Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
19 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Physical and mechanical properties
2.2. Production of samples
3. Results and discussions
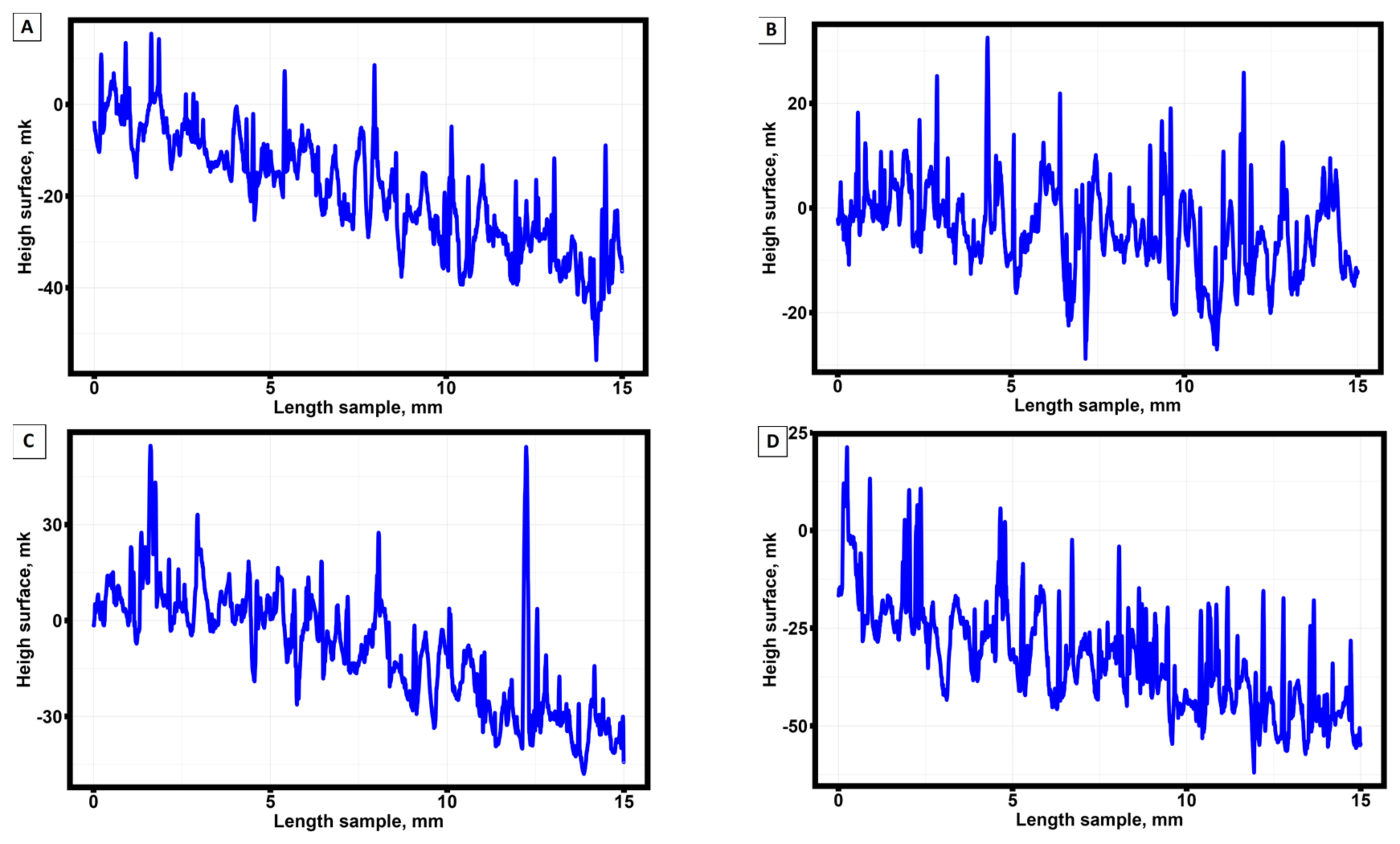
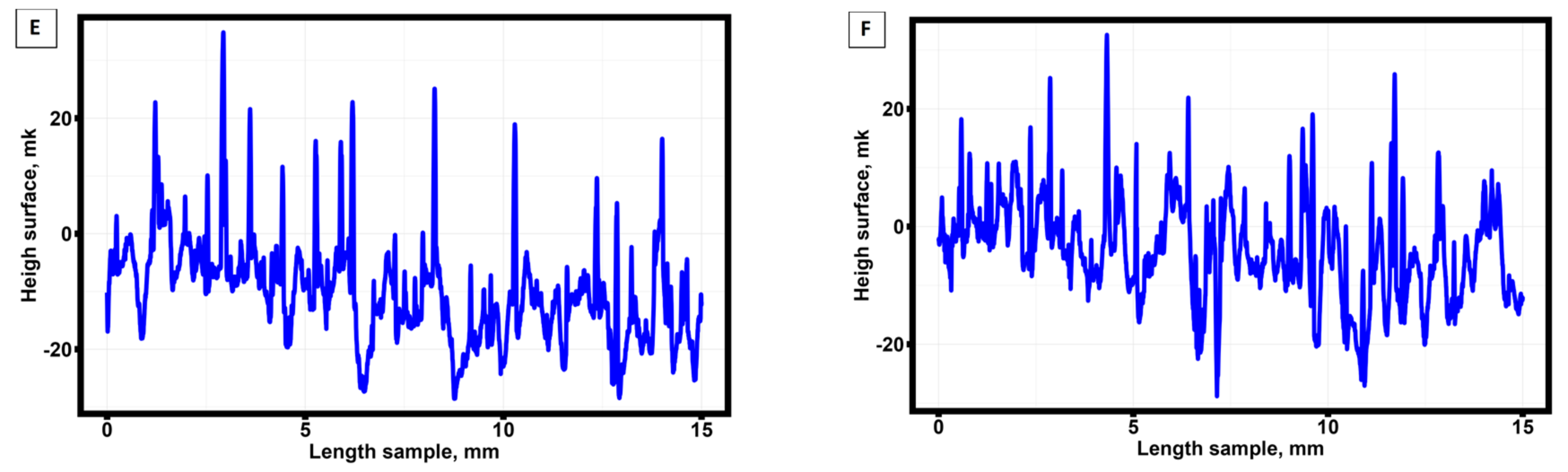
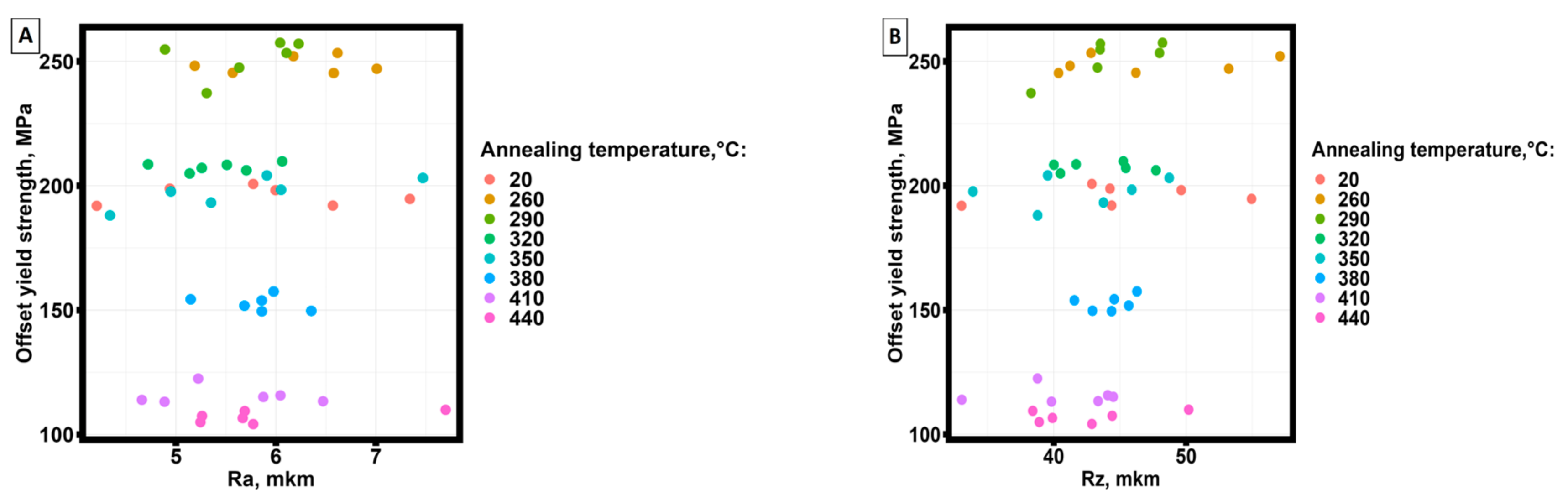
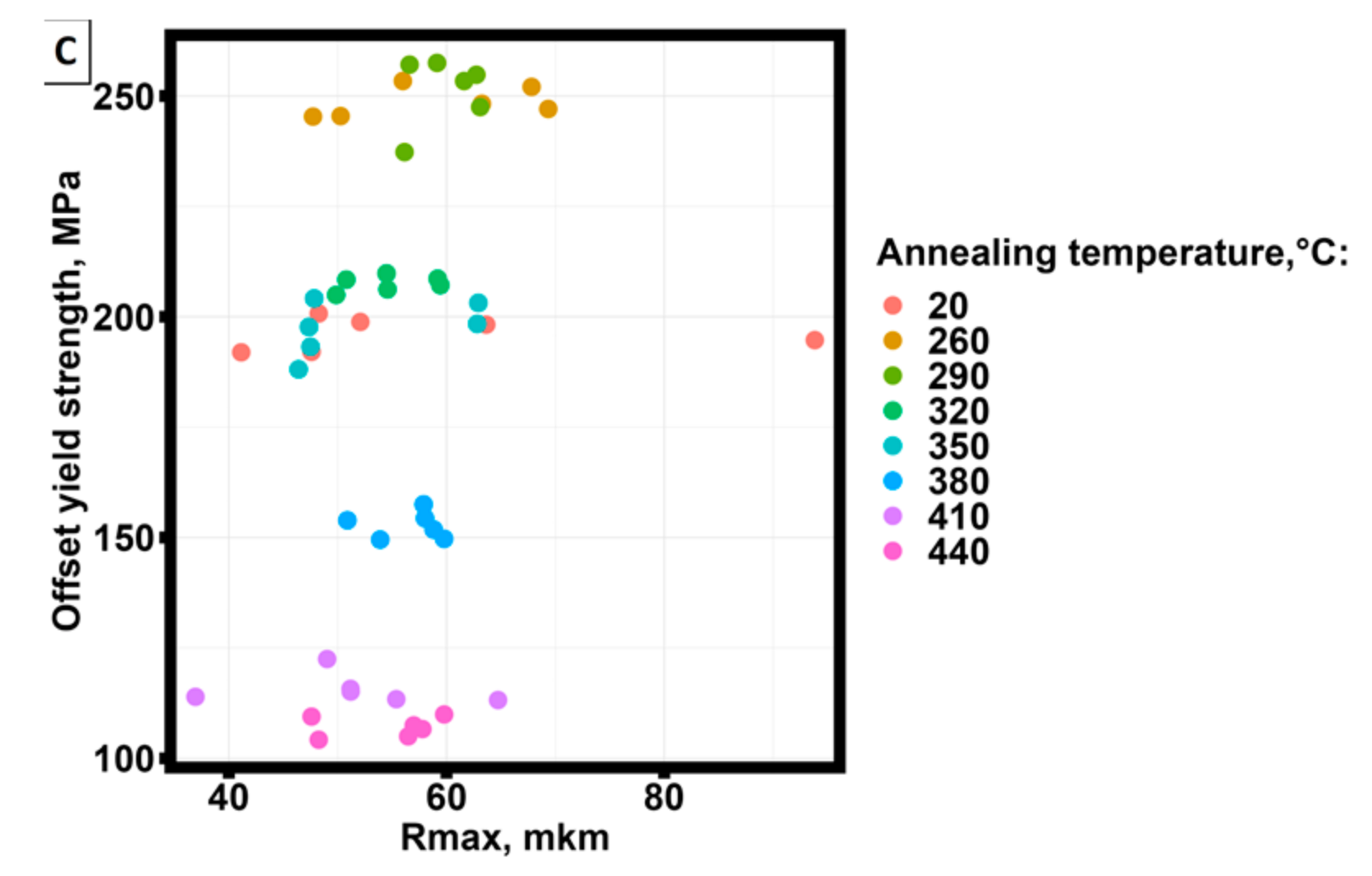
3.1. Surface roughness of samples manufactured by selective laser melting technology from AlSi10Mg material.
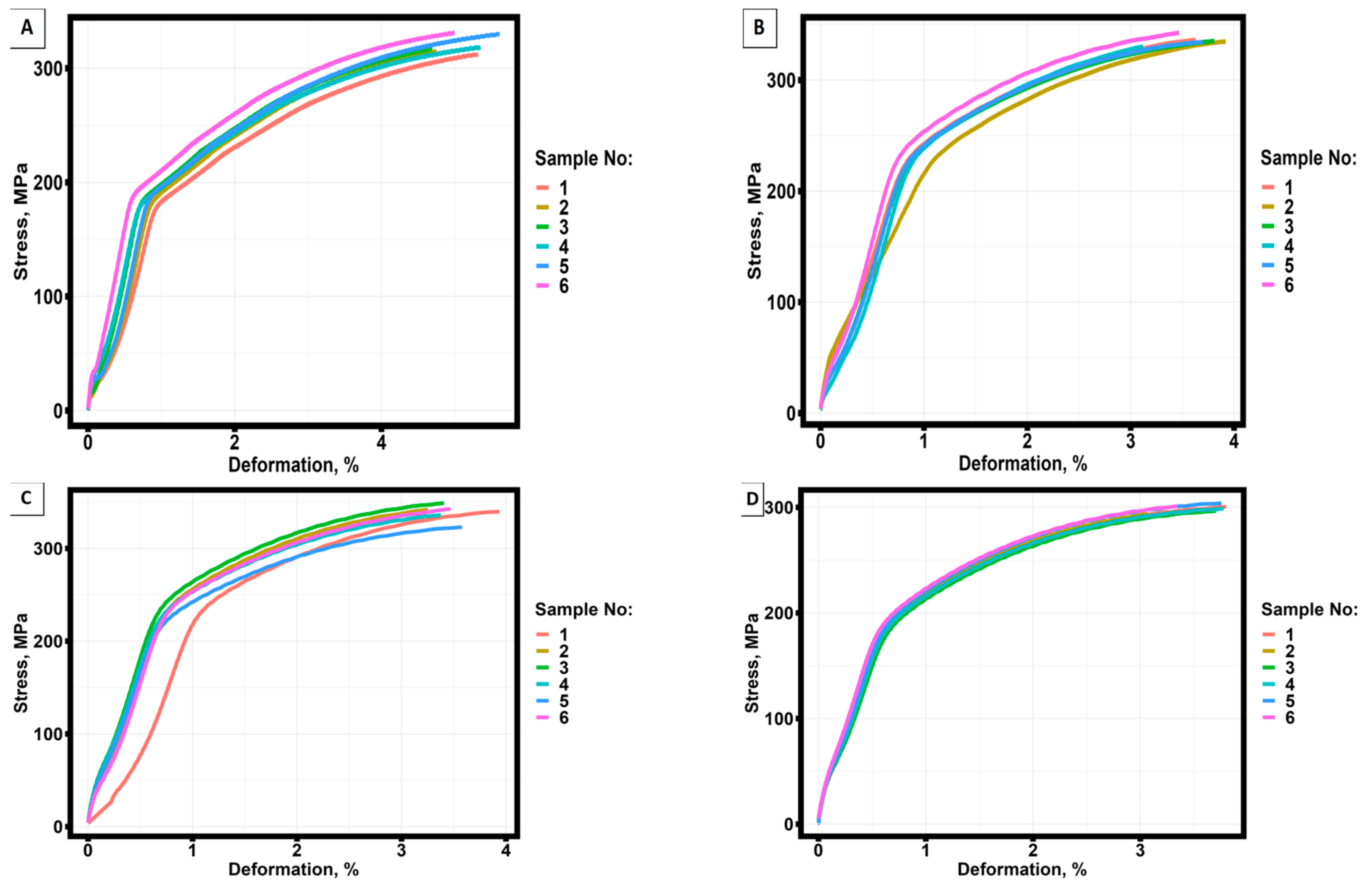
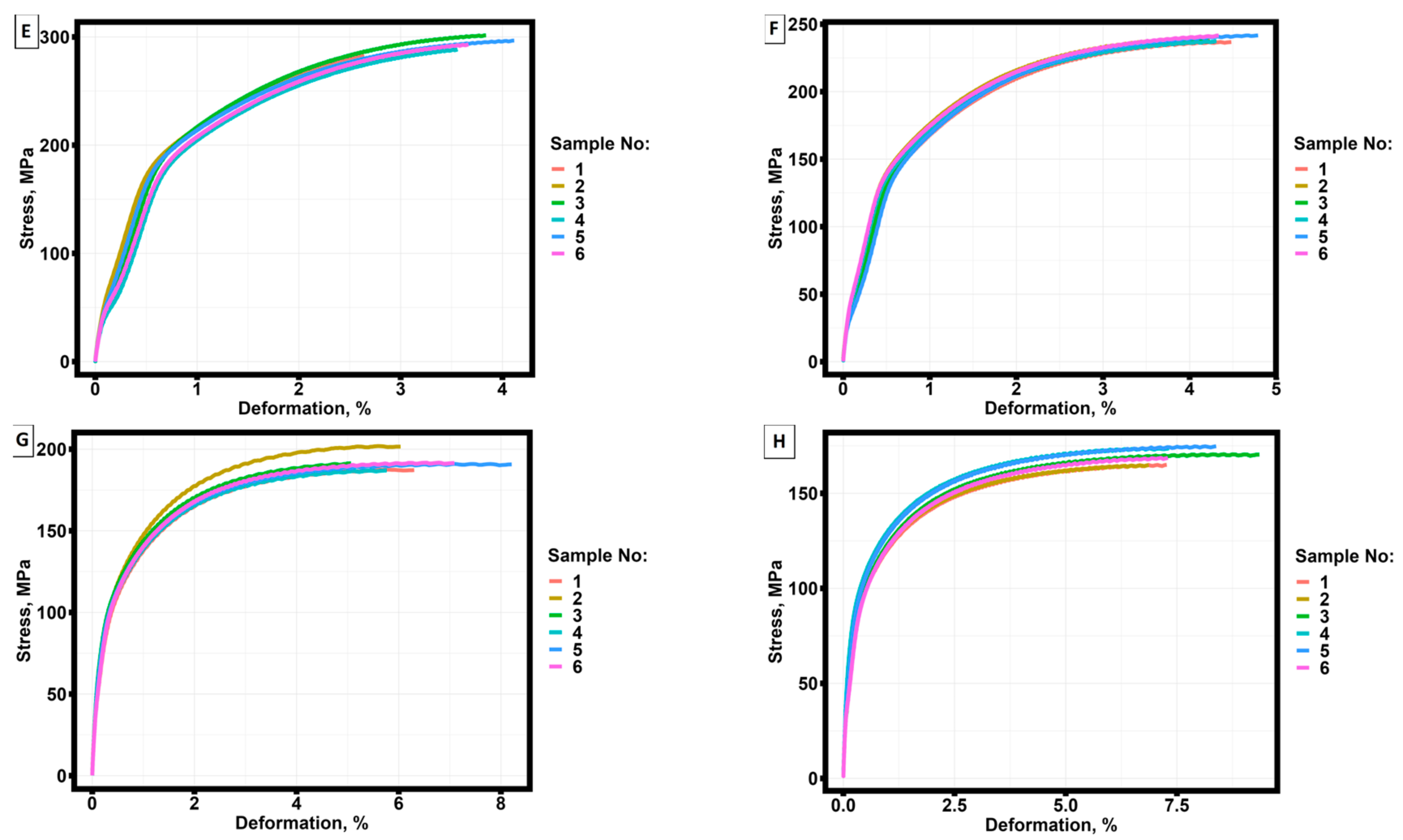
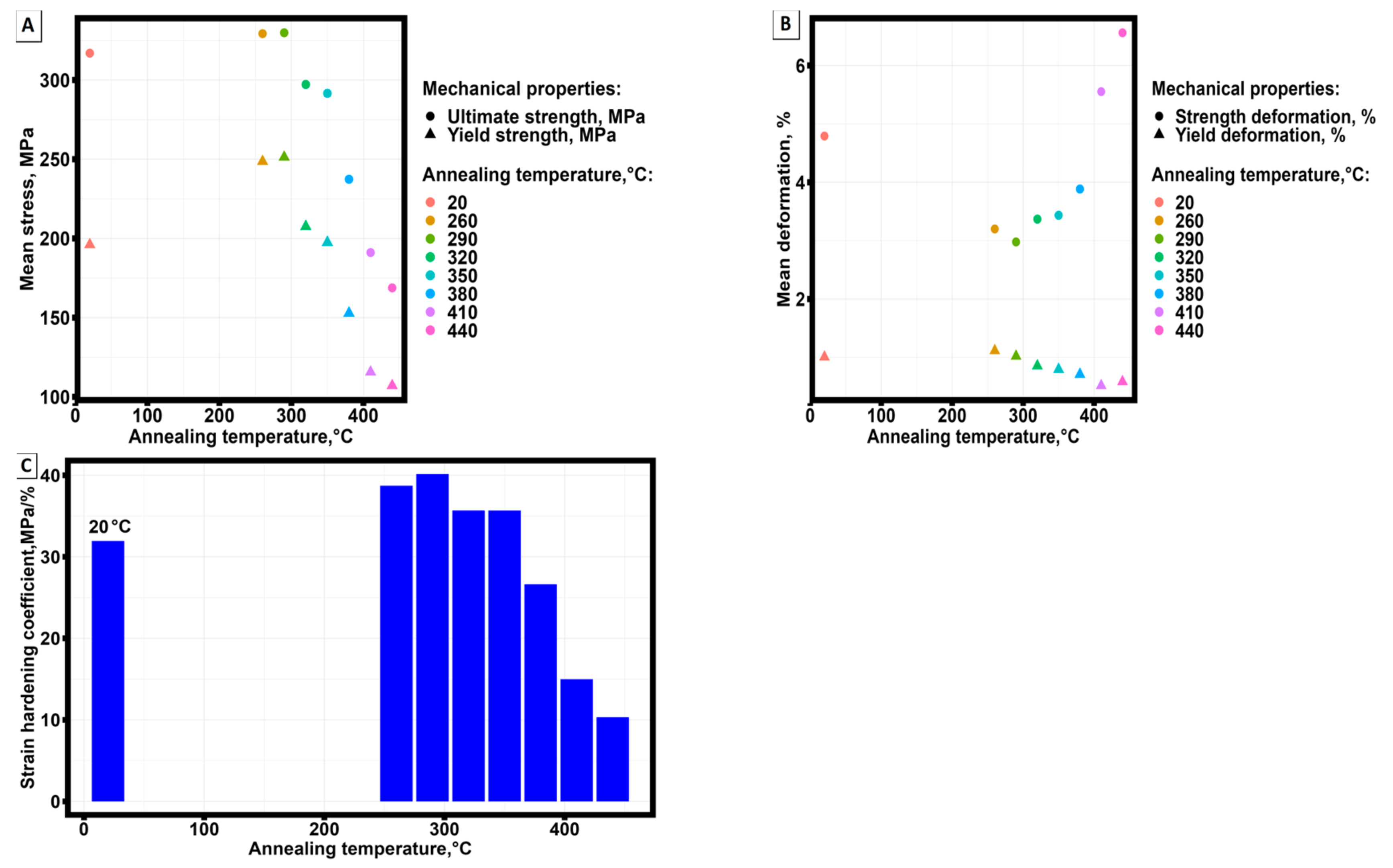
3.2. Mechanical test results for groups of specimens manufactured by selective laser melting technology from AlSi10Mg material, pre-treated at different temperatures.
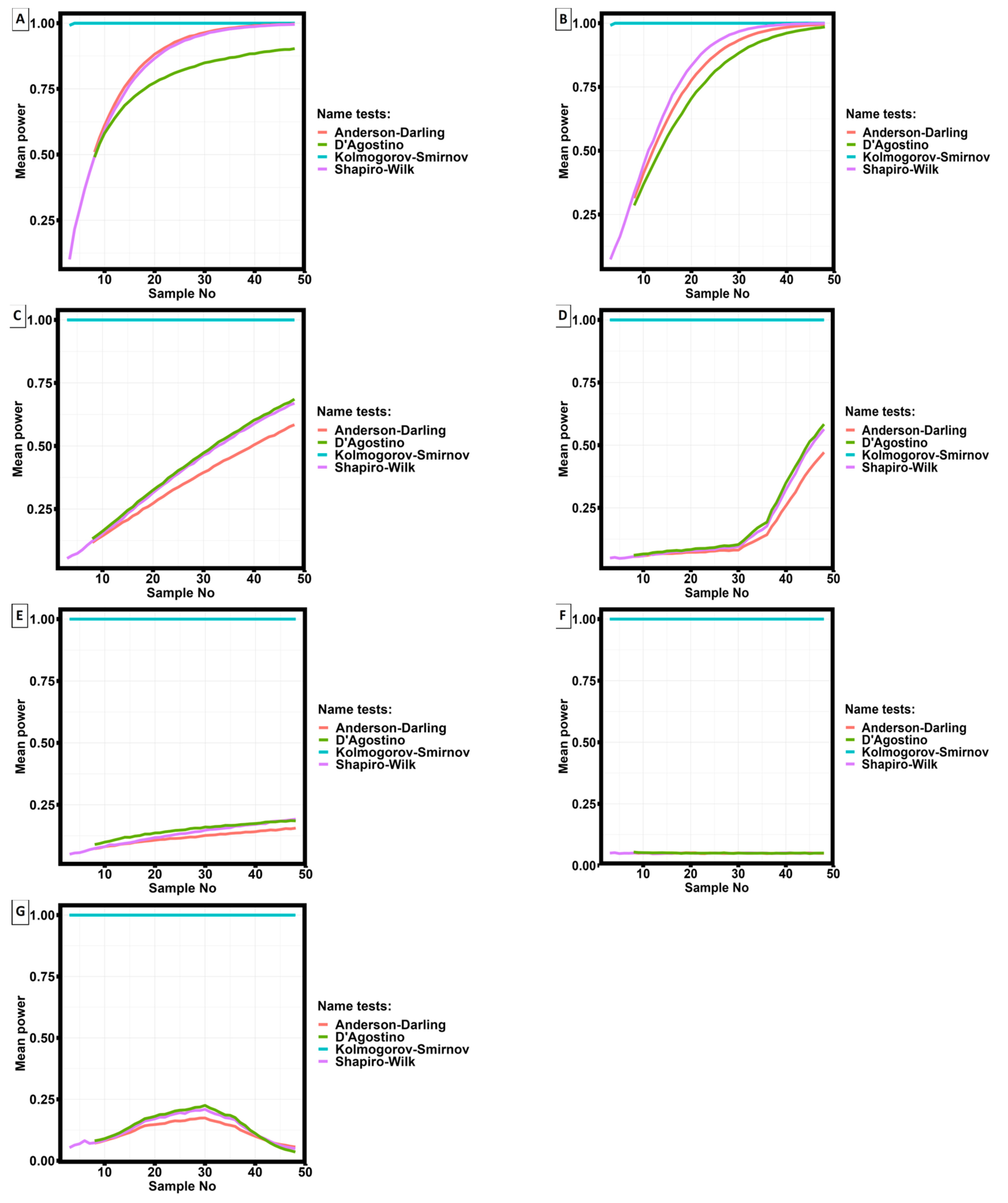
3.3. Statistical analysis of the results.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO/ASTM 52900:2015 [ASTM F2792] Additive Manufacturing-General Principles-Terminology; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ian Gibson, David Rosen, Brent Stucker. Additive Manufacturing Tecnologies. 3D Printing, Rapid Prototyping and Direct Digital Manufacturing//Springer, 2015 – P.P.
- Sandeep Rauta, Vijaykumar S. Jattib, Nitin K. Khedkarc, T.P.Singhd. Investigation of the effect of built orientation on mechanical properties and total cost of FDM parts // Procedia materials science 6 (2014) 1625-1630. 2014.
- Ludmila Novakova - Marcincinova, Jozef Novak - Marcincin. Verification of mechanical Properties of ABS materials used in FDM rapid prototyping technology// Proceedings in manufacturing systems/vol. 8. ISS. 2. 2013. 87-92.
- P. Dudek. FDM 3D printing technology in manufacturing composite elements. Archives of metallurgy and materials// vol. 58. 2013/ ISS.4/dol.: 10. [CrossRef]
- Borgue, R. 3D printing: the dawn of a new era in manufacturing? / R. Borgue // Assembly Automation. 2013. Vol. 33. ¹4. P. 307-311.
- S.A.M. Tofail, E.P. S.A.M. Tofail, E.P. Koumoulos, A. Bandyopadhyay, S. Bose, L. O'Donoghue, C. Charitidis, Additive manufacturing: scientific and technological challenges, market uptake and opportunities, Mater. Today 21 (2018) 22e37.
- J.M. Lee, S.L. J.M. Lee, S.L. Sing, M.M. Zhou, W.Y. Yeong, 3D bioprinting processes: a perspective on classification and terminology, Int. J. Bioprint. 4 (2) (2018) 151.
- J. Haubrich, J. J. Haubrich, J. Gussone, P. Barriobero-Vila, P. Kürnsteiner, E.A. Jagle, D. Raabe, € N. Schell, G. Requena, The role of lattice defects, element partitioning and intrinsic heat effects on the microstructure in selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V, Acta Mater. 167 (2019) 136e148.
- T. DebRoy, H.L. T. DebRoy, H.L. Wei, J.S. Zuback, T. Mukherjee, J.W. Elmer, J.O. Milewski, A.M. Beese, A. Wilson-Heid, A. De, W. Zhang, Additive manufacturing of metallic componentseprocess, structure and properties, Prog. Mater. Sci. 92 (2018) 112e224.
- Khmyrov, R.S.; Grigoriev, S.N.; Okunkova, A.A.; Gusarov, A.V. On the possibility of selective laser melting of quartz glass. Phys. Procedia. 2014, 56, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khmyrov, R.S.; Protasov, C.E.; Grigoriev, S.N.; Gusarov, A.V. Crack-free selective laser melting of silica glass: single beads and monolayers on the substrate of the same material. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 85, 1461–69 (Publons 43). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protasov, C.E.; Khmyrov, R.S.; Grigoriev, S.N.; Gusarov, A.V. Selective laser melting of fused silica: Interdependent heat transfer and powder consolidation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 104, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, S.N.; Volosova, M.A.; Peretyagin, P.Y.; Seleznev, A.E.; Okunkova, A.A.; Smirnov, A. The Effect of TiC Additive on Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Al2O3 Ceramic. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusarov, A.V.; Grigoriev, S.N.; Volosova, M.A.; Melnik, Y.A.; Laskin, A.; Kotoban, D.V.; Okunkova, A.A. On productivity of laser additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 261, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. Asgari, A. H. Asgari, A. Odeshi, K. Hosseinkhani, M. Mohammadi, On dynamic mechanical behavior of additively manufactured AlSi10Mg_200C, Mater. Lett. 211 (2018) 187e190.
- Y. Chen, J.X. Y. Chen, J.X. Zhang, X.H. Gu, N.W. Dai, P. Qin, L.C. Zhang, Distinction of corrosion resistance of selective laser melted Al-12Si alloy on different planes, J. Alloys Compd. 747 (2018) 648-658.
- Leon, Avi, and Eli Aghion. "Effect of surface roughness on corrosion fatigue performance of AlSi10Mg alloy produced by Selective Laser Melting (SLM)." Materials Characterization 131 (2017): 188-194. [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, Idan, Adin Stern, and Nachum Frage. "Microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi10Mg parts produced by the laser beam additive manufacturing (AM) technology." Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis 3 (2014): 448-453. [CrossRef]
- Kamarudin, K. , et al. "Dimensional accuracy and surface roughness analysis for AlSi10Mg produced by selective laser melting (SLM)." MATEC Web of Conferences. Vol. 78. EDP Sciences, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Zhichao Dong, Yabo Liu, Weijie Li, Jun Liang, Orientation dependency for microstructure, geometric accuracy and mechanical properties of selective laser melting AlSi10Mg lattices //Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 791 (2019): 490-500, ISSN 0925-8388. 4. [CrossRef]
- Mertens, Anne, et al. "Microstructure and properties of SLM AlSi10Mg: understanding the influence of the local thermal history." Procedia Manufacturing 47 (2020): 1089-1095. [CrossRef]
- Kempen, Karolien, et al. "Mechanical properties of AlSi10Mg produced by selective laser melting." Physics Procedia 39 (2012): 439-446. [CrossRef]
- Jing, C. H. E. N. Jing, C. H. E. N., et al. "Microstructure, porosity and mechanical properties of selective laser melted AlSi10Mg." Chinese Journal of Aeronautics 33.7 (2020): 2043-2054. [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, Ch Srinivasa, et al. "Effect of build atmosphere on the mechanical properties of AlSi10Mg produced by selective laser melting." Materials Today: Proceedings 5.9 (2018): 17231-17238. [CrossRef]
- Praneeth, Jammula, Sriram Venkatesh, and L. Sivarama Krishna. "Process parameters influence on mechanical properties of AlSi10Mg by SLM." Materials Today: Proceedings (2023). [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, Nesma T., et al. "Reducing porosity in AlSi10Mg parts processed by selective laser melting." Additive manufacturing 1 (2014): 77-86. [CrossRef]
- Limbasiya, Nandita, et al. "A comprehensive review on the effect of process parameters and post-process treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg." Journal of Materials Research and Technology (2022). [CrossRef]
- Maleki, Erfan, Sara Bagherifard, and Mario Guagliano. "Correlation of residual stress, hardness and surface roughness with crack initiation and fatigue strength of surface treated additive manufactured AlSi10Mg: Experimental and machine learning approaches." Journal of Materials Research and Technology 24 (2023): 3265-3283. [CrossRef]
- Majeed, Arfan, et al. "Surface quality improvement by parameters analysis, optimization and heat treatment of AlSi10Mg parts manufactured by SLM additive manufacturing." International Journal of Lightweight Materials and Manufacture 2.4 (2019): 288-295. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Pei, et al. "The AlSi10Mg samples produced by selective laser melting: single track, densification, microstructure and mechanical behavior." Applied surface science 408 (2017): 38-50. [CrossRef]
- Ammar, H. R., A. M. Samuel, and F. H. Samuel. "Porosity and the fatigue behavior of hypoeutectic and hypereutectic aluminum–silicon casting alloys." International journal of Fatigue 30.6 (2008): 1024-1035. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Wenhui, et al. "Influence of re-melting on surface roughness and porosity of AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by selective laser melting." Journal of Alloys and Compounds 792 (2019): 574-581. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Tao, et al. "Effect of processing parameters on overhanging surface roughness during laser powder bed fusion of AlSi10Mg." Journal of Manufacturing Processes 61 (2021): 440-453. [CrossRef]
- Boschetto, Alberto, Luana Bottini, and Francesco Veniali. "Roughness modeling of AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by selective laser melting." Journal of Materials Processing Technology 241 (2017): 154-163. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Tao, et al. "The influence of process parameters on vertical surface roughness of the AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by selective laser melting." Journal of Materials Processing Technology 266 (2019): 26-36. [CrossRef]
- Read, Noriko, et al. "Selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg alloy: Process optimisation and mechanical properties development." Materials & Design (1980-2015) 65 (2015): 417-424. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Lin-zhi, Sen Wang, and Jiao-jiao Wu. "Experimental investigation on densification behavior and surface roughness of AlSi10Mg powders produced by selective laser melting." Optics & Laser Technology 96 (2017): 88-96. [CrossRef]
- Han, Xuesong, et al. "Investigation on selective laser melting AlSi10Mg cellular lattice strut: Molten pool morphology, surface roughness and dimensional accuracy." Materials 11.3 (2018): 392. [CrossRef]
- Li, Bao-Qiang, et al. "Research on surface roughness of AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by laser powder bed fusion." Metals 8.7 (2018): 524. [CrossRef]
- Zyguła, Krystian, et al. "Mechanical properties and microstructure of AlSi10Mg alloy obtained by casting and SLM technique." World Scientific News 104 (2018): 456-466.
- Maleki, Erfan, Sara Bagherifard, and Mario Guagliano. "Correlation of residual stress, hardness and surface roughness with crack initiation and fatigue strength of surface treated additive manufactured AlSi10Mg: Experimental and machine learning approaches." Journal of Materials Research and Technology 24 (2023): 3265-3283. [CrossRef]
- Schneller, Wolfgang, et al. "Effect of post treatment on the microstructure, surface roughness and residual stress regarding the fatigue strength of selectively laser melted AlSi10Mg structures." Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 3.4 (2019): 89. [CrossRef]
- Yadroitsev, I.; Bertrand, Ph.; Antonenkova, G.; Grigoriev, S.; Smurov, I. Use of track/layer morphology to develop functional parts by selectivelaser melting. J. Laser Appl. 2013, 25, 052003 (Publons 55). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, Francesco, et al. "On the selective laser melting (SLM) of the AlSi10Mg alloy: process, microstructure, and mechanical properties." Materials 10.1 (2017): 76. [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, Nesma T., et al. "The microstructure and mechanical properties of selectively laser melted AlSi10Mg: The effect of a conventional T6-like heat treatment." Materials Science and Engineering: A 667 (2016): 139-146. [CrossRef]
- Patakham, U., et al. "MPB characteristics and Si morphologies on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of SLM AlSi10Mg." Materials Science and Engineering: A 821 (2021): 141602. [CrossRef]
- E.V. Shelekhov, T.A. Sviridova. Programs for X-rayanalysis of polycrystals, Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 42 (2000)309–313. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- S. Grazulis, D.S. Grazulis, D. Chateigner. Crystallography open database an open-accesscollection of crystal structures, J. Appl. Cryst. 2009; 42 (2009), 726–729. [Google Scholar]
- Kashyap, Anil, ed. Dynamic stochastic models from empirical data. Academic Press, 1976.
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality. Biom. Trust 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Agostino, Ralph B.; Pearson, E. S. (1973). "Tests for Departure from Normality. Empirical Results for the Distributions of b2 and √b1". Biometrika. 60 (3): 613–622.
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Sulla determinazione empirica di une legge di distribuzione. G. Ist. Ital. Attuari 1933, 4, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- W. Anderson, On the Distribution of the Two-Sample Cramer-von Mises Criterion// Ann. Math. Statist. 33(3): 1148-1159 (September, 1962).
- Smirnov, A.; Nikitin, N.; Peretyagin, P.; Khmyrov, R.; Kuznetsova, E.; Solis Pinargote, N.W. Experimental and Statistical Modeling for Effect of Nozzle Diameter, Filling Pattern, and Layer Height of FDM-Printed Ceramic–Polymer Green Body on Biaxial Flexural Strength of Sintered Alumina Ceramic. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorodumov, S.V.; Neganov, D.A.; Studenov, E.P.; Poshibaev, P.V.; Nikitin, N.Y. Statistical analysis of mechanical test results for samples of pipes from trunk oil pipelines after long-term operation. Industr. Lab. Diagn. Mater. 2022, 88, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, Henry B., and Donald R. Whitney. "On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other." The annals of mathematical statistics (1947): 50-60.
- Bannykh, I.O. , Sevostyanov M.A., Prutskov M.E. Investigation of heat treatment effect on mechanical properties and structure of high-nitrogen austenitic steel 02Kh20AG10N4MFB. Russian Metallurgy (Metally) volume 4(2016), pp. 39-44.
- Benstock, Daniel, and Frederic Cegla. "Extreme value analysis (EVA) of inspection data and its uncertainties." Ndt & E international 87 (2017): 68-77.
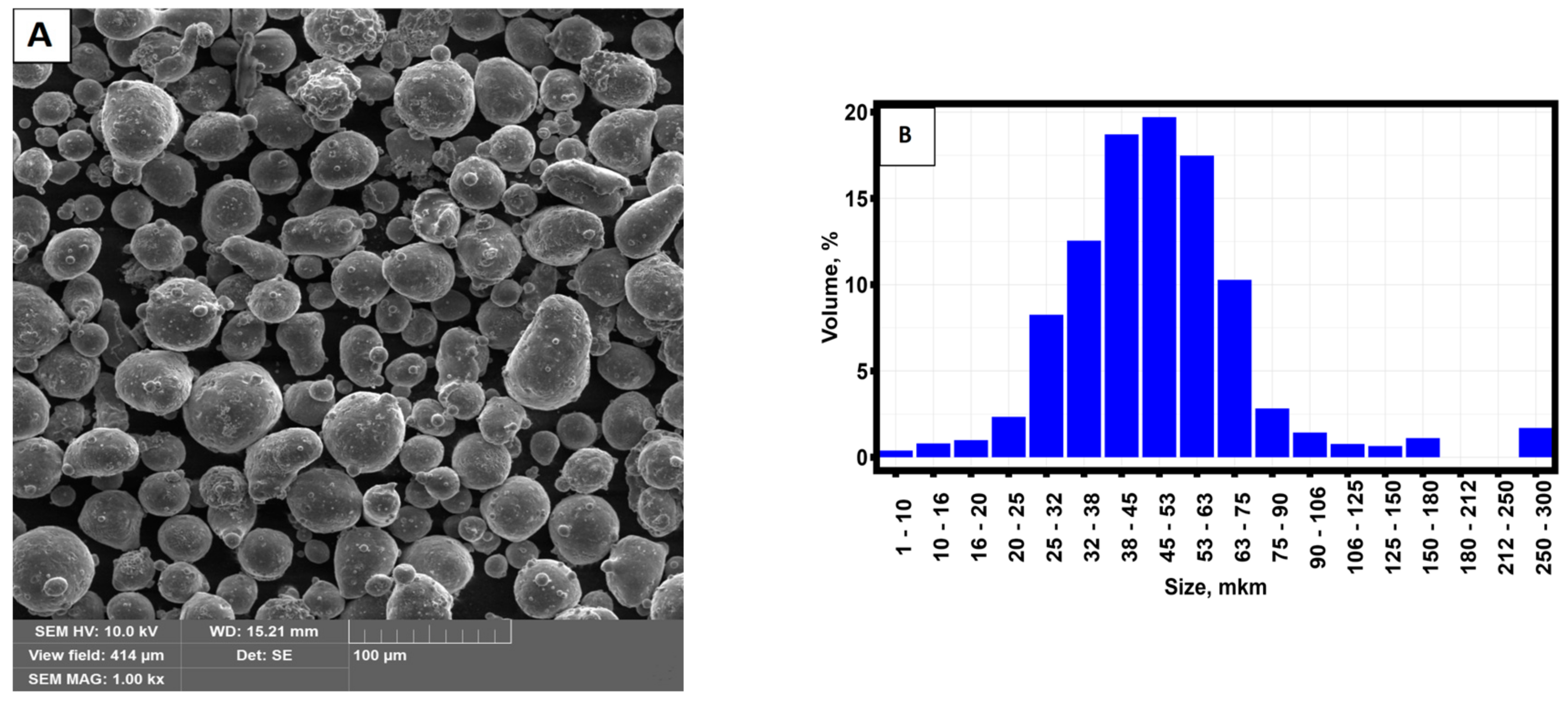
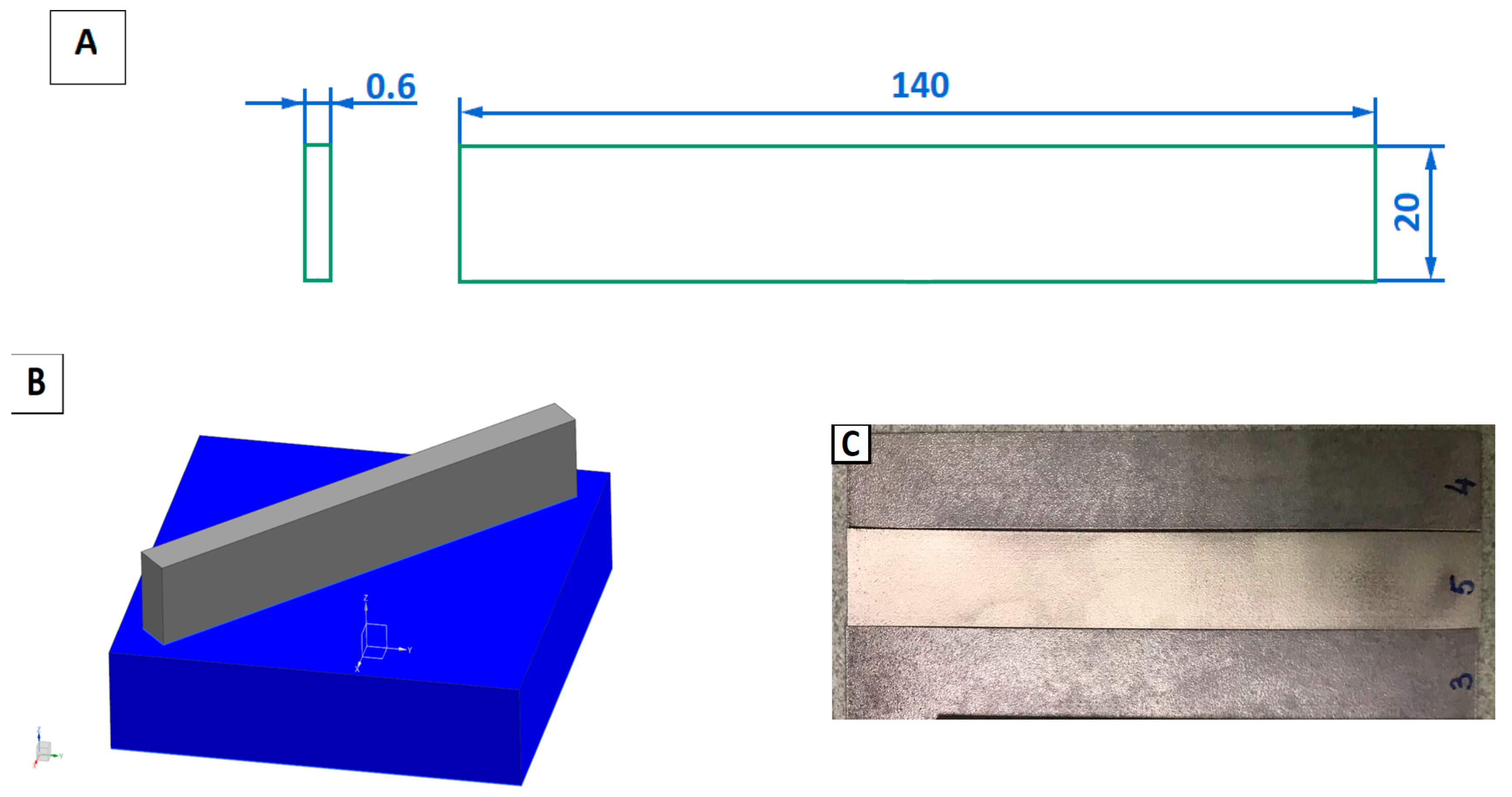
| Elements | Al | Si | Mg | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (wt %) | 88.1850 | 9.9550 | 0.3275 | 1.5325 |
| No samples | Annealing temperature, °С | Ra, µm | Rz, µm | Rmax, µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 4,208 | 33,040 | 41,141 |
| 2 | 20 | 5,996 | 49,628 | 63,651 |
| 3 | 20 | 7,340 | 54,939 | 93,837 |
| 4 | 20 | 6,569 | 44,376 | 47,602 |
| 5 | 20 | 4,939 | 44,248 | 52,086 |
| 6 | 20 | 5,773 | 42,879 | 48,261 |
| 1 | 260 | 6,578 | 40,366 | 47,733 |
| 2 | 260 | 5,568 | 46,201 | 50,272 |
| 3 | 260 | 7,009 | 53,217 | 69,349 |
| 4 | 260 | 6,175 | 57,088 | 67,814 |
| 5 | 260 | 5,188 | 41,231 | 63,253 |
| 6 | 260 | 6,616 | 42,818 | 55,988 |
| 1 | 290 | 6,227 | 43,522 | 56,607 |
| 2 | 290 | 4,890 | 43,501 | 62,743 |
| 3 | 290 | 6,042 | 48,215 | 59,128 |
| 4 | 290 | 5,632 | 43,301 | 63,093 |
| 5 | 290 | 5,307 | 38,282 | 56,144 |
| 6 | 290 | 6,106 | 47,990 | 61,618 |
| 1 | 320 | 5,258 | 45,442 | 59,432 |
| 2 | 320 | 5,509 | 40,011 | 50,797 |
| 3 | 320 | 5,137 | 40,503 | 49,863 |
| 4 | 320 | 5,704 | 47,719 | 54,580 |
| 5 | 320 | 6,063 | 45,255 | 54,490 |
| 6 | 320 | 4,721 | 41,693 | 59,186 |
| 1 | 350 | 4,949 | 33,899 | 47,363 |
| 2 | 350 | 4,340 | 38,783 | 46,409 |
| 3 | 350 | 5,909 | 39,543 | 47,841 |
| 4 | 350 | 7,470 | 48,722 | 62,929 |
| 5 | 350 | 5,351 | 43,755 | 47,505 |
| 6 | 350 | 6,051 | 45,896 | 62,821 |
| 1 | 380 | 5,147 | 44,567 | 58,023 |
| 2 | 380 | 5,685 | 45,664 | 58,818 |
| 3 | 380 | 5,858 | 41,558 | 50,893 |
| 4 | 380 | 5,859 | 44,367 | 53,910 |
| 5 | 380 | 5,977 | 46,287 | 57,900 |
| 6 | 380 | 6,354 | 42,925 | 59,778 |
| 1 | 410 | 4,659 | 33,058 | 36,935 |
| 2 | 410 | 5,223 | 38,778 | 49,032 |
| 3 | 410 | 6,045 | 44,076 | 51,182 |
| 4 | 410 | 4,886 | 39,830 | 64,734 |
| 5 | 410 | 6,471 | 43,348 | 55,387 |
| 6 | 410 | 5,874 | 44,498 | 51,197 |
| 1 | 440 | 5,773 | 42,879 | 48,261 |
| 2 | 440 | 5,245 | 38,904 | 56,476 |
| 3 | 440 | 5,261 | 44,417 | 56,988 |
| 4 | 440 | 5,688 | 38,412 | 47,601 |
| 5 | 440 | 7,698 | 50,192 | 59,783 |
| 6 | 440 | 5,668 | 39,901 | 57,787 |
| Statistical parameter | Annealing temperature, °С | Ra, µm | Rz, µm | Rmax, µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value, µm | 20 | 5.804 | 44.852 | 57.763 |
| Median, µm | 5.885 | 44.312 | 50.174 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 1.121 | 7.329 | 19.173 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 7.34 | 54.939 | 93.837 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 4.208 | 33.04 | 41.141 | |
| Mean value, µm | 260 | 6.189 | 46.820 | 59.068 |
| Median, µm | 6.377 | 44.510 | 59.621 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 0.692 | 6.865 | 9.111 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 7.009 | 57.088 | 69.349 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 5.188 | 40.366 | 47.733 | |
| Mean value, µm | 290 | 5.701 | 44.135 | 59.889 |
| Median, µm | 5.837 | 43.511 | 60.373 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 0.524 | 3.667 | 3.059 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 6.227 | 48.215 | 63.093 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 4.89 | 38.282 | 56.144 | |
| Mean value, µm | 320 | 5.399 | 43.437 | 54.725 |
| Median, µm | 5.384 | 43.474 | 54.535 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 0.468 | 3.132 | 4.030 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 6.063 | 47.719 | 59.432 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 4.721 | 40.011 | 49.863 | |
| Mean value, µm | 350 | 5.678 | 41.766 | 52.478 |
| Median, µm | 5.63 | 41.649 | 47.673 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 1.080 | 5.388 | 8.068 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 7.47 | 48.722 | 62.929 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 4.34 | 33.899 | 46.409 | |
| Mean value, µm | 380 | 5.813 | 44.228 | 56.554 |
| Median, µm | 5.859 | 44.467 | 57.962 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 0.396 | 1.747 | 3.421 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 6.354 | 46.287 | 59.778 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 5.147 | 41.558 | 50.893 | |
| Mean value, µm | 410 | 5.526 | 40.598 | 51.411 |
| Median, µm | 5.549 | 41.589 | 51.190 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 0.712 | 4.373 | 9.040 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 6.471 | 44.498 | 64.734 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 4.659 | 33.058 | 36.935 | |
| Mean value, µm | 440 | 5.889 | 42.451 | 54.483 |
| Median, µm | 5.678 | 41.39 | 56.732 | |
| Standard deviation, µm | 0.915 | 4.458 | 5.202 | |
| Maximum value, µm | 7.698 | 50.192 | 59.783 | |
| Minimum value, µm | 5.245 | 38.412 | 47.601 |
| No samples | Annealing temperature, °С | σ0.2, MPa | σU, MPa | ε0.2,% | εU,% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 191.948 | 308.964 | 1.173 | 4.998 |
| 2 | 20 | 198.216 | 310.750 | 1.129 | 4.478 |
| 3 | 20 | 194.706 | 313.314 | 0.936 | 4.406 |
| 4 | 20 | 192.044 | 314.810 | 0.928 | 4.988 |
| 5 | 20 | 198.825 | 326.616 | 1.057 | 5.222 |
| 6 | 20 | 200.728 | 327.219 | 0.824 | 4.653 |
| 1 | 260 | 245.334 | 328.600 | 1.036 | 3.136 |
| 2 | 260 | 245.452 | 334.828 | 1.308 | 3.919 |
| 3 | 260 | 247.062 | 328.213 | 1.095 | 3.261 |
| 4 | 260 | 252.070 | 321.049 | 1.169 | 2.735 |
| 5 | 260 | 248.233 | 327.996 | 1.095 | 3.170 |
| 6 | 260 | 253.389 | 334.916 | 0.996 | 2.981 |
| 1 | 290 | 257.103 | 333.964 | 1.383 | 3.406 |
| 2 | 290 | 254.805 | 334.178 | 0.986 | 2.791 |
| 3 | 290 | 257.494 | 341.998 | 0.912 | 2.903 |
| 4 | 290 | 247.495 | 328.838 | 0.922 | 2.879 |
| 5 | 290 | 237.288 | 316.883 | 0.931 | 3.025 |
| 6 | 290 | 253.389 | 322.998 | 0.996 | 2.862 |
| 1 | 320 | 207.151 | 294.796 | 0.869 | 3.175 |
| 2 | 320 | 208.406 | 293.716 | 0.868 | 3.074 |
| 3 | 320 | 204.945 | 296.520 | 0.888 | 3.706 |
| 4 | 320 | 206.205 | 298.721 | 0.862 | 3.776 |
| 5 | 320 | 209.819 | 298.073 | 0.845 | 3.136 |
| 6 | 320 | 208.615 | 301.139 | 0.805 | 3.343 |
| 1 | 350 | 197.684 | 283.684 | 0.749 | 2.640 |
| 2 | 350 | 188.093 | 288.349 | 0.631 | 3.194 |
| 3 | 350 | 204.146 | 301.434 | 0.831 | 3.839 |
| 4 | 350 | 203.145 | 288.471 | 0.975 | 3.559 |
| 5 | 350 | 193.197 | 294.468 | 0.715 | 3.710 |
| 6 | 350 | 198.387 | 293.003 | 0.875 | 3.666 |
| 1 | 380 | 154.363 | 235.000 | 0.789 | 3.926 |
| 2 | 380 | 151.798 | 238.317 | 0.632 | 3.744 |
| 3 | 380 | 153.899 | 236.487 | 0.743 | 3.759 |
| 4 | 380 | 149.531 | 235.273 | 0.647 | 3.821 |
| 5 | 380 | 157.501 | 239.803 | 0.829 | 4.186 |
| 6 | 380 | 149.708 | 239.161 | 0.618 | 3.865 |
| 1 | 410 | 113.933 | 186.648 | 0.543 | 5.369 |
| 2 | 410 | 122.491 | 201.566 | 0.563 | 5.230 |
| 3 | 410 | 115.744 | 190.155 | 0.479 | 4.499 |
| 4 | 410 | 113.202 | 186.602 | 0.504 | 5.130 |
| 5 | 410 | 113.399 | 190.513 | 0.486 | 6.981 |
| 6 | 410 | 115.118 | 191.084 | 0.534 | 6.101 |
| 1 | 440 | 104.216 | 164.398 | 0.600 | 6.432 |
| 2 | 440 | 104.979 | 164.362 | 0.567 | 6.293 |
| 3 | 440 | 107.472 | 169.422 | 0.632 | 7.125 |
| 4 | 440 | 109.452 | 173.549 | 0.516 | 6.747 |
| 5 | 440 | 109.941 | 173.112 | 0.562 | 6.346 |
| 6 | 440 | 106.627 | 167.986 | 0.635 | 6.415 |
| Statistical parameter | Annealing temperature, °С | σ0.2, MPa | σU, MPa | ε0.2,% | εU,% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean value | 20 | 196.078 | 316.946 | 1.008 | 4.791 |
| Median | 196.461 | 314.062 | 0.996 | 4.821 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.713 | 7.986 | 0.134 | 0.326 | |
| Maximum value | 200.728 | 327.219 | 1.173 | 5.222 | |
| Minimum value | 191.948 | 308.964 | 0.824 | 4.406 | |
| Mean value | 260 | 248.590 | 329.267 | 1.117 | 3.200 |
| Median | 247.648 | 328.407 | 1.095 | 3.153 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.407 | 5.168 | 0.111 | 0.397 | |
| Maximum value | 253.389 | 334.916 | 1.308 | 3.919 | |
| Minimum value | 245.333 | 321.049 | 0.996 | 2.735 | |
| Mean value | 290 | 251.262 | 329.810 | 1.021 | 2.978 |
| Median | 254.097 | 331.401 | 0.958 | 2.891 | |
| Standard deviation | 7.739 | 8.937 | 0.181 | 0.223 | |
| Maximum value | 257.494 | 341.998 | 1.383 | 3.406 | |
| Minimum value | 237.288 | 316.883 | 0.911 | 2.791 | |
| Mean value | 320 | 207.524 | 297.161 | 0.856 | 3.368 |
| Median | 207.779 | 297.297 | 0.865 | 3.259 | |
| Standard deviation | 1.776 | 2.719 | 0.029 | 0.303 | |
| Maximum value | 209.819 | 301.139 | 0.888 | 3.776 | |
| Minimum value | 204.945 | 293.716 | 0.805 | 3.074 | |
| Mean value | 350 | 197.442 | 291.568 | 0.796 | 3.434 |
| Median | 198.035 | 290.737 | 0.790 | 3.612 | |
| Standard deviation | 6.064 | 6.163 | 0.123 | 0.447 | |
| Maximum value | 204.146 | 301.434 | 0.975 | 3.839 | |
| Minimum value | 188.093 | 283.684 | 0.631 | 2.640 | |
| Mean value | 380 | 152.800 | 237.340 | 0.710 | 3.884 |
| Median | 152.849 | 237.402 | 0.695 | 3.843 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.066 | 2.040 | 0.090 | 0.163 | |
| Maximum value | 157.501 | 239.803 | 0.829 | 4.186 | |
| Minimum value | 149.531 | 235 | 0.618 | 3.744 | |
| Mean value | 410 | 115.648 | 191.095 | 0.518 | 5.552 |
| Median | 114.525 | 190.334 | 0.519 | 5.300 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.496 | 5.492 | 0.034 | 0.868 | |
| Maximum value | 122.491 | 201.566 | 0.563 | 6.981 | |
| Minimum value | 113.202 | 186.602 | 0.479 | 4.499 | |
| Mean value | 440 | 107.115 | 168.805 | 0.585 | 6.560 |
| Median | 107.050 | 168.704 | 0.584 | 6.424 | |
| Standard deviation | 2.314 | 4.032 | 0.046 | 0.319 | |
| Maximum value | 109.941 | 173.549 | 0.635 | 7.125 | |
| Minimum value | 104.216 | 164.362 | 0.516 | 6.293 |
| Physical parameter | Closest type of distribution |
|---|---|
| σ0.2 [MPa] | Weibull |
| σU [MPa] | Weibull |
| ε0.2,% | Weibull |
| εU,% | Weibull |
| Ra, µm | Log-normal |
| Rz, µm | Logistical |
| Rmax, µm | Logistical |
| Kolmogorov - Smirnov statistics | σ0.2, MPa | σU, MPa | ε0.2,% | εU,% | Ra, µm | Rz, µm | Rmax, µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | 1 | 1 | 0.68409 | 0.99585 | 0.99999 | 1 | 1 |
| p-value | < 2.2✕ 10-16 | 8,9✕ 10-16 | < 2.2✕ 10-16 | 8,9✕ 10-16 | < 2.2✕ 10-16 | < 2.2✕ 10-16 | < 2.2✕ 10-16 |
| Investigated quantity | Statistical significance level by Kruskal-Wallis test |
|---|---|
| σ0,2 [MPa] | 1.18✕10-7 |
| σU [MPa] | 1.44✕10-7 |
| ε0,2,% | 9.89✕10-7 |
| εU,% | 9.95✕10-7 |
| Ra, µm | 0.72 |
| Rz, µm | 0.67 |
| Rmax, µm | 0.43 |
| Annealing temperature pairs | Results of applying the Mann-Whitney criterion for mechanical properties of samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ0.2, MPa | σU, MPa | ε0.2,% | εU,% | |
| 20 – 260 | 0.002165 | 0.008658 | 0.3095 | 0.002165 |
| 20 – 290 | 0.002165 | 0.02597 | 0.8182 | 0.002165 |
| 20 – 350 | 0.6991 | 0.002165 | 0.04113 | 0.002165 |
| 260 – 290 | 0.1994 | 0.9372 | 0.07765 | 0.3095 |
| 260 – 320 | 0.002165 | 0.002165 | 0.002165 | 0.3939 |
| 260 – 350 | 0.002165 | 0.002165 | 0.002165 | 0.3939 |
| 290 – 350 | 0.002165 | 0.002165 | 0.01515 | 0.09307 |
| 320 – 350 | 0.002165 | 0.09307 | 0.3939 | 0.5887 |
| 350 – 380 | 0.002165 | 0.002165 | 0.2403 | 0.01515 |
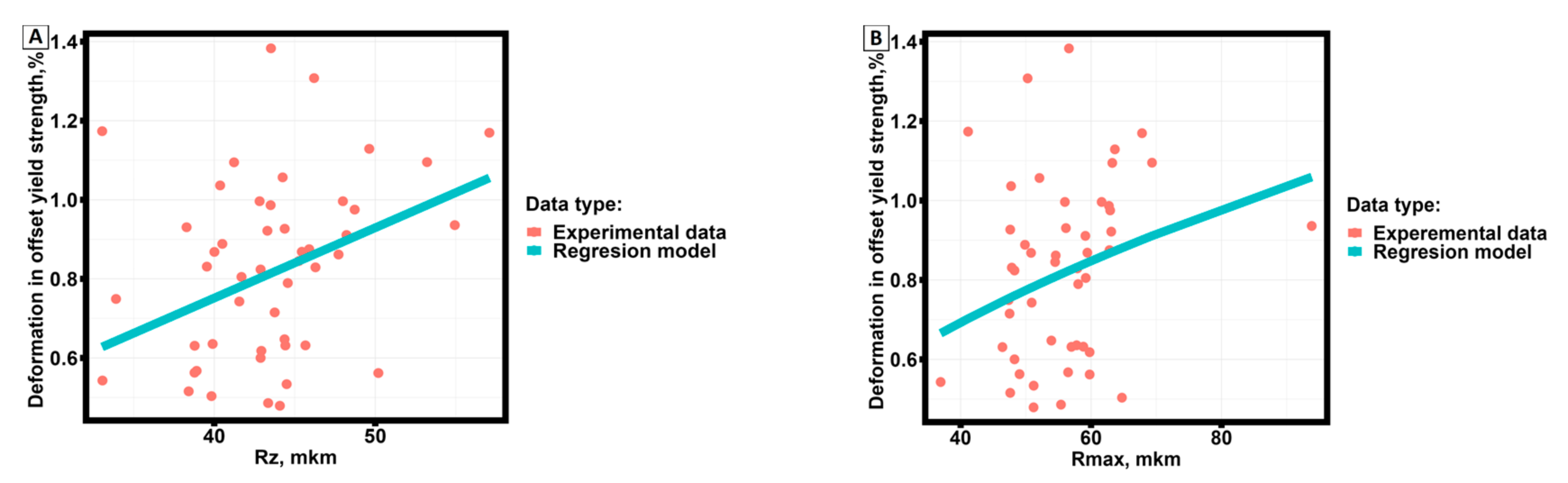
| Pairs examined for correlation | Kendall correlation coefficient | Statistical significance level | Determination coefficient, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| σ0.2 – Ra | 0.2822 | 0.3282 | -- |
| σU – Ra | 0.1073171 | 0.2822 | -- |
| ε0,2,% - Ra | 0.1259982 | 0.2069 | -- |
| εU, % - Ra | 0.09760426 | 0.3282 | -- |
| σ0.2 – Rz | 0.1774623 | 0.07545 | -- |
| σU – Rz | 0.1676275 | 0.09298 | -- |
| ε0,2,% - Rz | 0.2342502 | 0.01894 | 5.5 |
| εU, % - Rz | -0.06829269 | 0.4937 | -- |
| σ0.2 – Rmax | 0.1792369 | 0.07257 | -- |
| σU – Rmax | 0.1268293 | 0.2037 | -- |
| ε0.2,% - Rmax | 0.2040816 | 0.04091 | 4.2 |
| εU, % - Rmax | -0.1764967 | 0.07693 | -- |
| Correlation values | Equations | Standard deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ε0,2 | Rz | 0.1812 | |
| Rmax | 0.2347 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





