1. Introduction
The prevalence of deafness in newborns worldwide is two to three out of every 1,000 births [
1,
2], with more than 50% of the cases attributed to genetic factors [
3]. In China, the neonatal deafness prevalence rate ranges from 1 ‰ to 3.47 ‰ [
4]. The consequences of untreated deafness, including hereditary deafness, can have a serious impact on a child's speech, language, education, and social integration [
3]. Hereditary deafness is a monogenic disorder that follows the Mendelian inheritance pattern and exhibits significant genetic heterogeneity [
4]. It is estimated that 30% of hereditary deafness is syndromic, and 70% is non-syndromic [
3,
5]. Of the non-syndromic cases, autosomal dominant and X- linked inheritance account for about 15% and 1%, respectively, while autosomal recessive inheritance is responsible for up to 80% [
5]. With the emergence of next-generation sequencing technologies and the decline of sequencing costs, knowledge about the genetic etiology of deafness is rapidly increasing [
5]. To date, over 100 related genes are associated with non-syndromic deafness [
6]. In the Chinese population, the two primary causative genes for autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness are the gap junction beta 2 gene (
GJB2; OMIM: 121011) and solute carrier family 26 member 4 (
SLC26A4; OMIM: 605646) [
4,
7,
8]. For intervention and prevention of hereditary deafness, the key is to identify the genetic etiology. Genetic testing can help identify the causative genes, which is essential for accurate genetic counseling, prognosis, and the potential development of possible gene therapy strategies in the future [
5,
9].
It is worth noting that 95% of newborns with deafness identified by newborn hearing screening had hearing parents [
5], suggesting that normal hearing parents who carry the autosomal recessive gene for deafness are at risk of having an affected offspring [
10]. Combined newborn hearing and genetic screening has become widespread and is considered tertiary prevention of deafness [
2,
11], which allows early detection of the molecular etiology and significantly shortens the time to diagnosis and intervention for deafness [
11]. Advancing genetic screening for deafness from the newborn to the prenatal period, namely carrier screening of pregnant females or couples at risk, together with prenatal diagnosis such as chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis, can provide secondary prevention of deafness [
2,
12]. Compared to prenatal carrier screening, preconception carrier screening is more recommended [
12]. Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) or gamete donation is an option if high-risk couples are detected to be at risk of reproduction [
2,
12]. Thus, preconception carrier screening can prevent and interrupt the birth of a child with hereditary deafness while avoiding the risk of termination of pregnancy or recurrent abortions [
2]. Essentially, it is a form of primary prevention for deafness [
2]. A couple who are both confirmed carriers of the same autosomal recessive disorder has a 25% probability of having an affected child with each pregnancy. If the mother carries an X-linked recessive disease, the male offspring of the couple has a 50% probability of being affected [
13]. In 2013, the first study of carrier screening for the deafness gene in women of childbearing age showed that eight out of nine couples carrying a mutation in the same deafness gene received the prenatal diagnosis and subsequently prevented the birth of one affected fetus [
14]. Accordingly, preconception or prenatal carrier screening for hereditary deafness enables those screened to consider their reproductive risk and promotes additional reproductive options [
12,
15,
16], contributing to reducing the incidence of hereditary deafness in newborns [
2,
10]. However, studies of preconception or prenatal carrier screening for hereditary deafness are limited, and more investigations are needed.
There is no consensus on which genes for hereditary deafness should be tested for preconception or prenatal carrier screening. Given the high carrier rates of the
GJB2 and
SLC26A4 genes in the Chinese population [
17] and following the latest recommendations of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics in 2021 [
12],
GJB2-associated autosomal recessive deafness-1A (DFNB1A; OMIM: 220290) and
SLC26A4-associated autosomal recessive deafness-4 (DFNB4) with enlarged vestibular aqueduct (OMIM: 600791) or Pendred syndrome (PDS; OMIM: 274600) were included in this study for preconception or prenatal carrier screening. This study aimed to perform carrier screening in individual females or couples before or early in pregnancy to determine carrier rates of the
GJB2 and
SLC26A4 genes and their mutations. In addition, we provided genetic counseling to all subjects and followed up on reproductive decision-making, pregnancy outcomes and neonatal health status in high-risk couples.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and study design
A total of 9,993 subjects, including 1,783 couples, were enrolled in this study from Jiangxi Maternal and Child Health Hospital (from March 2020 to July 2023) and Dalian Woman and Children's Medical Center (from August 2020 to July 2023) in China. These subjects attended an expanded carrier screening program (including preconception or prenatal) for 155 monogenic disorders. The study focused on preconception or prenatal carrier screening for hereditary deafness of our interest, consisting of DFNB1A (GJB2 gene) and DFNB4 or PDS (SLC26A4 gene). The criteria for inclusion were: no family history of hereditary deafness without the phenotype of deafness; couples of childbearing age preparing for pregnancy or with gestational weeks of less than sixteen; couples seeking a healthy child through assisted reproductive technology; and couples of close consanguinity. Those with a family history of hereditary deafness or gestational age of sixteen weeks or greater were excluded. Genetic counseling prior to testing was provided to all subjects. All subjects signed an informed consent form. Approval for this study was granted by the Institutional Review Board of BGI.
Two strategies were used for carrier screening: sequential and concurrent screening. In sequential screening, females were tested first, and their partners were recalled if they carried at least one mutation in the autosomal recessive deafness gene. In concurrent screening, the couples underwent genetic testing at the same time. After testing, subjects likely to carry the pathogenic deafness gene were provided genetic counseling. Additionally, high-risk couples were given recommendations such as prenatal diagnosis, PGT or gamete donation.
2.2. Selection of hereditary deafness diseases and sequencing
DFNB1A (OMIM: 220290) and DFNB4 with enlarged vestibular aqueduct (OMIM: 600791) or PDS (OMIM: 274600) were selected for preconception or prenatal carrier screening in this study.
The peripheral blood samples of the subjects were collected in 2-5 mL, and genomic DNA was extracted. The target regions (exons and splice site sequences of genes) in genomic DNA were captured using a set of oligonucleotide probes, followed by detection using high-throughput sequencing technology. Bioinformatic analysis of the assay results was used to identify the likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants of the target genes. According to the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics [
18], the screened loci were interpreted and reports were generated.
2.3. Follow up
High-risk couples were followed up on their reproductive decision-making (e.g., prenatal diagnosis and PGT), pregnancy outcomes, and neonatal health conditions.
2.4. Statistical analysis
Numbers (percentage) were reported for categorical variables, and means (standard deviation) for continuous variables. All statistical analyses were performed with R version 4.2.3.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline characteristics of enrolled subjects
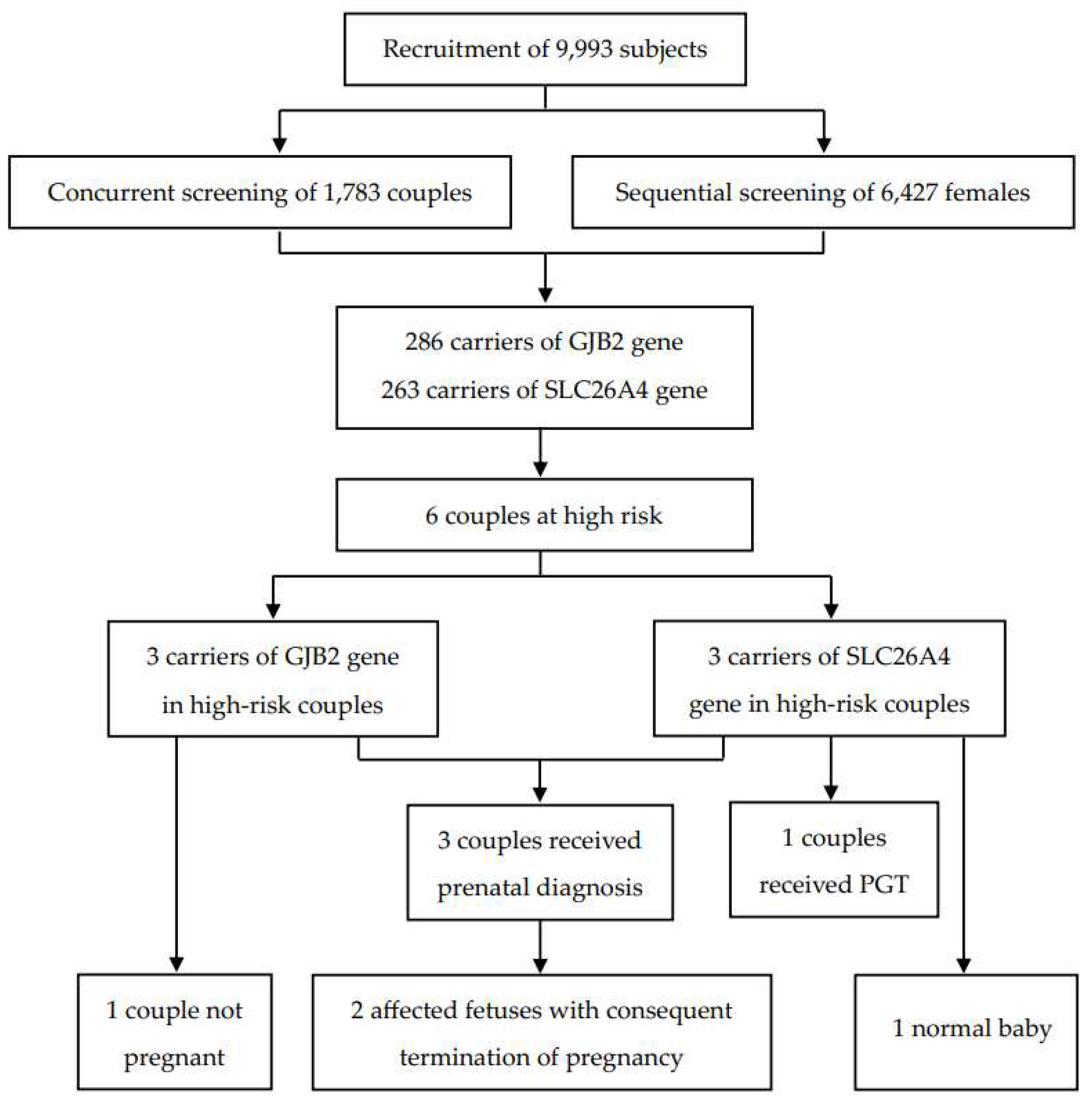
Of the 9,993 subjects recruited for this study, 82.2% (n = 8,210) were females, and 17.8% (n = 1,783) were males (i.e., 17,83 couples and 6,427 females). A greater number of 69.1% (n = 6,903) were from Jiangxi Province, and the remaining 30.9% (n = 3,090) were from Liaoning Province.
Figure 1 shows the strategy and flowchart for carrier screening in this study.
3.2. Carrier frequencies of genes and variants associated with deafness
In total, 549 subjects were identified as carriers of deafness-related genes, yielding a carrier frequency of 5.49%. As shown in
Table 1, there were 286 carriers of the GJB2 gene with a frequency of 2.86%, and 263 carriers of the SLC26A4 gene with a frequency of 2.63%.
Table 2 shows the top three carrier frequencies of variants in the GJB2 and SLC26A4 genes. The top three variants in the GJB2 gene were c.235delC with a frequency of 1.89%, c.299_300del with a frequency of 0.58%, and c.176_191del with a frequency of 0.11%. For the SLC26A4 gene, they were c.919-2A>G with a frequency of 1.08%, c.2168A>G with a frequency of 0.21%, and c.1229C>T with a frequency of 0.20%. In addition, six subjects carried compound heterozygotes with a combination of variants in the GJB2 and SLC26A4 genes, and three subjects carried compound heterozygous variants in the SLC26A4 gene (Tables S1 and S2). The detailed variant spectra of the GJB2 and SLC26A4 genes were shown in Table S1 and Table S2.
Table 1.
Carrier frequencies of deafness genes among 9,993 subjects.
Table 1.
Carrier frequencies of deafness genes among 9,993 subjects.
| OMIM gene |
Gene |
OMIM phenotype |
Type of hereditary deafness |
Count |
Carrier frequency (%) |
| 121011 |
GJB2 |
220290 |
DFNB1A |
286 |
2.86 |
| 605646 |
SLC26A4 |
600791/274600 |
DFNB4/PDS |
263 |
2.63 |
| - |
- |
- |
- |
549 |
5.49 |
Table 2.
The top three carrier frequencies of variants in the GJB2 and SLC26A4 genes among 9,993 subjects.
Table 2.
The top three carrier frequencies of variants in the GJB2 and SLC26A4 genes among 9,993 subjects.
| Gene |
Variant |
SNP ID |
Count |
Carrier frequency (%) |
| GJB2 |
|
|
|
|
| |
c.235delC (p.Leu79Cysfs) |
rs80338943 |
189 |
1.89 |
| |
c.299_300del (p.His100fs) |
rs111033204 |
58 |
0.58 |
| |
c.176_191del (p.Gly59fs) |
rs750188782 |
11 |
0.11 |
| SLC26A4 |
|
|
|
|
| |
c.919-2A>G |
rs111033313 |
108 |
1.08 |
| |
c.2168A>G (p.His723Arg) |
rs121908362 |
21 |
0.21 |
| |
c.1229C>T (p.Thr410Met) |
rs111033220 |
20 |
0.20 |
3.3. Couples at high risk and status of follow-up
As shown in
Table 3, there were six couples (two pregnant and four not pregnant when recruited) carrying the same GJB2 or SLC26A4 gene. Among the high-risk couples carrying the GJB2 gene, two couples underwent prenatal diagnosis, resulting in the termination of their pregnancy due to the fetus being affected; and one was not pregnant at the time of follow-up. Of the high-risk couples carriers of the SLC26A4 gene, one was pregnant during the follow-up and underwent prenatal diagnosis with the fetus detected as heterozygous for the c.919-2A> mutation; one was performing preimplantation genetic testing to reduce the risk of affected offspring; and the remaining one did not receive a prenatal diagnosis but gave birth to a baby with normal hearing.
Table 3.
High risk couples and follow-up status.
Table 3.
High risk couples and follow-up status.
| Gene |
Gender |
Variant |
Prenatal diagnosis/ outcomes of fetus |
Affected fetus |
Pregnancy outcome |
| GJB2 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Female |
c.299_300del (p.His100fs) |
Yes/- |
Yes |
Termination |
| Male |
c.235delC (p.Leu79Cysfs) |
| |
Female |
c.235delC (p.Leu79Cysfs) |
Yes/- |
Yes |
Termination |
| Male |
c.235delC (p.Leu79Cysfs) |
| |
Female |
c.176_191del (p.Gly59fs) |
No/- |
- |
Not pregnant |
| Male |
c.235delC (p.Leu79Cysfs) |
| SLC26A4 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Female |
c.2168A>G (p.His723Arg) |
Yes/heterozygous variant of c.919-2A>G |
No |
- |
| Male |
c.919-2A>G |
| |
Female |
c.919-2A>G |
No/- |
Three blastocysts obtained by PGT await for testing |
- |
| Male |
c.1595G>T (p.Ser532Ile) |
| |
Female |
c.1692dup (p.Cys565fs) |
No/- |
No |
A normal baby |
| Male |
c.1226G>A (p.Arg409His) |
4. Discussion
In this study, preconception or prenatal carrier screening for the deafness genes GJB2 and SLC26A4 was performed in 9,993 individuals from China, with frequencies of 2.86% and 2.63%, respectively. The most common variant in GJB2 was c.235delC, while in SLC26A4, it was c.919-2A>G. In addition, three out of six high-risk couples underwent prenatal diagnosis with the successful avoidance of the birth of two fetuses with hereditary deafness, and one out of six chose PGT to reduce the risk of offspring being affected. The carrier frequencies of common deafness genes and their mutations in the Chinese population identified in this study might provide data support for future research and clinical genetic counseling. Moreover, this study suggested the importance of preconception or prenatal carrier screening for hereditary deafness to assess reproductive risk and guide reproductive decision-making. Such carrier screening was an effective early intervention strategy to reduce the incidence of neonatal deafness.
The carrier frequency of the GJB2 gene in this study was 2.86%, which was slightly higher than the frequency of 1.66% found in a preconception or prenatal expanded carrier screening study of 10,476 couples (i.e., 20,952 individuals) from southern China [
19]. However, a recent study of 3,555,336 neonates from the Chinese Newborn Concurrent Hearing and Genetic Screening cohort reported a similar carrier rate, with an overall
GJB2 carrier rate of 2.53% [
17]. Consistent with previous studies in the Chinese population [
10,
11,
17], our study found the top three carrier frequency variants of the
GJB2 gene to be c.235delC (1.89%), c.299_300del (0.58%) and c.176_191del (0.11%). A recent study conducted concurrent hearing and genetic screening for 180,469 newborns in Beijing showed that the frequencies of c.235delC, c.299_300del, and c.176_191del were 1.80%, 0.50%, and 0.12%, respectively [
11]. In another study of newborns, the carrier frequencies were 1.95%, 0.48%, and 0.11%, respectively [
17]. Variants in the
GJB2 gene are the leading cause of autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness in the Chinese population [
7,
8].
GJB2 encodes the gap junction protein, which is essential for the maintenance of cochlear homeostasis through the recycling of potassium in the inner ear [
20,
21]. The deafness associated with
GJB2 is sensorineural and varies in severity from mild to profound [
5]. Generally, it is present at birth [
5].
The second most common cause of autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness in the Chinese population is the
SLC26A4 gene [
7,
8]. We found that the frequency of the
SLC26A4 gene in preconception or prenatal carrier screening was 2.63%, which was comparable to the previously reported carrier rate of 2.05% in 3,555,336 newborns in China [
17], but higher than the 1.59% in 10,476 couples [
19]. Furthermore, the three most common variants of the
SLC26A4 gene were c.919-2A>G with a frequency of 1.08%, c.2168A>G with a frequency of 0.21% and c.1229C>T with a frequency of 0.20%. Similarly, these variants were the top three in frequency among 3,555,336 newborns in China, with frequencies of 1.32%, 0.24%, and 0.12%, respectively [
17]. The
SLC26A4 gene encodes the pendrin protein, which is expressed in the inner ear, thyroid and kidney [
21,
22].
SLC26A4 is the gene causing DFNB4 and PDS, whose related phenotypes are described as inner ear malformations, hearing impairment, vestibular dysfunction, and thyroid abnormalities [
22]. The hearing impairment associated with
SLC26A4 is typically fluctuant or progressive sensorineural [
22].
Carrier screening can provide an opportunity for individuals or couples to know their risk and consider available reproductive options at a preconception or prenatal stage, which demonstrates its clinical utility [
12]. If identified before pregnancy, high-risk couples have the options of preimplantation genetic testing, gamete or embryo donation, prenatal diagnosis (chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis), and adoption [
12]. If identified during pregnancy, however, the only option is a prenatal diagnosis [
12]. Of the six high-risk couples, except for one who did not become pregnant, four made an alternative reproductive choice (three underwent prenatal diagnosis and one chose PGT), resulting in the successful termination of the birth of two affected fetuses. Therefore, our results supported the clinical utility of preconception or prenatal carrier screening for hereditary deafness.
There were several limitations to the present study. Firstly, the sample was underrepresented because of the inclusion of only subjects from Jiangxi and Liaoning provinces in China. In addition, detailed information on ethnicity was not available for this study. Secondly, although the GJB2 and SLC26A4 genes are the major genetic causes of autosomal recessive non-syndromic deafness in the Chinese population, other related deafness genes that were not screened might have been missed. The discrepancy between the carrier frequencies obtained in this study and those in other studies may be due to variations in the representativeness of the samples (e.g., ethnicity and geographical location) and the coverage of the genes and their variants screened. Therefore, future studies should optimize carrier screening for deafness genes and their variants suitable for different ethnic backgrounds and geographical locations. Finally, complete information on pregnancy outcomes in high-risk couples could not be tracked.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study performed preconception or prenatal carrier screening for the common deafness genes GJB2 and SLC26A4 in 9,993 individuals from China, showing carrier frequencies of 2.86% and 2.63%, respectively. In addition, four out of six high-risk couples made alternative reproductive decisions, followed by the successful prevention of the birth of two affected fetuses. These findings confirmed the clinical utility of preconception or prenatal carrier screening for hereditary deafness. Meanwhile, this study demonstrated the necessity of preconception or prenatal carrier screening for hereditary deafness in the high-risk population, which helped radically reduce the incidence of newborn deafness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S., D.W., B.Y., Y.L., L.W., and L.Y.; Methodology, Y.L., L.W., and L.Y.; Software, L.Y.; Formal analysis, Y.L., L.W., and L.Y.; Resources, Y.S., D.W., and B.Y.; Data curation, Y.S., D.W., B.Y., Y.Y., Y.L., and Z.C.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Y.L., L.W., and L.Y.; Writing—review and editing, Y.S., D.W., B.Y., Y.L., L.W., L.Y., Y.Y., Y.L., and Z.C.; Supervision, Y.S., D.W., and B.Y.; Project administration, Y.S., D.W., B.Y., Y.S., Y.Y., Y.L., and Z.C.; Funding acquisition, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Innovative Research Groups of Hubei Province (No. 2023AFA038), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82071058), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFF0702303).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures conducted in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the National Research Committee and the Declaration of Helsinki of 1975. Approval for this study was granted by the Institutional Review Board of BGI (No. BGI-S103-T6).
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects signed an informed consent form.
Data Availability Statement
Requests may be addressed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
PGT, preimplantation genetic testing; DFNB1A, nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal recessive 1A; DFNB4, deafness autosomal recessive 4; PDS, Pendred syndrome; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.
References
- Alford, R.L.; Arnos, K.S.; Fox, M.; Lin, J.W.; Palmer, C.G.; Pandya, A.; Rehm, H.L.; Robin, N.H.; Scott, D.A.; Yoshinaga-Itano, C. American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guideline for the clinical evaluation and etiologic diagnosis of hearing loss. Genetics in medicine : official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 2014, 16, 347-355. [CrossRef]
- Clinical practice guideline for the genetic diagnosis and counseling of hearing loss in China (2023). Zhonghua er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi = Chinese journal of otorhinolaryngology head and neck surgery 2023, 58, 3-14. [CrossRef]
- WHO. World report on hearing; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2021.
- Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Su, Y.; Lin, Q.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, S.; Kang, D.; Todd, N.W.; Mattox, D.; et al. Comprehensive genetic testing of Chinese SNHL patients and variants interpretation using ACMG guidelines and ethnically matched normal controls. European journal of human genetics : EJHG 2020, 28, 231-243. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Tayoun, A.A.; DiStefano, M.; Pandya, A.; Rehm, H.L.; Robin, N.H.; Schaefer, A.M.; Yoshinaga-Itano, C. Clinical evaluation and etiologic diagnosis of hearing loss: A clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genetics in medicine : official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 2022, 24, 1392-1406. [CrossRef]
- G, V.C.; RJH, S. Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage. Available online: https://hereditaryhearingloss.org (accessed in September 2023).
- Ouyang, X.M.; Yan, D.; Yuan, H.J.; Pu, D.; Du, L.L.; Han, D.Y.; Liu, X.Z. The genetic bases for non-syndromic hearing loss among Chinese. Journal of human genetics 2009, 54, 131-140. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; He, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Hu, C.; et al. Application of a New Genetic Deafness Microarray for Detecting Mutations in the Deaf in China. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0151909. [CrossRef]
- Kremer, H. Hereditary hearing loss; about the known and the unknown. Hearing research 2019, 376, 58-68. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zha, S.; Lü, N.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, W.; Zha, J. Carrier frequencies of hearing loss variants in newborns of China: A meta-analysis. Journal of evidence-based medicine 2019, 12, 40-50. [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.; Huang, L.H.; Wang, G.J.; Gao, X.; Qu, C.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Ma, F.R.; Zhang, J.; Xing, W.L.; Xi, S.Y.; et al. Concurrent Hearing and Genetic Screening of 180,469 Neonates with Follow-up in Beijing, China. American journal of human genetics 2019, 105, 803-812. [CrossRef]
- Gregg, A.R.; Aarabi, M.; Klugman, S.; Leach, N.T.; Bashford, M.T.; Goldwaser, T.; Chen, E.; Sparks, T.N.; Reddi, H.V.; Rajkovic, A.; et al. Screening for autosomal recessive and X-linked conditions during pregnancy and preconception: a practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genetics in medicine : official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 2021, 23, 1793-1806. [CrossRef]
- Van Steijvoort, E.; Chokoshvili, D.; J, W.C.; Peeters, H.; Peeraer, K.; Matthijs, G.; Borry, P. Interest in expanded carrier screening among individuals and couples in the general population: systematic review of the literature. Human reproduction update 2020, 26, 335-355. [CrossRef]
- Yin, A.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Mai, M.; Ding, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X. The carrier rate and mutation spectrum of genes associated with hearing loss in South China hearing female population of childbearing age. BMC medical genetics 2013, 14, 57. [CrossRef]
- Henneman, L.; Borry, P.; Chokoshvili, D.; Cornel, M.C.; van El, C.G.; Forzano, F.; Hall, A.; Howard, H.C.; Janssens, S.; Kayserili, H.; et al. Responsible implementation of expanded carrier screening. European journal of human genetics : EJHG 2016, 24, e1-e12. [CrossRef]
- Best, S.; Long, J.C.; Fehlberg, Z.; Theodorou, T.; Hatem, S.; Archibald, A.; Braithwaite, J. The more you do it, the easier it gets: using behaviour change theory to support health care professionals offering reproductive genetic carrier screening. European journal of human genetics : EJHG 2023, 31, 430-444. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, C.; Guan, J.; Yin, L.; Lan, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q. The Frequency of Common Deafness-Associated Variants Among 3,555,336 Newborns in China and 141,456 Individuals Across Seven Populations Worldwide. Ear and hearing 2023, 44, 232-241. [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genetics in medicine : official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics 2015, 17, 405-424. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xiang, J.; Fan, C.; Asan; Shang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Cai, W.; Chen, S.; et al. Pilot study of expanded carrier screening for 11 recessive diseases in China: results from 10,476 ethnically diverse couples. European journal of human genetics : EJHG 2019, 27, 254-262. [CrossRef]
- Mammano, F. Inner Ear Connexin Channels: Roles in Development and Maintenance of Cochlear Function. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, A.M.; Smith, R.J.H. The Epidemiology of Deafness. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Honda, K.; Griffith, A.J. Genetic architecture and phenotypic landscape of SLC26A4-related hearing loss. Human genetics 2022, 141, 455-464. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).