1. INTRODUCTION
Lung cancer is a devastating disease responsible for significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, lung cancer contributes to over 1.7 million deaths each year, making it the leading cancer-related cause of death globally. Conventional therapeutic strategies such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapy have led to some clinical advancements, but the prognosis for patients with lung cancer, especially non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), remains unsatisfactory. This dire situation warrants the exploration of novel therapeutic approaches with greater potential and least adverse effects, and one such potential pharmacological target is monoamine oxidase (MAO).(Dhabal et al., 2018)
Monoamine oxidases, enzymes categorized into two isoforms, MAO-A and MAO-B, are involved in the oxidative deamination of various monoamine neurotransmitters, contributing to several aspects of human physiology. In recent years, a growing body of evidence has highlighted the connection between the abnormal expression of these enzymes and different malignancies, including NSCLC. The upregulation of MAO-A and its metabolite, hydrogen peroxide, has been observed in various cancer types, implicating a possible pro-oncogenic role.
The initial development of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) was focused primarily on their neuropharmacological effects, finding application for the treatment of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. However, recent studies have started to explore the anticancer effects of these inhibitors, unravelling their therapeutic potential in cancer treatment. In this assay, we delve into the underlying molecular mechanisms, discussing the rationale behind the use of MAOIs in lung cancer management, and critically analysing potential clinical implications and emerging strategies associated with their use. To set the stage for understanding the potential of MAOIs in lung cancer treatment, it is essential to contextualize the limitations of existing treatment methods. Despite significant advancements in NSCLC management, including the introduction of targeted therapies and immunotherapies, the five-year survival rate for patients remains disconcertingly low, barely exceeding 20%. This poor prognosis is attributable to a combination of factors, including late diagnosis, intrinsic or acquired resistance to therapy, tumor heterogeneity, and metastatic spread. In this context, the search for alternative treatments, new pharmacological targets, and combinatory therapy strategies becomes vital to improve patient outcomes substantially. (Y. Huang et al., 2021)
The connection between monoamine oxidase enzymes and cancer has been increasingly reinforced by experimental studies. MAO-A, in particular, has been found to be overexpressed in numerous malignancies, including prostate, breast, and colorectal cancer. Moreover, recent research conducted on NSCLC cell lines and tumor samples has found aberrant MAO-A expression in association with aggressive tumor features, indicating that disruption of MAO-A activity could potentially hold therapeutic validity.
MAO enzymes, including MAO-A and MAO-B, are involved in the oxidative deamination of monoamine neurotransmitters in the central nervous system, such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin (Youdim and Bakhle, 2000). These enzymes have recently been linked to lung cancer development (Wu et al., 2018). MAO-A and MAO-B are known to be overexpressed in various cancers, including lung cancer (Wu et al., 2015). Their overexpression not only contributes to tumor growth and progression but is also associated with poor patient outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer (Wu et al., 2017). Increased levels of MAO-derived hydrogen peroxide in cancer cells have been found to promote tumor growth and metastasis via activating various signaling pathways, including the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway (Yang et al., 2017). Inhibition of MAO enzymes has shown potential therapeutic benefits in lung cancer treatment. MAO inhibitors have demonstrated anti-tumor and anti-metastatic effects in preclinical in vitro and in vivo lung cancer models (Sarrouilhe et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2019).
One of the proposed mechanisms by which MAO-A could contribute to tumor progression is through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydrogen peroxide. The production of hydrogen peroxide during the metabolism of monoamine neurotransmitters can lead to an imbalance in cellular oxidant-antioxidant equilibrium, favouring the accumulation of ROS. This imbalance has been implicated in the induction of proliferative, pro-survival, and pro-angiogenic signaling pathways that promote tumorigenesis, malignant transformation, and tumor progression. In this sense, MAOIs could play a pivotal role in redressing this imbalance, curbing proliferation and metastasis. (Y. Huang et al., 2021; Zingone et al., 2017)
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs traditionally prescribed to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), and Parkinson's disease. These medications work by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase enzymes, which are responsible for breaking down monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. MAOIs help increase the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain, thereby improving mood and alleviating depressive symptoms. There are two main types of MAOIs: non-selective, irreversible inhibitors (e.g., phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and isocarboxazid) and selective, reversible inhibitors (e.g., moclobemide and selegiline). Each type has its own benefits, side effects, and drug interactions. Recent research has explored the possibility of utilizing MAOIs in the treatment of lung cancer, particularly non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the most common form of the disease. The rationale behind this potential application stems from the observation that monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A), a subtype of the MAO enzyme, is overexpressed in NSCLC patient samples, and its inhibition could potentially halt tumor growth. MAOIs may limit cancer cell growth by inhibiting metabolic processes, suppressing angiogenesis, and inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. The exact mechanism of action of MAOIs in lung cancer is not yet fully understood, and further investigation is necessary to elucidate this and optimize their use. As with any new therapeutic strategy, sensitivity and resistance to the treatment, the risk of side effects, and drug-drug interactions should be thoroughly evaluated in preclinical and clinical trials to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy. Thus, while the use of MAOIs in lung cancer treatment is still in its infancy, it represents an intriguing approach that may offer new therapeutic options for patients suffering from this devastating disease.
MAOIs, both reversible and irreversible, have been shown to possess potent anticancer properties in several in vitro and in vivo models, extending beyond their ability to modulate ROS. Some of these effects include inhibiting cell proliferation and migration, inducing cell cycle arrest, promoting apoptosis, and sensitizing cancer cells to conventional treatments. These findings indicate that their potential application in lung cancer therapy goes beyond merely mitigating oxidative damage.
2. MECHANISMS OF ACTION AND PHARMACODYNAMICS OF MAO INHIBITORS IN THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER(Yang et al., 2020, 2021)
While Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors are traditionally used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders like depression, they have also been investigated for potential utility in the treatment of certain types of cancer, including lung cancer.
The exact mechanism of action of MAO inhibitors in the context of lung cancer is not fully understood, but some proposed mechanisms include:
i. Inhibition of Monoamine oxidase enzymes: MAO inhibitors specifically block the activity of monoamine oxidase enzymes (MAO-A and MAO-B). These enzymes are responsible for the breakdown of biogenic amines, which play a role in the regulation of various physiological processes. In cancer cells, dysregulation of these amines can promote tumor growth and progression. By inhibiting MAO enzymes, MAO inhibitors may restore the balance of these amines and restrict cancer cell growth.
ii. Induction of Apoptosis: Emerging evidence suggests that some MAO inhibitors can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in lung cancer cells by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bcl-2 family members or activating caspases. This can help control cancer development and reduce tumor growth.
iii. Inhibition of Angiogenesis: Another proposed mechanism is that MAO inhibitors may inhibit angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) in tumors. Tumor cells depend on blood vessels for nutrients and oxygen. MAO inhibitors may have the ability to suppress vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) or other pro-angiogenic factors, thus inhibiting angiogenesis and ultimately reducing tumor growth and metastasis.
iv. Modulation of cell signaling pathways: MAO inhibitors might also modulate critical cell signaling pathways like the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK pathways, which are often dysregulated in lung cancer cells. These signaling pathways play a crucial role in promoting cell proliferation, invasion, and survival in cancer cells.
v. Immunomodulation: Some research indicates that MAO inhibitors can modulate the tumor microenvironment by influencing immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells. This can impact the immune response against tumor cells and might help in controlling tumor growth and metastatic potential.
Despite these potential mechanisms, it's important to note that more extensive research and clinical trials are needed to better understand the therapeutic potential of MAO inhibitors for lung cancer treatment. As of now, the use of MAO inhibitors to treat lung cancer is not well-established and is primarily experimental.(Yang et al., 2020)
PHARMACODYNAMICS refers to the effects of a drug on the body, particularly its mechanism of action and therapeutic outcomes. In the context of lung cancer, the anti-tumor activity of MAO inhibitors is not yet fully elucidated. However, preclinical studies have proposed several potential mechanisms:(B. Huang et al., 2020; Son et al., 2016)
i. Apoptosis induction: MAO inhibitors may induce apoptosis in lung cancer cells by increasing intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reducing mitochondrial membrane potential.
ii. Anti-angiogenesis: Downregulation of pro-angiogenic factors like vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is associated with the use of MAO inhibitors, potentially impeding tumor growth and invasion.
iii. Autophagy inhibition: Autophagy inhibition and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) have been separately studied for their potential role in the treatment of lung cancer. Combining these mechanisms could potentially offer unique benefits, but such investigations require further research. Autophagy is a cellular process that allows cells to recycle or degrade cellular components and maintain cellular homeostasis. It plays a role both in promoting cell survival and cell death. In cancer cells, autophagy could act as a double-edged sword: promoting cell survival under stressful conditions such as hypoxia, nutrient deprivation, or drug exposure, but also leading to cell death in malignant cells.
Inhibition of autophagy has emerged as a potential therapeutic strategy in lung cancer. Autophagy inhibition can make cancer cells more vulnerable to chemotherapeutic agents, leading to more effective treatments and a reduced risk of resistance. Several autophagy inhibitors, such as hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and Atg7 siRNA, have been studied for their effects on lung cancer cells. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that primarily target the monoamine oxidase enzymes, MAO-A and MAO-B. Originally, these drugs were designed to treat psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Recent research has shown that MAOIs can influence cancer cell proliferation and survival, making them of interest to oncology researchers.
In lung cancer, there is evidence that supports the effects of MAOIs on cell proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis. Certain MAOIs, such as clorgyline, have demonstrated potent anti-tumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines and animal models. The combination of autophagy inhibition and MAOIs in the treatment of lung cancer may offer complementary or synergistic effects. By impeding autophagy, cancer cells become more susceptible to the cytotoxic effects of MAOIs, thereby enhancing their capacity to eliminate cancer cells. However, the pharmacodynamic interactions of autophagy inhibitors and MAOIs need to be investigated in greater depth to ensure their efficacy and safety.
Overall, while both autophagy inhibition and MAOIs have the potential to improve lung cancer treatment, more research is needed to explore their combined effects, molecular mechanisms, optimal dosing, and potential drug-drug interactions.
iv. Modulation of the immune response: By altering the balance of various monoamine neurotransmitters and cytokines, MAO inhibitors may influence the tumor microenvironment and promote anti-tumor immune responses.
"The relationship between biogenic amines, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and lung cancer progression has been a topic of ongoing debate. While the main role of biogenic amines in cellular metabolism is to regulate vascular tone, they have also been shown to modulate ROS levels under certain conditions. Some previous findings suggest that the increased production of ROS may be associated with higher risks for various pathologies, including lung cancer, potentially as a result of oxidative stress-mediated cellular damage and DNA mutations (Cerutti, P. A. (1985). Prooxidant states and tumor promotion. Science, 227(4685), 375-381).
However, recent studies have provided evidence that moderate ROS levels might serve as signaling molecules, modulating various cellular processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis (Schieber, M., & Chandel, N. S. (2014). ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Current Biology, 24(10), R453-R462). This dual role of ROS in tumor progression suggests a more complex relationship between biogenic amines, ROS, and lung cancer than initially expected.
It is important to note that the effects of biogenic amines on ROS levels may vary depending on the specific amine and the cellular context. For instance, some biogenic amines, such as serotonin, can stimulate ROS production and induce the activation of pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic pathways, which might contribute to lung cancer development (Chanvorachote, P., & Nimmannit, U. (2012). Roles of ROS in the modulation of apoptosis. BioSystems, 107(1), 1-7). In contrast, other amines, like melatonin, have antioxidant properties that can help scavenge excessive ROS and confer protection against oxidative stress and tumorigenesis (Reiter, R. J., et al. (2017). Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant. Journal of Pineal Research, 63(1), e12424).
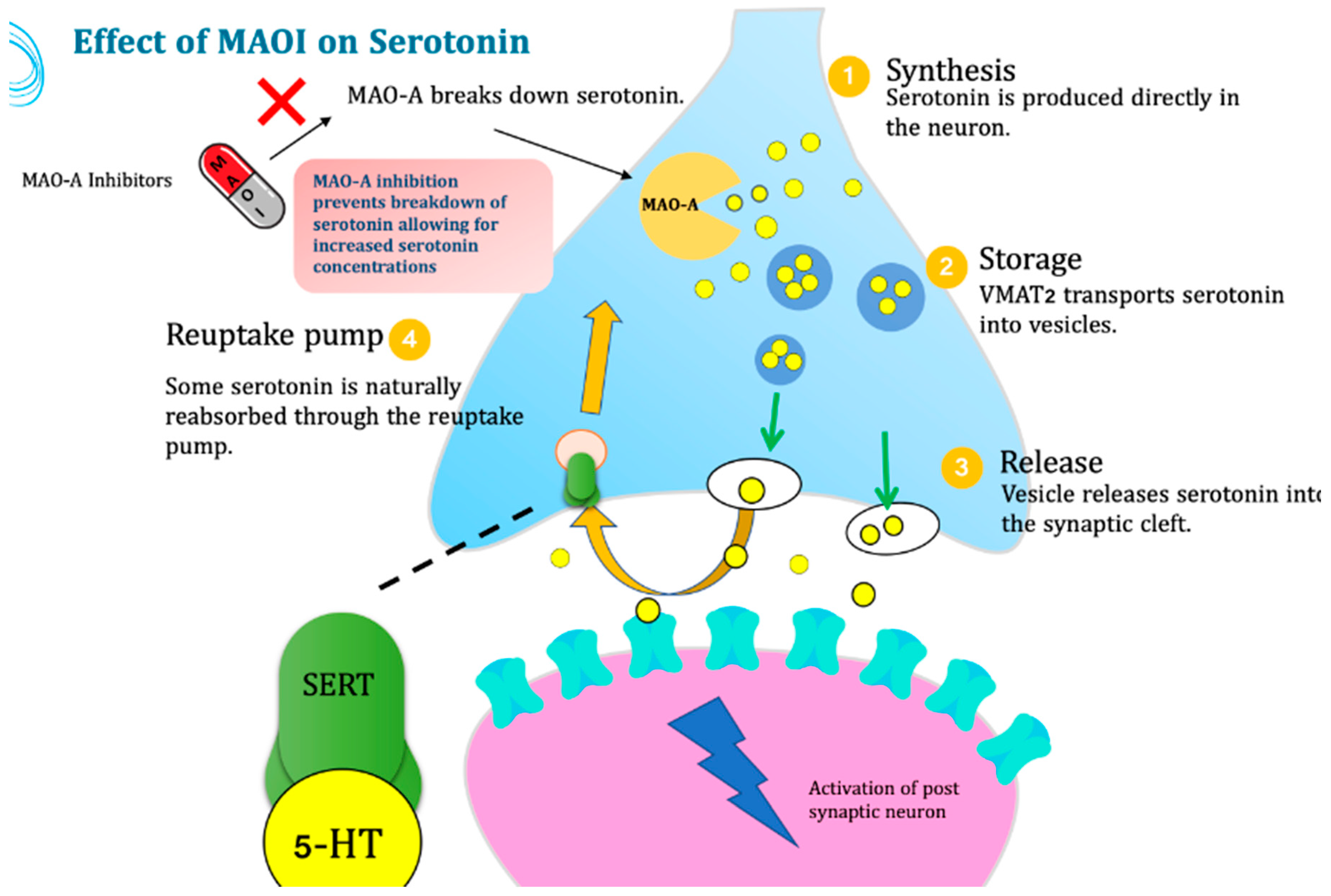
Figure 1.
Pharmacodynamic Effect of MAOI on Serotonin.
Figure 1.
Pharmacodynamic Effect of MAOI on Serotonin.
3. PHARMACOKINETICS OF MAOIS IN THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors are a class of drugs primarily used for treating neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression and Parkinson's disease. However, recent research has suggested potential anti-cancer effects, particularly in lung cancer. MAO inhibitors act by inhibiting MAO enzymes (MAO-A and MAO-B), which play a role in the catabolism of monoamine neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine in the central nervous system. (Shih, 2018). "Serotonin, an indoleamine neurotransmitter, is known to play a crucial role in various physiological and behavioral processes; however, it also serves as a substrate for monoamine oxidases (MAOs)."
PHARMACOKINETICS refers to how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. While there is limited data on the pharmacokinetics of MAO inhibitors in lung cancer treatment specifically, here is a general discussion of their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. (B. Huang et al., 2020)
i. Absorption: MAO inhibitors are typically well-absorbed orally, reaching peak plasma concentrations within a few hours of administration. The bioavailability of most MAO inhibitors is relatively high, ranging from 50% to 95%.
ii. Distribution: MAO inhibitors easily penetrate the blood-brain barrier and are distributed throughout various tissues, including the brain, liver, and kidneys. The plasma protein binding of these drugs is typically low to moderate, allowing for efficient tissue distribution.
iii. Metabolism: MAO inhibitors undergo hepatic metabolism mainly through oxidation reactions. The primary metabolites are usually pharmacologically inactive, with some exceptions like nortriptyline and desipramine formed from amitriptyline and imipramine, respectively.
iv. Excretion: MAO inhibitors and their metabolites are eliminated predominantly through renal excretion. The elimination half-life of these drugs ranges from 2 to 24 hours, depending on the specific agent and the patient's individual pharmacokinetics.
There are two main groups of MAOIs: reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) and irreversible nonselective MAOIs. Both groups have distinct pharmacokinetic properties that we will summarize below.
1. Irreversible nonselective MAOIs:
Examples of this group include phenelzine, tranylcypromine, and isocarboxazid. These drugs irreversibly inhibit both MAO-A and MAO-B enzymes, which are responsible for breaking down various neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine.
Pharmacokinetics of nonselective MAOIs:
- Oral administration is common, with varying absorption rates.
- High protein binding, leading to a prolonged duration of action.
- Metabolism occurs primarily in the liver, through Phase I and Phase II reactions.
- The metabolites are excreted in urine and feces.
- These inhibitors have a prolonged half-life, ranging from 2 to 5 days.
2. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs):
Moclobemide and toloxatone belong to this group. They selectively inhibit only the MAO-A enzyme and have a reversible mode of action. This results in fewer side effects and lower dietary restrictions compared to irreversible nonselective MAOIs.
Pharmacokinetics of RIMAs:
- Rapid oral absorption, with peak plasma concentrations achieved within an hour.
- Lower protein binding (approximately 50%) compared to nonselective MAOIs.
- Moclobemide is primarily metabolized by the liver enzymes CYP2C19 and CYP2D6.
- The metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine.
- RIMAs have a shorter half-life (1.5 to 4 hours) leading to a lower risk of drug interactions and tyramine reactions.
4. THERAPEUTIC POTENTIAL OF MAO INHIBITORS IN LUNG CANCER
The therapeutic potential of MAO inhibitors in lung cancer is partly due to their ability to inhibit cancer cell growth and induce apoptosis. They have also been shown to modulate the tumor microenvironment, making it less conducive for cancer cells to survive and proliferate. MAO inhibitors may exhibit synergistic effects when combined with existing chemotherapeutic agents, indicating the possibility of more effective, personalized treatments for lung cancer patients. (Liu et al., 2018)
5. BENEFITS AND LIMITATIONS OF MAOIS IN THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER
5.1. BENEFITS OF MAOIS IN THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER(H. W. Lee et al., 2017)
i. Inhibition of tumor growth
MAOIs have been shown to inhibit the growth of lung cancer cells in vitro. Several studies have demonstrated that MAOIs such as tranylcypromine and phenelzine can induce apoptosis and reduce the proliferation of lung cancer cells by inhibiting MAO-A. This may help slow down disease progression and increase the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
ii. Reducing cancer-related fatigue
Cancer-related fatigue is a common symptom among lung cancer patients and can significantly impact their quality of life. Recent studies have suggested that MAOIs may help reduce fatigue by increasing the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. This may improve energy levels and cognitive function in lung cancer patients.
iii. Targeting cancer stem cells
Cancer stem cells are a subset of cells within tumors that have the ability to self-renew and initiate tumor growth. They are often resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, making them a major obstacle in cancer treatment. Recent studies have suggested that MAOIs may be effective in targeting these cells by inhibiting their self-renewal and inducing apoptosis.
Enhancing the efficacy of certain chemotherapeutic agents: The use of MAOIs, specifically type A, has been found to enhance the efficacy of some chemotherapeutic agents when combined in the treatment of lung cancer. One mechanism by which MAOIs improve the potency of these agents is through the inhibition of the efflux transporters that are accountable for drug resistance in cancer cells. This results in a higher concentration of chemotherapeutic drugs inside the cancer cells, thereby making them more effective in killing the cancerous cells (Zhao et al., 2020). Another mechanism can be related to the role of MAOIs in modulating oncogene expression and intracellular signaling pathways, which can improve the sensitivity of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs (Asati et al., 2016). These benefits suggest that combining MAOIs with existing chemotherapy-based treatments could help patients achieve better outcomes in their fight against lung cancer.
5.2. LIMITATIONS OF MAOIS IN THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER(Liu et al., 2018)
i. Side effects
MAOIs can cause side effects such as dizziness, dry mouth, and constipation. In some cases, they can also cause severe side effects such as hypertensive crisis, a medical emergency that can lead to stroke or heart attack. This may limit their usefulness in some patients, particularly those with underlying cardiovascular diseases.
ii. Drug interactions
MAOIs can interact with a wide range of drugs and supplements, including antidepressants, opioids, and over-the-counter cold medications. These interactions can lead to severe side effects, including serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by high fever, seizures, and loss of consciousness.
iii. Limited clinical evidence
Despite promising in vitro studies, there is limited clinical evidence to support the use of MAOIs in the treatment of lung cancer. Most of the current evidence is based on small, non-randomized studies, and more robust clinical trials are needed to establish their efficacy and safety.
MAOIs have shown promise as a potential therapy for lung cancer. They have been shown to inhibit tumor growth, reduce cancer-related fatigue, and target cancer stem cells. However, they are also associated with several limitations, including potential side effects, drug interactions, and limited clinical evidence. More research is needed to establish their efficacy and safety in larger, randomized clinical trials.
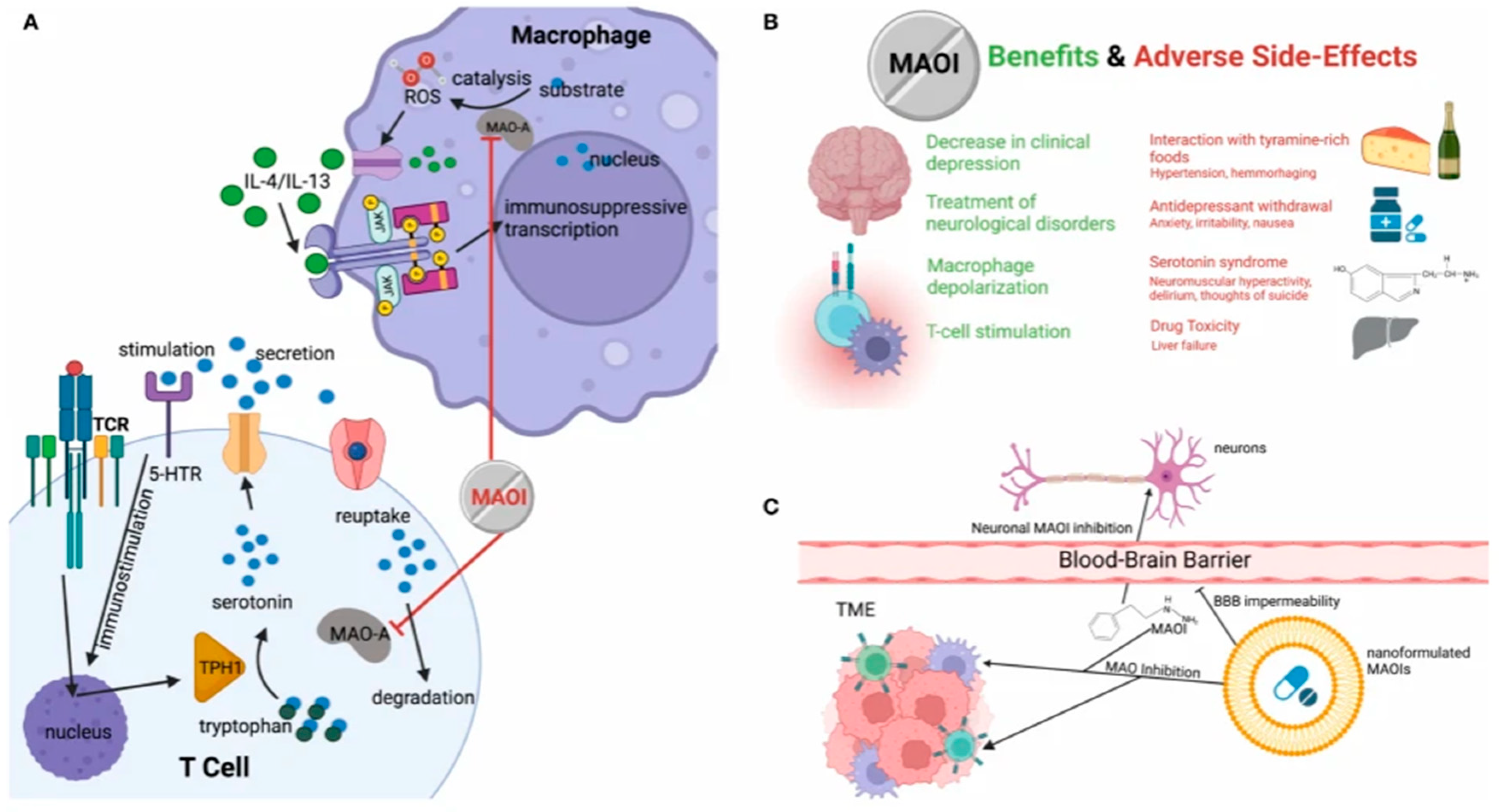
Figure 2.
Potential of MAOI of ICB therapy.
Figure 2.
Potential of MAOI of ICB therapy.
6. PHARMACOLOGICAL CHALLENGES AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS OF MAO INHIBITORS IN THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER
6.1. PHARMACOLOGICAL CHALLENGES(Ghosh et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2021)
i. Selectivity and Potency: Developing highly selective MAO inhibitors that target only the specific between MAO – A & MAO - B isoforms associated with lung cancer could reduce unwanted side effects and improve treatment outcomes. This would minimize the impact on other physiological pathways and avoid potential interactions with other medications.
ii. Dosing and Pharmacokinetics: Identifying the optimal dosing regimen and pharmacokinetics for MAO inhibitors in lung cancer therapy is necessary to achieve maximal efficacy while minimizing the risk of side effects. This includes determining the effective concentration, frequency of administration, and duration of treatment.
iii. Toxicity and Drug-Drug Interactions: Current MAO inhibitors are associated with significant toxicity and drug-drug interactions that might hinder their use for lung cancer treatment. There is a need for well-tolerated and safe compounds. MAO inhibitors can have dangerous interactions with other drugs, leading to serotonin syndrome or hypertensive crises. To safely employ these drugs in treatment regimens, thorough assessments of potential interactions and proper management strategies must be established.
iv. Tumor Microenvironment: The complexity of the tumor microenvironment in lung cancer poses challenges in drug delivery and efficacy. Developing MAO inhibitors that can specifically target the tumor microenvironment remains crucial.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are primarily known for their use in treating depressive disorders, but their potential role in cancer treatment has been investigated in recent years, including for lung cancer. It is important to differentiate between side effects and adverse effects when discussing the impact of these drugs on patients.
Side Effects:
Side effects are typically unintended, but not necessarily harmful, consequences of drug therapy that can be expected to occur during its normal usage. Common side effects associated with the use of MAOIs include:
1. Headache
2. Dizziness
3. Dry mouth
4. Insomnia or sleep disturbances
5. Gastrointestinal issues (e.g., nausea, constipation)
6. Weight gain
These side effects, while sometimes uncomfortable, are mostly considered manageable during the course of treatment.
Adverse Effects:
Adverse effects, on the other hand, are more severe, harmful, or unintended reactions that can lead to significant complications or harm to the patient. The following adverse effects may be associated with the use of MAOIs in treating lung cancer:
1. Hypertensive crisis: Consumption of tyramine-rich foods or ingestion of certain medications while taking MAOIs may lead to a sudden, often dangerous increase in blood pressure.
2. Serotonin syndrome: Concurrent use of other drugs that impact serotonin levels, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or certain pain medications, can result in a potentially fatal condition characterized by agitation, confusion, muscle rigidity, and fever.
3. Hepatotoxicity: Long-term use of MAOIs could potentially lead to liver damage.
4. Severe drug interactions: MAOIs may interact adversely with a variety of drugs, including other antidepressants, anesthetics, and chemotherapy agents.
The side effects of MAOIs are typically manageable consequences that arise during standard treatment, while adverse effects are more severe reactions with potential risks or complications for the patient. Considering the delicate balance of benefits and drawbacks, it is crucial to carefully monitor the use of MAOIs in the treatment of lung cancer to maximize positive outcomes and minimize the risk of harmful effects.
6.2. FUTURE DIRECTIONS(Yan et al., 2021)
i. Identification of Novel Targets and Agents: The discovery of new molecular targets within the MAO family could lead to the development of more effective inhibitors. High-throughput screening and rational drug design techniques can be employed to identify and optimize these novel agents.
ii. Combination Therapies: Combining MAO inhibitors with other chemotherapeutic agents, targeted therapies, or immunotherapies may potentiate the anti-tumor efficacy and overcome drug resistance, offering a more comprehensive approach to lung cancer treatment.
iii. Biomarker Discovery: Identifying specific biomarkers to predict treatment response to MAO inhibitors could enable personalized therapy and better prognosis, ensuring that only patients likely to benefit from these drugs are given them while avoiding unnecessary side effects in others.
iv. Preclinical and Clinical Trials: Rigorous preclinical studies and well-designed clinical trials are essential to confirm the safety, efficacy, and tolerability of MAO inhibitors in lung cancer treatment. These trials would also help establish dosing guidelines and identify potential biomarkers for patient selection.
v. Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery: Developing nanotechnology-based formulations for MAO inhibitors can enhance drug delivery, target specificity, and reduce toxicities.
7. THE BIOLOGICAL ROLE OF MAOIS IN LUNG CANCER:(Aljanabi et al., 2021; Mirzaei & Nazemi, 2022)
MAOIs have been shown to have anticancer properties, primarily in the treatment of breast cancer. A study published in the Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology found that MAOIs inhibited the growth of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells in vitro, and also reduced the size of tumors in mice with breast cancer. Another study published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry found that MAOIs could also inhibit the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells, which are typically more aggressive and difficult to treat than other types of breast cancer.
The potential anticancer effects of MAOIs are likely due to their ability to inhibit the activity of monoamine oxidase enzymes. In breast cancer cells, it has been suggested that monoamine oxidase enzymes play a role in the production of estrogen (Bhatnagar et al., 2016). Estrogen is known to stimulate the growth of breast cancer cells, so inhibiting its production could potentially slow or stop tumor growth.
Other researchers have suggested that MAOIs may also have an effect on the immune system, which could contribute to their anticancer properties. A study published in the Journal of Immunology found that MAOIs enhanced the activity of natural killer cells, which are an important part of the immune system's response to cancer.
8. MAO INHIBITORS AND ANTI-CANCER EFFECTS IN LUNG CANCER: RETHINKING TRADITIONAL PERSPECTIVES(Bardaweel et al., 2022; Kamiński et al., 1984; Kim et al., 2019)
i. Novel cancer treatment strategies: MAO inhibitors have primarily been used for treating psychiatric disorders, such as depression and anxiety. However, mounting evidence suggests their potential as anticancer agents. The ability of these compounds to combat cancer provides an unconventional perspective on cancer treatment strategies.
ii. Expanding our understanding of MAOI targets: Monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes, MAO-A and MAO-B, are best known for their role in neurotransmitter regulation. Investigating the effects of MAO inhibition on cancer cells allows us to broaden our understanding of potential targets in cancerous cell signaling pathways that may be modulated by MAOIs.
iii. Harnessing MAOI-induced apoptosis: Cancer cells harbor an exceptional ability to evade apoptosis or programmed cell death. Recent studies have revealed that certain MAO inhibitors can induce apoptosis in cancer cells, thus effectively reducing the growth and spread of various cancer types. Unlocking the molecular mechanisms behind this response can open new avenues for cancer research and treatment development.
iv. Anticancer synergy with other drugs: Anticancer synergy with other drugs in lung cancer refers to the potential enhancement of anti-tumor effects when multiple drugs are combined, particularly when one drug potentiates the effect of another drug, resulting in greater efficacy than either drug alone. There have been numerous studies and combinations explored to exploit synergistic effects in lung cancer treatment. Some examples of drugs with potential synergistic effects in lung cancer include:
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and chemotherapy: Studies have demonstrated the potential for synergistic effects when combining TKIs, such as erlotinib or gefitinib, with chemotherapy agents, like pemetrexed or cisplatin. These combinations have been found to increase progression-free survival and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors and chemotherapy: The combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab, with chemotherapy has shown synergistic effects in NSCLC. As a result, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved the combination of pembrolizumab and chemotherapy for untreated metastatic NSCLC.
Angiogenesis inhibitors and chemotherapy: Combining angiogenesis inhibitors like bevacizumab with standard chemotherapy has proven beneficial for some NSCLC subtypes. The synergistic combination has extended both progression-free survival and overall survival.
PARP inhibitors and platinum-based chemotherapy: Inhibition of poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerase (PARP) has been shown to potentiate the effects of platinum-based chemotherapy in preclinical studies. Synergism of PARP inhibitors, like olaparib, with platinum drugs, like cisplatin, might be a promising strategy for the improved treatment of lung cancer patients.
Targeted therapy and radiotherapy: Combining targeted therapies, such as EGFR inhibitors or ALK inhibitors, with radiotherapy has demonstrated positive synergistic effects in certain subgroups of NSCLC patients by sensitizing tumor cells to radiation.
v. The impact of MAOI-induced oxidative stress: MAO inhibition can lead to elevated intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can be detrimental to healthy cells but may present an advantage in targeting cancer cells. The increased oxidative stress could hinder the growth and survival of cancer cells or sensitize them to other therapies.
vi. Importance of personalized medicine approaches: As the relevance of MAO enzymes varies across different cancer types, personalized medicine approaches are crucial. By understanding the intricacies of MAO expression and function in individual cancers, clinicians can tailor treatments to suit patient-specific conditions, potentially improving the patient's prognosis.
vii. Unforeseen connections between cancer and psychiatric disorders: The potential therapeutic effects of MAO inhibitors on cancer cells raise vital questions about the relationship between cancer and psychiatric disorders. Exploring these connections could lead to transformative treatments for both cancer and mental health conditions.
In summary, the unconventional anticancer effects of MAO inhibitors may transform the way we perceive cancer treatment and research. Assessing the links between cancer, mental health, and MAO inhibition could not only provide fresh perspectives on novel therapeutic avenues but also enhance our understanding of cancer biology and the complex interplay between diseases.
9. MAOIS BINDING SITE FOR TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER(Jin et al., 2023; Ouyang et al., 2023)
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, a class of drugs, have emerged as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of lung cancer. The MAO enzymes, predominantly MAO-A and MAO-B, are found bound to the outer mitochondrial membrane in various tissues, including the lungs.
MAO inhibitors selectively block the active sites of these enzymes, preventing the degradation of monoamine neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. This results in the stabilization of these neurotransmitters, which are often dysregulated in cancer settings. MAO inhibitors function by binding to the active site of the monoamine oxidase enzyme, specifically to the flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactor, which is an essential component for catalytic activity. This binding event results in irreversible inhibition of the enzyme, thereby preventing the breakdown of neurotransmitters and causing an accumulation of these monoamine neurotransmitters within the tumor microenvironment.
Accumulation of monoamine neurotransmitters can lead to apoptotic cell death, as well as the inhibition of angiogenesis and tumor growth, ultimately providing therapeutic benefits for patients with lung cancer. However, it is important to note that more research and clinical trials are needed to better understand the efficacy and safety of using MAO inhibitors for lung cancer treatment. To effectively target lung cancer, researchers can develop MAO inhibitors that selectively bind to the active sites of MAO-A or MAO-B with high affinity, tailoring the therapy to specific cancer subtypes. This approach may lead to an improvement in treatment outcomes while minimizing potential side effects.
10. COMPUTER-AIDED MAO INHIBITORS DESIGN FOR LUNG CANCER TREATMENT
Computer-aided design of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors can play a significant role in developing novel drugs for the treatment of lung cancer. Monoamine oxidases are enzymes that catalyse the oxidative deamination of monoamines and are associated with various health conditions, including cancer. The design process involves several steps, such as exploring potential MAO protein targets, building a library of potential inhibitors, docking and virtual screening, and optimization of lead candidates. Here is an overview of these steps:(Duangkamol et al., 2023; Lepcha et al., 2023; Musa & Kolawole, 2023)
i. Literature review: Research existing MAO inhibitors and lung cancer treatment methods. Compare the effectiveness and limitations of current treatments, and identify possible targets for a novel MAO inhibitor.
ii. Identification of MAO protein targets: The first step is to identify relevant MAO isoforms (MAO-A or MAO-B) that are associated with lung cancer pathogenesis. Researchers can use bioinformatics tools and databases to effectively identify these targets and study their structural and functional properties.
iii. Building a library of potential MAO inhibitors: Using computational tools, researchers can compile a diverse library of potential MAO inhibitors. This can be achieved through de novo design, virtual screening of existing compound libraries, or by modifying existing inhibitors to improve their potency and selectivity.
iv. Docking and virtual screening: In silico molecular docking involves predicting how a small molecule will interact with the target protein, the MAO isoform identified in step 1. Virtual screening enables researchers to rank potential inhibitors based on their predicted binding affinity, allowing for the selection of lead candidates for further optimization.
v. Optimization of lead candidates: The selected lead candidates can then be optimized using various computational approaches, such as molecular dynamics simulations, QSAR (quantitative structure-activity relationship) Modeling, and pharmacophore Modeling. These methods allow researchers to understand the critical interactions between the inhibitors and the MAO proteins, improve potency, and reduce unwanted side effects.
vi. Experimental validation: Before moving forward with preclinical trials of the optimized inhibitors, their predicted activities must be validated experimentally. This involves synthesizing the compounds and using biochemical assays to test their inhibitory activities, followed by in vitro and in vivo testing in lung cancer cell lines and animal models.
vii. Virtual screening and compound selection: Run in silico compound libraries through molecular docking or machine learning-based virtual screening tools to identify potential inhibitors based on their predicted binding affinity and interaction pattern with the target protein.
viii. Hit-to-lead optimization: Optimize the chemical structures of selected compounds to improve their binding affinity, selectivity, and drug-like properties, using methods such as quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) Modeling or molecular dynamics (MD) simulations.
ix. ADMET prediction: Evaluate the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) of lead compounds using computational methods. Filter out unfavourable candidates based on the predicted ADMET properties.
x. Experimental validation: Synthesize and test the most promising compounds in vitro and in vivo to assess their inhibitory activity, selectivity, and cytotoxic effects on lung cancer cells.
xi. Iterate and refine: Refine the computational models based on experimental results, and optimize the most promising compounds through iterative cycles of in silico Modeling, synthesis, and biological testing.
xii. Preclinical and clinical trials: If the experimental validation yields promising results, the novel MAO inhibitors can be further tested in preclinical and clinical trials to establish their safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetic properties in the treatment of lung cancer.
11. EXPANDING ROLE OF BIOTECHNOLOGY IN MAOIS-BASED LUNG CANCER TREATMENT APPROACHES
The ongoing battle against lung cancer receives another boost from the rapidly advancing field of biotechnology, which has led to the development of novel therapeutics. One such promising avenue is the repositioning of traditional monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) to target lung cancer cells. MAOIs, primarily known for their role in the treatment of depressive disorders, are increasingly gaining attention for their oncotherapeutic potential. The biotechnological advancements in MAOIs' application have expanded our knowledge of complex molecular interactions that contribute to the progression of lung cancer, and in turn, point towards several new approaches in modifying these drugs for enhanced efficacy.(Lepcha et al., 2023)
One significant discovery made in this regard revolves around the dual inhibition of both MAO-A and MAO-B isoforms. The in-depth analysis of specific isoform targeting has revealed that selectively inhibiting only one isoform exerts differential cytotoxic effects on lung cancer cells, emphasizing the importance of the dually-targeted strategies. This insight leads to the development of novel, biotechnology-driven MAOIs, exhibiting improved anti-cancer effects and fewer systemic side effects.
Another breakthrough in MAOI research is the development of novel drug delivery systems to ensure targeted and controlled delivery of MAOIs to lung cancer cells while minimizing toxicity to normal cells. Biotechnological advancements, such as nanoparticle drug carriers, antibody-drug conjugates, and cell-penetrating peptides, have significantly improved the bioavailability, specificity, and pharmacokinetics of the MAOIs, making their use in lung cancer treatment more feasible and practical.(C.-H. Chen & Wu, 2023)
The biotechnological improvements in patient care include early detection and companion diagnostics. The development of advanced liquid biopsy-based assays has helped detect cancer-specific molecular targets in the blood, allowing clinicians to choose tailored therapeutic approaches based on the patient’s genetic make-up. Furthermore, identifying a biomarker for patients who may respond better to MAOI-based treatments is another step towards precision oncology.(Han et al., 2023)
12. CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the exploration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) in the management of lung cancer has led to a renaissance in cancer therapeutics. The traditional and well-established roles of MAOIs in neuropsychiatric disorders have paved the way for a new era of multidisciplinary research, shifting the focus to the potential benefits of MAOIs in cancer treatment. In this comprehensive review, we have provided a thorough analysis of the existing evidence on MAOI efficacy in lung cancer management, as well as delving into the molecular mechanisms involved, introducing novel pathways for clinical advancement.(H. M. Lee et al., 2020)
Lung cancer remains one of the most prevalent and deadly malignancies globally, with alarmingly high mortality rates. In the face of limitations in available therapeutic strategies, the drug repurposing of MAOIs offers a promising opportunity to enhance the current state of disease management. The anticancer potential of MAOIs is hypothesized to stem from their interference with the metabolism of biogenic amines, leading to dysregulated cellular signaling, and subsequently, cancer cell death.(Tsai et al., 2019)
The synergistic effect of combining MAOIs with conventional chemotherapeutics has been demonstrated in a variety of preclinical studies, offering patients with lung cancer an opportunity for improved outcomes. This also makes a case for examining the potential of MAOIs in other malignancies, furthering our understanding of drug repurposing in oncology. The mutational landscape of each patient's tumor plays a pivotal role in determining the most efficacious treatment approach. In lung cancer, mutations in genes such as EGFR and KRAS can dictate the appropriateness of targeting therapies. The potential impact of incorporating MAOIs in mutation-defined treatment regimens must be rigorously investigated to optimize efficacy and minimize the potential for adverse effects.(L. Chen et al., 2020)
To this end, robust biomarker development is essential for the successful implementation of MAOIs in lung cancer management. Identification of potential targets, patient stratification, and predicting response to treatment are all crucial aspects of patient-centred therapy. Integrating genomic and proteomic profiles of lung cancer patients could provide crucial insights into the optimal use of MAOIs in patient care.
Furthermore, the intricate interplay between the tumor microenvironment (TME) and the host immune system can either enhance or detract from the antitumor activities of therapeutics. Future research must consider this complex relationship when exploring the immunomodulatory effects of MAOIs in vivo. Failure to address the influence of the TME could result in the dismissal of potentially beneficial therapeutics or yield harmful effects due to immune overactivation.(Dhabal et al., 2018)
"In recent years, the concept of drug repurposing has garnered significant attention in the field of cancer treatment. Drug repurposing capitalizes on the already established safety profiles and molecular targets of existing drugs, thereby offering a faster, more cost-effective, and efficient strategy for developing novel cancer therapeutics. As the range of potential molecular targets in cancer continues to expand, repurposing FDA-approved drugs and compounds in clinical trials for other diseases presents a powerful opportunity to accelerate the identification of new treatment options for cancer patients. In the context of our article, incorporating a discussion on drug repurposing not only emphasizes the potential implications of our findings but also helps to place our review within the broader landscape of lung cancer therapy. Moreover, by shedding light on the value of repurposing drugs, our conclusion may encourage further investigations into this approach and facilitate the development of innovative and personalized lung cancer treatments.
The integration of novel nanotechnological delivery systems could further augment the therapeutic potential of MAOIs. By enhancing drug stability, reducing systemic toxicity, and prolonging drug release, nano-based delivery systems could improve patient outcomes and facilitate tumor-targeted drug delivery. The expansion of research in this realm is vital to propel MAOIs' translation from bench to bedside. The complexity of lung cancer biology calls for a more comprehensive approach to disease management. A concerted effort is needed to bridge the gap between preclinical findings, pharmacology, and clinical outcomes, addressing the translational research question that has hindered the progress of MAOI-based therapeutics in the oncological landscape. Future studies should focus on confirming targets, optimizing dosage regimens, and combining MAOIs with other treatment modalities to support the development of these novel agents into the clinical sphere.(Y. Huang et al., 2021)
In the face of current global economic constraints and the need for sustainable and cost-effective interventions, repurposing of MAOIs represents a newfound opportunity in the fight against lung cancer. Leading regulatory bodies and governments must invest in research that would accelerate the translation of the therapeutic potential of MAOIs into improved clinical practice. The utilization of real-world data and the establishment of open access research resources would facilitate widespread multinational collaboration, ultimately fostering an environment in which the benefits of MAOIs can be realized. The diverse landscape of applications that monoamine oxidase inhibitors offer is testament to the malleability and potential of these small molecules. Over the last decades, MAOIs have proven to be effective pharmacological agents in disorders ranging from neurodegenerative diseases to neuropsychiatric conditions. Today, their story may be broadened to include a chapter on their potential as anticancer therapeutics - a possibility that sparks hope for countless individuals affected by lung cancer around the world.(Zingone et al., 2017)
As we have demonstrated, the therapeutic potential of MAOIs in the realm of lung cancer management is immense, encompassing far-reaching spheres of influence. While the path ahead remains riddled with challenges, there is reason to be optimistic that through concerted interdisciplinary efforts, the field of oncology can continue to innovate, offering novel solutions to some of humanity's most pressing health challenges. Indeed, the use of MAOIs in lung cancer may well be a story of scientific discovery worth pursuing, ultimately benefiting the lives of millions of patients on a global scale.(Yang et al., 2021)
13. AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
The all authors confirm developed the first draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the planning, organization, data collection, and writing of the manuscript. All reviewed the manuscript and provided critical edits. The final version of the manuscript was approved by all authors and approved it for publication.
14. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Aljanabi, R., Alsous, L., Sabbah, D. A., Gul, H. I., Gul, M., & Bardaweel, S. K. (2021). Monoamine oxidase (MAO) as a potential target for anticancer drug design and development. Molecules, 26(19), 6019. [CrossRef]
- Bardaweel, S., Aljanabi, R., Sabbah, D., & Sweidan, K. (2022). Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel MAO-A inhibitors targeting lung cancer. Molecules, 27(9), 2887. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H., & Wu, B. J. (2023). Monoamine oxidase A: An emerging therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 13. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L., Guo, L., Sun, Z., Yang, G., Guo, J., Chen, K., Xiao, R., Yang, X., & Sheng, L. (2020). Monoamine oxidase A is a major mediator of mitochondrial homeostasis and glycolysis in gastric cancer progression. Cancer Management and Research, 12, 8023. [CrossRef]
- Dhabal, S., Das, P., Biswas, P., Kumari, P., Yakubenko, V. P., Kundu, S., Cathcart, M. K., Kundu, M., Biswas, K., & Bhattacharjee, A. (2018). Regulation of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) expression, activity, and function in IL-13–stimulated monocytes and A549 lung carcinoma cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 293(36), 14040–14064.
- Duangkamol, C., Wangngae, S., Wet-Osot, S., Khaikate, O., Chansaenpak, K., Lai, R.-Y., & Kamkaew, A. (2023). Quinoline-Malononitrile-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Probe for Monoamine Oxidase Detection in Living Cells. Molecules, 28(6), 2655. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S., Dutta, N., Banerjee, P., Gajbhiye, R. L., Sareng, H. R., Kapse, P., Pal, S., Burdelya, L., Mandal, N. C., & Ravichandiran, V. (2021). Induction of monoamine oxidase A-mediated oxidative stress and impairment of NRF2-antioxidant defence response by polyphenol-rich fraction of Bergenia ligulata sensitizes prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 172, 136–151. [CrossRef]
- Han, H., Li, H., Ma, Y., Zhao, Z., An, Q., Zhao, J., & Shi, C. (2023). Monoamine oxidase A (MAOA): A promising target for prostate cancer therapy. Cancer Letters, 216188. [CrossRef]
- Huang, B., Zhou, Z., Liu, J., Wu, X., Li, X., He, Q., Zhang, P., & Tang, X. (2020). The role of monoamine oxidase A in HPV-16 E7-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and HIF-1α protein accumulation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 16(14), 2692. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y., Zhao, W., Ouyang, X., Wu, F., Tao, Y., & Shi, M. (2021). Monoamine oxidase a inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation by abrogating aerobic glycolysis. Frontiers in Oncology, 11, 645821. [CrossRef]
- Jin, C., Li, J., Yang, X., Zhou, S., Li, C., Yu, J., Wang, Z., Wang, D., He, Z., & Jiang, Y. (2023). Doxorubicin-isoniazid conjugate regulates immune response and tumor microenvironment to enhance cancer therapy. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 631, 122509. [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, K. A., Bodzionyo, J., & Kozielskio, J. (1984). Monitoring treatment of pulmonary carcinomas by serial determination of monoamine oxidase. Arch. Geschwulstforsch, 54(5), 377–385.
- Kim, W. Y., Won, M., Salimi, A., Sharma, A., Lim, J. H., Kwon, S.-H., Jeon, J.-Y., Lee, J. Y., & Kim, J. S. (2019). Monoamine oxidase-A targeting probe for prostate cancer imaging and inhibition of metastasis. Chemical Communications, 55(88), 13267–13270. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. M., Sia, A. P. E., Li, L., Sathasivam, H. P., Chan, M. S. A., Rajadurai, P., Tsang, C. M., Tsao, S. W., Murray, P. G., & Tao, Q. (2020). Monoamine oxidase A is down-regulated in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 6115. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. W., Ryu, H. W., Baek, S. C., Kang, M.-G., Park, D., Han, H.-Y., An, J. H., Oh, S.-R., & Kim, H. (2017). Potent inhibitions of monoamine oxidase A and B by acacetin and its 7-O-(6-O-malonylglucoside) derivative from Agastache rugosa. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 104, 547–553. [CrossRef]
- Lepcha, T. T., Kumar, M., Sharma, A. K., Mal, S., Majumder, D., Jana, K., Basu, J., & Kundu, M. (2023). Uncovering the role of microRNA671-5p/CDCA7L/monoamine oxidase-A signaling in Helicobacter pylori mediated apoptosis in gastric epithelial cells. Pathogens and Disease, ftad006. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F., Hu, L., Ma, Y., Huang, B., Xiu, Z., Zhang, P., Zhou, K., & Tang, X. (2018). Increased expression of monoamine oxidase A is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and clinicopathological features in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology Letters, 15(3), 3245–3251. [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M., & Nazemi, H. (2022). In silico interactions between curcumin derivatives and monoamine oxidase-a enzyme. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry, 12, 3752–3761.
- Musa, M. A., & Kolawole, Q. (2023). 7, 8-Diacetoxy-3-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl)-4-phenylcoumarin Induces ROS-dependent Cell Death in the A549 Human Lung Cancer Cell Line. Anticancer Research, 43(3), 1001–1007. [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X., Zhu, D., Huang, Y., Zhao, X., Xu, R., Wang, J., Li, W., & Shen, X. (2023). Khellin as a selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitor ameliorated paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice. Phytomedicine, 154673. [CrossRef]
- Shih, J. C. (2018). Monoamine oxidase isoenzymes: genes, functions and targets for behavior and cancer therapy. Journal of Neural Transmission, 125, 1553–1566. [CrossRef]
- Son, B., Jun, S. Y., Seo, H., Youn, H., Yang, H. J., Kim, W., Kim, H. K., Kang, C., & Youn, B. (2016). Inhibitory effect of traditional oriental medicine-derived monoamine oxidase B inhibitor on radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J., Chiu, W.-C., Chen, C.-J., Chen, P.-C., McIntyre, R. S., & Chen, V. C.-H. (2019). Antidepressant prescription and risk of lung cancer: a nationwide case-control study. Pharmacopsychiatry, 52(03), 134–141. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Li, B., Kim, Y. J., Wang, Y.-C., Li, Z., Yu, J., Zeng, S., Ma, X., Choi, I. Y., & Di Biase, S. (2021). Targeting monoamine oxidase A for T cell–based cancer immunotherapy. Science Immunology, 6(59), eabh2383. [CrossRef]
- Yan, J., Zhang, H., & Zhu, J. (2021). Recent advances of small molecule fluorescent probes for distinguishing monoamine oxidase-A and monoamine oxidase-B in vitro and in vivo. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 55, 101686. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., Li, Y., Zhao, D., Cui, W., Li, H., Li, X., Li, Y., & Wang, D. (2021). Repurposing of a monoamine oxidase A inhibitor-heptamethine carbocyanine dye conjugate for paclitaxel-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology Reports, 45(3), 1306–1314. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., Zhao, D., Li, Y., Li, Y., Cui, W., Li, Y., Li, H., Li, X., & Wang, D. (2020). Potential monoamine oxidase A inhibitor suppressing paclitaxel-resistant non-small cell lung cancer metastasis and growth. Thoracic Cancer, 11(10), 2858–2866. [CrossRef]
- Zingone, A., Brown, D., Bowman, E. D., Vidal, O. M., Sage, J., Neal, J., & Ryan, B. M. (2017). Relationship between anti-depressant use and lung cancer survival. Cancer Treatment and Research Communications, 10, 33–39. [CrossRef]
- Asati, V., Bharti, S. K., & Mahapatra, D. K. (2016). MAO inhibition potential of newly synthesized 2-pyrazoline derivatives containing 1,2,4-triazole/1,2,4-triazine scaffold. Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry, 31(6), 1505–1509. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H., Huang, Y., Xue, C., Chen, Y., Hou, X., Guo, Y.,... & Ka, W. (2020). Anti-tumor effects of the silencing of programmed cell death-5 combined with chemotherapy in lung cancer. Oncology Letters, 19(1), 262-270. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).