Submitted:
21 October 2023
Posted:
23 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Inner Ear Gene Therapy Strategies
2.1. Gene Replacement
2.2. Gene Suppression
2.3. Gene Editing
3. Delivery Vectors
3.1. Adeno-Associated Virus
3.2. Lentivirus
3.2. Adenovirus
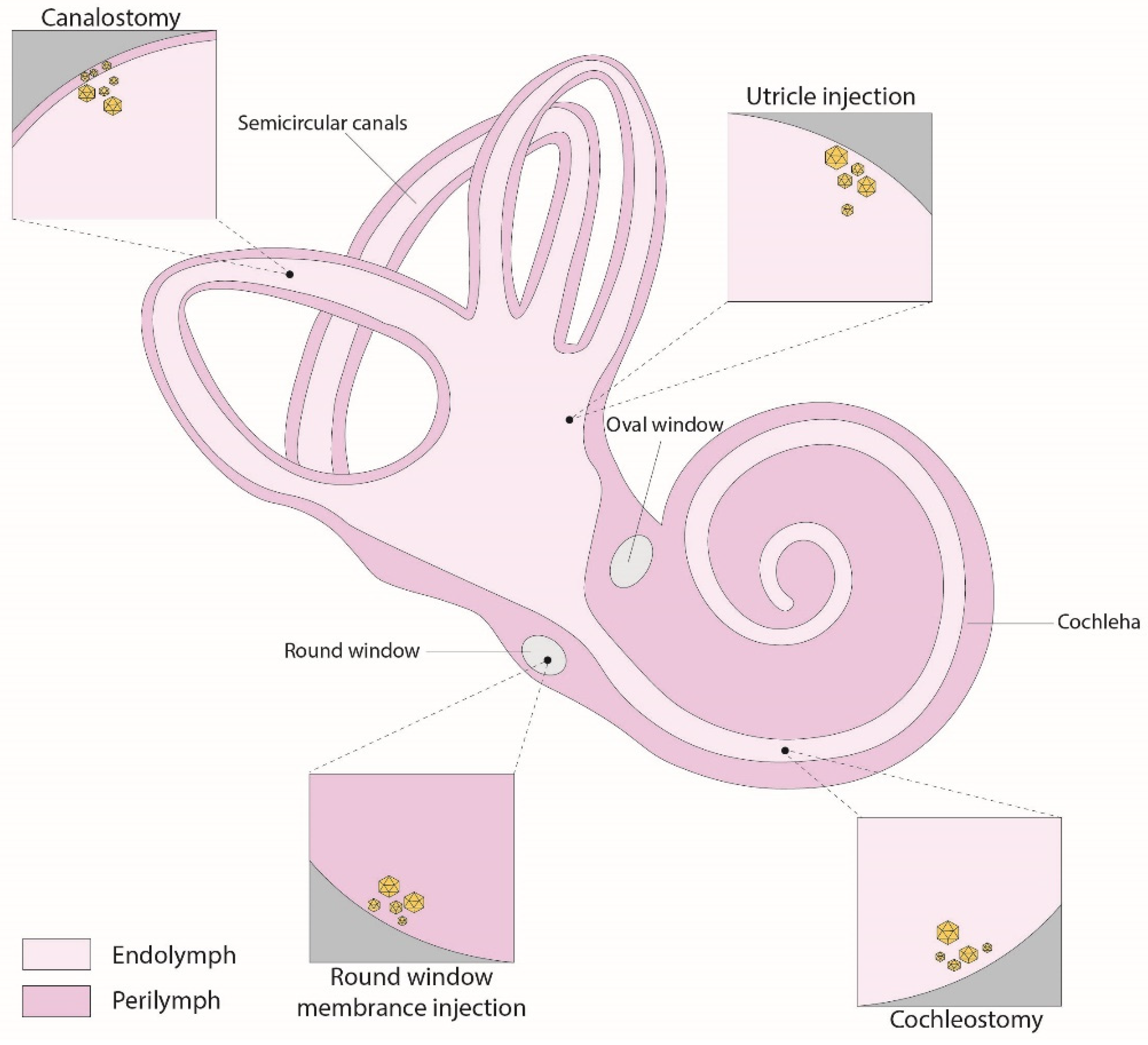
4. Inner Ear Delivery Approaches
4.1. Round-Window Injection
4.2. Canalostomy
4.3. Cochleostomy
4.4. Utricle
5. Challenges and limitations
5.1. The Mouse as a Model for Human Deafness
5.2. Genetic Heterogenicity
5.3. Applications in Mature Mice
5.3. Implications of the Immune Response
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheffield, A.M.; Smith, R.J.H. The epidemiology of deafness. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2019, 9.
- Olusanya, B.O.; Davis, A.C.; Hoffman, H.J. Hearing loss: Rising prevalence and impact. Bull World Health Organ 2019, 97, 646-646A. [CrossRef]
- Carpena, N.T.; Lee, M.Y. Genetic hearing loss and gene therapy. Genomics Inform 2018, 16, e20.. [CrossRef]
- Alford, R.L.; Arnos, K.S.; Fox, M.; Lin, J.W.; Palmer, C.G.; Pandya, A.; Rehm, H.L.; Robin, N.H.; Scott, D.A.; Yoshinaga-Itano, C.; et al. American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guideline for the clinical evaluation and etiologic diagnosis of hearing loss. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 347–355. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; He, Y.; Shu, Y. Advances in gene therapy hold promise for treating hereditary hearing loss. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 934–950. [CrossRef]
- Geleoc, G.S.; Holt, J.R. Sound strategies for hearing restoration. Science 2014, 344. 1241062. [CrossRef]
- Delmaghani, S.; El-Amraoui, A. Inner ear gene therapies take off: Current promises and future challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2309. [CrossRef]
- Petit, C.; Bonnet, C.; Safieddine, S. Deafness: from genetic architecture to gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 665–686. [CrossRef]
- Amariutei, A.E.; Jeng, J.-Y.; Safieddine, S.; Marcotti, W. Recent advances and future challenges in gene therapy for hearing loss. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 230644. [CrossRef]
- Klimara, M.J.; Smith, R.J.H. Advances in cochlear gene therapies. Curr Opin Pediatr 2023, 35, 631–640. [CrossRef]
- Dror, A.A.; Avraham, K.B. Hearing Impairment: A Panoply of Genes and Functions. Neuron 2010, 68, 293–308. [CrossRef]
- Taiber, S.; Gwilliam, K.; Hertzano, R.; Avraham, K.B. The Genomics of Auditory Function and Disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2022, 23, 275–299. [CrossRef]
- Müller, U.; Barr-Gillespie, P.G. New treatment options for hearing loss. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 346–365. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.; Shubina-Oleinik, O.; Holt, J.R. Emerging Gene Therapies for Genetic Hearing Loss. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2017, 18, 649–670. [CrossRef]
- Taiber, S.; Avraham, K.B. Genetic Therapies for Hearing Loss: Accomplishments and Remaining Challenges. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 713, 134527. [CrossRef]
- Askew, C.; Chien, W.W. Adeno-associated virus gene replacement for recessive inner ear dysfunction: Progress and challenges. Hear. Res. 2020, 394, 107947. [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, G.; Calvet, C.; Giorgi, M.; Lecomte, M.-J.; Safieddine, S. Towards the Clinical Application of Gene Therapy for Genetic Inner Ear Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1046. [CrossRef]
- Ivanchenko, M.V.; Hanlon, K.S.; Hathaway, D.M.; Klein, A.J.; Peters, C.W.; Li, Y.; Tamvakologos, P.I.; Nammour, J.; Maguire, C.A.; Corey, D.P. AAV-S: A versatile capsid variant for transduction of mouse and primate inner ear. Mol. Ther. - Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 21, 382–398. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ma, X.; Skidmore, J.M.; Cimerman, J.; Prieskorn, D.M.; Beyer, L.A.; Swiderski, D.L.; Dolan, D.F.; Martin, D.M.; Raphael, Y. GJB2 gene therapy and conditional deletion reveal developmental stage-dependent effects on inner ear structure and function. Mol. Ther. - Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 23, 319–333. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Lin, X. Gene therapy via canalostomy approach preserves auditory and vestibular functions in a mouse model of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome type 2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Kim, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, X. Virally mediated Kcnq1 gene replacement therapy in the immature scala media restores hearing in a mouse model of human Jervell and Lange-Nielsen deafness syndrome. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1077–1086. [CrossRef]
- György, B.; Sage, C.; Indzhykulian, A.A.; Scheffer, D.I.; Brisson, A.R.; Tan, S.; Wu, X.; Volak, A.; Mu, D.; Tamvakologos, P.I.; et al. Rescue of Hearing by Gene Delivery to Inner-Ear Hair Cells Using Exosome-Associated AAV. Mol. Ther. 2016, 25, 379–391. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-A.; Cho, H.-J.; Bae, S.-H.; Lee, B.; Oh, S.-K.; Kwon, T.-J.; Ryoo, Z.-Y.; Kim, H.-Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Kim, U.-K.; et al. Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase B3-Targeted In Utero Gene Therapy Rescues Hearing Function in a Mouse Model of Congenital Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 590–602. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Hu, S.W.; Lv, J.; Xun, M.; Gao, K.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Hearing of Otof-deficient mice restored by trans-splicing of N- and C-terminal otoferlin. Hum. Genet. 2022, 142, 289–304. [CrossRef]
- Ivanchenko, M.V.; Hathaway, D.M.; Klein, A.J.; Pan, B.; Strelkova, O.; De-La-Torre, P.; Wu, X.; Peters, C.W.; Mulhall, E.M.; Booth, K.T.; et al. Mini-PCDH15 gene therapy rescues hearing in a mouse model of Usher syndrome type 1F. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Chan, Y.-H.; Hu, C.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Xiao, R.; Hsu, C.-J.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Wu, C.-C.; Cheng, Y.-F. Gene therapy with a synthetic adeno-associated viral vector improves audiovestibular phenotypes in Pjvk-mutant mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 7. [CrossRef]
- Mathiesen, B.K.; Miyakoshi, L.M.; Cederroth, C.R.; Tserga, E.; Versteegh, C.; Bork, P.A.R.; Hauglund, N.L.; Gomolka, R.S.; Mori, Y.; Edvall, N.K.; et al. Delivery of gene therapy through a cerebrospinal fluid conduit to rescue hearing in adult mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabq3916. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Cai, R.; Wu, H. Gene Therapy Restores Auditory Functions in an Adult Vglut3 Knockout Mouse Model. Hum. Gene Ther. 2022, 33, 729–739. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-A.; Kim, S.H.; Ryu, N.; Ma, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-R.; Jung, J.; Hsu, C.-J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.-Y.; Wangemann, P.; et al. Gene therapy for hereditary hearing loss by SLC26A4 mutations in mice reveals distinct functional roles of pendrin in normal hearing. Theranostics 2019, 9, 7184–7199. [CrossRef]
- Shubina-Oleinik, O.; Nist-Lund, C.; French, C.; Rockowitz, S.; Shearer, A.E.; Holt, J.R. Dual-vector gene therapy restores cochlear amplification and auditory sensitivity in a mouse model of DFNB16 hearing loss. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi7629. [CrossRef]
- Taiber, S.; Cohen, R.; Yizhar-Barnea, O.; Sprinzak, D.; Holt, J.R.; Avraham, K.B. Neonatal AAV gene therapy rescues hearing in a mouse model of SYNE4 deafness. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 13, e13259. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Solanes, P.; Nist-Lund, C.; Spataro, S.; Shubina-Oleinik, O.; Marcovich, I.; Goldberg, H.; Schneider, B.L.; Holt, J.R. Single and Dual Vector Gene Therapy with AAV9-PHP.B Rescues Hearing in Tmc1 Mutant Mice. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 973–988. [CrossRef]
- Marcovich, I.; Baer, N.K.; Shubina-Oleinik, O.; Eclov, R.; Beard, C.W.; Holt, J.R. Optimized AAV vectors for Tmc1 gene therapy in a humanized mouse model of DFNB7/11. Biomolecules 2022, 12.
- Pan, B.; Askew, C.; Galvin, A.; Heman-Ackah, S.; Asai, Y.; Indzhykulian, A.A.; Jodelka, F.M.; Hastings, M.L.; Lentz, J.J.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; et al. Gene therapy restores auditory and vestibular function in a mouse model of Usher syndrome type 1c. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 264–272. [CrossRef]
- Emptoz, A.; Michel, V.; Lelli, A.; Akil, O.; Boutet de Monvel, J.; Lahlou, G.; Meyer, A.; Dupont, T.; Nouaille, S.; Ey, E.; et al. Local gene therapy durably restores vestibular function in a mouse model of Usher syndrome type 1G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114, 9695–9700. [CrossRef]
- Isgrig, K.; Shteamer, J.W.; Belyantseva, I.A.; Drummond, M.C.; Fitzgerald, T.S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Jones, S.M.; Griffith, A.J.; Friedman, T.B.; Cunningham, L.L.; Chien, W.W. Gene therapy restores balance and auditory functions in a mouse model of Usher syndrome. Mol Ther 2017, 25, 780-791. [CrossRef]
- Dowdy, S.F. Overcoming cellular barriers for RNA therapeutics. Nat Biotechnol 2017, 35, 222-229.
- Rossor, A.M.; Reilly, M.M.; Sleigh, J.N. Antisense oligonucleotides and other genetic therapies made simple. Pract Neurol 2018, 18, 126-131. [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Fukushima, K.; Nishizaki, K.; Smith, R.J. In vitro and in vivo suppression of Gjb2 expression by RNA interference. Hum Mol Genet 2005, 14, 1641-1650. [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.B.; Ranum, P.T.; Moteki, H.; Pan, B.; Goodwin, A.T.; Goodman, S.S.; Abbas, P.J.; Holt, J.R.; Smith, R.J.H. Rna interference prevents autosomal-dominant hearing loss. Am J Hum Genet 2016, 98, 1101-1113. [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Shibata, S.B.; Ranum, P.T.; Moteki, H.; Smith, R.J.H. Targeted allele suppression prevents progressive hearing loss in the mature murine model of human TMC1 deafness. Mol Ther 2019, 27, 681-690. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, G.; Cui, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Tang, H.; Wang, D.; et al. Preventing autosomal-dominant hearing loss in Bth mice with CRISPR/CasRx-based RNA editing. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 79.
- Lentz, J.J.; Jodelka, F.M.; Hinrich, A.J.; McCaffrey, K.E.; Farris, H.E.; Spalitta, M.J.; Bazan, N.G.; Duelli, D.M.; Rigo, F.; Hastings, M.L. Rescue of hearing and vestibular function by antisense oligonucleotides in a mouse model of human deafness. Nat Med 2013, 19, 345-350. [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Depreux, F.F.; Jodelka, F.M.; Lentz, J.J.; Rigo, F.; Jones, T.A.; Hastings, M.L. Rescue of peripheral vestibular function in Usher syndrome mice using a splice-switching antisense oligonucleotide. Hum Mol Genet 2017, 26, 34823494.
- Robillard, K.N.; de Vrieze, E.; van Wijk, E.; Lentz, J.J. Altering gene expression using antisense oligonucleotide therapy for hearing loss. Hear Res 2022, 426, 108523.
- Lentz, J.J.; Pan, B.; Ponnath, A.; Tran, C.M.; Nist-Lund, C.; Galvin, A.; Goldberg, H.; Robillard, K.N.; Jodelka, F.M.; Farris, H.E.; et al. Direct delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to the middle and inner ear improves hearing and balance in Usher mice. Mol Ther 2020, 28, 2662-2676. [CrossRef]
- Halloy, F.; Biscans, A.; Bujold, K.E.; Debacker, A.; Hill, A.C.; Lacroix, A.; Luige, O.; Stromberg, R.; Sundstrom, L.; Vogel, J.; Ghidini, A. Innovative developments and emerging technologies in RNA therapeutics. RNA Biol 2022, 19, 313-332. [CrossRef]
- Ponnath, A.; Depreux, F.F.; Jodelka, F.M.; Rigo, F.; Farris, H.E.; Hastings, M.L.; Lentz, J.J. Rescue of outer hair cells with antisense oligonucleotides in Usher mice is dependent on age of treatment. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2018, 19, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kempton, J.B.; Jiang, H.; Jodelka, F.M.; Brigande, A.M.; Dumont, R.A.; Rigo, F.; Lentz, J.J.; Hastings, M.L.; Brigande, J.V. Fetal antisense oligonucleotide therapy for congenital deafness and vestibular dysfunction. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 5065-5080. [CrossRef]
- Gaj, T.; Gersbach, C.A.; Barbas, C.F., 3rd. ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol 2013, 31, 397-405. [CrossRef]
- Niggemann, P.; Gyorgy, B.; Chen, Z.Y. Genome and base editing for genetic hearing loss. Hear Res 2020, 394, 107958. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zou, L.; Li, K.; Hou, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Song, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Template-independent genome editing in the Pcdh15av-3j mouse, a model of human DFNB23 nonsyndromic deafness. Cell Rep 2022, 40, 111061.
- Cui, C.; Wang, D.; Huang, B.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Lv, J.; Zhang, L.; Han, L.; Liu, D.; Chen, Z.Y.; et al. Precise detection of CRISPR-Cas9 editing in hair cells in the treatment of autosomal dominant hearing loss. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2022, 29, 400-412.
- Abdelnour, S.A.; Xie, L.; Hassanin, A.A.; Zuo, E.; Lu, Y. The potential of CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing as a treatment strategy for inherited diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 699597. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.H.; Shubina-Oleinik, O.; Levy, J.M.; Pan, B.; Newby, G.A.; Wornow, M.; Burt, R.; Chen, J.C.; Holt, J.R.; Liu, D.R. In vivo base editing restores sensory transduction and transiently improves auditory function in a mouse model of recessive deafness. Sci Transl Med 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, M.; Gu, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Gene editing in a Myo6 semi-dominant mouse model rescues auditory function. Mol Ther 2022, 30, 105-118. [CrossRef]
- Noh, B.; Rim, J.H.; Gopalappa, R.; Lin, H.; Kim, K.M.; Kang, M.J.; Gee, H.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.H.; Jung, J. In vivo outer hair cell gene editing ameliorates progressive hearing loss in dominant-negative Kcnq4 murine model. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2465–2482. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Xu, C.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R.; Han, S.; Wang, X.; et al. Rescue of autosomal dominant hearing loss by in vivo delivery of mini dCas13X-derived RNA base editor. Sci Transl Med 2022, 14, eabn0449. [CrossRef]
- Gyorgy, B.; Nist-Lund, C.; Pan, B.; Asai, Y.; Karavitaki, K.D.; Kleinstiver, B.P.; Garcia, S.P.; Zaborowski, M.P.; Solanes, P.; Spataro, S.; et al. Allele-specific gene editing prevents deafness in a model of dominant progressive hearing loss. Nat Med 2019, 25, 1123-1130. [CrossRef]
- Grimm, D.; Zolotukhin, S. E Pluribus Unum: 50 years of research, millions of viruses, and one goal-tailored acceleration of aav evolution. Mol Ther 2015, 23, 1819-1831.
- Keeler, A.M.; Flotte, T.R. Recombinant adeno-associated virus gene therapy in light of luxturna (and zolgensma and glybera): Where are we, and how did we get here? Annu Rev Virol 2019, 6, 601-621. [CrossRef]
- Fakhiri, J.; Landegger, L.D.; Grimm, D. Breaking the sound barrier: Towards next-generation AAV vectors for gene therapy of hearing disorders. Hear Res 2022, 413, 108092. [CrossRef]
- Naso, M.F.; Tomkowicz, B.; Perry, W.L., 3rd; Strohl, W.R. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) as a vector for gene therapy. BioDrugs 2017, 31, 317-334.
- Chien, W.W.; Monzack, E.L.; McDougald, D.S.; Cunningham, L.L. Gene therapy for sensorineural hearing loss. Ear Hear 2015, 36, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zidon, T.; Ritchie, T.; Engelhardt, J.F. Concatamerization of adeno-associated virus circular genomes occurs through intermolecular recombination. J Virol 1999, 73, 9468-9477. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2019, 18, 358–378. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Asokan, A.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-associated virus serotypes: Vector toolkit for human gene therapy. Mol Ther 2006, 14, 316-327. [CrossRef]
- Marrone, L.; Marchi, P.M.; Azzouz, M. Circumventing the packaging limit of AAV-mediated gene replacement therapy for neurological disorders. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2022, 22, 1163-1176. [CrossRef]
- Omichi, R.; Yoshimura, H.; Shibata, S.B.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Smith, R.J.H. Hair cell transduction efficiency of single- and dual-AAV serotypes in adult murine cochleae. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 2020, 17, 1167-1177. [CrossRef]
- Akil, O.; Dyka, F.; Calvet, C.; Emptoz, A.; Lahlou, G.; Nouaille, S.; Boutet de Monvel, J.; Hardelin, J.P.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Avan, P.; et al. Dual AAV-mediated gene therapy restores hearing in a DFNB9 mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 4496-4501. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.R.; Guo, J.Y.; He, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.Y.; Yang, Z.J.; Su, W.; Liu, K.; Gong, S.S.; Wang, G.P. Co-transduction of dual-adeno-associated virus vectors in the neonatal and adult mouse utricles. Front Mol Neurosci 2022, 15, 1020803. [CrossRef]
- Akil, O. Dual and triple AAV delivery of large therapeutic gene sequences into the inner ear. Hear Res 2020, 394, 107912. [CrossRef]
- Vannucci, L.; Lai, M.; Chiuppesi, F.; Ceccherini-Nelli, L.; Pistello, M. Viral vectors: A look back and ahead on gene transfer technology. New Microbiol 2013, 36, 1-22.
- Wanisch, K.; Yanez-Munoz, R.J. Integration-deficient lentiviral vectors: A slow coming of age. Mol Ther 2009, 17, 1316-1332. [CrossRef]
- Milone, M.C.; O'Doherty, U. Clinical use of lentiviral vectors. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1529-1541. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chang, Q.; Ahmad, S.; Zhou, B.; Kim, Y.; Li, H.; Lin, X. Early postnatal virus inoculation into the scala media achieved extensive expression of exogenous green fluorescent protein in the inner ear and preserved auditory brainstem response thresholds. J Gene Med 2013, 15, 123-133. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.J.; Mhatre, A.N.; Wareing, M.; Pettis, R.; Gao, W.Q.; Zufferey, R.N.; Trono, D.; Lalwani, A.K. Transgene expression in the guinea pig cochlea mediated by a lentivirus-derived gene transfer vector. Hum Gene Ther 1999, 10, 1867–1873. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.E.; Ehrhardt, A.; Kay, M.A. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat Rev Genet 2003, 4, 346-358. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Li, W.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.Y. Adenovirus vectors target several cell subtypes of mammalian inner ear in vivo. Neural Plast 2016, 2016, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, G. State-of-the-art human gene therapy: Part I. Gene delivery technologies. Discov Med 2014, 18, 67-77.
- Lasaro, M.O.; Ertl, H.C. New insights on adenovirus as vaccine vectors. Mol Ther 2009, 17, 1333-1339. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Bishop, E.S.; Zhang, R.; Yu, X.; Farina, E.M.; Yan, S.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, Z.; Shu, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene delivery: Potential applications for gene and cell-based therapies in the new era of personalized medicine. Genes Dis 2017, 4, 43-63. [CrossRef]
- Plontke, S.K.; Hartsock, J.J.; Gill, R.M.; Salt, A.N. Intracochlear drug injections through the round window membrane: Measures to improve drug retention. Audiol Neurootol 2016, 21, 72-79. [CrossRef]
- Akil, O.; Seal, R.P.; Burke, K.; Wang, C.; Alemi, A.; During, M.; Edwards, R.H.; Lustig, L.R. Restoration of hearing in the vglut3 knockout mouse using virally mediated gene therapy. Neuron 2012, 75, 283-293. [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Yin, S.; Wang, J. Inner ear gene transfection in neonatal mice using adeno-associated viral vector: A comparison of two approaches. PLoS One 2012, 7, e43218. [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Shibata, S.B.; Ranum, P.T.; Smith, R.J.H. Enhanced viral-mediated cochlear gene delivery in adult mice by combining canal fenestration with round window membrane inoculation. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, K.; Oh, S.H.; Kanzaki, S.; Brown, N.; Raphael, Y. The functional and structural outcome of inner ear gene transfer via the vestibular and cochlear fluids in mice. Mol Ther 2001, 4, 575-585. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Choi, J.W.; Ishibashi, Y.; Isgrig, K.; Grati, M.; Bennett, J.; Chien, W. Refining surgical techniques for efficient posterior semicircular canal gene delivery in the adult mammalian inner ear with minimal hearing loss. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 18856.
- Suzuki, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Xiao, R.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Liberman, M.C. Cochlear gene therapy with ancestral AAV in adult mice: Complete transduction of inner hair cells without cochlear dysfunction. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 45524.
- Chien, W.W.; Isgrig, K.; Roy, S.; Belyantseva, I.A.; Drummond, M.C.; May, L.A.; Fitzgerald, T.S.; Friedman, T.B.; Cunningham, L.L. Gene therapy restores hair cell stereocilia morphology in inner ears of deaf whirler mice. Mol Ther 2016, 24, 17-25. [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, L.A.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Goddard, J.C.; Fekete, D.M.; Lang, H. Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene delivery into the scala media of the normal and deafened adult mouse ear. Gene Ther 2011, 18, 569–578. [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, H.; Dai, P.; Gao, G.; Chen, Z.Y. Identification of adeno-associated viral vectors that target neonatal and adult mammalian inner ear cell subtypes. Hum Gene Ther 2016, 27, 687–699. [CrossRef]
- Chien, W.W.; McDougald, D.S.; Roy, S.; Fitzgerald, T.S.; Cunningham, L.L. Cochlear gene transfer mediated by adeno-associated virus: Comparison of two surgical approaches. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 2557-2564. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Nist-Lund, C.; Solanes, P.; Goldberg, H.; Wu, J.; Pan, B.; Schneider, B.L.; Holt, J.R. Efficient viral transduction in mouse inner ear hair cells with utricle injection and AAV9-PHP.B. Hear Res 2020, 394, 107882. [CrossRef]
- Dror, A.A.; Avraham, K.B. Hearing loss: Mechanisms revealed by genetics and cell biology. Annu Rev Genet 2009, 43, 411-437. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kempton, J.B.; Brigande, J.V. Gene therapy in mouse models of deafness and balance dysfunction. Front Mol Neurosci 2018, 11, 300. [CrossRef]
- Litovsky, R. Development of the auditory system. Handb Clin Neurol 2015, 129, 55-72.
- Lim, R.; Brichta, A.M. Anatomical and physiological development of the human inner ear. Hear Res 2016, 338, 9-21. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Huang, M.; Shu, Y.; Ruprecht, A.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Wang, Q.; Gao, G.; Kong, W.J.; Chen, Z.Y. Delivery of adeno-associated virus vectors in adult mammalian inner-ear cell subtypes without auditory dysfunction. Hum Gene Ther 2018, 29, 492-506. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.Y.; Johnson, K.R.; Erway, L.C. Assessment of hearing in 80 inbred strains of mice by ABR threshold analyses. Hear Res 1999, 130, 94-107. [CrossRef]
- Kane, K.L.; Longo-Guess, C.M.; Gagnon, L.H.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R.J.; Johnson, K.R. Genetic background effects on age-related hearing loss associated with Cdh23 variants in mice. Hear Res 2012, 283, 80-88. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.R.; Tian, C.; Gagnon, L.H.; Jiang, H.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R. Effects of Cdh23 single nucleotide substitutions on age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6 and 129S1/Sv mice and comparisons with congenic strains. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 44450.
- Mianne, J.; Chessum, L.; Kumar, S.; Aguilar, C.; Codner, G.; Hutchison, M.; Parker, A.; Mallon, A.M.; Wells, S.; Simon, M.M.; et al. Correction of the auditory phenotype in C57BL/6N mice via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology directed repair. Genome Med 2016, 8, 16. [CrossRef]
- Arjomandnejad, M.; Dasgupta, I.; Flotte, T.R.; Keeler, A.M. Immunogenicity of recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors for gene transfer. BioDrugs 2023, 37, 311-329. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Sung, C.Y.W.; Grati, M.; Chien, W. Immune responses in the mammalian inner ear and their implications for AAV-mediated inner ear gene therapy. Hear Res 2023, 432, 108735. [CrossRef]
- Reichel, F.F.; Dauletbekov, D.L.; Klein, R.; Peters, T.; Ochakovski, G.A.; Seitz, I.P.; Wilhelm, B.; Ueffing, M.; Biel, M.; Wissinger, B.; et al. AAV8 can induce innate and adaptive immune response in the primate eye. Mol Ther 2017, 25, 2648-2660. [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, J.W.; Mehat, M.S.; Sundaram, V.; Robbie, S.J.; Barker, S.E.; Ripamonti, C.; Georgiadis, A.; Mowat, F.M.; Beattie, S.G.; Gardner, P.J.; et al. Long-term effect of gene therapy on Leber's congenital amaurosis. N Engl J Med 2015, 372, 1887-1897. [CrossRef]
- "Gene Therapy Trial for Otoferlin Gene-Mediated Hearing Loss." https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05821959, May 2023.
- "A Study of DB-OTO, an AAV Based Gene Therapy, in Children/Infants with Hearing Loss Due to Otoferlin Mutations." https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT05788536, Updated May 12, 2023.
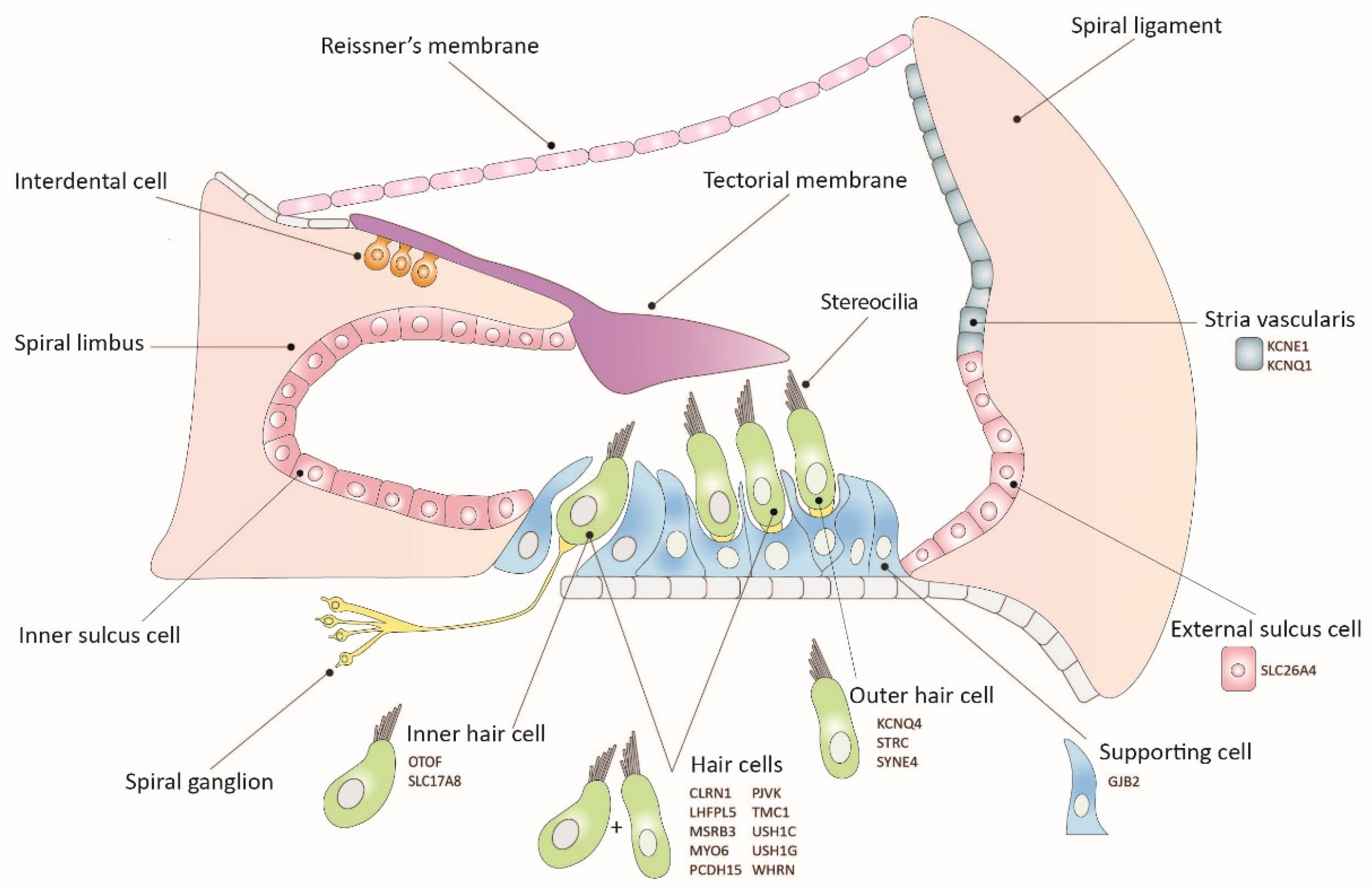
| Gene (form of hearing loss) | Animal model | Hearing impairment |
Strategy | Injection age | Injection route | Vector | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLRN1 (USH3A) | TgAC1/Clrn1 KO* | Delayed onset progressive | Replacement | P1 | RWM | AAV-S | [18] |
| GJB2 (DFNA3A/DFNB1A) | Gjb2 iCKO | Severe to profound | Replacement | P28 | RWM | AAV2/Anc80L65 | [19] |
| KCNE1 (JLNS2) | Kcne1 KO | Severe (balance defect) | Replacement | P0–P2 | PSCC | AAV1 | [20] |
| KCNQ1 (JLNS1) | Kcnq1 KO | Severe (balance defect) | Replacement | P0–P2 | RWM, Scala media | AAV1 | [21] |
| LHFPL5 (DFNB66/67) | Lhfpl5 KO | Profound (balance defect) | Replacement | P1-P2 | RWM, Scala media | exo-AAV1 | [22] |
| MSRB3 (DFNB74) | Msrb3 KO | Profound | Replacement | E12.5 | EUGO | AAV2/1 | [23] |
| OTOF (DFNB9) | Otof KO | Profound | Replacement | P0-P2 | RWM | Dual vector: AAV9/PHP.eB | [24] |
| PCDH15 (DFNB23/USH1F) | Pcdh15 KO | Profound (balance defect) | Mini-gene replacement | P1 | RWM | AAV2/9-PHP.B | [25] |
| PJVK (DFNB59) | Pjvk KO | Progressive (balance defect) | Replacement | P0-P1 | RWM | AAV2/Anc80L65 | [26] |
| SLC17A8 (DFNA25) | VGlut3 KO | Profound | Replacement | 6-12 weeks | Cisterna magna | AAV2/9-PHP.B | [27] |
| VGlut3 KO | Profound | Replacement | 5, 8, and 20 weeks | PSCC | AAV8 | [28] |
|
| SLC26A4 (DFNB4) | Slc26a4 KO | Profound (balance defect) | Replacement | E12.5 | EUGO | AAV2/1 | [29] |
| STRC (DFNB16) | Strc KO | Severe | Replacement | P0–P1 | Utricle | Dual vector: AAV9/PHP.B | [30] |
| SYNE4 (DFNB76) | Syne4 KO | Severe to profound progressive | Replacement | P0-P1.5 | PSCC | AAV2/9.PHP.B | [31] |
| TMC1 (DFNB7/11) | Tmc1 KO,Tmc1-Baringo | Profound | Replacement | P1, P7 | Utricle | AAV2/9-PHP.B | [32] |
| Tmc1 KO, Tmc1N1931/N1931 | Profound | Replacement | P1 | Utricle | AAV2/9-PHP.B | [33] | |
| USH1C/ (DFNB18/USH1C) | Ush1c c.216G>A | Severe (balance defect) | Replacement | P0-P1; P10-P12 | RWM | AAV2/Anc80L65 | [34] |
| USH1G/ (USH1G) | Ush1g KO | Profound (balance defect) | Replacement | P2.5 | RWM | AAV2/8 | [35] |
| WHRN (DFNB31) | Whrn wi/wi | Profound (balance defect) | Replacement | P1-P5 | PSCC | AAV2/8 | [36] |
| Gene (Deafness form) | Animal model | Hearing impairment | Strategy | Injection age | Injection Route | Vector | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GJB2 (DFNA3A) | Gjb2 p.R75W | Severe to profound | RNAi | P42-45 | RWM* | siRNAs | [39] |
| TMC1 (DFNA36) | Tmc1-Bth | Progressive | miRNA | P0-P2 | RWM | rAAV2/9 | [40] |
| Tmc1-Bth | Progressive | miRNA | P15-P16; P56-P60; P84-P90 | RWM, PSCC* | rAAV2/9 | [41] | |
| Tmc1-Bth | Progressive | RNA editing (CasRx) | P1-P2 | RWM | AAV2/9-PHP.eB | [42] | |
| USH1C (USH1C) | Ush1c c.216G>A | Severe (balance defect) | Antisense oligonucleotide | P1; P3; P5; P7 | Intraperitoneal | ASO-29 | [48] |
| Ush1c c.216G>A | Severe (balance defect) | Antisense oligonucleotide | P1; P5; P10; P20 | RWM | ASO-29 | [46] | |
| Ush1c c.216G>A | Severe (balance defect) | Antisense oligonucleotide | E12.5 | EUGO | ASO-29 | [49] |
| Gene (Deafness form) | Animal model | Hearing impairment | Strategy | Injection age | Injection Route | Vector | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCNQ4 (DFNA2A) | Kcnq4 c.827G>C | Progressive | Disruption | P0-P1 | PSCC*, RWM*, utricle, scala media | Dual vector: AAV2/Anc80L65 | [57] |
| Kcnq4 c.683G>A | Progressive | Disruption | P1–P2 | Scala media | AAV-PHP.eB | [53] | |
| MYO6 (DFNA22) | Myo6 p.C442Y | Progressive | Disruption | P0-P2 | Scala media | AAV-PHP.eB- | [56] |
| Myo6 p.C442Y | Progressive | RNA base editing | P0-P2 | Scala media | AAV-PHP.eB (RNA ABE) | [58] | |
| PCDH15 (DFNB23/USH1F) | Pcdh15av−3J | Profound (balance defect) | Frame restoration | P0-P2 | Scala media | AAV2/9 | [52] |
| TMC1 (DFNA36) | Tmc1-Bth | Progressive | Disruption | P1 | Utricle | Dual vector: AAV9-PHP.B | [32] |
| Tmc1-Bth | Progressive | Disruption | P1–P2 | Inner ear | Dual vector: AAV2/Anc80 L65 | [59] | |
| TMC1 (DFNB7/11) | Tmc1-Baringo | Profound | Base editing | P1 | Inner ear | Dual vector: AAV2/Anc80 L65 (CBE) | [55] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




