Submitted:
23 October 2023
Posted:
25 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
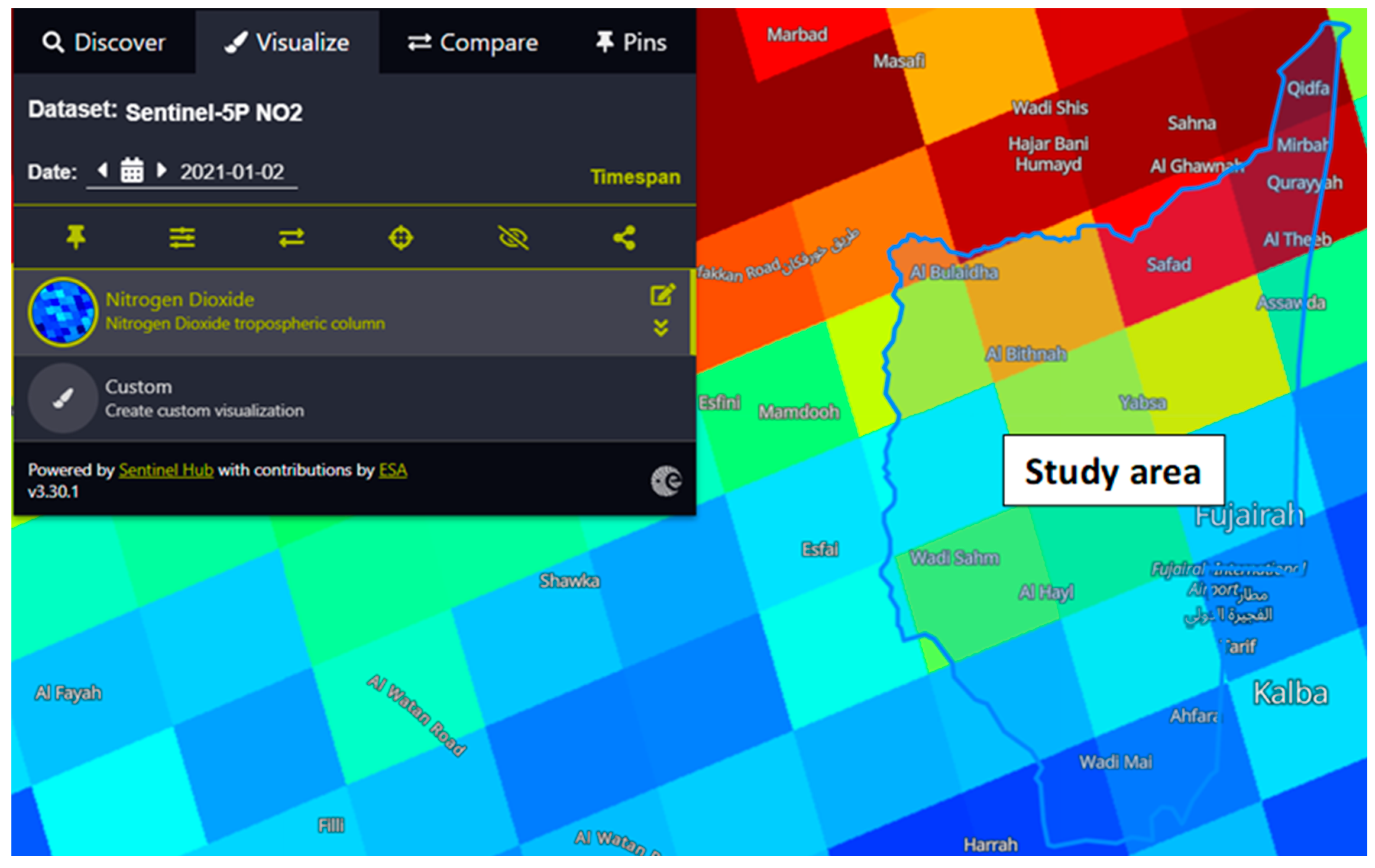
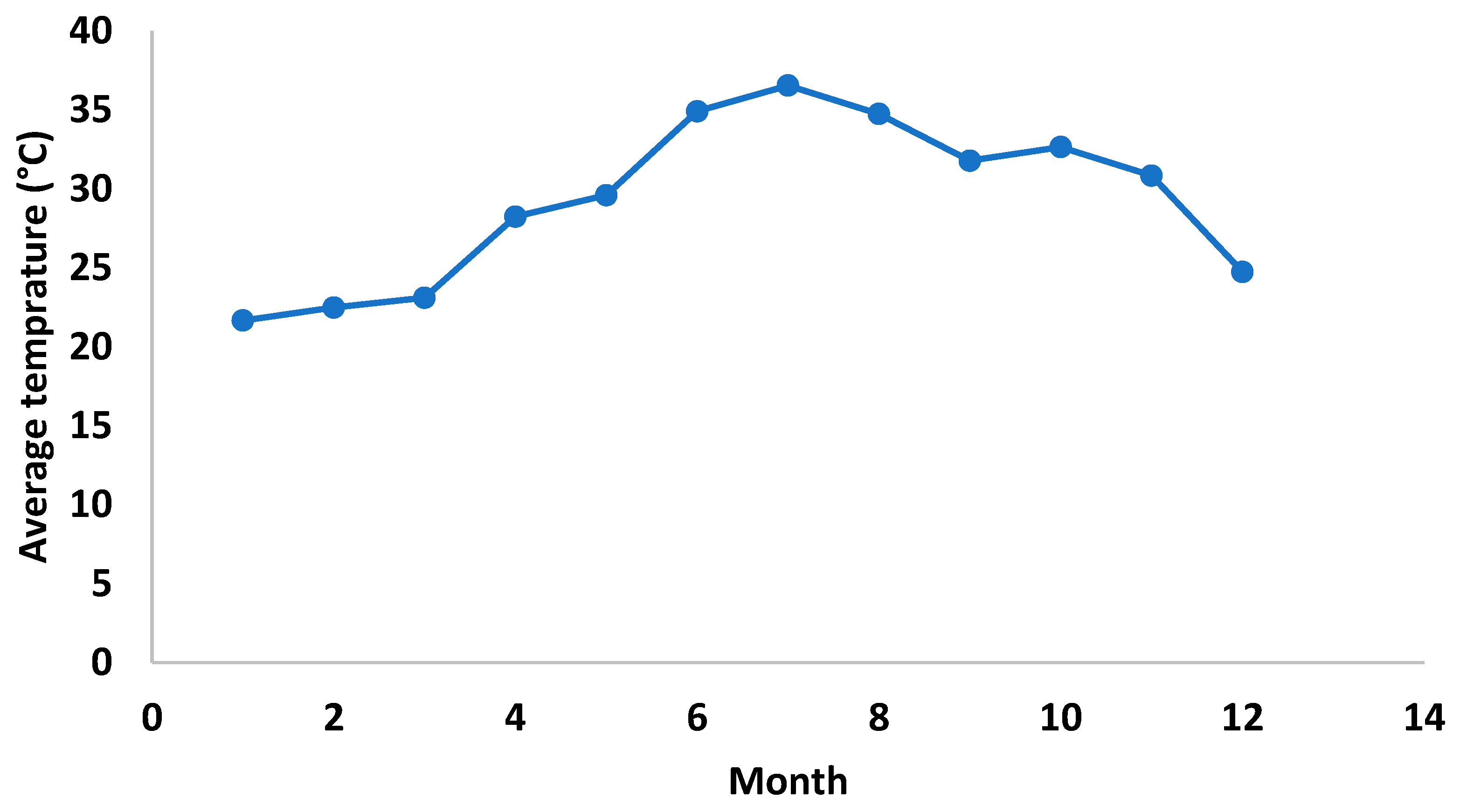
Study area
Data Mining:
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) data from ground-based stations
Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite
Results
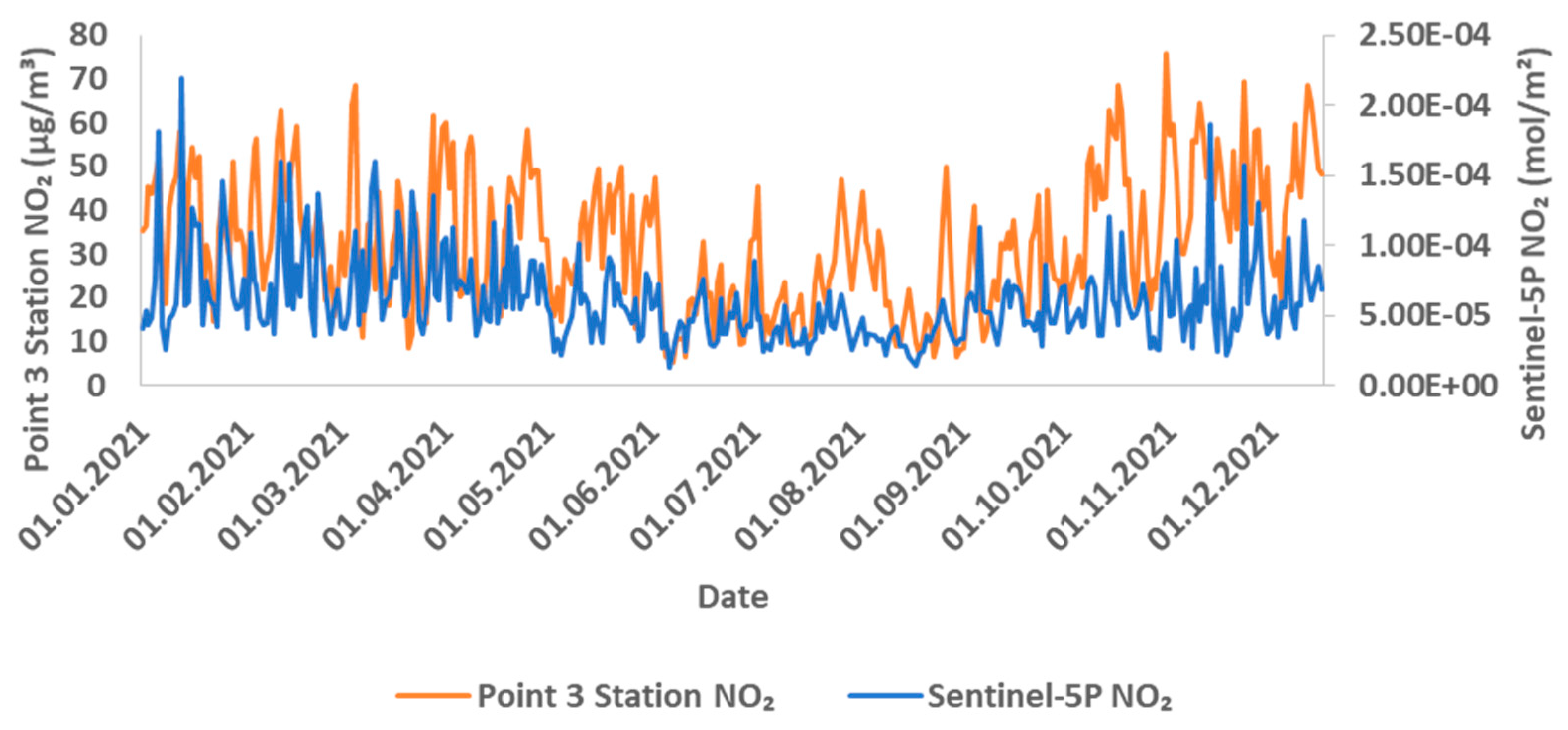
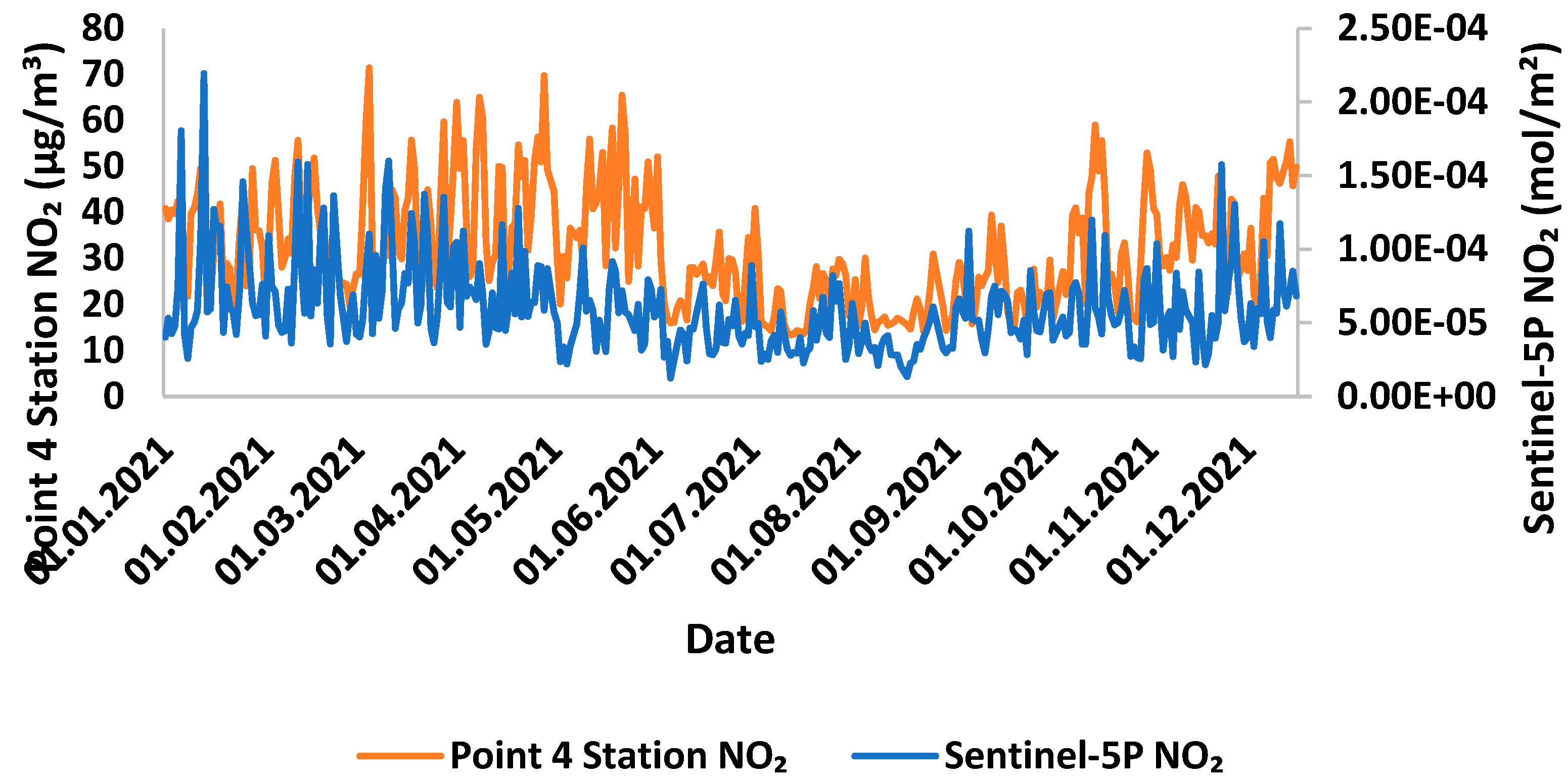
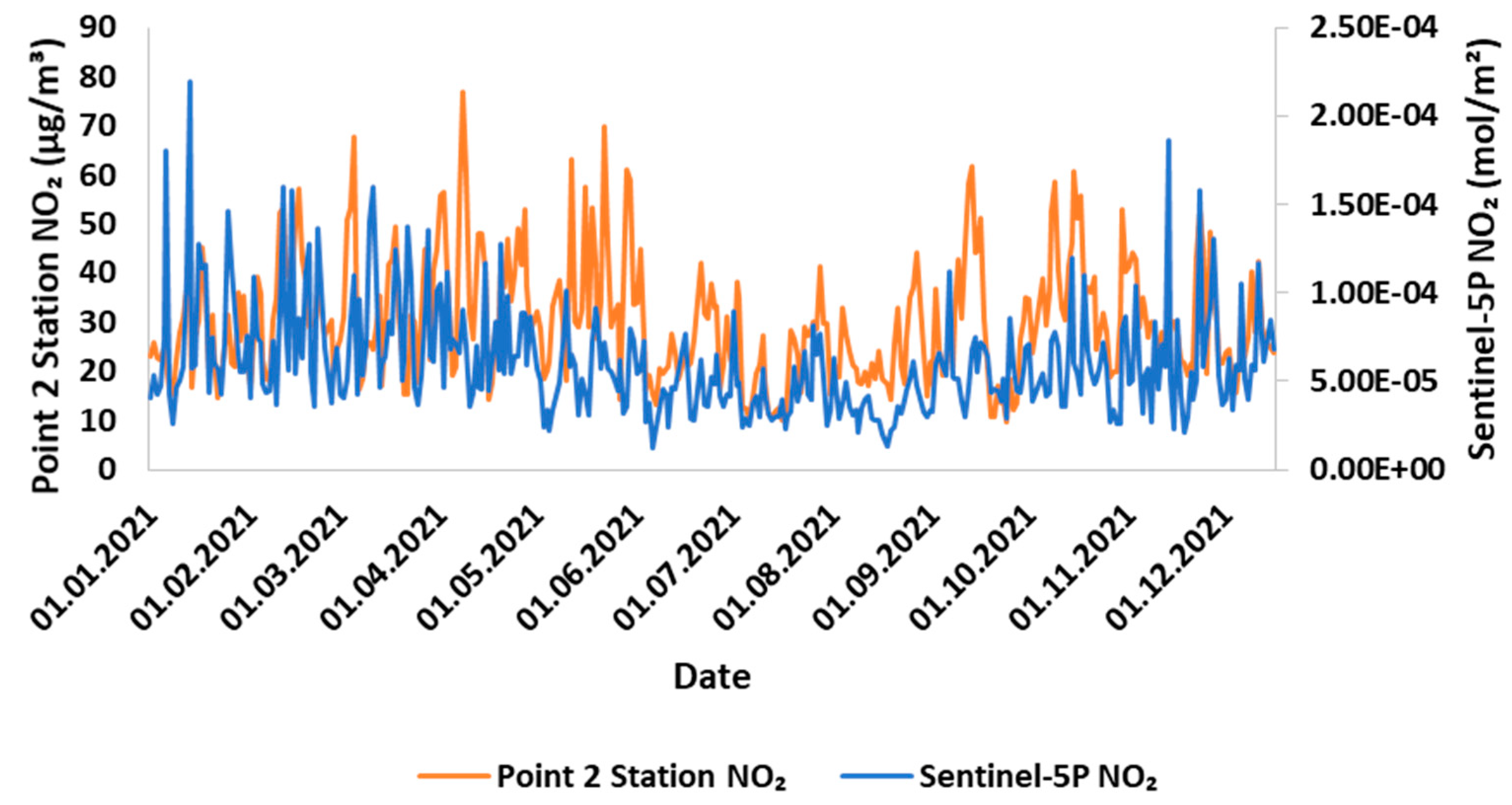
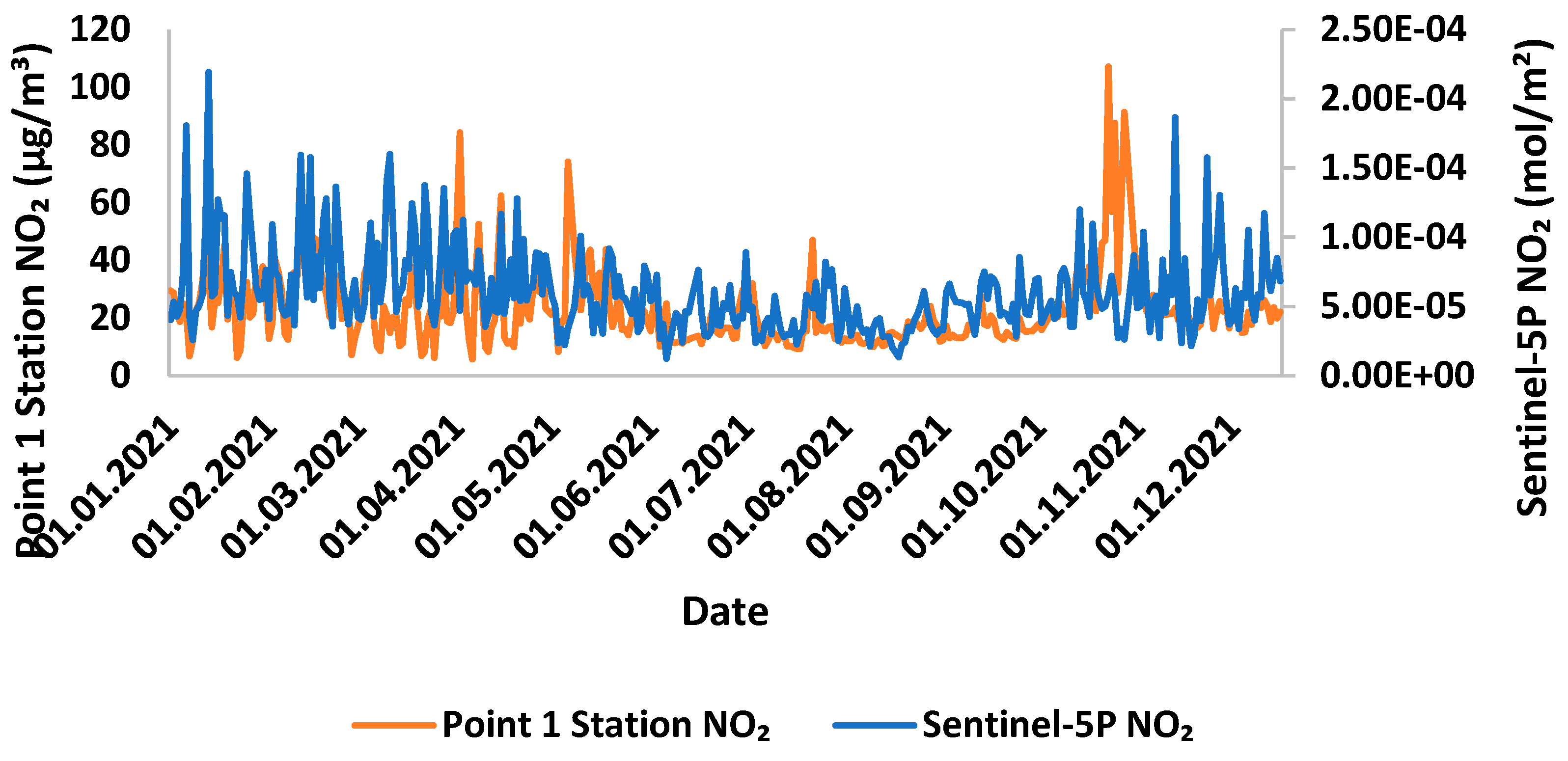
Comparison of NO2 measurements in Sentinel-5P and ground-based stations
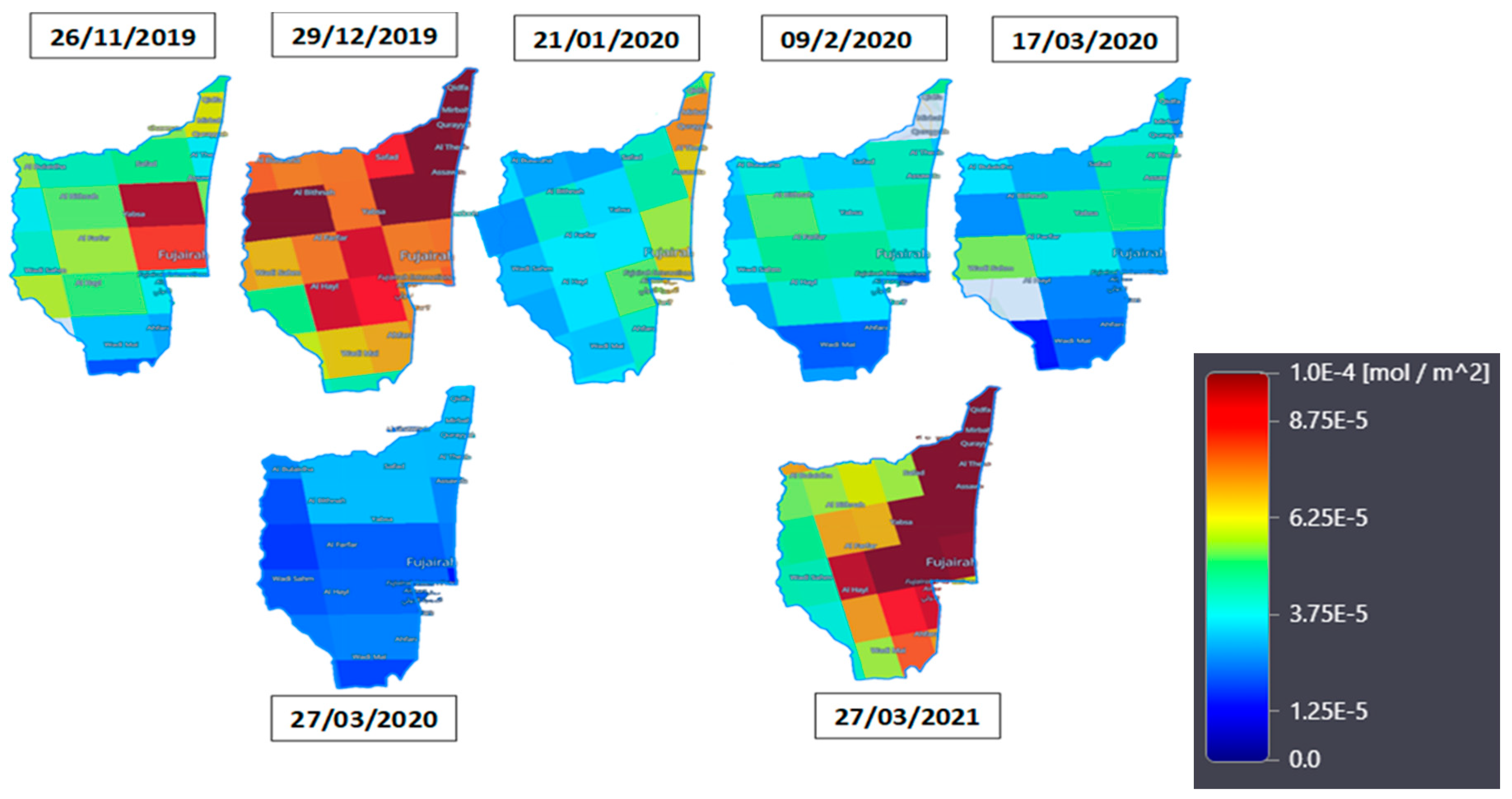
Comparison of NO2 pollution and covid-19 pandemic lockdown
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Seinfeld, J. Urban Air Pollution: State of the Science. 1989. Available online: www.sciencemag.org.
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environmental Pollution 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmo, N.R.S.; Saldiva, P.H.D.N.; Braga, A.L.F.; Lin, C.A.; de P, U.; Pereirai, L.A.A. A review of low-level air pollution and adverse effects on human health: Implications for epidemiological studies and public policy. Clinics 2011, 66, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO global air quality guidelines. 2021.
- Ambient (outdoor) air pollution. 22 Sep. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed Sep. 25, 2022).
- WHO. Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide Report on a WHO Working Group OZONE-adverse effects NITROGEN DIOXIDE-adverse effects AIR POLLUTANTS, ENVIRONMENTAL-adverse effects META-ANALYSIS AIR-standards GUIDELINES. 2003. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. climate change. 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/climate-indicators/greenhouse-gases (accessed Sep. 25, 2022).
- Loh, H.C.; Looi, I.; Ch’ng, A.S.H.; Goh, K.W.; Ming, L.C.; Ang, K.H. Positive global environmental impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: a review. GeoJournal 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanableh, A.; et al. Effects of the COVID-19 lockdown and recovery on People’s mobility and air quality in the United Arab Emirates using satellite and ground observations. Remote Sens Appl 2022, 26, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; et al. Significant changes in the chemical compositions and sources of PM2. 5 in Wuhan since the city lockdown as COVID-19. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 739, 140000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bherwani, H.; et al. Valuation of air pollution externalities: comparative assessment of economic damage and emission reduction under COVID-19 lockdown. Air Qual Atmos Health 2020, 13, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Buono, M.G.; Iannaccone, G.; Camilli, M.; Del Buono, R.; Aspromonte, N. The Italian outbreak of COVID-19: conditions, contributors, and concerns. In Mayo Clinic Proceedings; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 1116–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Teixidó, O.; et al. The influence of COVID-19 preventive measures on the air quality in Abu Dhabi (United Arab Emirates). Air Qual Atmos Health 2021, 14, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryati, I.; Khair, H.; Gusrianti, D. Distribution analysis of nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) and ozone (O 3 ) in Medan city with Geographic Information System (GIS). [CrossRef]
- About Fujairah. 20 Sep. 2022. Available online: http://fujegovt.ae/aboutfujairah.html (accessed Sep. 20, 2022).
- Fujairah’s population. 02 May 2021. Available online: https://www.wam.ae/en/details/1395302931971 (accessed Sep. 20, 2022).
- Gómez, A.C. ESA UNCLASSIFIED-For Official Use Exercise with EO Browser: Air Pollution (Sentinel-2, Sentinel-5P). 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre. NO2 Concentration in the Gulf Region & the UAE. 29 Sep 2021. Available online: https://storymaps.arcgis.com/stories/246700bd610b4cf682f31fd5118b659c (accessed Sep. 24, 2022).
- Hallquist, E.; Mc Queen, E. DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES INVESTIGATION OF THE NOX-NO2-WIND SPEED-RELATIONSHIP AND PRIMARY NO2 AT TWO MONITORING STATIONS IN GOTHENBURG, 2010 AND 2019. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ochando, L.C.; Julián, C.I.F.; Ochando, F.C. Airvlc: An application for real-time forecasting urban air pollution C` esar Ferri. 2015. Available online: http://www.aemet.

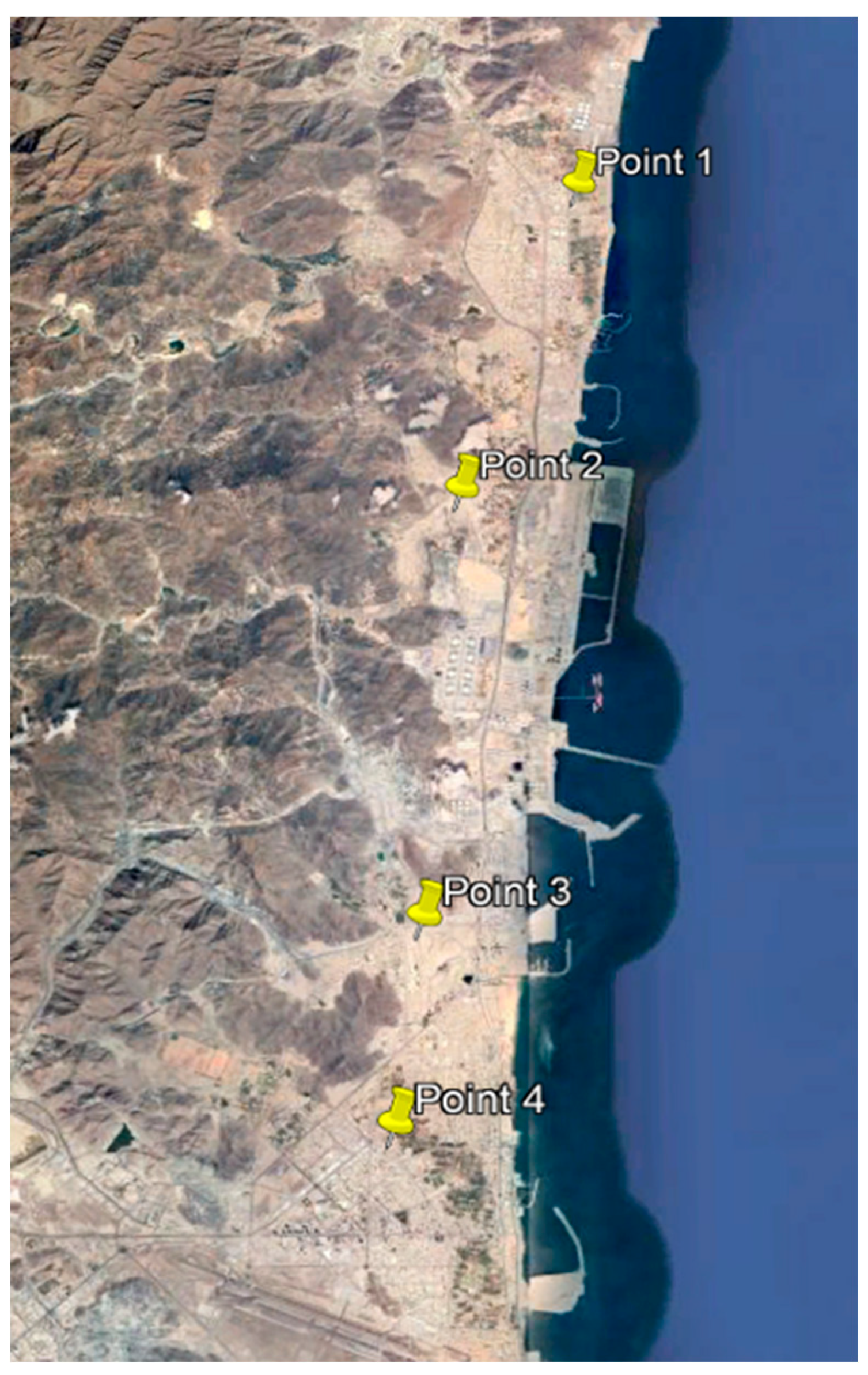
| Station Name | Classification Of Spatial Nature |
| Point 1 | Residential – Industrial |
| Point 2 | Residential – Industrial |
| Point 3 | Residential – Industrial |
| Point 4 | Residential – Urban |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




