1. Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is an inflammatory disorder of the pancreatic tissue, which is usually accompanied by severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Although the clinical course of AP is mild and self-limiting in most patients, up to 20% of them develop severe AP that contains manifestations of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and multiple organ failure (MOF). Overall mortality is 5%, and this rate may be as high as 25% in those with severe AP [
1]. The best predictor of poor outcome in AP is the development of persistent MOF and pancreatic necrosis. Therefore, it is important to predict the course and the severity of the disease in an early stage.
Most widely used classification system for determining the severity and course of AP is the revised Atlanta Classification. The severity of AP is graded as mild acute pancreatitis (MAP), moderately severe acute pancreatitis (MSAP), and severe acute pancreatitis(SAP) according to the revised Atlanta Classification [
2]. Beside the revised Atlanta Classification, several other prognostic scoring systems and classifications have been developed to predict the severity of AP [
3]. Ranson’s criteria, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score, the Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score, the bedside index of severity in acute pancreatitis (BISAP), and Balthazar index are other commonly used prognostic systems. Most of these scoring systems include multiple determinants or parameters that requires to be noted at 24 to 48 hours after hospitalization and, the estimation of severity of AP is delayed until to 48 hours of hospitalization [
4]. Thus, these scoring systems are limited use at admission [
5].
On the other hand, considering the complexity of prognostic scoring systems, several studies have been conducted on the role of simple laboratory parameters and indices in predicting disease severity of AP and mortality. Most widely studied laboratory parameters and indices are white blood cell (WBC) count, neutrophil count, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR), hematocrit, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, calcium, C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin [
5]. These laboratory parameters also have been used as a part of several prognostic scoring systems. Nevertheless, none of the laboratory parameters or prognostic scoring systems have sufficient accuracy for predicting the severity of AP and MOF [
6,
7].
The first 48 hours after the symptom onset is very important to identify the patients at risk for development of complications and, even death. This period is crucial to determine the aggressiveness of the treatment including fluid resuscitation, pain control and nutritional support. Therefore, it is important to decide at admission which patients require close monitoring or transfer to intensive care unit (ICU).
We aimed in the current study to assess the severity of acute pancreatitis in conjunction with a new index ‘‘neutrophil-creatinine index’’ and to compare this index with other laboratory parameters or indices at admission.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This retrospective study was conducted on adult patients that hospitalized with a diagnosis of AP in Gastroenterology Clinic of Tokat Gaziosmanpasa University Hospital from Turkey between January 2018 and December 2021. AP diagnosis was made according to the presence of at least two of the following three criteria: abdominal pain consistent with AP, serum amylase or lipase values at least three times greater than the upper limit of normal value, and characteristic findings of AP on radiological imaging studies. Among patients who diagnosed with AP, patients were excluded from the study who has any of the following diseases including chronic kidney disease, hematological disorders, pancreatic carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma, those pregnant women and patients who had incomplete records. Patients with recurrent pancreatitis were enrolled only at first admission.
Severity of AP were determined using the revised Atlanta Classification, and graded as: MAP with no organ failure and no local or systemic complications; MSAP with transient organ failure that resolved within 48 hours of admission or local complications; and SAP with persistent organ failure that defined as to continue for longer than 48 hours. Moreover, Ranson’s criteria scores were also noted from hospital records.
The data of patients including age, gender, AP etiology, radiologic imaging, and laboratory data on admission were extracted from hospital database. Recorded laboratory data were hemogram parameters including WBC count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet count, and routine biochemical tests including glucose, aspartate amino transferase (AST), alanine amino transferase (ALT), bilirubin, calcium, BUN, creatinine, CRP, amylase, and lipase. The NLR was defined as the ratio of neutrophil count to lymphocyte count and the PLR was defined as ratio of platelet count to lymphocyte count. The neutrophil-creatinine index (NCI) was calculated as follows:
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Results were analyzed SPSS software 20.0 and MedCalc software 22.0. Normality was assessed by means of the Shapiro–Wilk test. For quantitative variables, data were presented as mean ± standard deviations for normally distributed data, while median± standard error of mean or interquartile range (IQR) for non-normally distributed data. Groups compared using the Student t or Mann–Whitney U test (2 categories) or ANOVA or Kruskal–Wallis (>2 categories). In the case of qualitative variables, the associations were verified using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. The area under the receiver operator characteristic (AUROC) curve was used to identify optimal cut-off values for NCI, NLR and other laboratory parameters to recognize maximum sensitivity and specificity for AP severity. DeLong test was used to compare AUROCs. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the independent predictive value for AP severity among the variables which showed significant differences in univariate analysis. A p value less than 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteritics of Study Population
A total of 421 patients with AP were included in this study. According to the etiological classification 310 patients (74%) were in biliary group, and 111 of them (26%) were in non-biliary group. The overall mean age of patients was 62±18 years and, 251 patients (60%) were female. Of them, 213 patients (51%) were classified in MAP group, 158 (37%) in MSAP group and 50 (12%) in SAP group. Death was seen in 18 patients (4.3%). The baseline characteristics and laboratory parameters of the patients are summarized in
Table 1.
3.2. Comparison of Laboratory Parameters Related with Severity
3.2.1. Laboratory Parameters to Distinguish MSAP and SAP from MAP
Regarding the studied laboratory parameters, WBC count, neutrophil count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, BUN, creatinine, CRP, NLR, PLR and NCI levels were significantly increased among patients which is in the groups of MSAP or SAP when compared to MAP group (for all, p<0.05) (
Table 2).
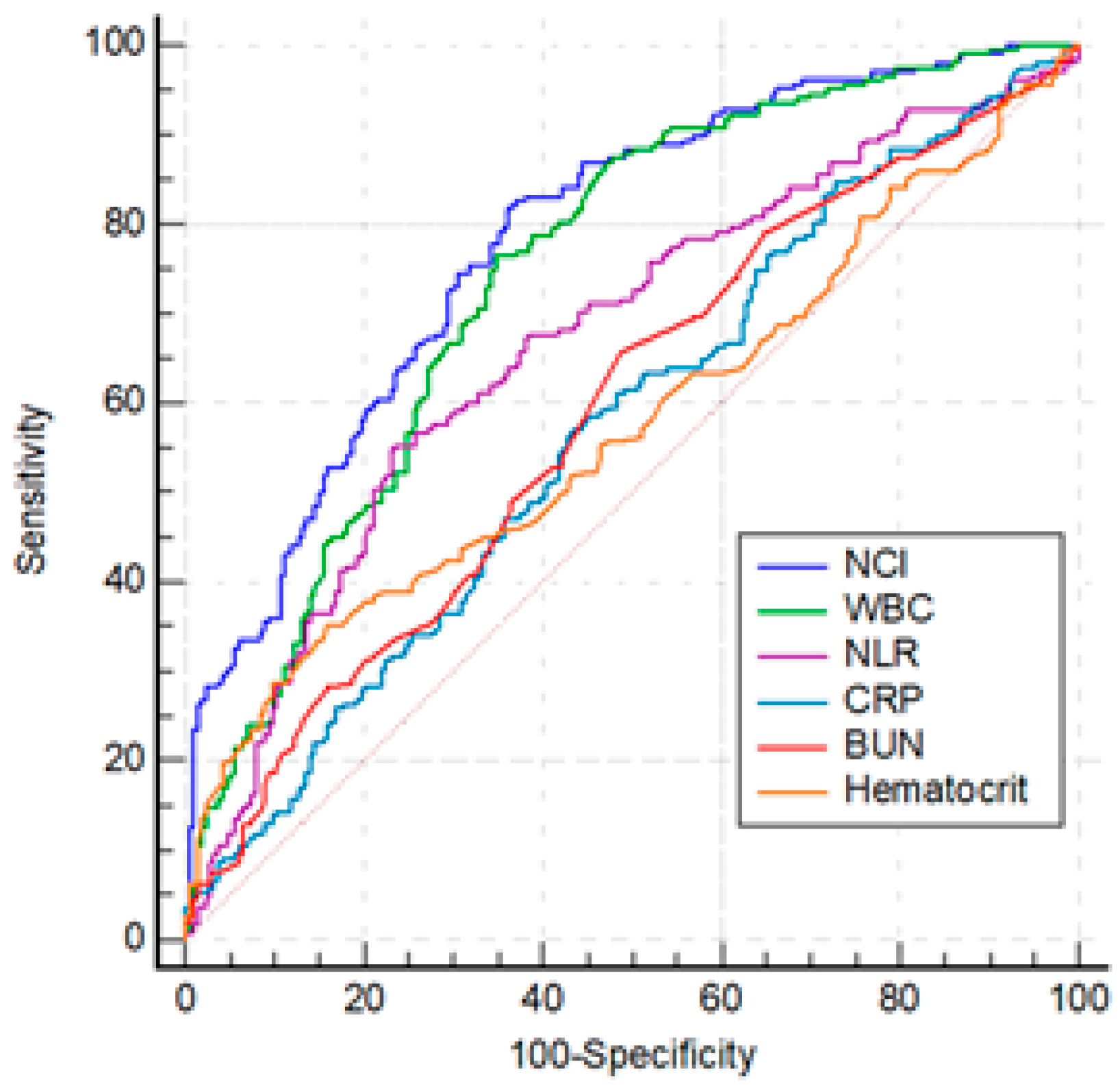
Among the statistically significant laboratory parameters WBC, hematocrit, BUN, and CRP were investigated by ROC analysis and optimal cut-off values were determined. NLR and NCI were studied indices in the analysis. The parameters that were used for the calculation of mentioned indices including neutrophil, lymphocyte and creatinine were excluded from the analysis (
Table 3 and
Figure 1). The differences between the AUROCs of CRP, hematocrit and BUN were not significant (p > 0.05). The AUROC of WBC was superior to all of parameters (p<0.05), except NCI. NCI was more effective than NLR, CRP, hematocrit, BUN (for all, p<0.01), and WBC (p=0.01).
Univariate analysis for the predicting MSAP and SAP demonstrated that age, gender, WBC, hematocrit, CRP, BUN, NLR and NCI were statistically significant independent predictive factors. All predictors were explored through multivariate logistic regression analyses, which revealed that only NCI was independent predictor of MSAP and SAP cases (
Table 4).
3.2.2. Laboratory Parameters to Distinguish MSAP from MAP
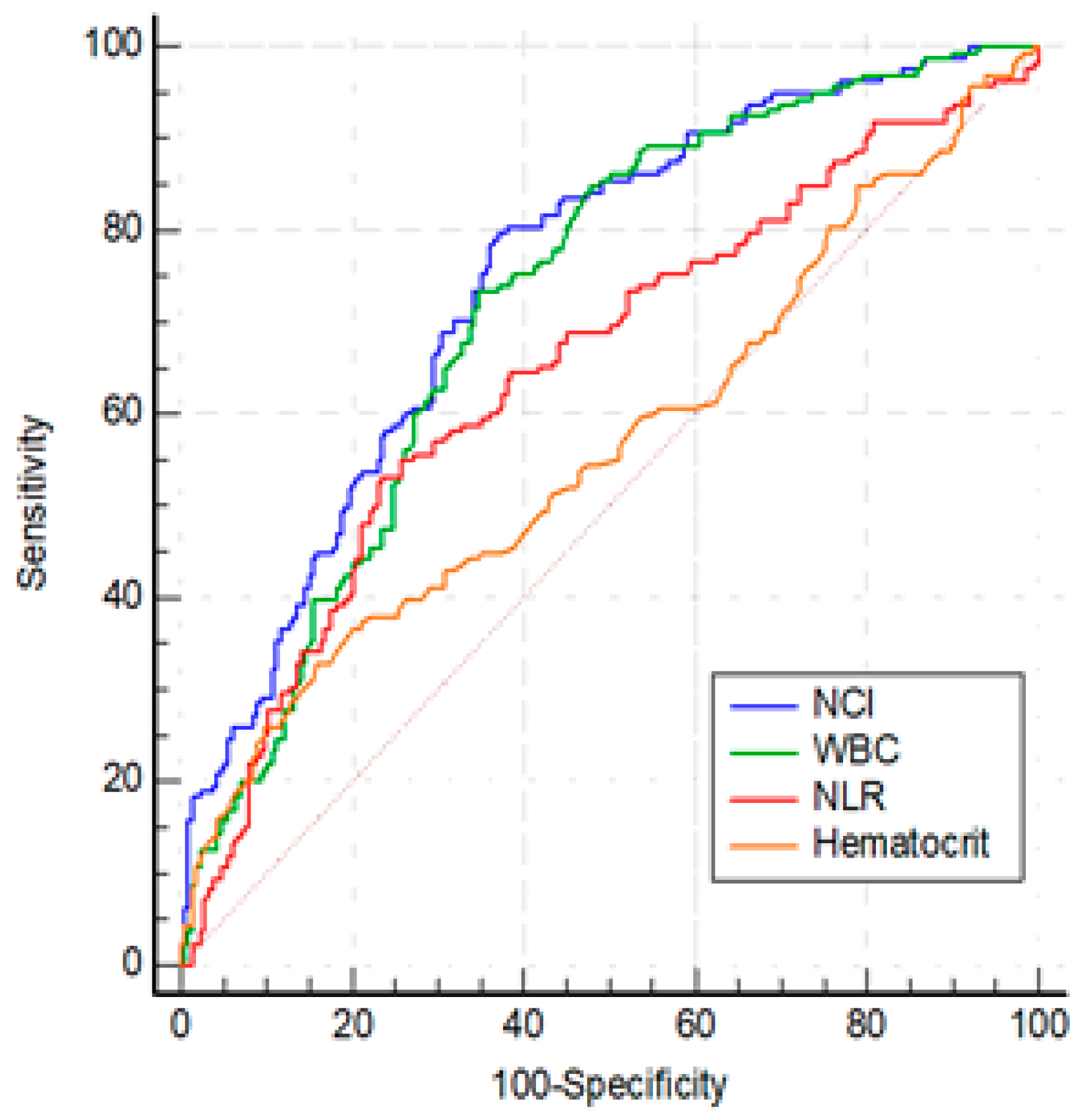
Regarding the studied laboratory parameters, WBC, neutrophil, hemoglobin, hematocrit, creatinine, NLR and NCI levels were significantly higher in MSAP group than MAP group (for all, p<0.05) (
Table 1). Among the statistically significant laboratory parameters WBC, hematocrit, NLR, and NCI were investigated by ROC analysis. The optimal cut-offs for predicting MSAP group were as follows: WBC > 10840/mm3 (AUC: 0.723, 95%CI: 0.674-0.768, p< 0.001), hematocrit > 43.3 (AUC: 0.566, 95% CI: 0.514-0. 607, p=0.032), NLR > 10.95 (AUC: 0.649, 95% CI: 0.598-0.698, p< 0.001) and, NCI ≥ 6.76 (AUC: 0.749, 95% CI: 0.701-0.792, p<0.001) (
Figure 2). The ability of NCI to discriminate MSAP from MAP was superior to NLR and hematocrit (for both, p < 0:01), and was similar to WBC(p=0.13).
Univariate analysis revealed that, age, male gender, WBC, hematocrit NLR and NCI were significantly different between the two groups. In multivariate regression analysis, NCI sustained its predictive value for predicting MSAP group (
Table 5).
3.2.3. Laboratory Parameters to Distinguish SAP from MSAP
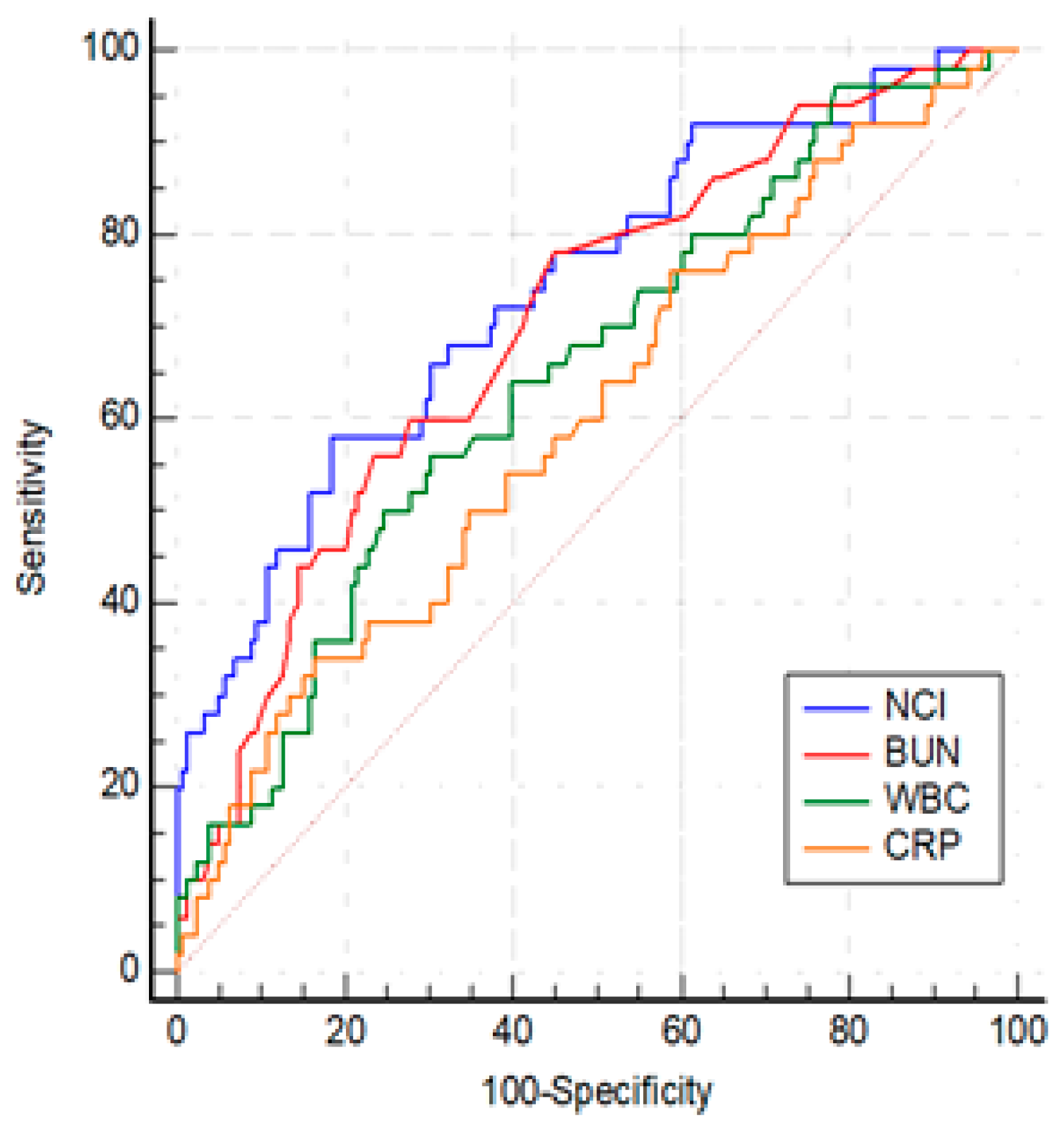
From the laboratory parameters at admission, WBC (p=0.002), neutrophil count (p=0.002), BUN (p <0.001), creatinine (p <0.001), CRP (p=0.030) and NCI (p <0.001) levels were significantly different between SAP and MSAP groups (
Table 1). Among the statistically significant laboratory parameters WBC, BUN, CRP and NCI were investigated by ROC analysis. The optimal cut-offs for predicting SAP group were as follows: WBC > 14900/mm3 (AUC: 0.649, 95% CI: 0.579- 0.713, p < 0.001), BUN > 17.5 (AUC: 0.703, 95% CI: 0.621- 0. 785, p< 0.001), CRP > 81.3 (AUC: 0.602, 95% CI: 0.532-0.669, p=0.029) and, NCI >15.6 (AUC: 0.742, 95% CI: 0.676-0.800, p<0.001) (
Figure 3). The best threshold for predicting SAP was AUROC of NCI. While there was no difference between AUROCs of NCI and BUN (p=0.38), NCI was more effective than WBC and CRP (for both, p < 0.01). The differences between WBC, BUN, and CRP were not significant (p > 0.05).
As shown in
Table 6, after adjusting the prognostic factors by multivariate logistic regression, NCI was the only independent predictor of SAP.
4. Discussion
The severity of AP can be predicted based upon clinical, laboratory, and radiologic features, and several severity scoring systems. The clinical scoring systems that used for the assessment of AP are complex. Moreover, to determine high risk patients with most of the clinical scoring systems take at least 48 hours. The ideal prognostic indicators for AP should be rapid, reproducible, inexpensive, minimally invasive and highly accurate [
8]. The fact that, we need simple laboratory parameters or indices to predict high risk patients at earlier stage of AP. In addition, identifying mild cases will prevent over-treatment and high costs. Currently hematocrit, BUN, creatinine and CRP are the most reliable laboratory parameters to evaluate severity [
9]. The present study focused on the predictive values of NCI, a novel index, for assessing clinical severity of AP.
Our results showed that NCI was the most predictive parameter among studied laboratory parameters and indices to distinguish AP subgroups. The ability of the NCI score at a cutoff point of 6.76 was the most predictive test at admission to distinguish MAP from MSAP. It was also found that 15.6 value for NCI was the most appropriate threshold to distinguish SAP from MSAP at the time of admission. Based on the results of this study, a NCI value at admission may provide to the clinician an insight for predicting disease course.
NCI consists of two components; neutrophil count and creatinine. The neutrophils, as major immune cells associated with the active inflammation response, play an important role in the early phase of AP. They are the first recruited cells to the injury site and contribute to the local inflammatory response and, necrosis in some cases. Beside early local pancreatic events, neutrophils contribute to the systemic complications and end organ damages [
10]. Activated neutrophils in AP, that have longer lifespan and increased functional activity, are responsible form pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion, cell migration and invasion [
11]. Depletion of neutrophils lead to significant reduction in pancreatic tissue damage [
12]. We found that both leucocyte count and neutrophil count were capable of significantly discriminating all of the AP subgroups. Leucocyte count has been widely used to determine disease severity in AP as a component of Ranson’s criteria. Only a few study evaluating neutrophil count in the assessment of AP prognosis. In a recent study by Silva-Vas et al., it was demonstrated that while leucocyte and neutrophil were different between AP subgroups, lymphocyte didn’t differ [
13]. Another study comparing laboratory parameters at admission for the prediction of local and systemic complication development in AP showed that leucocyte and neutrophil counts but not lymphocyte count were statistically significant parameters [
14]. In the mentioned study, while hemoglobin was the hemogram parameter showing the highest AUC value for the prediction of pancreatic necrosis and pseudocyst development, neutrophil count had the highest AUC value for the prediction of systemic complications like respiratory failure and sepsis.
On the other hand, neutrophil count has been widely studied parameter as a component of NLR in cancers and systemic inflammatory conditions like acute pancreatitis. A growing number of studies have shown that NLR is a useful tool for the assessment of AP severity. Junare et al. demonstrated that NLR is most predictive parameter among hemogram parameters and indices for ICU admission, organ failure, interventions and mortality [
15]. Another study showed that BISAP, NLR and total calcium were independent factors for predicting SAP among hemogram-derived indices, BUN, creatinine and calcium [
16]. In a meta-analysis assessing NLR within 24 hours of admission for predicting SAP, sensitivity and specificity values were found as 79% and 71% with a combined AUROC of 0.82 [
17]. Our results showed that though NLR is useful in discrimination MSAP from MAP and SAP separately, in multivariate analysis NCI was the only independent predictor. Moreover, AUROCs of NCI was superior to AUROCs of NLR.
Other component of NCI is creatinine. Increase in creatinine is a sign of kidney injury resulting from hypoxemia, hyperamylasemia causing impairment of renal microcirculation, a decrease in renal perfusion pressure due to abdominal compartment syndrome, intra-abdominal hypertension, hypovolemia, systemic hemodynamic alterations and release of several cytokines [
18,
19]. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a feared complication of SAP carrying a poor prognosis, with high mortality rate [
20]. Until recently, BUN was mostly used as an indicator of renal impairment in the assessment of AP severity. BUN is a component of BISAP and change in BUN level at second day is a criterion of Ranson’s criteria. Dai et al. showed that BUN level at admission was the only parameter for predicting a 30-day all-cause mortality [
19]. Another study comparing Ranson’s score, BISAP and several laboratory parameters at admission and 48. hour of admission demonstrated that while CRP was the only predictor of SAP at admission, BUN at 48. hour was the best predictor of SAP [
21]. In the mentioned study, BUN at 48. hour and BISAP were the best predictors of mortality and creatinine at 48. hour was the best predictor for ICU admission. Our results showed that although BUN is a useful tool for distinguishing SAP from MSAP, it is not capable of distinguishing MAP from MSAP. BUN is affected by intravascular volume status like hemoconcentration at the time of admission or hemodilution resulting from fluid replacement therapy, and creatinine seems a more specific parameter for the establishment of renal impairment.
The strengths of this study are that several laboratory parameters and indices were all examined together, and a new index was examined to discriminate AP severity subgroups. Our study has several limitations. It is a retrospective and monocentric study; thus, further prospective analyses with a larger population are needed to confirm the predictive value and accuracy of NCI. Due to retrospective nature of the study, the patients’ data was obtained from hospital records. The long-term follow-up and mortality data didn’t present in this study. We assessed the parameters at hospital admission and, several factors in hospital stay may influence the prognosis of AP like nosocomial infections.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, logistic regression analysis and the AUROC curve proved that NCI had a high clinical predictive value. NCI was the only predictive parameter among laboratory tests and indices to discriminate MAP, MSAP and SAP. This new index, that calculating by the multiplication of neutrophil count with serum creatinine, may give clues about prognosis in early time of AP.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Tokat Gaziosmanpasa University Hospital (protocol code: 22-KAEK-073 and date of approval: 29 June 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study that did not alter the patients’ management and clinical outcomes.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tonsi, A.F.; Bacchion, M.; Crippa, S.; Malleo, G.; Bassi, C. Acute pancreatitis at the beginning of the 21st century: The state of the art. World J Gastroenterol 2009, 15, 2945–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working, G. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, M.Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Bonis, P.A.; Tang, J.L.; Lau, J. Prediction Models of Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis in Adults: A Systematic Review. Ann Intern Med 2016, 165, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, E.L., 3rd. Predicting Clinical Severity in Acute Pancreatitis: Addressing the Admission Dilemma. Pancreas 2022, 51, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, D.C.; Rider, A.C.; Estrada, P.; Kim, D.; Pillow, M.T. Acute Pancreatitis: What’s the Score? J Emerg Med 2015, 48, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounzer, R.; Langmead, C.J.; Wu, B.U.; Evans, A.C.; Bishehsari, F.; Muddana, V.; Singh, V.K.; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C.; Yadav, D.; et al. Comparison of existing clinical scoring systems to predict persistent organ failure in patients with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Vaz, P.; Abrantes, A.M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gouveia, A.; Botelho, M.F.; Tralhao, J.G. Multifactorial Scores and Biomarkers of Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis: Applications to Research and Practice. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, J.A. Search for prognostic markers for acute pancreatitis. Lancet 2000, 355, 1924–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Tan, H.; Sun, B.; Li, L. Fibrinogen-like Protein 1 as a Predictive Marker for the Incidence of Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis. Medicina (Kaunas) 2022, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtezion, A. Inflammation in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2015, 31, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.W.; Meng, X.X.; Xu, P. Central role of neutrophil in the pathogenesis of severe acute pancreatitis. J Cell Mol Med 2015, 19, 2513–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Xia, L.; Lu, N. The Role of Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Acute Pancreatitis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 565758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Vaz, P.; Abrantes, A.M.; Morgado-Nunes, S.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gouveia, A.; Botelho, M.F.; Tralhao, J.G. Evaluation of Prognostic Factors of Severity in Acute Biliary Pancreatitis. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ning, J.; Li, Q.; Kuang, W.; Jiang, H.; Qin, S. Prediction of acute pancreatitis complications using routine blood parameters during early admission. Immun Inflamm Dis 2022, 10, e747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junare, P.R.; Debnath, P.; Nair, S.; Chandnani, S.; Udgirkar, S.; Thange, R.; Jain, S.; Deshmukh, R.; Debnath, P.; Rathi, P.; et al. Complete hemogram: Simple and cost-effective in staging and predicting outcome in acute pancreatitis. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2021, 133, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Tao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W. The early prognostic value of inflammatory markers in patients with acute pancreatitis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 2019, 43, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; He, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. Diagnostic Value of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Predicting the Severity of Acute Pancreatitis: A Meta-Analysis. Dis Markers 2020, 2020, 9731854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petejova, N.; Martinek, A. Acute kidney injury following acute pancreatitis: A review. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2013, 157, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Fan, Y.; Pan, P.; Tan, Y. Blood Urea Nitrogen as a Prognostic Marker in Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Dis Markers 2022, 2022, 7785497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanathan, D.K.; Johnson, P.G.; Thanikachalam, D.K.; Rajendran, P.; Gopalakrishnan, N. Acute Kidney Injury Complicating Severe Acute Pancreatitis: Clinical Profile and Factors Predicting Mortality. Indian J Nephrol 2022, 32, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Lopez, F.; Matas-Cobos, A.M.; Alegria-Motte, C.; Jimenez-Rosales, R.; Ubeda-Munoz, M.; Redondo-Cerezo, E. BISAP, RANSON, lactate and others biomarkers in prediction of severe acute pancreatitis in a European cohort. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017, 32, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).