Introduction
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane-bound particles released from cells into the extracellular space. EVs carry nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins from their cell of origin that can alter the function of the recipient cells through uptake or membrane binding. Thus, EVs are important in inter-cellular communication in physiological as well as pathological processes [
1,
2,
3].
Ionising radiation used in cancer therapy causes, among others, DNA damages, which are the primary cause of subsequent cellular effects. Similar damages can also be found in non-irradiated neighbouring or distant cells, termed non-targeted effects of radiation or radiation-induced bystander effects [
4,
5,
6]. Recent research has shown that EVs from irradiated cells may be one of the delivery methods of non-targeted effects of radiation [
7,
8,
9,
10], which may have several implications for radiotherapy [
11].
Studies on the role of EVs in non-targeted effects has, to our knowledge, only been performed using photon irradiation such as gamma- and X-rays [
12,
13,
14,
15]. Protons will deposit most of their energy in the so-called Bragg peak with no dose deposited deeper in the tissue [
16,
17], thus providing a clinical advantage over X-rays to reduce the dose to normal tissue surrounding the tumour. Therefore, proton irradiation is expected to reduce the amount of side effects in local normal tissue compared to X-rays, and is implemented in an increasing number of radiotherapy centres across the world. However, EVs derived from proton irradiated cancer cells may still induce non-targeted effects on normal cells.
We hypothesise that protons may induce differential protein profiles in EVs compared to X-rays due to the difference in how the two types of radiation deposit energy in tissue. Protons have an elevated relative biological effectiveness (RBE) compared to X-rays [
18,
19,
20].
RBE is defined as the ratio of a reference X-ray dose to the proton dose that induce the same biological effect. It depends on several variables such as linear energy transfer (LET), which describes the amount of energy transferred from each ionising particle to the tissue per distance unit. Accumulating research suggest that RBE increases at the distal edge of the Bragg peak, where the LET is highest [
21,
22,
23,
24]. Therefore, it is of interest to investigate the differences between low and high LET protons as well as comparing protons to X-rays.
The protein content and possible effects of EVs on recipient cells derived from proton irradiated cancer cells have, to our knowledge, not been investigated. The aim of this study was to investigate and compare the proteome of EVs derived from a human oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell line exposed to either protons or X-rays. Furthermore, the proteome of the EV-releasing OSCC cells after exposure to protons and X-rays was evaluated and compared to the irradiated OSCC-derived EVs. Such knowledge can be important for the understanding of how non-targeted effects in normal tissue can be limited and for the future implementation of proton therapy in the clinic.
Results
EV characterization and overview of protein content
Through nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) we found that the median EV size was approximately 200 µm, with sizes ranging typically from 60 – 250 nm, which was also confirmed through transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (Figure S1A-B). There were no significant differences in regard to the size of the EVs between the treatment modalities. X-rays gave a significantly higher EV concentration compared to the two proton treatment groups (high and low LET) (Figure S1C). However, this variation in EV concentration between X-rays and protons was also seen in the corresponding non-irradiated controls and is therefore most likely due to variations in cell batch and ambient conditions, not because of the radiation treatment itself.
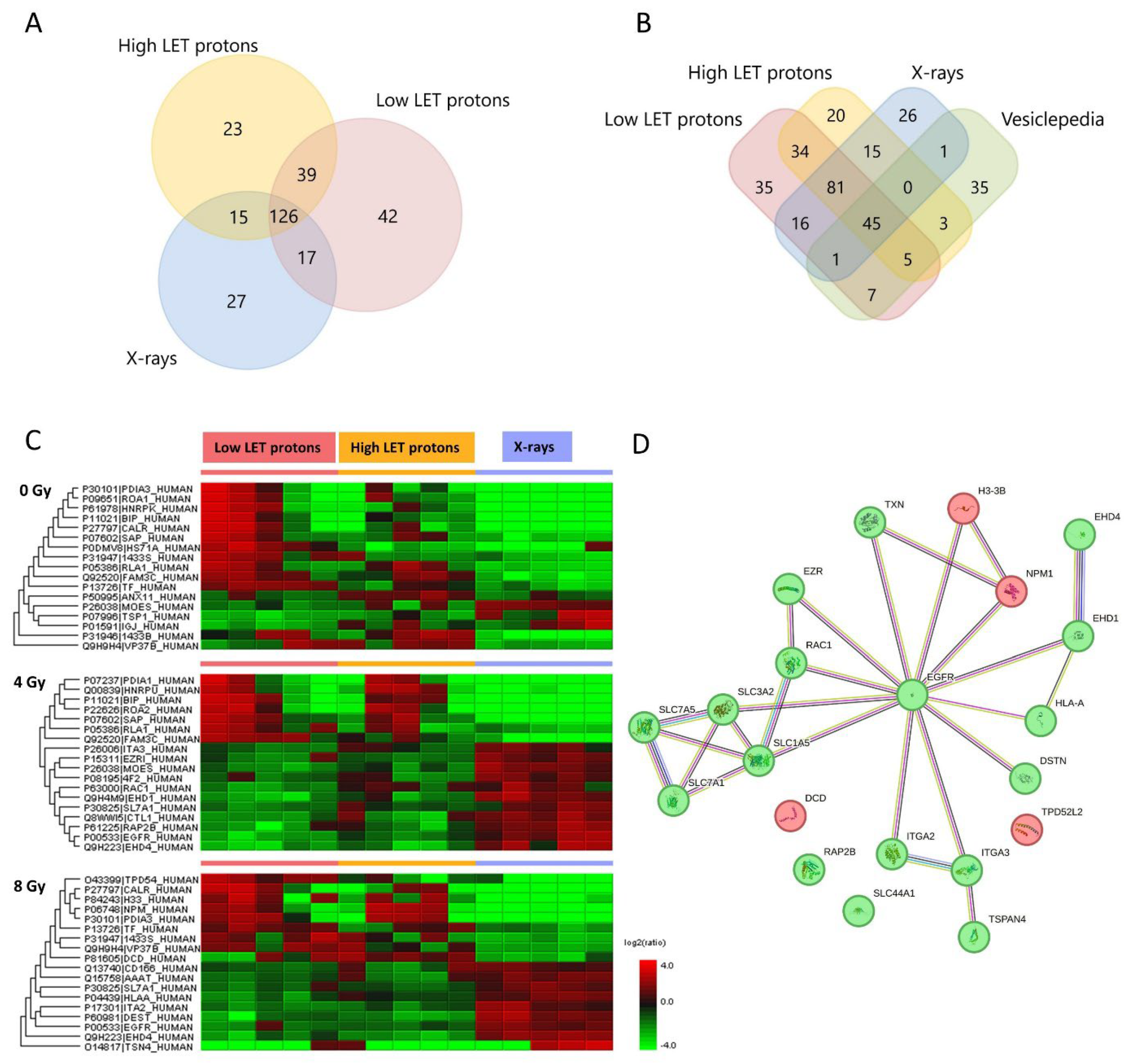
Proteomic analysis of the EVs identified 224 proteins after low LET proton irradiation, 203 proteins after high LET proton irradiation, 185 proteins after X-irradiation, and 186 proteins in non-irradiated controls (
Figure 1A). Compared to the 100 most predominant proteins generally detected in EVs according to the Vesiclepedia database (microvesicles.org), the majority were also detected in the EVs in this study (
Figure 1B), including CD9 and CD81, which are coined as typical EV markers [
2]. This aids in confirming that the isolated particles were EVs.
Up- and downregulated EV proteins after irradiation
From all the EV proteins identified (mentioned above), only some of them were significantly up- or downregulated (shown in the heat map in
Figure 1C). However, of these significantly expressed proteins some were also similarly expressed in the corresponding non-irradiated controls (seen in all the upregulated proteins in low LET protons 4 Gy). Therefore, we suspected these proteins not to be upregulated because of the radiation itself, and they were hence excluded from further analysis. After excluding proteins not different from the non-irradiated controls, we were left with the proteins shown in
Table 1.
Proteomic analysis of the EVs isolated from proton irradiated OSCC cells showed similar protein expression after high and low LET protons, except for three proteins; solute carrier family 7 member 5 (SLC7A5), thioredoxin (TXN), and Rac family small GTPase 1 (RAC1). Except for these three proteins, the protein profile in the EVs were the same after high and low LET protons. Therefore, in the further analysis of EV proteomics we combined the EV results from the high and low LET protons. EV proteins downregulated after proton compared to X-irradiation were mostly related to cell adhesion, migration, amino acid transport, cell cycle and growth, programmed cell death, and inflammatory response. EV proteins upregulated after protons compared to X-rays were related to cell proliferation, nucleosome assembly, cytoskeleton organization and immune system processes (
Table 1).
From the protein-protein interaction network analysis we observed that the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which was downregulated after protons compared to X-rays, functioned as a hub protein for all the other protein interaction networks (
Figure 1D). Additionally, the transporter proteins solute carrier family 1 member 5 (SLC1A5), solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2), solute carrier family 7 member 1 (SLC7A1), and solute carrier family 7 member 5 (SLC7A5) interacted with each other and formed a dense network. Moreover, EH domain-containing protein 1 (EHD1) and EH domain-containing protein 4 (EHD4) were also tightly connected with many interactions. EHD1 and EHD4 were downregulated after proton versus X-irradiation, EHD4 after both 4 and 8 Gy, while EHD1 only after 4 Gy.
Up- and downregulated OSCC cell proteins after irradiation
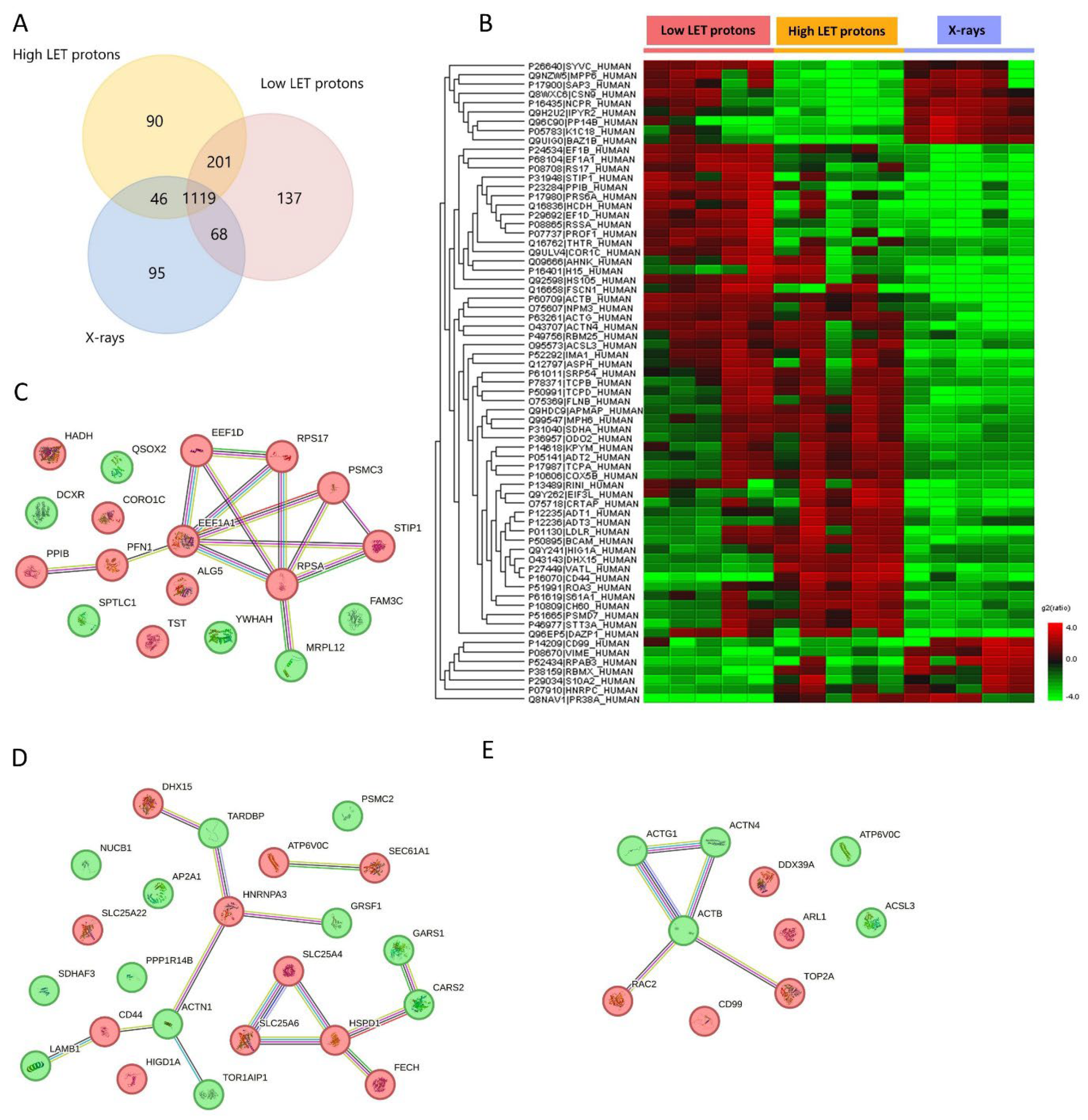
Proteomic analysis generally identified a larger number of proteins in OSCC cells than in their associated EVs after exposure to either proton or X-irradiation. After low LET protons, 1525 proteins were detected in the OSCC cells, while 1456 proteins were identified after high LET protons, 1328 proteins after X-rays, and 1310 proteins in non-irradiated controls (
Figure 2A). Differentially expressed proteins in the three treatment groups are presented in
Figure 2B and
Table 2 and 3.
Proteins that were upregulated in OSCC cells after irradiation with low LET protons were related to cell migration or adhesion, DNA replication, transcription or translation, and cell death, while downregulated proteins were related to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, regulation of ROS, and programmed cell death (
Table 2 and 3). Proteins upregulated in OSCC cells after irradiation with high LET protons had functions associated with programmed cell death, regulation of DNA damage response, and inflammatory response, while downregulated proteins were associated with cell migration or adhesion, RNA splicing, protein translation, and programmed cell death (
Table 2 and 3). Taken together, high LET protons cause upregulation of proteins important in DNA damage response and programmed cell death which is not seen after low LET protons, indicating more complex cell damage after high LET protons compared to low LET protons. After irradiation with X-rays, OSCC cells showed upregulation of proteins related to cell adhesion, mRNA splicing and transport, double-stranded DNA breaks, regulation of ROS, and programmed cell death, compared to high and low LET protons. On the other hand, proteins related to migration or angiogenesis, cell cycle and DNA repair, programmed cell death, and lipid metabolism were downregulated after X-rays compared to high and low LET protons (
Table 2 and 3).
Protein-protein networks using STRING analysis revealed several protein interactions (
Figure 2C-E). Due to the larger number of proteins up- or downregulated in OSCC cells compared to their associated EVs, three separate STRING analysis networks are shown in
Figure 2C-E, separated by treatment. After low LET protons most of the upregulated proteins were connected through protein-protein interactions where elongation factor 1-alpha 1 (EEF1A1) functioned as a hub protein with many interactions with other upregulated proteins (
Figure 2C). After high LET protons several separate protein interaction networks were identified (
Figure 2D). The largest interaction network was one where several up- and downregulated proteins were connected to each other, many of which were involved in RNA splicing and apoptosis. A smaller network with the upregulated ADP/ATP translocases SLC25A4 and SLC25A6 connected to the upregulated 60 kDa heat shock protein, all involved in apoptosis. After X-rays, one protein interaction network was found integrating 5 proteins, 2 upregulated and 3 downregulated, where downregulated actin beta (ACTB) functioned as a hub protein connecting to all the 4 others (
Figure 2E). Here, the downregulated ACTB involved in double stranded DNA break repair (homologous recombination) interact with the upregulated DNA topoisomerase 2 alpha (TOP2A) that makes double stranded DNA breaks. This indicates increased double stranded DNA breaks through TOP2A, however a decrease in DNA repair through homologous recombination. Taken together, this suggests that OSCC cells exposed to X-rays use an ACTB-independent pathway to homologous recombination, or non-homologous end joining as the DNA repair pathway.
Discussion
EVs from irradiated cells have been proposed to be one of the delivery vehicles of non-targeted effects of radiation, which may have several implication for radiotherapy [
11]. Previous studies have shown that ionising radiation affects the cargo of EVs and, as a result, alter the function of the recipient cell by promoting migration and cell survival [
12,
25]. However, these studies have all been performed using gamma- or X-rays. To our knowledge, the influence of proton irradiation on the cargo of EVs has not yet been studied. Therefore, the aim of our study was to investigate and compare the proteome of EVs derived from OSCC cells exposed to either protons or X-rays.
In the present study, we found that proton irradiation resulted in downregulation of several solute carrier family proteins in the OSCC derived EVs. Three of the downregulated solute carrier family proteins were SLC1A5, SLC7A5, and SLC3A2. The latter can form heterodimers with SLC7A11 and be involved in ferroptosis, which is a non-apoptotic form of cell death [
26]. It can also produce heterodimers with SLC7A5 and be involved in the mTORC1 signaling pathway, important in the rapid growth of tumor cells [
27]. Since we observed a downregulation of both SLC3A2 and SLC7A5 in EVs after proton irradiation, it is in the present study relevant to focus on the heterodimer between these two solute carrier proteins and its involvement in the mTORC1 pathway. It has previously been shown that upregulation of SLC3A2 in tumor biopsies was associated with poor survival of OSCC patients. Moreover,
in vitro experiments with knockdown of SLC3A2 has been associated with reduced migration, invasion, and proliferation, and increased apoptosis of OSCC cells [
28]. SLC3A2 has also been used as a cancer stem cell marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [
29]. Both the heterodimer SLC3A2/SLC7A5 and SLC1A5 play an important role in driving the uptake of glutamine and leucine, critical for metabolism and cellular function [
27]. In the present study we found that in EVs, proton compared to X-irradiation caused downregulation of all these three transporter proteins, potentially reducing the mTORC1 activation which would negatively impact downstream effects of this pathway [
30,
31,
32]. The main downstream pathway of mTORC1 is cell growth, however recent research has also shown a link between mTORC1 and DNA damage response [
33,
34]. Here, mTOR-deficient cells showed a defect in recovering from the G2/M checkpoint after DNA damage. This may suggest that EVs derived from proton rather than X-irradiated cells may reduce cell growth and DNA repair capability in recipient cells.
We observed an interesting downregulation of EGFR in EVs after protons, while it was upregulated after X-rays. EGFR is highly expressed in OSCC and has been documented to correlate with poor prognosis and resistance to radiation therapy [
35,
36,
37]. Therefore, downregulation of EGFR in EVs derived from proton irradiated OSCC cells could imply that protons are more efficient in non-targeted cell inactivation compared to X-rays. However, this needs to be further elucidated.
Our results show that several proteins preventing or negatively regulating apoptosis were upregulated in OSCC cells after irradiation with high LET protons but were downregulated after irradiation with low LET protons and X-rays. Only high LET protons induced upregulation of the solute carrier family proteins SLC25A4 and SLC25A6 in OSCC cells, which are known to be involved in negative regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation leading to apoptosis [
38,
39]. In addition, HSPD1, both a positive and negative regulator of apoptosis [
40,
41] was upregulated after irradiation with high LET protons. Of interest, a strong protein-protein interaction network with SLC25A4 and SLC25A6 was documented (
Figure 3D) suggesting a negative regulation of apoptosis in this case. Moreover, HIGD1A has also been shown to prevent apoptosis through positive regulation of cytochrome c oxidase [
42,
43] and was upregulated in cells after high LET protons. Lastly, SLC25A22 was also upregulated in cells after irradiation with high LET protons, and has been shown to promote proliferation and metastasis while inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis through the MAPK/ERK pathway [
44]. All these proteins preventing or negatively regulating apoptosis were upregulated for high LET protons, but downregulated for low LET protons and X-rays. Therefore, our results imply that high LET protons could cause less apoptosis in OSCC cells compared to low LET protons and X-rays. This may be seen in relation with that high LET protons cause more clustered DNA damage [
45] which can be challenging for cells to repair, and more cell death could be expected. It has indeed been shown in lymphocytes that protons are more efficient in cell killing, however not primarily through apoptosis, but to a large degree through necrosis [
46]. Thus, our results may suggest that even though high LET protons seem to cause less apoptosis than X-rays, there could still be another type of cell death more prominent after protons. This is expected, as it has previously been shown in lung cancer cells that apoptosis only contributes to 5-10 % of the total cell death after X-irradiation [
47]. While other types of cell death such as necroptosis and ferroptosis contributes to 8-10 % and 14-18%, respectively, of the total cell death. Ferroptosis is a recently discovered type of cell death [
48] which has gained interest in the last years. It is a non-apoptotic form of cell death depending on iron and the accumulation of lipid peroxides [
49,
50]. ACLS3 is known as an antiferroptotic protein [
26], and we found ACSL3 to be downregulated after X-irradiation, while it was upregulated after irradiation with both low and high LET protons. Thus it might seem that both high and low LET protons can cause less ferroptosis than X-rays in OSCC cells through upregulation of the antiferroptotic protein ACLS3. In summary, our results show that anti-apoptotic proteins were upregulated and an anti-ferroptotic protein was downregulated after proton irradiation compared to X-irradiation in OSCC cells. Taken together, this further support the hypothesis that proton and X-irradiation induce different types of cell death.
ACTB is involved in positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination (HR) [
51,
52]. Proton irradiation has previously been shown to increase the necessity for HR rather than non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) potentially due to more clustered DNA damage compared to X-rays [
45,
53,
54,
55]. In the present study, we found that ACTB was downregulated after irradiation with X-rays compared to protons. This might indicate that OSCC cells exposed to X-rays rather than protons use an ACTB-independent pathway for homologous recombination, or use non-homologous end joining as the DNA repair pathway. Taken together, this finding support previous research showing that proton and X-irradiation induce different types of DNA break repair systems.
Conclusions
In the present study, we investigated and compared the proteome of EVs derived from OSCC cells exposed to either protons or X-rays. Interestingly, we found differential protein profiles both in the EVs and in the OSCC cells after protons compared to X-rays. We observed a downregulation of EV proteins affecting cell growth and DNA damage repair after proton-, but not X-irradiation. In the OSCC cells, our results demonstrate that proton and X-irradiation induce distinct types of cell death as well as dissimilar DNA break repair systems. These results are of potential importance as EVs derived from proton irradiated cancer cells could be explored as a tool to increase the efficacy of cancer treatment of non-irradiated cancer cells.
Materials and methods
Cell irradiation
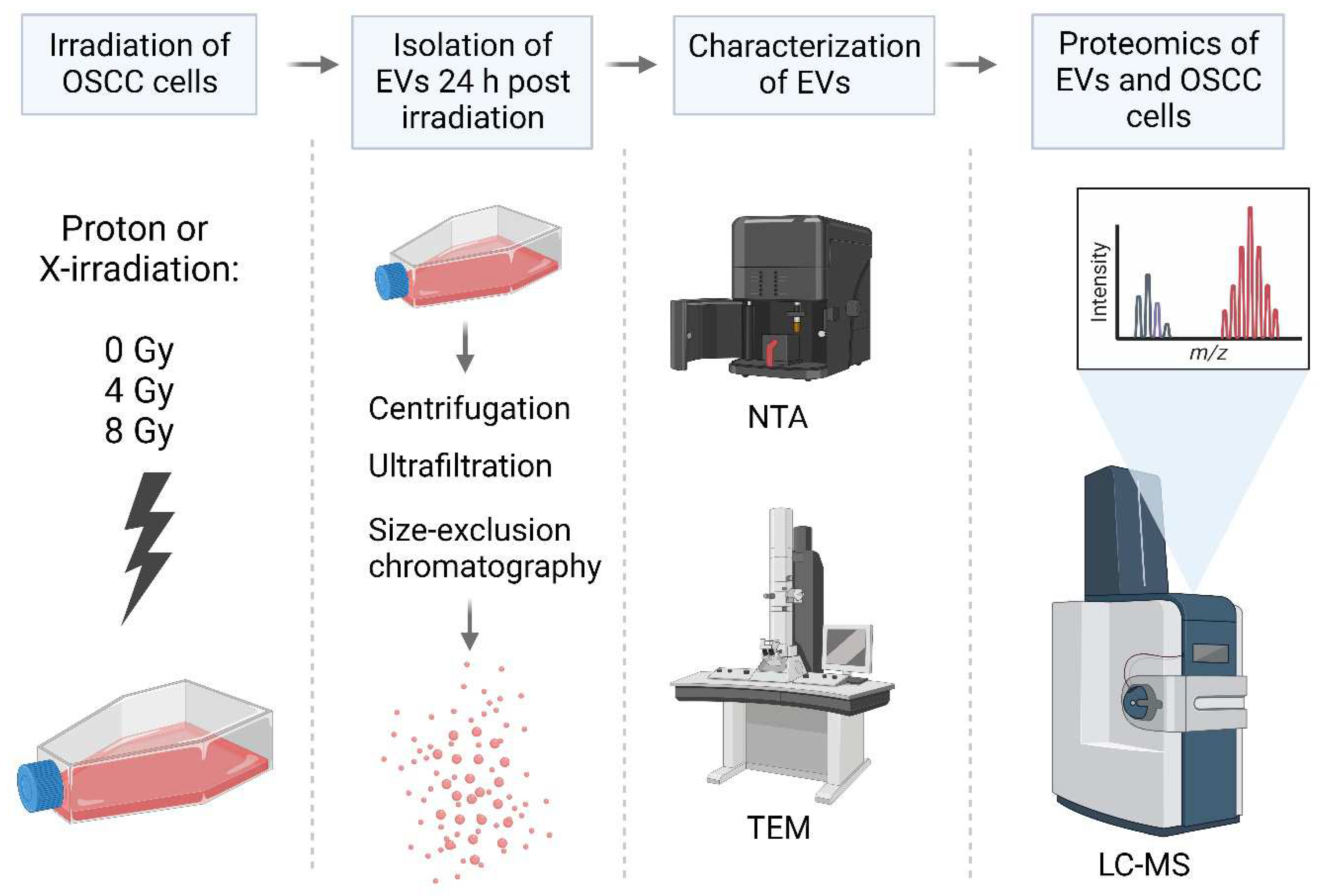
Human oral squamous cell carcinoma (PE/CA-PJ49/E10; ECACC; Salisbury, UK) cells were seeded in T80 flasks in a concentration of 2.5 x 106 cells in 15 mL of medium (Advanced DMEM + 1% exosome depleted FBS) in each flask. Cells were incubated for 48 hours (until 70-80% confluent) at 37C with 5% CO2. Before irradiation, the cell flasks were completely filled with 200 mL of preheated and CO2-equilibrated medium. The flasks were irradiated in a vertical position as the fixed proton nozzle was horizontally aligned. Thus, a vertical position was used for both proton and X-irradiation. For each biological replicate, three T80 flasks were irradiated at the same time, and the culture medium pooled during the EV isolation process (described below) to ensure enough EVs per replicate.
Cells were irradiated with 6 MV X-rays using a linear accelerator at Oslo University Hospital (Varian Medical Systems) or protons using a ProBeam system (Varian Medical Systems) at the Danish Centre for Particle Therapy, Aarhus University Hospital, with doses of 0 Gy (sham irradiation), 4 Gy and 8 Gy (n = 5 for all treatment and dose groups). For proton irradiation, two different treatment plans were used: plan 1 (low LET protons) where the cell flasks were placed at the entrance plateau of the pristine Bragg peak where the LET is approximately 1 keV/µm and plan 2 (high LET protons) where the cell flasks were positioned at the distal end of the Bragg peak where the LET is approximately 12.4 keV/µm (Figure S2, and Table S1 for simulated LET-values). Immediately after irradiation, the medium was discarded, and 15 mL of fresh medium was added to ensure that the EVs to be isolated from the medium represented EVs derived from the irradiated cells and not EVs derived from the cells before and during the irradiation and thereby being irradiated themselves. The conditioned medium was removed from the flasks 24 hours after irradiation to perform EV isolation. After removal of the conditioned media, the irradiated cells were scraped off using a cell scraper and pooled into one 15 mL tube before centrifuging at 1000g for 5 minutes. Then the supernatant was removed and the cells were stored in PBS in -80 C until proteomic analysis.
EV isolation
EVs were isolated from the media of irradiated E10 cells as previously described [
56] (
Figure 3). The media from each biological replicate were pooled into one tube, and the pooled samples were centrifuged at 4000g for 5 minutes (Megafuge 1.0 R, Heraeus Instruments) to remove cell debris. Then the supernatant was transferred to an empty tube and centrifuged at 15000g for 45 minutes (Centrifuge 5810 R, Eppendorf). Furthermore, the supernatant was concentrated by ultrafiltration using Amicon-Ultra columns (Merck Millipore, Tullagreen, Cork, Ireland) with a molecular cut off 100 kDa. Filter units were centrifuged at 4000g for 5 minutes for each 15 mL of sample until the entire sample volume was reduced to only 50-200 uL. Thereafter, each concentrated sample was loaded onto a size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) column (IZON qEVoriginal, 70nm, IZON Science) to separate the particles based on size. The eluate was collected into 16 sequential fractions of 0.5 mL. The protein concentration of each fraction was measured by spectrophotometry (Absorbance 280 nm, NanoDropOne, Thermofisher), and the first 4 protein-rich fractions known from experience to contain EVs were pooled (fractions 7-10). The pooled EV samples were stored in -80
C until proteomic analysis.
EV characterization
Particle concentration and size distribution was analysed by Nanoparticle Tracking Assay (NTA) on a NanoSight NS500 using NTA 3.4. EV morphology and size was further assessed using transmission electron microscopy (Philips CM120 BioTwin at IOB). The presence of characteristic EV markers was confirmed by comparing the 100 most common EV proteins according to the Vesiclepedia database (microvesicles.org) with the EV proteomic analysis (described below). We have submitted all relevant data of our experiment to the EV-TRACK knowledgebase (EV-TRACK ID: EV230980) [
57].
Proteomic analysis
In-solution digestion
Pooled EV samples and cell pellets were thawed on ice and 200 µl SILAC Phosphoprotein lysis buffer A and B (Invitrogen, Oslo, Norway) was added. The cell pellet was homogenized with a pestle (20x) for mechanical breakage of the cells and incubated for 10 min on ice. After this, the pooled EV samples and cell samples followed the same protocol. The samples were centrifuged at 2,400 g for 10 minutes at 4°C (Centrifuge 5415R, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) and the supernatant was transferred to a new tube. Next, the proteins were precipitated by adding four volumes of ice cold acetone, vortexing, and incubation at -20°C overnight. Subsequently, the samples were centrifuged at 16,000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C (Centrifuge 5415R, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) and the supernatant was discarded. The pellet containing the precipitated proteins were dissolved in 50 µl 6 M urea and 100 mM ammonium bicarbonate, pH 7.8. For reduction and alkylation of cysteines, 2.5 µl of 200 mM DTT in 100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8 was added and the samples were incubated at 37°C for 1 h followed by addition of 7.5 µl 200 mM iodoacetamide for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. The alkylation reaction was quenched by adding 10 µl 200 mM DTT at 37°C for 1 h. Subsequently, the proteins were digested with 10 µg trypsin GOLD (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) for 16 h at 37°C. The digestion was stopped by adding 5 µl 50 % formic acid and the generated peptides were purified using a 10 µl OMIX C18 micro-SPE pipette tip (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), and dried using a Speed Vac concentrator (Concentrator Plus, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany).
LC-MS analysis
The samples were analyzed by LC-MS using a timsTOF Pro (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) which was coupled online to a nanoElute nanoflow liquid chromatography system (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany) via a CaptiveSpray nanoelectrospray ion source. The dried peptides were dissolved in 4 µL 0.1% formic acid and 2 µL of sample was injected. The peptides were separated on a reversed phase C18 column (25 cm x 75 µm, 1.5 µm, PepSep (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). Mobile phase A contained water with 0.1% formic acid, and acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid was used as mobile phase B. The peptides were separated by a gradient from 0-35% mobile phase B over 60 min at a flow rate of 300 nl/min at a column temperature of 50°C. MS acquisition was performed in DDA-PASEF mode. The capillary voltage was set to 1.5 kV with a mass range of 100 to 1700 m/z. The number of PASEF ranges was set to 20 with a total cycle time of 1.16 s, charge up to 5, target intensity of 20 000, intensity threshold of 1 750, and active exclusion with release after 0.4 min. An inversed reduced TIMS mobility (1/k0) of 0.85-1.40 Vs/cm2 was used with a range time of 100 ms, an accumulation time of 100 ms, a duty cycle of 100%, and a ramp rate of 9.51 Hz. Precursors for data-dependent acquisition were fragmented with an ion mobility-dependent collision energy, which was linearly increased from 20 to 59 eV.
Database search
The LC/MS data were searched against the human Uniprot database (20,431 entries), with PEAKS X+ software version 10.5 (Bioinformatics Solutions, Waterloo, ON, Canada). The following parameters were used: digestion enzyme, trypsin; maximum missed cleavage, 2; fragment ion mass error tolerance, 0.03 Da; parent ion error tolerance, 15 ppm. Oxidation of methionine, and acetylation of the N-terminus were specified as variable modifications and carbamidomethylation of cysteines as a fixed modification. The maximum number of PTMs was set to 2. A false-discovery rate of 1 % was applied to the datasets.
Label-free quantitation
For label-free quantification (LFQ) using PEAKS, ID directed LFQ with outlier removal was applied. The following parameters were used on peptide features: quality ≥ 5, peptide ID count per group ≥ 1, detected in at least one sample per group. The following parameters were applied on protein: significance ≥ 20, fold change ≥ 1 (≥ 2 for the cell samples), significance method ANOVA with at least 2 peptides, and TIC was used for normalization of the data.
Protein analysis
Venn diagrams were created in FunRich version 3.1.3 using all detected proteins in the treatment groups in EVs or OSCC cells. Proteins found to be significantly up- or downregulated in the corresponding non-irradiated controls were excluded in further analysis. Also proteins that were up- or downregulated in less than 4 replicates were excluded from further analysis. All included significant EV proteins are shown in
Table 1, and all included cell proteins in
Table 2 and 3. Protein-protein interaction networks were created in STRING version 12.0 using all significantly up- or downregulated proteins in the treatment groups in EVs or OSCC cells.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.J.E., E.M., T.M.S., and H.K.G.; methodology, I.S.J, O.Z., M.S, and B.S.S.; formal analysis, I.S.J., O.Z., and B.T.; investigation, I.S.J., O.Z.; writing-original draft preparation, I.S.J., B.T.; writing-review and editing, I.S.J., O.Z., M.S., B.T., B.S.S., E.M., N.J.E., T.M.S., and H.K.G.; visualization, I.S.J.; supervision, N.J.E., E.M., T.M.S., and H.K.G.; project administration, H.K.G.; funding acquisition, N.J.E., E.M., T.M.S., and H.K.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. .
Funding
This work is supported by UiO Life Science at the University of Oslo under grant reference 2018/10221 and Southern-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority under grant number 2019050.
Data availability statement
All relevant data of our experiment has been submitted to the EV-TRACK knowledgebase (EV-TRACK ID: EV230980) [
57].
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Lisbeth Ann Abildtrup at the Institute of Odontology and Oral Health, Aarhus University, for letting us use their lab and centrifuge for EV isolation after proton irradiation. Our gratefulness also extends to Delmon Arous at the Department of Medical Physics, Cancer Clinic, Oslo University Hospital, for performing the LET simulations. Furthermore, we are appreciative of Reidun Øvstebø at the Blood Cell Research Group, Department of Medical Biochemistry, Oslo University Hospital, for letting us use the NTA and Nanodrop Pro at their lab.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Bucci, J.; Malouf, D.; Knox, M.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Exosomes in Cancer Radioresistance. Front Oncol 2019, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, T.; Hargitai, R.; Safrany, G.; Lumniczky, K. Extracellular Vesicles in Modifying the Effects of Ionizing Radiation. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, M.; Tuncay Cagatay, S.; Elbakrawy, E.M. Non-targeted effects of radiation: a personal perspective on the role of exosomes in an evolving paradigm. Int J Radiat Biol 2022, 98, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.; Fernandez-Palomo, C.; McNeill, F.E.; Seymour, C.B.; Rainbow, A.J.; Mothersill, C.E. Exosomes are released by bystander cells exposed to radiation-induced biophoton signals: Reconciling the mechanisms mediating the bystander effect. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0173685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, M.; McNeill, F.E.; Seymour, C.; Rainbow, A.J.; Mothersill, C.E. An observed effect of ultraviolet radiation emitted from beta-irradiated HaCaT cells upon non-beta-irradiated bystander cells. Radiat Res 2015, 183, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mayah, A.H.; Irons, S.L.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R.; Kadhim, M.A. Possible role of exosomes containing RNA in mediating nontargeted effect of ionizing radiation. Radiat Res 2012, 177, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jella, K.K.; Rani, S.; O'Driscoll, L.; McClean, B.; Byrne, H.J.; Lyng, F.M. Exosomes are involved in mediating radiation induced bystander signaling in human keratinocyte cells. Radiat Res 2014, 181, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mothersill, C.; Rusin, A.; Seymour, C. Relevance of Non-Targeted Effects for Radiotherapy and Diagnostic Radiology; A Historical and Conceptual Analysis of Key Players. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschelknaus, L.; Azimzadeh, O.; Heider, T.; Winkler, K.; Vetter, M.; Kell, R.; Tapio, S.; Merl-Pham, J.; Huber, S.M.; Edalat, L.; et al. Radiation alters the cargo of exosomes released from squamous head and neck cancer cells to promote migration of recipient cells. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yentrapalli, R.; Merl-Pham, J.; Azimzadeh, O.; Mutschelknaus, L.; Peters, C.; Hauck, S.M.; Atkinson, M.J.; Tapio, S.; Moertl, S. Quantitative changes in the protein and miRNA cargo of plasma exosome-like vesicles after exposure to ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 2017, 93, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mayah, A.; Bright, S.; Chapman, K.; Irons, S.; Luo, P.; Carter, D.; Goodwin, E.; Kadhim, M. The non-targeted effects of radiation are perpetuated by exosomes. Mutat Res 2015, 772, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, A.; Wojakowska, A.; Marczak, L.; Lysek-Gladysinska, M.; Smolarz, M.; Story, M.D.; Polanska, J.; Widlak, P.; Pietrowska, M. Ionizing radiation affects the composition of the proteome of extracellular vesicles released by head-and-neck cancer cells in vitro. J Radiat Res 2019, 60, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.; Garden, A.S.; Gunn, G.B.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Morrison, W.H.; Hernandez, M.; Crutison, J.; Lee, J.J.; Ye, R.; Fuller, C.D.; et al. Intensity-modulated proton beam therapy (IMPT) versus intensity-modulated photon therapy (IMRT) for patients with oropharynx cancer - A case matched analysis. Radiother Oncol 2016, 120, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Liu, K.; Hou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. The evolution of proton beam therapy: Current and future status. Mol Clin Oncol 2018, 8, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, A.L.; Schuemann, J.; Paganetti, H. A phenomenological relative biological effectiveness (RBE) model for proton therapy based on all published in vitro cell survival data. Phys Med Biol 2015, 60, 8399–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Mechanisms and review of clinical evidence of variations in relative biological effectiveness in proton therapy. International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics 2022, 112, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values for proton beam therapy. Variations as a function of biological endpoint, dose, and linear energy transfer. Phys Med Biol 2014, 59, R419–R472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, B.S.; Bassler, N.; Nielsen, S.; Horsman, M.R.; Grzanka, L.; Spejlborg, H.; Swakon, J.; Olko, P.; Overgaard, J. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) and distal edge effects of proton radiation on early damage in vivo. Acta Oncol 2017, 56, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, B.S.; Pawelke, J.; Bauer, J.; Burnet, N.G.; Dasu, A.; Hoyer, M.; Karger, C.P.; Krause, M.; Schwarz, M.; Underwood, T.S.A.; et al. Does the uncertainty in relative biological effectiveness affect patient treatment in proton therapy? Radiother Oncol 2021, 163, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saager, M.; Peschke, P.; Brons, S.; Debus, J.; Karger, C.P. Determination of the proton RBE in the rat spinal cord: Is there an increase towards the end of the spread-out Bragg peak? Radiother Oncol 2018, 128, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B. Why RBE must be a variable and not a constant in proton therapy. The British journal of radiology 2016, 89, 20160116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutschelknaus, L.; Peters, C.; Winkler, K.; Yentrapalli, R.; Heider, T.; Atkinson, M.J.; Moertl, S. Exosomes Derived from Squamous Head and Neck Cancer Promote Cell Survival after Ionizing Radiation. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0152213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Targeting ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer: a double-edged sword. Trends in Cancer 2021, 7, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachef, M.; Ali, A.K.; Almutairi, S.M.; Lee, S.H. Targeting SLC1A5 and SLC3A2/SLC7A5 as a Potential Strategy to Strengthen Anti-Tumor Immunity in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 624324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Sun, Z. Overexpression of membranal SLC3A2 regulates the proliferation of oral squamous cancer cells and affects the prognosis of oral cancer patients. J Oral Pathol Med 2021, 50, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linge, A.; Lohaus, F.; Lock, S.; Nowak, A.; Gudziol, V.; Valentini, C.; von Neubeck, C.; Jutz, M.; Tinhofer, I.; Budach, V.; et al. HPV status, cancer stem cell marker expression, hypoxia gene signatures and tumour volume identify good prognosis subgroups in patients with HNSCC after primary radiochemotherapy: A multicentre retrospective study of the German Cancer Consortium Radiation Oncology Group (DKTK-ROG). Radiother Oncol 2016, 121, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzagalli, M.D.; Bensimon, A.; Superti-Furga, G. A guide to plasma membrane solute carrier proteins. FEBS J 2021, 288, 2784–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, S.M.; Ali, A.K.; He, W.; Yang, D.S.; Ghorbani, P.; Wang, L.; Fullerton, M.D.; Lee, S.H. Interleukin-18 up-regulates amino acid transporters and facilitates amino acid-induced mTORC1 activation in natural killer cells. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, 4644–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terren, I.; Orrantia, A.; Vitalle, J.; Zenarruzabeitia, O.; Borrego, F. NK Cell Metabolism and Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, H.J.; Zhang, W.; Lin, S.H.; Yang, W.H.; Wang, J.Z.; Shen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, J.; et al. Systems biology approach reveals a link between mTORC1 and G2/M DNA damage checkpoint recovery. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Vassetzky, Y.; Dokudovskaya, S. mTORC1 pathway in DNA damage response. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2018, 1865, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, F.A.; Noguti, J.; Oshima, C.T.; Ribeiro, D.A. Effective targeting of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) for treating oral cancer: a promising approach. Anticancer Res 2014, 34, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohanapure, N.S.; Khandeparkar, S.G.S.; Saragade, P.B.; Gogate, B.P.; Joshi, A.R.; Mehta, S.R. Immunohistochemical study of epidermal growth factor receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2/neu, p53, and Ki67 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2022, 26, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahsavari, F.; Miri, R.; Ghorbanpour, M. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in oral and esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Dent Res J (Isfahan) 2020, 17, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, P.; Livstone, M.S.; Lewis, S.E.; Thomas, P.D. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform 2011, 12, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temkin, V.; Huang, Q.; Liu, H.; Osada, H.; Pope, R.M. Inhibition of ADP/ATP exchange in receptor-interacting protein-mediated necrosis. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, D.; Choy, G.; Tang, D.G. Cytosolic accumulation of HSP60 during apoptosis with or without apparent mitochondrial release: evidence that its pro-apoptotic or pro-survival functions involve differential interactions with caspase-3. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2007, 282, 31289–31301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, J.C.; Dohi, T.; Kang, B.H.; Altieri, D.C. Hsp60 regulation of tumor cell apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2008, 283, 5188–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Asano, Y.; Shintani, Y.; Aoyama, H.; Kioka, H.; Tsukamoto, O.; Hikita, M.; Shinzawa-Itoh, K.; Takafuji, K.; Higo, S. Higd1a is a positive regulator of cytochrome c oxidase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Chen, M.; Mu, W.J.; Luo, H.Y.; Guo, L. The functional role of Higd1a in mitochondrial homeostasis and in multiple disease processes. Genes Dis 2023, 10, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, P.; Liang, H.; Fu, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, C.; Chen, H.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Zeng, R.; et al. SLC25A22 promotes proliferation and metastasis by activating MAPK/ERK pathway in gallbladder cancer. Cancer Cell Int 2019, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymonowicz, K.; Krysztofiak, A.; Linden, J.V.; Kern, A.; Deycmar, S.; Oeck, S.; Squire, A.; Koska, B.; Hlouschek, J.; Vullings, M.; et al. Proton Irradiation Increases the Necessity for Homologous Recombination Repair Along with the Indispensability of Non-Homologous End Joining. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miszczyk, J.; Rawojc, K.; Panek, A.; Borkowska, A.; Prasanna, P.G.S.; Ahmed, M.M.; Swakon, J.; Galas, A. Do protons and X-rays induce cell-killing in human peripheral blood lymphocytes by different mechanisms? Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 2018, 9, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, G.; Zhang, Y.; Koppula, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Lin, S.H.; Ajani, J.A.; Xiao, Q.; Liao, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. The role of ferroptosis in ionizing radiation-induced cell death and tumor suppression. Cell Res 2020, 30, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Carter, B.Z.; Andreeff, M.; Ishizawa, J. Molecular Mechanisms of Ferroptosis and Updates of Ferroptosis Studies in Cancers and Leukemia. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, J.; Gan, L.; Xue, J. Ferroptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in cancer: Crucial cell death types in radiotherapy and post-radiotherapy immune activation. Radiother Oncol 2023, 184, 109689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Chen, K.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. Structure of the NuA4 acetyltransferase complex bound to the nucleosome. Nature 2022, 610, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, K.; Fradet-Turcotte, A.; Avvakumov, N.; Lambert, J.-P.; Roques, C.; Pandita, R.K.; Paquet, E.; Herst, P.; Gingras, A.-C.; Pandita, T.K. The TIP60 complex regulates bivalent chromatin recognition by 53BP1 through direct H4K20me binding and H2AK15 acetylation. Molecular cell 2016, 62, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosse, N.; Fontana, A.O.; Hug, E.B.; Lomax, A.; Coray, A.; Augsburger, M.; Paganetti, H.; Sartori, A.A.; Pruschy, M. Deficiency in homologous recombination renders Mammalian cells more sensitive to proton versus photon irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2014, 88, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, A.O.; Augsburger, M.A.; Grosse, N.; Guckenberger, M.; Lomax, A.J.; Sartori, A.A.; Pruschy, M.N. Differential DNA repair pathway choice in cancer cells after proton- and photon-irradiation. Radiother Oncol 2015, 116, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitti, E.T.; Kacperek, A.; Parsons, J.L. Targeting DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Enhances Radiosensitivity of HPV-Positive and HPV-Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma to Photons and Protons. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, E.M.; Vestad, B.; Steffensen, L.A.; Aass, H.C.D.; Saeed, M.; Ovstebo, R.; Costea, D.E.; Galtung, H.K.; Soland, T.M. Efficient extracellular vesicle isolation by combining cell media modifications, ultrafiltration, and size-exclusion chromatography. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0204276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Agostinis, P.; Akay, O.; Anand, S.; Anckaert, J.; Martinez, Z.A.; Baetens, T.; Beghein, E.; Bertier, L.; et al. EV-TRACK: transparent reporting and centralizing knowledge in extracellular vesicle research. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).