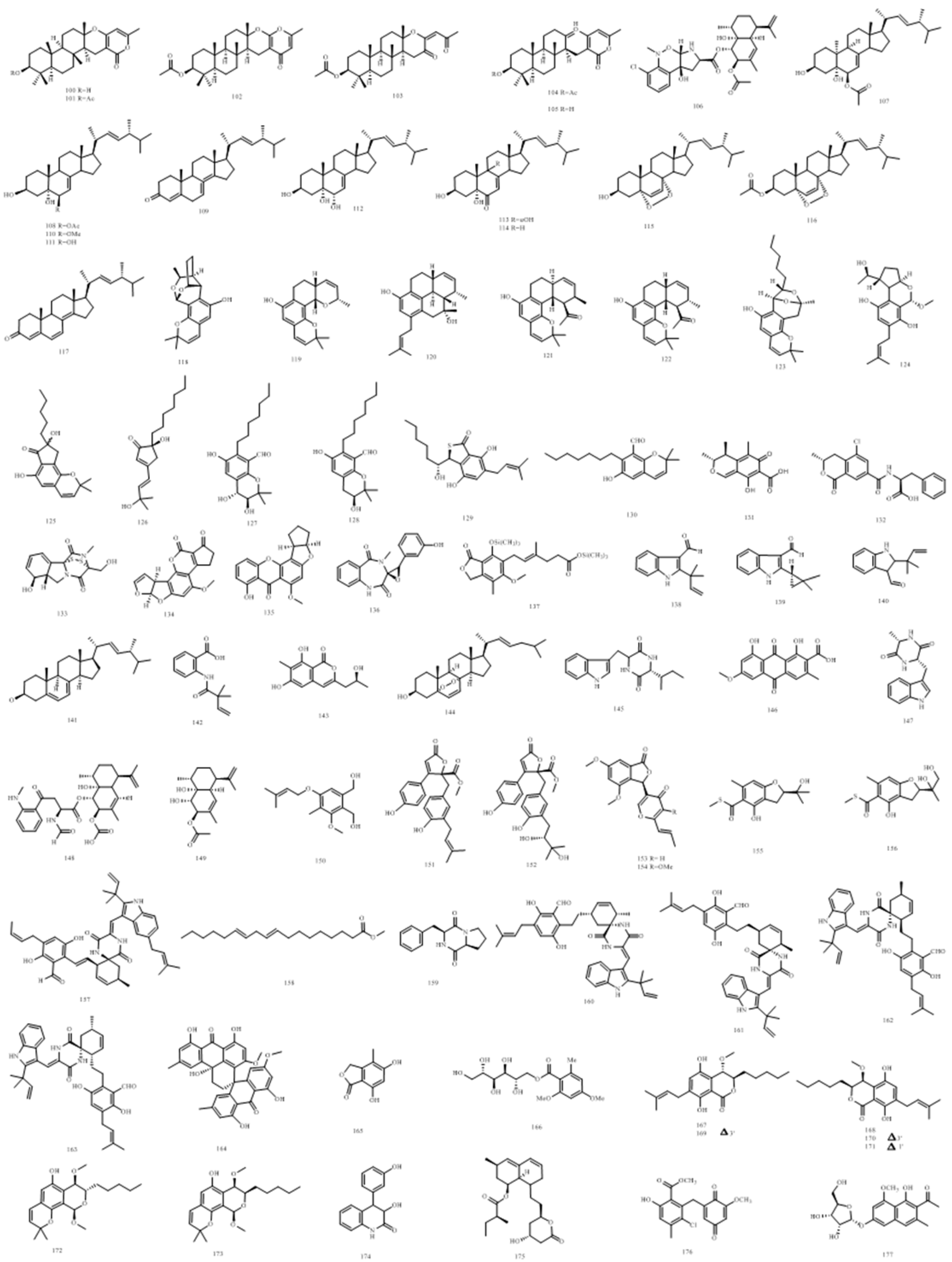
| Other compounds | |||||
| 100 | chevalone A | E. chevalieri | [32] | ||
| 101 | chevalone B | cytotoxic activity | E. chevalieri | [32] | |
| 102 | chevalone C | antimicrobial activity cytotoxic activity |
E. chevalieri | [32] | |
| 103 | chevalone D | antimalarial activity cytotoxic activity |
E. chevalieri | [32] | |
| 104 | aszonapyrone A | E. chevalieri | [32] | ||
| 105 | aszonapyrone B | E. chevalieri | [32] | ||
| 106 | CJ-12662 | antimalarial activity antimicrobial activity cytotoxic activity |
E. chevalieri | [32] | |
| 107 | 3β,5α-dihydroxy-10α-methyl-6β-acetoxy-ergosta-7,22-diene | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 108 | 3β,5α-dihydroxy-6β-acetoxyergosta-7,22-diene | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 109 | (22E,24R)-ergosta-7,22-dien-3β-ol | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 110 | (22E,24R)-ergosta-7,22-dien-6β-methoxy-3β,5α-diol | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 111 | (22E,24R)-ergosta-7,22-dien-3β,5α,6β-triol | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 112 | (22E,24R)-ergosta-7,22-dien-3β,5α,6α-triol | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 113 | (22E,24R)-3β,5α,9α-trihydroxyergosta-7,22-dien-6-one | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 114 | (22E,24R)-3β,5α-dihydroxyergosta-7,22-dien-6-one | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 115 | (22E,24R)-5α,8α-epidioxyergosta-6,22-dien-3β-ol | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 116 | (22E,24R)-5α,8α-epidioxyergosta-6,22-dien-3β-acetate | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 117 | (22E,24R)-ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraen-3-one | E.rubrum | [59] | ||
| 118 | euroticin A | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [14] | ||
| 119 | euroticin B | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [14] | |
| 120 | euroticin C | antioxidative activity cytotoxic activity |
Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [60] | |
| 121 | euroticin D | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [60] | ||
| 122 | euroticin E | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [60] | ||
| 123 | euroticin F | cytotoxic activity antioxidative activity |
Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [62] | |
| 124 | euroticin G | antioxidative activity α-glucosidase inhibitory activity |
Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [62] | |
| 125 | euroticin H | cytotoxic activity α-glucosidase inhibitory activity |
Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [62] | |
| 126 | euroticin I | cytotoxic activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [62] | |
| 127 | salicylaldehydium A | cytotoxic activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [61] | |
| 128 | salicylaldehydium B | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [61] | ||
| 129 | asperglaucin A | antimicrobial activity | Aspergillus chevalieri SQ-8 | [16] | |
| 130 | asperglaucin B | antimicrobial activity | Aspergillus chevalieri SQ-8 | [16] | |
| 131 | citrinin | Eurotium | [63] | ||
| 132 | ochratoxin A | Eurotium | [63] | ||
| 133 | gliotoxin | Eurotium | [63] | ||
| 134 | aflatoxins | Eurotium | [63] | ||
| 135 | sterigmatocystin | Eurotium | [63] | ||
| 136 | cyclopenol | Eurotium sp. SF-5130 | [52] | ||
| 137 | mycophenolic acid | E. repens | [64] | ||
| 138 | 2-(2-methyl-3-en-2-yl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde | E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 139 | (2,2-dimethylcyclopropyl)-1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde | E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 140 | 2-(1,1-dimethyl-2-propen-1-yl)-1H-indole-3-carboxaldehyde | Eurotium sp.SCSIO F452 | [65] | ||
| 141 | ergosterol | E. chevalieri | [32] | ||
| 142 | 2[(2,2-dimethylbut-3-enoyl)amino]benzoic acid | E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 143 | 6,8-dihydroxy-3-(2-hydroxypropyl)-7-methyl-1H-isochromen-1-one | E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 144 | ergosterol 5,8-endoperoxide | E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 145 | (11S,14R)-cyclo(tryptophylvalyl) | E. chevalieri KUFA 0006 | [19] | ||
| 146 | cinnalutein | E. chevalieri MUT 2316 | [66] | ||
| 147 | cyclo-L-Trp-L-Ala | E. chevalieri MUT 2316 | [66] | ||
| 148 | eurochevalierine | antimalarial activity antimicrobial activity cytotoxic activity |
E. chevalieri | [32] | |
| 149 | sequiterpene | E. chevalieri | [32] | ||
| 150 | zinniol | E.rubrum SH-823 | [67] | ||
| 151 | butyrolactone I | E.rubrum SH-823 | [67] | ||
| 152 | aspernolide D | E.rubrum SH-823 | [67] | ||
| 153 | vermistatin | E.rubrum SH-823 | [67] | ||
| 154 | methoxyvermistatin | E.rubrum SH-823 | [67] | ||
| 155 | eurothiocin A | α-glucosidase inhibitory activity | E.rubrum SH-823 | [67] | |
| 156 | eurothiocin B | α-glucosidase inhibitory activity | E.rubrum SH-823 | [67] | |
| 157 | 7-isopentenylcryptoechinuline D | E.rubrum | [31] | ||
| 158 | methyl linoleate | Eurotium sp.SCSIO F452 | [65] | ||
| 159 | cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Phe) | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [57] | ||
| 160 | eurotinoid A | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [68] | |
| 161 | eurotinoid B | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [68] | |
| 162 | eurotinoid C | antioxidative activity | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [68] | |
| 163 | dihydrocryptoechinulin D | cytotoxic activity antioxidative activity |
Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [68] | |
| 164 | eurotone A | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | [69] | ||
| 165 | 5,7-dihydroxy-4-methylphthalide | antimicrobial activity |
E. repens E. repens |
[18] [39] |
|
| 166 | cristatumside A | E. cristatum EN-220 | [30] | ||
| 167 | eurotiumide A | insecticidal activity | Eurotium sp. XS-200900E6 | [20] | |
| 168 | eurotiumide B | insecticidal activity | Eurotium sp. XS-200900E6 | [20] | |
| 169 | eurotiumide C | insecticidal activity | Eurotium sp. XS-200900E6 | [20] | |
| 170 | eurotiumide D | insecticidal activity | Eurotium sp. XS-200900E6 | [20] | |
| 171 | eurotiumide E | Eurotium sp. XS-200900E6 | [20] | ||
| 172 | eurotiumide F | Eurotium sp. XS-200900E6 | [20] | ||
| 173 | eurotiumide G | Eurotium sp. XS-200900E6 | [20] | ||
| 174 | viridicatol | Eurotium sp. SF-5130 | [52] | ||
| 175 | monacolin K | E. cristatum | [70] | ||
| 176 | cristaquinone A | anti-inflammatory activity | E. cristatum | [37] | |
| 177 | 6-O-α-D–ribofuranoside | E. cristatum EN-220 | [30] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





