Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
19 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. IR-spectroscopic Analysis Results
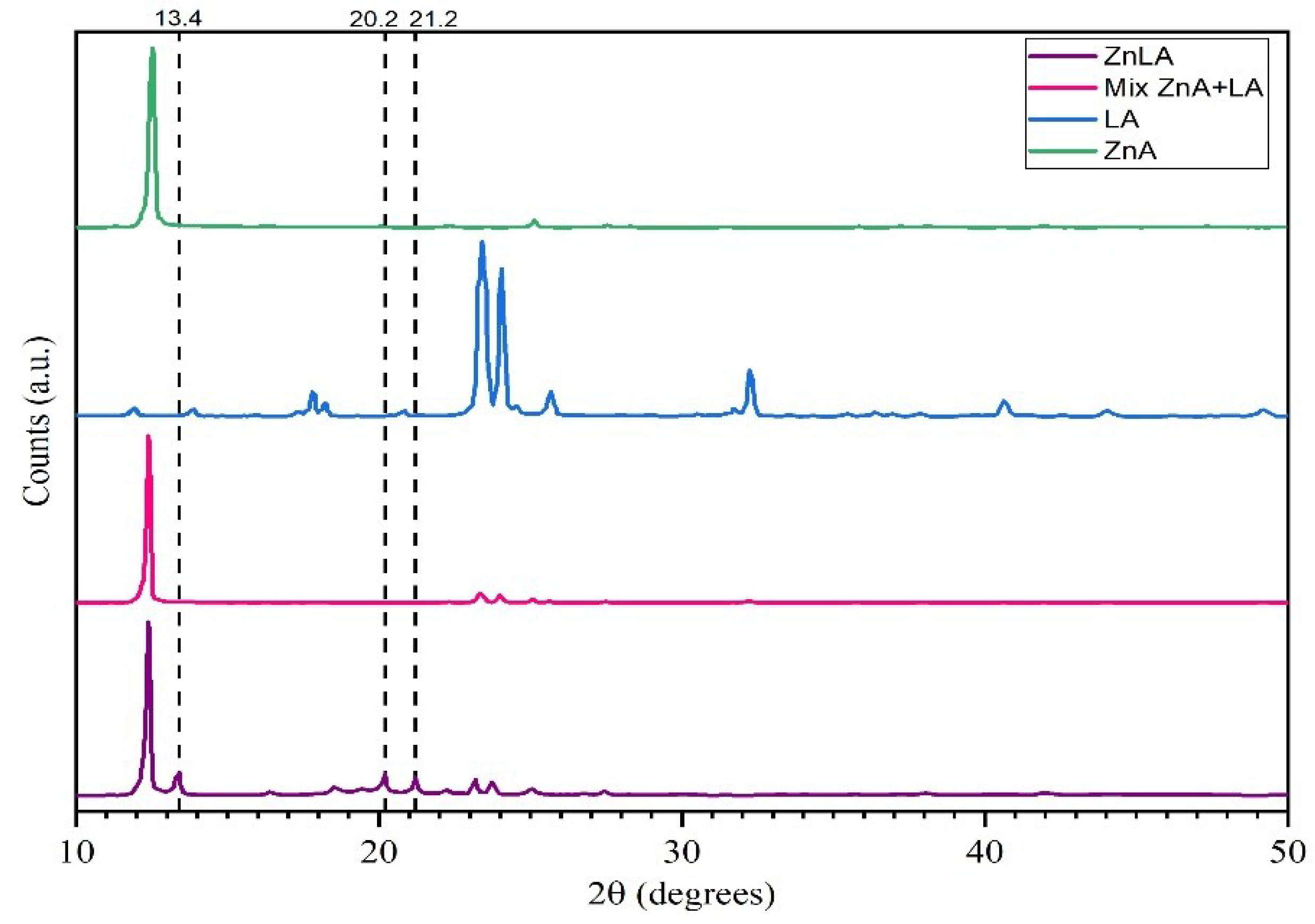
2.2. XRD Analysis Results
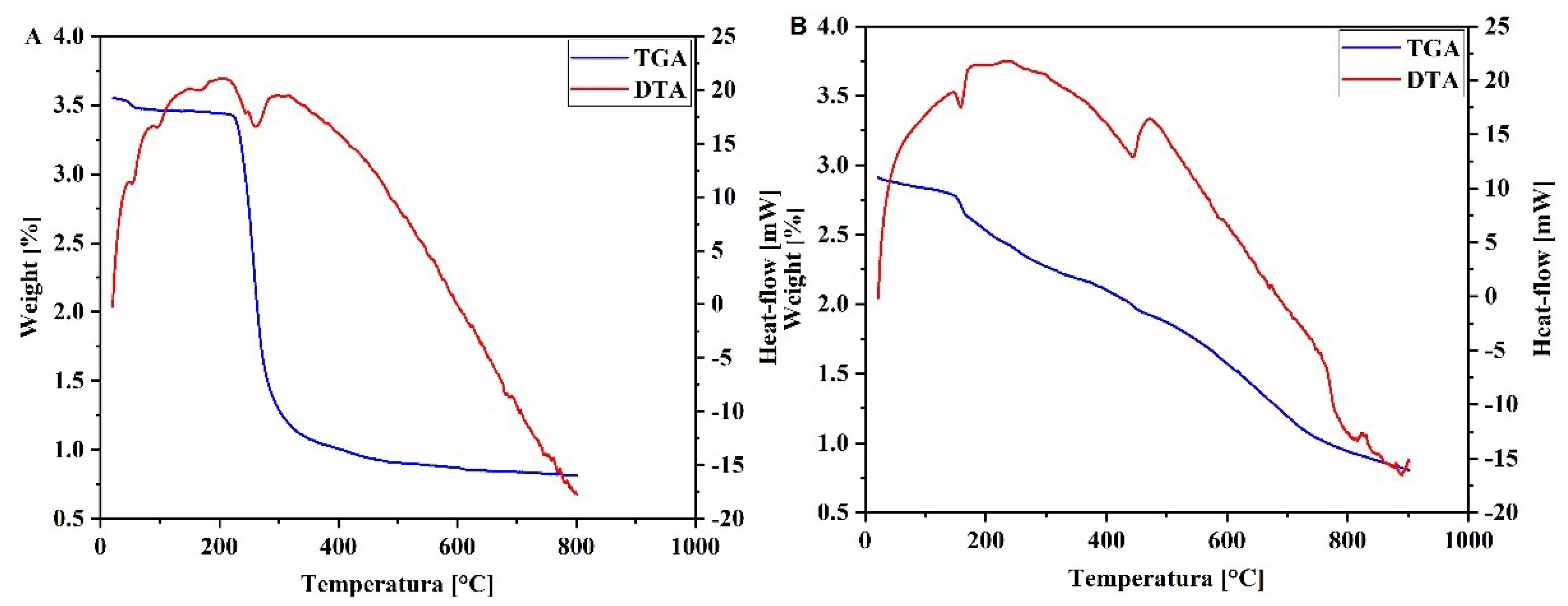
2.3. DTA-TGA analysis results
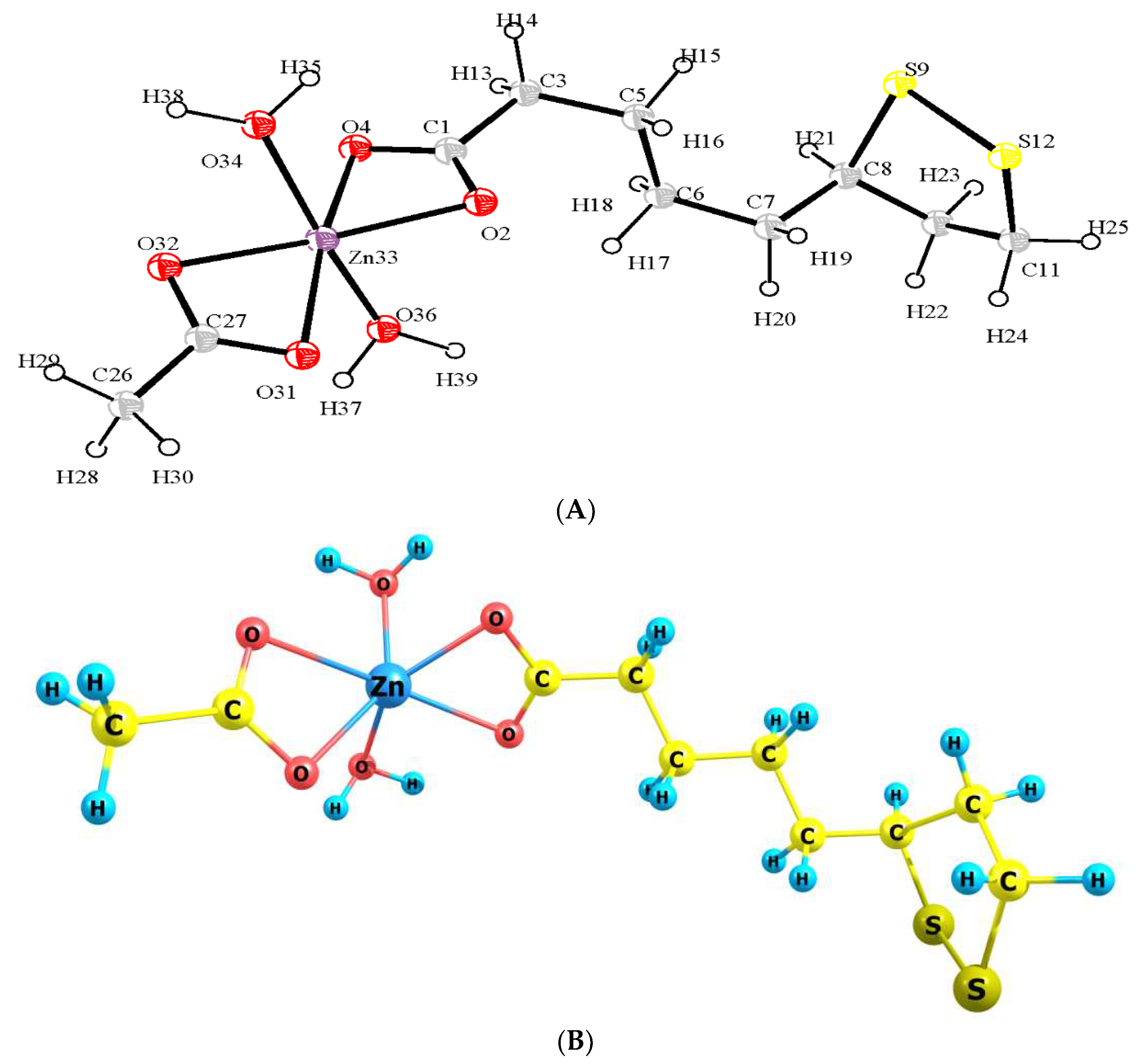
2.4. Mulliken Population Analysis (MPA)
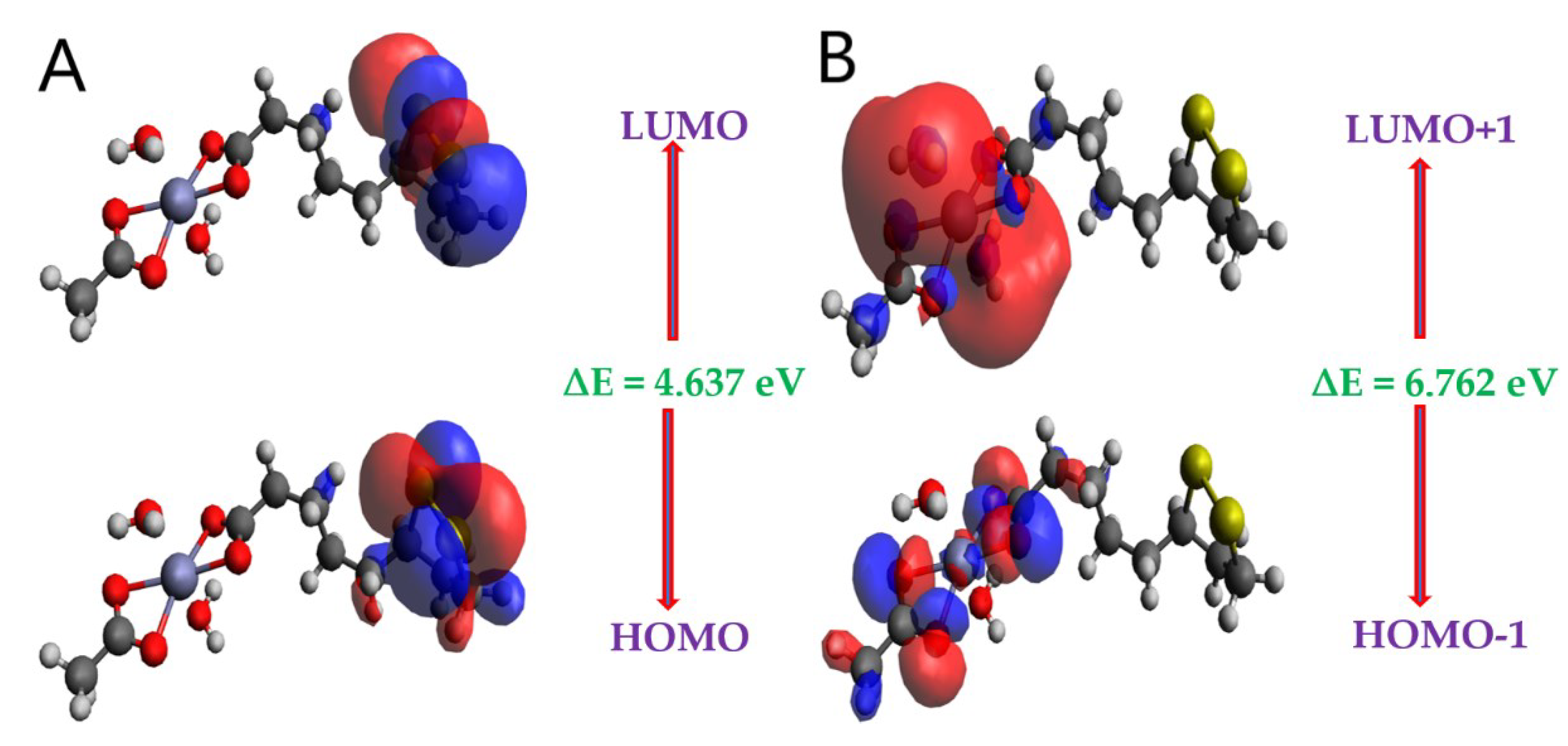
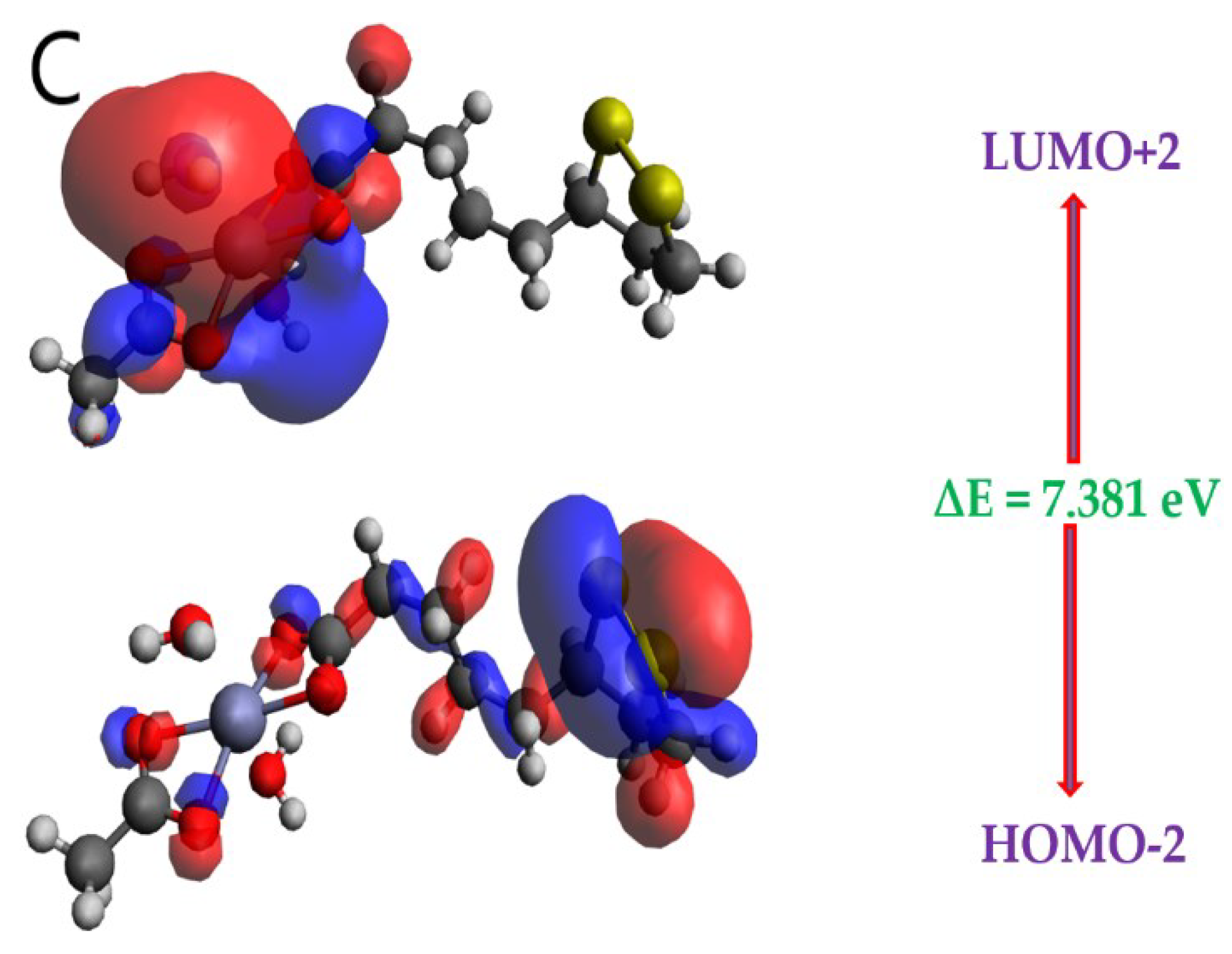
2.5. Frontier Molecular Orbital (FMO) Analysis
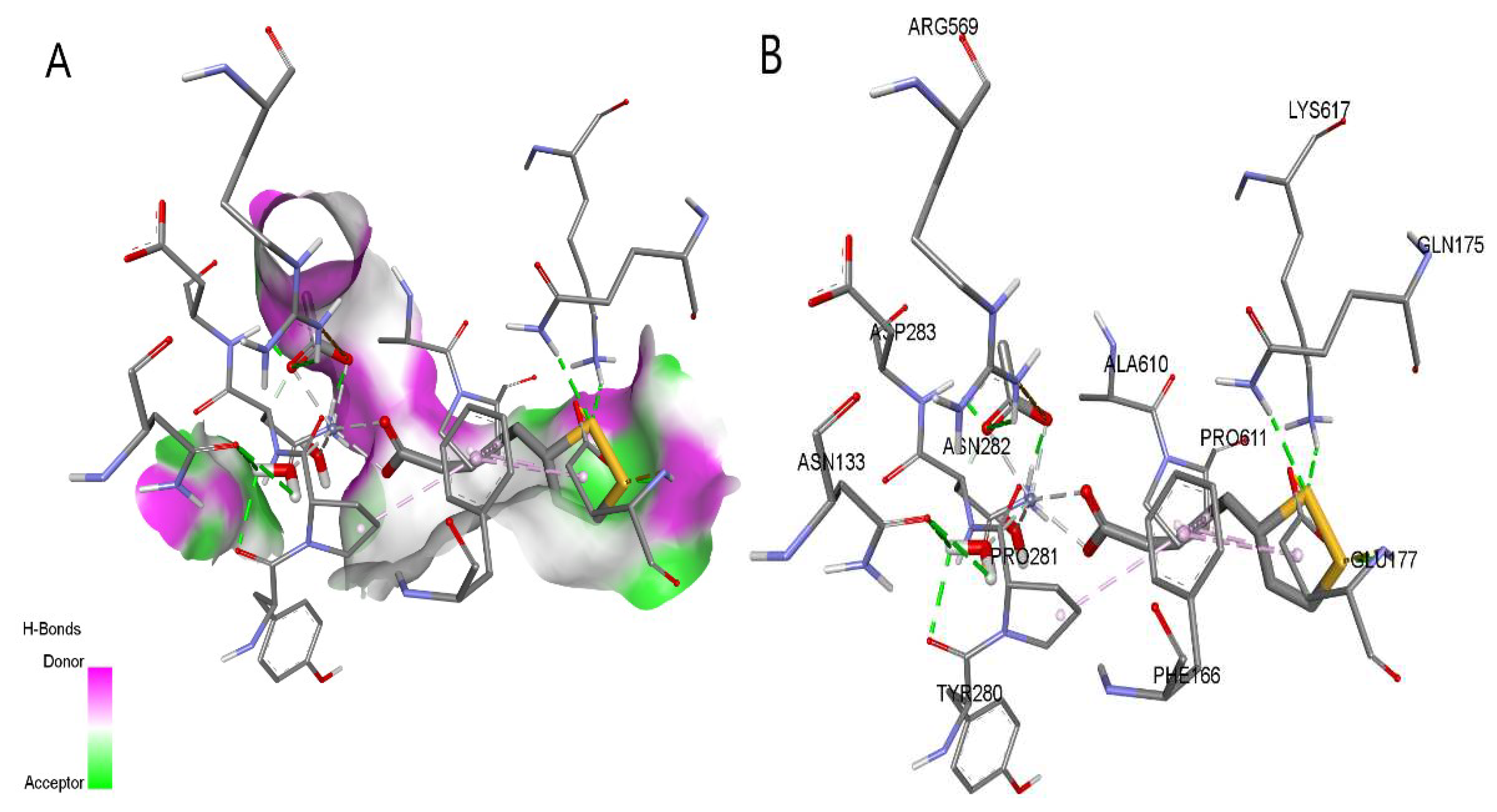
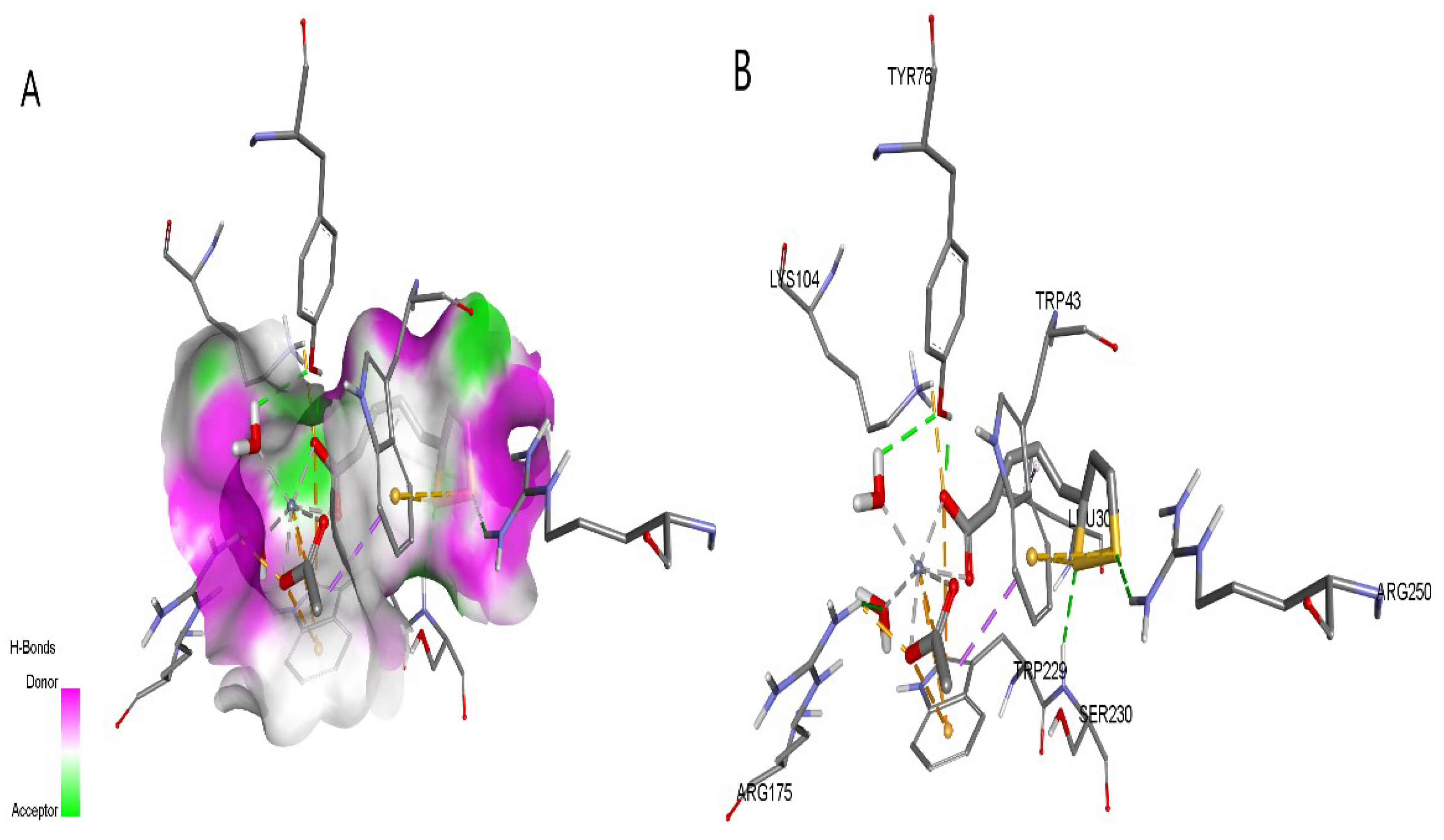
2.6. Molecular Docking Analysis (Studies)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis
3.3. IR-spectroscopy of ZnLA
3.4. Powder X-ray Diffractometry of ZnLA
3.5. TGA-DTA Analysis
3.6. Computational Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walkup, G.K.; Burdette, S.C.; Lippard, S.J.; Tsien, R.Y. A New Cell-Permeable Fluorescent Probe for Zn 2+. J Am Chem Soc 2000, 122, 5644–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psomas, G. Copper(II) and Zinc(II) Coordination Compounds of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Structural Features and Antioxidant Activity. Coord Chem Rev 2020, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P.; Thakur, V.; Chattopadhyay, M. Role of Minerals and Trace Elements in Diabetes and Insulin Resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabosseau, P.; Rutter, G.A. Zinc and Diabetes. Arch Biochem Biophys 2016, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Pigera, S.; Galappatthy, P.; Katulanda, P.; Constantine, G.R. Zinc and Diabetes Mellitus: Understanding Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. DARU, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2015; 23. [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson, C.J.; Koh, J.Y.; Bush, A.I. The Neurobiology of Zinc in Health and Disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellei, M.; Del Bello, F.; Porchia, M.; Santini, C. Zinc Coordination Complexes as Anticancer Agents. Coord Chem Rev 2021, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.Y.; Pi, J.; Jin, H.; Cai, J.Y.; Deng, S.P. Synthesis, Characterization and Anticancer Activity of Kaempferol-Zinc(II) Complex. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2016, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, W.C.; Whiteoak, R.; Thompson, R.P.H. Zinc Concentrations in Leucocytes of Patients Receiving Antiepileptic Drugs. J Clin Pathol 1988, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Khan, M.Z.H.; Ma, F.; Liu, X. A Novel Zinc Complex with Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity. BMC Chem 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abendrot, M.; Chȩcińska, L.; Kusz, J.; Lisowska, K.; Zawadzka, K.; Felczak, A.; Kalinowska-Lis, U. Zinc(II) Complexes with Amino Acids for Potential Use in Dermatology: Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Antibacterial Activity. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, S.; Yuan, L.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Z. Synthesis, Structure Characterization, and Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity Study of Iso-Orientin-Zinc Complex. J Agric Food Chem 2021, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, T.R. Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidative Activity and DNA Binding Properties of the Copper(II), Zinc(II), Nickel(II) Complexes with 1,2-Di(4′-Iminonaringenin)Ethane. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2008, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salga, M.S.; Ali, H.M.; Abdulla, M.A.; Abdelwahab, S.I.; ElhassanTaha, M.M.; Yagoub, U. Synthesis and Gastroprotective Activities of Some Zinc (II) Complexes Derived from (E)-2-(1-(2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Ethylimino)Ethyl)Phenol and (E)-4-(1-(2-(Piperazin-1-Yl)Ethylimino)Ethyl)Benzene-1,3-Diol Schiff Bases against Aspirin Induced Ulceration. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Nowak-Król, A.; Nagler, O.; Kraus, F.; Zhu, N.; Zheng, N.; Müller, M.; Schmidt, D.; Xie, Z.; Würthner, F. Tetrahydroxy-Perylene Bisimide Embedded in a Zinc Oxide Thin Film as an Electron-Transporting Layer for High-Performance Non-Fullerene Organic Solar Cells. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2019, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Wang, B.; Zhu, L. DNA Binding, Cytotoxicity, Apoptotic Inducing Activity, and Molecular Modeling Study of Quercetin Zinc(II) Complex. Bioorg Med Chem 2009, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Gunsalus, I.C.; Schnakenberg, G.H.F.; Soper, Q.F.; Boaz, H.E.; Kern, S.F.; Parke, T. V. Isolation, Characterization and Structure of α-Lipoic Acid. J Am Chem Soc 1953, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, R.; Niebch, G.; Borbe, H.O.; Fieger-Büschges, H.; Ruus, P.; Nowak, H.; Riethmüller-Winzen, H.; Peukert, M.; Blume, H. Enantioselective Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability of Different Racemic α-Lipoic Acid Formulations in Healthy Volunteers. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1996, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.C.; Aruoma, O.I.; Evans, P.J.; O’neill, C.; Van Der Vliet, A.; Cross, C.E.; Tritschler, H.; Halliwell, B. Lipoic and Dihydrolipoic Acids as Antioxidants. A Critical Evaluation. Free Radic Res 1994, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, L.; Witt, E.H.; Tritschler, H.J. Alpha-Lipoic Acid as a Biological Antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med 1995, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibullo, D.; Li Volti, G.; Giallongo, C.; Grasso, S.; Tomassoni, D.; Anfuso, C.D.; Lupo, G.; Amenta, F.; Avola, R.; Bramanti, V. Biochemical and Clinical Relevance of Alpha Lipoic Acid: Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity, Molecular Pathways and Therapeutic Potential. Inflammation Research 2017, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cores, Á.; Michalska, P.; Pérez, J.M.; Crisman, E.; Gómez, C.; Villacampa, M.; Menéndez, J.C.; León, R. Enantioselective Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Aza-CGP37157–Lipoic Acid Hybrids for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M.; Wozniak, M. Lipoic Acid Decreases the Viability of Breast Cancer Cells and Activity of PTP1B and SHP2. Anticancer Res 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gora̧ca, A.; Huk-Kolega, H.; Piechota, A.; Kleniewska, P.; Ciejka, E.; Skibska, B. Lipoic Acid - Biological Activity and Therapeutic Potential. Pharmacological Reports 2011, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Reljanovic, M.; Mehnert, H.; Gries, F.A. α-Lipoic Acid in the Treatment of Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Germany: Current Evidence from Clinical Trials. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes 1999, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.; Hanefeld, M.; Ruhnau, K.J.; Mei\ner, H.P.; Lobisch, M.; Schütte, K.; Gries, F.A. Treatment of Symptomatic Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy with the Anti-Oxidant α-Lipoic Acid - A 3-Week Multicentre Randomized Controlled Trial (ALADIN Study). Diabetologia 1995, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, D.P.; Lobato, R.D.F.G.; Cavalcanti, J.R.L.D.P.; Sampaio, L.R.L.; Araújo, P.V.P.; Silva, M.C.C.; Neves, K.R.T.; Fonteles, M.M.D.F.; Sousa, F.C.F. De; Vasconcelos, S.M.M. The Contributions of Antioxidant Activity of Lipoic Acid in Reducing Neurogenerative Progression of Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. International Journal of Neuroscience 2011, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmquist, L.; Stuchbury, G.; Berbaum, K.; Muscat, S.; Young, S.; Hager, K.; Engel, J.; Münch, G. Lipoic Acid as a Novel Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias. Pharmacol Ther 2007, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maczurek, A.; Hager, K.; Kenklies, M.; Sharman, M.; Martins, R.; Engel, J.; Carlson, D.A.; Münch, G. Lipoic Acid as an Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2008, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G. Molecular Docking: Shifting Paradigms in Drug Discovery. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardirossian, N.; Head-Gordon, M. Thirty Years of Density Functional Theory in Computational Chemistry: An Overview and Extensive Assessment of 200 Density Functionals. Mol Phys 2017, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besley, N.A. Modeling of the Spectroscopy of Core Electrons with Density Functional Theory. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Naderi, R.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Synthesis and Characterization of an Effective Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Green Corrosion Inhibitive Complex Based on Zinc Acetate/Urtica Dioica. Appl Surf Sci 2017, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Alam, M.J.; Trzesowska-Kruszynska, A.; Kruszynski, R.; Alam, M.; Al-Resayes, S.I.; Dwivedi, S.; Khan, M.R.; Islam, M.S.; et al. Synthesis, Structural Investigations and Pharmacological Properties of a New Zinc Complex with a N4-Donor Schiff Base Incorporating 2-Pyridyl Ring. Inorganica Chim Acta 2019, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halevas, E.; Mavroidi, B.; Pelecanou, M.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G. Structurally Characterized Zinc Complexes of Flavonoids Chrysin and Quercetin with Antioxidant Potential. Inorganica Chim Acta 2021, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Portela, A.; Almeida, M.D.G.; Gomes, A.P.B.; Correia, L.P.; Da Silva, P.C.D.; Montenegro Neto, A.N.; De Medeiros, A.C.D.; Simões, M.O.S. Vapor Pressure Curve Determination of α-Lipoic Acid Raw Material and Capsules by Dynamic Thermogravimetric Method. Thermochim Acta 2012, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.C.; Hinchliffe, A. Mulliken Population Analysis and Quantum Mechanical Probability. J Mol Struct 1975, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demircioʇlu, Z.; Kaştaş, Ç.A.; Büyükgüngör, O. Theoretical Analysis (NBO, NPA, Mulliken Population Method) and Molecular Orbital Studies (Hardness, Chemical Potential, Electrophilicity and Fukui Function Analysis) of (E)-2-((4-Hydroxy-2-Methylphenylimino)Methyl)-3-Methoxyphenol. J Mol Struct 2015, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K. Role of Frontier Orbitals in Chemical Reactions. Science (1979) 1982, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, R.G.; Pearson, R.G. Absolute Hardness: Companion Parameter to Absolute Electronegativity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauk, A. Orbital Interaction Theory of Organic Chemistry. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, I. Molecular Orbitals and Organic Chemical Reactions, Reference Edition. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, R.G.; Donnelly, R.A.; Levy, M.; Palke, W.E. Electronegativity: The Density Functional Viewpoint. J Chem Phys 1977, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattaraj, P.K.; Sarkar, U.; Roy, D.R. Electrophilicity Index. Chem Rev 2006, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Lesar, A.; Milošev, I. Density Functional Study of the Corrosion Inhibition Properties of 1,2,4-Triazole and Its Amino Derivatives. Chem Phys Lett 2009, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, M.; Khalid, M.; Akhtar, T.; Tahir, M.N.; Khan, M.U.; Saleem, M.; Jawaria, R. Synthesis, Spectroscopic, SC-XRD Characterizations and DFT Based Studies of Ethyl2-(Substituted-(2-Benzylidenehydrazinyl))Thiazole-4-Carboxylate Derivatives. J Mol Struct 2019, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C. The Process of Structure-Based Drug Design. Chem Biol 2003, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, D. Bioinformatics Software Resources. Brief Bioinform 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.X.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: Improved Protein-Ligand Blind Docking by Integrating Cavity Detection, Docking and Homologous Template Fitting. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, G.; Nagasree, K.P.; Hanisha, M.; Kumar, M.M.K. AUDocker LE: A GUI for Virtual Screening with AUTODOCK Vina. BMC Res Notes 2011, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T. Discovery Studio Modeling Environment. Ensemble 2015, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeerschd, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An Advanced Semantic Chemical Editor, Visualization, and Analysis Platform. J Cheminform 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A Programming Language for Software Integration and Development. J Mol Graph Model 1999, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado-Rojas, W.; Olivero-Verbel, J.; Ortega-Zuñiga, C. Searching of Protein Targets for Alpha Lipoic Acid. In Proceedings of the Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society; 2011; Vol. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Oikonomakos, N.G.; Tsitsanou, K.E.; Zographos, S.E.; Skamnaki, V.T.; Goldmann, S.; Bischoff, H. Allosteric Inhibition of Glycogen Phosphorylase a by the Potential Antidiabetic Drug 3-Isopropyl 4-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1,4-Dihydro-1-Ethyl-2-Methyl-Pyridine-3,5,6-Tricarboxylate. Protein Science 1999, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Figueroa, D.J.; Austin, C.P.; Liu, Y.; Bugianesi, R.M.; Slaughter, R.S.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; Kohler, M.G. Expression of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels in Human and Rhesus Pancreatic Islets. Diabetes 2004, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, N.; Endo, T.; Hosomi, S.; Setou, K.; Tanaka, S.; Ogawa, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Mizukami, T.; Arai, S.; Okuno, M.; et al. Structural Analysis of Crystalline R(+)-α-Lipoic Acid-α-Cyclodextrin Complex Based on Microscopic and Spectroscopic Studies. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharipov, A.; Boboev, Z.; Fazliev, S.; Gulyamov, S.; Yunuskhodjayev, A.; Razzokov, J. Development of an Improved Method for the Determination of Iodine/β-Cyclodextrin by Means of Hplc-Uv: Validation and the Thyroid-Stimulating Activity Revealed by in Vivo Studies. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dang, L.; Wei, H. Thermodynamic Analysis of Lipoic Acid Crystallized with Additives. J Therm Anal Calorim 2013, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-Functional Thermochemistry. III. The Role of Exact Exchange. J Chem Phys 1993, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti Correlation-Energy Formula into a Functional of the Electron Density. Phys Rev B 1988, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F. Extending DFT-Based Genetic Algorithms by Atom-to-Place Re-Assignment via Perturbation Theory: A Systematic and Unbiased Approach to Structures of Mixed-Metallic Clusters. Journal of Chemical Physics 2014, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vovna, V.I.; Korochentsev, V. V.; Dotsenko, A.A. Electronic Structures and Photoelectron Spectra of Zinc(II) Bis-β-Diketonates. Russian Journal of Coordination Chemistry/Koordinatsionnaya Khimiya 2012, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Du, H.; Peng, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Fei, J.; Meng, Y.; Yuan, L. Degradation of Several Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Laccase in Reverse Micelle System. Science of the Total Environment 2020, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizar, L.H.M.; Rios-Reyes, C.H.; Olvera-Maturano, N.J.; Robles, J.; Rodriguez, J.A. Chemical Reactivity of Quinclorac Employing the HSAB Local Principle - Fukui Function. Open Chem 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Balderrama, K.; Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Flores-Holguin, N. Calculation of Global and Local Reactivity Descriptors of Carbodiimides, a DFT Study. J Theor Comput Chem 2017, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.S.; Abbasi, S.W. Molecular Docking Studies for the Identification of Novel Melatoninergic Inhibitors for Acetylserotonin-O-Methyltransferase Using Different Docking Routines. Theor Biol Med Model 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA, D.S. Discovery Studio Visualizer V21.1.0.20298. BIOVIA, Dassault Systèmes, 2005. [Google Scholar]
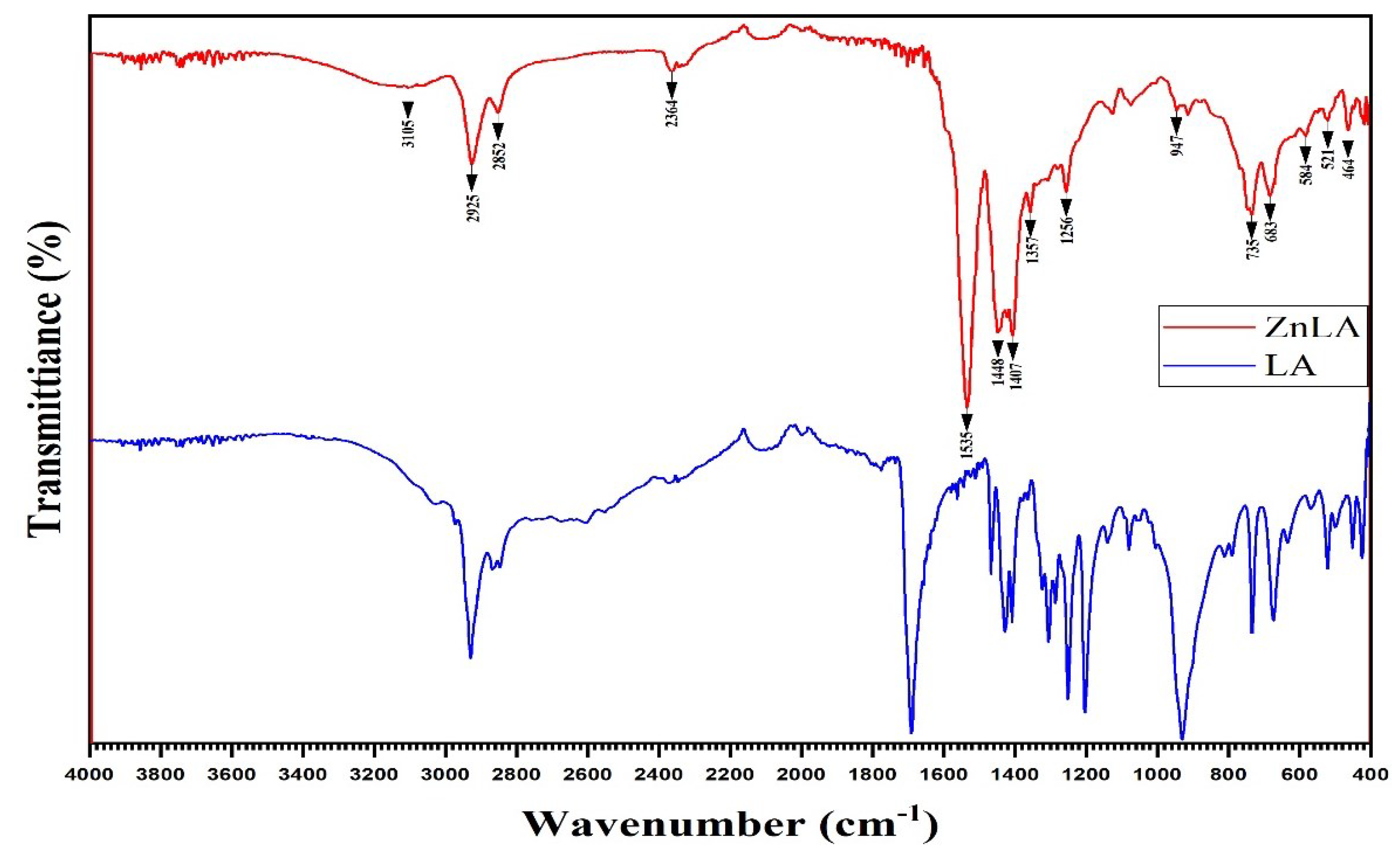
| LA, cm–1 | ZnLA, cm –1 | Functional Groups |
|---|---|---|
| - | 3266-3000 | |
| 2928, 2868 | 2925, 2852 | |
| 2369, 1690, 1426, 1407 | 2364, 1535, 1448, 1407 |
|
| - | 1357 | |
| - | 464 |
| Compound | 2θ |
|---|---|
| LA | 8; 17.8; 23.3; 23.9; 32.3 |
| ZnA | 12.8; 16.3; 22.3; 25.1; 27.7 |
| Mix. ZnA + LA(1:1 mole ratio) | 8; 12.5; 17.8; 23.3; 25.1; 27.5 |
| ZnLA | 8; 12.5; 13.4; 18.6; 19.5; 20.2; 21.2; 22.3; 25.1; 27.5 |
| Atom | Charge | Atom | Charge | Atom | Charge | Atom | Charge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.4760 | C11 | -0.1363 | H21 | 0.0838 | O31 | -0.4609 |
| O2 | -0.4738 | S12 | -0.1221 | H22 | 0.0722 | O32 | -0.4942 |
| C3 | -0.1527 | H13 | 0.0772 | H23 | 0.0983 | Zn33 | 0.6539 |
| O4 | -0.5080 | H14 | 0.0904 | H24 | 0.1112 | O34 | -0.3374 |
| C5 | -0.0195 | H15 | 0.0601 | H25 | 0.1096 | H35 | 0.2217 |
| C6 | -0.1411 | H16 | 0.0623 | C26 | -0.2693 | O36 | -0.3372 |
| C7 | -0.1504 | H17 | 0.0684 | C27 | 0.4705 | H37 | 0.2221 |
| C8 | 0.0643 | H18 | 0.0418 | H28 | 0.1006 | H38 | 0.2242 |
| S9 | -0.1253 | H19 | 0.0845 | H29 | 0.1028 | H39 | 0.2242 |
| C10 | -0.1620 | H20 | 0.0632 | H30 | 0.1068 |
| MO(s) | E (eV) | ∆E (eV) |
|---|---|---|
| HOMO | -5.426 | 4.637 |
| LUMO | -0.789 | |
| HOMO-1 | -7.033 | 6.762 |
| LUMO+1 | -0.271 | |
| HOMO-2 | -7.444 | 7.381 |
| LUMO+2 | -0.063 |
| Parametres | ZnLA | |
|---|---|---|
| HOMO energy | EHOMO (eV) | -5.426 |
| LUMO energy | ELUMO (eV) | -0.789 |
| Energy bandgap (ΔE) | ΔE = EHOMO - ELUMO (eV) | 4.637 |
| Ionization potential (I) | I = - EHOMO (eV | 5.426 |
| Electron affinity (A) | A = - ELUMO (eV) | 0.789 |
| Electronegativity (χ) | χ = (I+A)/2 (eV) | 3.107 |
| Global hardness (η) | η = (I-A)/2 (eV) | 2.318 |
| Global softness (σ or S) | S = 1/2 η (eV) | 0.216 |
| Global electrophilicity (ω) | ω = (µ2/2η) (eV) | 2.0823 |
| Chemical potential (µ) | µ = - (I+A)/2 (eV) | -3.107 |
| Protein (PDB ID) | Autodock Vina results | CB-Dock2 results | Contact residues with H-bonds | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding energy, kcal/mol | Binding energy, kcal/mol | ||||
| LA | ZnLA | LA | ZnLA | ||
| 2GPA | -5.9 | -7.6 | -5.9 | -8.3 | ARG49, THR94, GLY135, LEU136, ASN187, ASN284, ARG292, HIS341, HIS377, TYR573, LYS574, SER674, GLY675, GLY677 |
| 1ZSX | -6.6 | -7.3 | -6.6 | -8.1 | TRP43, TYR76, LYS104, ARG175, SER230, ARG250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





