Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
19 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Analysis of the Extracted Data
2.6. Search Results
3. Results
3.1. Titanium oxide
3.1.1. Photocatalytic Generation of ROS
3.1.2. Morphology and Topography of Surface
3.1.3. Thickness of the Coatings
3.1.4. Crystalline Structure of the Coatings
3.1.5. Precursors and ALD Temperature
3.1.6. Effect of Coatings on Different Strains
3.2. Doped TiO2 and Combined TiO2
3.3. Zinc Oxide
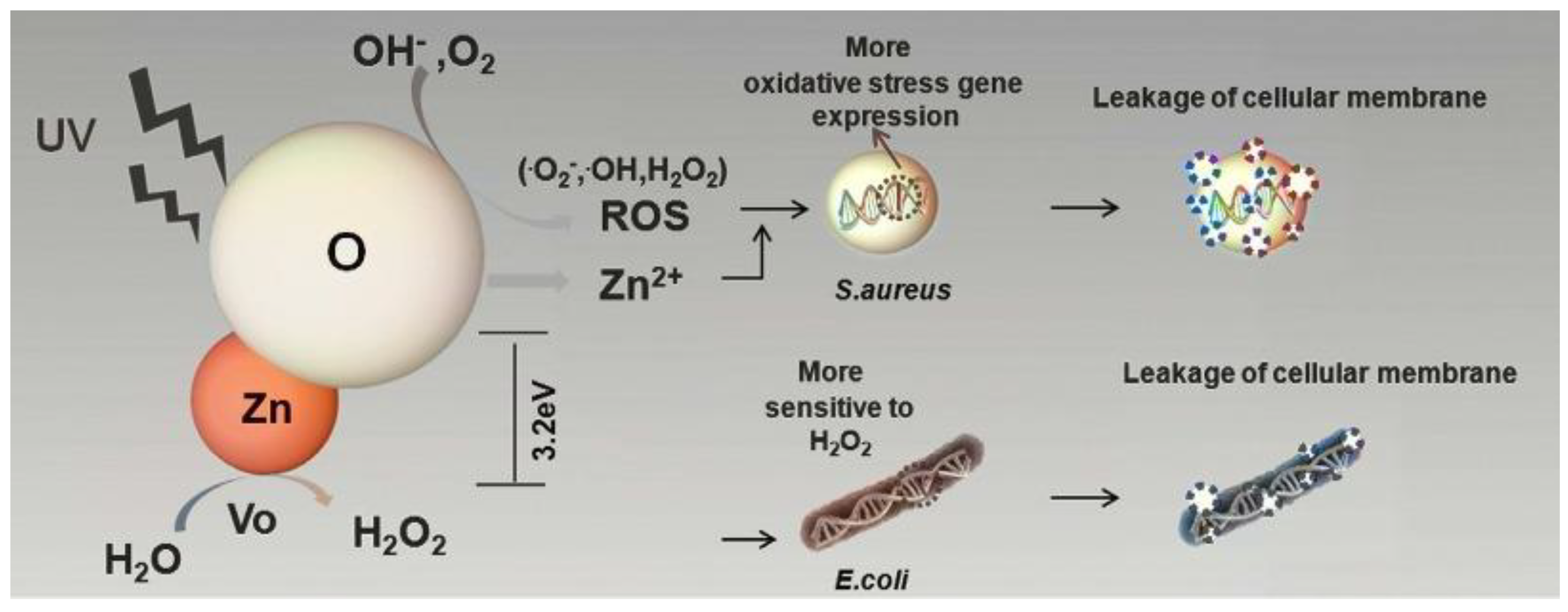
3.3.1. Mechanisms of ZnO Bactericidal Effect and Their Role
3.3.2. The Effect of Thickness
3.3.3. The Effect of the Deposition Temperature
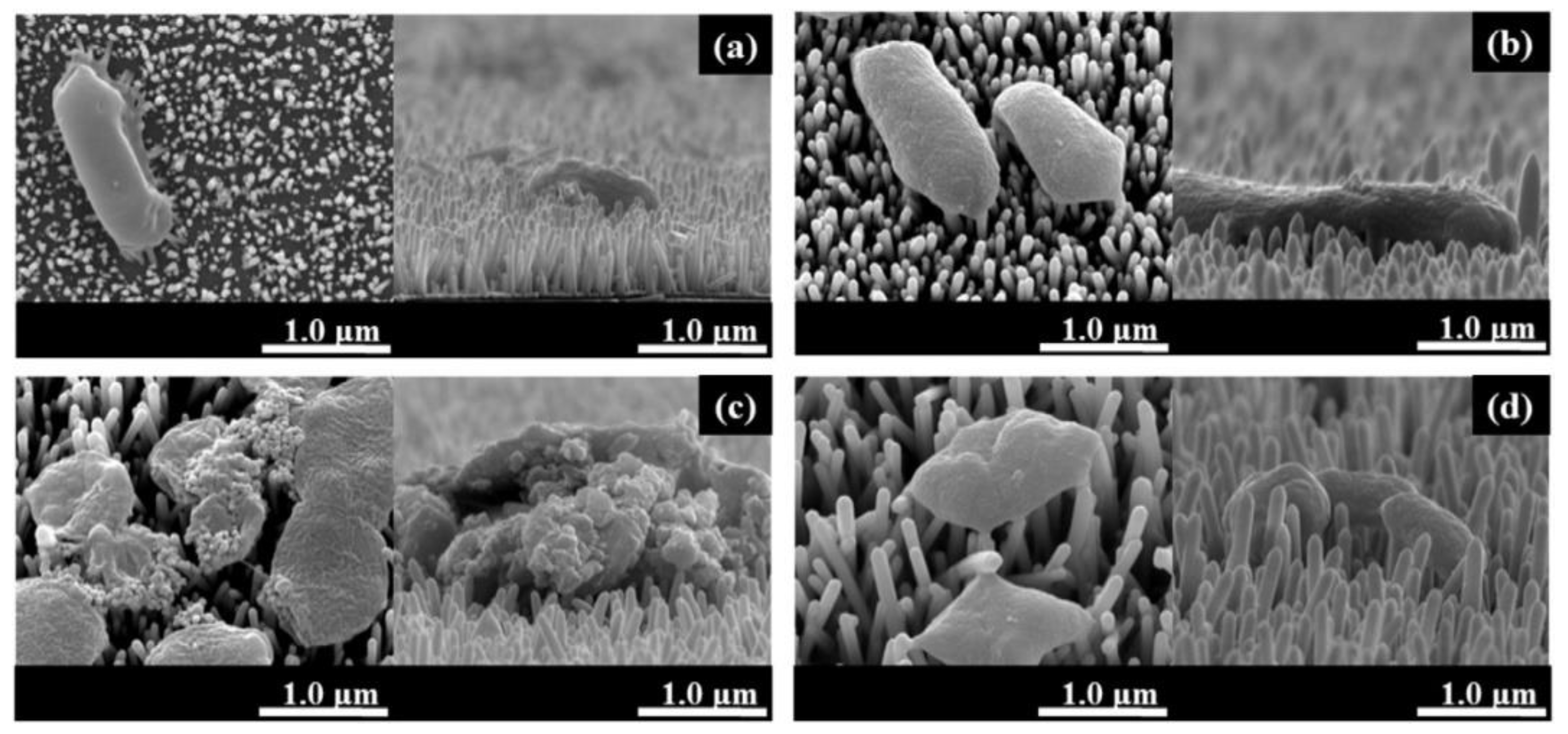
3.3.4. The Effect of the Morphology, Topography and Wettability
3.3.5. Effects on Various Types of Bacteria and Viruses
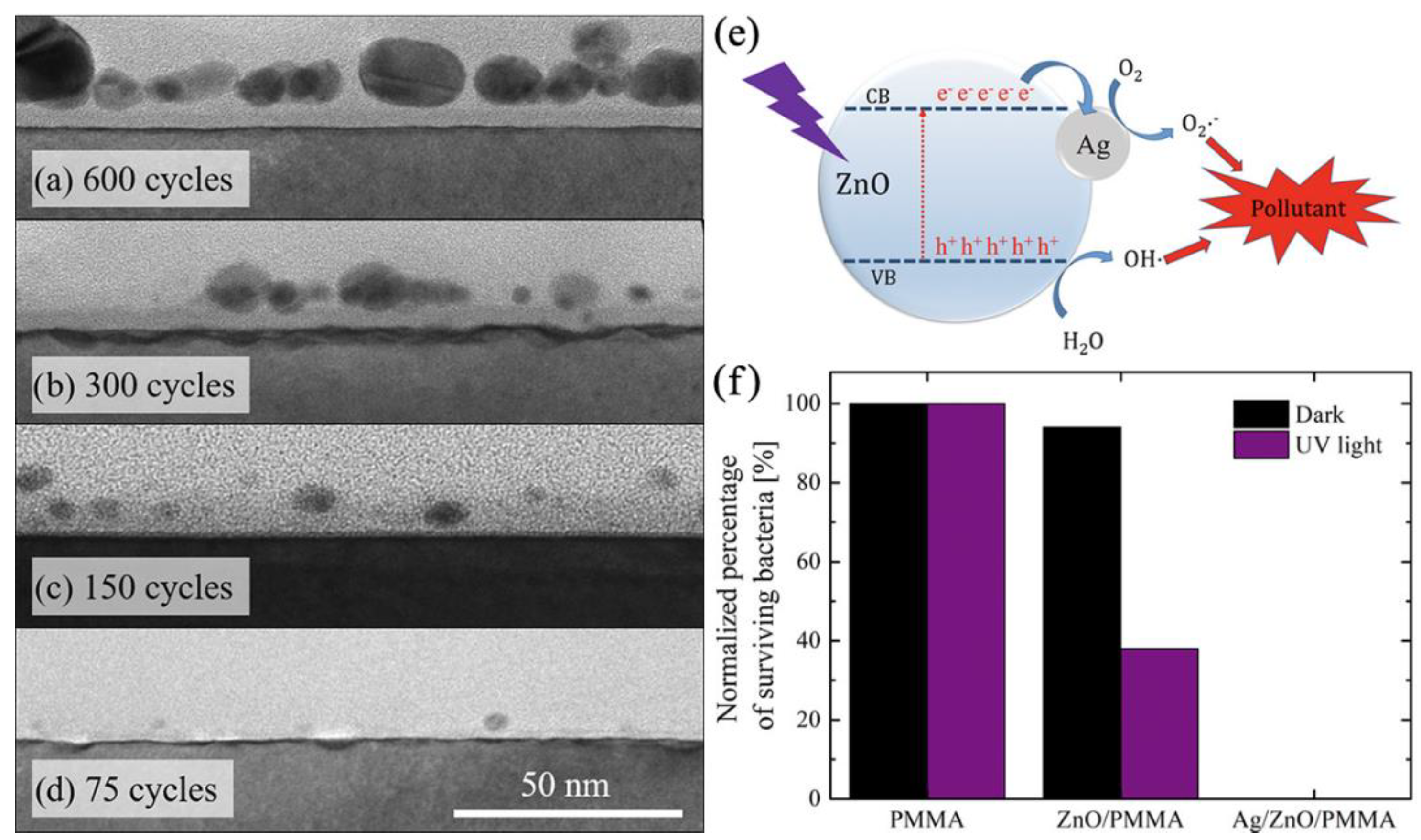
3.4. ZnO Based Nanocomposites and Nanolaminates
3.5. Other Compounds
3.6. Silver and Other Metals
3.6.1. ALD of Silver Nanoparticles and Nanocotings
3.6.2. ALD of Other Metallic Nanocotings
4. Applications for ALD Antibacterial Coatings
4.1. Medical Implants
4.2. Antibacterial Textile and Personal Protective Equipment
4.3. Purification and Disinfection of Water and Air
4.4.Оther Application
5. Analysis of the Results
5.1. Comparison of Different Antibacterial Coatings
5.2. Advantages, Disadvantages and Perspectives of ALD
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elbourne, A.; Crawford, R.J.; Ivanova, E.P. Nano-structured antimicrobial surfaces: From nature to synthetic analogues. J Colloid Interface Sci 2017, 508, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modaresifar, K.; Azizian, S.; Ganjian, M.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.E.; Zadpoor, A.A. Bactericidal effects of nanopatterns: A systematic review. Acta Biomater 2019, 83, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, T.; Heath, D.E.; O'Brien-Simpson, N.M.; O'Connor, A.J. Antimicrobial nanoparticle coatings for medical implants: Design challenges and prospects. Biointerphases 2020, 15, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, S.M.; Ladouceur, L.; Marshall, T.; Maclachlan, R.; Soleymani, L.; Didar, T.F. Antimicrobial Nanomaterials and Coatings: Current Mechanisms and Future Perspectives to Control the Spread of Viruses Including SARS-CoV-2. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12341–12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirvanimoghaddam, K.; Akbari, M.K.; Yadav, R.; Al-Tamimi, A.K.; Naebe, M. Fight against COVID-19: The case of antiviral surfaces. APL Mater 2021, 9, 031112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshaya, S.; Rowlo, P.K.; Dukle, A.; Nathanael, A.J. Antibacterial Coatings for Titanium Implants: Recent Trends and Future Perspectives. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouirfa, H.; Bouloussa, H.; Migonney, V.; Falentin-Daudre, C. Review of titanium surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater 2019, 83, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyikli, N.; Haider, A. Atomic layer deposition: an enabling technology for the growth of functional nanoscale semiconductors. Semiconductor Science and Technology 2017, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-J.; Wu, X. Superior Atomic Layer Deposition Technology for Amorphous Oxide Semiconductor Thin-Film Transistor Memory Devices. Chemistry of Materials 2020, 32, 1343–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshtyal, Y.; Olkhovskii, D.; Rumyantsev, A.; Maximov, M. Applications and Advantages of Atomic Layer Deposition for Lithium-Ion Batteries Cathodes: Review. Batteries 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Xia, C.; Alshareef, H.N. Electrode surface engineering by atomic layer deposition: A promising pathway toward better energy storage. Nano Today 2016, 11, 250–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graniel, O.; Weber, M.; Balme, S.; Miele, P.; Bechelany, M. Atomic layer deposition for biosensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 122, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Akbari, M.K.; Kumar, S.; Verpoort, F.; Zhuiykov, S. Atomic layer deposition – state-of-the-art approach to nanoscale hetero-interfacial engineering of chemical sensors electrodes: A review. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2021, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qin, Y. Interface Tailoring of Heterogeneous Catalysts by Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Catalysis 2018, 8, 10064–10081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswar, N.K.R.; Singh, S.A.; Heo, J. Atomic layer deposited photocatalysts: comprehensive review on viable fabrication routes and reactor design approaches for photo-mediated redox reactions. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2019, 7, 17703–17734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M. Is there a reproducibility crisis in science? Nature 2016, 533, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.J. Open science, the replication crisis, and environmental public health. Account Res 2023, 30, 34–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sønsteby, H.H.; Yanguas-Gil, A.; Elam, J.W. Consistency and reproducibility in atomic layer deposition. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films 2020, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Rojas, D.; Maindron, T.; Esteve, A.; Piallat, F.; Kools, J.C.S.; Decams, J.M. Speeding up the unique assets of atomic layer deposition. Materials Today Chemistry 2019, 12, 96–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.M. Atomic Layer Deposition: An Overview. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, N.E.; de Paula, C.; Bent, S.F. Understanding chemical and physical mechanisms in atomic layer deposition. J Chem Phys 2020, 152, 040902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremers, V.; Puurunen, R.L.; Dendooven, J. Conformality in atomic layer deposition: Current status overview of analysis and modelling. Applied Physics Reviews 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, J.; Ritala, M.; Leskelä, M. Atomic Layer Deposition of Noble Metals and Their Oxides. Chemistry of Materials 2013, 26, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wack, S.; Lunca Popa, P.; Adjeroud, N.; Guillot, J.; Pistillo, B.R.; Leturcq, R. Large-Scale Deposition and Growth Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles by Plasma-Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2019, 123, 27196–27206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, D.V.; Smirnov, V.M.; Zemtsova, E.G.; Yudintceva, N.M.; Shevtsov, M.A.; Valiev, R.Z. Enhanced Osseointegrative Properties of Ultra-Fine-Grained Titanium Implants Modified by Chemical Etching and Atomic Layer Deposition. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2018, 4, 3268–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basiaga, M.; Paszenda, Z.; Lisoń, J.; Taratuta, A.; Kazek-Kęsik, A.; Krok-Borkowicz, M.; Nuckowski, P.; Szindler, M.; Staszuk, M.; Major, Ł.; et al. Microstructure and antibacterial properties of a ZnO coating on a biomaterial surface. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Poologasundarampillai, G.; Todd, N.; Devlin-Mullin, A.; Moore, K.L.; Golrokhi, Z.; Gilchrist, J.B.; Jones, E.; Potter, R.J.; Sutcliffe, C.; et al. Biotransformation of Silver Released from Nanoparticle Coated Titanium Implants Revealed in Regenerating Bone. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 21169–21180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Wang, M. Atomic layer deposition of TaN thin film on Ti–6Al–4V dental implant for enhanced anti-corrosion and anti-bacterial properties. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids 2021, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, R.S.; dos Santos, V.P.; Cardoso, S.B.; Doria, A.C.O.C.; Figueira, F.R.; Rodrigues, B.V.M.; Testoni, G.E.; Fraga, M.A.; Marciano, F.R.; Lobo, A.O.; et al. TiO2 coatings via atomic layer deposition on polyurethane and polydimethylsiloxane substrates: Properties and effects on C. albicans growth and inactivation process. Applied Surface Science 2017, 422, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.F.; Li, J.; Wu, X.B.; Li, Z.Y.; Shen, J.; Nie, J.J.; Cui, Z.D.; Chen, D.F.; Liang, Y.Q.; Zhu, S.L.; et al. ALD-induced TiO(2)/Ag nanofilm for rapid surface photodynamic ion sterilization. Rare Metals 2022, 41, 4138–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
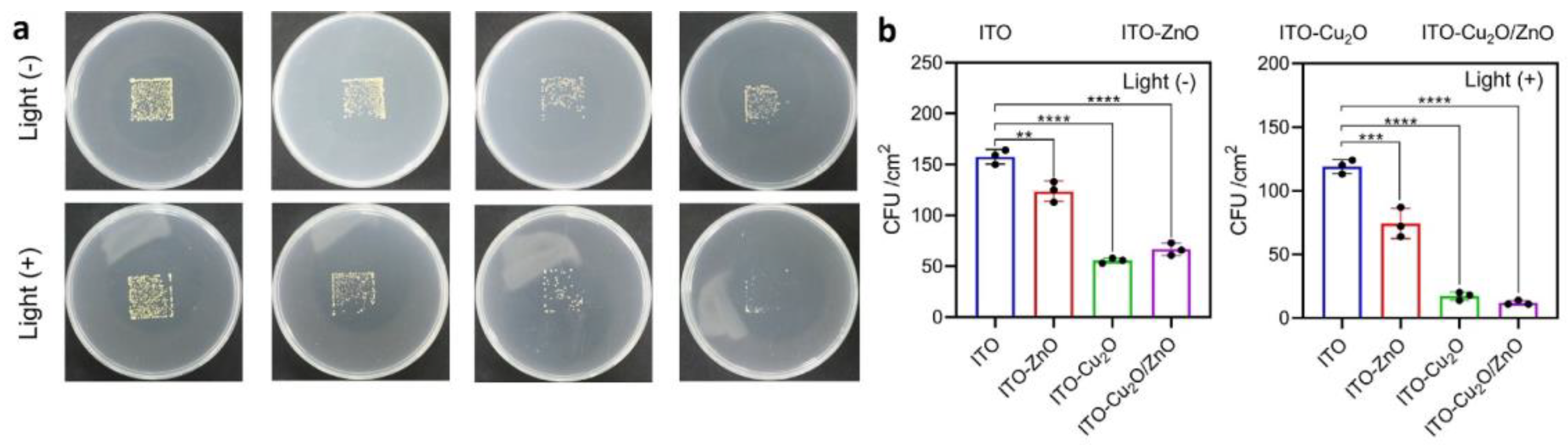
- Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, S.; Wu, S. Surface photodynamic ion sterilization of ITO-Cu2O/ZnO preventing touch infection. Journal of Materials Science & Technology 2022, 122, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.-H.; Cho, T.-Y.; Cho, S.-K. Performance of multifunctional antibacterial moisture barrier films with different Zn/Al ratios fabricated by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition. Applied Surface Science 2023, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, H.I.; Yilmaz, B.A.; Diler, S. Antibacterial Activity of Photodeposited Ag Nanoparticles on Cotton Fibers Enabled by Atomic Layer Deposition. Fibers and Polymers 2022, 23, 2769–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, B.; Lyu, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, W. Controllable coating of zinc oxide on protein-based fibers/fabrics for superior antibacterial performance preserving wearable abilities. Applied Surface Science 2023, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Fox, C.R.; Feit, C.; Kolanthai, E.; Sheiber, J.; Fu, Y.; Singh, S.; Banerjee, P.; Parks, G.D.; Seal, S. ALD based nanostructured zinc oxide coated antiviral silk fabric. RSC Adv 2022, 12, 19327–19339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puvvada, R.U.; Wooding, J.P.; Bellavia, M.C.; McGuinness, E.K.; Sulchek, T.A.; Losego, M.D. Bacterial Growth and Death on Cotton Fabrics Conformally Coated with ZnO Thin Films of Varying Thicknesses via Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD). Jom 2018, 71, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Reyes, J.; Romero-Moran, A.; Uribe-Vargas, H.; Lopez-Ruiz, B.; Sanchez-Salas, J.L.; Ortega, E.; Ponce, A.; Morales-Sanchez, A.; Lopez-Huerta, F.; Zuñiga-Islas, C. Study on the photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide nanostructures: Nanoparticles, nanotubes and ultra-thin films. Catalysis Today 2020, 341, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, A.; Farrugia, C.; Abela, S.; Refalo, P.; Grech, M.; Falqui, L.; Nicotra, G.; Sfuncia, G.; Mio, A.; Buccheri, M.A.; et al. Ag/ZnO/PMMA Nanocomposites for Efficient Water Reuse. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2020, 3, 4417–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, X.; Sun, M.; Porter, C.J.; Zhou, X.; Elimelech, M. Precisely Engineered Photoreactive Titanium Nanoarray Coating to Mitigate Biofouling in Ultrafiltration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 9975–9984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabiscol, E.; Tamarit, J.; Ros, J. Oxidative stress in bacteria and protein damage by reactive oxygen species. International Microbiology 2000, 3, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Thian, E.S.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Ren, L. Surface Design for Antibacterial Materials: From Fundamentals to Advanced Strategies. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2021, 8, e2100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gristina, A.G.; Naylor, P.; Myrvik, Q. Infections from biomaterials and implants: a race for the surface. Medical progress through technology 1988, 14, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
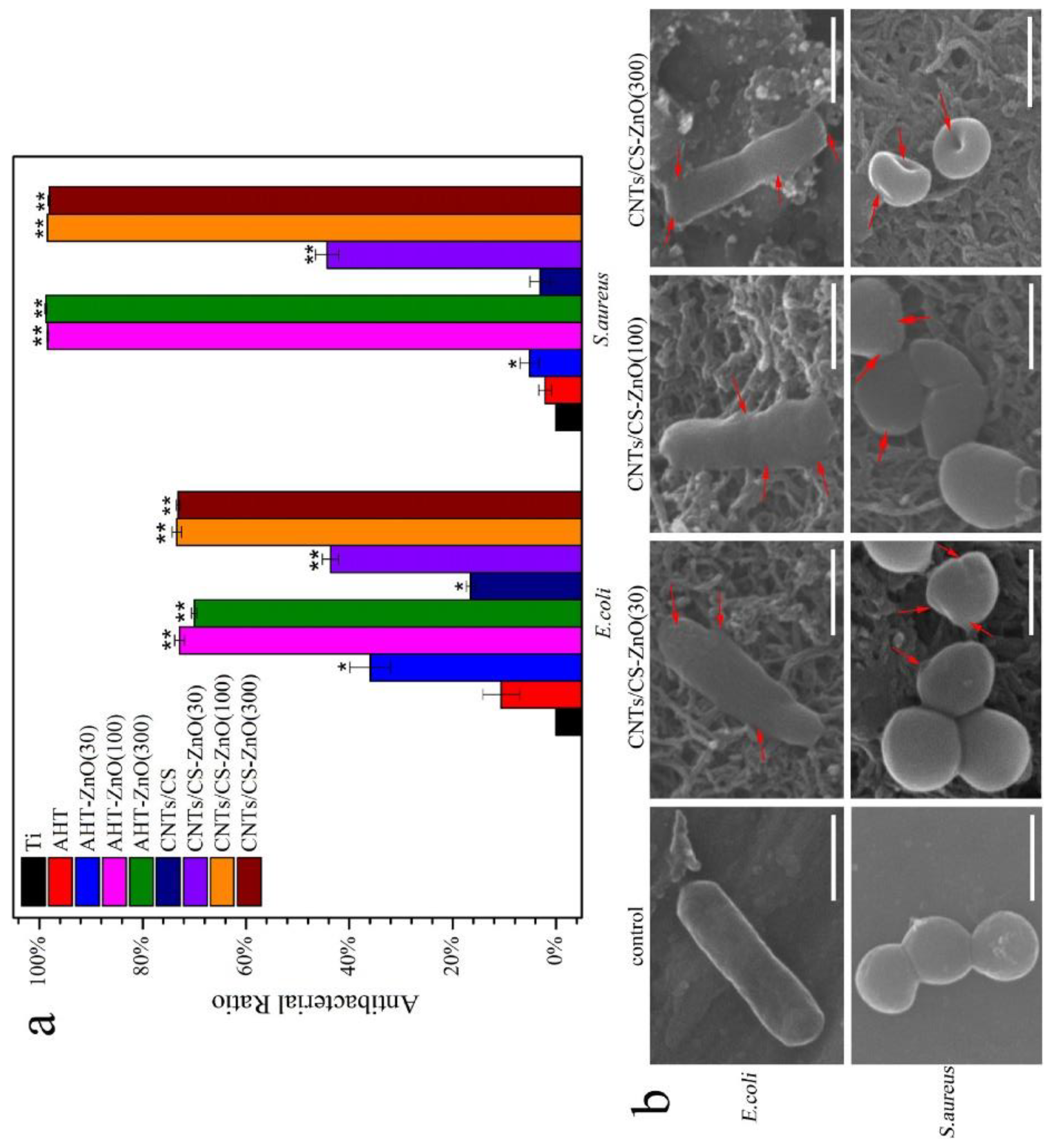
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Chu, P.K.; Wu, S. Biofunctionalization of carbon nanotubes/chitosan hybrids on Ti implants by atom layer deposited ZnO nanostructures. Applied Surface Science 2017, 400, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; XianjinYang; Yeung, K. W.K.; Pan, H.; Wu, S. Sr/ZnO doped titania nanotube array: An effective surface system with excellent osteoinductivity and self-antibacterial activity. Materials & Design 2017, 130, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Reyes, J.; Romero-Moran, A.; Sanchez-Salas, J.L. Enhanced photocatalytic bacterial inactivation of atomic-layer deposited anatase-TiO(2) thin films on rutile-TiO(2) nanotubes. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2020, 19, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Hegde, P.B.; Avasthi, S.; Sen, P. Scalable Hybrid Antibacterial Surfaces: TiO(2) Nanoparticles with Black Silicon. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7816–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuderi, V.; Buccheri, M.A.; Impellizzeri, G.; Di Mauro, A.; Rappazzo, G.; Bergum, K.; Svensson, B.G.; Privitera, V. Photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of titanium dioxide flat film. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing 2016, 42, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bhatia, R.; Webster, T.J. Atomic layer deposition of nano-TiO2 thin films with enhanced biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity for orthopedic implants. Int J Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 8711–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Jadhav, S.; Avasthi, S.; Sen, P. Designing Photocatalytic Nanostructured Antibacterial Surfaces: Why Is Black Silica Better than Black Silicon? ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 20202–20213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.J.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Brigmon, R.L.; Pellin, M.J.; Elam, J.W. Atomic Layer Deposition of TiO2 Thin Films on Nanoporous Alumina Templates: Medical Applications. JOM 2009, 61, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfinger, Y.; Natan, M.; Sukenik, C.N.; Banin, E.; Kronenberg, J. Biofilm prevention on cochlear implants. Cochlear Implants Int 2014, 15, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, G.; Huang, S.; Knoernschild, K.; Sukotjo, C.; Campbell, S.; Bishal, A.K.; Barao, V.A.; Wu, C.D.; Taukodis, C.G.; Yang, B. Improving Polymethyl Methacrylate Resin Using a Novel Titanium Dioxide Coating. J Prosthodont 2019, 28, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-M.; Grass, G.; Kim, G.-M.; Dresbach, C.; Zhang, L.; Goselea, U.; Knez, M. Low-temperature ZnO atomic layer deposition on biotemplates: flexible photocatalytic ZnO structures from eggshell membranes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2009, 11, 3608–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewski, M.; Gierałtowska, S.; Wachnicki, Ł.; Pietuszka, R.; Witkowski, B.S.; Słońska, A.; Gajewski, Z.; Godlewski, M.M. High-k oxides by atomic layer deposition—Applications in biology and medicine. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films 2017, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regonini, D.; Bowen, C.R.; Jaroenworaluck, A.; Stevens, R. A review of growth mechanism, structure and crystallinity of anodized TiO2 nanotubes. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports 2013, 74, 377–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, D.; Ezhov, I.; Yudintceva, N.; Shevtsov, M.; Rudakova, A.; Kalganov, V.; Tolmachev, V.; Zharova, Y.; Lutakov, O.; Kraeva, L.; et al. Antibacterial and Osteogenic Properties of Ag Nanoparticles and Ag/TiO(2) Nanostructures Prepared by Atomic Layer Deposition. J Funct Biomater 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyildiz, H.I.; Diler, S.; Islam, S. Evaluation of TiO2 and ZnO atomic layer deposition coated polyamide 66 fabrics for photocatalytic activity and antibacterial applications. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films 2021, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigal, I.P.; Markeev, A.M.; Gudkova, S.A.; Chernikova, A.G.; Mityaev, A.S.; Alekhin, A.P. Correlation between bioactivity and structural properties of titanium dioxide coatings grown by atomic layer deposition. Applied Surface Science 2012, 258, 3415–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, X.; Zhao, M.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Du, W.; Xiang, J.; Cheng, P.; Tang, N. Construction of precisely controllable and stable interface bonding Au-TiO2/PVDF composited membrane for biofouling-resistant properties. Surfaces and Interfaces 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, D.; Kozlova, L.; Rudakova, A.; Zemtsova, E.; Yudintceva, N.; Ovcharenko, E.; Koroleva, A.; Kasatkin, I.; Kraeva, L.; Rogacheva, E.; et al. Atomic Layer Deposition of Chlorine Containing Titanium–Zinc Oxide Nanofilms Using the Supercycle Approach. Coatings 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amashaev, R.R.; Maksumova, A.M.; Rabadanov, M.K.; Abdullaeva, N.; Abdulagatov, I.M. STUDY OF ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES OF MODIFIED TITANIUM OXIDE NANOFILMS SYNTHESIZED BY ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR LAYER DEPOSITION TECHNIQUES. New Materials, Compounds and Applications 2019, 3, 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Shahmohammadi, M.; Nagay, B.E.; Barão, V.A.R.; Sukotjo, C.; Jursich, G.; Takoudis, C.G. Atomic layer deposition of TiO2, ZrO2 and TiO2/ZrO2 mixed oxide nanofilms on PMMA for enhanced biomaterial functionalization. Applied Surface Science 2022, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Ginsburg, S.; Li, W.; Vilela, M.M.; Shahmohammadi, M.; Takoudis, C.G.; Wu, C.D. Effect of nano-ceramic coating on surface property and microbial adhesion to poly(methyl methacrylate). J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2023, 111, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemelä, J.-P.; Marin, G.; Karppinen, M. Titanium dioxide thin films by atomic layer deposition: a review. Semiconductor Science and Technology 2017, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulagatov, I.M.; Ragimov, R.M.; Khamidov capital Em, C.A.C.; Maksumova, A.M.; Abdullaeva, N.M. ALD coated polypropylene hernia meshes for prevention of mesh-related post-surgery complications: an experimental study in animals. Biomed Mater 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.-H.; Banis, M.N.; Vaccarello, D.; Ding, Z.-F.; Wang, S.-D.; Sham, T.-K. Revealing the Synergy of Mono/Bimetallic PdPt/TiO2 Heterostructure for Enhanced Photoresponse Performance. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2017, 121, 24861–24870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
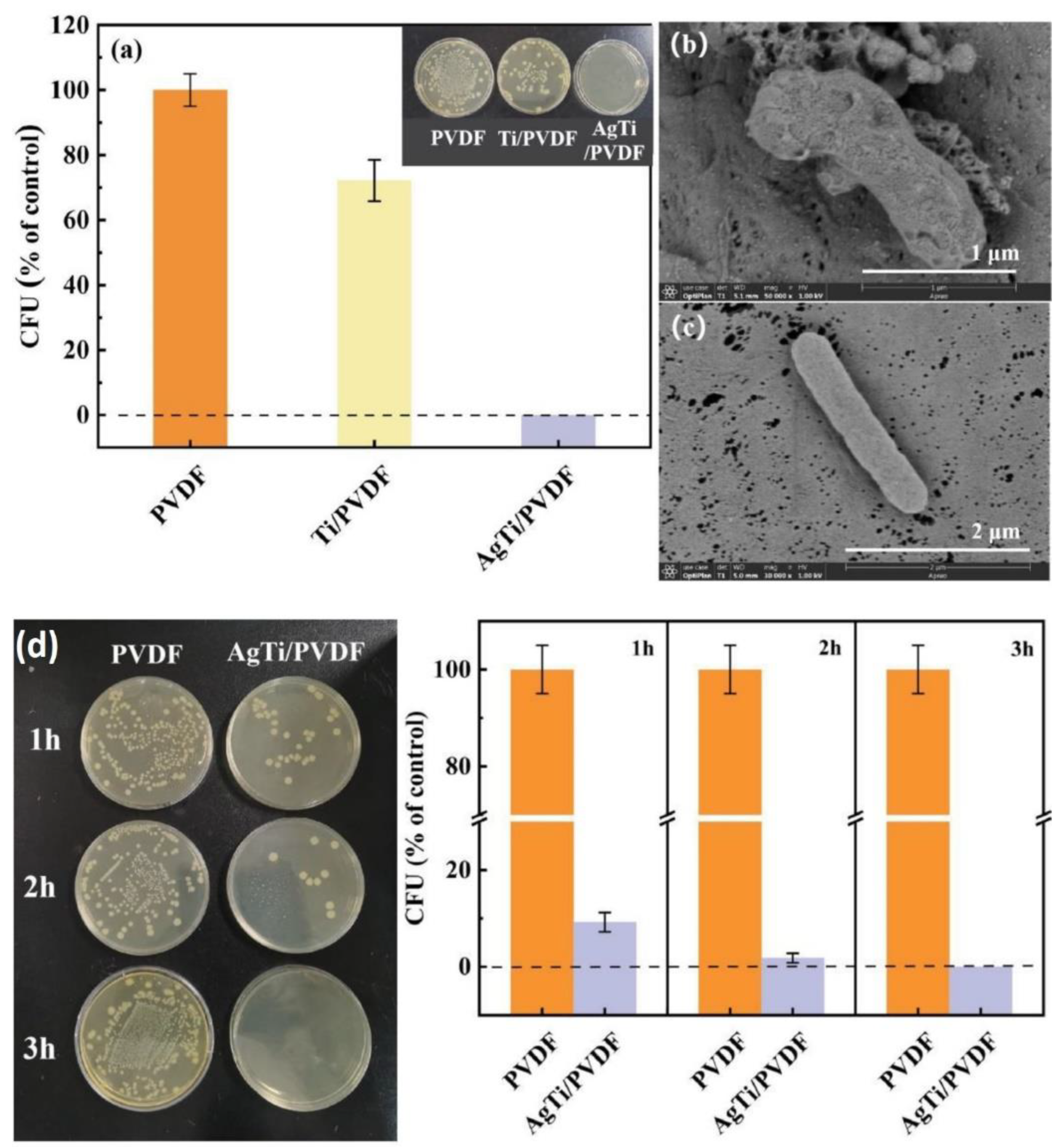
- Zhang, L.; He, D.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, P.; Tang, N. AgTi nanoparticle hybrid PVDF membrane with stable and high efficiency antibacterial performance by atomic layer deposition. Surfaces and Interfaces 2022, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopatsky, A.; Teplyakova, T.; Sheremetyev, V.; Yakimova, T.; Boychenko, O.; Kozik, M.; Shtansky, D.; Prokoshkin, S. Surface Modification of Biomedical Ti-18Zr-15Nb Alloy by Atomic Layer Deposition and Ag Nanoparticles Decoration. J Funct Biomater 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Han, G.D.; Neoh, K.C.; Kim, T.-S.; Shim, J.H.; Park, H.-D. Antibacterial activity of the thin ZnO film formed by atomic layer deposition under UV-A light. Chemical Engineering Journal 2017, 328, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääriäinen, M.L.; Weiss, C.K.; Ritz, S.; Pütz, S.; Cameron, D.C.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K. Zinc release from atomic layer deposited zinc oxide thin films and its antibacterial effect on Escherichia coli. Applied Surface Science 2013, 287, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amna, T.; Hassan, M.S.; Barakat, N.A.; Pandeya, D.R.; Hong, S.T.; Khil, M.S.; Kim, H.Y. Antibacterial activity and interaction mechanism of electrospun zinc-doped titania nanofibers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2012, 93, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, L.; Zuo, Y.; Xue, J.; Jansen, J.A. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activities of a novel nanohydroxyapatite/zinc oxide complex. J Biomed Mater Res A 2008, 85, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, T.; Wilke, C.M.; Wu, J.; Binh, C.T.; Kelly, J.J.; Gaillard, J.F.; Gray, K.A. Combined Toxicity of Nano-ZnO and Nano-TiO2: From Single- to Multinanomaterial Systems. Environ Sci Technol 2015, 49, 8113–8123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Wu, H.; Li, W.; Sun, Q. Antibacterial properties and mechanism of biopolymer-based films functionalized by CuO/ZnO nanoparticles against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Hazard Mater 2021, 402, 123542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mežnarić, S.; Jelovica Badovinac, I.; Šarić, I.; Peter, R.; Kolympadi Markovic, M.; Ambrožić, G.; Gobin, I. Superior UVA-photocatalytic antibacterial activity of a double-layer ZnO/Al2O3 thin film grown on cellulose by atomic layer deposition (ALD). Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, W.; Cheng, X. A Facile Approach to Fabricating Antibacterial Textile with High Efficiency and Compact Process. Advanced Materials Interfaces 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Xiong, S.; Rao, Y.; Low, Z.X.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Y. Atomic layer deposition of ZnO on polypropylene nonwovens for photocatalytic antibacterial facemasks. Nanotechnology 2023, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Fang, X.; Jia, H.; Liu, M.; Shi, X.; Xue, C.; Chen, T.; Wei, Z.; Fang, F.; Zhu, H.; et al. Zn or O? An Atomic Level Comparison on Antibacterial Activities of Zinc Oxides. Chemistry 2016, 22, 8053–8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, J. Atomic layer deposition of ZnO thin film on ZrO2 dental implant surface for enhanced antibacterial and bioactive performance. Materials Letters 2021, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.J.; Adiga, S.P.; Pellin, M.J.; Curtiss, L.A.; Stafslien, S.; Chisholm, B.; Monteiro-Rivierea, N.A.; Brigmon, R.L.; Elam, J.W. Atomic layer deposition of nanoporous biomaterials. Materials today 2010, 13, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vähä-Nissi, M.; Pitkänen, M.; Salo, E.; Kenttä, E.; Tanskanen, A.; Sajavaara, T.; Putkonen, M.; Sievänen, J.; Sneck, A.; Rättö, M.; et al. Antibacterial and barrier properties of oriented polymer films with ZnO thin films applied with atomic layer deposition at low temperatures. Thin Solid Films 2014, 562, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
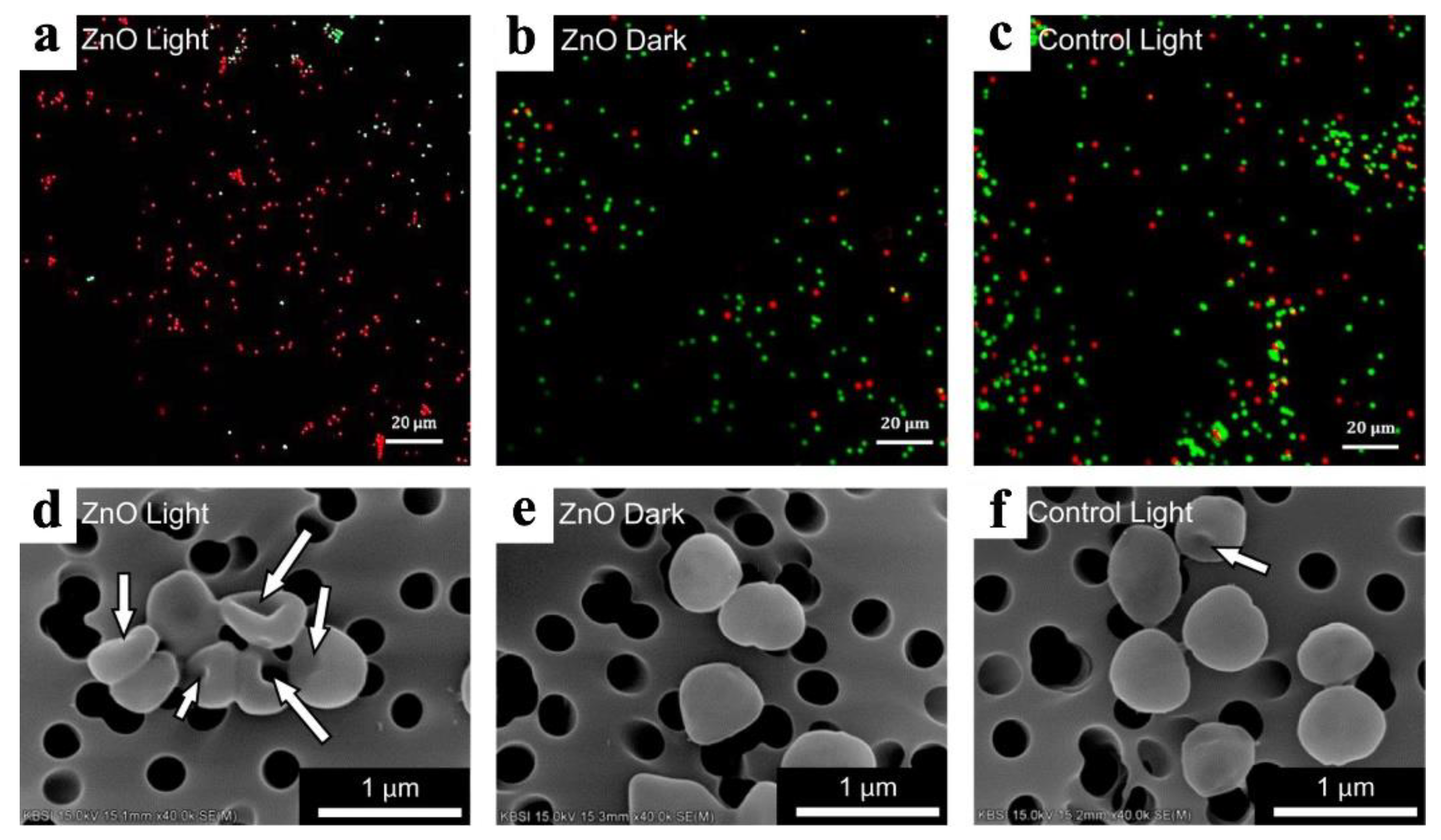
- Jeong, E.; Kim, C.U.; Byun, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, E.J.; Choi, K.J.; Hong, S.W. Quantitative evaluation of the antibacterial factors of ZnO nanorod arrays under dark conditions: Physical and chemical effects on Escherichia coli inactivation. Sci Total Environ 2020, 712, 136574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yao, L.; Al-Baadani, M.A.; Ping, L.; Wu, S.; Al-Bishari, A.M.; HiiRuYie, K.; Deng, Z.; Liu, J.; Shen, X. Preparation of multifunctional drug sustained-release system by atomic layer deposition of ZnO in mesoporous titania coating. Ceramics International 2020, 46, 9406–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.C.; Ungureanu, C.; Buse, E.; Nastase, F.; Tucureanu, V.; Suchea, M.; Draga, S.; Popescu, M.A. Antibacterial efficiency of cellulose-based fibers covered with ZnO and Al2O3 by Atomic Layer Deposition. Applied Surface Science 2019, 481, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, P.K.; Wu, S. Atomic-layer Fe2O3-modified 2D porphyrinic metal-organic framework for enhanced photocatalytic disinfection through electron-withdrawing effect. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2022, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wu, X.; Wu, S.; Pan, X.; Tu, J.; Chen, M.; Al-Bishari, A.M.; Al-Baadani, M.A.; Yao, L.; Shen, X.; et al. Atomic layer deposition of zinc oxide on microrough zirconia to enhance osteogenesis and antibiosis. Ceramics International 2019, 45, 24757–24767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
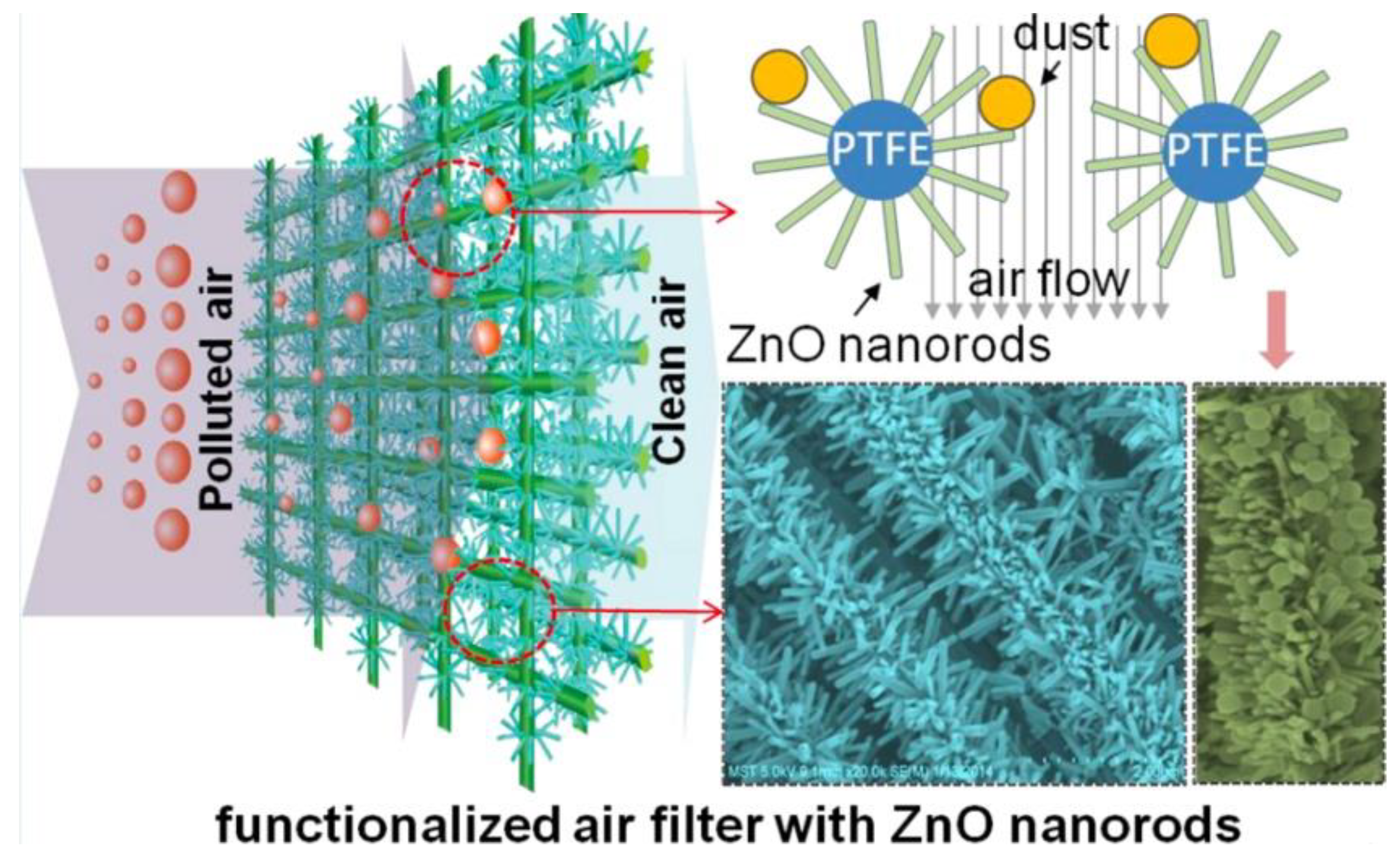
- Zhong, Z.; Xu, Z.; Sheng, T.; Yao, J.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y. Unusual Air Filters with Ultrahigh Efficiency and Antibacterial Functionality Enabled by ZnO Nanorods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015, 7, 21538–21544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoog, S.A.; Bayati, M.R.; Petrochenko, P.E.; Stafslien, S.; Daniels, J.; Cilz, N.; Comstock, D.J.; Elam, J.W.; Narayan, R.J. Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide-coated nanoporous alumina. Materials Science and Engineering: B 2012, 177, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicastillo, C.L.; Vidal, C.P.; Falco, I.; Sanchez, G.; Marquez, P.; Escrig, J. Antimicrobial Bilayer Nanocomposites Based on the Incorporation of As-Synthetized Hollow Zinc Oxide Nanotubes. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
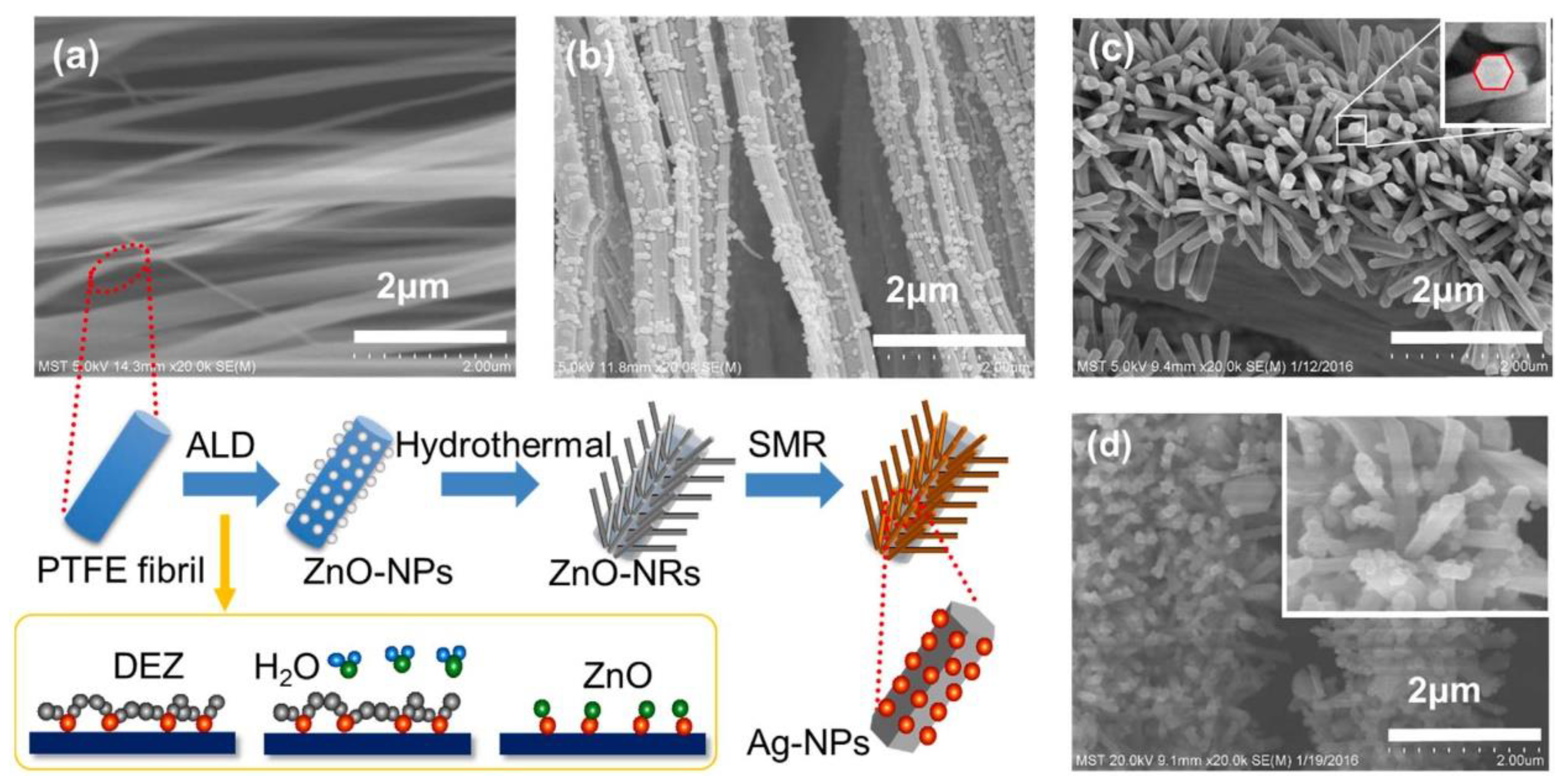
- Feng, S.; Li, D.; Low, Z.-x.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xing, W. ALD-seeded hydrothermally-grown Ag/ZnO nanorod PTFE membrane as efficient indoor air filter. Journal of Membrane Science 2017, 531, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Cui, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Liu, X. Superlattice Nanofilm on a Touchscreen for Photoexcited Bacteria and Virus Killing by Tuning Electronic Defects in the Heterointerface. Adv Mater 2023, 35, e2300380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa, M.W.; Nguyen, B.B.; Moriarty, R.A.; Kamalitdinov, T.; Fisher, J.P.; Kim, J.Y. Fabrication and evaluation of 3D printed BCP scaffolds reinforced with ZrO(2) for bone tissue applications. Biotechnol Bioeng 2018, 115, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Bohner, L.; Hanisch, M.; Kleinheinz, J.; Sielker, S. Influence of Implant Material and Surface on Differentiation and Proliferation of Human Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smieszek, A.; Donesz-Sikorska, A.; Grzesiak, J.; Krzak, J.; Marycz, K. Biological effects of sol-gel derived ZrO2 and SiO2/ZrO2 coatings on stainless steel surface--In vitro model using mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomater Appl 2014, 29, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.; Kim, Y.T.; Cho, H.; Ji, M.K.; Heo, J.; Lim, H.P. Atomic Layer Deposition of ZrO(2) on Titanium Inhibits Bacterial Adhesion and Enhances Osteoblast Viability. Int J Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 1509–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Song, S.; Meng, J.; Tan, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Cui, Z.; Liang, Y.; et al. 2D MOF Periodontitis Photodynamic Ion Therapy. J Am Chem Soc 2021, 143, 15427–15439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, A.; Ehlert, M.; Jedrzejewski, T.; Sadowska, B.; Wieckowska-Szakiel, M.; Holopainen, J.; Ritala, M.; Leskela, M.; Bartmanski, M.; Szkodo, M.; et al. Titania Nanotubes/Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposites Produced with the Use of the Atomic Layer Deposition Technique: Estimation of Bioactivity and Nanomechanical Properties. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, A.; Topolski, A.; Jedrzejewski, T.; Kozak, W.; Sadowska, B.; Wieckowska-Szakiel, M.; Szubka, M.; Talik, E.; Pleth Nielsen, L.; Piszczek, P. The Bioactivity and Photocatalytic Properties of Titania Nanotube Coatings Produced with the Use of the Low-Potential Anodization of Ti6Al4V Alloy Surface. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nene, A.; Galluzzi, M.; Hongrong, L.; Somani, P.; Ramakrishna, S.; Yu, X.F. Synthetic preparations and atomic scale engineering of silver nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 13923–13942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, A.; Jedrzejewski, T.; Kozak, W.; Sadowska, B.; Wieckowska-Szakiel, M.; Talik, E.; Makela, M.; Leskela, M.; Piszczek, P. Optimization of the Silver Nanoparticles PEALD Process on the Surface of 1-D Titania Coatings. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, N.; Hu, B.; Yang, R.; Liang, S.; Liang, S.; Faiola, F. Assessment of the developmental neurotoxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions with mouse embryonic stem cells in vitro. Journal of Interdisciplinary Nanomedicine 2018, 3, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottoni, C.A.; Maria, D.A.; Goncalves, P.; de Araujo, W.L.; de Souza, A.O. Biogenic Aspergillus tubingensis silver nanoparticles' in vitro effects on human umbilical vein endothelial cells, normal human fibroblasts, HEPG2, and Galleria mellonella. Toxicol Res (Camb) 2019, 8, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algazlan, A.S.; Almuraikhi, N.; Muthurangan, M.; Balto, H.; Alsalleeh, F. Silver Nanoparticles Alone or in Combination with Calcium Hydroxide Modulate the Viability, Attachment, Migration, and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitnikova, N.A.; Solovieva, A.O.; Permyakova, E.S.; Sheveyko, A.N.; Shtansky, D.V.; Manakhov, A.M. Silver Ions Incorporation into Nanofibers for Enhanced hMSC Viability. Chemistry 2022, 4, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, H.; Khan, S.A.; Ahmad, I.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Hirad, A.H.; Al-Sabri, A.E. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Olea europaea Leaf Extract for Their Enhanced Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Cytotoxic and Biocompatibility Applications. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Andrade, G.M.; Tanomaru-Filho, M.; Rodrigues, E.M.; Gomes-Cornelio, A.L.; Faria, G.; Bernardi, M.I.B.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M. Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and antibacterial activity of poly(vinyl alcohol)-coated silver nanoparticles and farnesol as irrigating solutions. Arch Oral Biol 2017, 84, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecer, E.N. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Origanum onites leaves: Cytotoxic, apoptotic, and necrotic effects on Capan-1, L929, and Caco-2 cell lines. Green Processing and Synthesis 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, S.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Patria, F.; Beccari, T.; Mandarano, M.; Ferri, I.; Lazzarini, A.; Curcio, F.; Albi, E. The Effect of Vitamin D3 and Silver Nanoparticles on HaCaT Cell Viability. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, C.; Tang, M.; Yang, Z.; Jia, W.; Ma, Y.; Jia, P.; Pei, D.; Wang, H. Nanotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles on HEK293T Cells: A Combined Study Using Biomechanical and Biological Techniques. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6770–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shan, K.; Shao, X.; Shi, X.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jacob, J.A.; Deng, L. Nanotoxic Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Normal HEK-293 Cells in Comparison to Cancerous HeLa Cell Line. Int J Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Qasim, M.; Park, C.; Yoo, H.; Choi, D.Y.; Song, H.; Park, C.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, K. Cytotoxicity and Transcriptomic Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y. Comparative study of the effects of gold and silver nanoparticles on the metabolism of human dermal fibroblasts. Regen Biomater 2020, 7, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, A.K.; Hackett, D.; Tchounwou, P.B. Genotoxicity study of silver nanoparticles in bone marrow cells of Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol 2015, 85, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mahdy, M.M.; Eldin, T.A.; Aly, H.S.; Mohammed, F.F.; Shaalan, M.I. Evaluation of hepatotoxic and genotoxic potential of silver nanoparticles in albino rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2015, 67, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Song, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, C.S.; Yu, I.J. In vivo Genotoxicity of Silver Nanoparticles after 90-day Silver Nanoparticle Inhalation Exposure. Saf Health Work 2011, 2, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zara, J.N.; Hsu, C.; Soofer, D.E.; Lee, K.S.; Siu, R.K.; Miller, L.S.; Zhang, X.; Carpenter, D.; et al. The antimicrobial and osteoinductive properties of silver nanoparticle/poly (DL-lactic-co-glycolic acid)-coated stainless steel. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8745–8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xiong, W.; Fang, Z.; Guan, H.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Alvarez, M.M.; Gao, B.; Huo, K.; et al. Strontium (Sr) and silver (Ag) loaded nanotubular structures with combined osteoinductive and antimicrobial activities. Acta Biomater 2016, 31, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elam, J.W.; Zinovev, A.V.V.; Pellin, M.J.; Comstock, D.J.; Hersam, M.C. Nucleation and Growth of Noble Metals on Oxide Surfaces Using Atomic Layer Deposition. ECS Transactions 2007, 3, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariniemi, M.; Niinistö, J.; Hatanpää, T.; Kemell, M.; Sajavaara, T.; Ritala, M.; Leskelä, M. Plasma-Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition of Silver Thin Films. Chemistry of Materials 2011, 23, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin-Mullin, A.; Todd, N.M.; Golrokhi, Z.; Geng, H.; Konerding, M.A.; Ternan, N.G.; Hunt, J.A.; Potter, R.J.; Sutcliffe, C.; Jones, E.; et al. Atomic Layer Deposition of a Silver Nanolayer on Advanced Titanium Orthopedic Implants Inhibits Bacterial Colonization and Supports Vascularized de Novo Bone Ingrowth. Adv Healthc Mater 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi Astaneh, S.; Bhatia, H.; Nagay, B.E.; Barao, V.A.R.; Jursich, G.; Sukotjo, C.; Takoudis, C.G. Is atomic layer deposition of silver possible on N95 masks? Appl Surf Sci 2022, 591, 153195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoops, H.C.M.; Faraz, T.; Arts, K.; Kessels, W.M.M. Status and prospects of plasma-assisted atomic layer deposition. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Zhao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, R.; Fu, S.; Qin, G. Antibacterial metals and alloys for potential biomedical implants. Bioact Mater 2021, 6, 2569–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altun, E.; Aydogdu, M.O.; Chung, E.; Ren, G.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Edirisinghe, M. Metal-based nanoparticles for combating antibiotic resistance. Applied Physics Reviews 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, K.; Ali-Löytty, H.; Saari, J.; Zubair, M.; Valden, M.; Lahtonen, K.; Kinnunen, N.; Gunell, M.; Saarinen, J.J. Functionalization of TiO2 inverse opal structure with atomic layer deposition grown Cu for photocatalytic and antibacterial applications. Optical Materials 2022, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
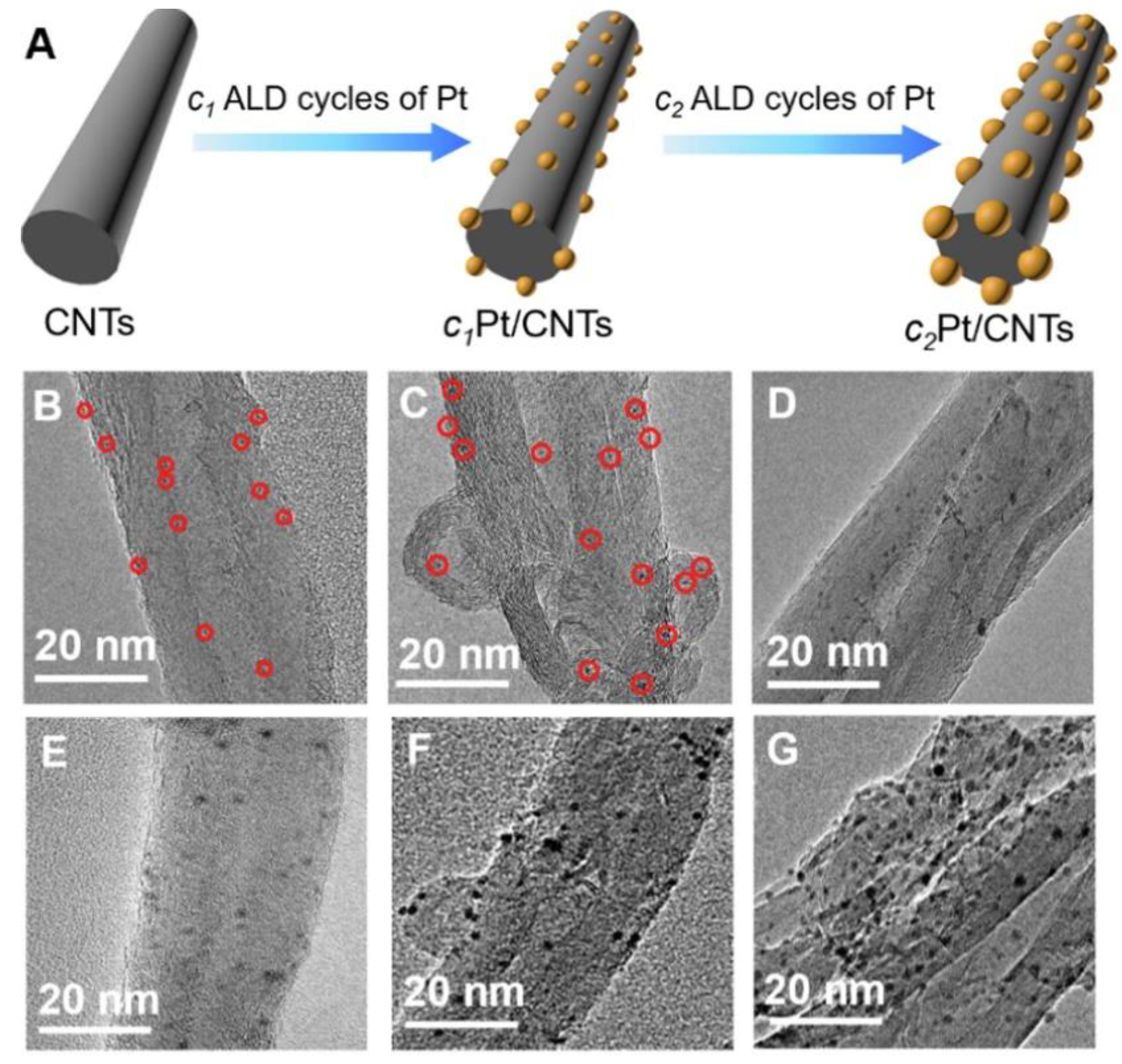
- Yang, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Bai, P.; Du, B.; Li, L.; Zhao, S.; Qin, Y.; et al. Mechanistic and kinetic insights into size-dependent activity in ultra-small Pt/CNTs nanozymes during antibacterial process. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.R.; D'Argenio, D.A.; MacCoss, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Jones, R.A.; Miller, S.I. Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 2005, 436, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangram, A.J.; Horan, T.C.; Pearson, M.L.; Silver, L.C.; Jarvis, W.R. Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 1999. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. American journal of infection control 1999, 27, 97–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pathak, J.L.; Hu, X.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Al-Baadani, M.A.; Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; Farkasdi, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Sustained Release of Zoledronic Acid from Mesoporous TiO(2)-Layered Implant Enhances Implant Osseointegration in Osteoporotic Condition. J Biomed Nanotechnol 2018, 14, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Qin, L. Review of Antibacterial Activity of Titanium-Based Implants’ Surfaces Fabricated by Micro-Arc Oxidation. Coatings 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Costa, R.C.; Silva, M.C.; Fonseca-Santos, J.M.; Chen, L.; Phakatkar, A.H.; Bhatia, H.; Faverani, L.P.; Barão, V.A.R.; Shokuhfar, T.; et al. Collagen membrane functionalized with magnesium oxide via room-temperature atomic layer deposition promotes osteopromotive and antimicrobial properties. Bioactive Materials 2023, 30, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Shi, X.; Fang, X.; Tao, H.; Zhu, H.; Yu, F.; Ding, X.; Liu, M.; Fang, F.; Yang, F.; et al. The "Pure Marriage" between 3D Printing and Well-Ordered Nanoarrays by Using PEALD Assisted Hydrothermal Surface Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 8393–8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-L.; He, J.; Ye, H.-X.; Zhao, C.-C.; Zhu, W.-W.; Lu, X.; Ren, F.-Z. Atomic layer deposition of zinc oxide onto 3D porous iron scaffolds for bone repair: in vitro degradation, antibacterial activity and cytocompatibility evaluation. Rare Metals 2021, 41, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sang, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q. The Antibacterial Polyamide 6-ZnO Hierarchical Nanofibers Fabricated by Atomic Layer Deposition and Hydrothermal Growth. Nanoscale Res Lett 2017, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miikkulainen, V.; Leskelä, M.; Ritala, M.; Puurunen, R.L. Crystallinity of inorganic films grown by atomic layer deposition: Overview and general trends. Journal of Applied Physics 2013, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviroh, P.O.; Akbarzadeh, R.; Pan, D.; Coetzee, R.A.M.; Jen, T.C. New development of atomic layer deposition: processes, methods and applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater 2019, 20, 465–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brobbey, K.J.; Haapanen, J.; Gunell, M.; Toivakka, M.; Mäkelä, J.M.; Eerola, E.; Ali, R.; Saleem, M.R.; Honkanen, S.; Bobacka, J.; et al. Controlled time release and leaching of silver nanoparticles using a thin immobilizing layer of aluminum oxide. Thin Solid Films 2018, 645, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, A.A.; Markeev, A.M.; Tetyukhin, D.V.; Kozlov, E.N.; Molchanov, S.A. Applications of atomic layer deposition in implant dentistry. European Cells and Materials 2014, 27, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Picosun Customer Interview: CONMET LLC. 2016. Available online: https://press.picosun.com/picosun-customer-interview-conmet-llc.
- Yoo, K.S.; Kim, D.-G.; Lee, S.; Lee, W.-B.; Park, J.-S. Atmospheric pressure spatial ALD of Al2O3 thin films for flexible PEALD IGZO TFT application. Ceramics International 2022, 48, 18803–18810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Nijboer, M.P.; Kovalgin, A.Y.; Nijmeijer, A.; Roozeboom, F.; Luiten-Olieman, M.W.J. Atmospheric-pressure atomic layer deposition: recent applications and new emerging applications in high-porosity/3D materials. Dalton Trans 2023, 52, 10254–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.; Hatanpää, T.; Mizohata, K.; Meinander, K.; Niinistö, J.; Räisänen, J.; Ritala, M.; Leskelä, M. Studies on Thermal Atomic Layer Deposition of Silver Thin Films. Chemistry of Materials 2017, 29, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
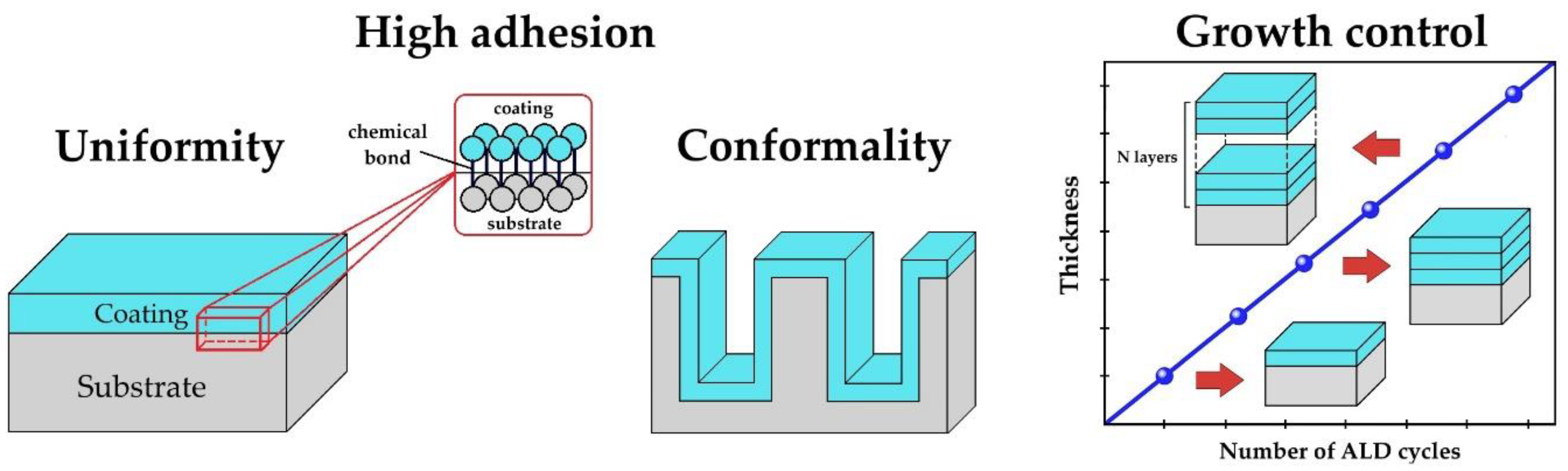

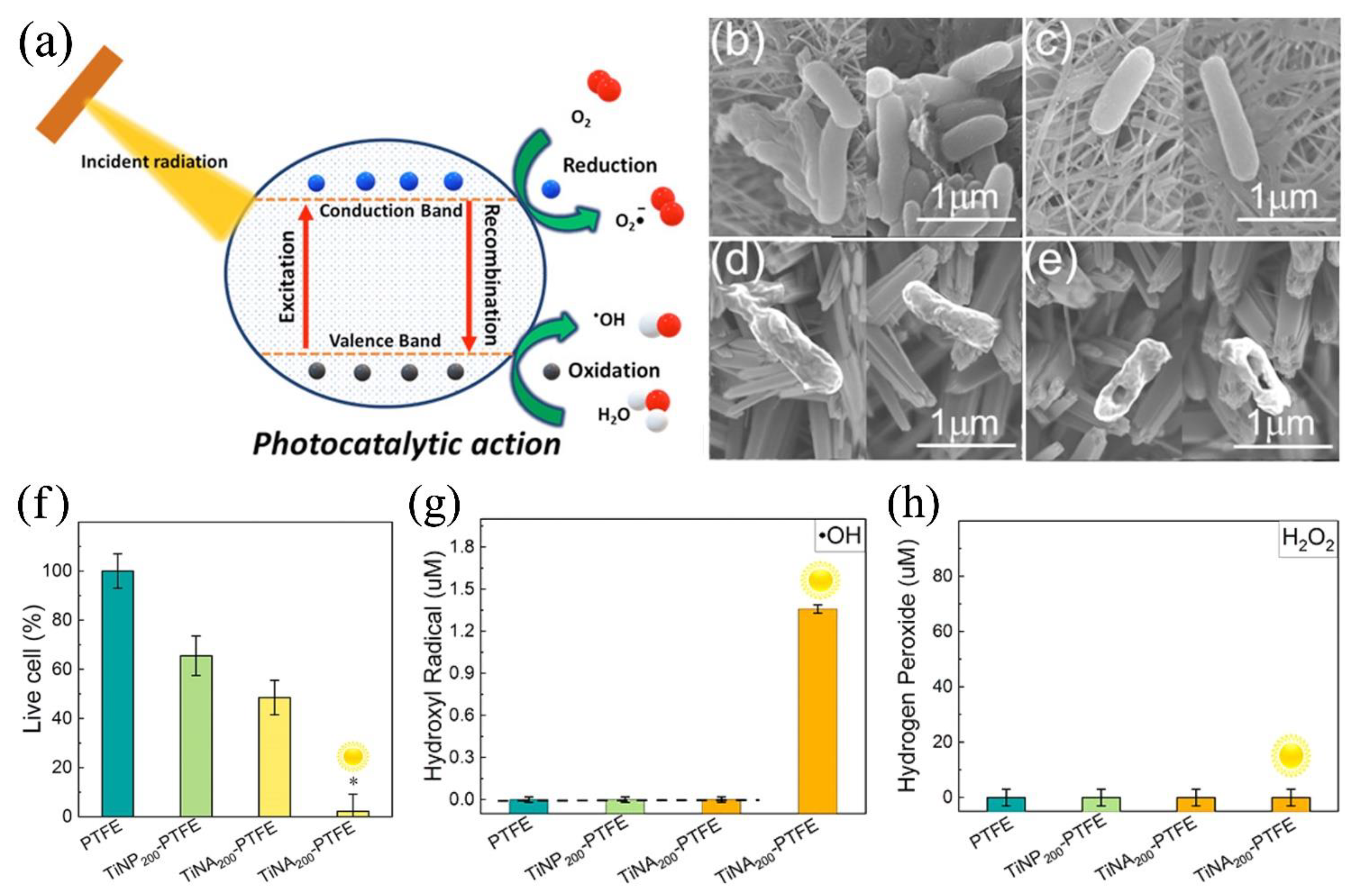
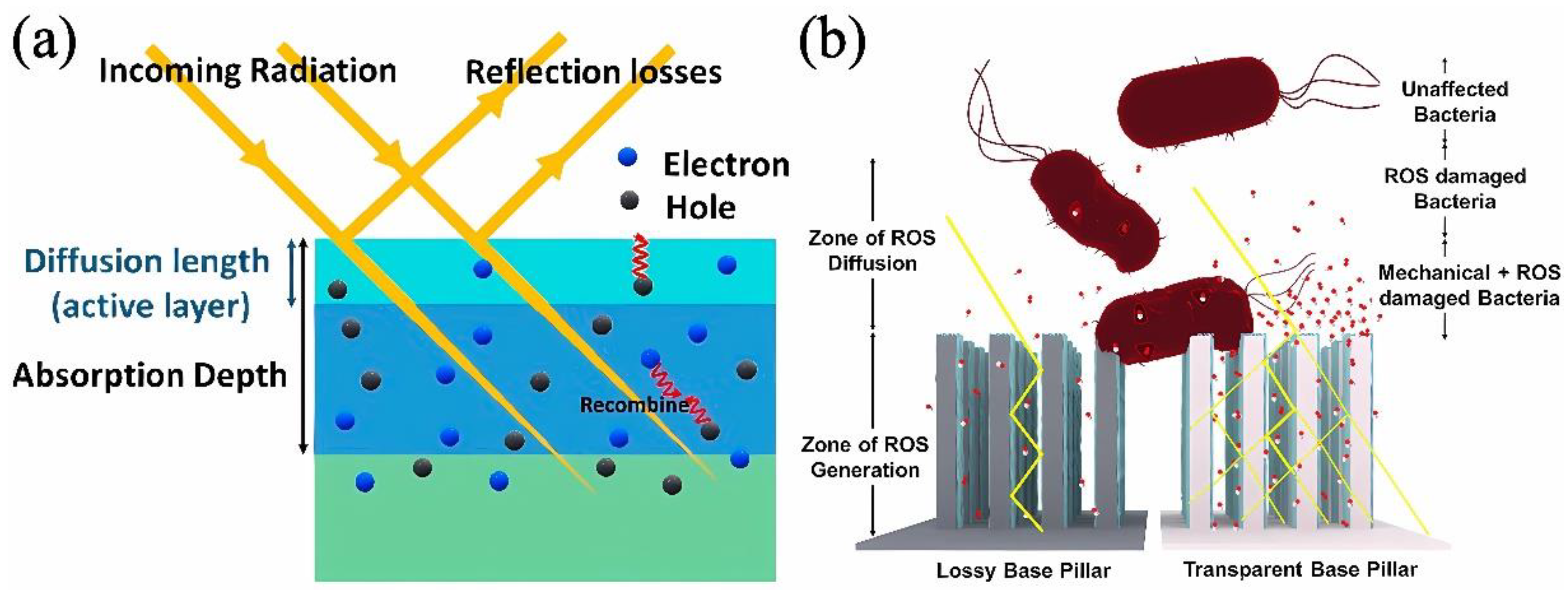
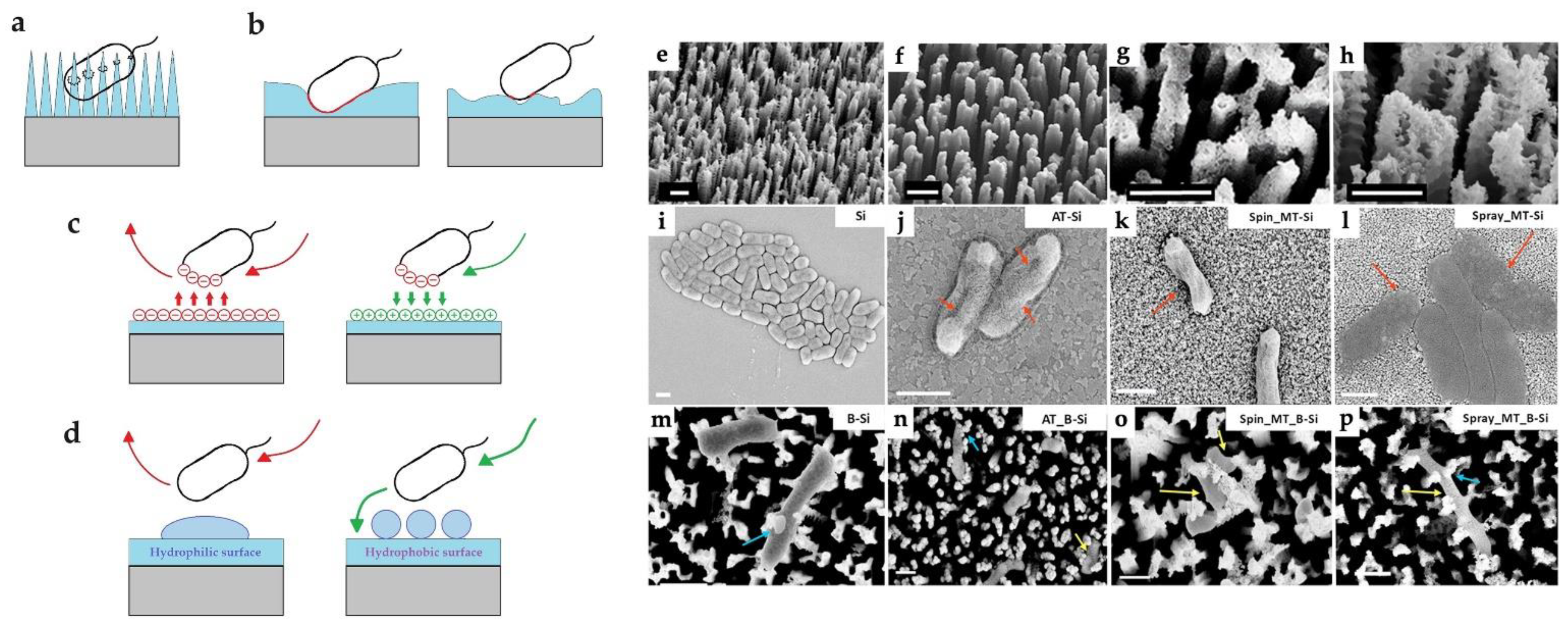
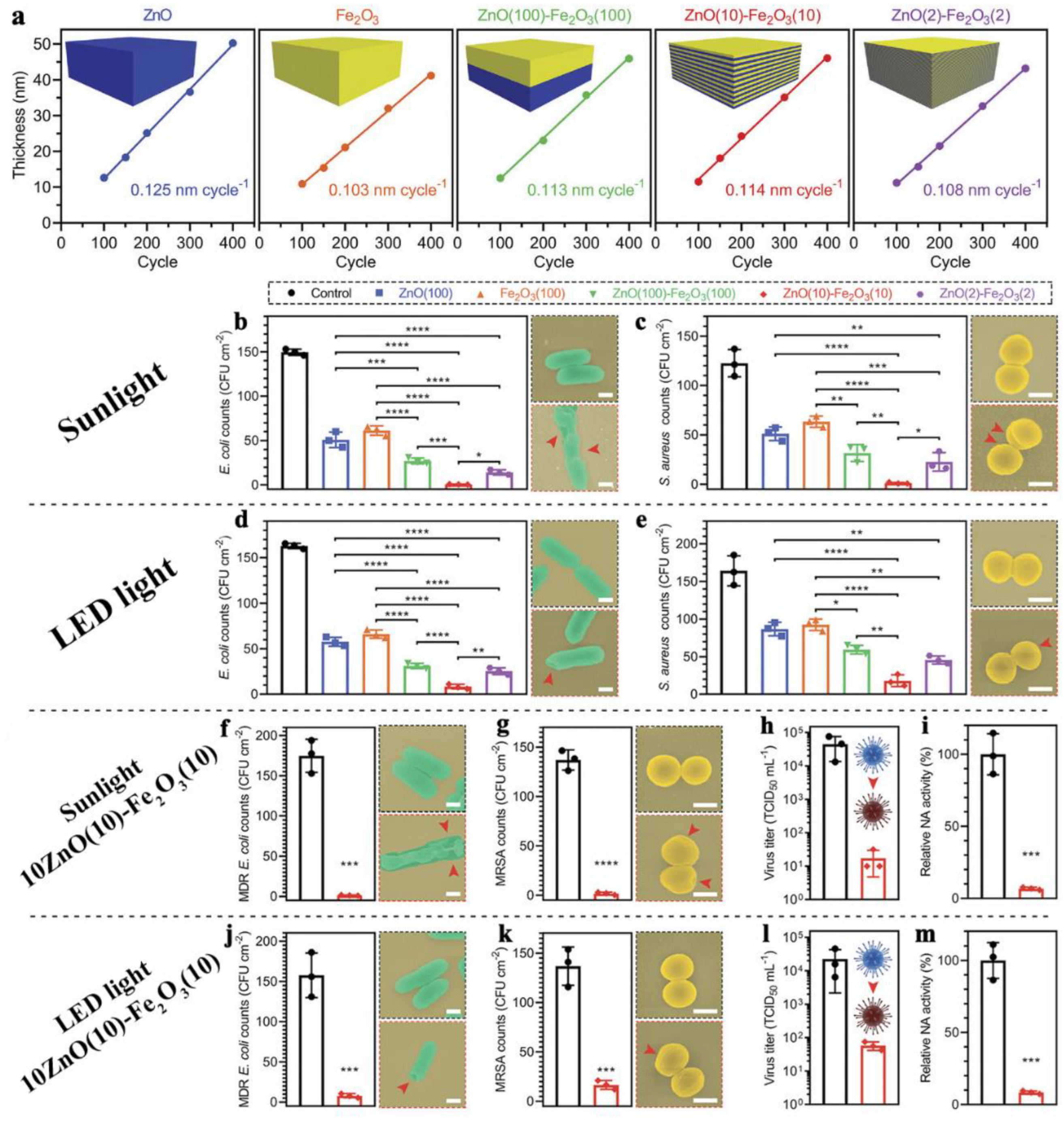
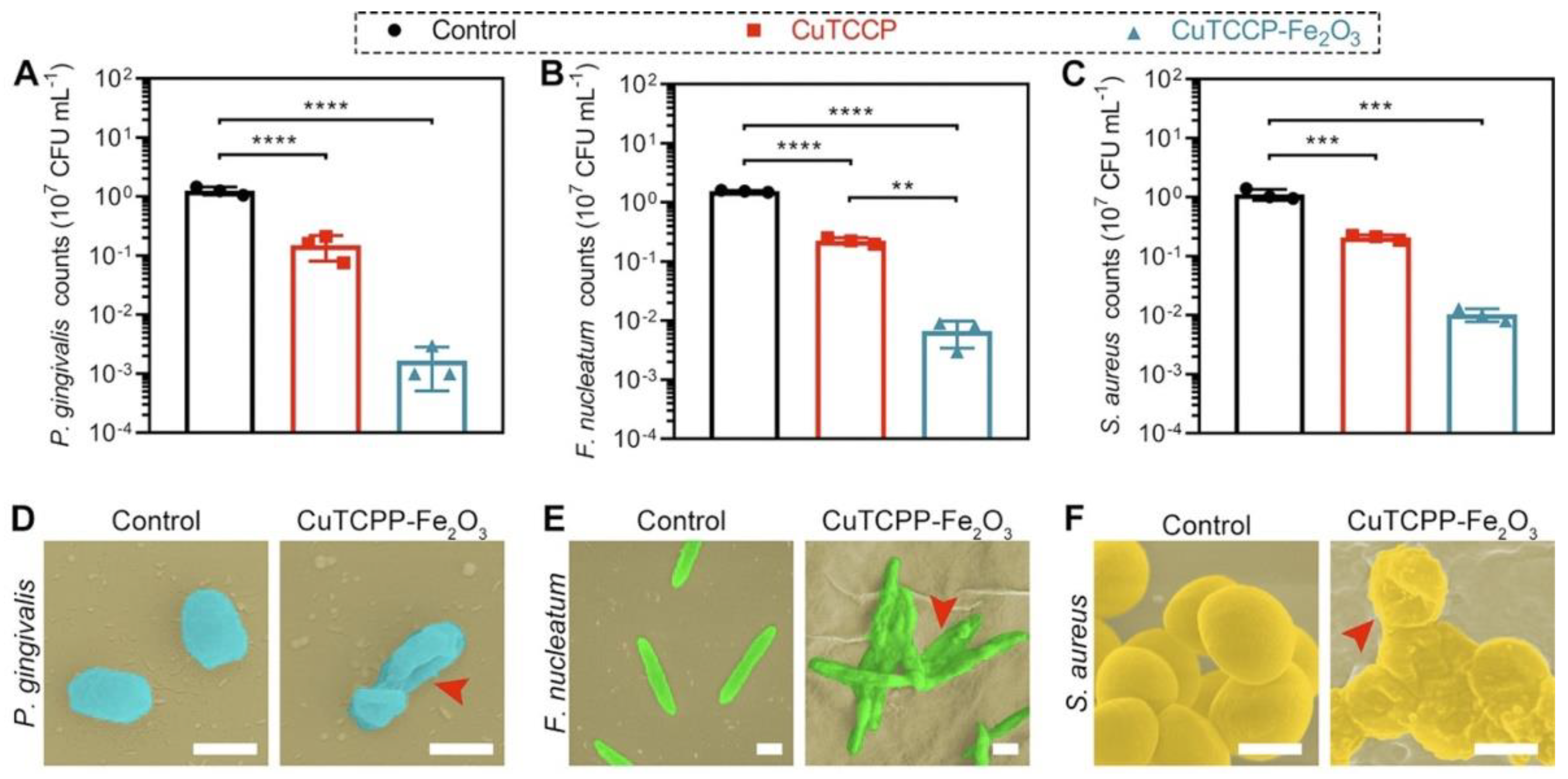
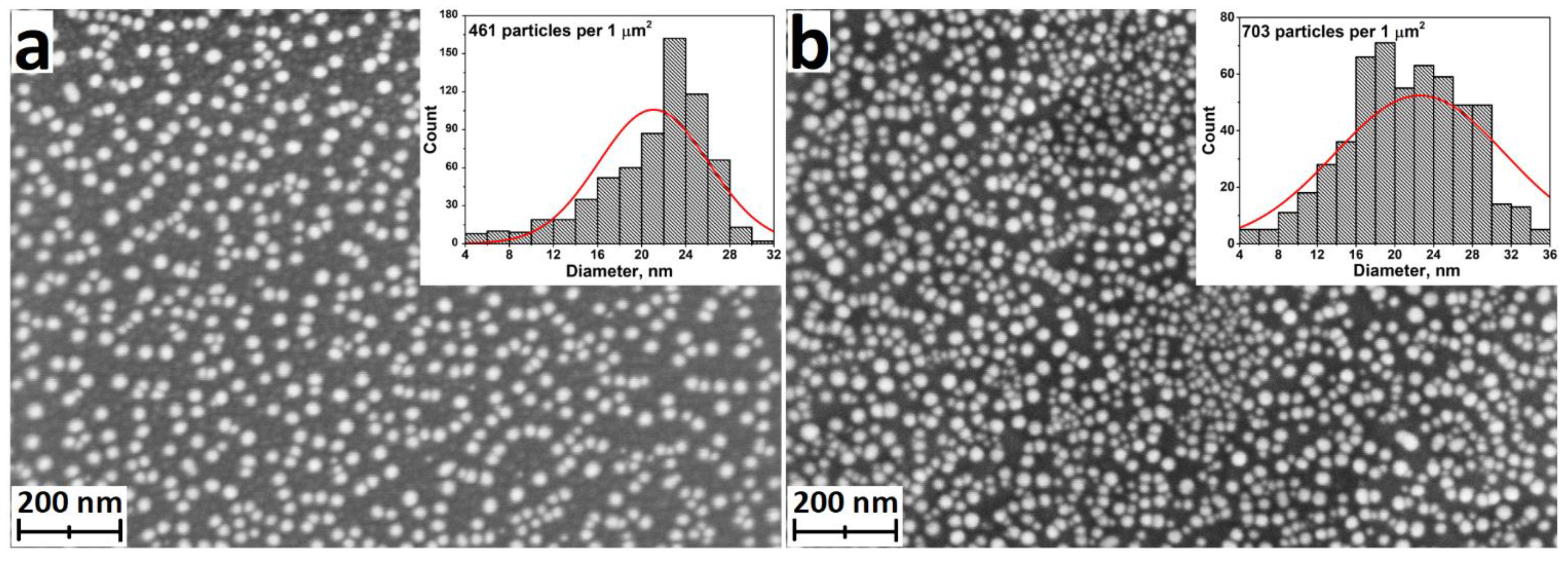
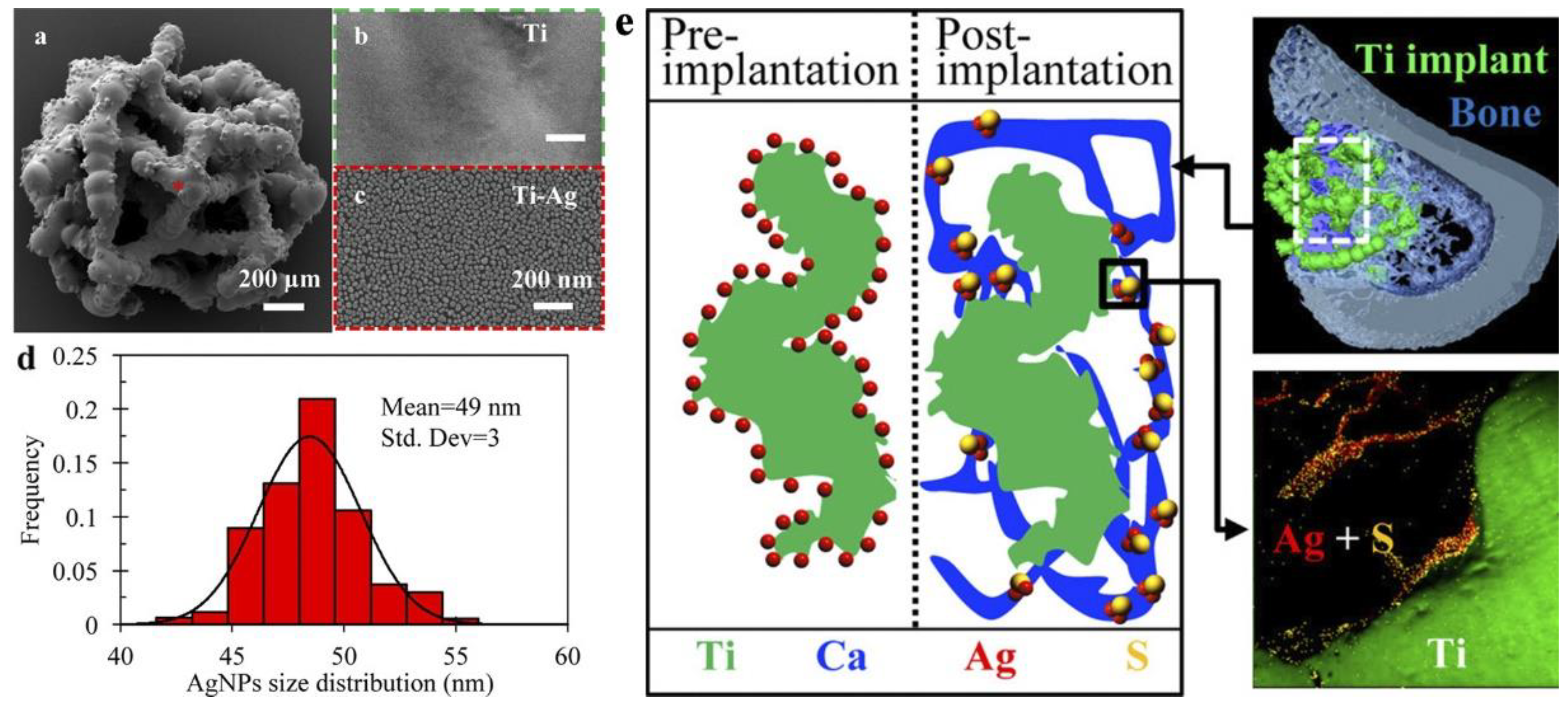
| Motivation | Support/Precursors | ALD Temperature/Thickness | Bacteria / IIRADIATION | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial coatings for purifying water | Si / TiCl4/ H2O | 100, 200, 300 °C / 50 nm | E. coli /UV irradiation | Increasing ALD temperature from 200°C to 300°C improves TiO2 photocatalytic activity but does not have an impact on antibacterial activity. E. coli survival: 200°C – 61%, 300°C – 66% | [48] |
| Study the effect of coatings with different morphology and structure on osteoblast, fibroblast functions and bacterial activities | Ti/ TDMAT/ H2O | 120,160, 190 °C /100nm | S. aureus, E. coli, MRSA | TiO2 inhibit adhesion and growth bacteria and fibroblast but improve osteoblasts adhesion and proliferation. The 160 °C sample (amorphous) showed the best antibacterial activity. Increase in nanoscale roughness and greater hydrophilicity contribute to increased protein adsorption, which may affect the cellular/bacterial activities. | [49] |
| The study of photocatalitic processess in antibacterial activity TiO2 | Black Si and SiO2 nanopillars /(no data) | No data / 50nm | E. coli | The increase in the light absorption does not lead to an increase in ROS production. TiO2-coated nanopillars arrays made of SiO2 have 73% higher bactericidal efficacies than those made of Si. | [50] |
| Study of the synergic effect present in mixed anatase/rutile TiO2 on antibacterial properties | Rutile-TiO2 nanotubes (RTNT) /TDMAT / H2O | 250 °CAnnealing – 450C 2h / 10nm | E. coli /UV light irradiation | Considerable increase in photocatalytic activity and ROS generation using RTNT coated with anatase-TiO2 compared to only rutile or anatase. Considerable increase in bactericidal activity using RTNT coated with A-TiO2 compared to single R or A-TiO2 nanotubes | [45] |
| Surface coating of nanoporous Al2O3 for controlled pore size reduction | Porous Al2O3 membranes / TiCl4/H2O | 300 °C/ 4.3 and 8.6 nm | S. aureus, E. coli,UV irradiation | 20 nm pore size TiO2-coated nanoporous alumina membrane inhibited microbial adhesion while the 100 nm pore size TiO2-coated membrane did not. | [51] |
| Examine the efficiency of a bacteria-resistant coating for the PDMS cochlear implants | PDMS1 / TDMAT/O2 plasma | 100 °C / (10–40 nm) | E. coli | TiO2-coated surfaces save the integrity of polymeric materials and reduce E. coli colonization and biofilm formation with protein quantity on ALD- and LPD treated samples being reduced by 44 and 41% (BCA).CLSM - biofilm reduction of 91 and 89% for ALD- and LPD-coated surfaces | [52] |
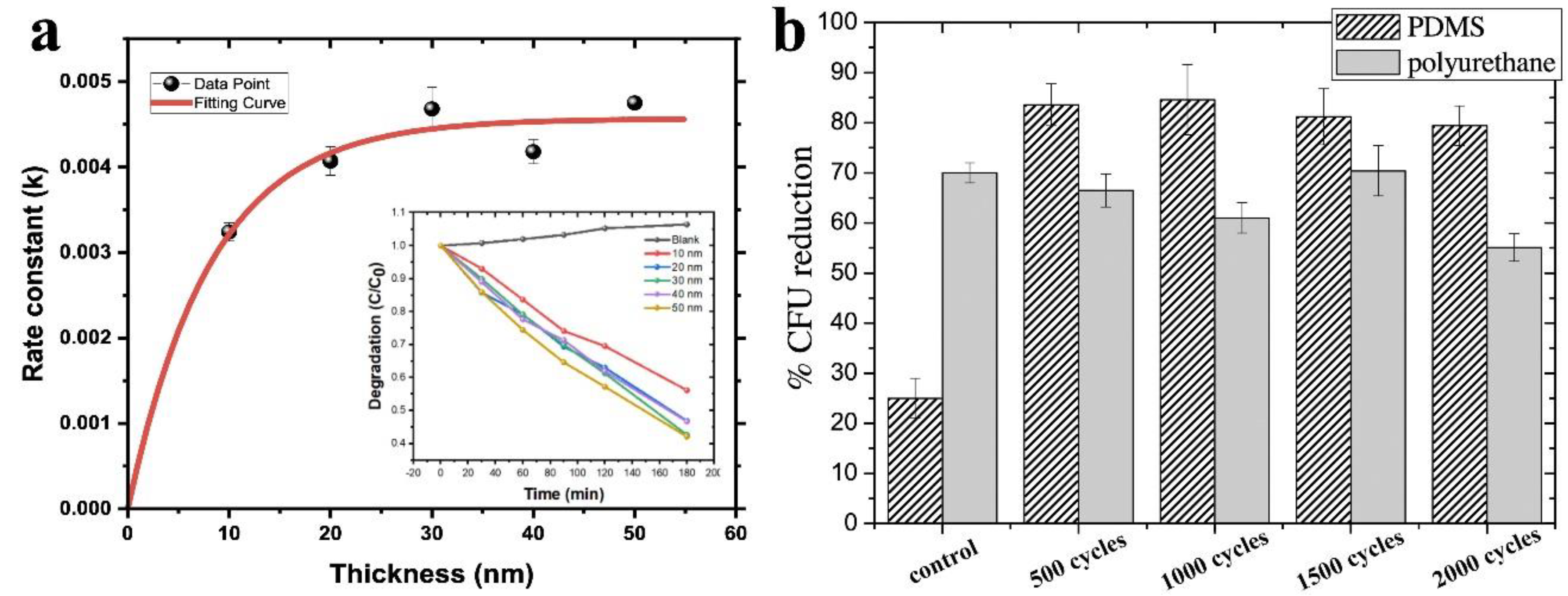
| Studies of antibacterial properties of TiO2 deposited on polymers used for catheters and contact lenses | PU and PDMS/TiCl4/H2O | 80 °C/ 50-200nm | Candida albicansUV and without UV | TiO2 suppressed the yeast hyphal transition of C. albicans onto PU+TiO2, however, a high adhesion of C. albicans was observed. For PDMS+TiO2 substrate, the yeast adhesion did not change, as observed in control. After UV treatment TiO2+PDMS had better reduction in CFU (up to 59.5%) compare to uncoated PDMS, while no difference was observed to TiO2-covered PU | [29] |
| Improve the surface characteristics of denture PMMA | PMMA/ TDMAT/O3 | 65 °C / 30 nm | Candidaalbicans | The Candida albicans reduction reached 63% to 77% for the attachment test and 56% for biofilm formation. | [53] |
| Support/ALD Conditions | Characteristics | Bacteria | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 nanotubes 10-84 nm / 25 cycles of PEALD Ag(fod)(PEt3)1 +H2, 120 oC | 7.8–9.2 nm dispersed Ag particles and dense Ag layer | S. aureus | Low level of Ag+ releasing The sample with the smallest nanotube diameter and a continuous layer of Ag showed the best bactericidal results. | [102] |
| 3d Ti scaffolds / direct liquid injection of 0.1M (hfac)Ag(1,5-COD)2 in toluene and propan-1-ol. 500 ALD cycles (125 °C) | Effective layer - 13 nm (NPs 40-90nm diameter) | S. aureus (MRSA) S. epidermidis. | On bare titanium scaffolds, S. epidermidis growth was slow but on Ag-coated were significant further reductions (2 order of inhibition) in both bacterial recovery and biofilm formation. MRSA growth was similarly slow on bare titanium and not further affected by Ag coating. | [122] |
| 3d Ti scaffolds / direct liquid injection 0.1M (hfac)Ag(1,5-COD) in toluene and propan-1-ol. 500 ALD cycles (125 °C) | Average NPs 49nm in diameter | In vivo - implants in rat tibial defects | No effect of Ag on bone formation and osseointegration after 2−12 weeks of implantation. Ag is a part of less toxic Ag2S within the newly formed bone tissue adjacent to the implant surface | [27] |
| Ti / ALD TiO2 (TiCl4+H2O)+Ag (Ag(fod)(PEt3) +H2) | 20–28 nm on Si16–30 nm on Ti | S. aureus | The ALD combination of TiO2+Ag is significantly more active against S. aureus than pure TiO2 and Ag | [57] |
| N95 medical mask (PP, polyester) / Ag(fod)(PEt3) + (CH3)2NH*BH3 | 16 nm | S. aureus | 76% reduction in S. aureus CFU was observed after 24h. At early stage (2h) Ag had no bactericidal effect | [123] |
| Characteristics | TiO2 | Doped TiO2 | ZnO | Ag | ZrO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial efficacy | + | ++ | +++ | +++ | 0 | + | 0 |
| Biocompatibility | +++ | ++ | + | + | ++ | + | + |
| ALD temperature | From 65°С | From 65°С | From RT | 120 - 160°C | ~200°С | ~180°С | From RT |
| Growth rate, uniformity and conformality | ++ | ++ | +++ | + | ++ | ++ | +++ |
| Morphology of the coating | Dense coating | Dense coating | Dense nanocrystalline coating | NPs | Dense coating | Dense coating | Dense coating |
| Stability in aqueous environment | +++ | ++ | + | + | +++ | + | +++ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





