Submitted:
20 October 2023
Posted:
23 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Protein S-Glutathionylation
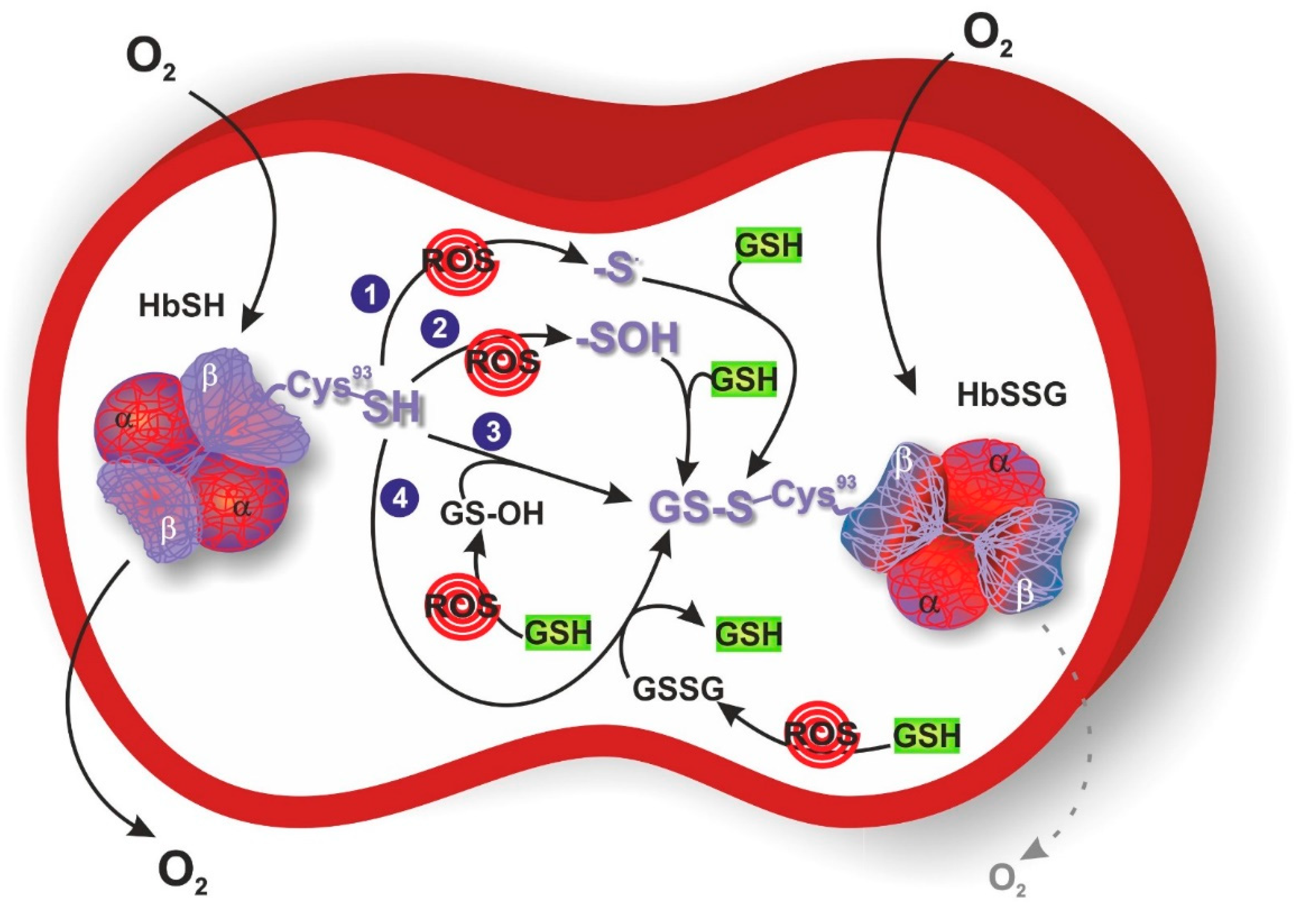
3. S-Glutathionylation of Hemoglobin
4. Glutathionyl Hemoglobin and Methemoglobin
5. Methods for the Detection of Glutathionyl Hemoglobin
6. Glutathionyl Hemoglobin and Diseases
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelic, M.D.; Mandic, A.D.; Maricic, S.M.; Srdjenovic, B.U. Oxidative stress and its role in cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 2021, 17, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newsholme, P.; Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.N.; Carlessi, R.; de Bittencourt, P.I., Jr. Molecular mechanisms of ROS production and oxidative stress in diabetes. Biochem J 2016, 473, 4527–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phull, A.R.; Nasir, B.; Haq, I.U.; Kim, S.J. Oxidative stress, consequences and ROS mediated cellular signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Chem Biol Interact 2018, 281, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoor, A.J.; Pothineni, N.V.K.; Palagiri, D.; Mehta, J.L. Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2017, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Shkurat, T.P.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease: a brief review. Ann Med 2018, 50, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction-linked neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol Res 2017, 39, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engin, A. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 2017, 960, 443–467. [Google Scholar]
- Ornatowski, W.; Lu, Q.; Yegambaram, M.; Garcia, A.E.; Zemskov, E.A.; Maltepe, E.; Fineman, J.R.; Wang, T.; Black, S.M. Complex interplay between autophagy and oxidative stress in the development of pulmonary disease. Redox Biol 2020, 36, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, B.B.; Abdulmahdi, W.; Pawar, R.; Wolin, M.S. Oxidant Mechanisms in Renal Injury and Disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 2016, 25, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.J.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, S.; Kim, K. Protein Glutathionylation in the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017, 2017, 2818565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, P.L.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Galvez, B.G.; Ruiz-Hurtado, G.; Ordovas, J.M.; Ruilope, L.M.; Lucia, A. Lifestyle interventions for the prevention and treatment of hypertension. Nat Rev Cardiol 2021, 18, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wronka, M.; Krzeminska, J.; Mlynarska, E.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. The Influence of Lifestyle and Treatment on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, K.; von Schacky, C.; McKenzie, A.L.; Worm, N.; Nixdorff, U.; Lechner, B.; Krankel, N.; Halle, M.; Krauss, R.M.; Scherr, J. Lifestyle factors and high-risk atherosclerosis: Pathways and mechanisms beyond traditional risk factors. Eur J Prev Cardiol 2020, 27, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venetsanopoulou, A.I.; Alamanos, Y.; Voulgari, P.V.; Drosos, A.A. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis: genetic and environmental influences. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2022, 18, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, T. Protein glutathionylation and oxidative stress. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2007, 855, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, F.M.; Kosman, D.J. Molecular Defects in Friedreich’s Ataxia: Convergence of Oxidative Stress and Cytoskeletal Abnormalities. Front Mol Biosci 2020, 7, 569293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.F.; Sultana, R.; Perluigi, M.; Coccia, R.; Cai, J.; Pierce, W.M.; Klein, J.B.; Turner, D.M.; Butterfield, D.A. An increase in S-glutathionylated proteins in the Alzheimer’s disease inferior parietal lobule, a proteomics approach. J Neurosci Res 2007, 85, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, M.; Parakh, S.; Atkin, J.D. The role of s-nitrosylation and s-glutathionylation of protein disulphide isomerase in protein misfolding and neurodegeneration. Int J Cell Biol 2013, 2013, 797914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabens Liedhegner, E.A.; Gao, X.H.; Mieyal, J.J. Mechanisms of altered redox regulation in neurodegenerative diseases--focus on S--glutathionylation. Antioxid Redox Signal 2012, 16, 543–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, F.A. Red cell membrane damage. J Heart Valve Dis 1998, 7, 387–395. [Google Scholar]
- Niwa, T.; Naito, C.; Mawjood, A.H.; Imai, K. Increased glutathionyl hemoglobin in diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia demonstrated by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Clin Chem 2000, 46, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemonte, F.; Pastore, A.; Tozzi, G.; Tagliacozzi, D.; Santorelli, F.M.; Carrozzo, R.; Casali, C.; Damiano, M.; Federici, G.; Bertini, E. Glutathione in blood of patients with Friedreich’s ataxia. Eur J Clin Invest 2001, 31, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, F.; Tsutsui, S.; Horie, M.; Shimokata, K.; Niwa, T. Glutathionyl hemoglobin in uremic patients undergoing hemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int Suppl 2001, 78, S155–S158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailloux, R.J.; Gill, R.; Young, A. Chapter 13 - Protein S-glutathionylation and the regulation of cellular functions. Oxidative Stress, Academic Press 2020, 10.1016/B978-0-12-818606-0.00013-4, 217-247.
- Shelton, M.D.; Chock, P.B.; Mieyal, J.J. Glutaredoxin: role in reversible protein s-glutathionylation and regulation of redox signal transduction and protein translocation. Antioxid Redox Signal 2005, 7, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R.; Colombo, G.; Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A. Protein S-glutathionylation: a regulatory device from bacteria to humans. Trends Biochem Sci 2009, 34, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musaogullari, A.; Chai, Y.C. Redox Regulation by Protein S-Glutathionylation: From Molecular Mechanisms to Implications in Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A.; Aldini, G.; Carini, M.; Rossi, R.; Dalle-Donne, I. S-nitrosation versus S-glutathionylation of protein sulfhydryl groups by S-nitrosoglutathione. Antioxid Redox Signal 2005, 7, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, D.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A.; Colombo, R.; Dalle-Donne, I. S-glutathionylation: from redox regulation of protein functions to human diseases. J Cell Mol Med 2004, 8, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieyal, J.J.; Gallogly, M.M.; Qanungo, S.; Sabens, E.A.; Shelton, M.D. Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications of reversible protein S-glutathionylation. Antioxid Redox Signal 2008, 10, 1941–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P. Kinetics and mechanisms of thiol-disulfide exchange covering direct substitution and thiol oxidation-mediated pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal 2013, 18, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haendeler, J. Thioredoxin-1 and posttranslational modifications. Antioxid Redox Signal 2006, 8, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, D.W.; Chock, P.B.; Mieyal, J.J. Glutathione-thiyl radical scavenging and transferase properties of human glutaredoxin (thioltransferase). Potential role in redox signal transduction. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 14607–14613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, C.E.; Chakravarthi, S.; Watkins, R.H.; Bulleid, N.J. Oxidative protein folding in the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Soc Trans 2004, 32, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.G.; Bhatnagar, A. Protein S-glutathiolation: redox-sensitive regulation of protein function. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2012, 52, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailloux, R.J.; Willmore, W.G. S-glutathionylation reactions in mitochondrial function and disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 2014, 2, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Muralidharan, M.; Srivastava, D.; Das, R.; Bhat, V.; Mandal, A.K. Assessment of Cysteine Reactivity of Human Hemoglobin at Its Residue Level: A Mass Spectrometry-Based Approach. Hemoglobin 2017, 41, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, G.; Muralidharan, M.; Pinto, J.; Srinivasan, K.; Mandal, A.K. Structural perturbation of human hemoglobin on glutathionylation probed by hydrogen-deuterium exchange and MALDI mass spectrometry. Bioconjug Chem 2011, 22, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, F.M. The Redox Potential of the beta-(93)-Cysteine Thiol Group in Human Hemoglobin Estimated from In Vitro Oxidant Challenge Experiments. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, M.; Mitra, A.; Maity, D.; Pal, D.; Mandal, A.K. Structural analysis of glutathionyl hemoglobin using native mass spectrometry. J Struct Biol 2019, 208, 107386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craescu, C.T.; Poyart, C.; Schaeffer, C.; Garel, M.C.; Kister, J.; Beuzard, Y. Covalent binding of glutathione to hemoglobin. II. Functional consequences and structural changes reflected in NMR spectra. J Biol Chem 1986, 261, 14710–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, G.; Muralidharan, M.; Narayanan, S.; Pinto, J.; Srinivasan, K.; Mandal, A.K. Glutathionylation induced structural changes in oxy human hemoglobin analyzed by backbone amide hydrogen/deuterium exchange and MALDI-mass spectrometry. Bioconjug Chem 2012, 23, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Mawatari, S. Oxidation of hemoglobin to methemoglobin in intact erythrocyte by a hydroperoxide induces formation of glutathionyl hemoglobin and binding of alpha-hemoglobin to membrane. Arch Biochem Biophys 2003, 417, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skold, A.; Cosco, D.L.; Klein, R. Methemoglobinemia: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. South Med J 2011, 104, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, A.; Lurie, A.A. Concise review: methemoglobinemia. Am J Hematol 1993, 42, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.O.; Lewander, W.J.; Woolf, A.D. Methemoglobinemia: etiology, pharmacology, and clinical management. Ann Emerg Med 1999, 34, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, S. Methemoglobinemia. Ann Emerg Med 1982, 11, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawatari, S.; Murakami, K. Different types of glutathionylation of hemoglobin can exist in intact erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 2004, 421, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, D.; Milzani, A.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Rossi, R. Measurement of S-glutathionylated proteins by HPLC. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garel, M.C.; Beuzard, Y.; Thillet, J.; Domenget, C.; Martin, J.; Galacteros, F.; Rosa, J. Binding of 21 thiol reagents to human hemoglobin in solution and in intact cells. Eur J Biochem 1982, 123, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, A.; Mozzi, A.F.; Tozzi, G.; Gaeta, L.M.; Federici, G.; Bertini, E.; Lo Russo, A.; Mannucci, L.; Piemonte, F. Determination of glutathionyl-hemoglobin in human erythrocytes by cation-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 2003, 312, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biroccio, A.; Urbani, A.; Massoud, R.; di Ilio, C.; Sacchetta, P.; Bernardini, S.; Cortese, C.; Federici, G. A quantitative method for the analysis of glycated and glutathionylated hemoglobin by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 2005, 336, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bursell, S.E.; King, G.L. The potential use of glutathionyl hemoglobin as a clinical marker of oxidative stress. Clin Chem 2000, 46, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.K.; Woodi, M.; Sood, V.; Krishnaswamy, P.R.; Rao, A.; Ballal, S.; Balaram, P. Quantitation and characterization of glutathionyl haemoglobin as an oxidative stress marker in chronic renal failure by mass spectrometry. Clin Biochem 2007, 40, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, C.; Kajita, M.; Niwa, T. Determination of glutathionyl hemoglobin in hemodialysis patients using electrospray ionization liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 1999, 731, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, C.; Niwa, T. Analysis of glutathionyl hemoglobin levels in diabetic patients by electrospray ionization liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: effect of vitamin E administration. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 2000, 746, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abed, Y.; VanPatten, S.; Li, H.; Lawson, J.A.; FitzGerald, G.A.; Manogue, K.R.; Bucala, R. Characterization of a novel hemoglobin-glutathione adduct that is elevated in diabetic patients. Mol Med 2001, 7, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamariam, B. Free radicals in diabetic endothelial cell dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 1994, 16, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfo, M. Molecular pathogenesis of Friedreich ataxia. Arch Neurol 1999, 56, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, S.V.; Clements, D.; MacLeod, K. Biomarkers of oxidative stress are significantly elevated in Down syndrome. Free Radic Biol Med 1998, 25, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastore, A.; Tozzi, G.; Gaeta, L.M.; Giannotti, A.; Bertini, E.; Federici, G.; Digilio, M.C.; Piemonte, F. Glutathione metabolism and antioxidant enzymes in children with Down syndrome. J Pediatr 2003, 142, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.H.; Maeng, H.Y.; Sun, Y.K.; Kim, Y.A.; Park, D.W.; Park, T.S.; Lee, S.T.; Choi, J.R. Oxidative status in iron-deficiency anemia. J Clin Lab Anal 2009, 23, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shet, A.S.; Pinto, S.M.; Mitra, G.; Mandal, A.K. Glutathionyl hemoglobin is elevated in iron deficiency anemia. Acta Haematol 2012, 127, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Agrawal, M.; Gautam, M.; Sharma, P.; Gautam, A.S.; Gautam, S. Role of antioxidants in generalised anxiety disorder and depression. Indian J Psychiatry 2012, 54, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Srinivasan, K.; Johnson, P.; Thomas, T.; Mandal, A.K. Elevated levels of glutathionyl haemoglobin as an oxidative stress marker in patients with major depressive disorder. Indian J Med Res 2019, 149, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Pryor, W.A. Cigarette smoke radicals and the role of free radicals in chemical carcinogenicity. Environ Health Perspect 1997, 105 Suppl 4, 875–882. [Google Scholar]
- Muscat, J.E.; Kleinman, W.; Colosimo, S.; Muir, A.; Lazarus, P.; Park, J.; Richie, J.P., Jr. Enhanced protein glutathiolation and oxidative stress in cigarette smokers. Free Radic Biol Med 2004, 36, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Lin, W.P.; Chiu, S.D.; Fan, C.H. Multistage mass spectrometric analysis of human hemoglobin glutathionylation: correlation with cigarette smoking. Chem Res Toxicol 2014, 27, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Disease/treatment | Values | Reference |
| HD | HbSSG β (%) | |
| Normal n=20 | 3.7±0.3 | |
| HD n=10 | 18.6±0.9a | Naito et al. (1999) [59] |
| HD n=10 | 20.8±0.9b | |
| Normal n=20 | 3.0±1.6 | |
| HD n=30 | 8.0±3.6 | Takayama et al. (2001) [27] |
| HD n=12 | 8.7±3.2 a | |
| HD n=12 | 8.7±2.8 b | |
| CAPD | HbSSG β (%) | |
| Normal n=20 | 3.0±1.6 | |
| CAPD n=10 | 5.9±2.7 | Takayama et al. (2001) [27] |
| DM | HbSSG β (%) | |
| Normal n=20 | 3.7±0.3 | |
| DM n=10 | 10.2±0.8c | Naito et al. (2000) [60] |
| DM n=10 | 4.1±0.4d | |
| Normal n=20 | 3.7±0.3 | |
| DM n=37 | 7.9±0.5 | Niwa et al. (2000) [25] |
| HbSSG A1d3 (%) | ||
| Normal n=9 | 1.2±0.1 | |
| DM n=20 | 2.3±0.3 | Al-Abed et al. (2001) [61] |
| HLD | HbSSG β (%) | |
| Normal n=20 | 3.7±0.3 | |
| HLD n=17 | 8.1±0.8 | Niwa et al. (2000) [25] |
| FRDA | HbSSG β (%) | |
| Normal n=20 | 8.0±1.8 | |
| FRDA n=14 | 15.0±1.5 | Piemonte et al. (2001) [26] |
| DS Normal n=64 DS n=46 |
HbSSG β (%) 2.65±1.1 1.47±0.6 |
Pastore et al. (2003) [63] |
| IDA Normal n=15 IDA n=23 |
HbSSG β (%) 7.7±3.7 16.9±9.6 |
Shet et al. (2012) [65] |
| MDD Normal n=17 MDD n=26 MDD n=11 MDD n=11 |
HbSSG β (%) 5.73 8.34 8.07e 7.68f |
Mathew et al. (2019) [67] |
| CS Nonsmokers n=354 Smokers n=97 |
HbSSG β (%)g 5.6 8.1 |
Muscat et al. (2004) [71] |
|
Nonsmokers n=20 Smokers n=20 |
HbSSG α (%)h 2.24±0.91 3.61±1.41 |
Chen et al. (2014) [70] |
|
Nonsmokers n=20 Smokers n=20 |
HbSSG β(%)i 3.79±1.42 6.69±2.33 |
Chen et al. (2014) [70] |
|
Nonsmokers n=20 Smokers n=20 |
HbSSG β (%)l 0.54±0.68 0.56±0.39 |
Chen et al. (2014) [70] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





