1. Introduction
Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) presents ongoing challenges due to difficulties in prenatal diagnosis, anatomical variability, and long-term cardiovascular effects. Even after timely repair, patients remain at heightened cardiovascular risk. Regular hypertension screening and surveillance imaging are crucial in adults to monitor repair site complications (1).
First described in 1760 by the anatomist Morgagni, CoA is a congenital heart defect characterized by a narrowing of the aorta, typically occurring just distal to the left subclavian artery. It accounts for approximately 5-8% of all congenital heart diseases, with an incidence estimated at 4 per 10,000 live births (1,2). Clinical presentation varies significantly depending on several factors, including the severity of the CoA and the presence of concomitant cardiac lesions, particularly those associated with left-sided heart obstruction (1). In instances of severe CoA, neonates may manifest cardiovascular collapse, particularly upon ductal closure. Infants with CoA may present with a wide range of symptoms, from mild hypertension to severe heart failure, depending on the severity of the coarctation and associated cardiac anomalies (4).
In 1944, the Swedish surgeon Clarence Crafoord achieved the first successful surgical CoA repair by performing an aortic end-to-end anastomosis on two patients aged 12 and 27 years old (5,6). Presently, the most prevalent techniques for surgical repair, particularly in infants and neonates with isolated coarctation, involve resection with end-to-end anastomosis (EEA) and the modified Crafoord technique (extended resection with end-to-end anastomosis (EEEA)) (7,8). Subclavian flap aortoplasty (SCAP) is an alternative surgical option for CoA repair in patients under two years of age. In cases where the stenosis extends beyond resection and end-to-end anastomosis feasibility, patch aortoplasty (PP) employing a prosthetic patch can augment the stenotic region, especially for older patients (8).
Despite advances in pediatric cardiology and cardiac surgery, recoarctation remains a significant concern after surgical or interventional repair.
Our manuscript aims to provide a comprehensive review of the prognostic and risk factors for recoarctation after infantile CoA repair is rooted in the need for improved patient outcomes. Recoarctation can have serious consequences, including hypertension, left ventricular dysfunction, and aortic aneurysm formation. Identifying factors that predict or contribute to recoarctation is vital for early detection, intervention, and the development of personalized treatment strategies.
The primary objectives of this comprehensive review are to consolidate the existing data concerning infantile Coarctation of the Aorta (CoA) repair and recoarctation, specifically focusing on identifying prognostic and risk factors. By systematically evaluating the current literature, this review aims to provide clinicians, researchers, and healthcare professionals in pediatric cardiology with a comprehensive understanding of the factors contributing to recoarctation. Ultimately, this knowledge is vital for improving clinical outcomes, optimizing patient care, and informing future research directions in the pursuit of better outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by this congenital cardiac anomaly.
2. Methodology
For this extensive review, we have conducted a comprehensive search of electronic databases, including PubMed, MEDLINE, Embase, and relevant medical journals, was conducted to identify peer-reviewed articles, systematic reviews, and meta-analyses related to infantile CoA repair and recoarctation. The search terms included "coarctation of the aorta," "infantile coarctation repair," "recoarctation," and relevant variants.
Articles included in this review were selected based on their relevance to the topic, publication date (up to September 2023), and the availability of full-text articles. Studies focusing on pediatric populations and those reporting on prognostic and risk factors for recoarctation were considered. Non-English language articles were excluded.
Data extraction was performed systematically, including information on study design, patient demographics, surgical techniques, follow-up protocols, outcomes, and key findings related to prognostic and risk factors.
The quality of each selected study was assessed using established criteria for observational studies, randomized controlled trials, and systematic reviews. This assessment included study design, sample size, methodological rigor, and potential biases.
3. Coarctation Management
3.1. Surgical Approach
3.1.1. Resection with End-to-End Anastomosis
In 1945, Crafoord and Gross described the first successful surgical repair through a left lateral thoracotomy (5,9). This procedure involved the adequate mobilization of the descending aorta, isthmus, and distal arch, followed by clamping of the aorta proximal and distal to the coarctation. The arterial ligament (or the ductus arteriosus, if it is permeable) was also ligated and transected close to the aorta. The coarcted segment was then resected. Subsequently, the remaining aortic arch just distal to the left subclavian artery and descending aorta were connected with a direct end-to-end anastomosis. However, this initial repair was associated with a relatively high incidence of re-coarctation, with reported rates ranging from 41% to 51% (10-13). Re-coarctation was found to be age-dependent and most pronounced when the surgery was performed in neonates. Given the high incidence of re-coarctation, direct end-to-end anastomosis is not commonly utilized in contemporary surgical practice.
3.1.2. Subclavian Flap Repair
This technique was initially described by Waldhausen and colleagues in 1966 (14).The subclavian artery is dissected and ligated near the origin of the left vertebral artery. Creating a flap involves making an incision on the lateral wall of the subclavian artery, which is extended downwards over the aortic isthmus and across the stenosed segment. This flap is then folded downward and securely sutured into the incised aorta, enlarging the narrowed aortic region. When this technique is performed in older children, the rate of re-coarctation appears to be relatively low, ranging from 0% to 3% (15,16). However, when applied to neonates, re-coarctation may be as high as 23% (17). It's worth noting that while sacrificing the subclavian artery does not typically result in left arm ischemia, it may lead to claudication in the long term (18).
3.1.3. Interposition Graft
Introduced by Gross in 1951 (19), this approach involves excising the coarctation segment and subsequently employing a Dacron tube graft or aortic homograft interposition. Given the utilization of non-native tissue, this technique cannot grow alongside the patient, making it primarily suitable for cases where graft outgrowth is not a concern. In the context of adults, both short- and long-term outcomes are commendable: Yousif and colleagues documented a peri-operative mortality rate of 0% and zero instances of re-coarctation over a mean follow-up period of 10±7.6 years (20). Similar favorable results have been reported by various other research groups (21).
3.1.4. Patch Angioplasty
Given the elevated risk of re-coarctation associated with the end-to-end anastomosis technique, medical professionals began exploring alternative surgical approaches for addressing aortic coarctation. Vosschulte was a pioneering surgeon who initially introduced the concept of utilizing a prosthetic patch to enhance the aorta (22). This procedure involves making a longitudinal incision in the affected segment and then suturing a prosthetic patch across the incision to reinforce and expand this area. While the use of Dacron grafts resulted in a decreased rate of re-coarctation (23), it also presented a notable drawback—a high incidence of aortic aneurysm formation, ranging from 20% to 40%. Subsequently, adopting polytetrafluoroethylene materials reduced the occurrence of aneurysms to 7%, albeit at the cost of a higher re-coarctation rate, which reached 25%. Consequently, patch aortoplasty has largely fallen out of favor for treating uncomplicated aortic coarctation. Nevertheless, it still finds application in complex cases necessitating aortic arch reconstruction.
3.1.5. Extended End-to-End Anastomosis
Amato introduced this technique in 1977, and it remains a commonly employed procedure in contemporary practice (25). In contrast, to direct end-to-end anastomosis, this method involves clamping the proximal aorta across the aortic arch, which may include the left subclavian or even the left carotid artery along with the aortic arch. Distally, the aorta is clamped below the stenosed segment. After ligating and dividing the ductus arteriosus, the coarctation segment is excised, and the inferior aspect of the aortic arch is opened. A counter-incision is performed on the lateral wall of the descending aorta. The subsequent end-to-end anastomosis is larger than in the classic technique described by Crafoord, and it allows simultaneous enlargement of a moderately hypoplastic aortic arch. This procedure can be conducted with low peri-operative mortality rates, and reports indicate relatively low re-coarctation rates ranging from 4% to 13% (26-32).
3.2. Transcathether Interventions
3.2.1. Ballon Angioplasty
Transcatheter balloon angioplasty for native Coarctation of the Aorta (CoA) made its debut in the early 1980s (33). This procedure involves the placement of a balloon catheter across the coarctation site, typically via a retrograde approach, although an antegrade approach is also utilized. During the procedure, precise angiographic measurements are conducted to assess the dimensions of the coarctation site and the aorta proximal and distal to the lesion. Based on these measurements, an appropriately sized balloon is selected to dilate the narrowed area (34). The primary objective of this intervention is to induce a controlled tear in the intima and media layers by carefully stretching the constricted vessel segment. Subsequently, remodeling the aortic wall is anticipated to lead to a sustained resolution of CoA and prevent the risk of recoil (35).
Balloon angioplasty is often the preferred option for older children (36). It is also the treatment of choice for younger patients who experience recoarctation. However, it is important to note that the use of balloon angioplasty in neonates and very young infants is typically reserved for cases where associated ventricular dysfunction is present, to stabilize the patients for subsequent definitive surgical repair (37). The utilization of balloon angioplasty as the primary intervention in this extremely young age group has become less common due to its associated high recurrence rate and the potential risk of vascular complications (37).
In specific cases where neonates are too clinically compromised to undergo immediate surgical intervention, balloon angioplasty emerges as a palliative measure to stabilize their condition (38,39). Nonetheless, the percutaneous treatment of aortic coarctation in neonates and infants remains contentious due to concerns surrounding residual or recurrent stenosis and the potential formation of aneurysms at the dilation site (40). Urgent balloon dilation, however, has demonstrated its ability to reduce mortality rates significantly, serving as a bridge to surgical intervention for severely ill patients (41,42).
The procedure typically involves femoral artery access. Nevertheless, alternative access routes, such as carotid or axillary artery access, may be considered in cases involving low-body-weight infants. These alternative routes offer a direct, antegrade trajectory to the aortic isthmus, presenting several technical advantages. Notably, the axillary artery route is advantageous in smaller patients, including premature neonates and those with critical aortic coarctation, where femoral pulses may not be palpable. Additionally, axillary access is crucial in concomitant low cardiac output cases, where locating a femoral pulse can be challenging. Importantly, unlike carotid artery access, the axillary route is not an end artery and does not necessitate surgical cutdown and repair (42).
Balloon sizing is based on choosing an initial balloon diameter two to three times the minimal CoA diameter, ensuring it does not exceed the diameter of the aorta at the diaphragm. Typically, the procedure involves two or three dilations, each with a brief inflation time lasting less than 10 seconds.
Balloon angioplasty has shown remarkable acute success in infants under three months of age, with an approximate 50% restenosis rate, particularly in cases without aortic arc hypoplasia, and lower reintervention rates (43). A recent retrospective study involving 68 patients with native aortic coarctation conducted by Sandoval et al. (44) demonstrated the effectiveness and safety of balloon angioplasty in infants aged 3 to 12 months. Their findings indicated outcomes comparable to those observed in older children and adults. As a result, repeat angioplasty or stent placement can often obviate the need for surgical intervention.
3.2.2. Stent Implantation
Transcatheter stent implantation made its debut in the late 1980s and gained widespread acceptance as a therapeutic approach for CoA patients in the early 1990s (45). This method is the preferred treatment for both native and recurrent CoA in older children, adolescents, and adults (46,47). However, it presents technical intricacies compared to balloon angioplasty, necessitating larger vascular sheaths for access (48) . Once securely positioned within the aorta, the stent evenly distributes radial force and provides sustained relief from the gradient (49-51). Findings from the Congenital Cardiovascular Interventional Study Consortium (CCISC) and the Coarctation of Aorta Stent Trial (COAST) trials reveal that patients who undergo stent implantation experience a lower rate of acute complications compared to their counterparts who undergo surgery or balloon angioplasty (52,53). Nonetheless, they are more likely to require planned reinterventions for stent dilatation, particularly when the procedure is performed on younger patients (52) [ref]. Acute complications stemming from stent implantation encompass stent migration, stent embolization, vessel "jailing," and aortic dissection (52,53). Long-term complications entail planned reinterventions for stent dilatation, neo-intimal proliferation within the stent leading to stenosis, stent fracture, and the formation of aneurysms (52,53). The utilization of covered stents has demonstrated a decreased incidence of aneurysms and dissection following stent implantation (54).
A study conducted by Forbes et al. between 2002 and 2009, encompassing data from 36 institutions, compared the safety and efficacy of surgical and transcatheter treatment options for native coarctation, both in the acute phase and during follow-up (53). Their observations revealed that both surgical and stent therapies achieved lower upper-lower extremity blood pressure gradients compared to balloon angioplasty, both acutely and in the short term. However, these differences began to diminish in the intermediate follow-up period. Notably, patients undergoing stent implantation experienced fewer acute complications when juxtaposed with those undergoing the other two treatment modalities. However, a higher proportion of stent patients required planned interventions in the future (52). It's crucial to acknowledge that a younger age at the time of intervention correlates with a heightened risk of CoA recurrence (55). Nonetheless, a similar survival rate of approximately 93% at 10 years, 86% at 20 years, and 74% at 30 years postoperatively has been reported in older and contemporary postsurgical cohorts (54,55). Despite advances in management techniques and medical care, the long-term survival rates have mostly stayed the same.
In neonates and young infants with CoA, stent implantation is considered an alternative intervention to address the condition. This approach is typically favored when a percutaneous procedure is deemed more suitable. Stent implantation using pre-mounted coronary stents has gained prominence as a safe option to alleviate acute symptoms and serve as a bridge to surgery (56,57), particularly since it avoids the need for larger sheaths associated with stent delivery that poses challenges in very young patients.
Stent implantation offers advantages in maintaining vessel patency and can be a viable option for preterm neonates with CoA. Typically, surgical repair, including stent removal, is undertaken once the patient reaches an adequate body weight and overall condition for the procedure. However, it is essential to acknowledge that stents can cause significant tissue trauma and loss during surgical removal (58).
Recent advancements have introduced bioresorbable stents as a promising alternative with the potential for reduced tissue damage during surgical extraction. Nevertheless, their applicability in very-low-weight patients with aortic coarctation requiring long-term bridging to surgery remains under scrutiny, as early experiences have noted restenosis and stent failure attributed to the radial force loss in the scaffold (59). Further research is warranted to assess bioresorbable stents' feasibility and long-term outcomes in this patient population.
To sum up, surgical repair, particularly the extended end-to-end anastomosis technique, is most of the time the preferred surgical method for treating coarctation of the aorta. This approach is favored because it avoids using prosthetic material, allowing for the resection of the coarctation segment. Moreover, the extended end-to-end anastomosis involves a wider incision, which is less prone to restenosis. This surgical method is typically the preferred choice, especially in cases of native coarctation in infants and young children, patients requiring repair of associated cardiac defects, or individuals with complex coarctation anatomy.
In cases where coarctation reoccurs after the initial repair, balloon angioplasty often becomes the preferred intervention. It is a minimally invasive procedure involving inflating a balloon in the narrowed segment of the aorta to widen it. However, there is a concern for recoarctation and the formation of aneurysms in patients with native coarctation who undergo balloon angioplasty. The long-term effectiveness of this approach can vary, and close follow-up is crucial to monitor for potential complications.
Endovascular stent placement is another interventional option that provides structural support to the narrowed aortic segment. In some cases, it is preferred over balloon angioplasty because it is associated with decreased rates of aortic wall injury and aneurysm formation. Covered stents with a fabric covering may be used to protect against shear stress and prevent subsequent restenosis. However, it is essential to exercise caution when using stents to avoid covering vital branch vessels, as this can lead to complications.
Using stents in small children is a topic of debate, as it often requires larger sheath sizes, which can be challenging in young patients. Additionally, the limitations in accommodating somatic growth need to be carefully considered when choosing this approach, as children's bodies grow and change over time, potentially affecting the stent's effectiveness and fit. Each intervention method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of approach should be based on the patient's specific condition and individual factors. Regular follow-up is essential to ensure the chosen treatment's success and address potential issues that may arise over time (60).
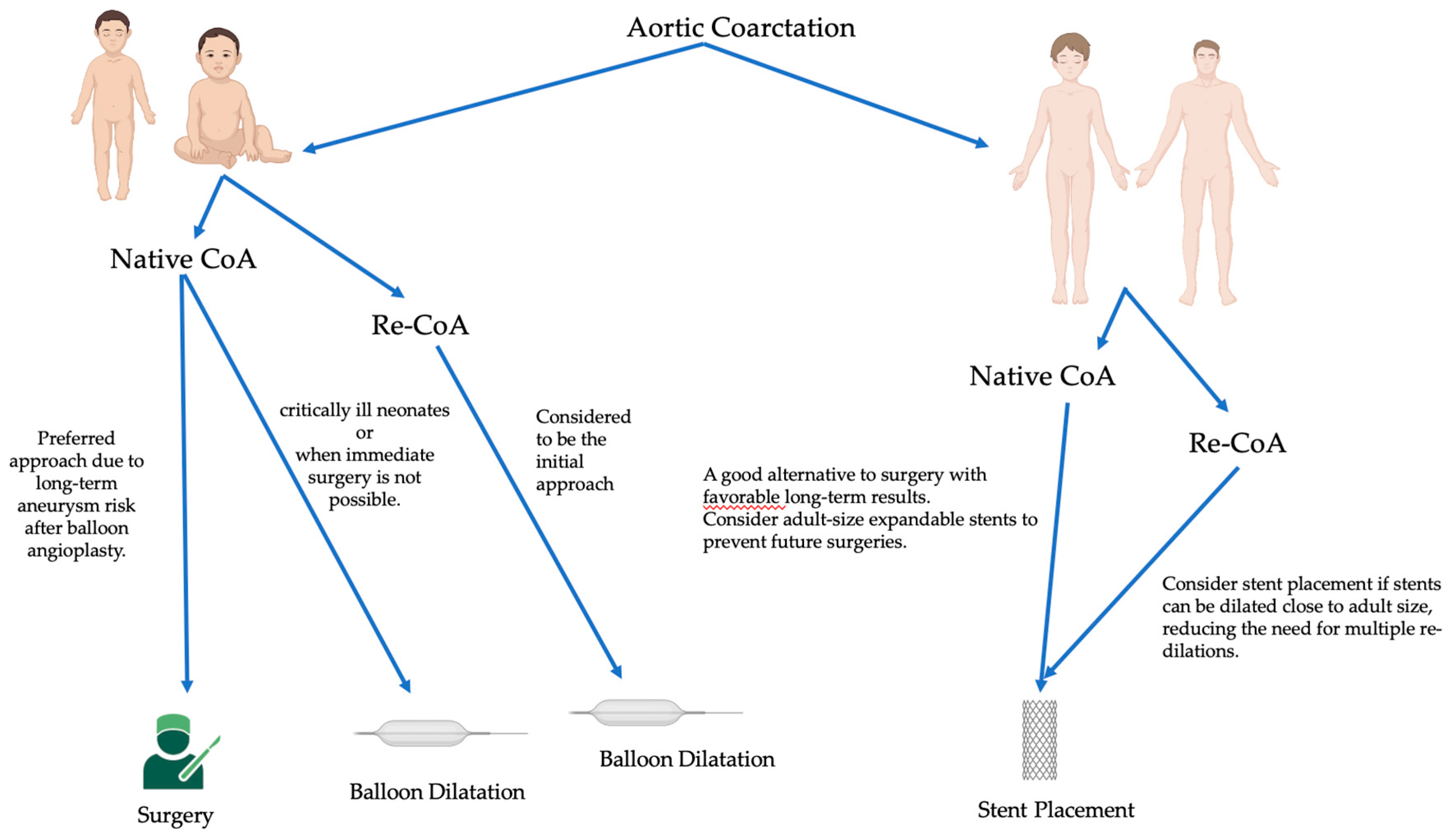
In general, the approach to coarctation management hinges on factors such as the patient's age at presentation, the complexity of the coarctation, and whether it's a native or recurrent obstruction (61-65) (
Figure 1).
For infants and young children with native coarctation, surgical repair is often preferred due to the reduced long-term risk of aneurysms compared to balloon angioplasty, the need for subsequent stent re-dilations, and the limitations posed by small arteries that can't accommodate larger sheath sizes (61,64). However, balloon angioplasty can be a palliative strategy in emergencies involving extremely ill neonates when immediate surgical intervention isn't feasible (64). Surgical repair is also suitable for cases with complex coarctation anatomy or when addressing associated cardiac defects is necessary.
In contrast, for older children, adolescents, or adults with a simple, juxtaductal, native coarctation, stent placement is a reasonable and less invasive alternative to surgery, with favorable long-term outcomes (61,64,65). Using stents that can expand to an adult size is important to avoid needing later surgical intervention.
Initial balloon angioplasty is a reasonable option for recurrent coarctation in younger children since the long-term risk of aneurysms is lower than with native coarctation (64). However, the success of balloon angioplasty varies, and surgical reintervention may be necessary if the obstruction relief is incomplete (62). Stent placement is also a consideration for recoarctation in older children and adolescents, particularly when the stent can be dilated close to adult size, minimizing the need for multiple re-dilations (65).
4. Discussion
In a 1994 study conducted by Kapetein AP et al. on 109 patients operated between 1953 and 1985, with 17% having isolated coarctation and a mean age of 11 ± 12 months at the time of surgery, aortic coarctation resection was performed due to nonelective conditions such as congestive heart failure or severe systemic hypertension. Of these patients, 48 underwent classic end-to-end anastomosis with silk sutures, while 26 had extended end-to-end anastomosis with polypropylene. The post-operation recoarctation rate was relatively low at 5.8%. However, long-term follow-up revealed that recoarctation occurred in 30 (41%) discharged patients. Over a 30-year follow-up period, Kaplan-Meier estimates showed an 86% rate of recoarctation in patients who had classic end-to-end anastomosis with silk sutures (n = 48), whereas none in the group with an "extended" anastomosis and polypropylene sutures (n = 26) experienced recoarctation. Cox analysis indicated that age at operation below 6 months was a prognostic factor for recoarctation. The extended anastomosis with polypropylene sutures was not a significant prognostic factor for recoarctation due to the shorter follow-up duration (66).
In a 2010 retrospective study by Dehaki M.G. et al. (67), involving 188 patients below the age of 14 years who underwent surgical repair for CoA between 1994 and 2004, with an average follow-up of 81.6±32.8 months and a mean age of 5.4±4.2 years, the recurrence rate was 10%. The median time for recurrence was 3.5 years after the primary repair. The repair methods in this study included patch repair in 59% of cases (using either Goretex or Dacron), end-to-end anastomosis in 20.7%, and subclavian flap repair in 16.5%. Notably, angiographically documented recurrence was more common in patch repair (12.7%) and end-to-end anastomosis (10.3%) compared to subclavian flap repair (3.2%).
According to a 2010 Turkish study led by Uguz et al. (68), involving 91 patients (35 neonates and 56 infants) with an average follow-up of 44 months, recoarctation occurred in 13 patients (12.1%). Within this group, eight neonates who had undergone primary operations experienced a 22.9% recoarctation rate. In contrast, five patients operated on during infancy (within the first 6 months of life) exhibited an 8.9% restenosis rate. Recoarctation developed within the first year after the initial repair in all 13 cases. Out of these 13 patients, 10 (11% of the entire study population) required reintervention between six months and two years after the initial repair. Seven (including 4 neonates) underwent successful balloon dilatation for their recoarctation, while three (including 2 neonates) had successful reoperations. None of these 10 patients displayed signs of stenosis recurrence during their last follow-up. In the remaining three patients (2 neonates), only mild recoarctation emerged, with 22, 24, and 27 mmHg gradients, respectively, which did not necessitate treatment. Importantly, no children who were operated on between six and 12 months of age exhibited recoarctation throughout the follow-up. Out of the 91 patients, only 7.7% required interventions for recoarctation, with 3.3% undergoing surgery. Regarding the surgical technique used for coarctation repair, 7.1% of patients who underwent extended end-to-end anastomosis experienced recoarctation. In comparison, only 2.9% of patients with end-to-end anastomosis repairs encountered recoarctation.
In a retrospective study by Jahangiri and colleagues (69), the early and long-term outcomes of subclavian flap angioplasty in neonates and infants were assessed. The study included 185 consecutive patients who underwent this procedure between 1974 and 1998, comprising 125 neonates and 60 infants, with a median age of 18 days. Among the patients, 66 (36%) had an additional ventricular septal defect, 41 (22%) were diagnosed with aortic arch hypoplasia preoperatively, 141 (76%) had an associated patent ductus arteriosus, and 41 (22%) had additional complex heart diseases. Follow-up assessments were performed using transthoracic Doppler echocardiography. The study reported an early mortality rate of 3% and identified recoarctation, defined as a Doppler gradient of 25 mm Hg or more, in 11 (6%) patients during a median follow-up period of 6.2 years (6.2 ± 4.6 years). Importantly, no complications related to the left arm were noted. Risk factors for mortality were found to be residual arch hypoplasia and low birth weight. In contrast, the persistence of arch hypoplasia after surgical treatment was the sole risk factor for recoarctation. However, it was determined that recoarctation was likely not due to a hypoplastic transverse arch but rather at the site of ductal tissue.The study showed excellent survival rates, with 98% and 96% survival at five and ten years, respectively. The freedom from reoperation for recoarctation was notably high, with rates of 95% at two years and 92% at 5, 10, and 15 years. The study reaffirms that subclavian flap repair remains an effective and low-mortality technique for aortic coarctation repair. Furthermore, it highlights that arch hypoplasia tends to regress in most patients after this procedure, underlining the effectiveness and long-term benefits of this surgical approach.
Another noteworthy study was conducted by Burch PT and colleagues (70) in the USA, involving a cohort of 167 neonates and infants aged less than 90 days, with a mean age of 16 days and a median weight of 3.4 kg. All patients underwent end-to-end anastomosis repair using various running sutures, including 6-0 or 7-0 polydioxanone sutures or 7-0 or 8-0 polypropylene sutures. Among the 125 patients who had the anastomosis performed with polydioxanone sutures, 9 (7.2%) experienced recurrent or residual coarctation, while 8 (19.5%) of the 41 individuals who underwent repair with polypropylene sutures had recurrence (p=.04). This study emphasized that low weight does not affect survival or reintervention rates after coarctation repair in neonates and infants less than 3 months of age.
Data from an Indian study, conducted by Sen S. et al. (71) in 2018 on 75 patients (34 neonates) who underwent coarctation repair. Twenty-eight patients underwent balloon angioplasty, and 47 patients underwent surgical repair (23 patients had pericardial patch coarctoplasty, 21 underwent resection and end-to-end anastomosis, 2 patients went for subclavian flap coarctoplasty and only one patient for interposition graft). For a more in-depth analysis of risk factors for reintervention, patients were categorized into neonates (age 0–1 month) and infants (age >1–12 months) at the time of presentation. Among neonates, 63.6% underwent balloon angioplasty, and 17.4% required surgical correction. Concerning the occurrence of recoarctation, patients who underwent balloon coarctoplasty were associated with a significantly higher rate of reintervention (Chi-squared test P = 0.007). In infants aged 1 month to 1 year, there was no significant difference in the choice of surgical technique and the rate of recoarctation.
In 1995, Rao P.S. and colleagues (72) performed a study on 29 infants diagnosed with native coarctation, no older than 3 months, in which they compared the outcomes based on the intervention type. Fourteen patients underwent surgical correction and 15 had balloon angioplasty. The two groups had no significant difference based on the patients' mean weight. Recoarctation occurred in 46%patients (6) from the group that underwent surgical correction during a mean follow-up of 4.5 years. For reintervention, all patients underwent balloon angioplasty. Regarding the patients that underwent balloon angioplasty as a primary intervention, recoarctation occurred in 50% (7 children) during a mean follow-up of 4 years. Two underwent surgical correction, and the other five underwent repeat balloon angioplasty.
Mohan et al.'s 2009 study (73) provided valuable insights into using stents for Coarctation of the Aorta (CoA) treatment in children weighing less than 30 kg. Their research included 60 children divided into two groups: 22 patients weighing less than 30 kg in the first group and 38 patients weighing 30 kg or more in the second group.The study's findings were notable. After stent implantation, there was a significant increase in the mean minimum diameters of the CoA and the CoA/descending aorta (CoA/DAo) ratio. Simultaneously, there was a considerable reduction in the mean systolic gradient in both groups post-stent intervention.Importantly, no significant differences were observed between the two groups in key metrics, including the CoA/DAo ratio, residual systolic gradients, and the reduction in systolic gradient following stent implantation. Furthermore, the study reported no significant complications in patients weighing less than or equal to 30 kg.In summary, Mohan et al.'s 2009 research emphasizes the effectiveness and safety of using large stents for short-term CoA management in small children. While the short-term outcomes are promising, it's crucial to note that these patients may require stent redilations, necessitating ongoing and vigilant follow-up. This study significantly enhances our understanding of CoA treatment strategies in this specific patient population, providing valuable insights for clinicians and affirming the feasibility and safety of using large stents in managing CoA in small children.
In their study with a follow-up period of approximately 81.6 months, Dehaki MG et al observed 188 patients under 14 years old. These patients were divided into three groups based on age: group I, being less than 1 year old, group II, ranging from 1 to 5 years old, and group III, spanning 5 to 14 years. The most common approaches for CoA (Coarctation of the Aorta) repair included patch repair in 111 patients (59%), excision and end-to-end anastomosis in 39 patients (20.7%), subclavian flap repair in 31 patients (16.5%), and other methods in a small percentage of patients. The overall incidence of recurrence was 10%, with varying rates among the age groups: 4% for group I, 15% for group II, and 10% for group III. Some patients underwent balloon angioplasty, which was successful in 61% of cases, while one required reoperation (74).
Corno AF et al. conducted a study over 30 years involving 141 patients, including neonates, infants, children, and adults. The most common CoA repair methods among adults included patch aortoplasty, resection and end-to-end anastomosis, pyloroplasty type, and other procedures. There was no recoarctation observed in the adult group. In the children's group, resection and end-to-end anastomosis were most frequently performed, followed by patch aortoplasty, subclavian flap repair, and other techniques. The recurrence rates varied depending on the approach, with end-to-end anastomosis at 1.8%, patch aortoplasty at 25.0%, and subclavian flap repair at 21.4%. Ten patients required surgical reoperation (75).
Padalino M.A. et al reported on a study with a median follow-up of 10.2 years, involving 341 patients with a median age of 25 days. The most common CoA repair approach was extended end-to-end anastomosis in 80.9% of cases, standard end-to-end anastomosis in 14.7%, and other techniques in 4.4%. The re-coarctation rate was 4.5%, and percutaneous procedures such as stenting or balloon dilatation were used for management (76).
Kaushal S.et al conducted a study with a mean follow-up duration of approximately 5.0 years, involving 201 patients, including neonates with a median age of 23 days. Their study's primary CoA repair approach was extended end-to-end anastomosis in 4% of cases. Three patients underwent balloon angioplasty, and five required reoperation (77).
Presbitero and colleagues conducted an extensive long-term follow-up study, spanning an average duration of 20 years, involving 244 patients. Among this cohort, 143 patients were subject to follow-up assessments. The primary methods for aortic coarctation (CoA) repair encompassed various surgical techniques, including end-to-end anastomosis, extended end-to-end anastomosis, prosthetic tube graft, and patch repair. Within this cohort, 15 patients experienced CoA recurrence, necessitating re-coarctation management (78). The study by Presbitero and colleagues focused on assessing the long-term outcomes in 226 patients who had undergone surgical repair for aortic coarctation. The evaluation was conducted 15 to 30 years after the surgical intervention, during which 26 patients did not survive the follow-up period, primarily due to causes related to the surgical repair itself or associated cardiovascular anomalies. The study's findings revealed that the survival rates for patients who had surgery between the ages of four and 20 years were 97%, 97%, and 92% at 10, 20, and 30 years post-operation, respectively. In contrast, for patients operated on after the age of 20, the corresponding survival rates were 93%, 85%, and 68%. Importantly, a statistically significant difference in survival rates became evident from the fifteenth year of follow-up. Notably, the survival of patients operated on before age 20 did not significantly differ from that of a comparable general Italian population. Regarding CoA management outcomes, recoarctation occurred in only 8% of patients who underwent end-to-end anastomosis, whereas it was observed in 35% of those who had undergone other surgical procedures. A significant observation was that two-thirds of the patients were hypertensive at the last visit. The actuarial curve demonstrated that while blood pressure was normal in most patients 5 to 10 years after the operation, the long-term prognosis indicated that only 32% of patients are expected to have normal blood pressure 30 years after coarctation repair. In conclusion, the study suggests that early surgical repair for aortic coarctation significantly enhances long-term survival. The research also highlights that intervention in older patients and in high blood pressure cases are pivotal predictors of late-onset hypertension. These findings underscore the importance of timely and effective surgical repair for aortic coarctation, emphasizing its potential impact on long-term outcomes (78).
In a retrospective study by Josep Rodes-Cabau et al., 80 patients aged over 1 year with isolated coarctation of the aorta (CoA) were analyzed for outcomes following either surgical repair (with 77% having an end-to-end anastomosis, 17% receiving a patch aortoplasty, and 9% undergoing an interposition graft. ) or transcatheter angioplasty. The mean follow-up was approximately 3 years, during which 30 patients received surgical repair and the rest underwent angioplasty. Immediate hemodynamic results were similar, but surgical patients experienced higher complication rates (50% vs. 18%) and longer hospitalization (7 days vs. 1 day). Notably, aortic aneurysms were more common in the angioplasty group (24% vs. 0%), with some requiring further intervention. While no surgical patients needed recoarctation repair, 32% of the angioplasty group required reintervention, but both groups showed similar blood pressure control at the latest follow-up.
Among the 30 patients who underwent surgical repair, the procedures varied, with 77% having an end-to-end anastomosis, 17% receiving a patch aortoplasty, and 9% undergoing an interposition graft. In contrast, among the 50 patients who received transcatheter treatment, 62% underwent balloon angioplasty, and 38% had stent implantation. Various types of stents were utilized of the stent implantation cases, including Palmaz 308, Palmaz 4014, Genesis 2910, Cheatham-Platinum, and covered Cheatham-Platinum. Additionally, 5 patients in the angioplasty group required staged dilation procedures to achieve optimal results.
5. Our Experience -Case Series
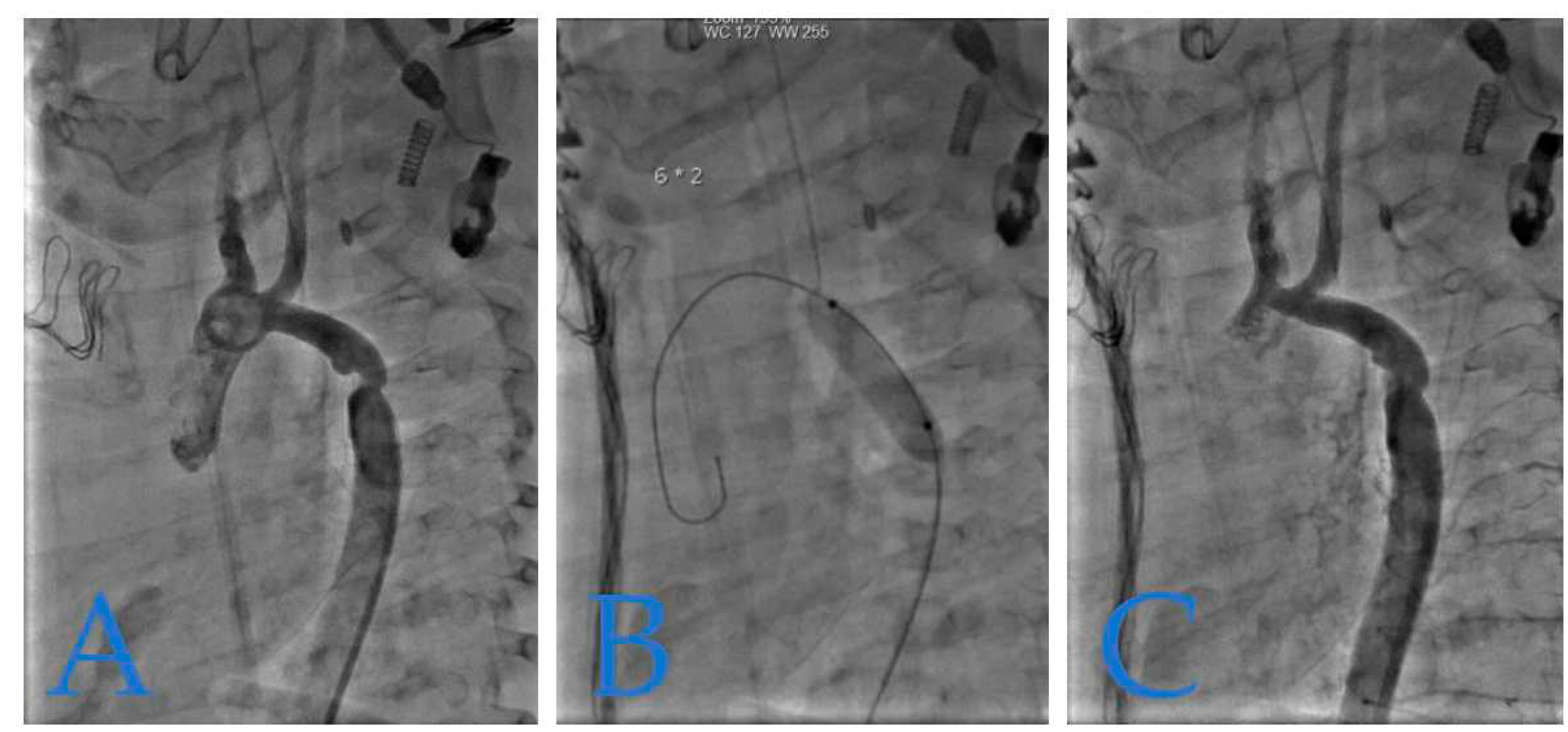
In
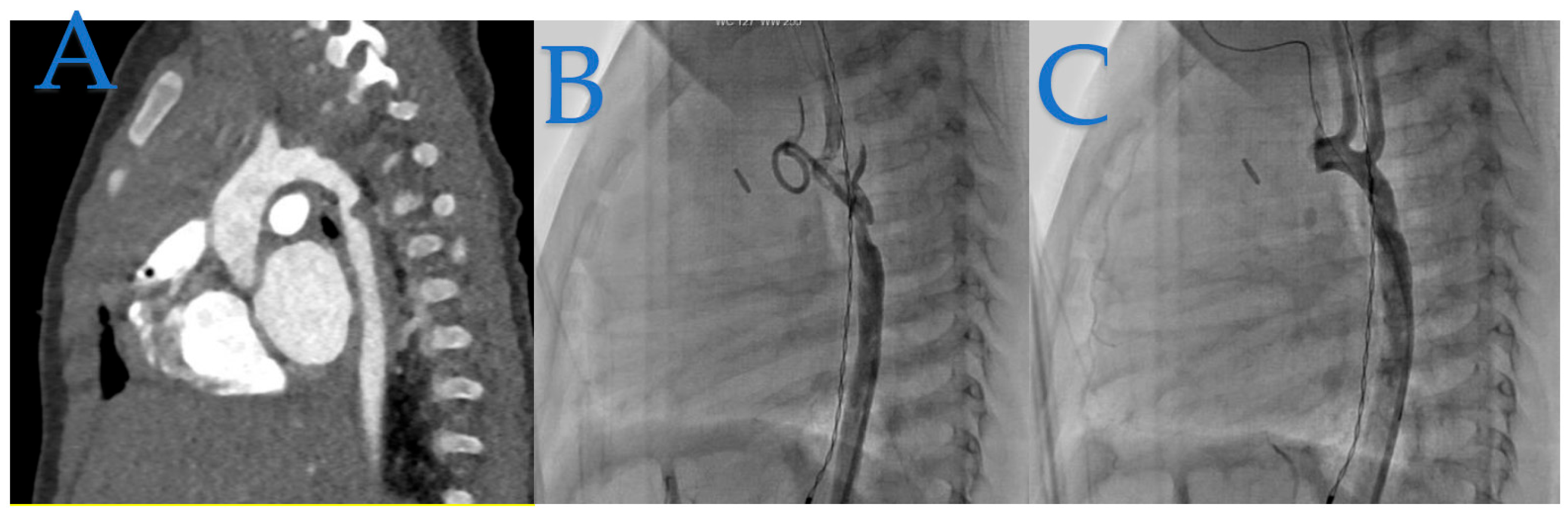
Figure 2, we present the case of a 4-month-old infant weighing 5.8 kg, who underwent coarctation correction surgery using an extended end-to-end anastomosis at just 2 weeks of age. However, at 4 months, the patient developed hypertension (HTA) and a significant blood pressure gradient of 40 mmHg, indicating recoarctation.
In
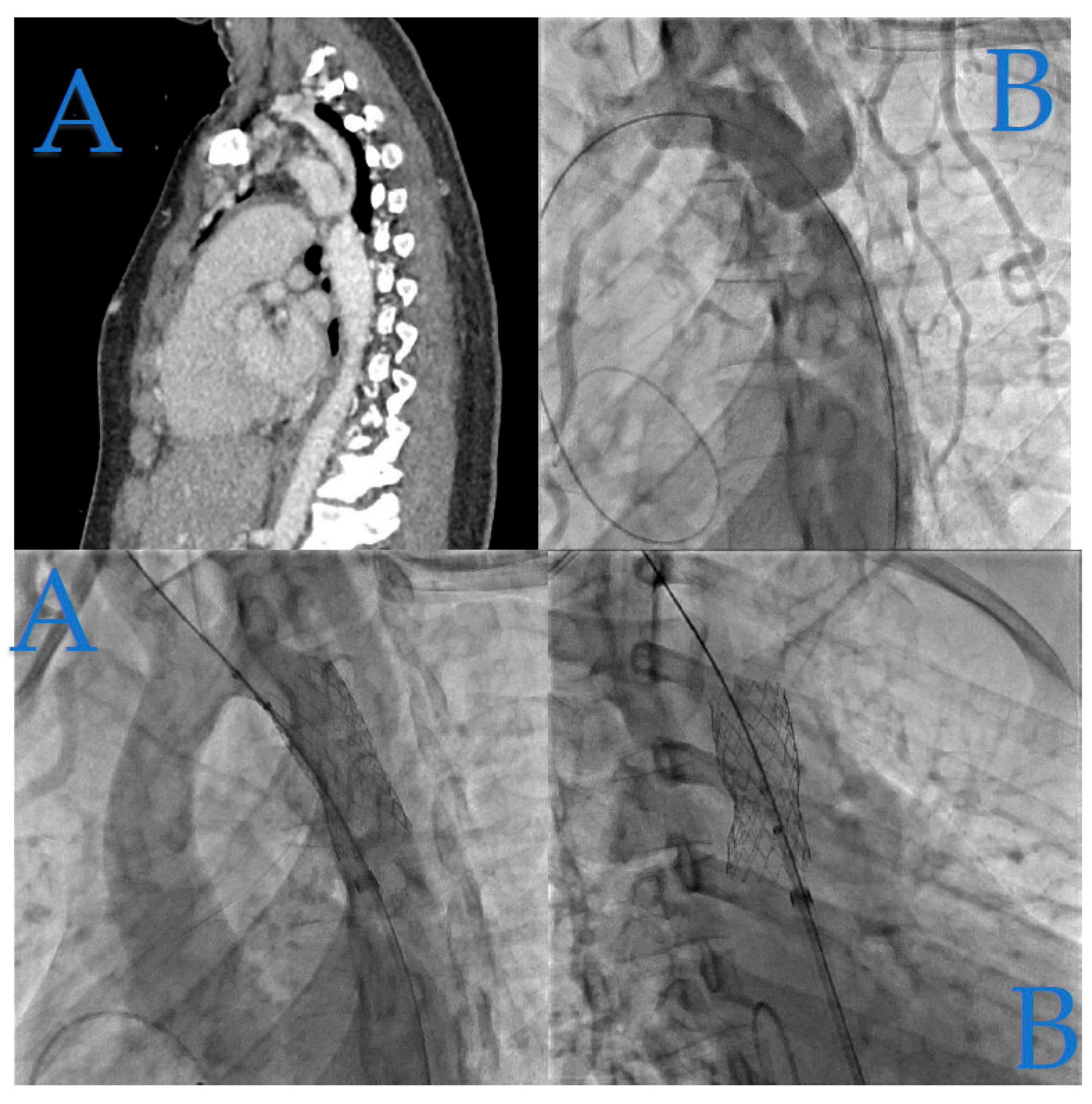
Figure 3, we illustrate the case of a 23-year-old woman who was incidentally diagnosed with native coarctation during a routine check-up for hypertension during her pregnancy.
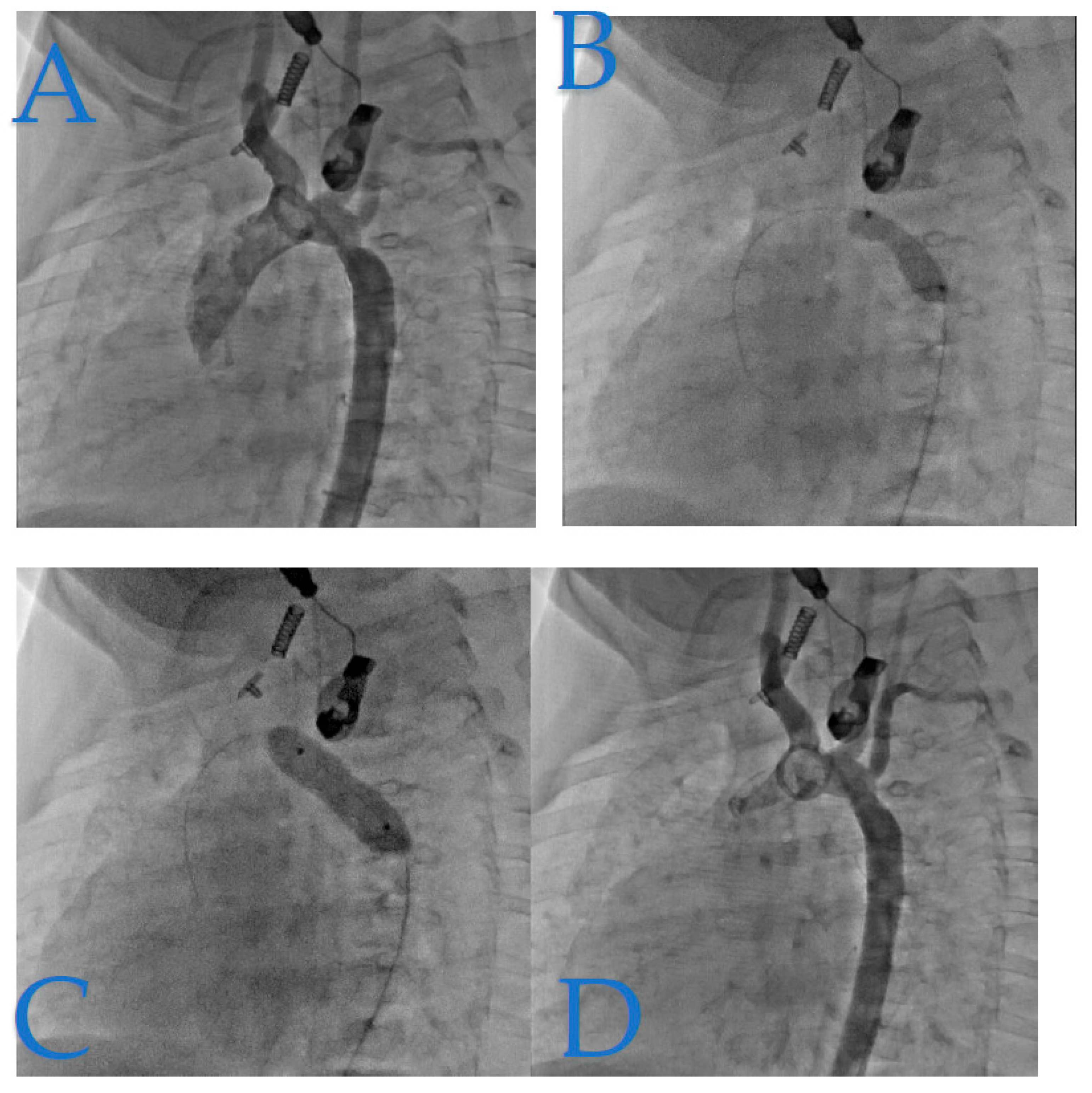
Figure 4 presents a case of isthmic recoarctation in a 6-month-old infant weighing 6.7 kg. The patient had undergone coarctation repair at 8 days of life through an extended end-to-end anastomosis via a left thoracotomy. However, immediate recoarctation occurred due to a clot on the anastomosis.
Figure 5 depicts recoarctation in a 4-month-old infant weighing 4.8 kg. The patient had previously undergone treatment for tight isthmic coarctation using the Waldhausen procedure at 14 days of life following cardiogenic shock. Notably, the left sub-cardiac artery was absent in this case.
Figure 6 presents a case of isthmic recoarctation in a 3-year-old patient weighing 12 kg. The patient had previously undergone a Crafoord extended procedure at 16 days of age.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, the choice of repair technique for coarctation of the aorta significantly influences the occurrence of recoarctation. Surgical repair, which involves resection of the narrowed segment and direct anastomosis, often provides durable results with a low likelihood of recoarctation. On the other hand, percutaneous techniques like balloon angioplasty can offer less invasive options for certain patients but may have a higher risk of recoarctation, especially in younger individuals. Decisions should be made based on the patient's age, anatomy, and overall health, focusing on achieving long-term success while minimizing the potential for re-narrowing of the aorta. Regardless of the chosen technique, regular follow-up and close monitoring are essential to ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals with coarctation of the aorta.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M.V.; methodology, C.M.V., G.L.; validation, J.B.T.; formal analysis, X.I., Z.J.; investigation, C.B., G.L., C.M.V.; resources, C.M.V..; data curation, C.M.V., C.B.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M.V., C.B., G.L.; writing—review and editing, X.I., J.B.T., Z.J.; visualization, J.B.T.; supervision, X.I.; project administration, X.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Doctor Iriart, Doctor Jalal and Prof Thambo have received financial support from the French Government as part of the “Investments of the future” program managed by the National Research Agency (ANR), Grant reference ANR-10-IAHU-04.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Raza, S.; Aggarwal, S.; Jenkins, P.; Kharabish, A.; Anwer, S.; Cullington, D.; Jones, J.; Dua, J.; Papaioannou, V.; Ashrafi, R.; et al. Coarctation of the Aorta: Diagnosis and Management. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, V.L.; Go, A.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Adams, R.J.; Berry, J.D.; Brown, T.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; Dai, S.; De Simone, G.; Ford, E.S.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2011 Update. A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, e18–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reller, M.D.; Strickland, M.J.; Riehle-Colarusso, T.; Mahle, W.T.; Correa, A. Prevalence of Congenital Heart Defects in Metropolitan Atlanta, 1998–2005. J. Pediatr. 2011, 153, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crafoord C, Nylin G. Congenital coarctation of the aorta and its surgical treatment. J Thorac Surg. 1945, 14, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvitting, J.P.; Olin, C.L. Clarence Crafoord: A giant in cardiothoracic surgery, the first to repair aortic coarctation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009, 87, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, R.E. Surgical correction for coarctation of the aorta. Surgery 1945, 18, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.; Ungerleider, S.K.; Pasquali, K.F.; Welke, A.S.; Wallace, Y.; Ootaki, M.D.; Quartermain; et al. Contemporary patterns of surgery and outcomes for aortic coarctation: An analysis of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Congenital Heart Surgery Database. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Gross R, Hufnagel C. Coarctation of the aorta. Experimental studies regarding its surgical correction. N Engl J Med 1945; 233, 287–293.
- Williams, W.G.; Shindo, G.; Trusler, G.; et al. Results of repair of coarctation of the aorta during infancy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1980; 79: 603-8.
- Kappetein, A.P.; Zwinderman, A.; Bogers, A.; et al. More than thirty-five years of coarctation repair. An unexpected high relapse rate. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1994; 107: 87-95.
- Hesslein, P.S.; McNamara, D.; Morriss, M.; et al. Comparison of resection versus partch aortoplasty for repair of coarctation in infants and children. Circulation 1981; 64: 164-8.
- Ziemer, G.; Jonas, R.; Perry, S.; et al. Surgery for coarctation of the aorta in the neonate. Circulation 1986; 74: I25-31.
- 13. Waldhausen JA, Nahrwold D. Repair of coarctation of the aorta with a subclavian flap. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1966; 51: 532-3.
- 14. Pandey R, Jackson M, Ajab S; et al. Subclavian flap repair: Review of 399 patients at median follow-up of fourteen years. Ann Thorac Surg 2006; 81: 1420-8. 1016.
- Barreiro, C.J.; Ellison, T.A.; Williams, J.A.; et al. Subclavian flap aortoplasty: Still a safe, reproducible, and effective treatment for infant coarctation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2007; 31: 649-53.
- Beekman RH, Rocchini A, Behrendt D; et al. Long-term outcome after repair of coarctation in infancy: Subclavian angioplasty does not reduce the need for reoperation. J Am Coll Cardiol 1986; 8: 1406-11.
- Pandey, R.; Jackson, M.; Ajab, S.; et al. Subclavian flap repair: Review of 399 patients at median follow-up of fourteen years. Ann Thorac Surg 2006; 81: 1420-8.
- Gross, R.E. Treatment of certain aortic coarctations by homologous grafts;a report of nineteen cases. Ann Surg 1951; 134: 753-68.
- Yousif, A.; Kloppenburg, G.; Morshuis, W.J.; et al. Repair of adult aortic coarctation by resection and interposition grafting. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2016; 23: 526-30.
- Charlton-Ouw, K.M.; Codreanu, M.E.; Leake, S.S.; et al. Open repair of adult aortic coarctation mostly by a resection and graft replacement technique. J Vasc Surg 2015; 61: 66-72.
- Vossschulte, K. Isthmusplastik zur Behandlung der Aortenisthmus- stenose. Thoraxchirurgie 1957; 4: 443-50.
- Venturini, A.; Perna, A.; Bianchi, G. Repair of coarctation of the tho- racic aorta without resection. Patch graft aortoplasty. Follow-up study of 46 cases. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1978; 19: 49-54.
- Walhout, R.J.; Lekkerkerker, J.; Oron, G.; et al. Comparison of polytetrafluoroethylene patch aorto- plasty and end-to-end anastomosis for coarctation of the aorta. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2003; 126: 521-8.
- Amato, J.J.; Rheinlander, H.; Cleveland, R. A method of enlarging the distal transverse arch in infants with hypoplasia and coarctation of the aorta. Ann Thorac Surg 1977; 23: 261-3.
- Brown, J.W.; Ruzmetov, M.; Hoyer, M.H.; et al. Recurrent Coarctation: Is Surgical Repair of Recurrent Coarctation of the Aorta Safe and Effective? Ann Thorac Surg 2009; 88: 1923-30, discussion 1930-1.
- Thomson, J.D.R.; Mulpur, A.; Guerrero, R.; et al. Outcome after extended arch repair for aortic coarctation. Heart 2006; 92: 90-4.
- Hager, A.; Schreiber, C.; Nutzl, S.; et al. Mortality and restenosis rate of surgical coarctation repair in infancy: A study of 191 pa- tients. Cardiology 2009; 112: 36-41.
- Burch, P.T.; Cowley, C.G.; Holubkov, R.; et al. Coarctation repair in neonates and young infants: Is small size or low weight still a risk factor? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009; 138: 547-52.
- Tabbutt, S.; Nicolson, S.C.; Dominguez, T.E.; et al. Perioperative course in 118 infants and children undergoing coarctation repair via a thoracotomy: A prospective, multicenter experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008; 136: 1229-36.
- Wright, G.E.; Nowak, C.A.; Goldberg, C.S.; et al. Extended resection and end-to-end anastomosis for aortic coarctation in infants: Results of a tailored surgical approach. Ann Thorac Surg 2005; 80: 1453-9.
- Kumar, T.K.; Zurakowski, D.; Sharma, R.; et al. Prediction of recurrent coarctation by early postoperative blood pressure gradient. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011; 142: 1130-6, 1136.e1.
- Singer, M.I.; Rowen, M.; Dorsey, T.J. Transluminal aortic balloon angioplasty for coarctation of the aorta in the newborn. Am Heart J. 1982, 103, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, A.R.; Syamasundar Rao, P. Coarctation of aorta-management options and decision making. Pediat Therapeut. 2012, 5, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gewillig, M.; Budts, W.; Boshoff, D.; Maleux, G. Percutaneous interventions of the aorta. Future Cardiol. 2012, 8, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.E.; Davidson, W.R., Jr.; Swallow, N.A.; Nickolaus, M.J.; Myers, J.L.; Clark, J.B. Long-term results of the subclavian flap repair for coarctation of the aorta in infants. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2013, 4, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruh, S.; Knirsch, W.; Dodge-Khatami, A.; Dave, H.; Pretre, R.; Kretschmar, O. Comparison of surgical and interventional therapy of native and recurrent aortic coarctation regarding different age groups during childhood. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011, 39, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, G.; Goyal, N.; Mandhan, G.; Sidana, P. Transfemoral balloon angioplasty of severe coarctation of aorta in 1200 g newborn. Ann. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2017, 10, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feltes, T.F.; Bacha, E.; Beekman, R.H., 3rd; Cheatham, J.P.; Feinstein, J.A.; Gomes, A.S.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Ing, F.F.; de Moor, M.; Morrow, W.R.; et al. Indications for cardiac catheterization and intervention in pediatric cardiac disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 2607–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, A.C.; Fischer, L.K.; Schwartz, T.; Jureidini, S.; Balfour, I.; Carpenter, D.; Demello, D.; Virgo, K.S.; Pennington, D.G.; Johnson, R.G. Comparison of angioplasty and surgery for neonatal aortic coarctation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 80, 1659–1664, discussion 1664–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzguenda, I.; Marini, D.; Ou, P.; Boudjemline, Y.; Bonnet, D.; Agnoletti, G. Percutaneous treatment of neonatal aortic coarctation presenting with severe left ventricular dysfunction as a bridge to surgery. Cardiol. Young 2009, 19, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meliota, G.; Lombardi, M.; Zaza, P.; Tagliente, M.R.; Vairo, U. Balloon angioplasty of aortic coarctation in critically ill newborns using axillary artery access. Ann. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2020, 13, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothman, A.; Galindo, A.; Evans, W.N.; Collazos, J.C.; Restrepo, H. Effectiveness and safety of balloon dilation of native aortic coarctation in premature neonates weighing < or =2,500 grams. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, J.P.; Kang, S.L.; Lee, K.J.; Benson, L.; Asoh, K.; Chaturvedi, R.R. Balloon Angioplasty for Native Aortic Coarctation in 3- to 12-Month-Old Infants. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, e008938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Laughlin, M.P.; Perry, S.B.; Lock, J.E.; Mullins, C.E. Use of endovascular stents in congenital heart disease. Circulation 1991, 83, 1923–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, T.J.; Kim, D.W.; Du, W.; et al. Comparison of surgical, stent, and balloon angioplasty treatment of native coarctation of the aorta: An observational study by the CCISC (Congenital Cardiovascular Interventional Study Consortium). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2664–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, A.R.; Rao, P.S. Development of aortic coarctation following device closure of patent ductus arteriosus. J Invasive Cardiol. 2013, 25, 464–467. [Google Scholar]
- Gewillig, M.; Budts, W.; Boshoff, D.; Maleux, G. Percutaneous interventions of the aorta. Future Cardiol. 2012, 8, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, G.; Abecasis, M.; Anjos, R.; Marques, M.; Koukoulis, G.; Aguiar, C.; Neves, J.P. Aortic coarctation repair in the adult. J Card Surg. 2014, 29, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez de Lezo, J.; Romero, M.; Pan, M.; et al. Stent repair for complex coarctation of aorta. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015, 8, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkema, E.J.; Leiner, T.; Grotenhuis, H.B. Diagnosis, imaging and clinical management of aortic coarctation. Heart 2017, 103, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, E.E.; Davidson WRJr Swallow, N.A.; Nickolaus, M.J.; Myers, J.L.; Clark, J.B. Long-term results of the subclavian flap repair for coarctation of the aorta in infants. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2013, 4, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, T.J.; Kim, D.W.; Du, W.; et al. Comparison of surgical, stent, and balloon angioplasty treatment of native coarctation of the aorta: An observational study by the CCISC (Congenital Cardiovascular Interventional Study Consortium). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2664–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.; Fuster, V.; Steele, P.M.; Driscoll, D.; McGoon, D.C. Coarctation of the aorta. Long-term follow-up and prediction of outcome after surgical correction. Circulation 1989, 80, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.L.; Burkhart, H.M.; Connolly, H.M.; et al. Coarctation of the aorta: Lifelong surveillance is mandatory following surgical repair. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegeman, R.; Breur, J.M.P.J.; Heuser, J.; Jansen, N.J.G.; de Vries, W.B.; Vijlbrief, D.C.; Molenschot, M.M.C.; Haas, F.; Krings, G.J. Primary coronary stent implantation is a feasible bridging therapy to surgery in very low birth weight infants with critical aortic coarctation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 261, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mini, N.; Zartner, P.A.; Schneider, M.B.E. Stenting of critical aortic coarctation in neonates between 600 and 1,350 g. Using a transfemoral artery approach: A single center experience. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1025411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorenflo, M.; Boshoff, D.E.; Heying, R.; Eyskens, B.; Rega, F.; Meyns, B.; Gewillig, M. Bailout stenting for critical coarctation in premature/critical/complex/early recoarcted neonates. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 75, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallmon, H.; Berger, F.; Cho, M.Y.; Opgen-Rhein, B. First use and limitations of Magmaris® bioresorbable stenting in a low birth weight infant with native aortic coarctation. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2019, 93, 1340–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torok, R.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Fleming, G.A.; Hill, K.D. Coarctation of the aorta: Management from infancy to adulthood. World J Cardiol. 2015, 7, 765–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, C.A.; Williams, R.G.; Bashore, T.M.; Child, J.S.; Connolly, H.M.; Dearani, J.A.; del Nido, P.; Fasules, J.W.; Graham, T.P.; Hijazi, Z.M.; et al. ACC/AHA 2008 Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (writing committee to develop guidelines on the management of adults with congenital heart disease). Circulation 2008; 118: e714-e833. [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.C.; Du, W.; Cowley, C.G.; Forbes, T.J.; Kim, D.W. A prospective observational multicenter study of balloon angioplasty for the treatment of native and recurrent coarctation of the aorta. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2014; 83: 1116-1123. [CrossRef]
- Cowley, C.G.; Orsmond, G.S.; Feola, P.; McQuillan, L.; Shaddy, R.E. Long-term, randomized comparison of balloon angioplasty and surgery for native coarctation of the aorta in childhood. Circulation 2005; 111: 3453-3456. [CrossRef]
- Feltes, T.F.; Bacha, E.; Beekman, R.H.; Cheatham, J.P.; Feinstein, J.A.; Gomes, A.S.; Hijazi, Z.M.; Ing, F.F.; de Moor, M.; Morrow, W.R.; et al. Indications for cardiac catheterization and intervention in pediatric cardiac disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 2607–2652. [CrossRef]
- Kische, S.; D’Ancona, G.; Stoeckicht, Y.; Ortak, J.; Elsässer, A.; Ince, H. Percutaneous treatment of adult isthmic aortic coarctation: Acute and long-term clinical and imaging outcome with a self- expandable uncovered nitinol stent. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 2015, 8, Pii: e001799
. [CrossRef]
- Kappetein, A.P.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Bogers, A.J.; Rohmer, J.; Huysmans, H.A. More than thirty-five years of coarctation repair. An unexpected high relapse rate. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1994 107: 87-95. [PubMed]
- Dehaki, M.G.; Ghavidel, A.A.; Givtaj, N.; Omrani, G.; Salehi, S. Recurrence rate of different techniques for repair of coarctation of aorta: A 10 years experience. Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2010, 3, 123–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uğuz, E.; Ozkan, S.; Akay, H.T.; Gűltekin, B.; Aslamaci, S. Surgical repair of coarctation of aorta in neonates and infants: A 10 years experience. Turk Gogus Kalp Dama 2010; 18: 094-099.
- Jahangiri, M.; Shinebourne, E.A.; Zurakowski, D.; Rigby, M.L.; Redington, A.N.; Lincoln, C. Subclavian flap angioplasty: Does the arch look after itself? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000, 120, 224–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burch, P.T.; Cowley, C.G.; Holubkov, R.; Null, D.; Lambert, L.M.; Kouretas, P.C.; Hawkins, J.A. Coarctation repair in neonates and young infants: Is small size or low weight still a risk factor? J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009, 138, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Garg, S.; Rao, S.G.; Kulkarni, S. Native aortic coarctation in neonates and infants: Immediate and midterm outcomes with balloon angioplasty and surgery. Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2018, 11, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.S.; Chopra, P.S.; Koscik, R.; Smith, P.A.; Wilson, A.D. Surgical versus balloon therapy for aortic coarctation in infants < or = 3 months old. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994, 23, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, U.R.; Danon, S.; Levi, D.; Connolly, D.; Moore, J.W. Stent implantation for coarctation of the aorta in children <30 kg. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009, 2, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaki, M.G.; Ghavidel, A.A.; Givtaj, N.; Omrani, G.; Salehi, S. Recurrence rate of different techniques for repair of coarctation of aorta: A 10 years experience. Ann Pediatr Cardiol. 2010, 3, 123–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corno, A.F.; Botta, U.; Hurni, M.; Payot, M.; Sekarski, N.; Tozzi, P.; von Segesser, L.K. Surgery for aortic coarctation: A 30 years experience. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001, 20, 1202–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padalino, M.A.; Bagatin, C.; Bordin, G.; Tua, L.; Francescato, A.; Pradegan, N.; Piperata, A.; Vida, V.L.; Castaldi, B.; Boccuzzo, G.; et al. Surgical repair of aortic coarctation in pediatric age: A single center two decades experience. J Card Surg. 2019, 34, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, S.; Backer, C.L.; Patel, J.N.; Patel, S.K.; Walker, B.L.; Weigel, T.J.; Randolph, G.; Wax, D.; Mavroudis, C. Coarctation of the aorta: Midterm outcomes of resection with extended end-to-end anastomosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009, 88, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presbitero, P.; Demarie, D.; Villani, M.; Perinetto, E.A.; Riva, G.; Orzan, F.; Bobbio, M.; Morea, M.; Brusca, A. Long term results (15-30 years) of surgical repair of aortic coarctation. Br Heart J. 1987, 57, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodés-Cabau, J.; Miró, J.; Dancea, A.; Ibrahim, R.; Piette, E.; Lapierre, C.; Jutras, L.; Perron, J.; Tchervenkow, C.I.; Poirier, N.; et al. Comparison of surgical and transcatheter treatment for native coarctation of the aorta in patients > or = 1 year old. The Quebec Native Coarctation of the Aorta study. Am Heart J. 2007, 154, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).