1. Introduction
Voice conversion (VC) aims to modify the speech signal spoken by a source speaker to make it sound as if it was spoken by a different speaker, referred to as the target speaker while keeping the linguistic content unchanged. VC has a wide range of applications, including personalized speech synthesis, speech enhancement, speaker identification, human-robot interaction, and movie dubbing.
Generally, voice conversion systems differ in terms of how the datasets are obtained and utilized during training. Systems using parallel training data require recordings of the same linguistic content from paired source and target speakers, while those using non-parallel training data (i.e., non-parallel VC) are trained on unpaired speech data. A recent comprehensive overview of VC techniques and their performance evaluation methods, from statistical approaches to deep learning, can be found in [
1,
2]. Various methods have been proposed for parallel voice conversion tasks using statistical modeling, such as Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) [
3,
4] and frequency warping [
5,
6]. Although these methods are low-cost in terms of time and resources, spectral details are typically lost when using low-dimensional representations, leading to overly smoothed speech waveforms. To overcome this issue, more advanced models have been developed, taking advantage of machine learning-based techniques such as Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) [
7,
8], Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) [
9] and Sequence-To-Sequence (Seq2Seq) [
10,
11], which achieved superior performance in terms of naturalness and similarity when compared to conventional VC methods [
2].
While previous VC methods have shown promising outcomes, they face a significant limitation: the requirement for parallel training data, which may not always be readily available in practice.
In recent years, VC research utilizing non-parallel training data has seen substantial improvements, largely due to the effectiveness of deep learning techniques in learning mapping functions. Successful techniques have been developed, such as those in [
12,
13,
14,
15]. For example, approaches including CyleGAN-VC [
16,
17], StarGAN-VC [
18,
19] and VAW-GAN [
20,
21], have employed generative adversarial networks (GANs) [
22] to improve both speech quality and similarity to the target speaker, particularly when a large amount of speech data is available. Other approaches, introduced in [
13,
15], use Seq2Seq models and aim to separate linguistic features from speaker identity components. During the training process, the model learns linguistic representations from acoustic features using the encoder output as the reference. At run-time conversion, the Seq2Seq decoder is used to reconstruct the acoustic features, taking advantage of target speaker representations.
The recent advances in non-parallel VC involve the use of linguistic features extracted from the automatic speech recognition (ASR) model trained using a large multi-speaker corpus, such as Phonetic PosterioGram (PPG) and bottleneck features. PPGs refer to frame-level contextual representations derived from the posterior probabilities associated with each phonetic class, using a speaker-independent ASR system (SI-ASR).
The application of these techniques has received particular attention in relevant studies [
10,
23,
24,
25,
26] where a conversion model is first used to convert PPGs extracted from the source speech into spectral features of the target speaker. Subsequently, a vocoder is applied using the converted features to generate the target speaker’s speech waveforms. WaveNet [
24] serves as the primary neural vocoder widely utilized in VC methods. However, it has a limitation in generating only one speech sample at a time, which presents challenges for real-time applications. Moreover, despite the success of PPGs, one of their limitations is the lack of smoothness in the trajectory of the generated waveforms, leading to speech artifacts, particularly in run-time conversion.
In this paper, we propose an innovative non-parallel voice conversion framework that relies on an autoregressive model, a fusion of PPGs and speaker-embedding linguistic features, and an LPCNet vocoder for any-to-one voice conversion. This method allows us to transform the voice of an arbitrary speaker, including those who were not part of the training data, into the voice of a known speaker. Our approach focuses on improving the robustness of VC techniques in terms of speech quality, naturalness, and speaker similarity.
In summary, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
We propose a VC framework using an autoregressive conversion model to obtain acoustic features with higher precision, thereby generating a smooth trajectory and reducing speech error problems.
We use a high-fidelity LPCNet-based vocoder, which improves the efficiency of speech synthesis
and can generate speech in real time.
We leverage the use of SI-PPGs, which exclude the attention-based duration conversion module. Additionally, we incorporate speaker embeddings obtained from the speaker encoder network as auxiliary features, which improves the overall training stability and minimizes pronunciation artifacts.
We evaluate the effectiveness of our system by performing “any-to-one” voice conversion pairs on the popular American CMU-ARCTIC database.
Experiments on both objective and subjective evaluations showed that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art systems, demonstrating clearer pronunciation and greater speaker similarity.
The remaining sections of this paper are organized as follows:
Section 2 introduces the related work that has motivated our research.
Section 3 describes the method we propose.
Section 4 details the experimental setup.
Section 5 presents the results and discussion. We conclude in
Section 6.
2. Related Work
Non-parallel VC techniques are even more challenging because they do not need parallel data for training. Some successful non-parallel VC methods include variational autoencoder (VAE) [
21,
52], generative adversarial network (GAN) [
22] and its variants such as CycleGAN [
17] and StarGAN [
18]. Although these methods have focused on transforming a non-parallel corpus into a quasi-parallel corpus and then on learning a conversion function (which is not so straightforward), they can lead to a degradation of speech quality.
Recent methods based on the use of linguistic features PPGs and vocoders have also been proposed and have proven to be effective [
10,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27]. PPGs are high-level contextual representations obtained from the posterior probabilities of each phonetic class using a speaker-independent ASR system. Although PPG techniques have been applied successfully, they still have inherent limitations, e.g., the quality of the PPGs is highly dependent on the ASR system.
While conventional parametric vocoders, as mentioned in the work of Kawahara et al. [
28], could be utilized, they tend to produce synthesized speech of lower quality than neural vocoders. In particular, WaveNet, presented by Liu et al. [
24], represents a very successful implementation of a neural vocoder. WaveNet operates as an autoregressive generative model, known for its ability to generate high-fidelity audio waveforms. WaveNet’s autoregressive structure greatly improves the continuity of the generated waveforms; however, its drawback lies in the slowness of real-time synthesis, due to the one-by-one generation of waveform samples. In response to this limitation, an alternative to WaveNet has been proposed in the form of WaveRNN [
29], which seeks to improve the quality of the WaveNet model. WaveRNN uses a layer of sparse gated recurrent units (GRUs) rather than the dilated causal convolutions used in WaveNet.
Recently, a highly efficient neural vocoder, known as LPCNet [
30], has been introduced, drawing inspiration from WaveRNN. LPCNet leverages the principles of linear predictive coding (LPC) to model vocal tract responses and incorporates linear prediction techniques into the WaveRNN architecture, resulting in a reduction in the complexity of generating raw speech waveforms. Notably, LPCNet achieves the synthesis of higher-quality speech compared to WaveRNN, even when using the same network size. Moreover, LPCNet exhibits real-time or faster-than-real-time performance on a single CPU core, thanks to efficient vectorization techniques. Since its inception, LPCNet has emerged as a popular choice for various speech synthesis tasks.
Hence, numerous approaches have been proposed to improve the inference speed of LPCNet [
31,
32,
33]. In addition, there is considerable enthusiasm for high-fidelity neural vocoders that exploit generative adversarial networks for their lightweight architectures and fast speech generation capabilities [
34,
35,
36]. Nevertheless, the training of these vocoders can pose challenges, potentially leading to audible artifacts like pitch errors and periodicity artifacts, attributed to their non-autoregressive (non-AR) structures [
37].
Our proposed method differs from conventional PPG-VC techniques, such as the works of Zhou et al. [
23] and Sun et al. [
38], in that we use the acoustic features of the previous step as input to generate next-step output through the proposed AR structure, resulting in a smooth waveform and low speech distortion. Indeed, taking advantage of the PPGs, our proposal allows for any-to-one conversion due to its speaker-independent characteristics. In addition, as part of our approach, we use speaker embeddings derived from a speaker encoder network, originally trained for the classification of multiple speakers [
39], as additional features to more accurately capture the characteristics of target speakers. The concatenation of PPGs and speaker embedding features results in a more intelligible converted speech.
For speech synthesis, instead of the basic WaveNet vocoder, used in such baseline systems as [
10,
40], we use a high-fidelity LPCNet-based vocoder [
30], which combines linear prediction with recurrent neural networks. LPCNet has a considerable advantage in terms of the simplicity of the model. WaveNet, on the other hand, is a much more complex model, involving more neurons. As a result, it often requires a larger dataset during training to achieve high audio-quality speech.
3. Method
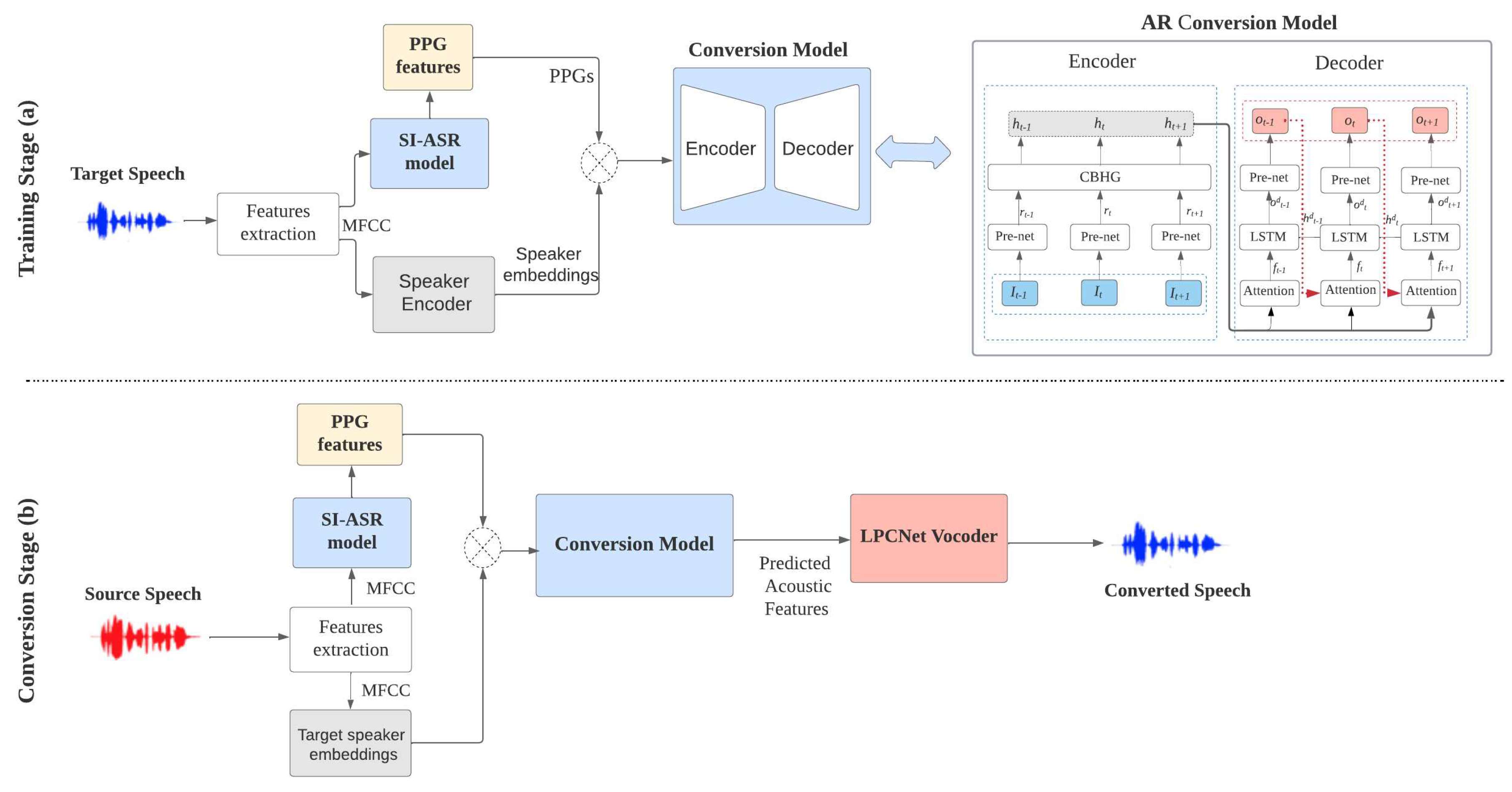
The architecture of the proposed non-parallel VC framework, shown in
Figure 1, comprises three
main components: (1) Linguistic features extraction, (2) Autoregressive conversion model, and (3)
LPCNet synthesizer. We use an SI-ASR model to extract PPG linguistic features, which are used as
input. The conversion model includes an encoder and an autoregressive decoder, which aims to
convert the linguistic features into acoustic features. We adopt the LPCNet vocoder as a synthesizer
that uses the predicted acoustic features to reconstruct the speech waveform. All these components are
described in the following subsections.
3.1. Linguistic Features Extraction
To generate PPG features, an ASR system is used to balance the difference between speakers. We used a speaker-independent ASR model (SI-ASR) based on the Kaldi toolkit [
41]. The model is trained to estimate posterior probabilities using a large multi-speaker corpus. More specifically, the input of the SI-ASR consists of acoustic features
extracted at each frame
t. The outputs are posterior probabilities vectors, denoted
, which represent the PPG’s linguistic features calculated as follows:
where
denotes the posterior probability of each phonetic class
s.
The speaker embeddings are generated through a DNN-based speaker encoder, which was initially trained for multi-speaker classification, following the methodology employed in the [
39] research. During the training stage, these speaker embeddings are calculated and preserved for later use. Subsequently, the extracted SI-PPG features are judiciously combined with the speaker embeddings to be used as the input data to the conversion model.
3.2. Autoregressive Conversion ModelConversion Model
We adopt an encoder-decoder recurrent network for the conversion model. The encoder we use is based on the Tacotron model [
42]. Firstly, a sequence of features including the combined SI-PPGs and speaker embeddings is taken as input. The input vectors are then passed through a Pre-Net, a non-linear transformation, which includes a bottleneck layer with dropout to facilitate convergence. The pre-net outputs are further processed using a CBHG module [
42] to produce the final encoder representation. The effectiveness of CBHG stems from its ability to learn context-dependent representations at a high level. CBHG’s architecture consists of a 1-D convolutional bank, highway networks [
43], and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (Bi-GRU) [
44] layers.
We define a sequence of linguistic features of length N as the encoder input, where . Here, N represents the number of frames and is the dimension of the features sequence. The Pre-Net layer produces a set of output vectors denoted as , where .
The encoder outputs sequence (i.e., the hidden representations) are obtained, where , is the dimension of the encoder output vectors.
For the decoder, we use an attention-based decoder, which is an autoregressive RNN model. This means that it predicts a sequence of acoustic features using the encoder outputs. The architecture consists of an attention layer, an LSTM layer, and a Pre-Net layer. The attention layer employs a “Bahdanau” attention mechanism, which compresses the encoder output into a fixed-length context vector. This context vector is then combined with the output of the attention layer and used as input for the LSTM layer.
We define the sequence of acoustic features representing the decoder output as
, where
. First, at each step
t, the attention layer generates a fused representation, denoted as
, which is computed by concatenating the previous acoustic feature
with the encoder output
using the following formulas:
where
is the concatenated representations as
Secondly, the LSTM layer is initialized using two inputs: the generated fusion representation denoted
, and the decoder hidden state from the previous step denoted
. The decoder LSTM output
is produced as
The LSTM output is then fed into the pre-net layer to generate the decoder output. The Pre-Net serves as bottleneck information needed to learn the autoregressive decoder.
The acoustic feature vector representing the decoder output is finally generated.
3.3. LPCNet Synthesizer
To generate the converted speech, a waveform synthesizer based on a variant of WaveRNN vocoder [
29] is used. We chose LPCNet vocoder [
30], an efficient neural vocoder, which combines linear prediction with RNN to considerably improve the audio quality of the resynthesized speech. LPCNet generates speech from Bark-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (BFCCs) [
45] and two pitch (period, correlation) parameters. This presents a high-level control of the spectral shape outputs as it directly depends on the shape of the linear predictive coding filter.
To implement the model, we were inspired by open-source code made available by the Mozilla and Google LLC teams [
30]. To achieve better control over high-frequency features, we increased the dimension of the input features from 18-D Bark-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (BFCCs) to 30-D BFCCs. This resulted in the extraction of 32-D acoustic features comprising 30-D BFCCs, 1-D pitch period, and 1-D pitch correlation.
3.4. Model Training
In the training stage, acoustic features are first extracted from the target speech signals. PPGs are then computed using the SI-ASR model from the MFCC features. Speaker embeddings are also computed from the target speech as auxiliary features through a speaker encoder neural network. These embeddings will then serve as a reference for all subsequent real-time conversions to the target speaker. The conversion model takes PPG features and speaker embeddings as inputs and predicts acoustic features as outputs.
All parameters of the conversion model are optimized using the mean squared error (MSE) loss between the ground truth and the predicted acoustic feature vectors through the back-propagation algorithm (BP).
At run-time conversion, the PPG features are extracted from the source speech. These features are then concatenated with the previously calculated speaker embeddings of the target speaker and fed into the conversion model to predict acoustic features. Finally, the LPCNet vocoder utilizes the predicted features to generate the speech waveform. This process is shown in
Figure 1.
4. Experiments
The following subsections outline the experimental datasets, implementation details, and the various experiments conducted to evaluate the proposed method.
4.1. Database
We use the American CMU-ARCTIC database [
46] for VC experiments. The multi-speaker TIMIT corpus [
47] was used to train the SI-ASR system. The CMU-ARCTIC database is a collection of parallel recordings of seven professional speakers of different genders and accents. Each speaker recorded a set of 1132 sentences in the form of “.wav” audio files. All the speech signals are sampled at a sampling rate of 16 kHz, windowed by a 25 ms Hamming window, and shifted every 5 ms. In this paper, only the utterances of native US English speakers were taken into account: two females (SLT and CLB) and two males (BDL and RMS). A total of 500 utterances were selected for each speaker to form the non-parallel training set. A further 50 non-overlapping utterances were selected for testing and evaluation. In our experiments, we performed an any-to-one speech conversion, using the female speaker SLT as the target speaker and two male speakers (BDL, CLB), and a female speaker (RMS) as the source speakers as follows: BDL to SLT, CLB to SLT, and RMS to SLT.
4.2. Implementation Details
For each input utterance, the PPGs are obtained using a DNN-based SI-ASR model with four hidden layers. This model is implemented using the Kaldi speech recognition toolkit [
41] and trained on TIMIT corpus [
47]. For DNN-ASR training, we use 40-dimensional filterbank acoustic features, extracted every 10 ms frameshift, with 25 ms window size as input. The output of this model is the sequence of PPG feature vectors. For each waveform input, PPG feature vectors of dimension 512 (
) are extracted. The conversion model takes as input a sequence of 512-D PPG features and speaker embeddings, which are used as additional features to better capture different aspects of the target speaker’s characteristics. The speaker embeddings are derived from a DNN-based speaker encoder trained for multi-speaker classification as applied in the [
39] study. To compute speaker embeddings for the target speaker, we choose a reference recording with a long duration from the training data. We also extract 39th-order mel-cepstral coefficients (MCCs) from spectral envelopes, which are utilized as spectral features for objective evaluation.
To train the conversion model, we choose a batch size of 32, an Adam optimizer with , , and an initial learning rate of . We used Mean Square Error (MSE) as the loss function. Firstly, we used a Pre-Net, which consisted of a dense layer with a dropout rate of , and an output dimension of 512. Secondly, we incorporated a CBHG module with a 1-D convolutional bank comprising 16 sets of 1-D convolutional filters, each with 128 output channels and ReLU activation. These convolutional outputs were then fed into a highway network (consisting of four fully connected layers) followed by a Bi-GRU (with 128 units per direction) to extract 256-dimensional context-feature representations (where ) as encoder outputs. In the third step, the 256-dimensional encoder outputs were combined with previously predicted acoustic features through an attention RNN layer.
The fused representations were then passed through an LSTM layer of 512 cells. Finally, the outputs of the LSTM layer were fed into a decoder Pre-Net with a dropout rate of to predict acoustic features (where ) to be used by LPCNet for speech synthesis.
The LPCNet operates at a 16 kHz sampling rate and a frame rate network that processes 10 ms frames. We use 32-D acoustic features including 30-D Bark-scale frequency cepstral coefficients, 1-D pitch period, and 1-D pitch correlation. The LPCNet is trained for 200 epochs, the batch size is 32, and the learning rate is set to 1 × .
4.3. Compared Methods
To evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed system (Proposed) on the VC task, four recent state-of-the-art systems (S1, S2, S3, S4) designed for VC were chosen for comparison using parallel and non-parallel training data. Note that all systems were tested under the same conditions for a fair and complete evaluation. The details are described below:
Baseline system 1 (S1): Refers to parallel VC system [
11] based on ASR and text-to-speech (TTS)-oriented pretraining strategy using Transformer models for sequence-to-sequence VC. This method provides a significant improvement in performance in terms of intelligibility and speech quality, even when training data are limited.
Baseline system 2 (S2): Refers to parallel baseline VC system [
10] based on sequence-to-sequence mapping model with attention, which achieved better performance on naturalness and speaker similarity when compared with conventional methods.
Baseline system 3 (S3): Refers to non-parallel VC system [
48] based on a variant of the GAN model called StarGAN. This system can generate converted speech signals at a high speed, allowing for real-time applications and requiring only a few minutes of training to produce realistic speech.
Baseline system 4 (S4): Refers to non-parallel baseline VC system [
40], which aims to jointly train conversion model and WaveNet vocoder using mel-spectrograms and Phonetic Posteriorgrams.
5. Results and Discussion
Objective and subjective evaluations were performed to assess the performance of our systems in terms of speech quality and speaker similarity. The assessment utterances are taken from the 25 utterances in the test set.
5.1. Objective Evaluations
We objectively evaluated the similarity between the target and converted speech by using Mel Cepstral Distortion (MCD), a widely used metric for spectral distortion in speech conversion, calculated using Equation (
5). The MCD results of both our proposed and baseline methods were evaluated.
where
and
represent the
coefficient of the converted and target MCCs vectors, respectively. D denotes the dimension of MCCs (39-dimensional features), calculated with a 25ms window size and 10ms window shift.
To measure the intelligibility of the speech generated by the different systems we also calculated the Word Error Rates (WER) from the ASR transcriptions. We used the Word Error Rate Matlab toolbox [
49] to calculate the Levenstein distance [
50] between the hypothesis sentence (ASR transcription output) and the reference sentence (original utterance). The Levenstein distance WER considers insertions, deletions, and substitutions observed in the ASR transcription output. The WER formula is given in the following Equation (
6). The smaller the WER scores, the better the speech intelligibility.
The MCDs results obtained with the proposed and baseline methods on the validation set are summarized in
Table 1. A lower MCD value signifies the better performance of the VC system.
Comparing the proposed method to the baseline methods S3 et S4, which are based on non-parallel
training data, the results clearly show that the proposed method performs better for all conversion
pairs. The average MCD values obtained by the method we propose are significantly lower than those
obtained by S4, namely 6.46 dB vs. 7.19 dB, but almost equivalent to those obtained by S3, i.e., 6.46 vs.
6.48. We can explain this by using the autoregressive structure that incorporates the outputs from the
previous step to predict the outputs of the next step, which results in smoother waveforms. We can
confirm this by using the efficient LPCNet vocoder to generate waveforms, while S3 and S4 adopt the
WORLD [
51] and WaveNet vocoders, respectively.
On the other hand, by comparing the proposed method to the baseline methods based on parallel
training data, we can show that our system produces considerably better MCD values than those
obtained by S2 for all conversion pairs. For example, in the case of the RMS-to-SLT conversion pair, our
proposal achieved an MCD value of 6.37, whereas S2 obtained a value of 7.34, resulting in a relative
reduction of0.97. Furthermore, we compare the baseline S1 and our method based on parallel and
non-parallel voice conversion. We observe that the proposed method gives slightly better MCD values
than S1, i.e., an average of 6.86 vs.6.46.
Table 2 gives the WER scores obtained for our VC method and the state-of-the-art methods.
The proposed method demonstrated lower WER scores (i.e., better intelligibility) compared to state-of-the-art methods for both male and female speakers.
From the female speaker’s WER, it can be seen that our method notably reduces errors compared to the male speaker’s WER. Specifically, when comparing the WER from baseline S4 with our proposed method, there was a substantial relative reduction of %. However, there was a slight degradation in the WER from baseline S2, amounting to %.
These results demonstrate that the conversion model trained on a non-parallel corpus performs comparably, and in some cases better, than its counterparts trained on a parallel corpus. This shows the effectiveness of our method in improving speech quality and reducing pronunciation errors. However, it is essential to note that the direct comparison of parallel and non-parallel VC methods is not entirely fair, as the non-parallel VC only uses the target speaker’s data during training.
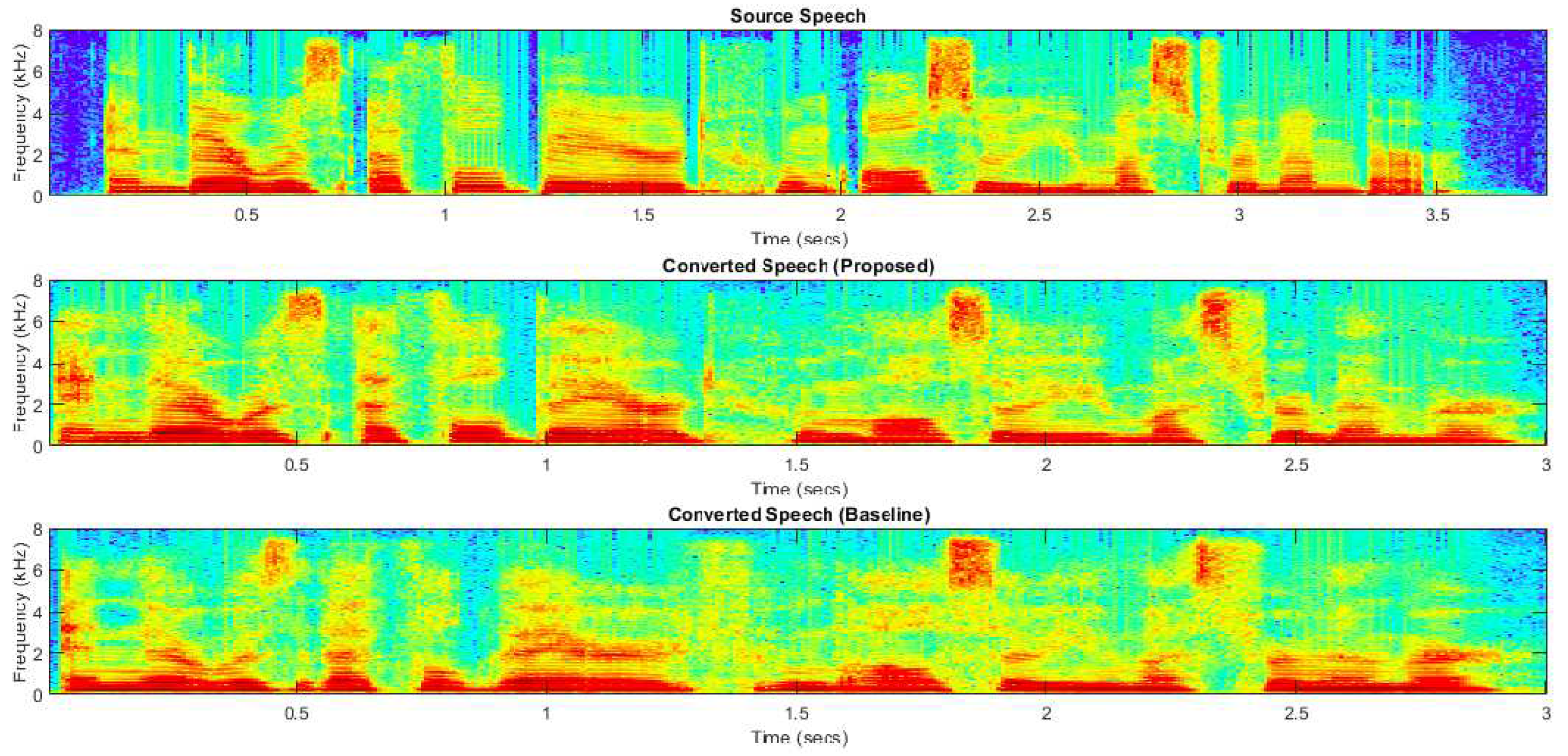
Figure 2 illustrates improvements in spectrogram visualization by comparing the converted speech between the proposed and baseline (S1) systems. Our observations indicate that the proposed method effectively mitigates speech artifacts. However, for the S1 system, the reconstructed speech exhibits audible artifacts, occasionally appearing within non-speech segments.
5.2. Subjective Evaluations
We perform subjective listening tests to assess the performance of our systems in terms of speech quality and speaker similarity of the generated speech from the five conversion methods (proposed, S1, S2, S3, and S4). It should be noted that all tests were performed under the same conditions.
We first conduct the Mean Opinion Score (MOS) test, admittedly the most pertinent subjective test. For each conversion pair, 10 pairs (sentences) were randomly selected from the 25 paired samples of the test set. A group of fifteen listeners (five males and ten females) took part in the listening tests where each participant had to listen to 10 speech samples, which were converted according to each of the systems mentioned above. In this experiment, each converted sample was randomly presented to listeners who were asked to independently judge the quality of the speech in terms of speech quality and naturalness on a five-level scale (ranging from 1, for the lowest quality, to 5 for the best quality). Each participant has the chance to replay each stimulus before giving his/her note.
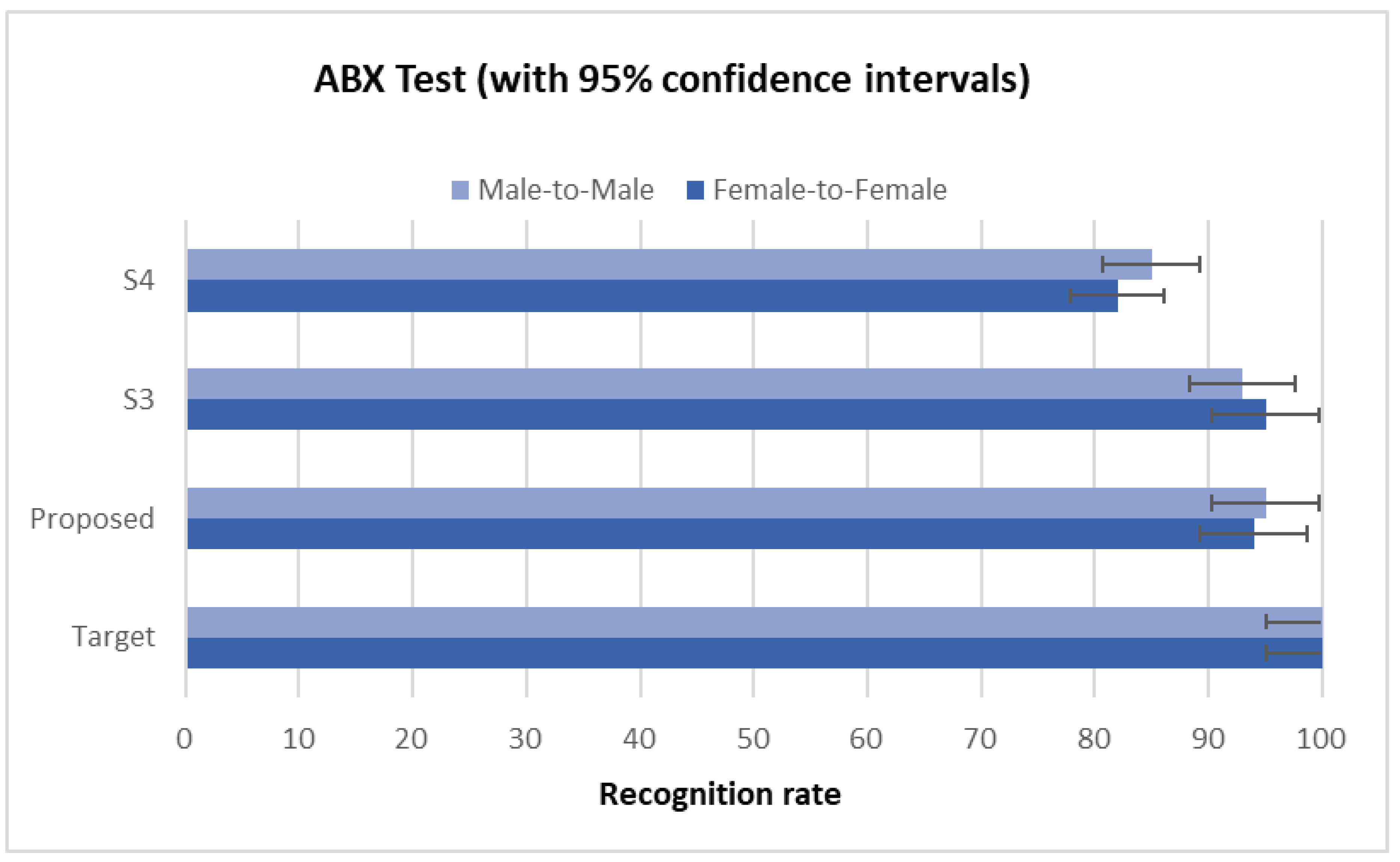
We then performed an ABX similarity test to evaluate the recognition of the target speaker. The setup is similar to the MOS test. X was the converted sample in each pair, and A and B were the source and target samples, respectively. Listeners are requested to judge the proximity of the converted sample X to both source sample A and target sample B by giving a score of either 0 or 1 (0 for the choice of source speaker and 1 point for the choice of target speaker) after each listening session. The final result is given as a percentage for the converted voices X that is recognized as the target speaker. In the case of Male-to-Female and Female-to-Male conversion, the inter-gender conversions were easily recognized.
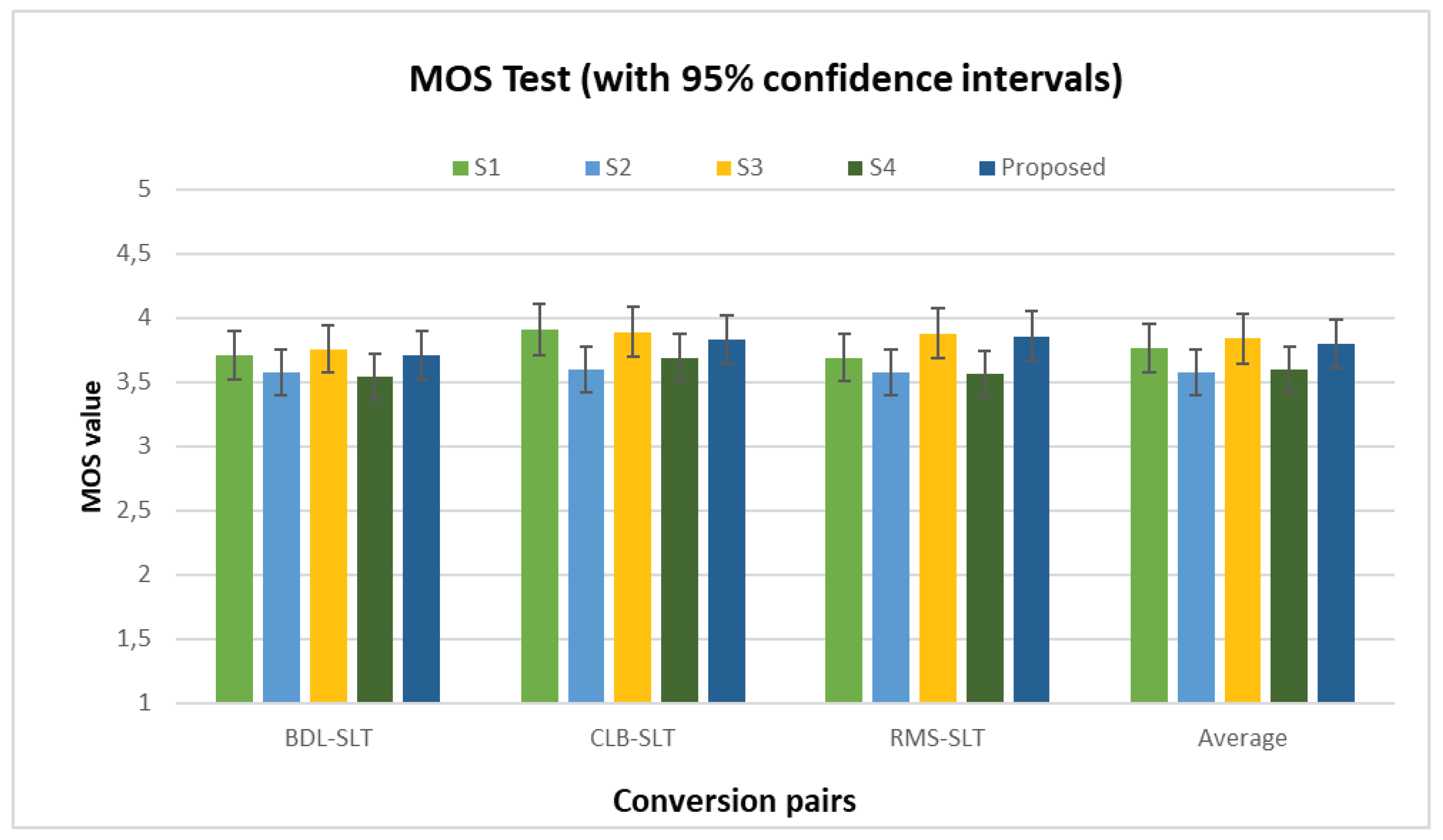
The results of the subjective MOS and ABX tests obtained on the validation set are depicted in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, respectively.
From
Figure 3, it can be observed that the S4 system yields lower MOS values than the other three methods, which confirms the results of the objective experiments. In the RMS-to-SLT conversion pair, we notice that the method we propose proved to be close and has slightly lower efficiency compared to the S2 system. Respective MOS values are
and
. In all conversion pairs performed, we can further see that the MOS scores of our proposed method are higher than those of the S4 method on naturalness.
Figure 4 presents the results of the similarity test obtained from the Male-to-Male and Female-to-Female conversion pairs. As can be seen, listeners preferred the proposed system and the baseline S3 since the stimuli provided by both methods seem to them more similar and closer to the target than those provided by the other methods.
Figure 4.
ABX results with 95% confidence intervals on similarity obtained from Female-to-Female and Male-to-Male conversion pairs.
Figure 4.
ABX results with 95% confidence intervals on similarity obtained from Female-to-Female and Male-to-Male conversion pairs.
To evaluate the degree of preference for the different conversion systems, we also conduct an AB preference test to compare between proposed methods (designated A) and baseline methods (designated B). Similar to the ABX test, 10 pairs were randomly selected from the 25 paired test samples. For every pair of samples, listeners were asked to listen to utterances presented in a random order and decide which of the two samples was better in terms of speech quality.
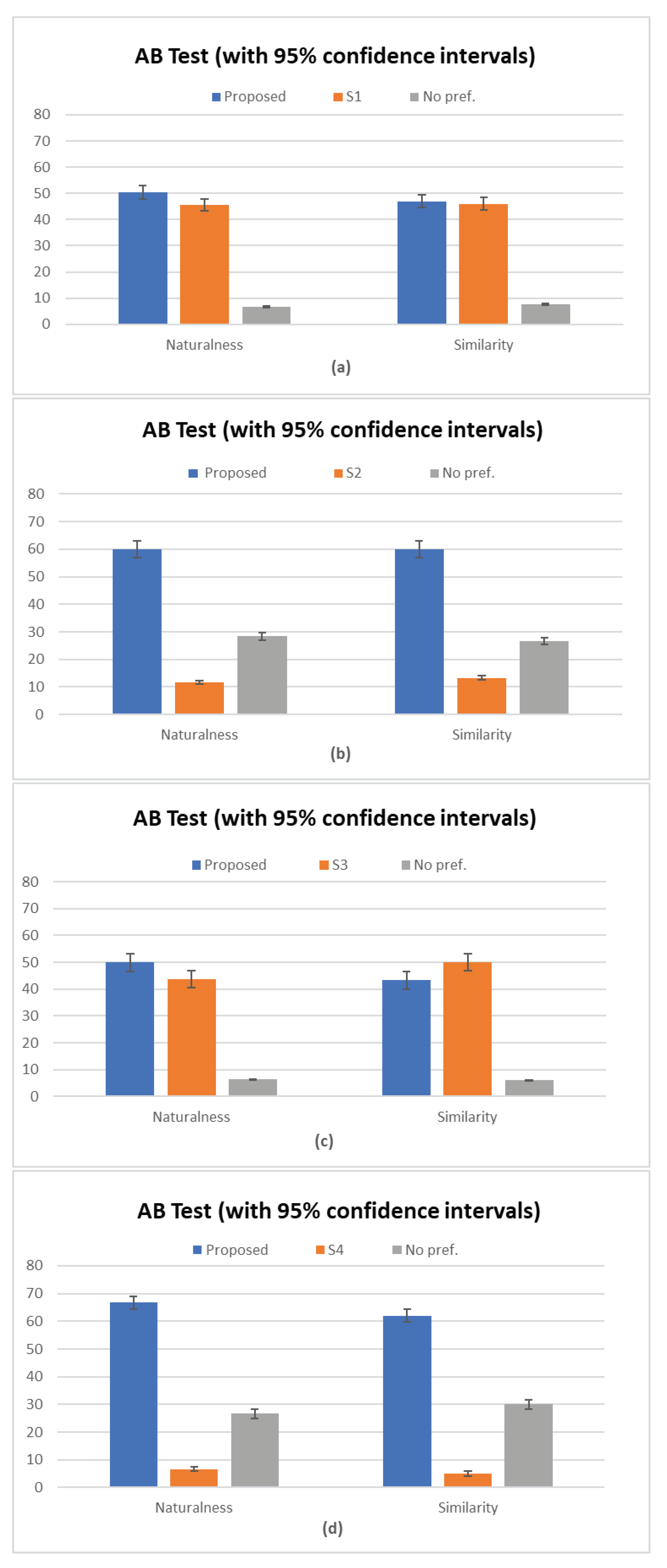
The obtained results of the AB test on naturalness and similarity are respectively presented in
Figure 5 along with the average of the scores with 95% confidence interval.
Overall, we can see in
Figure 5 (b) et (d) that the proposed method outperforms the baseline S2 and S4 in terms of naturalness and speaker similarity of the converted speech. In
Figure 5a, comparing the baseline S1 to our proposed system on naturalness, we see that
% of the listeners prefer the proposed method,
% prefer the baseline method, and the remaining 5% show no significant preference between the two converted samples. On the other hand, when comparing the baseline S3 to our proposed system on similarity,
Figure 5c shows that listeners preferred S3, with a preference rate of 50%. In
Figure 5d, we see the preference of our system in both naturalness and similarity, with an average preference rate of
% compared to
% for baseline S4.
This indicates that our proposed system outperforms the S2 and S4 baseline systems in terms of naturalness and similarity scores while showing comparable performance to the S3 baseline system.
Therefore, based on the above test results, it can be concluded that our non-parallel VC system significantly outperforms the baseline non-parallel methods and can achieve a level of conversion performance comparable to that of parallel VC methods, both in terms of speech quality and similarity to the target speaker.
6. Conclusions
In this study, we introduce a non-parallel voice conversion framework that leverages an autoregressive model, linguistic Phoneme PosteriorGram (PPG) features, and an LPCNet vocoder to enable any-to-one speech conversion. In contrast to data-parallel approaches, our system does not require parallel training data, can be easily adapted to real-time applications, and is exceptionally flexible for any-to-one voice conversion tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method improves the naturalness of the converted speech and its similarity to the target speaker. In our future work, we intend to explore techniques aimed at stabilizing and expediting the learning process in non-parallel VC. Additionally, we aspire to extend our approach to cross-lingual speech conversion and investigate the influence of linguistic diversity on the performance of our model.
Author Contributions
Contributions: Conceptualization, K.E. and J.D.M.; methodology, K.E. and J.D.M.; software, K.E.; validation, J.D.M. and M.F.; data curation, K.E.; writing—original draft preparation, K.E; writing—review and editing, J.D.M. and M.F.; visualization, K.E.; supervision, J.D.M. and M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sisman, B.; Yamagishi, J.; King, S.; Li, H. An Overview of Voice Conversion and its Challenges: From Statistical Modeling to Deep Learning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 29, 132–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczyna, T.; Piotrowski, Z. Overview of Voice Conversion Methods Based on Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Black, A.W.; Tokuda, K. Voice conversion based on maximum-likelihood estimation of spectral parameter trajectory. IEEE Trans. ASLP 2007, 15, 2222–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helander, E.; Virtanen, T.; Nurminen, J.; Gabbouj, M. Voice conversion using partial least squares regression. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2010, 18, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erro, D.; Alonso, A.; Serrano, L.; Navas, E.; Hernáez, I. Towards physically interpretable parametric voice conversion functions. In Proceedings of the 6th Advances in Nonlinear Speech Processing International Conference, Mons, Belgium, 19–21 June 2013; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Wu, Z.; Lee, S.W.; Hy, N.Q.; Chng, E.S.; Dong, M. Sparse representation for frequency warping based voice conversion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 4235–4239. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Lee, S.W.; Tian, X.; Dong, M.; Chng, E.S. High-quality voice conversion using prosodic and high-resolution spectral features. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 5265–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.-C.; Tian, X.; Yamagishi, J.; Das, R.K.; Kinnunen, T.; Ling, Z.; Toda, T. Voice Conversion Challenge 2020: Intra-lingual semi-parallel and cross-lingual voice conversion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.12527.
- Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Wen, X. Voice conversion with transformer network. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 7759–7759. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Ling, Z.H.; Liu, L.J.; Jiang, Y.; Dai, L.R. Sequence-to-sequence acoustic modeling for voice conversion. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Hayashi, T.; Wu, Y.C.; Kameoka, H.; Toda, T. Pretraining techniques for sequence-to-sequence voice conversion. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzine, K.; Frikha, M.; Di Martino, J. Non-Parallel Voice Conversion System Using An Auto-Regressive Model. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advanced Systems and Emergent Technologies (IC_ASET), Hammamet, Tunisia, 22–25 March 2022; pp. 500–504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, H. Transfer learning from speech synthesis to voice conversion with non-parallel training data. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1290–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Noh, H.R.; Nam, W.J.; Lee, S.W. Duration controllable voice conversion via phoneme-based information bottleneck. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2022, 30, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Meng, H. Any-to-Many Voice Conversion with Location-Relative Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Kameoka, H. CycleGAN-VC: Non-parallel voice conversion using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the EUSIPCO, Rome, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 2114–2118. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, G.W.; Jeon, M.; Kim, H.K. Non-Parallel Voice Conversion Using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks with Self-Supervised Representations. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 20th Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 8–11 January 2023; pp. 931–932. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qiu, X.; Cao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, B. Non-parallel Voice Conversion Based on Perceptual Star Generative Adversarial Network. Circuits, Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 41, 4632–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameoka, H.; Kaneko, T.; Tanaka, K.; Hojo, N. StarGAN-VC: Non-parallel many-to-many Voice Conversion Using Star Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE SLT, Athens, Greece, 18–21 December 2018; pp. 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, Y.; Ijima, Y.; Nishida, K.; Takamichi, S. Non-parallel voice conversion using variational autoencoders conditioned by Phonetic PosteriorGrams and d-vectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE ICASSP, Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5274–5278. [Google Scholar]
- Seki, S.; Kameoka, H.; Kaneko, T.; Tanaka, K. Non-parallel Whisper-to-Normal Speaking Style Conversion Using Auxiliary Classifier Variational Autoencoder. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 44590–44599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaa, Y.; Alfonse, M.; Aref, M.M. A survey on generative adversarial networks-based models for Many-to-many non-parallel voice conversion. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Computing and Informatics (ICCI), New Cairo, Egypt, 9–10 March 2022; pp. 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tian, X.; Xu, H.; Das, R.K.; Li, H. Cross-lingual voice conversion with bilingual phonetic posterior-gram and average modeling. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 6790–6794. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.J.; Ling, Z.H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Dai, L.R. WaveNet Vocoder with Limited Training Data for Voice Conversion. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 1983–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Chng, E.S.; Li, H. A Speaker-Dependent WaveNet for Voice Conversion with Non-Parallel Data. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Lu, H.; Hu, N.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Xie, L.; Yu, D. Phonetic posteriorgrams based many-to-many singing voice conversion via adversarial training. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.01837. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.Z.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chang, S.H.; Lai, Y.H. Phonetic posteriorgram-based voice conversion system to improve speech intelligibility of dysarthric patients. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 215, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, H.; Masuda-Katsuse, I.; Cheveigne, A. Restructuring speech representations using a pitch-adaptive time frequency smoothing and an instantaneous-frequency-based f0 extraction: Possible role of a repetitive structure in sounds. Speech Commun. 1999, 27, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalchbrenner, N.; Elsen, E.; Simonyan, K.; Noury, S.; Casagr, E.N.; Lockhart, E.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Efficient neural audio synthesis. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2410–2419. [Google Scholar]
- Valin, J.M.; Skoglund, J. LPCNet: Improving neural speech synthesis through linear prediction. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 5891–5895. [Google Scholar]
- Kanagawa, H.; Ijima, Y. Lightweight LPCNet-Based Neural Vocoder with Tensor Decomposition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Vipperla, R.; Park, S.; Choo, K.; Ishtiaq, S.; Min, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mehrotra, A.; Ramos, A.G.; Lane, N.D. Bunched lpcnet: Vocoder for low-cost neural text-to-speech systems. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.04574. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, V.; Kudinov, M.; Sadekova, T. Gaussian LPCNet for multisample speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6204–6208. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Kumar, R.; De Boissiere, T.; Gestin, L.; Teoh, W.Z.; Sotelo, J.; De Brebisson, A.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.C. Melgan: Generative adversarial networks for conditional waveform synthesis. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, R.; Song, E.; Kim, J.M. Parallel WaveGAN: A fast waveform generation model based on generative adversarial networks with multi-resolution spectrogram. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6199–6203. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, J.; Kim, J.; Bae, J. Hifi-gan: Generative adversarial networks for efficient and high fidelity speech synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 17022–17033. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, M.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, K.; Seetharaman, P.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Chunked autoregressive GAN for conditional waveform synthesis. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.10139. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Li, K.; Wang, H.; Kang, S.; Meng, H. Phonetic posteriorgrams for many-to-one voice conversion without parallel data training. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Seattle, WA, USA, 11–15 July 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Weiss, R.; Wang, Q.; Shen, J.; Ren, F.; Nguyen, P.; Pang, R.; Lopez, Moreno, I.; Wu, Y. Transfer learning from speaker verification to multispeaker text-to-speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Meng, H. Jointly Trained Conversion Model and WaveNet Vocoder for Non-Parallel Voice Conversion Using Mel-Spectrograms and Phonetic Posteriorgrams. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Graz, Austria, 15-19 September 2019; pp. 714–718. [Google Scholar]
- Povey, D.; Ghoshal, A.; Boulianne, G.; Burget, L.; Glembek, O.; Goel, N.; Vesely, K. The Kaldi speech recognition toolkit. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2011 Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Big Island, HI, USA, 11–15 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Skerry-Ryan, R.J.; Stanton, D.; Wu, Y.; Weiss, R.J.; Jaitly, N.; Saurous, R.A. Tacotron: Towards end-to-end speech synthesis. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.10135. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Greff, K.; Schmidhuber, J. Highway networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00387. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, B.C. An Introduction to the Psychology of Hearing; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kominek, J.; Black, A.W. The CMU Arctic speech databases. In Proceedings of the Fifth ISCA Workshop on Speech Synthesis, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 14–16 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Garofolo, J.S. Timit acoustic-phonetic continuous speech corpus. Linguist. Data Consort. 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameoka, H.; Kaneko, T.; Tanaka, K.; Hojo, N. Nonparallel voice conversion with augmented classifier star generative adversarial networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 2982–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polityko, E. Word Error Rate. MATLAB Central File Exchange. Available online: https://ch.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/ fileexchange/55825-word-error-rate (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Levenshtein, V.I. Binary codes capable of correcting deletions, insertions, and reversals. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1966, 10, 707–710. [Google Scholar]
- Morise, M.; Yokomori, F.; Ozawa, K. WORLD: A vocoder-based high-quality speech synthesis system for real-time applications. IEICE Trans. Inform. Syst. 2016, 99, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.V.; Akagi, M. Cross-lingual voice conversion with controllable speaker individuality using variational autoencoder and star generative adversarial network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 47503–47515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).