1. Introduction
Ischemic stroke is a common neurological disorder in clinical practice. It refers to the abnormality of cerebral blood supply arteries, leading to localized ischemia and hypoxia of brain tissue, resulting in ischemic necrosis and neurological syndromes [
1]. Patients with acute ischemic stroke are in a relatively critical condition, with higher disability and mortality rates. Moreover, the pre-symptoms of this disease are easily confused with other conditions, leading to a potential missed treatment window [
2]. Additionally, the occurrence of this disease can affect patients’ neurological function, which not only impacts their daily life but also poses a certain threat to their life safety [
3].
Currently, for early ischemic stroke patients, thrombolysis or mechanical thrombectomy is recommended for treatment. However, studies have shown [
4] that although thrombolysis and arterial thrombectomy have been widely used in the treatment of early ischemic stroke, these approaches have strict time window limitations. Therefore, the main treatment options in clinical practice for early ischemic stroke still involve antiplatelet aggregation, anticoagulation, intracranial pressure reduction, and neurotrophic drugs [
5]. The onset of early ischemic stroke is often associated with factors such as long-term arterial atherosclerosis leading to vascular stenosis, thrombus formation, and vessel occlusion. Therefore, timely and effective regulation of patients’ coagulation mechanisms is of great significance in promoting their microcirculation and improving prognosis [
6]. Antiplatelet aggregation is an important measure for the treatment of ischemic stroke patients. In recent years, the dual therapy regimen combining aspirin and clopidogrel has been highly praised in clinical practice, as both drugs are commonly used antiplatelet medications [
7]. Studies have shown [
8] that the dual therapy regimen combining aspirin and clopidogrel is effective in treating patients with acute ischemic stroke, and it further improves the hypercoagulable state compared to the conventional monotherapy regimen. However, there are still concerns about the safety of dual therapy according to some clinical studies [
9].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Basic Information
The study was conducted from August 2020 to August 2021 and included a total of 80 patients with early ischemic stroke admitted during this period as the study population. Basic information of the patients was collected. Inclusion: 1) Patients diagnosed with early ischemic stroke confirmed by relevant tests and with cerebral infarction lesions clearly identified by imaging examination; 2) Adult patients; 3) Time from onset of symptoms to hospital admission ≤ 24 hours; 4) Patients experiencing their first stroke; 5) Patients voluntarily participating in the study and signing the relevant informed consent. Exclusion: 1) Allergic reactions or relevant contraindications to the drugs, methods, or devices used in this study; 2) Recurrent stroke; 3) Concomitant malignant tumor disease; 4) Concomitant severe organ dysfunction; 5) Presence of congenital or autoimmune diseases; 6) Presence of hematological disorders or coagulation dysfunction; 7) Concomitant psychiatric disorders or pre-existing cognitive or behavioral disorders; 8) Intracranial hemorrhage. The patients were randomly divided into a control group and an observation group, with 40 patients in each group.
2.2. Method
Control group: Within 48 hours of onset, patients received monotherapy with a monoclonal antibody [Bayer aspirin (Bayer Healthcare Ltd., J20130078)] at a dose of 300 mg/day. After 7 days of continuous use, the maintenance dose was reduced to 100 mg/day, with a total treatment duration of 4 weeks.
Observation group: Within 48 hours of onset, patients received combination therapy with dual antibodies [aspirin (Bayer Pharmaceutical, J20130078) + clopidogrel (Lepu Pharmaceutical, H20123115)]. On the first day, the dose was aspirin 300 mg + clopidogrel 75 mg, and from the second day onwards, it was switched to a maintenance dose, i.e., aspirin 100 mg/day + clopidogrel 75 mg/day. After 3 weeks, patients switched to monotherapy with aspirin 100 mg/day, with a total treatment duration of 4 weeks.
2.3. Observation indicators
(1) Clinical efficacy: Cure: Complete disappearance of symptoms and signs; Significant improvement: Significant improvement in symptoms and signs; Effective: Some improvement in symptoms and signs; Ineffective: No significant change in symptoms and signs; Death: Loss of vital signs.
(2) Changes in neurological and cognitive function: Neurological function of patients was assessed using the GCS and NIHSS at T1, T2, T3. Cognitive function was evaluated using the MoCA. The total score of GCS is 15, with higher scores indicating a lighter level of consciousness. The total score of NIHSS is 42, with lower scores indicating milder neurological impairment. The total score of MoCA is 30, with higher scores indicating better cognitive function recovery.
(3) Levels of hematological indicators: Plasma levels of D-dimer, fibrinogen, and peak systolic velocity were measured before and after treatment using an automated biochemical analyzer.
(4) Levels of inflammatory markers: Serum levels of CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α were measured before and after treatment using the ELISA method.
(5) Adverse reactions: Adverse reactions observed in this study included gastrointestinal reactions, nausea and vomiting, abnormal liver and kidney function, skin symptoms, mental symptoms, and recurrence within 90 days.
2.4. Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 8 was used for graphic software; SPSS 26.0 was used for data analysis. The t-test was used for comparison of quantitative data, and (±s) represents the mean ± standard deviation. The chi-square test (x²) was used for comparison of categorical data, and n (%) represents the number and percentage. A significance level of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Basic Information
The basic information of the two groups of patients was comparable, and there were no significant differences in the comparison (P>0.05), as shown in
Table 1.
Table 1.
Comparison of Basic Information.
Table 1.
Comparison of Basic Information.
| |
Control group (n=40) |
Observation group (n=40) |
t/x² |
P |
| Gender |
|
|
0.208 |
0.648 |
| Male |
23 |
25 |
|
|
| Female |
17 |
15 |
|
|
| Age |
56-73 |
53-76 |
|
|
| Average age (years) |
63.12±5.67 |
63.24±5.73 |
-0.094 |
0.925 |
| Onset time (h) |
2.3-11.4 |
3.3-11.5 |
|
|
| Average time (h) |
8.34±1.23 |
8.29±1.25 |
0.18 |
0.858 |
| Infarction site |
|
|
|
|
| Basal ganglia |
23 |
21 |
0.202 |
0.653 |
| Brain lobe |
14 |
15 |
0.054 |
0.816 |
| Cerebellum |
2 |
2 |
0.0 |
1.0 |
| Brainstem |
1 |
2 |
0.346 |
0.556 |
| Combined underlying disease |
|
|
|
|
| Hypertension |
31 |
30 |
0.069 |
0.793 |
| Diabetes |
20 |
22 |
0.201 |
0.654 |
| Coronary heart disease |
25 |
24 |
0.053 |
0.818 |
3.2. Comparison of clinical efficacy
The overall treatment effectiveness in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05), as shown in
Table 2.
Table 2.
Comparison of clinical efficacy.
Table 2.
Comparison of clinical efficacy.
| Group |
Number of cases |
Cure |
Markedly effective |
Efficient |
Invalid |
Die |
Total effective rate (%) |
| Control group |
40 |
4 |
10 |
14 |
10 |
2 |
70.0 |
| Observation group |
40 |
10 |
12 |
15 |
2 |
1 |
92.5 |
| x² |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
6.646 |
| P |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
0.01 |
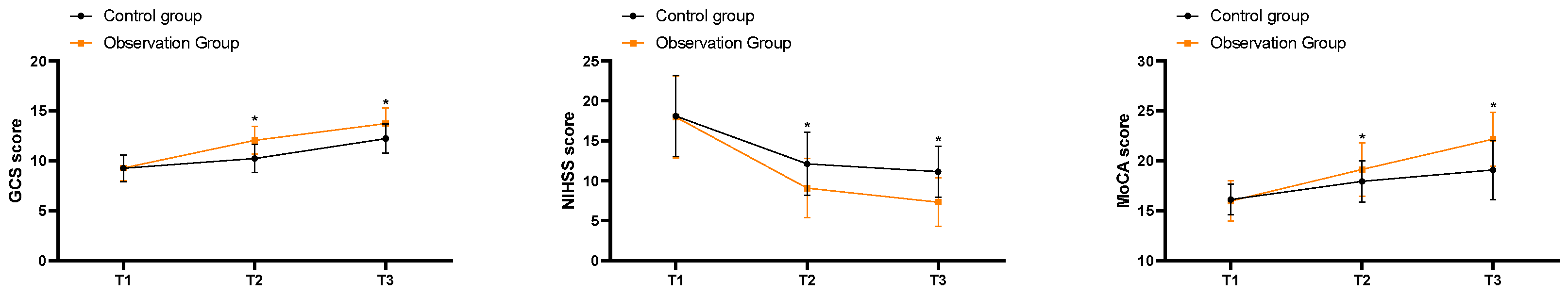
3.3. Comparison of Changes in Neurocognitive Function
As shown in
Figure 1, the GCS scores in the control group at T1, T2, and T3 were (9.26±1.34, 10.23±1.42, 12.23±1.48), the NIHSS scores were (18.09±5.06, 12.12±3.97, 11.14±3.18), and the MoCA scores were (16.13±1.53, 17.94±2.05, 19.08±2.97). In the observation group, the GCS scores at T1, T2, and T3 were (9.28±1.29, 12.06±1.38, 13.72±1.56), the NIHSS scores were (17.98±5.16, 9.07±3.72, 7.32±3.04), and the MoCA scores were (15.98±2.03, 19.12±2.65, 22.17±2.71). The GCS and MoCA scores at 2 weeks and 4 weeks of treatment were significantly higher in the observation group compared to the control group, while the NIHSS scores were significantly lower in the observation group (P<0.05).
Figure 1.
Comparison of Changes in Neurocognitive Function. Note: * indicates comparison P<0.05; Before treatment (T1), 2 weeks of treatment (T2), 4 weeks of treatment (T3).
Figure 1.
Comparison of Changes in Neurocognitive Function. Note: * indicates comparison P<0.05; Before treatment (T1), 2 weeks of treatment (T2), 4 weeks of treatment (T3).
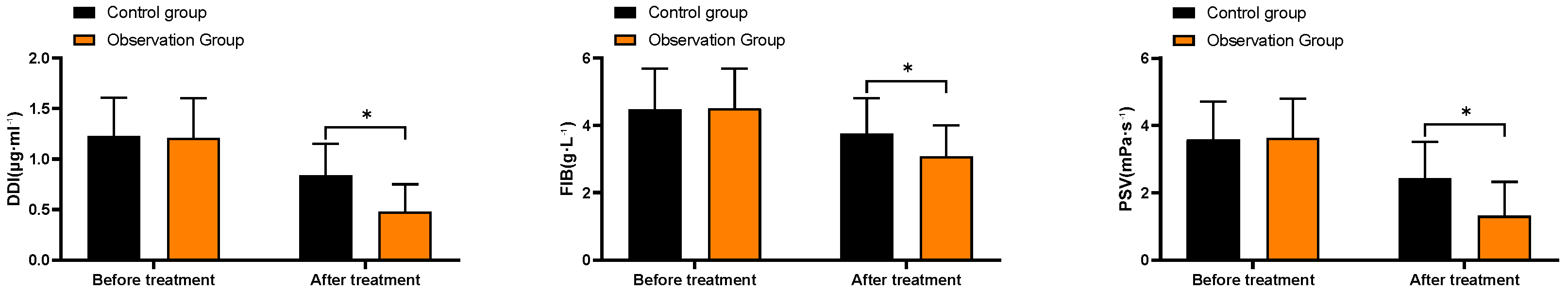
3.4. Comparison of Hematological Index Levels
As shown in
Figure 2, the DDI levels before and after treatment in the control group were (1.23±0.38, 0.84±0.31), FIB levels were (4.48±1.21, 3.75±1.06), and PSV levels were (3.58±1.13, 2.43±1.08). The DDI levels before and after treatment in the observation group were (1.21±0.39, 0.48±0.27), FIB levels were (4.51±1.18, 3.08±0.92), and PSV levels were (3.62±1.17, 1.31±1.01). The DDI, FIB, and PSV levels in the observation group after treatment were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05).
Figure 2.
Comparison of Hematological Index Levels. Note: * indicates comparison P<0.05.
Figure 2.
Comparison of Hematological Index Levels. Note: * indicates comparison P<0.05.
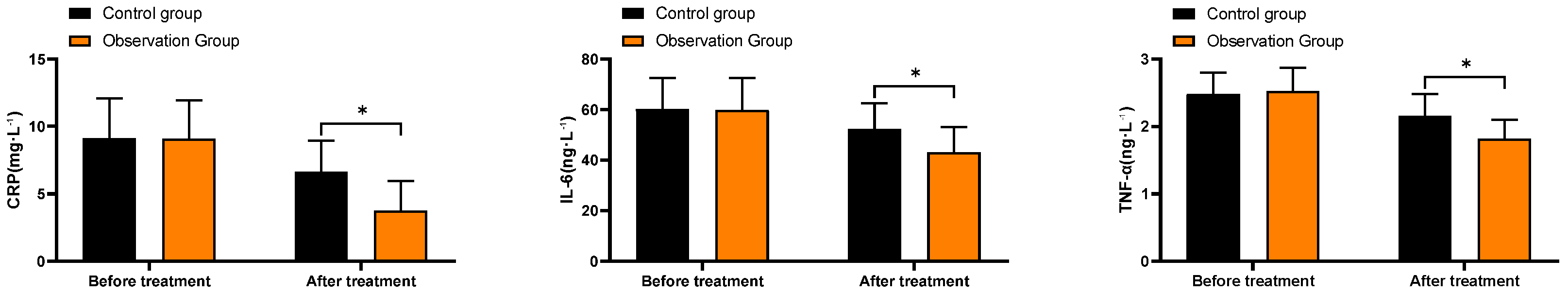
3.5. Comparison of Inflammatory Marker Levels
As shown in
Figure 3, the CRP levels before and after treatment in the control group were (9.13±2.95, 6.62±2.34), IL-6 levels were (60.15±12.37, 52.32±10.08), and TNF-α levels were (2.48±0.32, 2.16±0.32). The CRP levels before and after treatment in the observation group were (9.07±2.86, 3.75±2.21), IL-6 levels were (59.89±12.52, 43.18±9.85), and TNF-α levels were (2.53±0.34, 1.82±0.28). The CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in the observation group after treatment were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05).
Figure 3.
Comparison of Inflammatory Marker Levels. Note: * indicates comparison P<0.05.
Figure 3.
Comparison of Inflammatory Marker Levels. Note: * indicates comparison P<0.05.
3.6. Comparison of adverse reactions
The comparison of the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups (P>0.05) is shown in
Table 3.
Table 3.
Comparison of adverse reactions.
Table 3.
Comparison of adverse reactions.
| Adverse reactions |
Control group (n=40) |
Observation group (n=40) |
x² |
P |
| Gastrointestinal reaction |
3 |
4 |
- |
- |
| Feel sick and vomit |
1 |
2 |
- |
- |
| Abnormal liver and Kidney function |
0 |
1 |
- |
- |
| Skin symptoms |
1 |
0 |
- |
- |
| Mental symptoms |
1 |
1 |
- |
- |
| Stroke recurrence |
6 |
7 |
- |
- |
| Total incidence (%) |
30.0 |
37.5 |
0.503 |
0.478 |
4. Discussion
To date, the pathogenesis of early acute mild ischemic stroke has not been fully elucidated in clinical practice. Most studies [
10,
11] suggest that the disease is caused by the combined effect of multiple factors. Currently, no specific drugs have been discovered for the treatment of early acute ischemic stroke, so the clinical approach to treating this condition primarily focuses on reducing patient mortality and mitigating neurological damage [
12]. Intravenous thrombolysis, arterial thrombectomy, and drug interventions are commonly used clinical methods for treating early acute mild ischemic stroke. However, the clinical application of these two treatment methods is limited due to factors such as the time window for thrombolysis and the technical requirements for arterial thrombectomy [
13]. Given the limitations of thrombolysis or thrombectomy, antiplatelet therapy with medications has become the most commonly used measure in clinical practice. Aspirin and clopidogrel are both evidence-based antiplatelet drugs, and studies [
14] have shown that the dual antiplatelet regimen of aspirin and clopidogrel can effectively improve the clinical symptoms of ischemic stroke patients and reduce the risk of disease recurrence. Research conducted by scholar Yang [
15] and others compared the efficacy and safety of dual antiplatelet therapy with single antiplatelet therapy in 4,139 cases of early acute ischemic stroke or TIA patients with a high risk of recurrence. The results showed that the dual antiplatelet therapy group had better clinical efficacy compared to the single antiplatelet therapy group, and the incidence of adverse reactions and the risk of stroke recurrence within 90 days were relatively lower in the dual antiplatelet therapy group. Subsequent relevant studies [
16] have further supported this conclusion. The clinical efficacy results in this study are consistent with domestic and international research [
17]. However, there are certain differences between this study and previous research in terms of adverse reactions and recurrence.
Aspirin is a commonly used derivative of salicylic acid in clinical practice. It effectively inhibits the activity of cyclooxygenase in platelets, thereby blocking the generation of thromboxane A2 and exerting effects such as inhibiting platelet aggregation and thrombus formation [
18]. Clopidogrel is a platelet membrane adenosine diphosphate receptor inhibitor that effectively inhibits the generation of adenosine diphosphate, blocks platelet aggregation and binding to adenosine diphosphate, and activates and amplifies already aggregated platelets and adenosine diphosphate [
19]. The combined use of these two drugs can further promote thrombus dissolution, inhibit platelet aggregation and adhesion, and thereby prevent thrombus formation [
20]. Studies have confirmed the superior effectiveness and safety of dual antiplatelet therapy compared to monotherapy. However, there is relatively limited research on the impact of early application of dual antiplatelet therapy on neurological and cognitive function, hematological indicators, and inflammatory markers in patients with acute ischemic stroke. In this study, the observation group showed superior improvement in neurocognitive function, indicating that the dual therapy approach resulted in more significant improvement in both neurological and cognitive functions compared to the monotherapy approach. Related research [
21] has shown that the blood viscosity of patients with ischemic stroke is significantly increased compared to the normal population, leading to persistent thrombotic status and subsequent secondary vascular and neural damage even after treatment. FIB is one of the indicators reflecting high blood viscosity, and patients in the acute phase of stroke generally exhibit abnormal FIB levels. Elevated levels of FIB further increase the risk of thrombus formation [
22]. In this study, the observation group showed superior improvement in hematological parameters, indicating that early application of the dual therapy approach effectively improves the hypercoagulable state in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Related research [
23] has found that inflammatory reactions are involved in the occurrence and development of acute ischemic stroke, and as the patient’s condition progresses, the body’s inflammatory response also intensifies. Serum CRP, IL-6, and TNF-α are commonly seen inflammatory factors in clinical practice, and in patients with acute ischemic stroke, these inflammatory mediators are significantly elevated [
24]. In this study, the observation group demonstrated superior improvement in inflammation markers, which may be attributed to the effective blockade of inflammatory factor release by the dual therapy approach, thereby further alleviating excessive expression of inflammatory responses in patients’ bodies.
In summary, compared to the single antiplatelet regimen, the dual antiplatelet regimen is more effective in treating early ischemic stroke. It can further promote the recovery of neurological and cognitive functions, improve hematology and inflammatory response indicators, and its safety is comparable to the single antiplatelet regimen.
Author Contributions
Qiming Chen wrote the main manuscript text and Huanli Ma prepared figures and tables. All authors reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research authorship or publication of this article.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study has been approved by Baozhang Hospital’s ethics committee and Patients and their families were informed of the research content and voluntarily signed the informed consent consent. All the methods were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Rabinstein, AA, Update on Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Continuum (Minneap Minn), 2020. 26 (2): p. 268-286. [CrossRef]
- Putaala, J., Ischemic Stroke in Young Adults. Continuum (Minneap Minn), 2020. 26 (2): p. 386-414.
- Herpich, F. and F. Rincon, Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Crit Care Med, 2020. 48(11): p. 1654-1663. [CrossRef]
- Jolugbo, P. and R.A.S. Ariëns, Thrombus Composition and Efficacy of Thrombolysis and Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke, 2021. 52(3): p. 1131-1142. [CrossRef]
- Paul, S. and E. Candelario-Jalil, Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp Neurol, 2021. 335: p. 113518. [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.S. and R.G. Nogueira, Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Continuum (Minneap Minn), 2020. 26(2): p. 310-331.
- Johnston, S.C., et al., Clopidogrel and Aspirin in Acute Ischemic Stroke and High-Risk TIA. N Engl J Med, 2018. 379(3): p. 215-225. [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y., et al., Outcomes Associated With Clopidogrel-Aspirin Use in Minor Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack: A Pooled Analysis of Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients With Acute Non-Disabling Cerebrovascular Events (CHANCE) and Platelet-Oriented Inhibition in New TIA and Minor Ischemic Stroke (POINT) Trials. JAMA Neurol, 2019. 76(12): p. 1466-1473.
- Paciaroni, M., et al., Benefits and Risks of Clopidogrel vs. Aspirin Monotherapy after Recent Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc Ther, 2019. 2019: p. 1607181. [CrossRef]
- Farina, M., et al., The Nrf2 Pathway in Ischemic Stroke: A Review. Molecules, 2021. 26(16). [CrossRef]
- Ajoolabady, A., et al., Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther, 2021. 225: p. 107848. [CrossRef]
- Datta, A., et al., Cell Death Pathways in Ischemic Stroke and Targeted Pharmacotherapy. Transl Stroke Res, 2020. 11(6): p. 1185-1202. [CrossRef]
- Joundi, R.A. and B.K. Menon, Thrombus Composition, Imaging, and Outcome Prediction in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurology, 2021. 97(20 Suppl 2): p. S68-s78. [CrossRef]
- Kheiri, B., et al., Clopidogrel and aspirin after ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Thromb Thrombolysis, 2019. 47(2): p. 233-247. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., Z. Huang, and X. Zhang, Efficacy and safety of clopidogrel and/or aspirin for ischemic stroke/transient ischemic attack: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021. 100(50): p. e27804. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H., et al., Optimal Duration of Aspirin Plus Clopidogrel After Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke, 2019. 50(4): p. 947-953. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., et al., Ticagrelor plus aspirin versus clopidogrel plus aspirin for platelet reactivity in patients with minor stroke or transient ischaemic attack: open label, blinded endpoint, randomised controlled phase II trial. Bmj, 2019. 365: p. l2211. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q., et al., Clopidogrel plus aspirin versus aspirin alone for acute minor ischaemic stroke or high risk transient ischaemic attack: systematic review and meta-analysis. Bmj, 2018. 363: p. k5108. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.C., et al., Time Course for Benefit and Risk of Clopidogrel and Aspirin After Acute Transient Ischemic Attack and Minor Ischemic Stroke. Circulation, 2019. 140(8): p. 658-664. [CrossRef]
- Albay, C.E.Q., F.G.D. Leyson, and F.C. Cheng, Dual versus mono antiplatelet therapy for acute non- cardio embolic ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, an efficacy and safety analysis - updated meta-analysis. BMC Neurol, 2020. 20(1): p. 224.
- Wang, A., et al., Effect of Hypertension on Efficacy and Safety of Ticagrelor-Aspirin Versus Clopidogrel-Aspirin in Minor Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke, 2022. 53(9): p. 2799-2808. [CrossRef]
- Tancin Lambert, A., et al., Biomarkers Associated with Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Pilot Study from the NOR-FIB Study. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra, 2020. 10(1): p. 11-20. [CrossRef]
- Maida, C.D., et al., Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci, 2020. 21(18). [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., et al., Inflammation-Related circRNA Polymorphism and Ischemic Stroke Prognosis. J Mol Neurosci, 2021. 71(10): p. 2126-2133. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).