Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
19 October 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
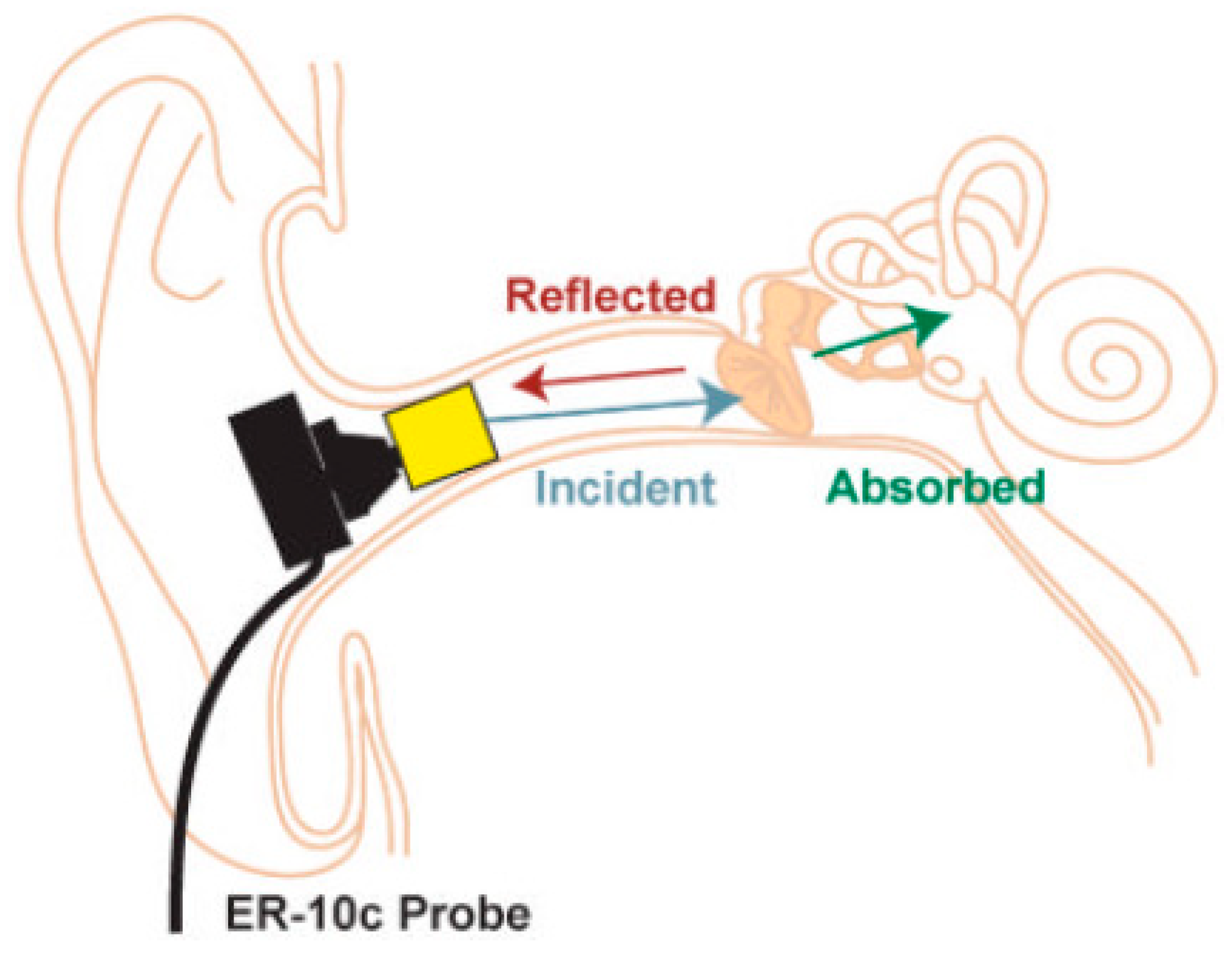
3. Materials Models
Finite Element Model
4. Results
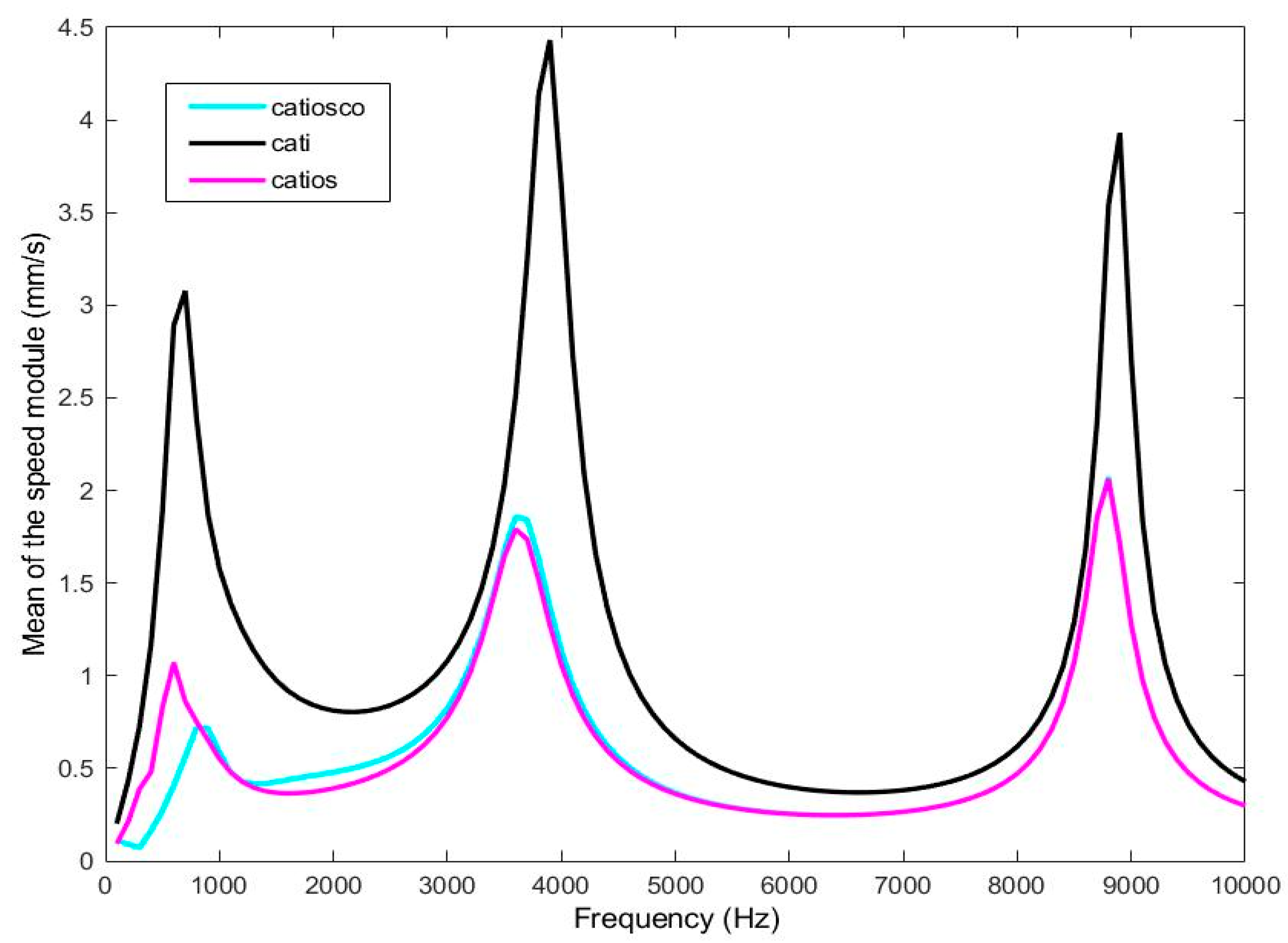
4.1. Tympanic membrane velocity
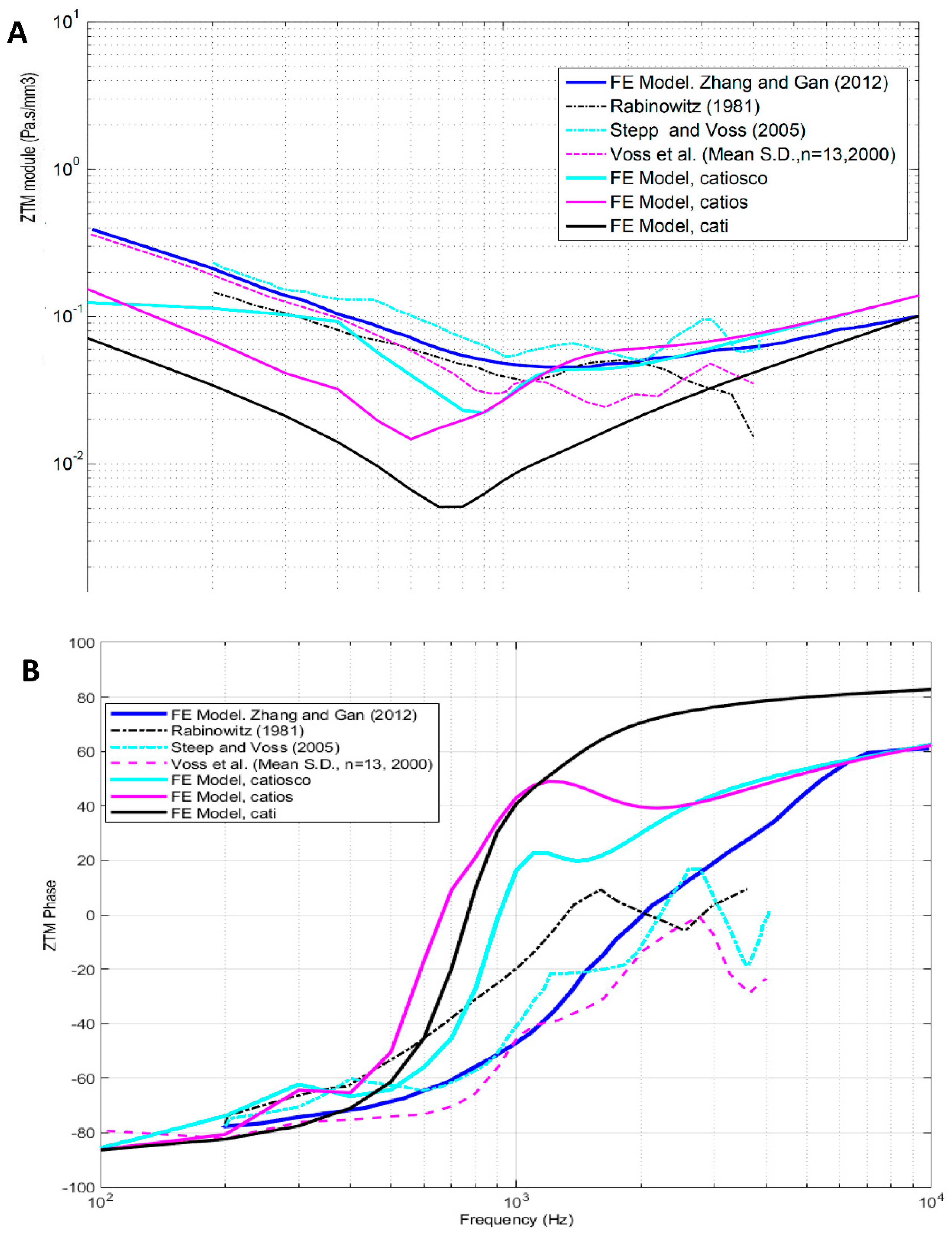
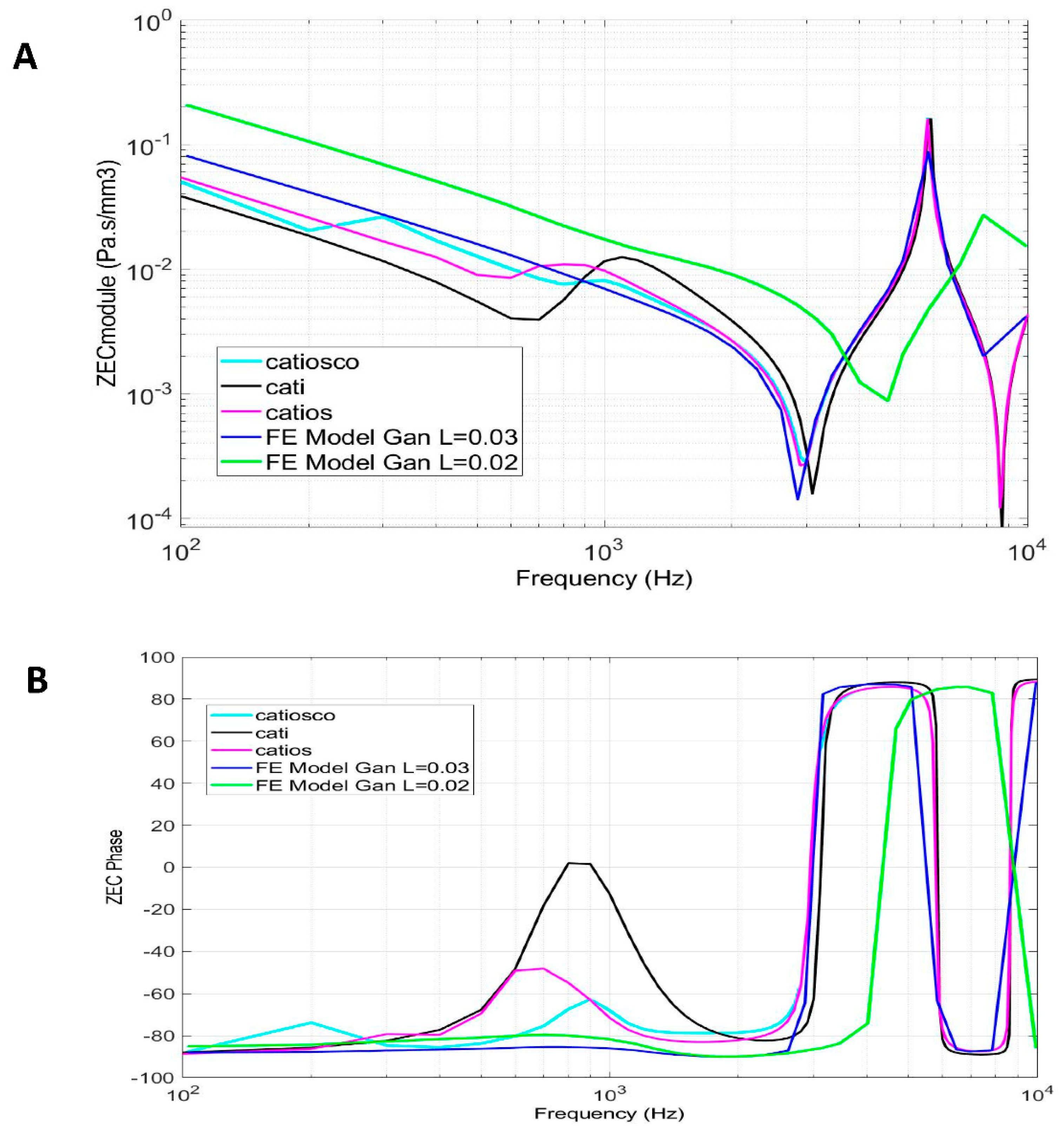
4.2. External auditory canal characteristic impedance
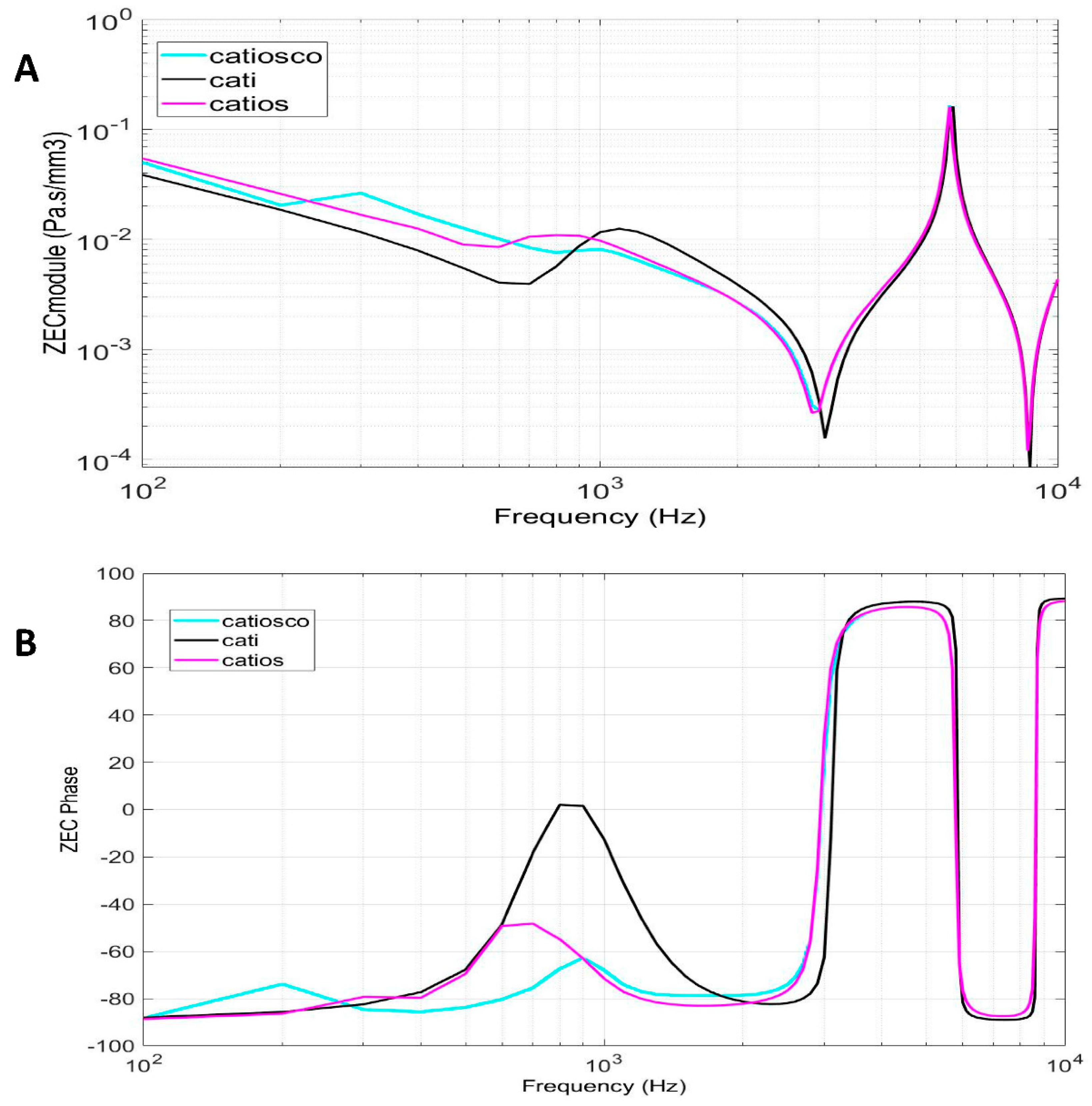
4.3. Tympanic membrane impedance (direct calculation)
4.4. External auditory canal impedance (backward calculation) based on tympanic membrane impedance.
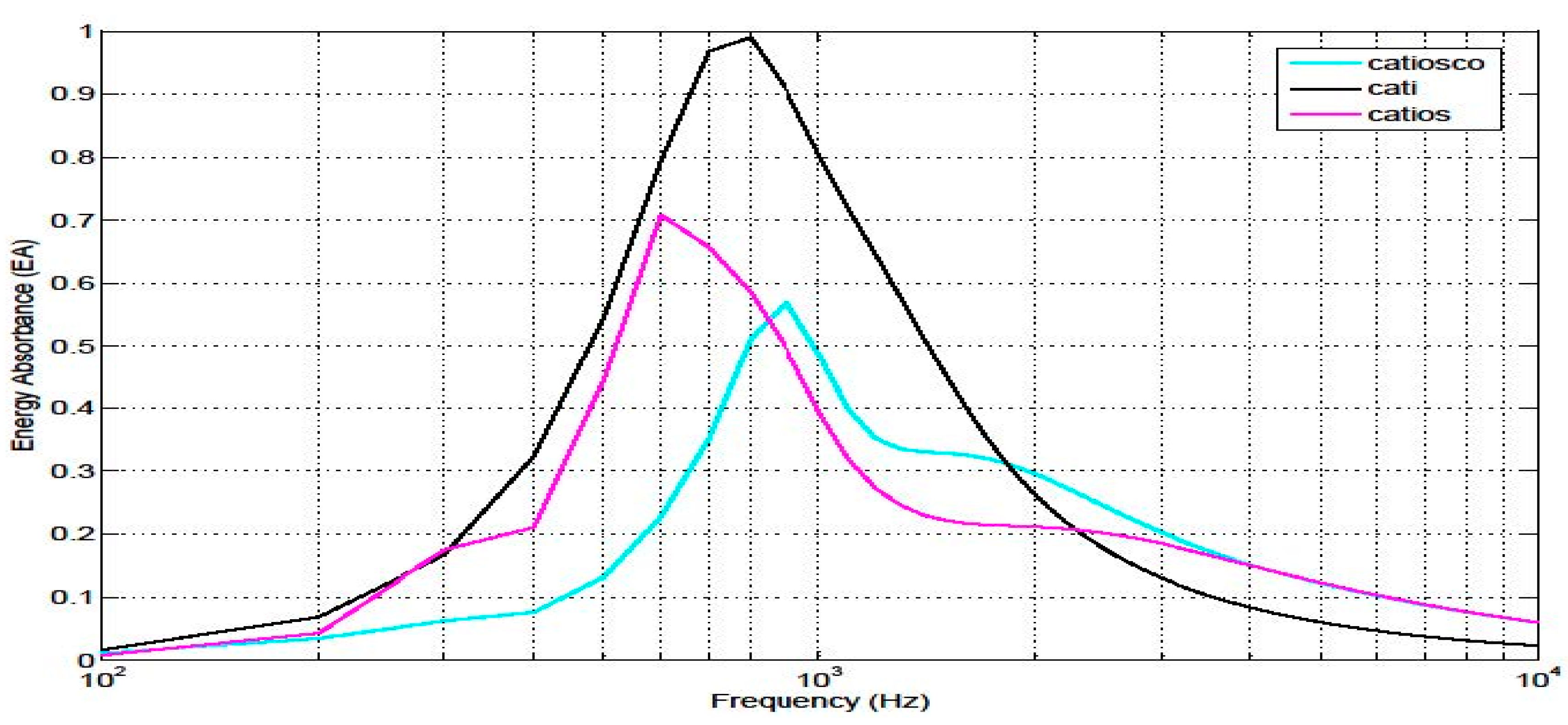
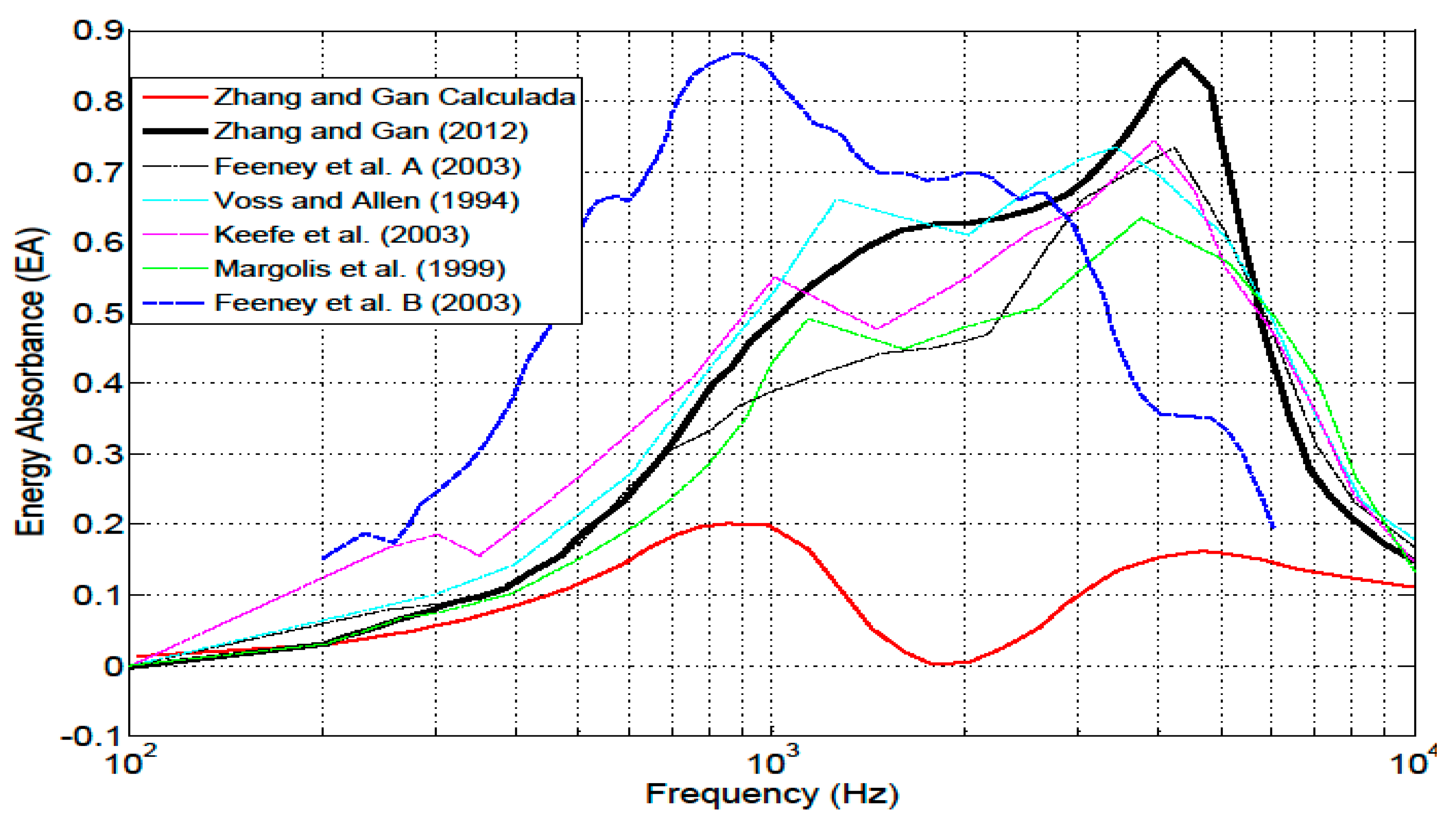
4.5. Energy absorbance at the tympanic membrane
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Møller, A.R. Improved Technique for Detailed Measurements of the Middle Ear Impedance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1960, 32, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, W.M. Measurement of the acoustic input immittance of the human ear. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 70, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, V.D.; Nelson, J.A.; Cooper, W.A.; Egolf, D.P. Measurements of acoustic impedance at the input to the occluded ear canal. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1993, 30, 129. [Google Scholar]
- Keefe, D.H.; Ling, R.; Bulen, J.C. Method to measure acoustic impedance and reflection coefficient. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, S.E.; Allen, J.B. Measurement of acoustic impedance and reflectance in the human ear canal. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanborn, P.E. Predicting hearing aid response in real ears. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 3407–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnaz, N.; Bork, K.; Polka, L.; Longridge, N.; Bell, D.; Westerberg, B.D. Energy Reflectance and Tympanometry in Normal and Otosclerotic Ears. Ear Hear. 2009, 30, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jønsson, S.; Schuhmacher, A.; Ingerslev, H. Wideband impedance measurement in the human ear canal; In vivo study on 32 subjects. Brüel & Kjær Sound & Vibration A/S, Skodsborgvej 307, DK-2850, Denmark 2018, arXiv:1811.03389.
- Niemczyk, E.; Lachowska, M.; Tataj, E.; Kurczak, K.; Niemczyk, K. Wideband acoustic immitance—Absorbance measurements in ears after stapes surgery. Auris Nasus Larynx 2020, 47, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chris, S.; Lisa, H.; Patrick, F.; Hideko, H. Wideband Acoustic Immittance: Tympanometric Measures. Ear Hear. 2013, 34, 65s–71s. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, J.C.; Gorga, M.; Cohn, E.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Sanford, C.A.; Keefe, D.H. Wideband acoustic transfer functions predict middle-ear effusion. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, D.H.; Sanford, C.A.; Ellison, J.C.; Fitzpatrick, D.F.; Gorga, M.P. Wideband aural acoustic absorbance predicts conductive hearing loss in children. Int. J. Audiol. 2012, 51, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, B.W.; Shaw, E.A.G. Estimation of acoustical energy reflectance at the eardrum from measurements of pressure distribution in the human ear canal. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1982, 72, 766–773. [Google Scholar]
- Utsuno, H.; Tanaka, T.; Fujikawa, T.; Seybert, A.F. Transfer function method for measuring characteristic impedance and propagation constant of porous materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 86, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoye, R.; Vermeir, G.; Lauriks, W.; Kruse, R.; Mellert, V. Measuring the free field acoustic impedance and absorption coefficient of sound absorbing materials with a combined particle velocity-pressure sensor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudde, H.; Letens, U. Scattering matrix of a discontinuity with a nonrigid wall in a lossless circular duct. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 1826–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, N.H.; Smith, J.; Tarnopolsky, A.Z.; Wolfe, J. Acoustic impedance measurements—Correction for probe geometry mismatch. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 2889–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, M.R.; Daigle, G.A. Transverse pressure distributions in a simple model ear canal occluded by a hearing aid test fixture. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, 3689–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brass, D.; Locke, A. The effect of the evanescent wave upon acoustic measurements in the human ear canal. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 101, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, A.; Castro-Egler, C.; Gonzalez-Herrera, A. Analysis of the mechano-acoustic influence of the tympanic cavity in the auditory system. Biomed. Eng. Online 2016, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, A.; Gonzalez-Herrera, A. Effect of the middle ear cavity on the response of the human auditory system. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Egler, C.; García-González, A. Semiautomatic algorithm for 3D modelling of finite elements of the cochlea. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2017, 7, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, A.; Durán-Escalante, A.; Castro-Egler, C. 3D Modelling and Numerical Analysis of Human Inner Ear by Means of Finite Elements Method. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Eng. 2016, 10, 596–606. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, A.; Castro-Egler, C.; Gonzalez-Herrera, A. Influence of the auditory system on pressure distribution in the ear canal. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2018, 18, 1850021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.Z.; Reeves, B.P.; Wang, X. Modeling of Sound Transmission from Ear Canal to Cochlea. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, R.Z.; Sun, Q.; Feng, B.; Wood, M.W. Acoustic–structural coupled finite element analysis for sound transmission in human ear—Pressure distributions. Med. Eng. Phys. 2006, 28, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, R.Z.; Feng, B.; Sun, Q. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Modeling of Human Ear for Sound Transmission. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 32, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A.; Bradshaw, J.J.; Gan, R.Z. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Modeling of Blast Wave Transmission From the External Ear to a Spiral Cochlea. J. Biomech. Eng. 2022, 144, 014503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gan, R.Z. Finite element modeling of energy absorbance in normal and disordered human ears. Hear Res. 2013, 301, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgaard, K.R.; Fernandez-Grande, E.; Laugesen, S. Compensating for oblique ear-probe insertions in ear-canal reflectance measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 3499–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudde, H.; Engel, A. Measuring and Modeling Basic Properties of the Human Middle Ear and Ear Canal. Part III: Eardrum Impedances, Transfer Functions and Model Calculations. In Acta Acustica United with Acustica; S. Hirzel Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1998; Volume 84. [Google Scholar]
- Hudde, H.; Engel, A. Measuring and Modeling Basic Properties of the Human Middle Ear and Ear Canal. Part II: Ear Canal, Middle Ear Cavities, Eardrum, and Ossicles. In Acta Acustica United with Acustica; S. Hirzel Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1998; Volume 84. [Google Scholar]
- Hudde, H.; Engel, A. Measuring and Modeling Basic Properties of the Human Middle Ear and Ear Canal. Part I: Model Structure and Measuring Techniques. In Acta Acustica United with Acustica; S. Hirzel Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1998; Volume 84. [Google Scholar]
- Hudde, H. Measurement of the eardrum impedance of human ears. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1983, 73, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosowski, J.J.; Nakajima, H.H.; Hamade, M.A.; Mahfoud, L.; Merchant, G.R.; Halpin, C.F. ; Ear-Canal Reflectance, Umbo Velocity, and Tympanometry in Normal-Hearing Adults. Ear Hear. 2012, 33, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Valero, J.P. Modelado y Análisis Numérico Con el Método de los Elementos Finitos del Canal Auditivo Externo y Membrana Timpánica; Riuma, Málaga, Spain, 2013.
- Castro Egler, C. Modelado 3D & Análisis Numérico del Oído Interno Mediante Elementos Finitos. 2020. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10630/19420 (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Stepp, C.E.; Voss, S.E. Acoustics of the human middle-ear air space. J. Acoust. Soc. Am 2005, 118, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, S.E.; Rosowski, J.J.; Merchant, S; N., *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Peake, W.T. Acoustic responses of the human middle ear. Hear. Res. 2000, 150, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasetshwane, D.M.; Neely, S.T. Inverse solution of ear-canal area function from reflectance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 3873–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.B.; Jeng, P.S.; Levitt, H. Evaluation of human middle ear function via an acoustic power assessment. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2005, 42, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebothoma, B.; Khoza-Shangase, K.; Mol, D.; Masege, D. The sensitivity and specificity of wideband absorbance measure in identifying pathologic middle ears in adults living with HIV. South Afr. J. Commun. Disord. 2021, 30, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, P.; Keefe, D.H.; Simmons, J.L.; Gorga, M.P. Prediction of conductive hearing loss based on acoustic ear-canal response using a multivariate clinical decision theory. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 105, 1749–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, D.H.; Simmons, J.L. Energy transmittance predicts conductive hearing loss in older children and adults. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 114, 3217–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, M.P.; Grant, I.L.; Marryott, L.P. Wideband energy reflectance measurements in adults with middle-ear disorders. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 2003, 46, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Soylemez, E.; Sanuc, M.B.; Bayrak, M.H.; Sener, V. Sound energy absorbance changes in the elderly with presbycusis with normal outer and middle ear. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2023, 280, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | Subsystem Modelled | Name |
 |
External auditory canal Tympanic membrane |
CATI |
 |
External auditory canal Tympanic membrane Ossicular chain Cochlea simplified |
CATIOS |
 |
External auditory canal Tympanic membrane Ossicular chain Cochlea Vestibuli Semicircular canals |
CATIOSCO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





